






Bratislava
18 March 2024
oe.cd/slovakia

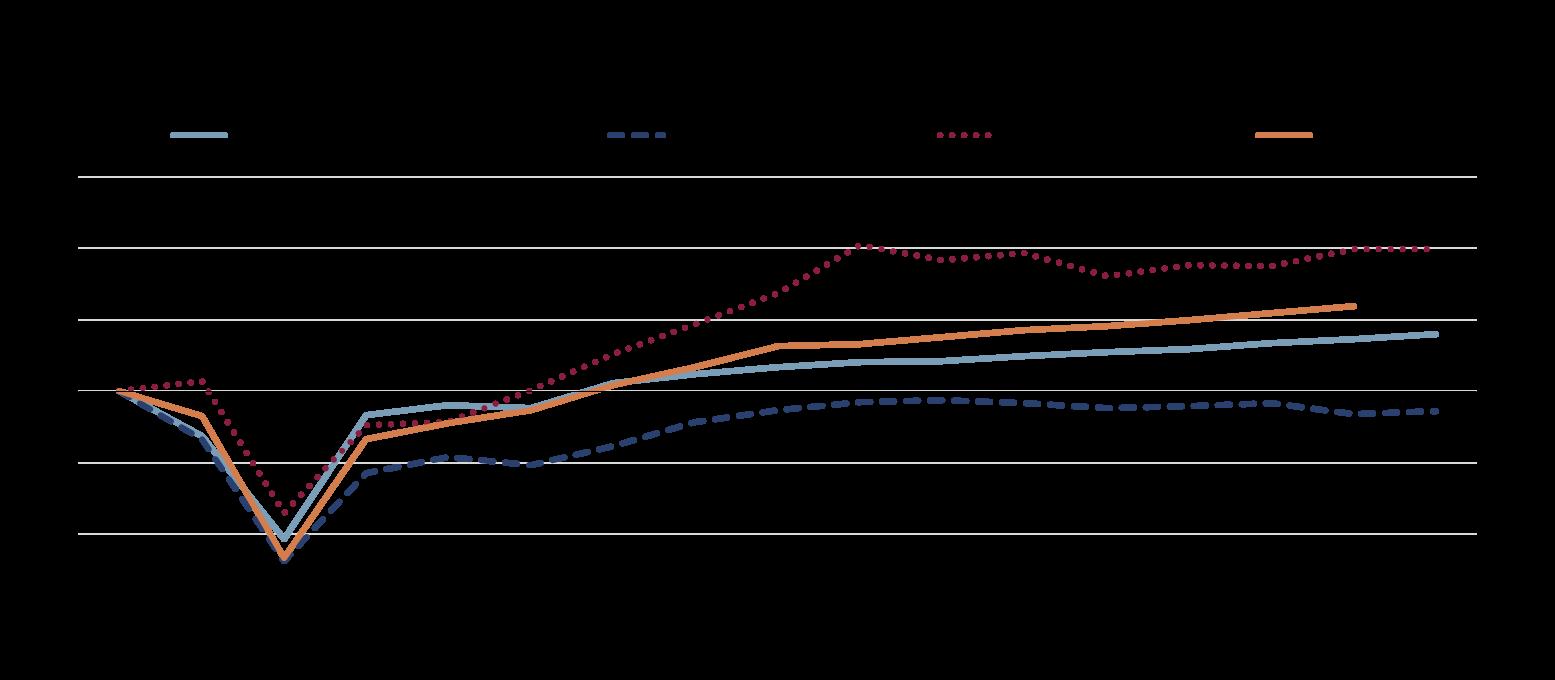

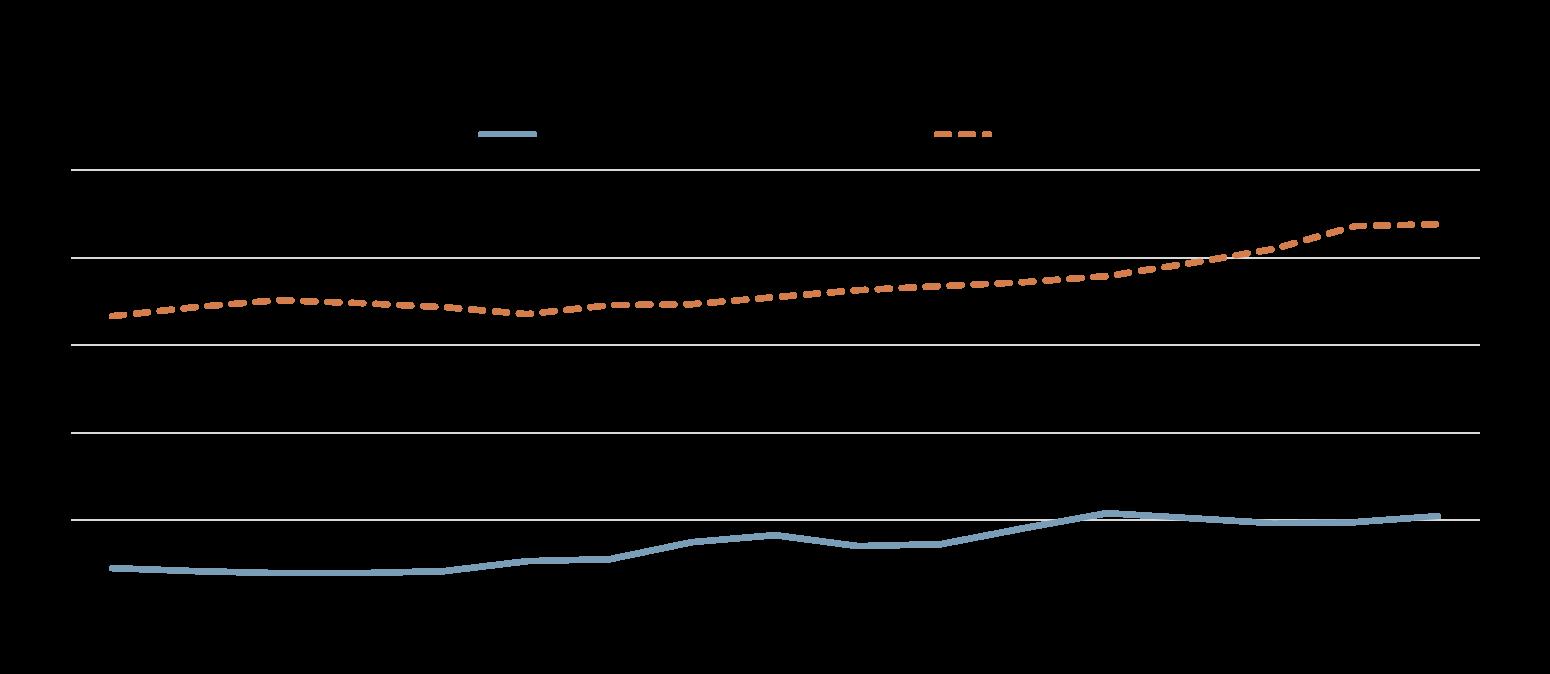
