EUROPEAN EDITION
MEDICAL PLASTICS news USING METROLOGY TO SOLVE COMMON QUALITY CHALLENGES THE IMPORTANCE OF TPU IN THE MEDICAL INDUSTRY ADVICE FOR OEM PART DESIGN ENGINEERS
FROM BIOPLASTICS TO BIOPRODUCTS
Bormioli Pharma’s support of a circular economy coupled with its approach to innovation has taken it from simply offering bioplastics to developing bioproducts.
ISSUE 62
September - October 2021
WWW.MEDICALPLASTICSNEWS.COM
You expect precision. We deliver. contract manufacturing injection moulding medical devices Our manufacturing includes cleanroom environments, automation, and assembly services, delivering total value solutions that reduce investment and improve cost.
www.carclo-ctp.co.uk +44 208 685 0500 sales@carclo-usa.com United States
• United Kingdom
• Czech Republic • India
• China
CONTENTS Sep/Oct 2021, Issue 62
Regulars 5 Comment Corrine Lawrence highlights how working practices and company ethos can affect manufacturing efficiency. 6 Digital spy 12 Cover story Roberto Valenti discusses how Bormioli Pharma’s approach to innovation has taken it from simply offering bioplastics to developing bioproducts. 26 09:2021
Features 8 Events: The talk of the show A preview of the conferences complementing The Mediplas Zone at this year’s Interplas event. 11 Labelling: The silver lining to cloud-based labelling Loftware’s Susan Gosnell provides small manufacturers with limited resources a solution to meet labelling compliance and validation requirements.
14 Testing & inspection: A measured approach Using metrology to solve common quality challenges can enhance competitiveness, says Jason McGlynn of The Sempre Group. 16 Elastomerics: TPU — your flexible friend Permali’s Fraser Rankin discusses TPU and its importance and growing prevalence in the medical industry. 18 Thermoforming: The heat is on Todd McDonald at TEQ highlights why thermoforming is proving itself a popular manufacturing technique for medical packaging. 22 Designing medical devices: Design tips … on a plate Martin Larsen of Rich Plastics offers OEM part design engineers advice on design issues relating to well plates and microplates. 24 Anticounterfeiting & serialisation Swiss start-up Morphotonix provides a safe and reliable technology to protect brands and lives.
WWW.MEDICALPLASTICSNEWS.COM
3
Medtech | Digital HealthTech | Medical Plastics | Manufacturing | Software | Inspection and Metrology Regulation | Design | Early-Stage | Innovation | Pharmaceutical | Manufacturing
1-2-1 Meetings Programme New Product Launches 3 Conference Stages Technology Pavilions Dynamic Features Start-Up Zone
8-9
JUNE 2022
Med-tech innovation expo #MedTechExpo @MedTechOnline
Be inspired by thought-leaders and discover new solutions, materials, machines and applications from almost 200 exhibitors. Join the fastest growing event in medtech. We’ll see you there!
NEC | BIRMINGHAM | UK
Save the Date
PLATINUM PARTNER
www.med-techexpo.com
Co-located Shows
Medical Device Supply Chain Intelligence
editorial content producer | corrine lawrence corrine.lawrence@rapidnews.com advertising | caroline jackson caroline.jackson@rapidnews.com
Editor’s Comment
vp sales & sales talent | julie balmforth julie.balmforth@rapidnews.com head of studio & production | sam hamlyn graphic designer | matt clarke publisher | duncan wood Medical Plastics News Europe Print Subscription – Qualifying Criteria UK & Europe – Free US/Canada – £249 ROW – £249 Medical Plastics News NA Print Subscription – Qualifying Criteria US/Canada – Free UK & Europe – £249 ROW – £249 FREE on iOS and Android devices Subscription enquiries to subscriptions@rapidnews.com Medical Plastics News is published by: Rapid Life Sciences Ltd, Carlton House, Sandpiper Way, Chester Business Park, Chester, CH4 9QE T: +44(0)1244 680222 F: +44(0)1244 671074 © 2021 Rapid Life Sciences Ltd While every attempt has been made to ensure that the information contained within this publication is accurate the publisher accepts no liability for information published in error, or for views expressed. All rights for Medical Plastics News are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part without prior written permission from the publisher is strictly prohibited.
BPA Worldwide Membership ISSN No:
C O R R I N E L AW R E N C E
EFFICIENTLY INEFFICIENT
I
continue to read reports of companies going out of business and work forces facing redundancy, but just when I thought many are reining in their purse strings and trying to work smarter and more efficiently to recover from the havoc wreaked by the coronavirus pandemic, I find myself regularly presented with stories that beggar belief. My source? Not the internet, not press releases … but my husband. After being made redundant last year due to the pandemic, my husband gratefully found employment in a 24/7 labelling factory. On his first day his supervisor advised him to check his machine before each shift in case the previous shift operator had sabotaged it (there’s a productivity rivalry between the two shift teams). If instances of bullying occur, my husband was encouraged to seek revenge “with interest” to deter repeat performances. Operators ‘cherry pick’ their work despite there being a priority list. Spelling mistakes and typos on the labels are ignored because “they’ve always been like that”. During nightshifts, when management is absent, operators steal out (without clocking off ) to purchase fast food. Recently, one nightshift employee went missing for more than an hour (how come it took that long to realise he was missing?); after the canteen, washrooms and car park were searched, he was discovered in a different area of the factory catching up on some missed TV. Was he reprimanded? No.
wondered why he, the new guy, knew it and no one else did. After punching in the code and cajoling the machine back to life, my husband approached the colleague who told him the password to question why no one else knew it. He was met with: “Shhh, that’s our little secret.” The ethos of that workforce is to follow the path of least resistance. Yet, should the company decide to make redundancies, the staff will be in an uproar. Last week, 16 employees were issued a warning for not wearing their uniform baseball caps which, I hasten to add, serve no health and safety purpose. Management had identified the culprits by going through the factory CCTV. If only they’d spend as much time enforcing other aspects of the business, perhaps their balance sheet would be a little healthier; last year’s turnover was £20 million, yet the net profit was only £22,000! My point? The current economic challenges have not removed complacency and lethargy in many companies. Counterproductive practices are not always identified. Before you scoff at the above examples, are you sure they’re not happing in your company. Really sure?
