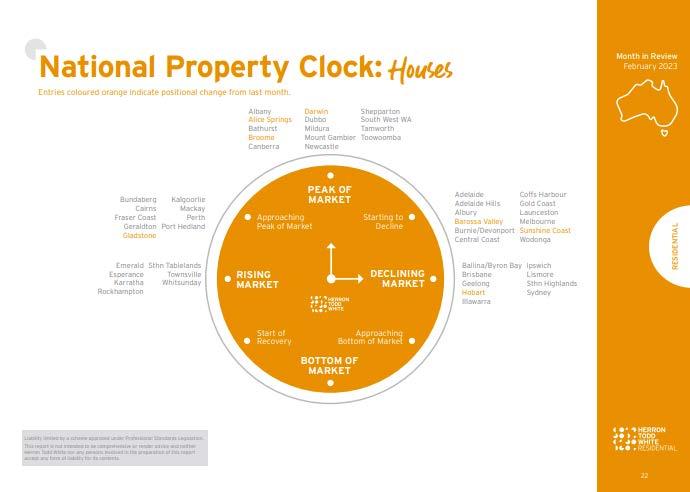
February report.


Our purpose.
To create a place where we can facilitate our people’s growth.




To create a place where we can facilitate our people’s growth.


Family.
Our colleagues are our broader family, assist when needed and when in need.
Mutuality. Respect our colleagues and our clients as you would like to be respected.

Realising potential. Unlock your full potential, encourage and support your colleagues.
Embrace change. Strive for excellence; be open minded and willing to embrace change.
Health and energy. Work towards being well balanced within yourself.




Melbourne has been experiencing steady population growth over the past few decades, and this trend is expected to continue in the coming years..
Various factors contribute to Melbourne's population growth, including strong economic growth, employment opportunities, cultural diversity, and a high standard of living. Melbourne is also a popular destination for international students, with several leading universities located in the city.
The Victorian Government has projected that Melbourne's population will reach 8 million by 2050, with an average annual growth rate of around 2%. This growth is expected to be driven by both natural increase (births minus deaths) and net overseas migration.
The continued population growth is likely to have significant implications for Melbourne's housing market, with increased demand for housing and infrastructure. As a result, it is crucial for the government and the property industry to plan for and manage population growth sustainably to ensure that Melbourne remains an attractive and livable city for both current and future residents.
Melbourne has been a popular destination for international students for many years, with a range of leading universities and educational institutions located in the city. According to the Australian government's Department of Education, Skills and Employment, Melbourne was the second most popular city in Australia for international students in 2020, with over 187,000 international students enrolled across various courses and levels of study and as we return to these levels it will have a significant impact 2023
The return of international students is likely to have significant implications for Melbourne's economy, with the education sector being a significant contributor to the city's GDP. It will also have an impact on the city's housing market, as many international students require accommodation during their studies, and this can create demand for rental properties in certain areas of the city.
As we navigate through these times its important to make educated decisions when buying or selling your principal place of residency or investment property. Please seek out any professionals in this area. Here at O’Brien Real Estate “OurPurpose” is to “ facilitategrowth“ so please reach out if you have any questions

