THE FRANKLIN
The Science Magazine of Notting Hill & Ealing High School ◆ Autumn 2021



Epigenetics is the study of changes in the way an organism's genes are expressed rather than any alteration of the genetic code itself It involves research into the different biological mechanisms that turn genes on and off
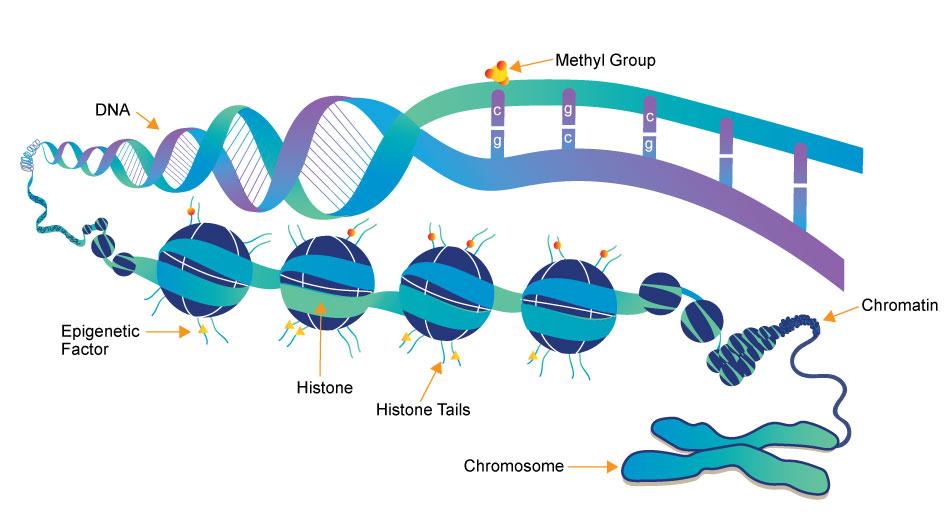
DNA gives our cells instructions for various proteins to be produced inside the cell Simply put, this is how genetics work But epigenetics influence the way in which our cells read these genes and therefore whether or not the cells should produce these various proteins So instead of changing your DNA sequence, epigenetics change the way these sequences are read by your cells Behaviours and
situations such as how much you exercise and what you eat can all cause epigenetic changes
An example of epigenetic changes is DNA methylation This is when a chemical group called a methyl group is added to DNA in certain places and results in blocking proteins that connect to DNA to ‘read’ the gene This normally turns a gene ‘off’ To remove the chemical group from the DNA, a process called demethylation would have to take place This usually turns genes ‘on’
Epigenetics causes certain genes to be turned on and others to be turned off, this difference in expression is the reason we are all unique
Certain Factors cause your epigenetics to alter, due to both aging and as a response to your environment and behaviours:
➢ Throughout your life, your epigenetics will transform and this means that your epigenetics at birth are not the same as your ones during adulthood or childhood
➢ Some epigenetic changes are reversible, meaning some changes can be taken away or added because of certain behaviours or your environment
An example of this is smoking In the gene AHHR, at specific parts, smokers usually have less DNA methylation than people who don’t smoke Yet after quitting smoking, former smokers could start to have increased DNA methylation for this gene, until reaching similar levels to non-smokers

➢ Epigenetics can also have an effect on your health With infections, microbes can weaken your immune system by changing your epigenetics Consequently, this helps the pathogens to survive As well as this, certain epigenetic changes can increase y i k f tti Th b h i f p e p c
Sources
CathEnnis(2018) Epigenetics101:abeginner’sguidetoexplaining everything|CathEnnis [online]theGuardian Availableat: https://wwwtheguardiancom/science/occams-corner/2014/apr/25/epigene tics-beginners-guide-to-everything CDC(2020) WhatisEpigenetics?[online]CentersforDiseaseControland Prevention Availableat: https://wwwcdcgov/genomics/disease/epigeneticshtm WhatisEpigenetics?(2018) ASuperBriefandBasicExplanationof EpigeneticsforTotalBeginners [online]Availableat: https://wwwwhatisepigeneticscom/what-is-epigenetics/
Year 7 have been learning to draw accurate micrographs

Overall, seeing as epigenetics are reversible, scientists wonder what the outcome would be of different combinations of genes being turned on or off If you could reverse a gene’s state to get rid of the bad while keeping the good, hypothetically you would be able to cure diseases such as cancer, slow down aging and much more
One of the most important organisms that our world relies on are bees Despite being known as small irritable insects these creatures have a huge impact on our planet and lives

The earliest record of bees was found in Myanmar (the border of Bangladesh and India) A bee was found encased in Amber and has been dated as 100 million years old It is likely that bees originated from the Far East and were originally like wasps, eating other insects instead of nectar and pollen There are over 4,000 different species of bees and around 25,000 individual species but there are more to be discovered Bees belong to the insect superfamily ‘Apoidea’ which also includes ‘sphecoid wasps’ from which bees are believed to be descended from About 4000 species of bees are in the US and over 250 in Britain
Bees have some useful talents that have helped us humans throughout the years The first ability comes from their gift of being perfectly adapted to pollinate Bee pollination helps plants grow, breed and produce food They do this by entering flowering plants to seek food and whilst inside, pollen gets caught onto their bodies so when the bee leaves and goes to find more food in another plant, the pollen remains stuck on them and carried to another plant This helps humans as without pollination we wouldn’t be able to eat lots of different foods such as fruits and vegetables (e.g broccoli, squash, apples and almonds).