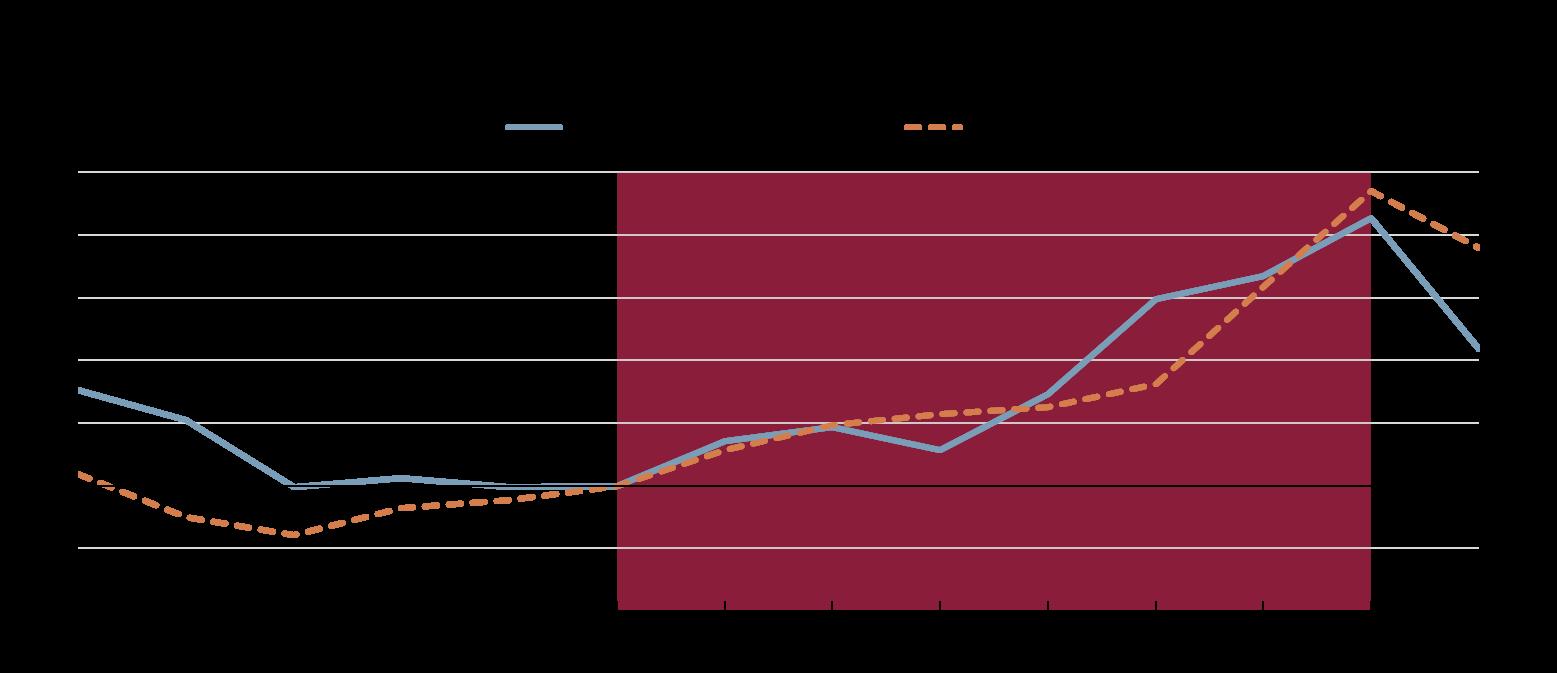
Note: Harmonised CPI inflation for the Slovak Republic and euro area. OECD weighted average excluding Türkiye.