Clocking on one morning, my husband discovered that most of the night shift had done practically nothing because a machine had gone down during the night and no one knew the password to reset it. Flabbergasted, my husband
2047 - 4741 (Print) 2047 - 475X (Digital) WWW.MEDICALPLASTICSNEWS.COM
5
DIGITAL
COATING UPDATE
spy DEVICE UPDATE
www.medovate.co.uk
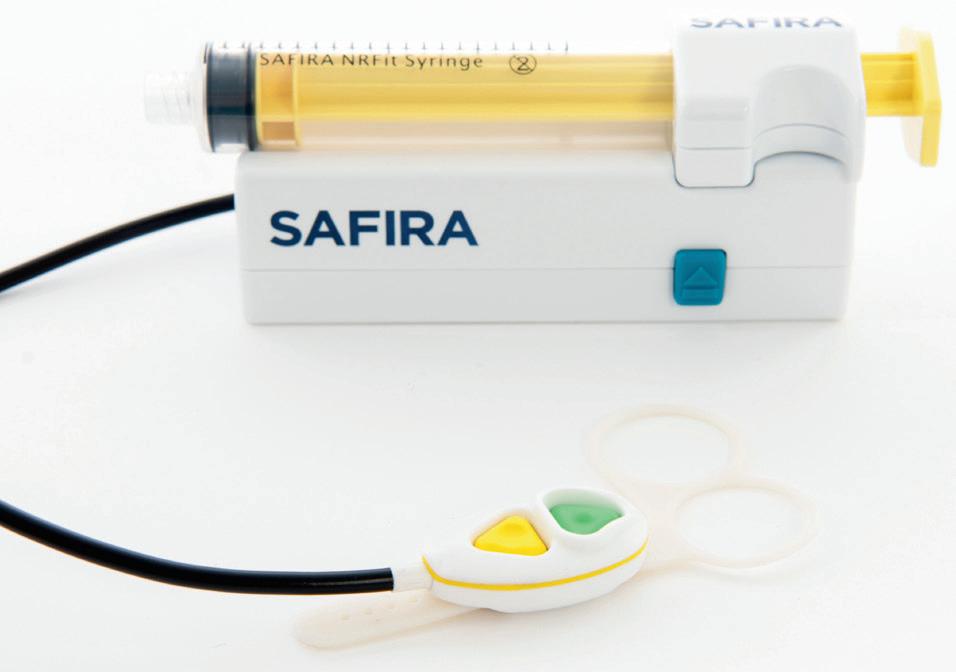
CE Mark regulatory approvals for Medovate’s SAFIRA range
M
edovate has successfully secured additional CE Mark regulatory approvals for its SAFIRA (SAFer Injection for Regional Anaesthesia) technology to include an NRFit syringe and a palm operator. Within the last year, the company has achieved CE Mark regulatory approval covering five devices in its SAFIRA range: infusion driver, foot pedal, luer syringe, NRFit syringe and palm operator. These latest product range additions are intended to further improve patient safety and
offer greater control to anaesthetists. The NRFit syringe provides a second option to the universal luer connection syringes with which the system was originally introduced. With the provision of a brand-new Palm Operator, Medovate hopes to offer anaesthetists more versatility and choice. The palm operator uses the same colour coding as the original foot pedal operator, which remains a key part of the product range for the infusion and aspiration of anaesthetics.
www.amcor.com
Amcor to extend CR27 heat seal coating technology to customers in Europe
S
ince the acquisition of Bemis Company on 11 June 2019, global packaging company Amcor has achieved a milestone in healthcare packaging. By adapting its approach to product development and innovation, and deploying know-how and processes gained in the acquisition, Amcor can now provide unrestricted to customers in Europe key healthcare packaging solutions that were part of the Bemis portfolio. Amcor has long-standing experience with high-quality, heat-sealing adhesives for medical-grade papers and Tyvek material. Adding to that is the well-known, high-performance
Tyvek adhesive and the CR27 heat seal coating technology developed by Bemis, which will now be available in Europe for the first time under the Amcor brand and will be produced in Winterbourne, UK. Amcor’s customers, including medical device manufacturers customers, will be offered to experience the benefits of CR27 heat seal coating technology for medical, sterile barrier applications. Such benefits include enhanced strength and excellent porosity — without compromising on barrier properties; it is also air permeable and suitable for EtO and gamma irradiation sterilisation.
M&A UPDATE
https://atp-ag.com/en/
COMBINING STRENGTHS AND MARKET POSITIONS
A
dhesive tape specialist CCT Coating & Converting Technologies is becoming part of water-based specialty adhesive tapes manufacturer ATP Adhesive Systems Group (ATP) based in Switzerland. The combination
6
strengthens the market position of both companies and allows them to offer a wider range of tailormade solutions to its customers. ATP is a specialist in highperformance adhesive tapes, exclusively focusing on water-
based technology. The company offers tailor-made solutions through its in-house R&D capabilities. With production sites in Germany and the UK, as well as headquarters and a development centre in Switzerland, the
WWW.MEDIC ALPL ASTICSNEWS.COM
company employs approximately 400 staff. US-based CCT Coating & Converting Technologies has provided coating and converting capabilities of specialised adhesive tapes during the past 20 years. CCT’s founder Robert Dempsey as well as CEO Rich Hipp together with their team will continue to run the firm’s operations from their Philadelphia location. The management teams of both companies expect to significantly increase its service offering especially to its US customers.
DIGITAL SPY
PROCESSING UPDATE
www.wittmann-group.com
Energy efficient injection moulding machines
W
ITTMANN BATTENFELD has succeeded in winning new customers in many markets with its SmartPower injection moulding machines. The range of compact machines are claimed to offer nearsilent operation, highly repeatable process capabilities and wide platens, in addition to “extreme” energy efficiency performance. According to customer feedback, the machines’ energy efficiency has come up as a topic of particular significance. The magnitude of savings realised on the production floor compared with similar machine models has exceeded expectations.
The SmartPower was compared with a machine that had been supplied in the early 1990s. Unsurprisingly perhaps the test results were “astounding” — the SmartPower machine was six times more energy efficient and six times less costly to run than the older machine. Joint WITTMANN BATTENFELD UK managing director Tracy Cadman said: “Our leading customers in the UK and Ireland are increasingly realising that low energy production is helping to future proof businesses, not only for cost but also in terms of transparent Industry 4.0 production and securing a low environmental footprint.”
talking
POINT
WWW.MANUFACTURERSALLIANCE.CO.UK
GARY SHEADER, MANAGING DIRECTOR, MANUFACTURERS’ ALLIANCE What is the Manufacturers’ Alliance and how does it help manufacturers? We are an experienced team of manufacturing professionals delivering a range of support for owners and managers of manufacturing organisations across Northern England and Wales, helping them to achieve business growth through excellent leadership. Our services include an academy of learning programmes, regular peer group membership meetings, thought leadership events and on-site support.
SUSTAINABILITY UPDATE
www.berryglobal.com
Berry Healthcare facilities earns ISCC accreditation
T
he Berry Healthcare facilities of Astra Plastique, Bellignat and Offranville in France have been awarded International Sustainability and Carbon Certificate (ISCC) Plus accreditation, enabling the sites to sell to healthcare customers ISCC Plus certified packaging and plastic components that contribute to a circular economy approach based on advanced recycling and mass balance. With this certification, customers can attest to their usage of certified circular polymers (based on advanced recycling mass balance) throughout. Berry Healthcare facilities in France will be able to offer this advanced recycling resin in both circular PP and PE. This meets customer requirements for sustainable products and packaging, with the ability to produce primary packaging and drug delivery
devices for healthcare applications containing a high percentage of recycled material, from 30% to 100%. As well as supporting customers’ sustainability goals, this helps them to meet the requirements of forthcoming EU Plastic Packaging Levy and the UK’s Plastic Packaging Tax. Importantly, because the advanced recycled resin has the same properties as virgin material, there is no need for any qualification tests.
Tell us about the range of learning experiences you have recently rolled out. Our Academy focuses on leadership and management development for front line and middle managers. The academy programme courses cover a wide range of topics, including how to manage teams to high performance; managing non-compliance; and improving productivity. During lockdown, we hosted (via webinars) Thought Leadership Events to help manufacturers navigate challenges, particularly those associated with Covid and Brexit. We have also launched two new peer groups centred around specific business needs including how to embrace smart, connected factory technologies and implement this for factory future proofing with our Industry 4.0 group. What kind of help or support do most UK manufacturers need? Without a doubt, it is peer-to-peer support. We have plucked some of the finest manufacturing leaders in the UK to lead our programmes, events and group services. Our members find that being present in a trusted group of people who are all in manufacturing is the only place available to them to share and resolve common challenges, as well as being inspired by their success feeding their own ambitions for innovation.
EVENTS
MPN TAKES A LOOK AHEAD AT THE CONFERENCES COMPLEMENTING THE MEDIPLAS ZONE AT THIS YEAR’S INTERPLAS EVENT.