Pollination is not just vital for the food we eat directly but it is also vital for the foraging crops, such as beans and clover used to feed the livestock we depend on for meat Just as importantly, it helps feed many other animals in the food chain and maintains the genetic diversity of the flowering plants On the topic of food, certain species of bee also have another
use, which is their ability to create honey Bees gather pollen or nectar from plants and once their nectar sacs are full, the bee returns to the hive Nectar is delivered to one of the “indoor” bees and is then passed mouth to mouth until its moisture content is reduced from about 70% to 20% This changes the nectar into honey Humans have discovered this and then made bee farms, which is where they keep multiple hives and harvest the honey made by the bees

Just like all animals, bees have ways of defending themselves The most famous way is by stinging their attacker When a bee is confused, stepped on or threatened it will sting It’s “stinger” is located at the end of its abdomen and when the bee feels one of the emotions above a venom is released into a space on the sting between the barbs and the stylet The only problem that bees face when using this defensive skill is that there is no way of withdrawing the sting and once a bee has stung something it dies The venom the bee releases is known as a formic acid or more commonly known as methanoic acid, which is a colourless solution with a pungent odeur The chemical formula of this is HCOOH Another skill bees have is that they can fly This is not such an attacking move but a defensive one, it also allows them to quickly move from one place to another Bees have special wings which aren’t rigid but twist and rotate during flight The wings make short, quick, sweeping movements (front and back, front and back) which means they have enough motion to lift making it possible for bees to fly An interesting thing to add about bees, is that similar to the
hummingbird, they have the ability to fly, or ‘hover’ rather in one spot.
Bees provide humans with lots of resources they need to survive but unfortunately like multiple other organisms bees are going extinct This is due to multiple different reasons some of which are: changes in land use, habitat loss (deforestation), disease, invasive non-native plant/animal species, farming practices, pollution, pesticide and climate change. The majority of these methods are caused by humans despite the fact that without bees we humans may not necessarily survive. But just as there are ways of leading bees to extinction, there are also ways of helping bees survive. Firstly preventing the problems above, not only helps bees but will also help our planet and other organisms. However, solutions directed at bees are: growing a bee friendly garden, leaving out some sugar which is a food source for bees, eating sustainable honey and supporting bee charities (e.g the bumblebee conservation trust)
In conclusion, despite bees being seen as painful, frustrating insects they have uses that not many people are aware of, and majority of which are necessary for human survival. As a school there are many ways to help bees such as: growing a bee friendly garden filled with lots of flowers and plants so the bees have access to nectar, contributing to the charities that help bees and setting up small plates of sugar water as a place where bees can come to restore their energy.