Source: OECD Price Statistics database.





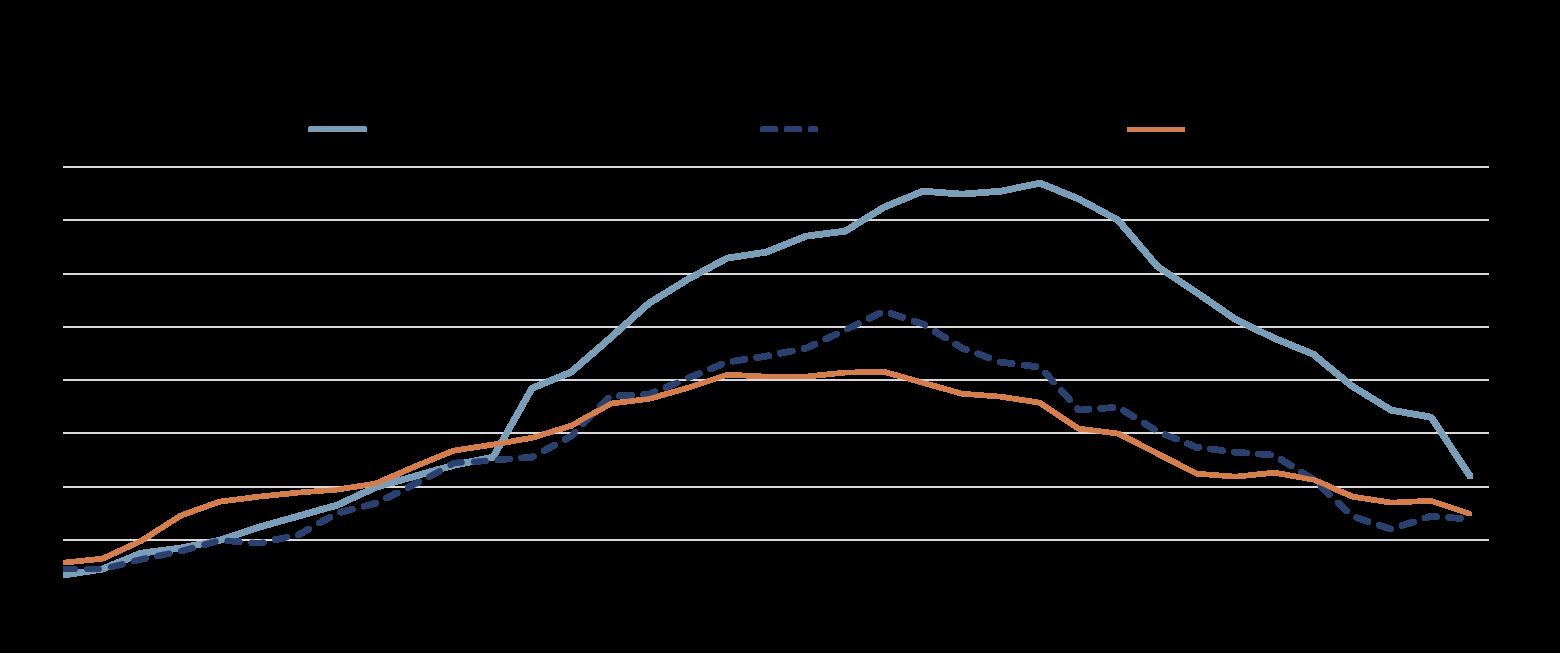
Note: 2023 data refer to OECD estimates.
Source: OECD Economic Outlook: Statistics and Projections database.

