1 minute read
HOW TO ACHIEVE OPTIMAL HEALTHCARE ACOUSTICS
from INTEGRATED PROJECT DELIVERY SYSTEM (IPD) utilizing DESIGN for MANUFACTURING & ASSEMBLY (DfMA) -2
Many sounds are present in clinical environments, including those from, individualized discussions, patient interaction, equipment, rolling carts, HVAC systems, and among other sources. These can be irritating and at times disruptive to patients depending on their current conditions (i.e., age, hearing ability, medication intake, cultural background, and pre-existing fears and anxieties).
Acoustics in healthcare environments are complex and require a careful, strategic design. Specific acoustical considerations in healthcare settings include supporting patient well-being and privacy; supporting communication among staff; and meeting standards and regulations of Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA). Evidence Based Design acknowledges acoustical control as a key component in healthcare design. In this Calhoun facility, acoustical control was an essential necessity. Numerous steps were taken to control sound levels and transmission. Maintaining patient privacy was our highest concern. The following are some of the targeted mitigation measures implemented into our facility.
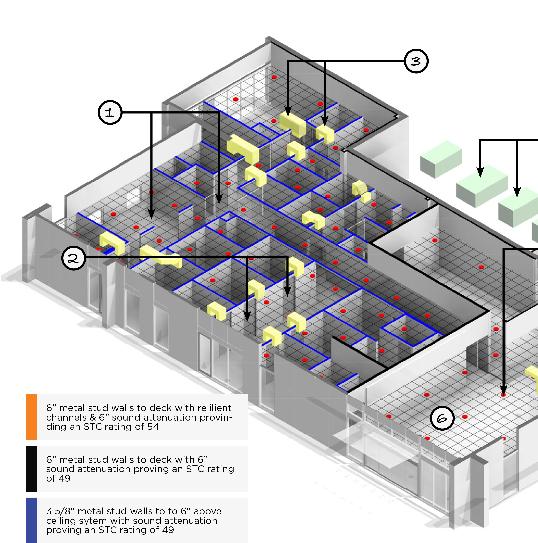
1. Vulcanized Composition Rubber Underlayment: Flooring is an especially important design element within the healthcare environment. Not only is it necessarily found in all spaces, but the type of flooring specified greatly influences the outcome of each space. ECO Silence Underlayment made from Vulcanized Composition Rubber (recycled tires) is an underlayment designed to exceed IIC requirements while maintaining a low profile. Our 2mm underlayment can achieve Delta IIC ratings up to 25dB and IIC ratings up to 72 dB. Rubber underlayment not only provides acoustical properties it adds additional cushion underfoot. Caregiver staff spends most of their workday on their feet and this reduces leg and back fatigue.
2. Interior solid core doors with high pressure laminate, HPL is considered to be one of the most durable decorative surface materials in the healthcare industry. All doors have acoustic sound seals to block sounds from entering or exiting the rooms.
3. The above-door transfer grille simply has two grilles located above the door between the room and common space, one on each wall, with offset baffles to limit sound transmission.
4. Rooftop HVAC units are high SEER units with lower fan speed to mitigate noise transmission
5. Sound Masking in Healthcare Clinics: It was essential to install a state-of-the-art Sound Masking System in our clinic. Our primary focus is to provide our patients’ right to speech privacy, as well as the physical and psychological effects of noise on patients and caregivers. Studies have shown that noise increases distractions affect health and mood decreases productivity, and increases error rates. Sound masking is part of a proactive approach in providing patients with speech privacy and comfort and providing our caregivers with the productive “space” they need to excel.
6. Lay-in ceiling with sound attenuation providing a CAC value of 42. Typical throughout










