Evolving Environment. Transforming Landscapes
Duisburg, Ruhr Region

Winter Semester 2022-2023
E’Lina Liza, Shubhrata Naik, Mayu Masuda, Azadeh Ziaee. https://www.dw.com/en/port-of-duisburg-turns-300/g-19568482
Research
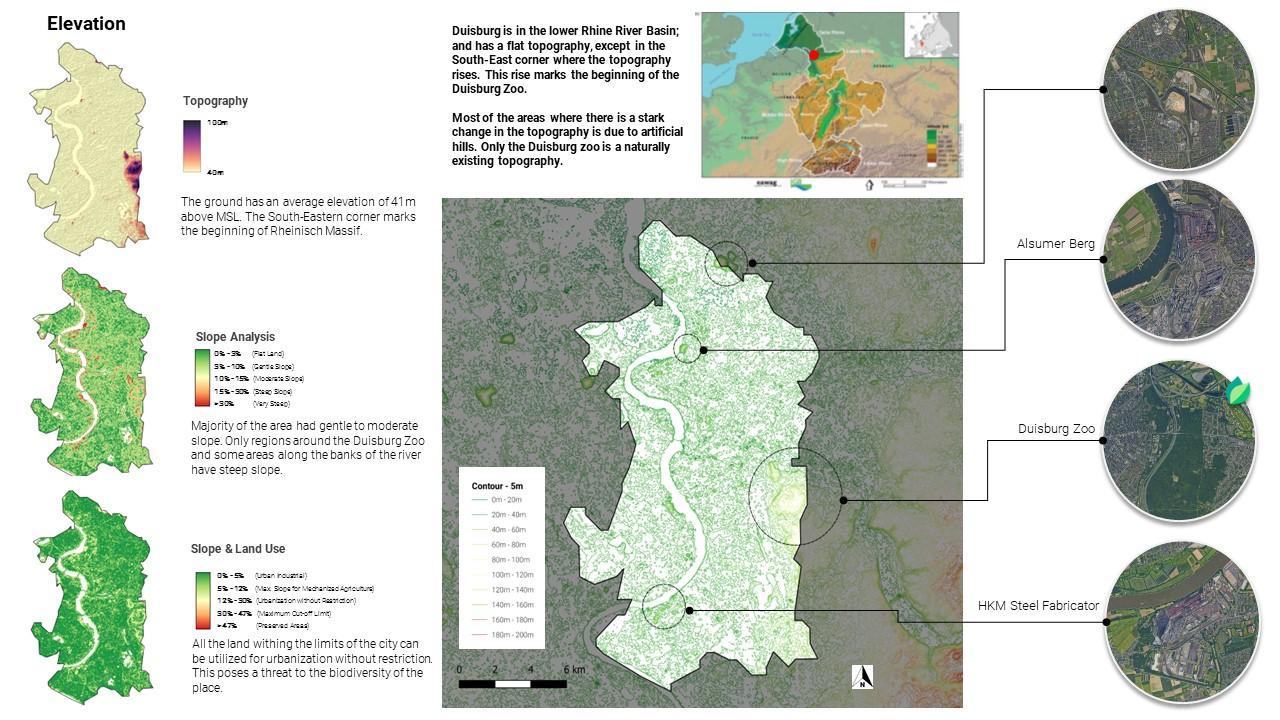
1.Topography
2. Vegetation
3. Urban
4. Infrastructure
ComparativeAnalysis
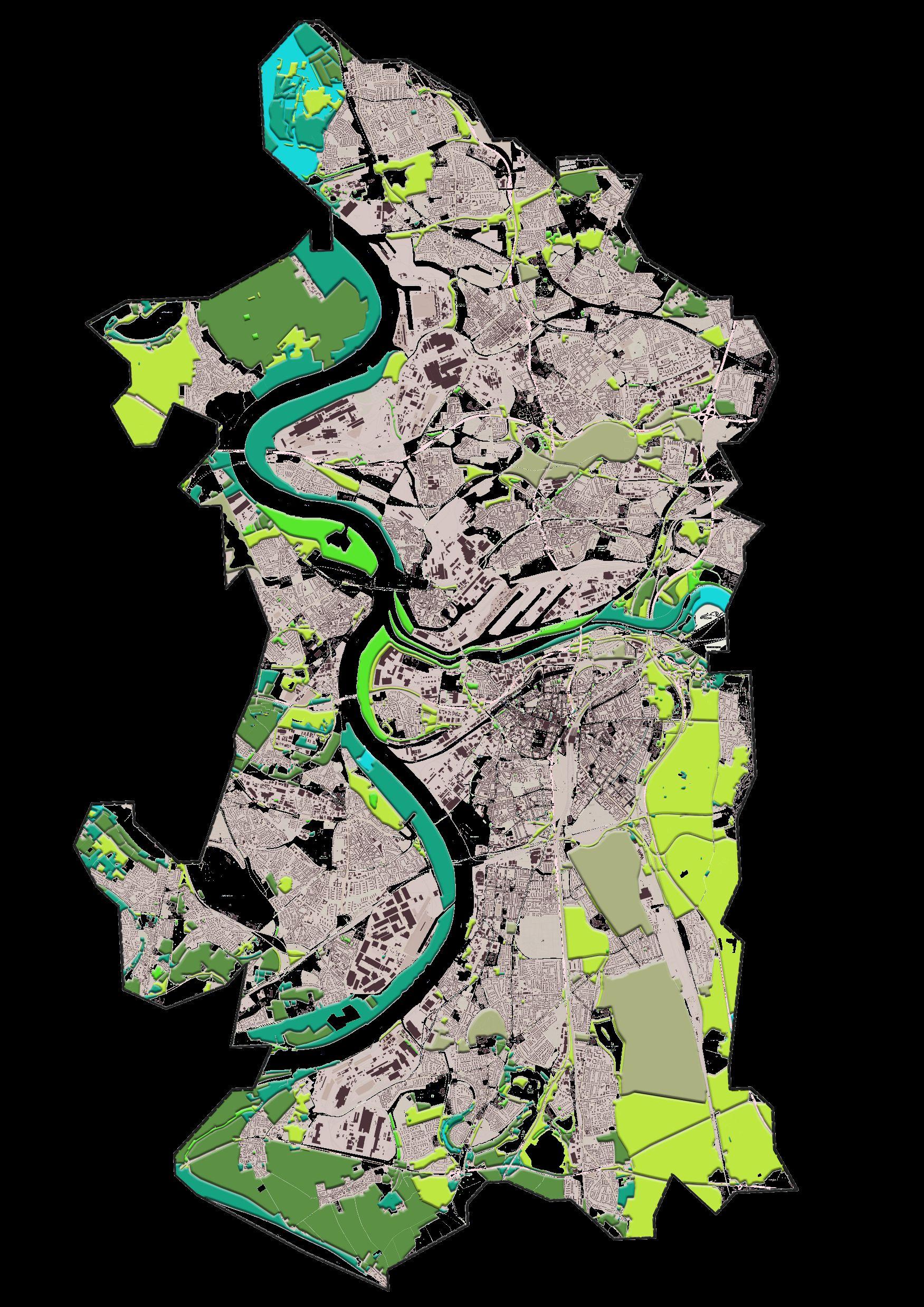
Map 1: Landscape dynamics analysis
Topography + Water + Vegetation +Agriculture + Infrastructure
Map 2.1 : Landscape transformations
Natural LandscapeTransformation - In year 2001 and 2022
Map 2.2 : Landscape transformations
Artificial LandscapeTransformation - In year 1890 and 1926 (Heavy Industrialization era)
SWOTAnalysis map and Guidelines
Agenda
Research Topography
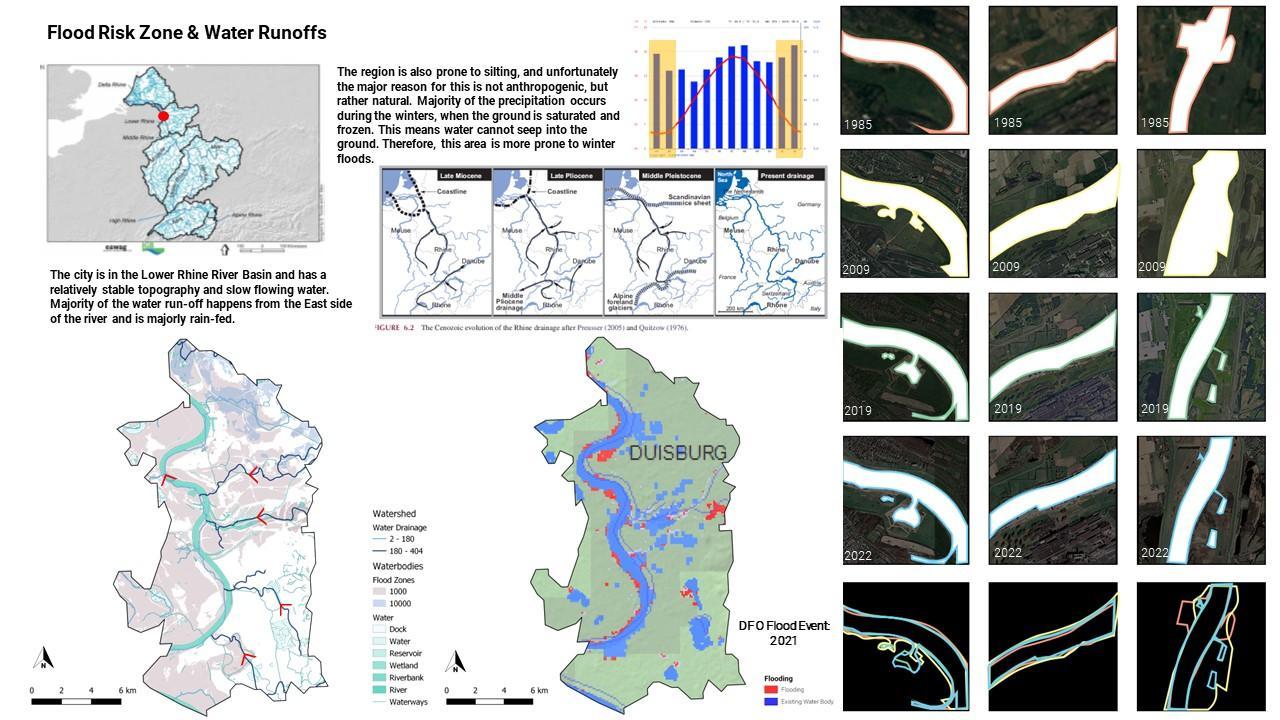
Topography, soil aspects, water, floods, rain
1 2 3
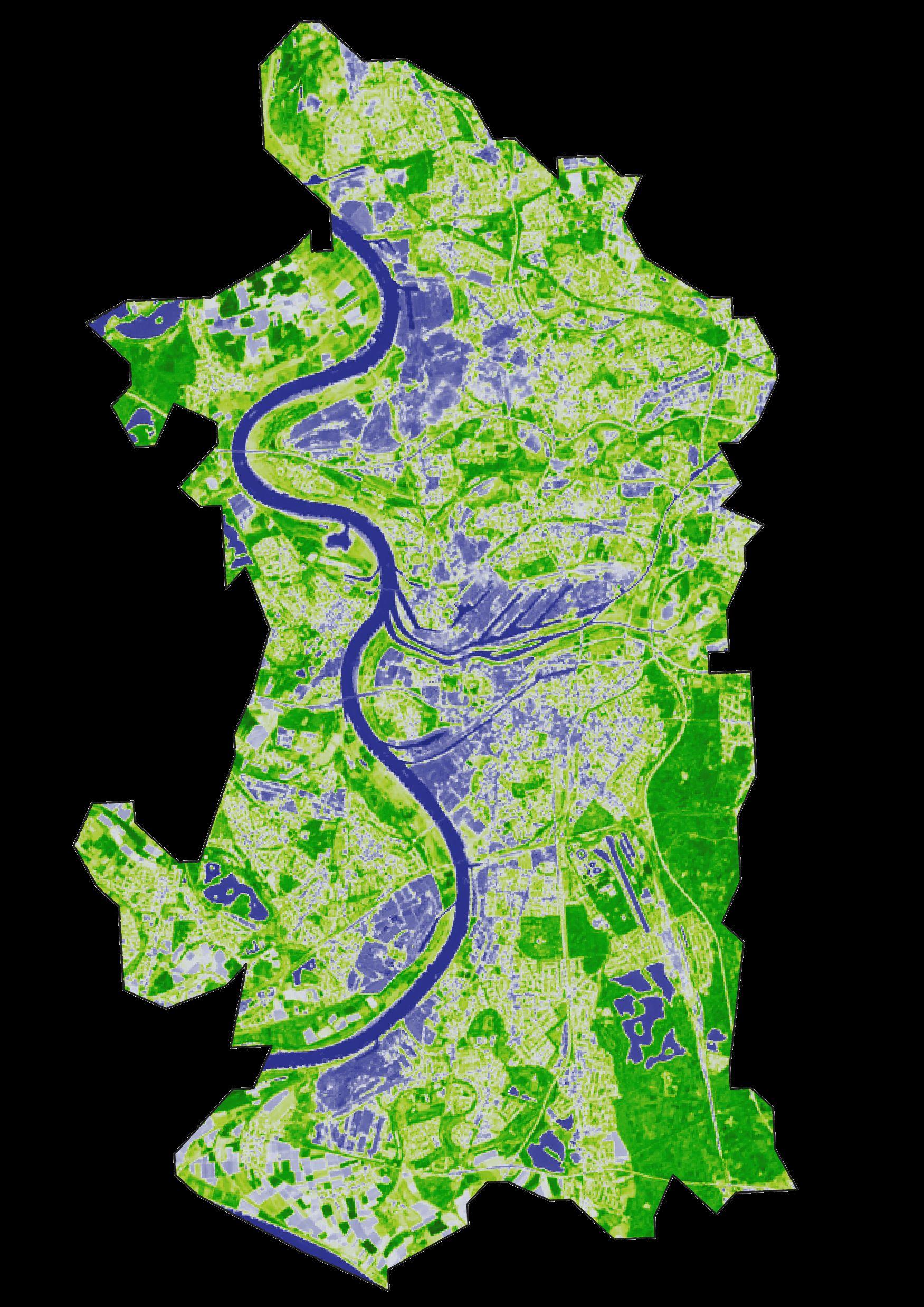
Research Vegetation
Green areas
Vegetation types, forests, parks, protected areas, open spaces, agriculture mosaic
Vegetation layers
Farmland
Forest
▪ Vegetation type including farmland forest, nature reserve (major part of vegetation) are majorly located on peripheral boundaries of Duisburg.