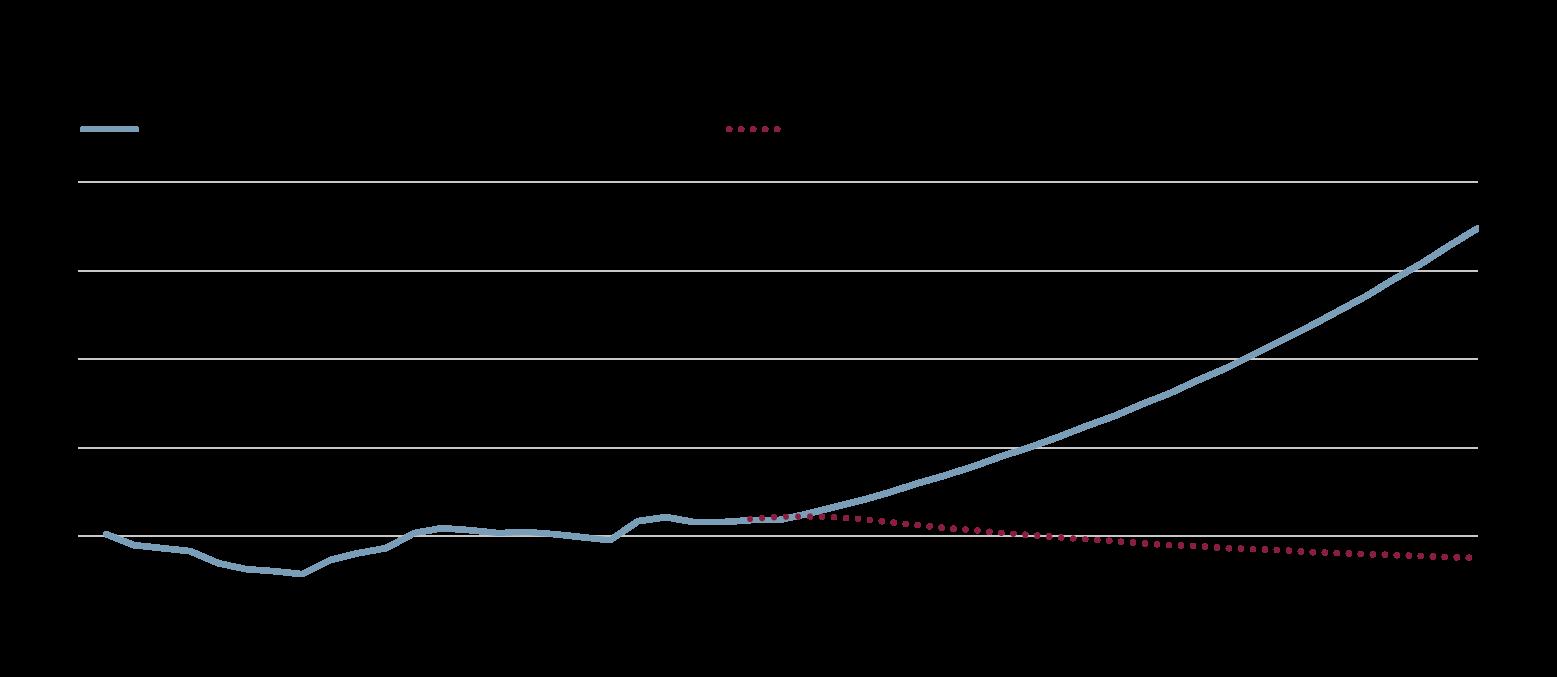
Note: The “Without offsetting ageing-related costs” scenario is based on the OECD Economic Outlook 114 database with updates until 2025 and the OECD Long-Term Economic Model thereafter. Ageing-related costs are based on the EU Ageing Report 2021 and Ministry of Finance. The “Structural reforms and ambitious fiscal consolidation scenario” are based on the OECD Long-Term growth Model and reform scenario outlined in Box 1.1 of the Survey, which implies a 0.5 p.p. higher real GDP growth rate on average over the projection period compared to the “Without offsetting ageing-related costs” scenario. In addition, the scenario assumes an improvement of the primary balance by 1.1 p.p. of GDP per year between 2023 and 2028.
Source: OECD Long-term Economic Model; EU Ageing Report 2021; Ministry of Finance.



database, https://www.oecd.org/els/family/database.htm.