T
here are myriad reasons to attend this year’s Interplas (28–30 September 2021, Birmingham, UK) event, but did you know it has its own medical plastics zone? The highly specialised area of manufacturing plastic parts for the medical industry is one of the fastest-growing sectors in the plastics industry and the Mediplas Zone will return once again in 2021 to focus the spotlight on the essential aspects and considerations of medical device manufacturing that are unique to the sector. Organised in conjunction with Medical Plastics News magazine, this special feature zone will enable visitors to quickly identify the exhibitors showcasing technologies, materials and services relevant to their field. In addition, the Mediplas Zone will be complemented by a conference track on the Main Stage programme where experts will deliver sound advice crucial to medical device designers and manufacturers on a range of issues. It’ll be great to see you there!
Can Attention to the Design of Plastics in Medical Devices Support Patient Safety? Speaker: SARAH JENNINGS, NATIONAL PATIENT SAFETY LEAD, NHS ENGLAND & NHS IMPROVEMENT Date and time: Wednesday 29 September, 14:00–14:30
The National Patient Safety Team at NHS England & NHS Improvement provide clinical and non-clinical patient safety expertise for the NHS. We utilise information from within healthcare, and patient safety incident data reported into the National Reporting & Learning System (NRLS) when things go wrong in healthcare. This enables identification of new and under recognised patient safety themes and trends. Reviewing medical devices within the ‘system’ of use, including users and the environment, can identify design features that may support the user in maintaining patient safety or present hazards due to the environment in which it is used. This talk will outline the role of the National Patient Safety team and provide examples of how designers and manufacturers of plastic components can support patient safety.
Innovative Drug Delivery for Improved Patient Compliance Speaker: SIMON CHIDGEY, SALES AND MARKETING DIRECTOR, CONSUMER PACKAGING, BERRY GLOBAL Date and time: Wednesday 29 September, 14:30–15:00
The patient and provider relationship has never evolved so quickly as we observed in 2020. What the future holds in patient care is still to be written, but the use of technology for improved communication and improved patient outcomes across the healthcare system will only grow. This is exactly where some of the greatest innovation and leading patient-centred design is taking hold with Berry Global’s Healthcare Division. Join this seminar to hear how a global leader in inhalation devices has identified a path to bring patient-centred design with the needs of healthcare systems around the world.
Manufacturing Technologies for a Post-Pandemic World — Injection Moulded 3D Micro and Nano-Structured Surfaces for Reduced Antimicrobial and Antiviral Activity on Consumer Goods Speaker: BEN WHITESIDE, DIRECTOR, CENTRE FOR POLYMER MICRO AND NANO TECHNOLOGY, UNIVERSITY OF BRADFORD Date and time: Wednesday 29 September, 15:00–15:30
The University of Bradford is pioneering research into the production of functional nanostructures on injection moulded components with 3D surfaces. By making significant developments in tooling approaches, processing technologies and characterisation methods, they can produce highly detailed yet robust surface structures using standard engineering polymers that have been proved to reduce droplet adhesion, bacterial attachment and the subsequent formation of biofilms. This approach offers a low-cost method for adding physical functionality to moulded products while avoiding the need for additives or coatings which add cost and reduce recycling options. 8
So clear it’s like it’s not even here: highly transparent CYROLITE® for diagnostic applications.
We invented CYROLITE® over 40 years ago – and we’ve used the time ever since to perfect its properties. The result is highly advanced acrylic polymers that boast outstanding optical properties such as superior UV transmittance. At the same time, CYROLITE® offers excellent flow properties, thus enabling them to be molded into extremely thin-walled components. It goes without saying that CYROLITE® meets all the relevant USP Class VI, ISO 10993-1, and REACH standards. For more reasons why CYROLITE® is the clear choice, visit www.cyrolite.com.
Polymers for Healthcare Applications
Whether it’s medical devices, pharmaceutical packaging or diagnostic equipment – countless healthcare applications can be realized using polymers from our portfolio. Our team of experts will provide technical service, product safety, risk management and a deep understanding of market needs. Do you process polymers? Then we are your reliable partner.
ALBIS (UK) Ltd. albisuk@albis.com www.albis.com
Cleanroom Particle Counters
Portables
Handhelds
Continuous Monitoring Cleanroom Certification • Cleanroom Monitoring PMT (GB) Ltd. | Tel: +44 (0)1684 312950 | email: info@pmtgb.com
LABELLING
The silver lining to cloud-based labelling
LIMITED RESOURCES NEED NOT DETERMINE WHETHER SMALL MEDICAL DEVICE MANUFACTURERS CAN MEET TO LABELLING COMPLIANCE AND VALIDATION REQUIREMENTS SAYS SUSAN GOSNELL, PRODUCT MANAGER AT LOFTWARE.
S
mall medical device manufacturers often find themselves scrambling to achieve the necessary compliance and validation, risking costly mistakes. Validating systems and processes, including labelling, to ensure they are compliant with stringent regulatory standards is tough and occasionally expensive.
The latest cloud labelling solutions integrate with other cloud solutions, allowing for seamless functionality and minimising the need for local infrastructure resources and cost.
If companies bungle the software validation process or put incorrect and noncompliant data on the labels, they are likely to incur penalties including compliance failure fines. Some companies attempting to comply with regulations in other geographic regions that focus on device traceability, each with a unique device identifier- (UDI) like component, can find the whole process overwhelming, particularly if they have only a small and busy IT team.
Similar to many labelling systems, validation systems hosted in the cloud have vendor-supplied documentation that streamlines the process and eases the burden of installation qualification. A more relaxed software release schedule eases the validation burden on life sciences companies because the software is updated once rather than multiple times a year, giving them a continuously updated and maintained labelling solution without increasing the validation workload on their IT staff.
PUTTING A PLAN IN PLACE MDR-compliant labelling has certain requirements which differ from those demanded under the FDA’s UDI system rules; for example, under MDR, manufacturers must ensure the label specifically states the device is a medical one using an MD symbol in a box. Small medical device manufacturers who rely on time-consuming and errorprone manual or legacy labelling processes to facilitate these label updates run the risk of mislabelling, which can lead to noncompliance. They may have limited staff numbers and lack structured processes concerning roles and responsibilities pertaining to label design, changes and approval. As project leads work toward a compliant labelling process, it is important, therefore, to establish defined roles and access for each stage of the process. When dealing with a compliance initiative, up-to-date, correct and compliant labelling is imperative. This involves having all the relevant label design elements in place to comply with MDR or FDA regulations. Frequently, label templates are hard coded, meaning IT staff must be involved in making changes. These personnel are often tasked with multiple mission-critical projects in the organisation, which can delay labelling projects. For many small manufacturers with limited resources, finding a solution can be a challenge. A ROADMAP FORWARD Validation-ready cloud labelling solutions have emerged to ease regulatory compliance and time-consuming validation requirements. These solutions, built with the needs of regulated companies in mind, digitise the quality control processes and facilitate compliant labelling with role-based access, approval workflows and electronic signatures. Outside of compliance, cloudbased labelling drives scalability and productivity for small medical device manufacturers and boosts overall efficiency.
The manufacturer will need to work closely alongside the vendor and review the documentation. If needed, the vendor can provide the full validation acceleration pack, as well as professional services to assist with simplifying the validation process. Tailored consultancy and advice concerning validation is usually available from the vendor. Given the considerable hassles of compliance for small device manufacturers, cloud-based labelling systems offer the benefits of a full label management system to ease compliance and validation. With this future-proof technology, medical device manufacturers can be confident that they are running the most upto-date software, enabling them to address fast-changing new regulations.
WWW.MEDICALPLASTICSNEWS.COM
11
COVER STORY
ROBERTO VALENTI, HEAD OF MATERIALS DEVELOPMENT AT BORMIOLI PHARMA, DISCUSSES HOW THE COMPANY’S SUPPORT OF A CIRCULAR ECONOMY COUPLED WITH ITS APPROACH TO INNOVATION HAS TAKEN IT FROM SIMPLY OFFERING BIOPLASTICS TO DEVELOPING BIOPRODUCTS.