Best Regards,
Dean O'Brien Director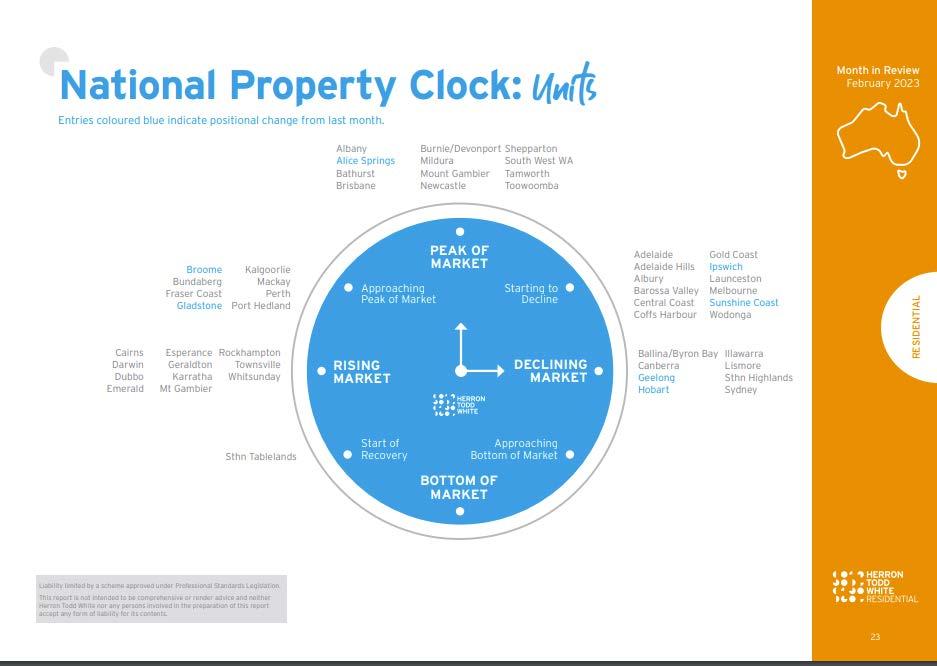







Former immigration department deputy believes government has ‘significantly underestimated’ net migration
Get our morning and afternoon news emails, free app or daily news podcast
Australia is on track for net migration of more than 300,000 people this year, more than 25% higher than Treasury forecasts, due to a surge in arrivals, according to a former top immigration official.
Abul Rizvi, the former deputy secretary of the immigration department, said that Treasury forecasts of a 235,000-person annual boost to population from migration – the long term prepandemic average – have “significantly underestimated” net figures.
Rizvi’s intervention comes as the treasurer, Jim Chalmers, signalled the government could adopt a proposal from the Business Council of Australia for permanent migration to be set as a percentage of the total population, automatically raising the current cap of 195,000.
Asked about the BCA submission to the migration review on Friday, Chalmers told Radio National he is “personally up for” a conversation about “if there is a way that we can streamline some of these processes to get the right mix at the same time as we recognise that migration’s not a substitute training”.
The October budget forecast net overseas migration of 235,000 both in 2022-23 and 2023-24, which it explains is based on an assumption that migration will “continue in line with pre-pandemic trends”.
The government’s population statement, released on Friday, further explained this figure is “derived using a 14-year average from 2004–05 to 2017–18”.
The estimate is composed of 190,000 permanent migrants and 13,750 humanitarian migrants entering Australia a year, plus 66,000 “temporary migrants who reside in Australia for several years but never transition to permanent residence”, less 20,000 permanent residents and 15,000 Australian citizens who emigrate.

But Rizvi told Guardian Australia that actual arrivals in the year to date are much higher than those estimates and that “because of this factor alone Treasury has underestimated net migration”.
Rizvi cited data, published by the Australian Bureau of Statistics in December, which showed that arrivals outstripped departures in October by almost 200,000.
“If you have a large excess of visitor arrivals over departures, a substantial proportion are going to end up as net migration,” he said.
In October alone there were 1.2 million arrivals and 1 million departures. A surge of 430,470 short-term visitors arrived, dwarfing the 360,460 who departed. Similarly, 721,860 Australian citizens arrived for the short-term, more than the 609,160 people who departed.
“Treasury are assuming net migration will be 235,000 but I think it is on track for well over 300,000 this year,” Rizvi said.
“I’ve never seen anything like this in 30 years – it’s out of the realm of anything we’ve seen before,” he added, referring to the excess of arrivals over departures.
The exact figure is unknown because the final net migration figure will not be determined until next financial year and it is still unclear what portion of temporary visits will be extended by further visa grants.
In the 11 months to November 2022, Rizvi said there was an “unprecedented excess of visitor arrivals over departures of 340,000” and this was “likely to grow further in December 2022” when the latest ABS figures are released next week.
“In 2019, 71% of excess visitor arrivals contributed to net migration. In 2018, it was around 40% and in 2017, it was 70%.”
Even applying a conservative estimate of 40% of that cohort remaining, or 136,000 people, would more than double Treasury’s estimate of 66,000 temporary visitors contributing to net migration in 2022-23.
Rizvi suggested the surge in arrivals may be driven in part by parents and other relatives visiting Australia temporarily while waiting for a more permanent visa “Also, with the labour market being as strong as it is people have arrived, finding alternatives such as a student visa, which is now effectively a work visa, or applying onshore for a working holiday visa.”.
The Centre for Population’s statement projected that with net migration of 235,000 a year, Australia would reach a population of 39.2 million in 2060-61, signalling a smaller population than forecast and older on average due to the impacts of the pandemic and the global Covid shutdown.
But under a “high migration scenario” of 470,000 a year, Australia’s population would reach 49.3 million in that time, with a younger median age (41) than the baseline scenario (42.8).
The statement noted “significant uncertainties” in projecting migration patterns, including the “upside risk” of fewer people leaving Australia than forecast and the “downside risk” that more might leave.
Student numbers, in particular, were sensitive to “movement restrictions in student source countries”, it said.
we have a small favour to ask. Tens of millions have placed their trust in the Guardian’s fearless journalism since we started publishing 200 years ago, turning to us in moments of crisis, uncertainty, solidarity and hope. More than 1.5 million supporters, from 180 countries, now power us financially – keeping us open to all, and fiercely independent. Will you make a difference and support us too?
Unlike many others, the Guardian has no shareholders and no billionaire owner. Just the determination and passion to deliver high-impact global reporting, always free from commercial or political influence Reporting like this is vital for democracy, for fairness and to demand better from the powerful

And we provide all this for free, for everyone to read. We do this because we believe in information equality. Greater numbers of people can keep track of the global events shaping our world, understand their impact on people and communities, and become inspired to take meaningful action. Millions can benefit from open access to quality, truthful news, regardless of their ability to pay for it.
Whether you give a little or a lot, your funding will power our reporting for the years to come
The quality of our service stems from the importance we place on the people behind our network.