▪ Whereas Grass, Meadow, are located around Rhein and Ruhr river.
The landscape park
Duisburg-Nord (leisure park )

Overlapped Vegetation Map
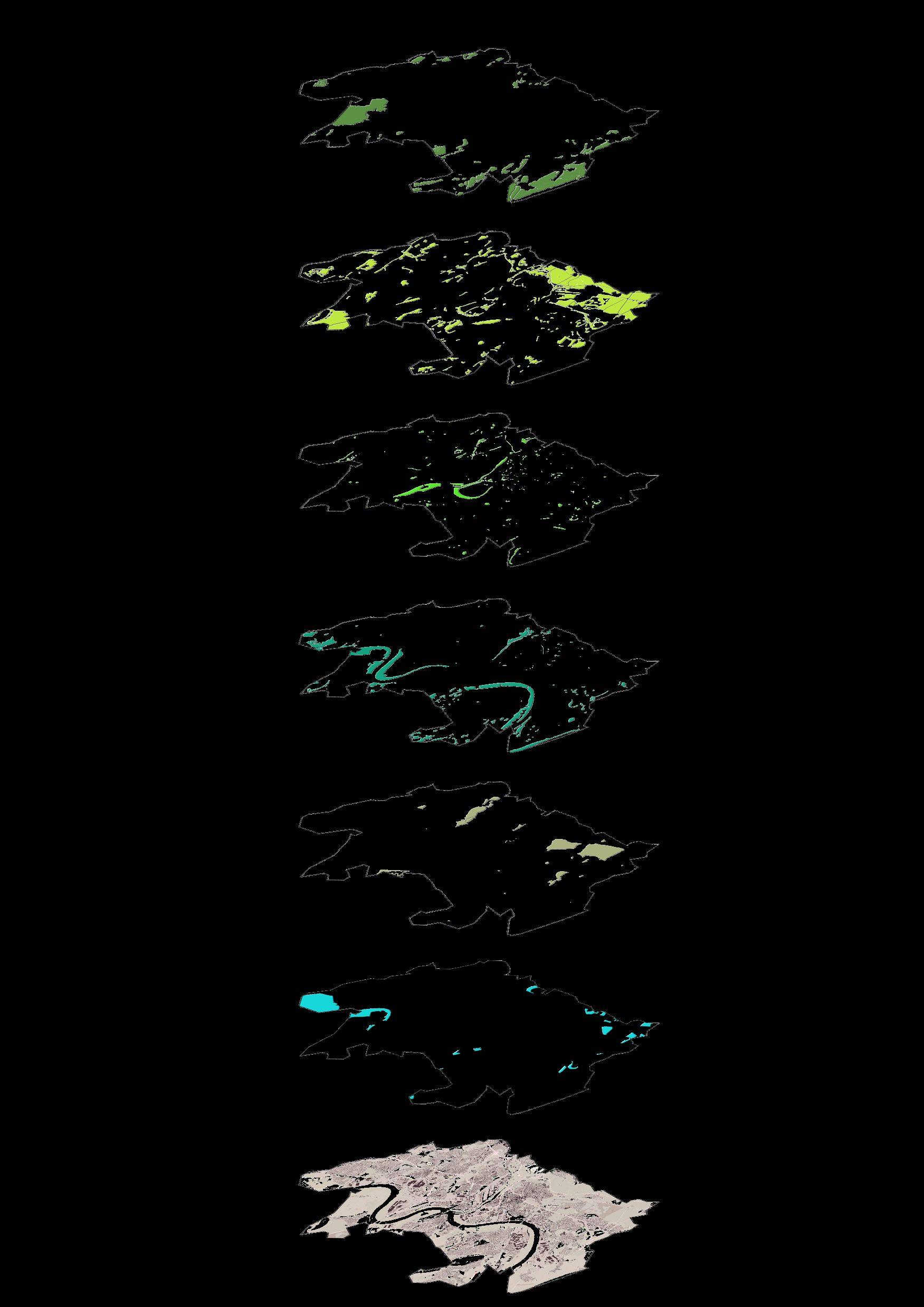

Grass
Meadow
Recreation ground
Nature reserve
▪ Built - 1990s
▪ On a former ironworks industrial area.
https://www.urbangreenbluegrids.com/p rojects/landscape-park-duisburg-nord/ Sportpark Duisburg
▪ Before the end of 19 century – Forest area of the Krupp company
▪ At the end of the 19th century – Silting out the slag produced in the steel industry .
▪ In 1919 – Recreation area (Sportpark Duisburg)
https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sportpark_Du isburg Recreation area (part of forest area)
• Sechs-Seen-Platte
• Spielplatz
• Outdoor swimming pool
Open spaces
Research Urban
Territory occupation history and the major contemporary challenges
War, reconstruction, historical heritage, urban expansion axes, morphological patterns
Urban_Historical transition
1840 1895 1925 1940 1944 1945 1962 1972 1990 2022 Bombing during WW2 Industrial area is heavily destroyed due bombing The streets and places in the central remain as cultural center The segregation between residential area and work area Increase of industrialization after 1880 Absorption of the outer communities Enlargement of the city Along with the absorption of out cities https://www.britannica.com/place/Duisburg
1840_Streetnetwork