A
ccording to European Bioplastics, the association representing the industry in Europe, bioplastics are not just one single material, but comprise a whole family of materials with different properties and applications that comply with one of the following three features: biobased, biodegradable or both. The term ‘biobased’ means that the material or product is derived — at least partially — from biomass, such as corn, starch, sugar cane, cellulose or other raw materials that are not included in the human or breeding food chain. Biodegradable means that the material can perform a chemical process during which microorganisms convert materials into natural substances, without the need for any artificial additives. Biobased and biodegradable are not, therefore, synonyms, as the biodegradation process does not depend on the resource basis of a material, but rather is linked to its chemical structure.
FROM BIOPLASTICS
TO BIOPRODUCTS
Bioplastics represent an answer for the industry to develop a more circular economy, that — according to the Ellen MacArthur Foundation — is “restorative and regenerative by design, aiming to keep products, components and materials at their highest utility and value at all times, distinguishing between technical and biological cycles”.1 With this definition in mind, bioplastics fit into this new economic concept as they help to break away from the linear economy characterised by ‘make, use, dispose of’ in favour of a more circular model based on ‘make, use, reuse, recycle’, contributing to closing the loop in regenerating CO2 and using renewable raw materials to make everyday products more sustainable. BEYOND BIOPLASTICS Bormioli Pharma, for example, goes beyond the simple concept of bioplastic, which better suits raw material producers, to ‘bioproduct’, a wider philosophy that it applies to all of its production. This approach provides a new way to create and develop products and value, committing to production and development choices that bring life 12
This approach provides a new way to create and develop products and value, committing to production and development choices that bring life cycle assessment benefits W W W. M E D I C A L P L A S T I C S N E W S . C O M
SUSTAINABILITY
cycle assessment (LCA) benefits. This tailor-made product development is conducted step-by-step together with the client, supporting and advising them on the most suitable choices that can be applied based on their specific needs and requirements. This circular innovation approach is the result of 10-years’ experience in the research of alternative plastic packaging solutions. During this time, the company has been investigating a range of sustainable products, starting with mechanical recycled polyethylene terephthalate (rPET) bottle solutions, which are already used and commercialised within the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical markets. Over the years, the company has looked for new, sustainable innovations, starting from chemical rPET for pharma use, up to the latest breakthrough that the company intends to introduce to its pharma partners later this year: PET containers partially manufactured from monoethylene glycol, (MEG) via the recovery of CO2 emissions and subsequent gasification and fermentation processes. The company’s commitment to guaranteeing ever-lower greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions is based on some fundamental pillars. First, it focuses on European producers to ensure the strictest environmental commitments and to cut GHG emissions derived from logistics; then, its products are specifically engineered to make recycling at the end of the lifecycle easier. Finally, the company constantly support clients with specific tests to combine a circular economy with the strictest safety criteria that the pharmaceutical market requires, making the packaging validation phase simpler. PRODUCTS As regards specific bioproducts, Bormioli Pharma’s range of containers and accessories are manufactured from different polymers such as polylactic acid (PLA), Green PE, Green PP and BioPET. Bio-based solutions are particularly present in Bormioli Pharma’s forLife portfolio — a range of packaging products for nutraceuticals and food supplements. Growing interest is also being seen in the oral drugs market, with the development of pillboxes manufactured from bio-based plastics. The company’s dosing solutions (for example, spoons and scoops) made with eco-friendly materials need to follow the usual approval process. PLA solutions are preferred for pharma packaging accessories such as cups and spoons. Fully degradable within 60 days in industrial compost facilities, these solutions feature a food-grade certification for the EU and the US, as well as excellent physical/mechanical properties. Although recycling regulations vary from country to country, the company aims to contribute to the creation of a ‘seventh recycling chain’ specifically created for compostable plastics that could further facilitate the disposal of these products.
REFERENCE 1. https://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/assets/downloads/publications/ TCE_Ellen-MacArthur-Foundation_26-Nov-2015.pdf
Other concepts manufactured by Bormioli Pharma using bioplastics that have been introduced to players in the pharmaceutical industry are Green PE bottles, Green PE-PP caps and containers and BioPET bottles. The former (Green PE bottles and Green PP caps) are manufactured from up to 100% biobased plastic, and their adoption has no impacts on the packaging lines. The latter are produced from the polymerisation of renewable materials and are entirely recyclable. All of these solutions are compliant with food contact pharma regulations both in the EU and the US. OPEN INNOVATION Bormioli Pharma’s open innovation approach to continuous development of advanced solutions has already guaranteed outstanding results in research fields such as product usability and IoT (internet of Things) integration, through the creation of an open environment and multiplying the company’s R&D efforts thanks to the contributions of external players, such as end users, clients and partners, but also start-ups, research centres, universities, innovation hubs and accelerators. This ecosystem allows the company to understand clients’ needs and new challenges and opportunities. The topics of circular economy and innovation are increasingly being addressed; they’re even constituting the focus of strategic, international policies, such as the European Green Deal and Recovery Plan. Bormioli Pharma contributes to promoting sustainability within the pharmaceutical industry as it combines the principle of a circular economy with the strict normative framework required by this specific sector, thus favouring a widespread adoption of biopackaging by markets and patients.
WWW.MEDICALPLASTICSNEWS.COM
13
TESTING & INSPECTION
JASON MCGLYNN, COMMERCIAL MANAGER FOR IRELAND AT INDUSTRIAL METROLOGY PROVIDER, THE SEMPRE GROUP, EXPLAINS HOW MEDICAL MANUFACTURERS CAN USE METROLOGY TO SOLVE COMMON QUALITY CHALLENGES AND ENHANCE THEIR COMPETITIVENESS.
A
ccording to MedTech Europe, the European medical technology market was estimated to be worth €140 billion in 2020, naming the UK as the third largest market in this area.1 UK manufacturers are always looking for new ways to remain competitive in this growing sector, while providing the accurate and high-quality products needed by patients. For medical device manufacturers, the health and safety of patients is a top priority, so device quality cannot be left to chance. Despite this, metrology is often treated as a policing mechanism, only used to validate products and detect defects at the end of production. As regulations become increasingly stringent, medical device manufacturers should consider how they can better use metrology equipment to improve quality management across production. ACCURACY Medical devices are decreasing in size, while increasing in complexity — manufacturers are producing small, intricate parts such as polymer dental implants. As a result, manufacturers must meet much tighter tolerances; precision is key to ensure the best outcome for the patient.
calibrated correctly. ISO 17025 accreditation and certification from the United Kingdom Accreditation Service (UKAS) demonstrates the competence and performance capabilities of organisations that provide certification, testing, inspection and calibration services. It is beneficial to work with one of the few companies able to offer UKAS calibration for optical or vision coordinatemeasuring machines (CMMs), as they will ensure machine reliability. BOTTLENECKS Medical device manufacturers will often validate large numbers of parts to achieve regulatory compliance. Although this is clearly an important step for patient safety, it can slow down production in an industry where speed is critical. Manufacturers typically use measurement equipment at the end of a production line. To do so, they must first manually remove the components from the production line, thus creating costly bottlenecks while parts queue for available metrology systems.
Tactile measurement may compromise the quality of these smaller components. Manufacturers therefore require nano- and micro-precision noncontact measurement equipment for accurate validation. For example, Sensofar 3D optical profilers offer three optical techniques to provide highly detailed surface inspection and analysis.² This equipment effectively validates the accuracy of devices, so long as it is 14
By this stage it’s often too late to rectify any issues. If the product is found to be defective, time and energy has already been wasted on a product that could have been scrapped or saved earlier in the production process. The manufacturer has also lost the opportunity to identify the root cause of any problems that could have been addressed before it created more defective parts.
