5 minute read
Building Regulations
Part B, Part K and Part M Compliance
Part B Compliance
Advertisement
Part K Compliance
Fire Safety Protection
Part M Compliance
Accessibility
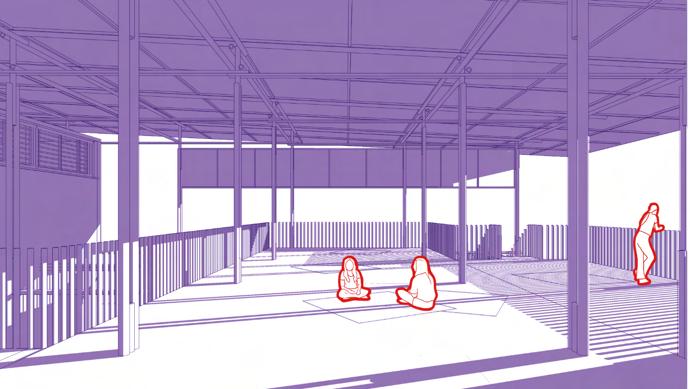
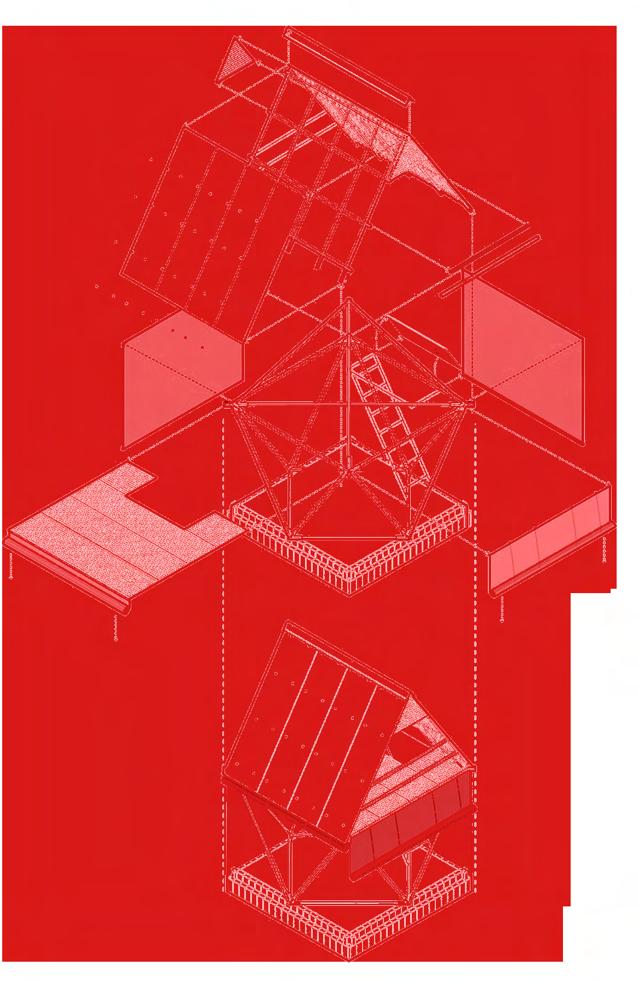
exits external space
Means of Escape Stairs Prevention of Spread Protection from Falling Warning + Rescue
50% of the floor space is open air space


Regular exits from every room to outside

All stairs minimum width of 1100 mm for accessible escape
Doors open with a minimum of 90 degrees
Feminist Lens.
Bamboo is a relatively new material, therefore building codes may not be up to speed with research.
Furthermore, since disasters such as Grenfell, materials such as bamboo and wood aren’t favoured and are often hard to insure, despite studies that show wood buildings burn slower than steel.
Bamboo use for structural members only as part of a mixed-material building for maximum fire safety
Borate-based fire resistant bamboo treatment applied to slow burning (doesn’t impact bamboo’s circular lifecylce)
Fire escape stairs external
Emergency bay space all around the building if needed
An appropriate fire warning system that appeals to both sense of sight and hearing will be implemented in each enclosed room
Even though the building is remote, there is easy access to main road connecting to the city
Ground Floor