Sources
BBCTeach (nd) Wouldwestarvewithoutbees?[online]Availableat: https://wwwbbccouk/teach/would-we-starve-without-bees/zkf292p#: :te xt=Pollination%20is%20not%20just%20important[Accessed17Aug 2021] BuzzAboutBeesnet (2010) TypesofBees:Thedifferentspecies, families andgenerasofbees [online]Availableat: https://wwwbuzzaboutbeesnet/types-of-beeshtml MaryAnnClark, Choi, J andDouglas, M (2018) Pollinationand Fertilization [online]Opentextbcca Availableat: https://opentextbcca/biology2eopenstax/chapter/pollination-and-fertilizati on/
On Wednesday, July 4th, Thailand banned certain sunscreens from being used in their marine parks This change was prompted by scientific studies that show that certain types of sunscreens can harm marine life
Healthy coral reefs provide millions for tourism and food industries, but their ecosystem is threatened by a number of factors, one of which is the harmful chemicals in sunscreen The chemicals that have been banned are oxybenzone, octinoxate, 4-methylbenzylidene camphor and butylparaben These ingredients have been linked to coral bleaching and deformities in other marine life, such as mussels
Coral live in symbiosis with algae (zooxanthellae) that live inside them, the algae provide 90% of the coral’s energy and provide valuable nutrients. Extreme stress can cause the coral to expel the algae, leaving the coral without its colour. If the stress passes, the algae can return to the coral, but eventually, the coral will starve to death. Stress can be caused by a number of factors including ocean acidification, this can be traced back to harmful compounds in sunscreens that have ended up in the ocean.
Some scientists argue that the ban is unnecessary as the studies used coral that was exposed to the sunscreens in ppm (parts per million) and ppb (parts per billion) quantities, this is much higher than the levels normally found in the environment. If you applied 30g of sunscreen (the recommended amount) containing 3% 4-methylbenzylidene camphor over your entire body, and 100% of it came off you would get a concentration of 0.99ppm if you swam in 909L of water. This estimate is quite conservative, since it’s commonly found that people usually wear less than half of the recommended amount of sunscreen,

and the amount that dissolves in water is around 25% in a 20 minute swim. The ocean is huge and contains around 1.34 x 1021 L of water or 70 Olympic swimming pools for every one of the 7.44billion people on earth. This means that in most areas of the ocean, levels of these compounds are untraceable. The areas in which this causes major issues are small secluded bays that are full of bathers and frequented by tourists
In conclusion, I believe that despite the evidence against the ban, Thailand has taken a step in the right direction as over time in secluded bays, the chemicals in the sunscreen will build up and start to kill off the coral This ban followed Hawaii’s ban of harmful sunscreen in 2018 and Craig Downs, one of the authors of the study showing the harmful effects of sunscreen on reefs, explained to the Washington Post in 2015 that "any small effort to reduce oxybenzone pollution could mean that a coral reef survives a long, hot summer, or that a degraded area recovers" I believe that if the ban on sunscreen proves effective and helps the reefs recover, then other countries may be prompted to change their policies around coral reefs
Notes:
ppm means “parts per million”, or milligrams per litre This is the equivalent of one-fiftieth(1/50)ofa dropdilutedinonelitre
ppbmeans “partsperbillion, ormicrogramsperlitre. 1ppbisathousandtimesmoredilutethan1ppm
Sources
IsYourSunscreenKillingCoralReefs?TheScience(withVideo) LabMuffin BeautyScience(2018),(availableat https://labmuffincom/is-your-sunscreen-killing-coral-the-science-with-vid eo/)
Thailandbanscoral-damagingsunscreensinmarineparks BBCNews (2021),(availableathttps://wwwbbccouk/news/world-asia-58092472)
Hawaiitobancertainsunscreensharmfultocoralreefs BBCNews(2018) , (availableathttps://wwwbbccouk/news/world-us-canada-43993407)
Many vaccines have been invented to protect people from the effects of infectious diseases A vaccine is a type of medicine that stimulates your immune system so if you come into contact with that disease again it is able to fight it off. They are there to protect someone from a disease rather than treat it Edward Jenner is considered the founder of vaccinology because in 1796 when he inoculated a 13 year old boy with cowpox he became immune to smallpox
In 1798 the first smallpox vaccine was invented