W W W. M E D I C A L P L A S T I C S N E W S . C O M
TESTING & INSPECTION
Manufacturers should consider investing in an automated quality management system (QMS) that offers an all-in-one solution for quality management, by collecting and storing data at every point, from drawing to final product. They eradicate the need for time-consuming paperwork and filing, allowing developers to easily communicate important quality information across the supply chain without the risk of human error affecting the data.
By considering the role of metrology earlier in the process, manufacturers can build a solution that becomes part of the production line, speeding up validation and avoiding any bottlenecks that can slow down production. DATA INTEGRITY Validated measurement systems can take hundreds of measurements in seconds and generate large reports of raw data that manufacturers can use to monitor quality. How manufacturers manage and use this data is vital to provide a fully traceable audit trail. For example, manually inputting measurement data into Excel documents or other isolated files can introduce opportunities for human error to create faults in the report. Also, gaps in the reporting make finding historic data, when required, difficult. Opting for 21 CFR Part 11-compliant equipment will ensure security and authenticity. Automated, real-time data collection software, such as Prolink SPC Data Collection Software, otherwise known as QC-CALC, can extract realtime data from any device to enable full analysis and automated reporting.³ An easy-to-use system can provide total visibility and control of data across the entire manufacturing process. Another benefit is the ability to automatically generate password-protected reports, which makes it easy to spot any changes during production, identify where they happened and why, and take steps to investigate and fix the issue. A FULLY TRACEABLE PROCESS When applying to regulatory bodies for approval, medical device manufacturers must document every stage of the product’s lifecycle to prove the device safely meets the intended use. Implementing a fully digitised approach to metrology from the outset enables manufacturers to automatically collect vital data that ensures full traceability and influences the success of production.
By considering the role of metrology earlier in the process, manufacturers can build a solution that becomes part of the production line, speeding up validation and avoiding any bottlenecks that can slow down production
Manufacturers can use automated systems to streamline time-consuming manual reporting processes. High QA Inspection Manager, for example, allows developers to automatically generate first article inspection (FAI) reports to verify the product’s design.⁴ The software can rapidly identify geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) from models, outline critical dimensions and input all the data from the ballooned drawing, populating a final report. Manufacturers can automatically compare the original ballooned drawing with the new report, offering full visibility to the manufacturer. Medical device quality is in everyone’s best interest. By integrating metrology into the production line, manufacturers can remove expensive bottlenecks, streamline production and improve traceability, helping them to gain a competitive edge in the industry. Focusing on quality also provides patients with safe and accurate medical devices that will help them enjoy a better quality of life. REFERENCES 1. https://www.medtecheurope.org/ datahub/market/ 2. https://www.thesempregroup. com/3d-profiling-microscopes/ sensofar-range/?utm_ source=Stone%20Junction&utm_ medium=blog&utm_ campaign=SEM133 3. https://www.thesempregroup. com/prolink-spc-data-collectionsoftware/?utm_source=Stone%20 Junction&utm_medium=PR&utm_ campaign=SEM018 4. https://www.thesempregroup. com/high-qa-inspectionplanning/?utm_source=Stone%20 Junction&utm_medium=PR&utm_ campaign=SEM018
WWW.MEDICALPLASTICSNEWS.COM
15
ELASTOMERICS
FRASER RANKIN, DIRECTOR OF SALES AND MARKETING AT PERMALI, DISCUSSES TPU AND ITS IMPORTANCE, AND GROWING PREVALENCE, IN THE MEDICAL FIELD.
W
hether for contact tracing, infection detection, controlling the spread, preventing or treating the disease, the ability to rapidly scale up manufacturing capabilities is vital in the global fight to control COVID-19. To do so, product-design and manufacturing teams must consider a variety of factors when deciding how to ensure proper scalability when choosing between adhesive or ultrasonic welding assembly methods Manufacturing products for the medical industry means operating in a highly innovative space, where material, technique and process boundaries are pushed to ensure optimum performance of each individual product and patient care. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the medical sector has increased product development and the turnaround speeds through large-scale production of life-saving products and personal protective equipment (PPE). Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) has played a large part in this. Its adaptability, range of features and scope of performance means it is perfectly positioned to manufacture within a variety of situations. TPUs can be, depending on the selected
grade, biocompatible, sterilised, antibacterial, flexible or rigid, and used for small areas, as well as large-scale applications. UNDERSTANDING TPU Essentially, TPU is a bridge between rubber and plastic, taking the best properties of both to create a material that can be adapted as required. It can be either polyester- or polyether-based, both of which lend themselves perfectly to different scenarios. These two groups are then further separated into grades to denote property differences, such as hardness, elongation and abrasion loss, all of which vary substantially. Tuftane polyester-based TPU grades are known for their abrasion, heat ageing and chemical resistance characteristics. Tuftane polyether-based grades, on the other hand, is used for applications where hydrolysis resistance and microbial performance is key at a variety of temperatures. The Tuftane brand is recognised across many sectors and applications for its tough, highly elastic and flexible film, which can be radiofrequency (RF) welded, ultrasonic welded, heat laminated, adhesive laminated, printed and thermo-formed post-blown film extrusion.1 Polyether is commonly used for medical applications, particularly when comfortable skin contact is preferred, and is formed through a two-part chemical reaction process which can be controlled and adjusted molecularly to change the final TPU grade. Alongside a range of other key properties, changes made to the process can affect specifically the following: • • • • • •
Tensile strength Fungal resistance Hydrolysis resistance Elongation Abrasion loss The natural appearance, which can be adapted post-manufacturing to dye as necessary • Slip characteristics.² MANUFACTURING FOR MEDICAL MARKETS TPU films that will be further manufactured for medical applications, must be created with key chemical properties, and in accordance with strict ISO standards. At a regulatory level, there are broader compliance programs such as the EU’s Directive 93/42/EEC, as well as national regulations.³ To assess the films’ biocompatibility for medical devices, ISO 10993-1:2018, for example, represents safety standards to manage a variety of biological risks.⁴ Tuftane TPU films are regularly assessed to ensure they are compliant for a range of devices and classifications within the medical device sector. BIOCOMPATIBILITY Biocompatibility considers whether a material can induce any unwanted response, such as catalysing a reaction or reacting negatively with any other material, skin, human parts or medicines. Medical-grade TPU films are extensively tested to meet standards to guarantee their safety, as the risk here is too high to overlook testing and quality assurance. As part of the extensive testing of Tuftane TPU films, only certain grades are specified for
16
W W W. M E D I C A L P L A S T I C S N E W S . C O M
ELASTOMERICS
medical use as per their biocompatibility and suitability. These are typically polyether varieties, although some polyester grades are also included. TPUs have an inherent resistance to the growth of fungus and microbials. In addition, the material can be sterilised using gamma sterilisation methods to comply with infection control in sensitive medical environments. Silver compounds can be added to TPU formulations to improve a medical device’s resistance to the growth of particularly dangerous microbials, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Escherichia coli (E-coli). MEDICAL APPLICATIONS Isolation barrier drapes, hoods and robotic sleeves As TPU can be biocompatible, resistant to bacteria and highly transparent, dependent on grade, it is an increasingly popular material choice in the design of isolation units and robotic arm sleeving. It is also a useful barrier for preventing the spread of infections, protecting expensive equipment and helping to protect staff by creating a bacterial resistant shield, while guaranteeing a level of care and visibility through its transparency qualities. Medical staff can easily monitor the health of the patient, while remaining safe and distant from infection. If medical staff do need to get close to a patient, using a TPU-based pressurised hood, fitted with breathing apparatus, will allow them to continue to provide a high level of care, while ensuring their own safety.