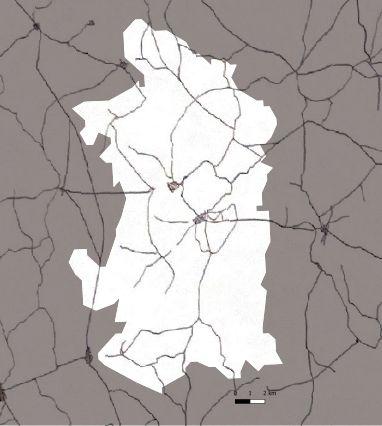
1880 1944 1962 1972
The streets and
in the central
as cultural center
segregation between residential area and work area Increase of industrialization Enlargement of the city Along with the absorption of out cities
Industrial area is heavily destroyed due bombing
places
remain
The
Die Entwicklung des Duisburger Stadtraumes der Einfluß von Innovationen auf Räume und Funktionen(1999) / HaaseAndrea
1890_Streetnetwork

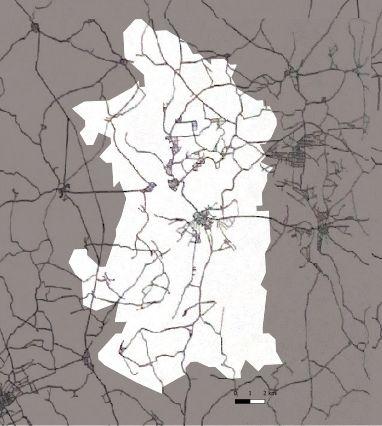
1880 1944 1962 1972
area is heavily destroyed due bombing The streets and places in the central remain as cultural center
segregation between residential area and work area Increase of industrialization Enlargement of the city Along with the absorption of out cities
Industrial
The
1926_Streetnetwork

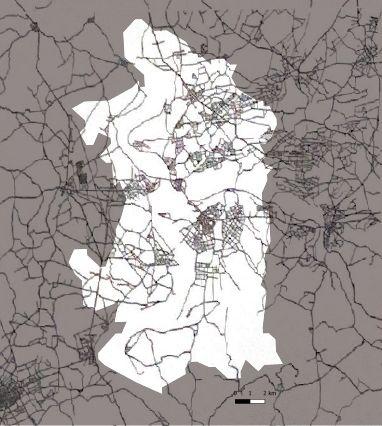
1880 1944 1962 1972
area is heavily destroyed due bombing
streets and places in the central remain as cultural center
segregation between residential area and work area
of industrialization
of the city
with the absorption of out cities
Industrial
The
The
Increase
Enlargement
Along
1939_Streetnetwork

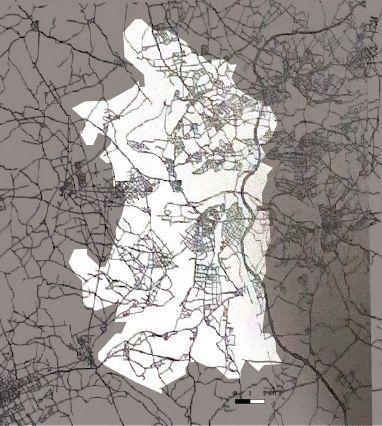
1880 1944 1962 1972
the
as cultural center
segregation between residential area and work area
of industrialization
of the city
with the absorption of out cities
Industrial area is heavily destroyed due bombing The streets and places in
central remain
The
Increase
Enlargement
Along
1962_Streetnetwork

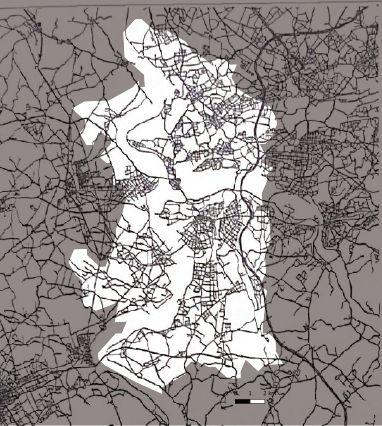
1880 1944 1962 1972
bombing
streets and places in the central
as cultural center
segregation between residential area and work area
of industrialization
of the city
with the absorption of out cities
Industrial area is heavily destroyed due
The
remain
The
Increase
Enlargement
Along
1979_Streetnetwork

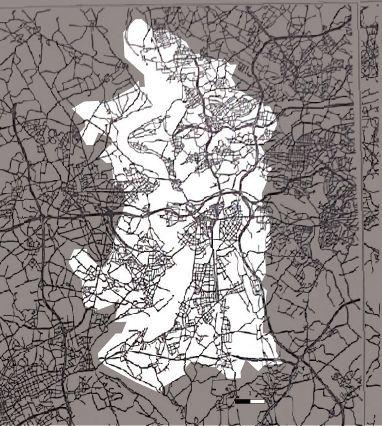
1944 1962 1972
1880
segregation between residential area and work area
of the city
of out
Industrial area is heavily destroyed due bombing The streets and places in the central remain as cultural center The
Increase of industrialization Enlargement
Along with the absorption
cities
1989_Streetnetwork

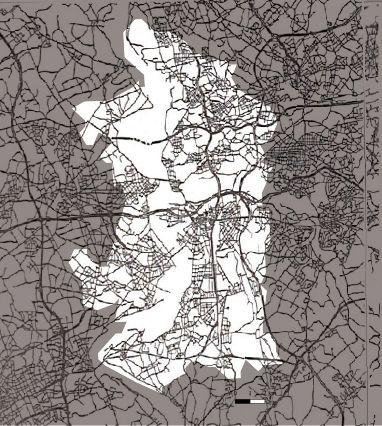
1880 1944 1962 1972
and
in the central
as cultural center
segregation between residential area and work area
of industrialization
of the city
with the absorption of out cities
Industrial area is heavily destroyed due bombing The streets
places
remain
The
Increase
Enlargement
Along
Urban expansion during industrialization before the WW2



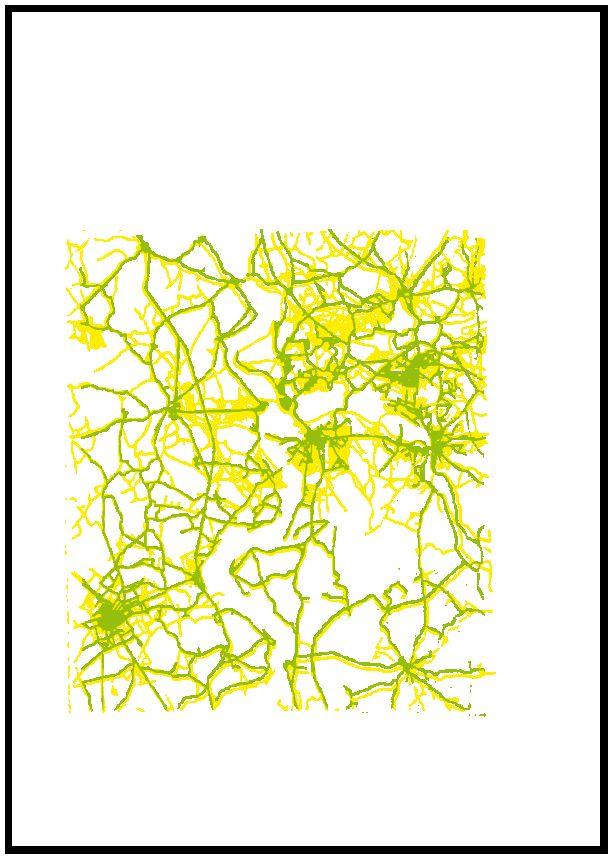
1880 1944 1962 1972 Industrial area is heavily destroyed due bombing The streets and places in the central remain as cultural center The segregation between residential area and work area Increase of industrialization Enlargement of the city Along with the absorption of out cities 1840-1890 1890-1926 1926-1939 1840 1890 1926 1939
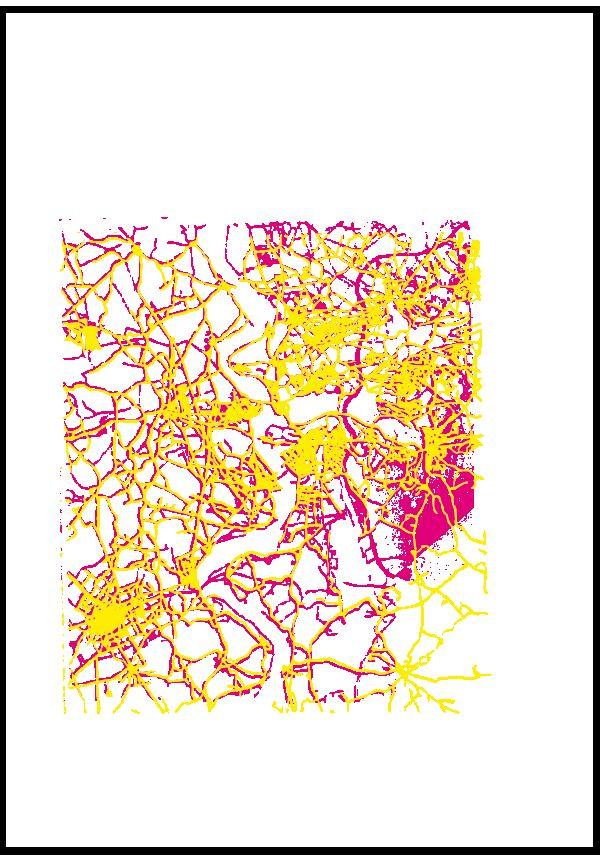
Urban expansion buffer
1989_Streetnetwork and urban expansion buffer