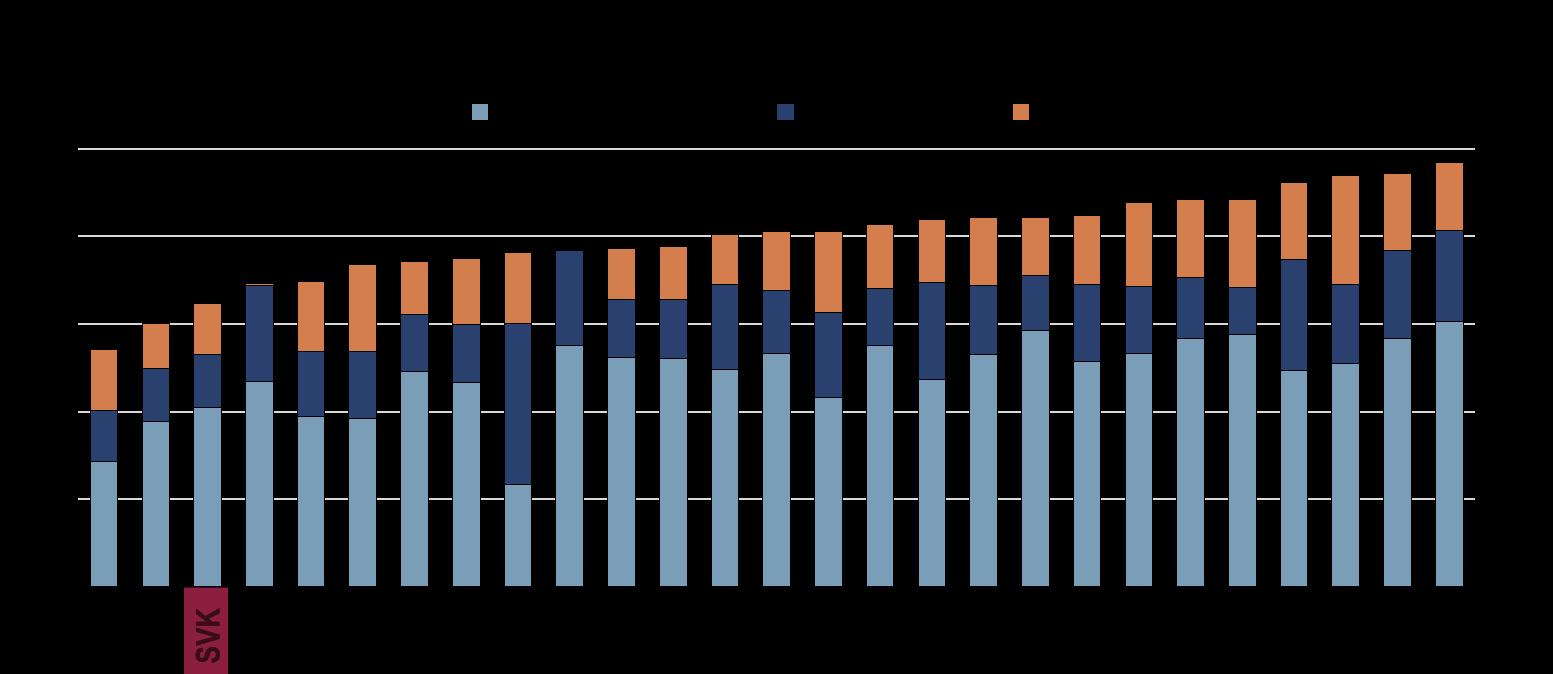
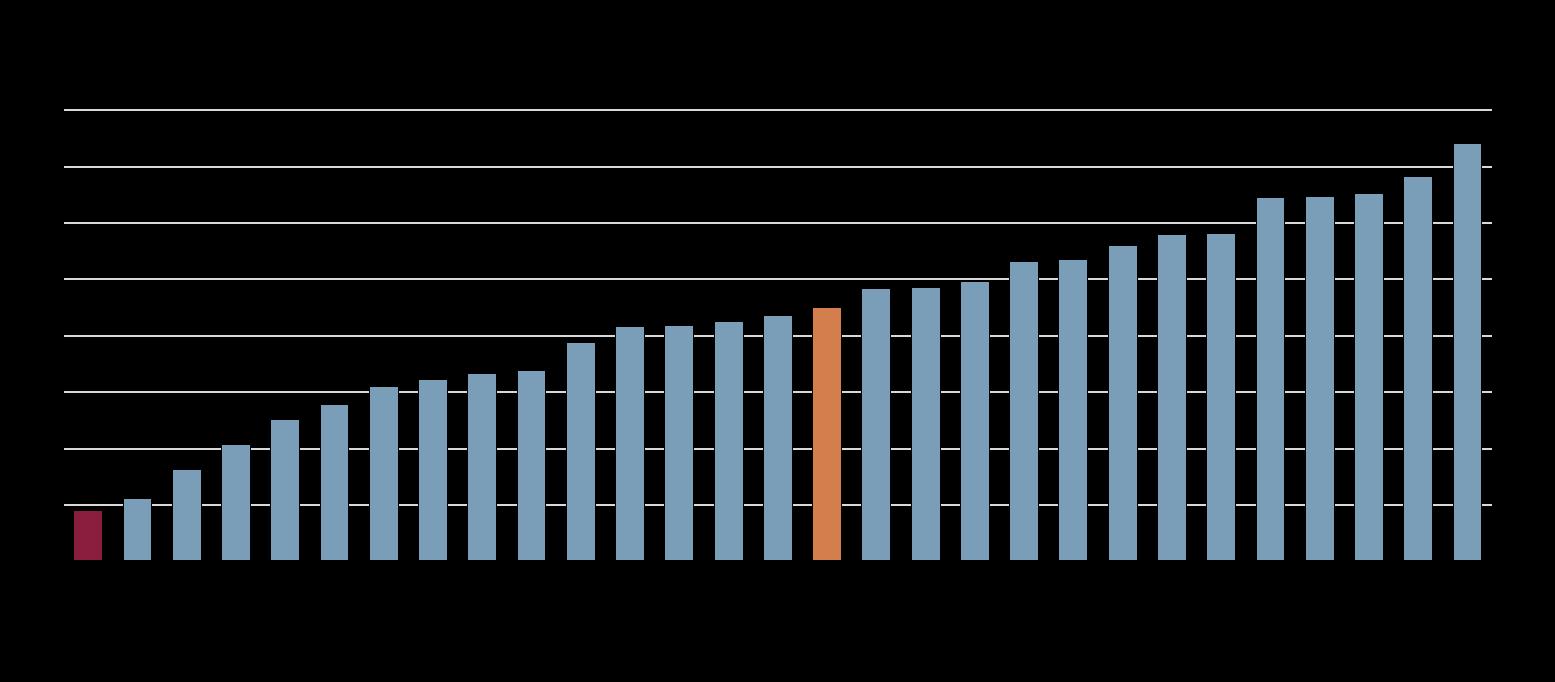
Note: EU structural funds include here the Cohesion Fund, European Regional Development Fund, European Social Fund and Youth Employment Initiative. Absorption rate is the percentage of funds spent relative to the total planned amount (EU funding and national co-financing).