Smallpox is caused by infection from the variola virus People who had smallpox had a fever and a distinctive rash Around three in ten people died because of it; When the smallpox outbreak emerged in the UK there were a thousand deaths per million It was transmitted from person to person, this is called airborne, human-to-human transmission Edward Jenner took fluid from a cowpox blister and scratched it into the arm of a young boy. The young boy developed a blister on the site of where the cowpox was scratched in but he soon recovered Later on when he inoculated the boy again, but this time with smallpox, he showed no signs of the disease
Over the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries the vaccine that was made eradicated the disease that led to global eradication of the disease in 1979 As smallpox was very infectious, people implemented hospital ships that were far away from the main population to try to stop the spread of the disease The ships were located 17 miles away from London bridge and the three of them were anchored in place
to stop movement and sea sickness. One of the three ships housed female patients, the other housed male patients and the other ship was where the food was made as well as living quarters for the staff The smallpox ships became redundant in 1903 when the Joyce Green hospital in Kent and the other river hospitals began to open The river hospitals had more beds for patients as well as being easier and safer to run After twenty years of service the ships were auctioned off for scraps
Many more vaccines have been developed to keep everyone safe from deadly diseases and one of these is the polio vaccine Polio is a disease caused by one of three types of the poliovirus. Children under 5 were the most likely to get infected 1 in 200 people who were infected had irreversible paralysis and 5%-10% of people completely paralyzed died because their breathing muscles became immobilized. It can infect the spinal cord which can cause paralysis
Philip Drinker and Agassiz Shaw Jr were the first people to create an ‘Iron lung', a machine to help people breathe This machine was a big tube-like container that would circulate air so that you would be able to breathe Whole wards of these were created such as the Lane-Fox ward at St Thomas’s hospital Polio can be spread through eating and drinking contaminated food and water
The polio vaccine was made by Dr Jonas Salk who was an American medical researcher It was announced on national radio on March 26th 1953 that Salk had an official vaccine for polio that worked Dr Sabin also created an oral polio vaccine Salk was born in 1914 in New York city. Polio is not around much anymore but a few cases are still reported every year in Asia, Afghanistan and Pakistan. It was eradicated from the UK in 1984 and in the USA it was eradicated in 1979, however they still give vaccinations in the uk so that it does return
Overall vaccines are very important to today’s society and without them life wouldn’t be the same
The world would be in a much worse position if we did not have the variety of vaccines available today I believe vaccine research will continue for current and developing diseases
Sources
Bibliography1 HistorycomEditors, Salkannouncespoliovaccine HISTORY (2018),(availableat https://wwwhistorycom/this-day-in-history/salk-announces-polio-vaccin e)2 Smallpox wwwwhoint,(availableat https://wwwwhoint/westernpacific/health-topics/smallpox)3 BBCHistory -EdwardJenner wwwbbccouk,(availableat https://wwwbbccouk/history/historic figures/jenner edwardshtml)
A black hole is a place in space where gravity pulls so much that light cannot escape They are invisible as no light can get out, and the gravitational pull is strong because a lot of matter has been squeezed into a very small space
Black holes vary in sizes, and it is thought that the smallest black holes are as small as one atom But
even if it were the size of an atom, it could potentially have the mass of a large mountain The largest black holes - called supermassive black holes - could have the mass of over 1 million suns, at least
Depending on the size and mass of the black holes, they are thought to have formed in a variety of ways The smallest black holes, called miniature black holes, are thought to have formed when the universe began: immediately after the Big Bang Randomly expanding reasons could have possibly squeezed some regions into dense, small areas, creating miniature black holes
Intermediate black holes, which are in size and mass in between miniature and supermassive black holes,
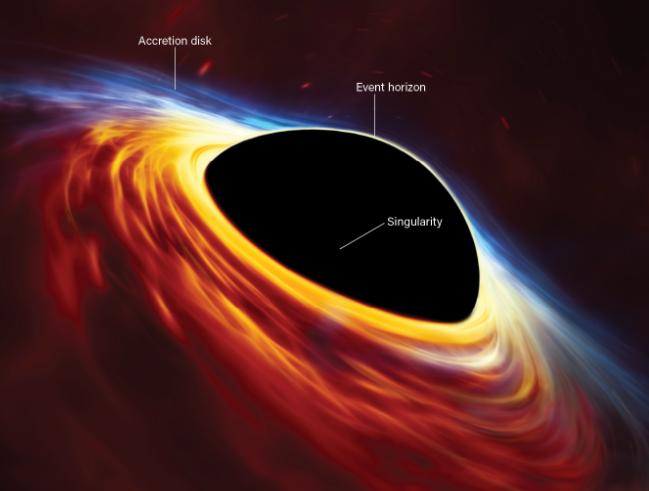