1944 1962
1880
Industrial area is heavily destroyed due bombing The streets and places in the central remain as cultural center
The segregation between residential area and work area Increase of industrialization
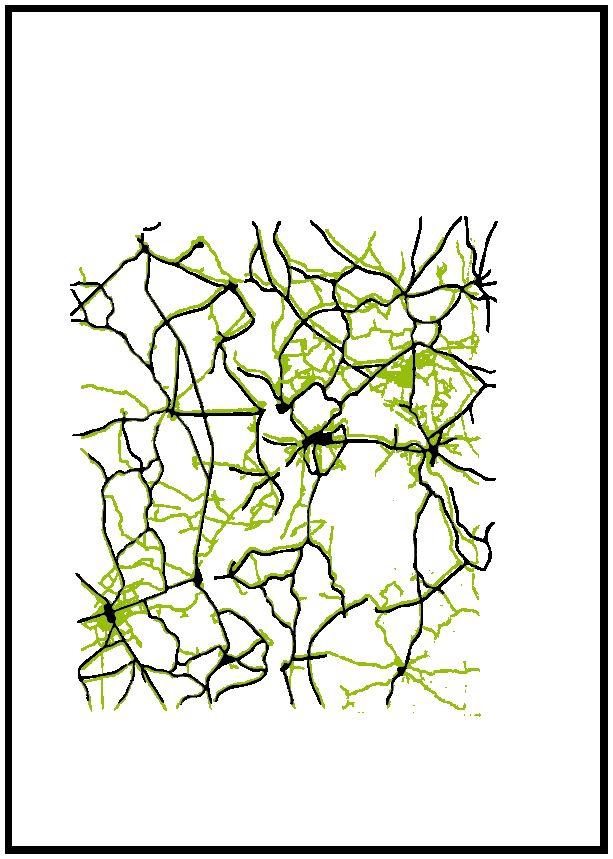
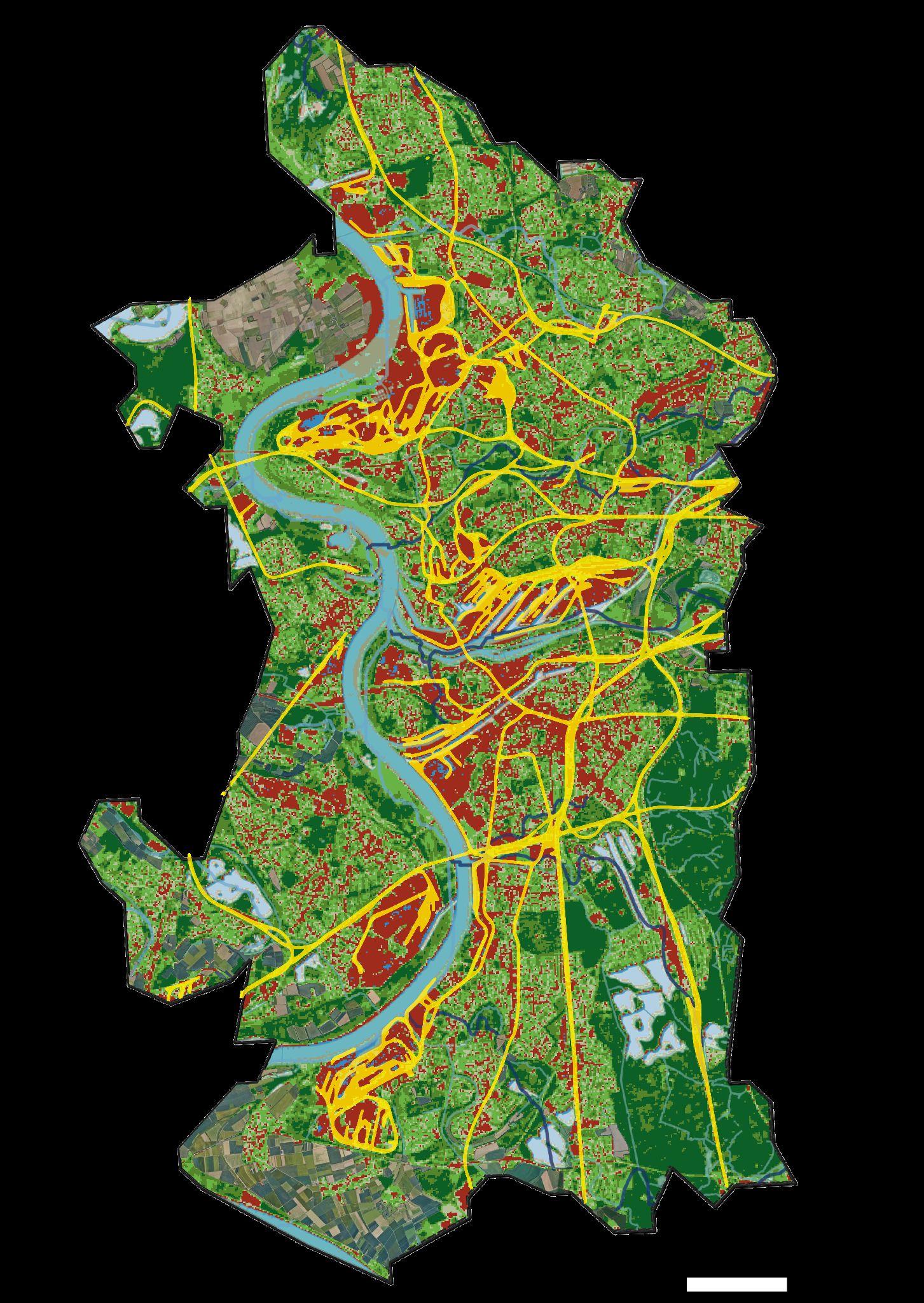
Research Infrastructure
Territory infrastructure
Connections, mobility, transport, roads, highways, trains, cycling paths, streets morphological characteristics.
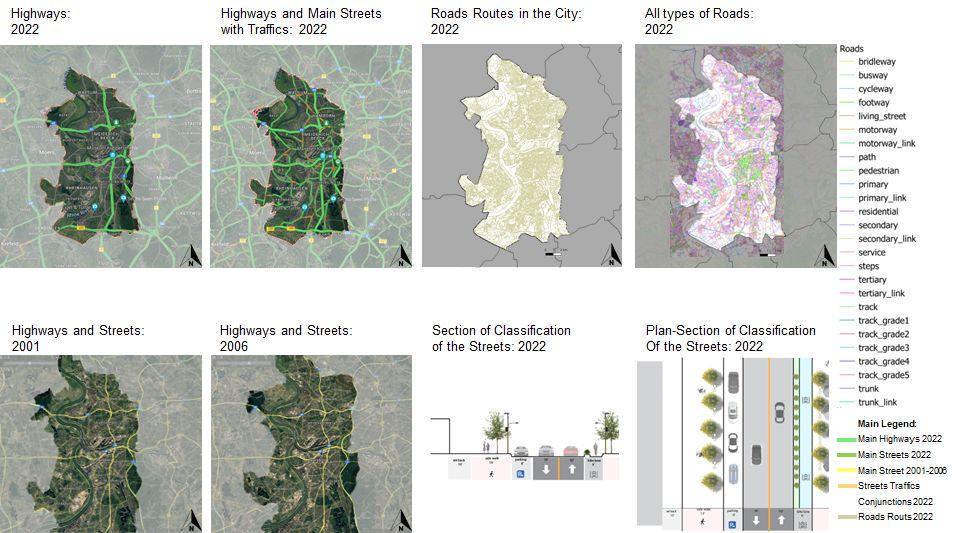