Source: Open Data Platform for the European Structural and Investment Funds.



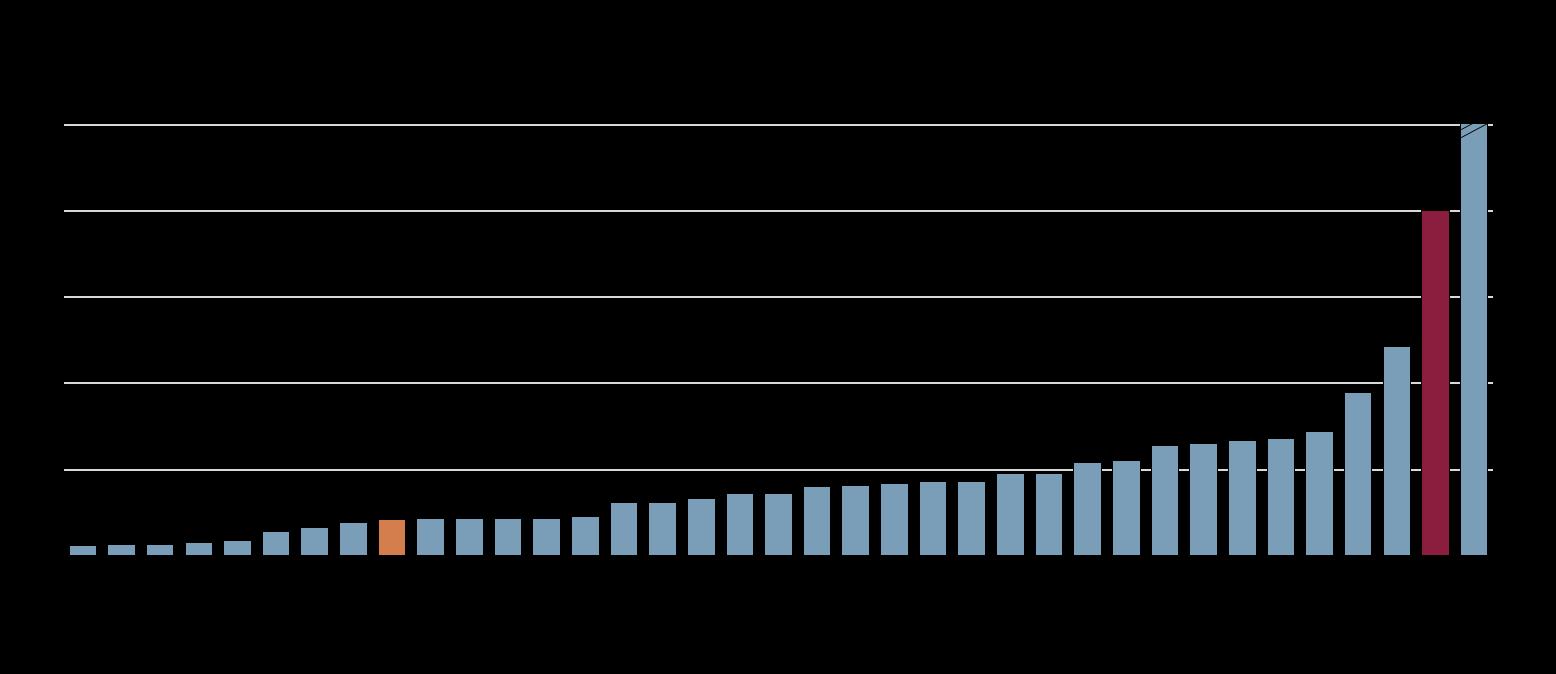

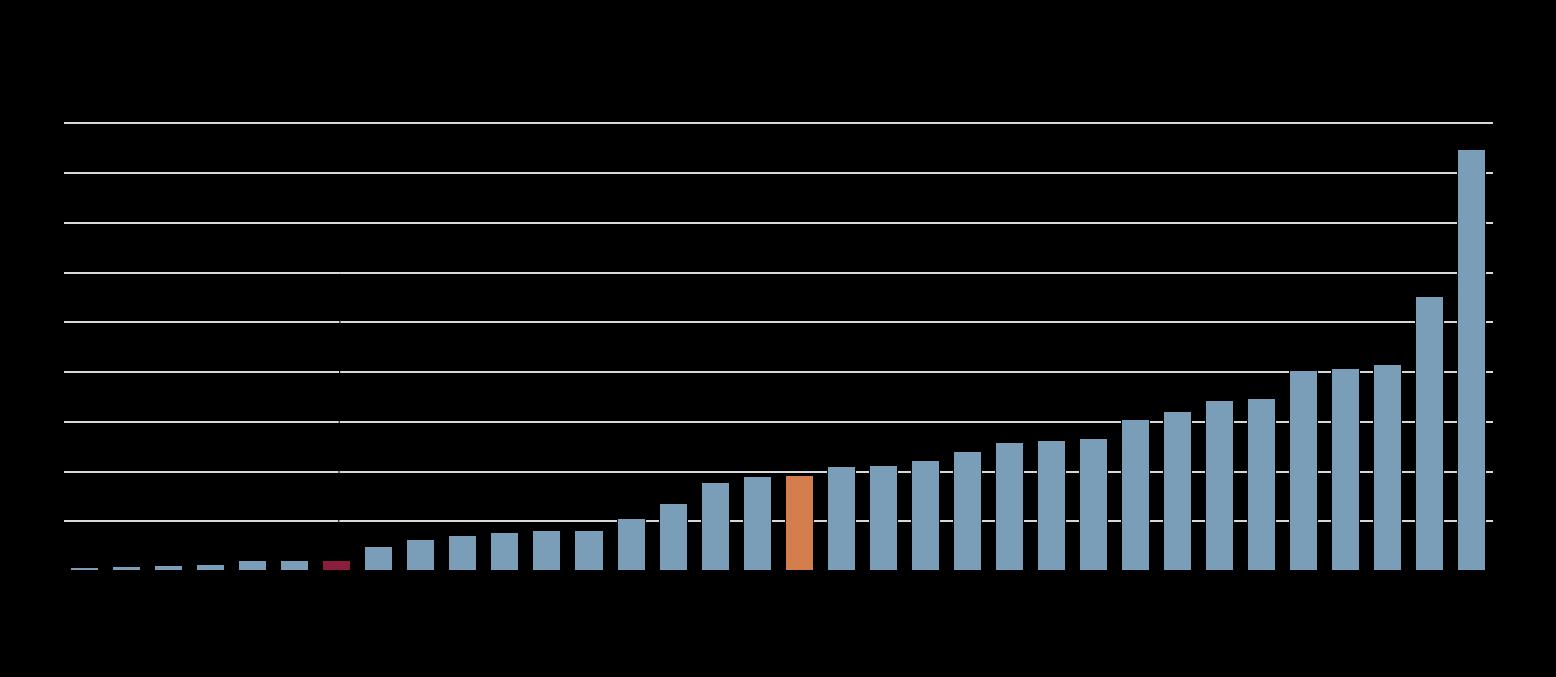