TPU is a bridge between rubber and plastic, taking the best properties of both to create a material that can be adapted as required
Pressure pads for beds and wheelchairs Patients confined to wheelchairs or hospital beds can develop pressure sores, which not only add an extra level of discomfort for patients but can also pose a high risk to their health. TPU’s flexibility, resistance to abrasion, durability, as well as its ability to remain sanitary, make it an ideal material for pressure pads, thereby assisting in the longevity and quality of care a patient receives, while maximising their comfort. Blood plasma bags and similar medical bags Blood plasma bags must be made from nonpermeable, biocompatible, anti-tear and antibacterial material to ensure their contents are sterile and, therefore, fit for injecting into a patient without any risks. In addition, they must be translucent to help healthcare workers readily identify the bag’s contents. TPU’s translucence, promotes its application for these bags. TPU, with its weld strength, puncture resistance and medical safety, is also a viable material for colostomy bags, which must be sterile and as discrete as possible. PROTECTING HEALTHCARE WORKERS DURING THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC During the pandemic, TPU producers such as Permali were tasked with producing more TPU than ever to assist in the healthcare field. As TPU can be used for a variety of medical applications, including vital PPE, the need for it has never been greater. During the crisis, rapid production of PPE and a stable supply chain were key to guaranteeing the safety of front-line workers. TPU producers were instrumental in providing a ready and reliable supply of governmentapproved TPU, thus supporting PPE and medical safety product manufacturers. Note: Tuftane is registered trademark of Permali REFERENCES 1. https://www.permali.co.uk/sectors/ medical-tpu-film/ 2. https://www.permali.co.uk/wpcontent/uploads/Tuftane-TechnicalData-Sheet-PDF-2.pdf 3. https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ eudr/1993/42 4. https://www.iso.org/standard/68936. html
WWW.MEDICALPLASTICSNEWS.COM
17
THERMOFORMING
THERMOFORMING IS PROVING ITSELF A POPULAR MANUFACTURING TECHNIQUE, ESPECIALLY IN THE PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL PACKAGING SECTORS. TODD MCDONALD, GLOBAL DIRECTOR OF SALES AND MARKETING AT TEQ HIGHLIGHTS WHY.
THE HEAT IS ON
T
he global market for thermoforming plastics estimated at $35.4 billion in 2020 is now projected to reach a revised size of $51.2 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of 5.4% during the 2020–2027 period.1 The increasing demand for thermoformed plastics from the healthcare and pharmaceutical packaging sectors is a force driving the market growth over the forecast period. The growth has been triggered by a hike in demand during the COVID-19 global crisis (Figure 1).
Figure 1: TEQ started manufacturing COVID-19 testing kit trays earlier this year with a pledge that they offer ‘superior presentation’ and ‘enhanced component protection’.
Demand is expected to rise across different healthcare packaging types including blister foils, pumps, closures and rigid plastics. Demand will also grow for packaging in dietary supplements, such as vitamins and for other essentials such as allergy medication that consumers need during a lockdown, for instance. The advanced technology of thermoforming has established itself as a favourite manufacturing technique for many industries and applications, with a major benefit being cost efficiency. The stiffness of thermoformed packaging allows manufacturers to create smaller units, offering space-saving benefits; it also offers a barrier to odours, and resistance to oil and grease. Packaging from cleanroom thermoforming also has the capacity to offer advanced protection of medical devices, the importance of which cannot be underestimated as the quality of the packaging is as important as the medical device contained therein — once the packaging’s integrity is compromised, sterility is lost and the device is potentially ruined. THERMOFORMED PLASTIC PACKAGING OFFERS THE HEALTH SECTOR A RANGE OF ADVANTAGES: Accurate product orientation: For those occasions when a nurse has to grab a product, the ability to quickly confirm its orientation is reassuring. With a thermoformed tray, the medical device remains securely in place so it can be removed swiftly and confidently. Device handling assurance: To ensure a device doesn’t compromise sterility, a nurse may need to control a device’s movement as its package is opened. A thermoformed package is more likely to prevent any unnecessary rotation or accidental removal. Clarity of products: Thermoformed packaging enables a nurse to see and identify a product clearly so the device can be better presented. It also allows a nurse to spot any defects. Consistent opening experience: Incorporating a generous peal area in the package design allows a nurse an easy access point for pealing the lid back from the package.
18
W W W. M E D I C A L P L A S T I C S N E W S . C O M
BIOMEDevice
December 8-9, 2021 SAN JOSE, CA, SAN JOSÉ MCENERY CONVENTION CENTER
JOIN
NorCal Biotech Community’s Regional Event
Biomedevicesanjose.com/MPN
18316_BIO_SJ21
REGISTER NOW at
THERMOFORMING
Additional protection: Rigid plastic offers sensitive medical devices additional protection; for example, a carefully designed package can stop a syringe from depressing. Increased ergonomics: A pouch can require both hands to twist it open, putting repetitive strain on a nurse’s wrists. With a sealed thermoformed tray, only one hand is needed to open the seal, while the other holds the tray in place. Other advantages of thermoforming include cost-effective tools and moulds, reasonable processing times from design to prototype, large surface-to-thickness ratios, the option to process large and multilayer parts, and a range of machinery that can work with thick- and thin-gauge plastic sheets (Figure 2).
Figure 2: TEQ manufactures custom thermoformed handling trays for a wide range of applications, including dry powder inhalers, auto-injectors, injectionmoulded components, pre-filled syringes and pharmaceutical bottles.
CLEANROOMS Cleanroom thermoforming is widely used for the production and packaging of pharmaceuticals and medical equipment. This method of thermoforming is done in an ISO- (International Organisation for Standardization) certified cleanroom so that any particulates circulating in the air are kept to a minimum. Thermoform packaging is extensively used to safeguard sterile instruments and implants. This packaging method permits the use of lightweight, clear plastic enclosures that stop microbial and dust particles from contaminating the sterile item. Cleanrooms have played a leading role during the horrors of the Covid pandemic as their controlled and sterile environment guarantees cleanliness, preventing potential contamination caused by bacteria or air pollutants. Companies making medical devices and their packaging have to meet stringent regulations. The ISO, which consists of a group of nongovernmental bodies operating in 164 countries, is entrusted with the power to enforce exacting standards for a range of commercial markets. In 2016, it published the latest edition of its ISO 13485, which sets out to ensure patient safety by regulating hygiene and contamination control in medical product development.
20
Cleanrooms must have the ability to deal with any air pollutants. Manufacturers use filtration units — such as ionisers, carbon filters and non-filter purifiers — to control airflow and stop airborne particles larger than a predefined size from entering. Another cleanroom contamination prevention tactic is providing a high standard of staff training, ensuring they wear correct personal protective equipment such as gowns, hairnets and overshoes. Manufacturers are also advised to keep correct supplies and equipment in clean spaces and, where appropriate, dispose of or sterilise them. Cleanroom apparel would normally feature gowns, face masks, sterile gloves, boot or shoe covers, coveralls and head covers. High-quality cleanroom wipes are essential supplies for a cleanroom environment and maintaining its sterilisation. A supply of cleanroom-grade cleaners and disinfectants in spray bottles are also important items of equipment. Cleanroom tacky mats or sticky mats, which are normally placed at the entrances to cleanrooms so any contaminants stuck to the bottom of footwear can be safely removed, are also found in most cleanrooms. LOOKING AHEAD Regular risk assessments ensure ongoing improvements can be made to foil any new contamination threats triggered by ever evolving technologies. Continued innovation and the advance in technology in the medical sector brings with it unlimited potential. In years to come manufacturers will face the usual pressures to slash costs and be even more efficient by introducing more automation on the assembly line, utilising the likes of robots and smart testing. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are also expected to play a role by boosting quality standards and early detection of potential issues. New developments and a move towards more complicated products such as nanotechnologies and the miniaturisation of devices are another new challenge that manufacturers have to face in an increasingly competitive sector. REFERENCE 1. Research and Markets, “Global Thermoforming Plastics Market to Reach $51.2 Billion by 2027”, April 2021.