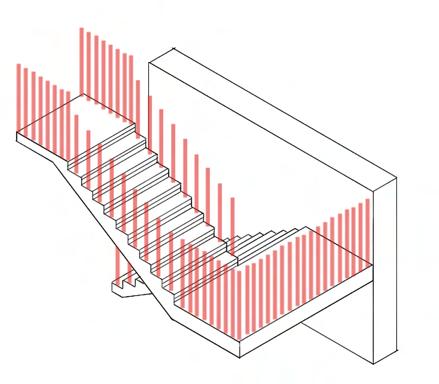
Stairs minimum width of 1000mm (fire stairs 1500mm)
Factory balcony access stairs comply with private stair regulations (professional environment) with rise and going relationship following guidance of when 2R + G = 550<654<700mm
Stair landings 1200 mm (minimum requirement 1100 mm)
Open risers have overlapping treads of 20 mm rise: 159 mm going: 260 mm width of one stair: 1500 mm length of landing: 1500 mm railing height: 1100 mm distance of railing from pitch: 950 mm
First floor is entirely open space with railings around the perimeter
Railings height of 1100 mm in accordance with guidance
Width between bamboo railings is 100 mm to prevent small children sliding through gaps and becoming stuck
The stairs exceed minimum standards of width and landing to allow for more comfortable twoway movement as this will be the main circulation route.
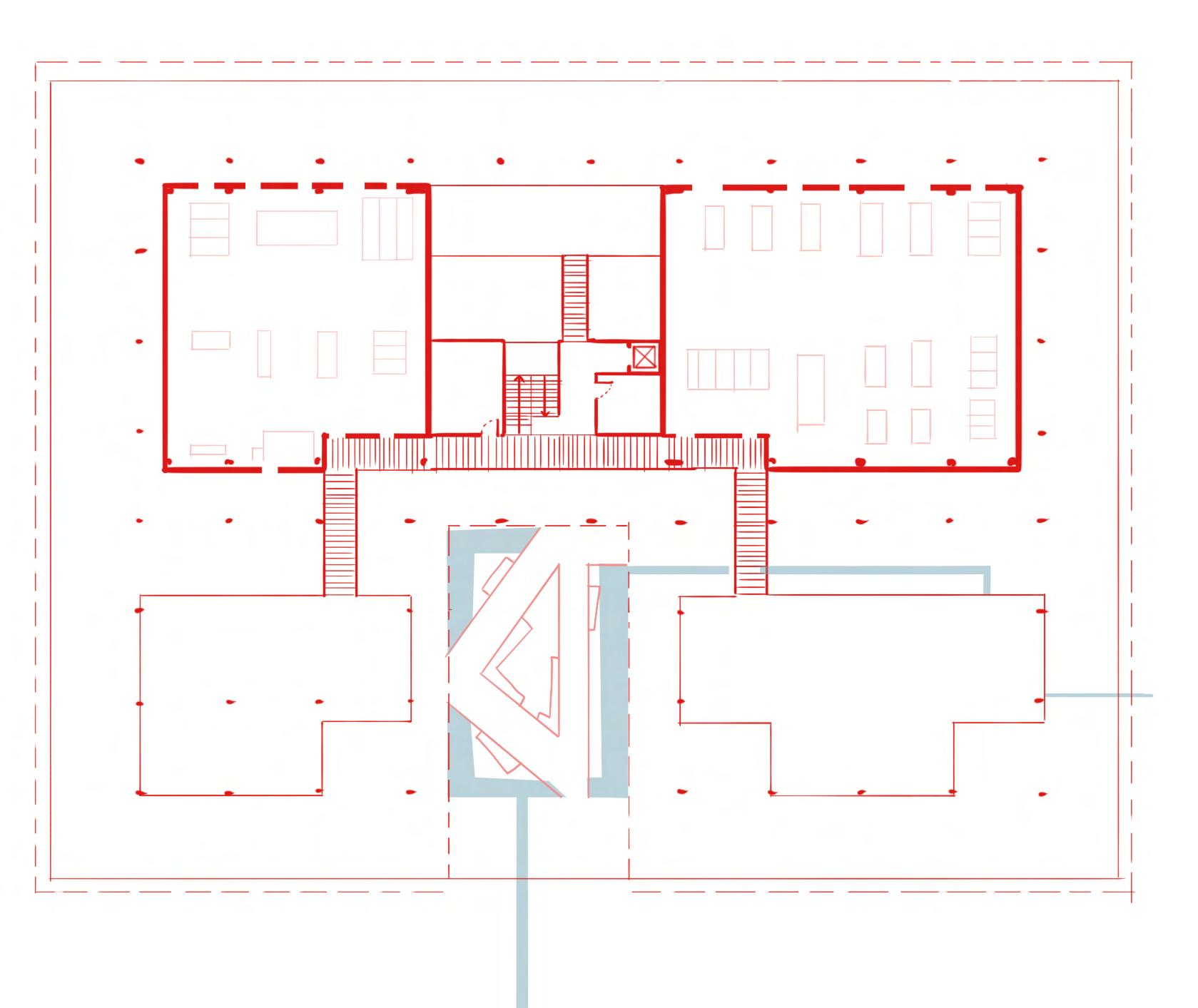
First Floor fire stairs fire exits exit distances railings main stairs
Accessible WC (nongendered) factory stairs shower
Accessible Cubicle changing table
Female WC multi-faith prayer room elevator
Accessibility turning circle
Facilities Loading Bays Sanitary Accomodation
Loading Bays located in materials area, separated from main building, but easy access if needed via smaller road
Building Acess + Circulation
Two general access stairs for day-to-day circulation
One low-tech lift - use for wheelchair users/ buggies/ general accessibility reasons
All circulation corridors/routes at least 1800 mm wide to facilities 180 degrees turning
Multi-faith prayer room with shelving to accommodate a range of faith books. Design is clean and simple for all users
External benches easily accessible for wheelchair users
Visual contrast between walls and doors with doors colour coded to represent different programmes to create a wayfinding system
Female WC Accessible WC Factory/ Learning
Feminist Lens.
Railing attachment width: 1900 mm depth: 1550 mm distance travelling: 3500 mm speed: 0.15 m/s
The bamboo railings will be attached using low-tech construction methods. A hexagonal nut with a tie will attach the railings to a horizontal bamboo pole which is attached to the brick by a steel tie.
Female only toilets have been prioritised as the users of the building are likely to be victims of gender-based violence as this is exacerbated due to climate change/ natural disaster events (3.1 Research), therefore single-sex spaces are important. Also, the main users of the building are women. The disabled toilet is non-gendered to accommodate male/non-binary people alongside disabled users.