Note: Number of sub-indicators (from 0 to 9) fulfilled per country.
Source: OECD Public Integrity Indicators, oecd-public-integrity-indicators.org.







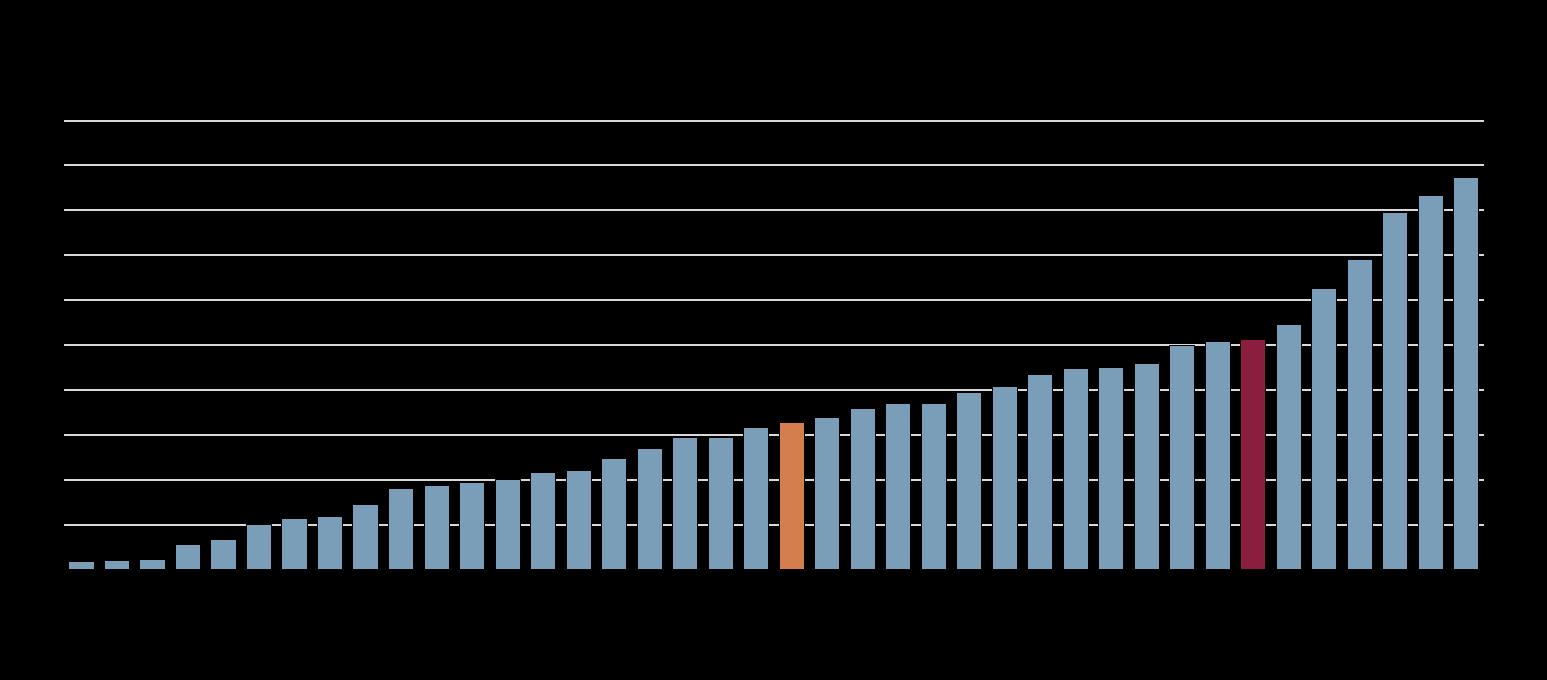