could form when stars in a cluster collide, causing a chain reaction and resulting in a black hole
The third way of which black holes are thought to have formed is by stars growing so large that they collapse under their own weight When this happens, it causes a supernova: a stellar explosion. Black holes which are formed like this can be either called stellar black holes, or supermassive black holes, depending on the size and mass However, lots is still unknown about the formation of black holes
Scientists cannot see black holes, however they can see how the gravitational pull affects the stars and gas and other matter around it, using telescopes that can detect x-rays, light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation In addition, when a black hole and star are close together, high energy light is made, which although cannot be seen with the naked eye, can be viewed with telescopes and satellites When a black hole and a star are close together, high energy light is made
It is a myth that black holes go around ‘eating’ moons, stars and planets, yet there is concern as to whether Earth could fall into a black hole However, Earth could not fall into a black hole as no black hole is close enough to the Earth If a black hole were to take the place of the Sun, then Earth still wouldn’t fall in; instead, the planets would orbit it In fact, black holes move very rarely because of their immense size, however, there are still occasionally instances of black holes moving, but that is a very unusual occurrence
Nothing inside a black hole can communicate with our universe, even in principle. If we were to find out, we would have to look from the outside Near a black hole, the flow of time slows down to extremes, and an object falling into a hole would appear to be frozen in time on ‘the horizon’
The horizon of a black hole is the edge of it, and anything that crosses this imaginary line would be swallowed inside it forever Einstein’s theory of gravity predicts that time itself could be destroyed at the centre of a black hole, however, nobody knows what would actually happen inside of one
After passing the event horizon of the hole, the object is thought to begin a process called ‘Spaghettification’. This is where the object is stretched out vertically and compressed, until it has been fully stretched out, with every part elongated in a different direction Eventually, the object would be torn apart inside the black hole The forces surrounding the black hole are so strong that nothing can withstand it, no matter its components In addition to these reasons, we cannot do a direct experiment to find out since no information or evidence could ever get out of the hole
Black holes do eventually become unstable and disappear into nothing but radiation.
In fact, Stephen Hawking theorised that there is a possibility that they also leak particles, in the form of what is known as ‘Hawking Radiation’ This would mean that if we waited for long enough, a black hole could evaporate, however, this theory has caused huge debate among scientists Unless we could
create a low-mass black hole (which will not “live” for as long as other black holes), nothing else in the universe will be around to see them disappear
NASA, WhatIsaBlackHole?NASA(2018),(availableat wwwnasagov/audience/forstudents/k-4/stories/nasa-knows/what-is-a-bl ack-hole-k4html)
E Landau, 10QuestionsYouMightHaveAboutBlackHoles –NASASolar SystemExploration NASASolarSystemExploration(2019),(availableat solarsystemnasagov/news/1068/10-questions-you-might-have-about-blac k-holes/)
NolaTaylorRedd, BlackHoles:Facts, Theory&Definition Spacecom(2019) , (availableathttps://wwwspacecom/15421-black-holesfacts-formation-discovery-sdcmphtml)
BlackHoles, Explained Science(2018),(availableat wwwnationalgeographiccom/science/article/black-holes#:~:text=There%2 0are%20four%20types%20of)
NASA, BlackHoles|ScienceMissionDirectorate Nasagov(2008),(available athttps://sciencenasagov/astrophysics/focus-areas/black-holes)
S Hawking, L Hawking, J Bielecki, Unlockingtheuniverse(Puffin, London, 2021)
Asupermassiveblackholeonthemove|Space|EarthSky earthskyorg (2021),(availableat https://earthskyorg/space/supermassive-black-hole-on-the-move)
WhattoExpectifEarthEverFallsIntoaBlackHole DiscoverMagazine, (availableatdiscovermagazinecom/ the-sciences/what-to-expect-if-earth-ever-falls-into-a-black-hole)
WhatWouldItBeLikeToFallIntoABlackHole?Futurism,(availableat https://futurismcom/what-would-it-be-like-to-fall-into-a-black-hole)
Spaghettification Wikipedia(2020),(availableat https://enwikipediaorg/wiki/Spaghettification)

pH
When you mix the two you get neutral!