Lift enclosure (as >2m vertical travelled) doubles as ramp into lift.

Low-tech design with bamboo handrails alongside light-weight metal door
Female only toilets prioritised as main building users are women
Accessible toilet inlcuded in female bathroom if user isn’t comfortable with sharing facility beyond their gender All accessible toilet doors open outwards and are 1000 mm (compliant with 950 mm minimum requirement)

Changing table in both accessible toilets
First Floor Ground Floor factory access road loading entrance materials shed
Canopy Roof
The sloping roof with overhangs allow for both shade as well as protection from rainfall. Elevated above the brick volumes, hot air moves through the gap, allowing for the cool air to filter through the building.
Water Infrastructure
The water that runs through the building helps to cool the building via evaporative cooling: to change its state from liquid to vapour heat is required and when the occurs, there is a drop in air temperature. Furthermore the water is shallow, meaning users can dip their feet in if needed to cool down.


Sun Path
The positioning of the canopy roof means the building is always shaded when the sun is at its highest point in the sky. It heats the tin roof, which is painted white to minimise heat absorbption. The shaded areas are protected by this heat and sun as a result, maximising thermal comfort



Cross Ventilation


Operable bamboo louvres and operable windows allow for crossventilation when needed into the factory space.
Water Drainage
Drainage downspouts attached to roof allow for water to filter down them and be taken away to the nearby river. A small amount of water is collected for the water tank to provide grey water for the building
Water Tank
Underground water tank supplies grey water for the building. This is a higher-tech solution, so local constuction workers are aided by international workers.
Sustainable Water Cycle
_Low flow fittings and appliances
_Rainwater and greywater recycling

_Sustainable Urban Drainage System
Good Health + Wellbeing
_Strong visual connection to outside

_Good indoor daylighting, lighting and glare control
_Thermal comfort standards
Environmental Design.
Passive design strategies
Bangladesh has a humid, warm climate influenced by pre-monsoon, monsoon and post-monsoon circulations and frequently experiences heavy precipitation and tropical cyclones. Historically its’ climate experiences temperatures around 26C, but with climate change accelerating, the country can expect hotter temperatures and heavier rainfall. Therefore, it was imperitive to design for this using passive cooling/solar strategies.

Water Infrastructure. Shading Device.
Addressing monsoon season in Bangladesh

Between the months of June and October, Bangladesh experiences a rain season. This is something have factered into my design. The building slopes downwards to direct the water into a bamboo drain pipe that is carried down by a steel pole that is connected to the underground water system. This is then directed to the nearby river.
Drainage Pipe 1:10 Detail halved-bamboo drainpipe
0.8 mm corrugated metal sheeting
60/60 mm mango wood battens; top chord of beam
Ø 110 mm bamboo pole; lower chord 2 x Ø 60 mm bamboo pole; purlins Ø 110 mm bamboo poles metal rod to structure downspout pebbles


Plan view of drainage pipes





When the roof overhang just isn’t enough...
In the early and late hours of the day, especially in winter, the overhang of the roof doesn’t prevent the sun from entering the space. This is when the sun is at its weakest therefore the shading device doesn’t need to prevent overheating, but just to add an extra layer of shade out of direct sunlight. The proposed shading device is made from Sari material due to the fact that it is cheap and readily available in Bangladesh.




100 mm reinforced concrete
2-ply PE foil
105/60 mm handmade brick lining compacted gravel fill hardcore
Iso view of drainage pipes drain connected to water system Precedent. METI School