W W W. M E D I C A L P L A S T I C S N E W S . C O M
Messe Frankfurt Group
16 – 19 NOVEMBER 2021 FRANKFURT / GERMANY 30 NOV & 01 DEC 2021 DIGITAL DAYS
Make the impossible possible! We know that additive manufacturing offers undreamed-of potential. In addition to the printer, however you also need the upstream and downstream processes plus the experts, who have mastered the technology. You’ll only find all this at Formnext! Experience AM live and in color in Frankfurt or online at the Digital Days. formnext.com
Where ideas take shape. # formnext BOOK YOUR TICKET NOW!
Live + digital
DESIGNING MEDICAL DEVICES
MARTIN LARSEN, DIRECTOR, RICH PLASTICS OFFERS OEM PART DESIGN ENGINEERS ADVICE ON DESIGN ISSUES RELATING TO WELL PLATES AND MICROPLATES.
C
DESIGN TIPS... ON A PLATE
OVID-19 has turned the medical industry upside down in many ways. First, it has affected development times: where previously tooling development projects might have taken 6 months, the pandemic has demanded urgency when time, among other commodities, was in short supply. Second, it has affected output: the world needed hundreds of millions of test plates, immediately. Every day, manufacturers were faced with having to increase production 10-fold or 100fold. Despite the seemingly insurmountable hurdles, the industry has come up trumps, bringing many advancements in injection mould tooling designs for medical products such as microplates, pipettes and tubes. Examples include improvements in designs to control warp/deformation of the plastics during processing and to eliminate bubbles in the plastic. Alongside such advancements is the industry’s increased demand for maximising output, specifically through shorter cycle times, increased number of cavities and extended tooling life. DESIGN FOR MANUFACTURABILITY OEM medical plastics part design engineers for the most part care about the function of the part, as it relates to the equipment with which it is intended to work. All dimensions must be achieved within the tolerances specified by the engineer. Once the injection mould supplier receives the part geometry (data) from the design engineer, the supplier will perform a Design for Manufacturability (DfM) analysis to understand whether the geometry is manufacturable. Results of this analysis will inform the tooling supplier whether to make recommendations to change the part geometry. The results will also highlight whether the manufacturer needs to add draft for demoulding, address thin steel conditions, and identify areas for potential sink marks and deformation, part ejection, cooling. In addition, the supplier will advise how best to construct the tooling, thus providing a preliminary design concept. The DfM will also specify the exact resin/polymer to be used and its shrinkage rate.
Figure 1: Two new cooling options: a) heat pipes design and b) 3D printed design.
(a)
The DfM review will go back and forth several times based on sharing experience and knowledge of similar programmes. Once the DfM has been 22
W W W. M E D I C A L P L A S T I C S N E W S . C O M
(b)
DESIGNING MEDICAL DEVICES
COOLING SYSTEM Cooling is used to keep the tool at the desired temperature during moulding production to optimise production output — the faster and more efficiently you can cool the part, the faster you can open the tool to complete the shot. Reducing cycle times by even a few seconds can increase productivity by thousands of parts per day/week/month … and, therefore, improve profit.
Figure 2: Three different mould flow analyses study the effects the gate position has on weld lines. Case 1 gives the better result.
agreed, the supplier performs a complete mould flow analysis to simulate the moulding conditions, providing valuable information on, for example, the cycle time, warp, deflections, gas traps, fill speed and balance fill. After a final review of the mould flow analysis with customer, the design will be accepted and approved. The final approval will initiate the production process, beginning with ordering steel and other components to be used in the production. On the acceptance date the quoted production build schedule will officially start. The following design considerations will help the tooling supplier to choose — and recommend to the customer — the choice of hot runner system: • The spacing between each of the hot runner drops. This is relevant to how the material flows into the tool, which in turn results in the best fill locations and even fill. • The volume of resin needed for each shot. • The selected resin material and its melt flow rate. • The stack height of the tool. Another important design consideration is the gate type and size, bearing in mind that occasionally two types of gates can be used. Positioning of the gates is also important as it determines the balance of feed in the part; cycle times; minimum internal pressures; and part surface finish. MOULD FLOW ANALYSIS Mould flow is a is powerful simulation tool used to analyse the chosen gate positions. The mould flow will highlight the weld lines of the material flow, gas traps that will be formed and warpage of the part once it has cooled, thus allowing the tooling supplier to change gate position, as well as the gate size and/or injection speed.
A proficient design team will perform several (six or eight are common) mould flow analyses with different melt and tool temperatures to find the optimum design. Mould flow analysis is not 100% accurate, but when combined with experience of similarly designed products it gives the supplier a clear steer on hot runner and gate choice.
Mould flow analysis is not 100% accurate, but when combined with experience of similarly designed products it gives the supplier a clear steer on hot runner and gate choice
Cooling lines are needed to remove heat from hot areas within the tool. These cooling lines ensure the flow of the material is even throughout the part. Ideally, the two halves (the core side and cavity side) of the tool need to cool at the same speed to ensure quick ejection. The most common method of cooling is by drilling holes into the core and cavity steel and running water through them. You add as many cooling lines as needed to cool the part evenly. A newer method for optimising cooling is to add heat transfer pipes (into the design) to extract heat from particularly small areas. An innovation in cooling technology is using 3D printing for complicated designs that could not normally be machined. Figure 1 shows two new options for cooling. VENTING The injection mould venting expels air from the plastic injection mould cavity during the injection process of the molten plastic material. Without venting, internal pressure will build up and damage the longevity of the tool — gas traps appear on the tool and eat into the steel. A good designer will not vent just at the end of the fill, they will also vent the entire outside of the tool and use the ejector pins and vent inserts in the tool to expel the air. Mould flow can be used to optimise and reduce weld lines (Figure 2). SUMMARY In today’s quickly changing medical tooling industry, we face rapid tooling production schedules and high demands on the tooling to produce millions of parts quickly to achieve profitability targets. When selecting tooling design and manufacturing partners, look for companies with extensive experience in the product you need to manufacture, including their ability to perform complete engineering analyses. As different resins require different tool designs and tooling steel, a supplier who has full knowledge of the resin materials you want to use is also highly recommended.
WWW.MEDICALPLASTICSNEWS.COM
23
ANTICOUNTERFEITING & SERIALISATION
HOW CAN MANUFACTURERS HELP CONSUMERS TO DISTINGUISH REAL FROM FAKE? SWISS START-UP MORPHOTONIX PROVIDES A SAFE AND RELIABLE WAY FORWARD TO PROTECT BRANDS AND LIVES.
W
hether a simple prefilled syringe, an auto-injector, or high-tech equipment for an examining room, plastic components within the medical industry must maintain strict standards to ensure patient safety, product reliability, and regulatory compliance. Unfortunately, it is far too easy to produce counterfeit products that cannot be distinguished from the genuine article by the naked eye alone. With the global medical device market estimated at over $450 billion in 2021 and the World Health Organization stating that 8% of devices on the market in 2010 were fake, the size of the problem and the resulting risk to patient safety cannot be underestimated.1,2 MOULD NANO-ENGRAVING TECHNOLOGY To ensure the authenticity of rigid plastic materials against counterfeiting, Morphotonix has designed, developed, and patented a unique advance in lithography-based nano-engraving. The technology is integrated without any extra steps in the manufacturing process and does not affect product integrity. Security features, which can be anything from complex diffractive designs to forensic signatures, are engraved directly into steel production moulds. These custom markings are then replicated on the surface of each plastic part without using labels, ink, or additional post-processing (Figure 1). The technology is so safe manufacturers can apply it to medical plastics and even directly onto pharmaceuticals such as medicine pills — the company, in fact, launched with proof-of-concept holographic designs on gourmet Swiss chocolate. The technology has already found many uses in a variety of industries, from auto parts to nutraceutical packaging to high-tech components.3 Overt, covert and machine-readable features are nano-engraved with a precision of 130,000 dpi.