Acids are red to green!
It's the coolest thing you've ever seen Alkalis are blue through purple
Too bad the pH scale isn't a circle!
The periodic table has 2 teams
Heavy metals and Non metal dreams Together they fight to see which team reacts with acid right
There are two types of litmus paper red and blue
When mixed with alkali they change colors oh yes they do!
Acids have a pH of less than seven an acid can be a lemon It has a pH of 2 A milder acid is a melon
Most soaps are an alkali Alkalis have a pH of more than seven Alkalis have a colour of blue an purple Ammonia solution has a pH of eleven
Water has a neutral pH Neutral pH is normally green Eggs are also neutral Alkalis have a pH of 8 to 14
Strong acids and alkalis are corrosive When using be very cautious Wear protective equipment
If you eat some you can feel nauseous
The pH scale has sides of two, Acids red and alkalis blue. Mix them together and you get green, It's the coolest thing you've ever seen!
Acids are 1-6, Watch them change colour as the indicator drips Alkali are 8-14, Sometimes they're in pools to keep them clean!
Wasp stings are alkaline, Meaning their number is high But acids are the sting of a bee, Meaning they're low like 5 3
Learning about the pH scale has been fun, But now it seems we’re done So next time you forget, This poem will help you I bet!
Acids and Alkalis have a pH Of 0-14, and that is great! If a substance has a pH of 7 It is very even, As it is equally acidic and alkaline, Which is completely fine!
Acids have a pH of 0-6, Which unfortunately can trick You into believing that they aren’t strong And if you do, you are wrong! They can eat through (almost) anything, Which is called corrosion. Weak acids taste sour, So do not underestimate acid’s power!
Alkalis have a pH of 8-14 And they can do lots - even make your oven clean! When they’re strong, it’s no surprise That they can corrode before your eyes! Weaker alkalis taste bitter, Which will make you reconsider Messing around with alkalis, As that would be very unwise!
Substances with pH 7 Can be made with titration! Just add acid to the alkali And watch them react and fly, As the substance turns green Neutralised, it would seem Neutral substances are truthful Such as pure water, which is useful!
Do not mess around with alkalis, Or acids, I advise, As without testing the pH, you do not know How strong the substance will go So be careful around the lab, And your time will be fab! That is all, for today, And now you know, experiment away!
Acids have a pH of 0-7, While an alkaline such as ammonia has a pH of 11, With harmful acids you must be cautious, But some you eat may make you feel nauseous
Alkalis which are also known as bases, Are dangerous as they are corrosive in most cases, The pH of an alkali ranges from 7-14, Examples of alkalis are bleach and chlorine
Not all acids and alkalis are dangerous though! Egg whites are alkalis which used to make dough, Apples are acids and have a pH of 4, Yet we eat them everyday right to the core
Universal indicator shows how strongly acidic or alkaline a solution is, When an acid and base react together they will fizz, Strong acids are red, strong alkalis are blue, Strong alkalis and acids will burn skin through.
I’ll teach you about acids, alkalis and litmus paper I hope you’re writing this down, I'll test you later Universal indicator is extremely useful
It tells you if it’s acid, alkali or neutral
If litmus paper’s red, better come to the conclusion, That without a doubt, there is acid in the solution Blues and pH scale from ten to fourteen Clearly indicate that the solution is alkaline Now, alkalis I rate
If your tummy’s not too great The dentist says ‘hooray!’
As they keep the cavities away British Bake Off would surely flounder Without the alkalis in baking powder
And in order to ensure that my toilet’s always clean, The alkalis in bleach help me keep it dead pristine What is very different is a lovely cup of tea
Ms Johnson says it's acidic, surprisingly Orange juice and lemon are obviously acids too, Coloured red on the pH scale, unlike alkalis of blue
We really enjoyed being the editors for this edition of the Franklin Having the chance to read and learn new topics on those which interest others in the school has allowed us both to widen our knowledge, out of the normal school curriculum. We want to thank all those who sent in a piece of writing or fantastic artwork, and we hope you enjoyed reading up on a particular topic as fascinating and enjoyable as we both did JasminePalmer&RameenAshfaq, Editors SophieAlexander, Illustrator MsL. Brown, EditorinChief