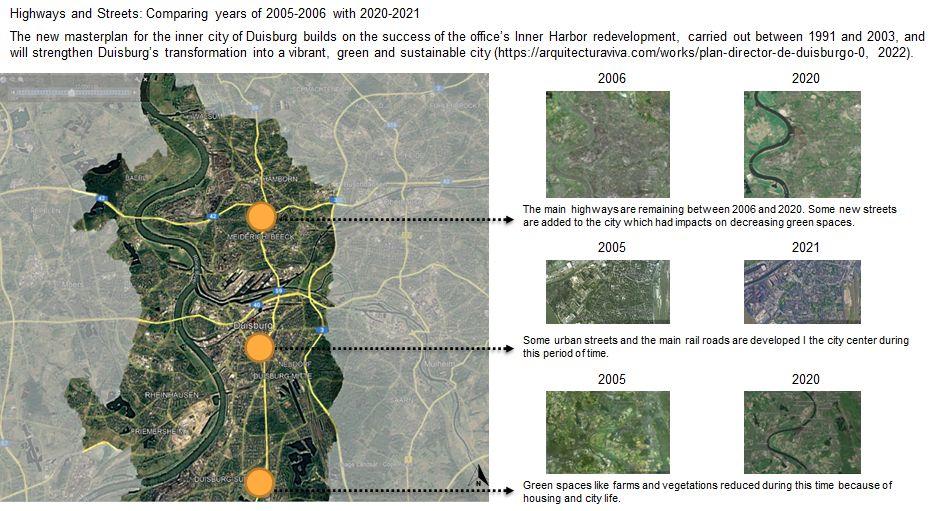
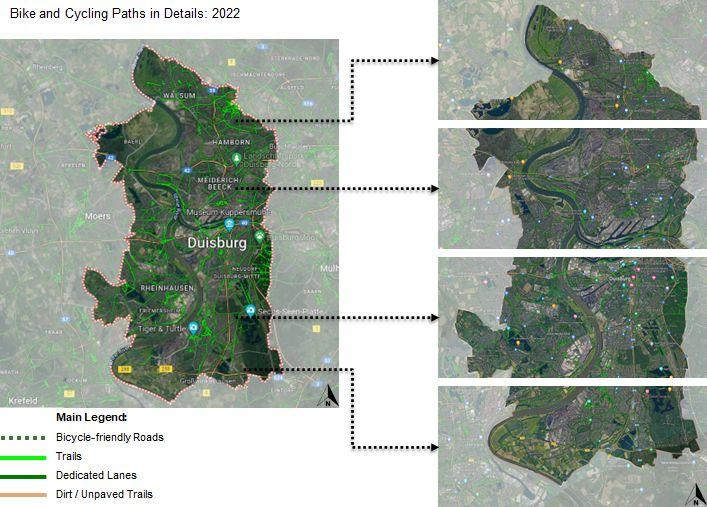
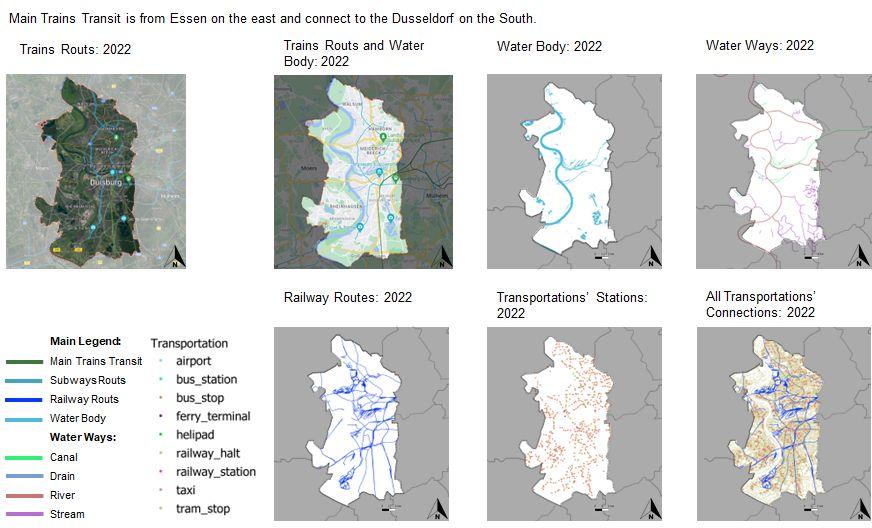
Comparative Analysis
Topography Vegetation Urban Infrastructure
MAP1: Landscape dynamics analysis (latest map)
Topography+Water body+Vegetation base(vegetation loss area)+Agricultural mosaic+Infrastructure
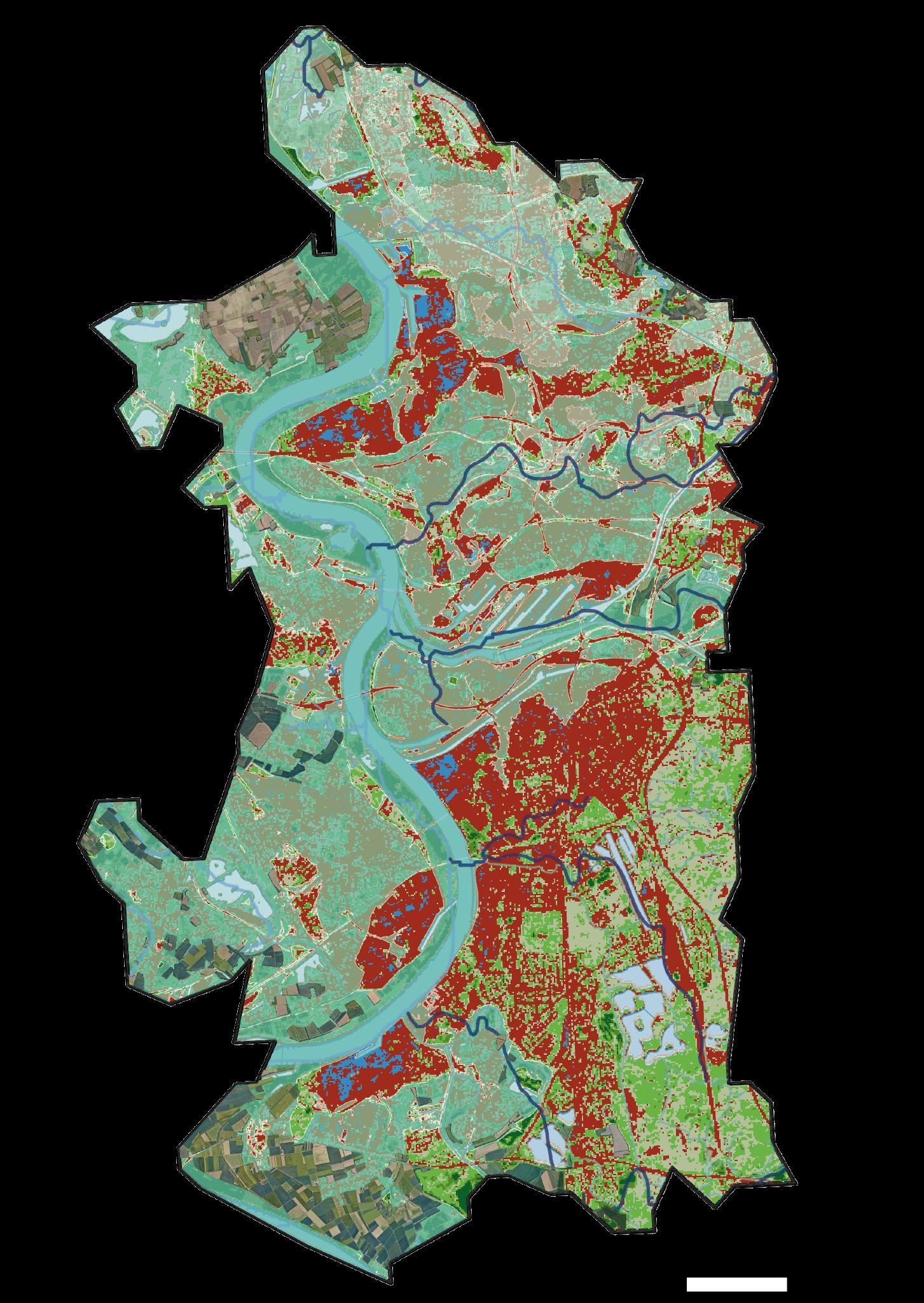
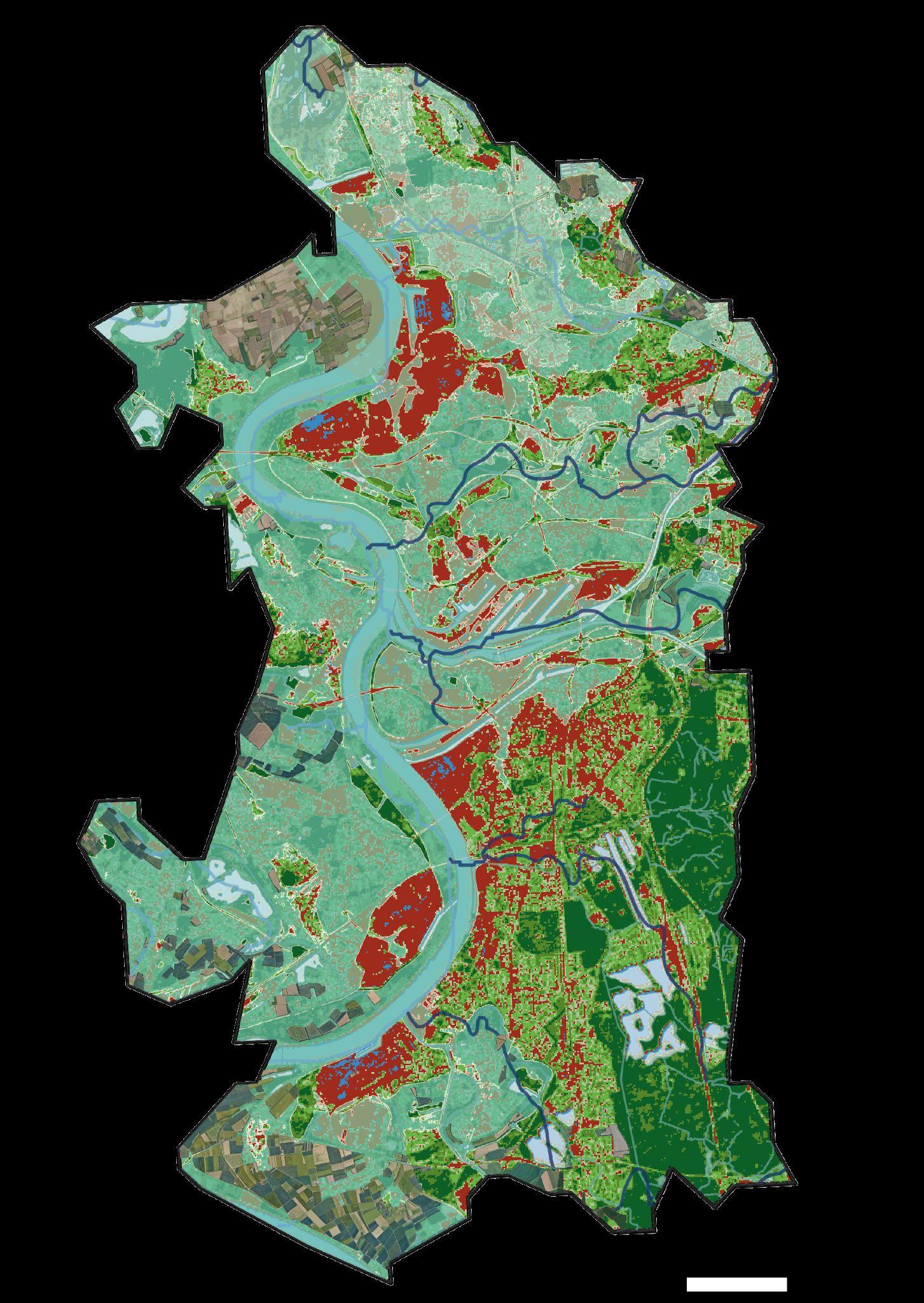
Maybe deciduous trees inhabit in the gap area
Flood risk area and Vegetation loss area , Is not overlapping In the summer.