New legislation introduced into US and Europe, and measures such as serialisation and unique device identification is insufficient to prevent counterfeiting.4,5 Traditional security measures involve labels, direct printing or taggants. In most products, these 24
VISIBLE AUTHENTICATION
WITH ZERO CONSUMABLES
To ensure the authenticity of rigid plastic materials against counterfeiting Morphotonix has designed, developed, and patented a unique advance in lithography-based nanoengraving
W W W. M E D I C A L P L A S T I C S N E W S . C O M
ANTICOUNTERFEITING & SERIALISATION
Figure 1: Overt Morphotonix security used on three different substrates: polymer, rubber, and pharmaceutical pills. usual approaches add complexity and can have high investment costs to adapt manufacturing lines. In the medical industry, these approaches may have additional failure points under standard usage conditions, such as sterilisation or exposure to UV or chemical interactions. Furthermore, the anticounterfeit measures may be on outer packaging, leaving the device itself unprotected. By comparison, the Morphotonix solution appears directly on the device component, dramatically increasing the level of protection. The Morphotonix solution is intrinsically embedded within the products themselves. The process does not involve any additives or post-processing that increase the production cost, face concerns about health interactions, or require additional detection machinery. There is no change to the material or its processing, and therefore no need to perform expensive and timeconsuming process and material revalidation. With a lifecycle of more than a million units per engraving, the process is extremely cost-effective at industrial scale.6 Features are designed according to the custom needs of each client, including functional and branding considerations — from instant authentication by consumers and in-field investigations to differentiated authentication channels for multiple stakeholders. The logistics to securely send out the mould inserts to Morphotonix is as simple as sending a shoe box-size package. The inserts are engraved in a nanotechnology cleanroom in Switzerland. Once they are marked with the custom design, they are returned to the customer’s production line. This entire process usually takes 6–8 weeks. FUTURE DEVELOPMENT Morphotonix is developing its technology so that it can be applied to other substrates.³ Each substrate has characteristics that present unique industrial manufacturing requirements. The company is currently looking at rubber so that vial septums for vaccines can be authenticated to prevent counterfeiting.
CASE STUDY A Swiss market leader in the global breastfeeding products industry integrated the Morphotonix security solution for a device selling millions of units, where authenticity is crucial to consumer confidence. Given the babies’ extreme sensitivity, being able to authenticate the high-quality, regulatory-compliant products, the customer decided to pre-emptively include Morphotonix highly secure technology which does not use any extra additives. To secure a smooth manufacturing process for a delicate product, Morphotonix merged its nano-engraving with Wild & Kupfer’s expertise in complex and high-precision molding.7 This successful collaboration led Wild & Küpfer to further recommend Morphotonix technology to their clients, contributing an effective advance to their product portfolio.
REFERENCES 1. https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/medical-devicesmarket-100085 2. https://www.who.int/medical_devices/global_forum/3rd_gfmd/ againstcounterfittingforgingdocuments.pdf 3. https://bit.ly/3h7k95v 4. https://www.congress.gov/bill/113th-congress/house-bill/3204 5. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A02017R0745-20200424 6. https://bit.ly/3DkPAmz 7. https://bit.ly/3zlVO39 WWW.MEDICALPLASTICSNEWS.COM
25
Four shows with one badge
1
Rapid News Group (RNG) and the PPMA are teaming up to offer visitors full access to four leading industrial events in one place.
2
Visit the PPMA Show, Med-Tech Innovation Expo, Interplas and TCT 3Sixty at the NEC Birmingham, 28–30 September 2021.
3
The shows cover processing & packaging machinery, plastics, additive manufacturing, and medical manufacturing.
4
Registration is open, so get your free visitor badge through the websites.
09:2021 NOVEL MEDICAL-GRADE TPE FILM FOR WOUNDHEALING APPLICATIONS
U
nited Soft Plastics (USP) has developed a custom extruded TPE film which delivers a high level of patient support and treatment-friendly wound healing. The developmental grade makes an effective contribution to increased protection for patients and medical nursing staff. The USP custom medicalgrade TPE, which was developed in conjunction with a Danish start-up under the brand name Impervious, relieves patients of undue irritation and pain. The TPE film is a latex-free alternative and does not have
to be torn off because it is permanently welded to the polybag as a stretchable, flexible and conical sealing strip thereby eliminating the use of adhesive tape. Michael Bodmann, USP general manager, Europe said the TPE film product represents a significant relief in everyday treatment for patients and medical nursing staff. The TPE grade exhibits a low Shore A hardness (25–35), high tear strength in connection with demanding transverse and longitudinal strain loads, and the indispensable requirement of a thin wall thickness (0.2–0.4 mm).
Partnership produces the world’s first polypropylene from CO2
C
arbon transformation company Twelve and biotechnology company LanzaTech have partnered to transform CO2 emissions into polypropylene, a key polymer used for medical devices including syringes and IV bags. Twelve’s carbon transformation technology converts CO2 into materials that are traditionally made from fossil fuels. The company helps brands eliminate emissions by replacing the petrochemicals in their products and supply chains with CO2 Made carbon
Advanced tray sealing technology
P
roseal’s cleanroomcompatible tray sealing machines have demonstrated they successfully replace the time-consuming manual placement of lidding onto trays for a faster and more efficient continuous sealing operation that can help to reduce material usage without compromising on
26
pack integrity. Typical applications include medication, syringes (both empty and filled), surgical instruments, surgery kits, artificial joints and implants. The machines can handle many different tray designs and materials with a wide choice of sealing films, such as Tyvek woven material, gas
barrier and UV blocking varieties. In addition, the company’s in-house testing facility enables the trialling of different trays and films to find the best solution for individual products. This ensures that any potential tray format is conducive to sealing and able to deliver the required levels of product protection.
W W W. M E D I C A L P L A S T I C S N E W S . C O M
negative chemicals and materials, as well as carbon neutral fuels. LanzaTech’s carbon recycling ‘Pollution To Products’ technology uses nature-based solutions to produce ethanol and other materials from waste carbon sources. The partnership will bring together the two platform technologies to enable additional product development from CO2 streams, representing just one of many pathways to scale carbon transformation solutions.
Trusted to protect… Life science products that provide care, improve health and save lives We are a global technology provider to the life sciences industry, providing innovative packaging solutions and complementary products and services. We drive our customers’ success by delivering the best total value by combining superior quality and customer support, and the most efficient technology. Custom Packaging Solutions Focused 100% on Healthcare Custom Medical Packaging solutions that provide superior quality and protection. Nelipak®-designed device packaging is based on market expertise from concept to the point-of-use. For more information, contact us: email: info@nelipak.com | phone: +31.478.529.000
Sealing Machines A range of custom-built medical tray and blister heat sealing machines
www.nelipak.com www.bhp-europe.com
Flexible Packaging Materials A wide range of flexibility in materials and functionalities
®
Nelipak Corporate Office Cranston, RI, USA
®
Nelipak Elsham, United Kingdom
®
Nelipak Phoenix, AZ, USA
®
Nelipak Venray, The Netherlands
Nelipak Galway, Ireland
®
Nelipak Heredia, Costa Rica
Nelipak Derry, Northern Ireland, UK
®
Nelipak Humacao, Puerto Rico
®
®
Nelipak Clara, Ireland
Medical Device and Pharmaceutical Packaging Full-service solutions that provide superior quality and protection
®
®
Nelipak Whitehall, PA, USA