However, in winter It’s overlapping
Deciduous trees area are vulnerable to flood risk

MAP1: Landscape dynamics analysis (latest map)

Topography+Water body+Vegetation base(vegetation loss area)+Agricultural mosaic+Infrastructure

Rail road is overlapping with Vegetation loss in summer


Main road is overlapping with Vegetation loss in winter
Rapidly developed industrial area is overlapping with vegetation loss areabelowtheriver
MAP2.1 : Landscape transformations - Natural landscape transformation



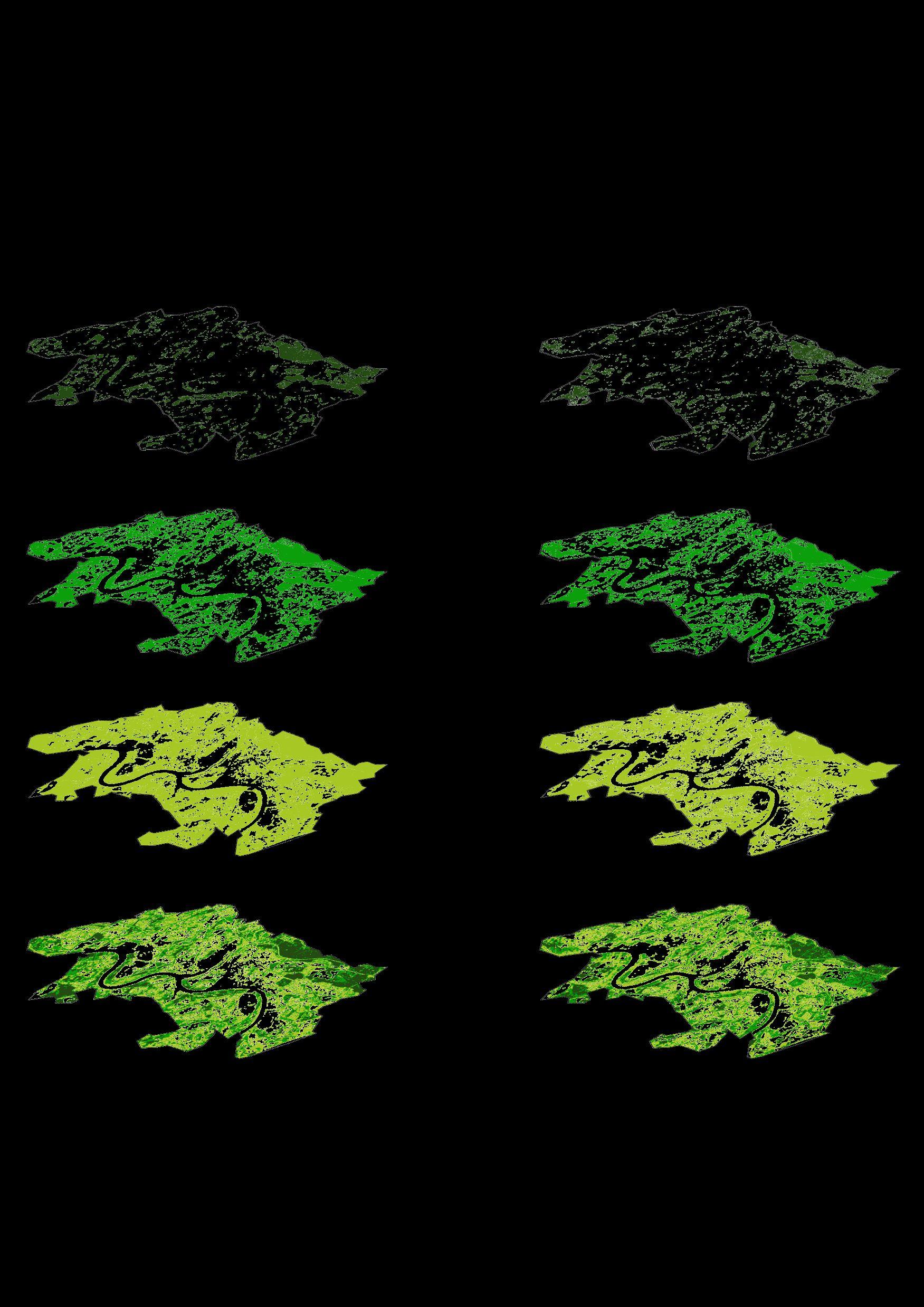





Period 1 (Year 2001) + Period 2 (Year 2022)




Overlapped vegetation of density 0.2, 0.3, 0.4 Overlapped vegetation of density 0.2, 0.3, 0.4 Vegetation map – 05.07.2001 ( Summer ) Vegetation map – 30.07.2022 ( Summer ) Major affected layer Major affected layer
Vegetation map
05.07.2001 ( Summer )

Overlapped Vegetation map of 2001 and 2022

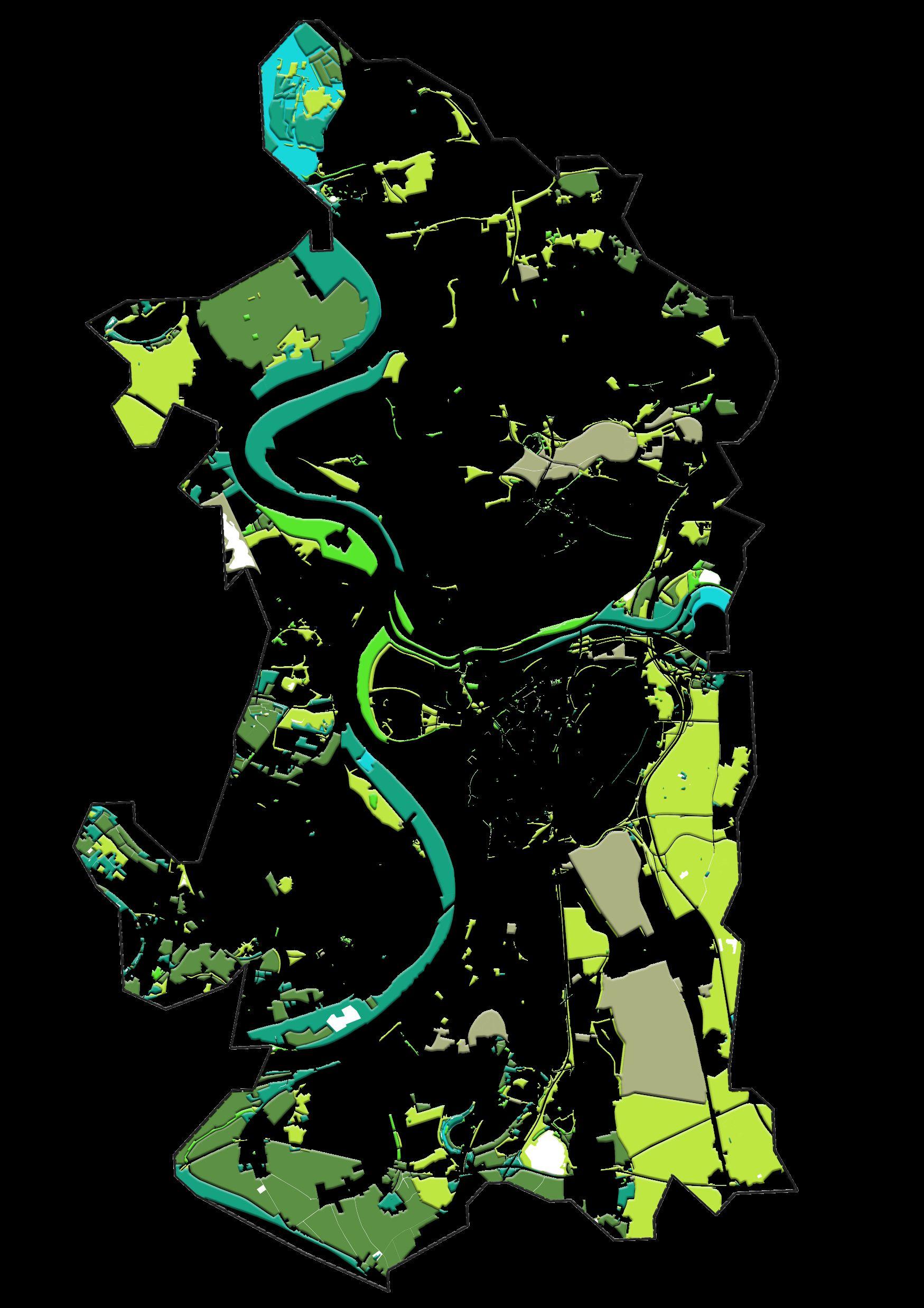
The areas that presented bigger changes between 2000 and 2020
Vegetation map


30.07.2022 ( Summer )
Overlapped Vegetation type map

Map showing buffer areas where there were vegetation in 2001 and now in 2022 these are disappeared.
Conclusion –

▪ Loss of vegetation in recent years.
▪ Overall Reduction of density of vegetation in recent years.
▪ Major reduction of density in Farmland layer.

MAP2.2 : Landscape transformations -Artificial landscape transformation

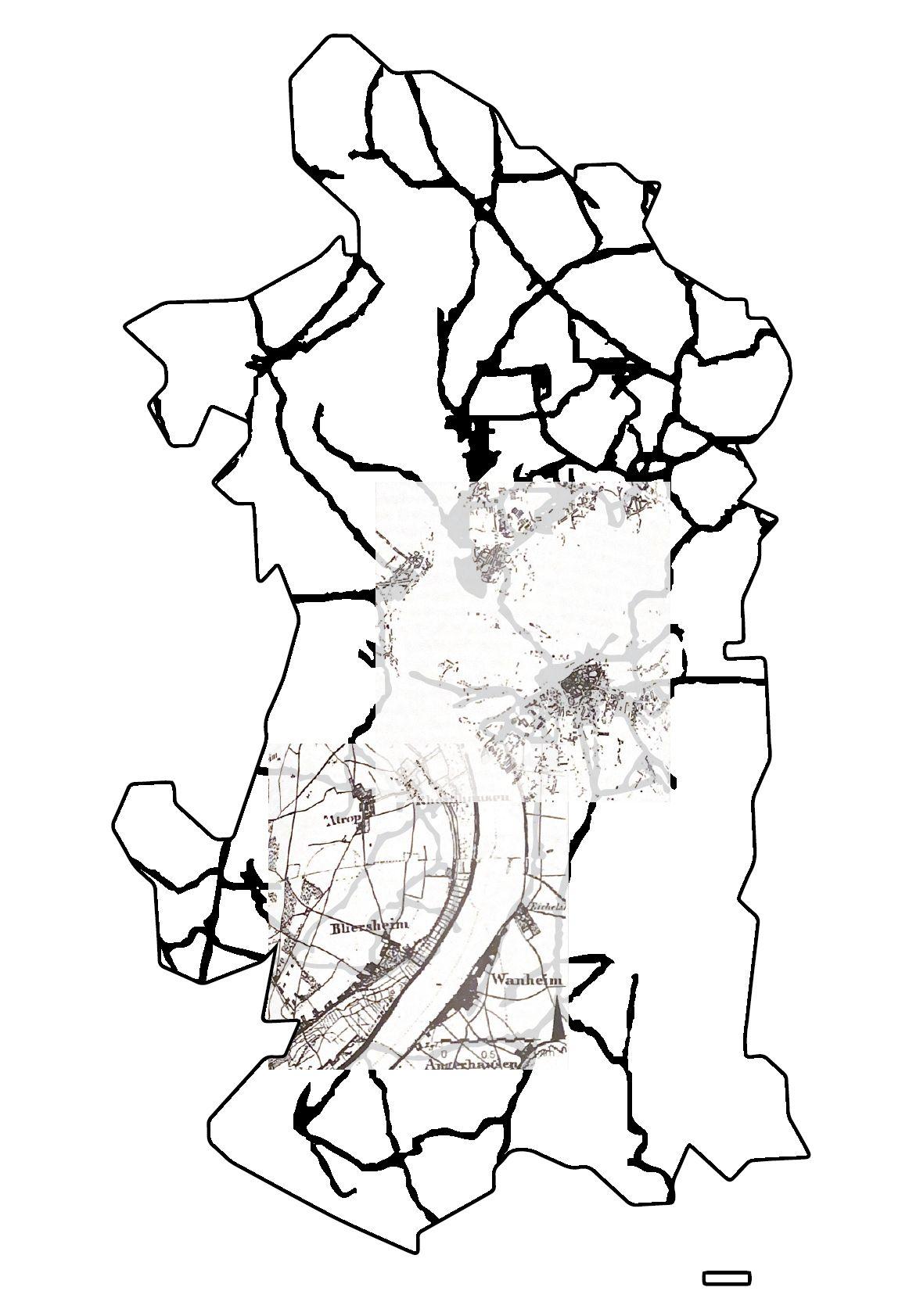
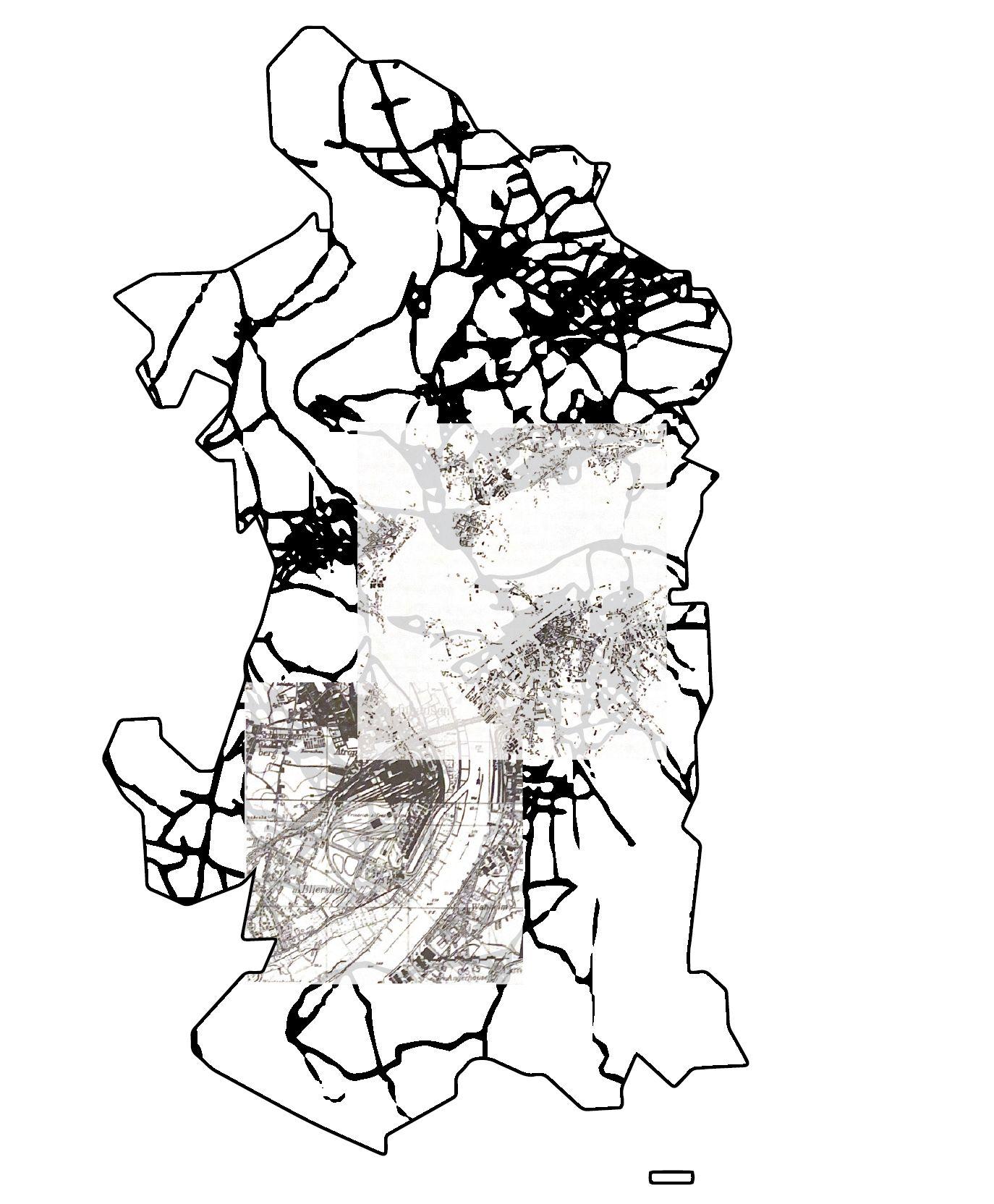
Period 1 (Year 1890) + Period 2 (Year 1926) Heavy Industrialization era

Build area and Infrastructure
Build area and infrastructure
map(1890)
map(1926)
1880 1944 1962 1972 The streets and places in the central remain as cultural center The segregation between residential area and work area Increase of industrialization Enlargement of the city Along with the absorption of out cities
SWOTAnalysis and Guideline:
SWOTMap
Guideline:
- Introduction
- Main Focus
- Suggestions Map
SWOTAnalysis Map

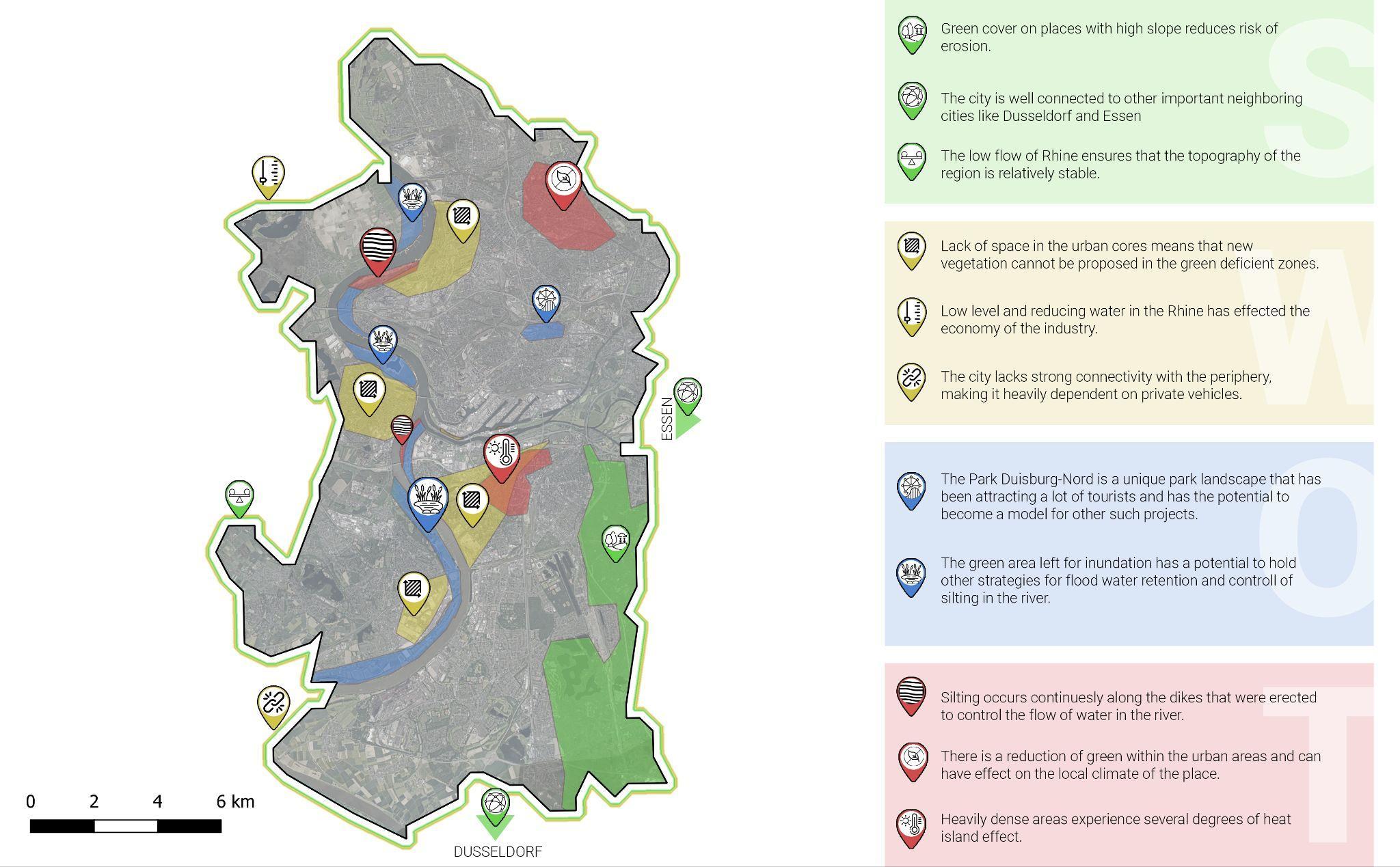
Very stable topography.
Habitat patch connectivity.
9% largest catchment in Urban area.
79.4% in cropland
More green spaces on peripheral boundaries of Duisburg.
Sustainable development -The landscape park Duisburg-Nordconversion of brown field (former industrial areas into leisure park).
City has parking for the residents car.
The highways are connected well to the other big cities in the vicinity of the Duisburg. The city has cycling paths which are beneficial for the inner city traveling.
Low water levels lead to transportation disruptions that cause a significant and economically meaningful decrease of industrial production. (Ademmer, Ed, 2020)
Ecological connectivity needs improvement
Loss of aluvial flood planes, causes issues.
Less vegetation in city center.
Increased urbanization.
The traffic conjunctions is a problem during traffic jam times for local people. Most of the people use their own cars instead of the public transportation.
Create more green spaces in city center Create more green spaces in city center
Railways connected to the other major cities in Germany. Thus, people can use it during weekends and holidays to travel to other cities.
River side can be a sidewalk and cycling paths for the residents.
Flooding in winter, as water can not seep into the frozen ground
One of the 14 large cities in the lower rhine
Loss of habitat
Flooding and other climate change issues
City has less parking parking spaces for people during weekends and weekdays, when all local people and tourists are in the street. The city has many bus and train stations but it is needed to have public transportation like bus stations in the border of the city.
T
S W O
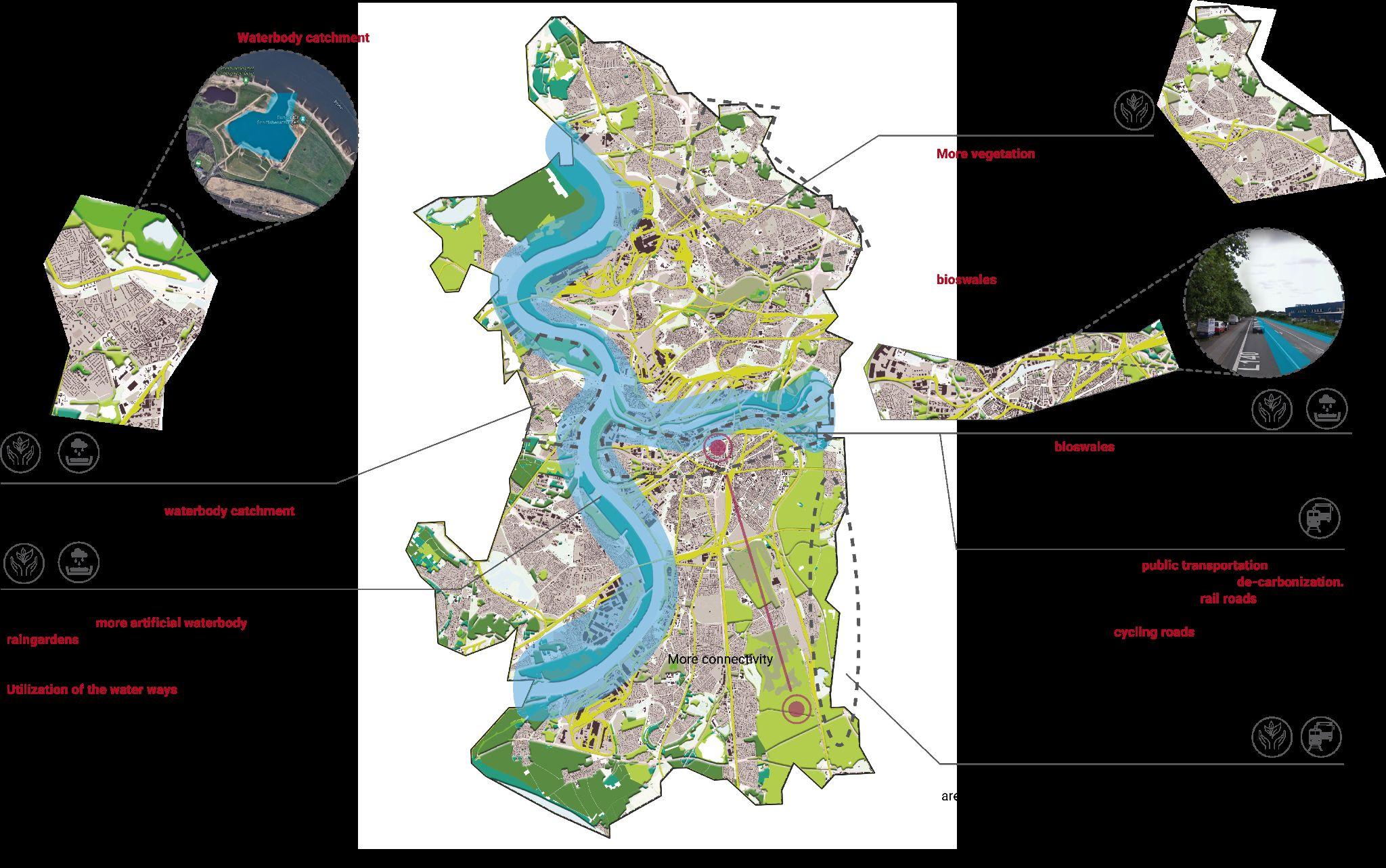
DUISBURG GUIDELINES

INTRODUCTION
Duisburg is the only city of the Rhine-Ruhr region lying on both the Rhine and Ruhr rivers.The city spreads along both sides of these rivers. The main issues we found are the vegetation loss, flood risks and traffic orientated urban area.
Therefore, we are aiming to enhance the ecological environment based solutions on our researches.
MAIN FOCUS
Improve ecological environment
Replacement of car lane with public transportation
Creating a water catchment area



Evolving Environment. Transforming Landscapes
Duisburg, Ruhr Region
E’Lina Liza, Shubhrata Naik, Mayu Masuda,
Azadeh Ziaee.
Thanks ForYourAttention
Winter Semester 2022-2023


















