Note: Social security contributions are treated as a part of total tax revenues.
Source: OECD Global Revenue Statistics database.






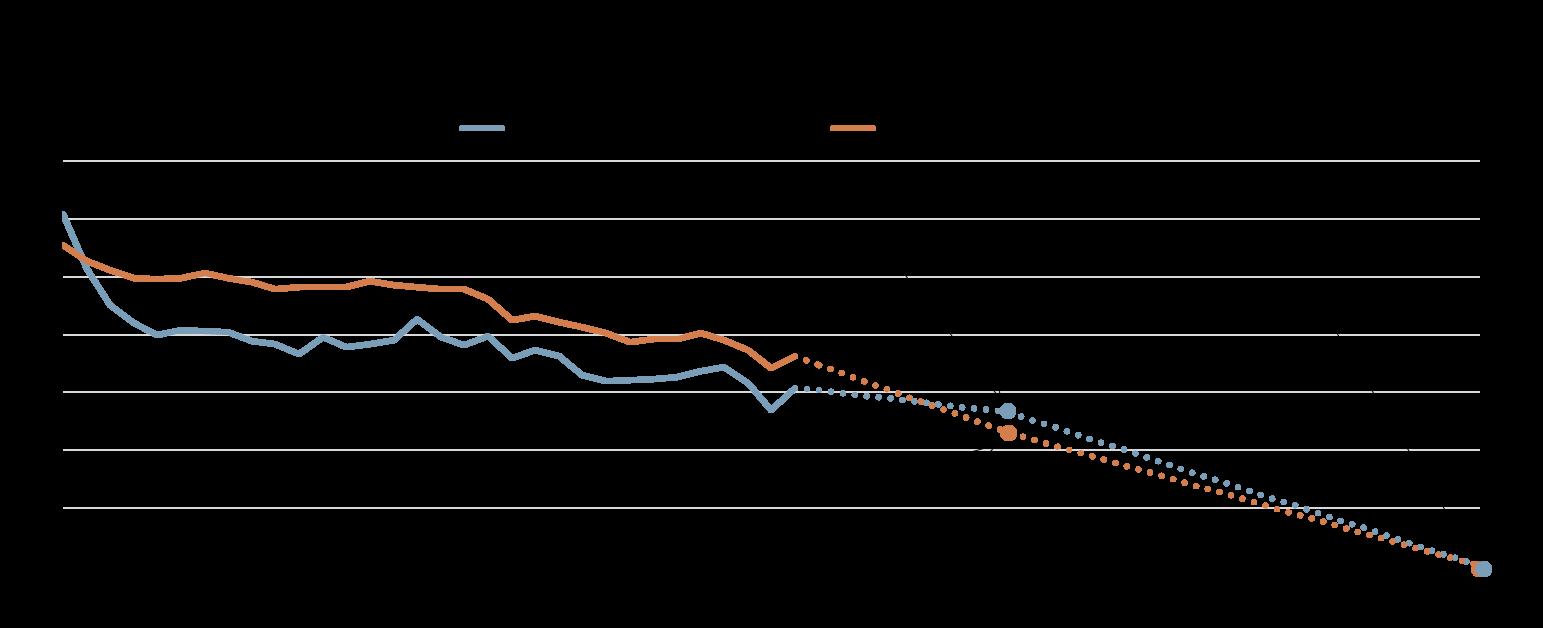
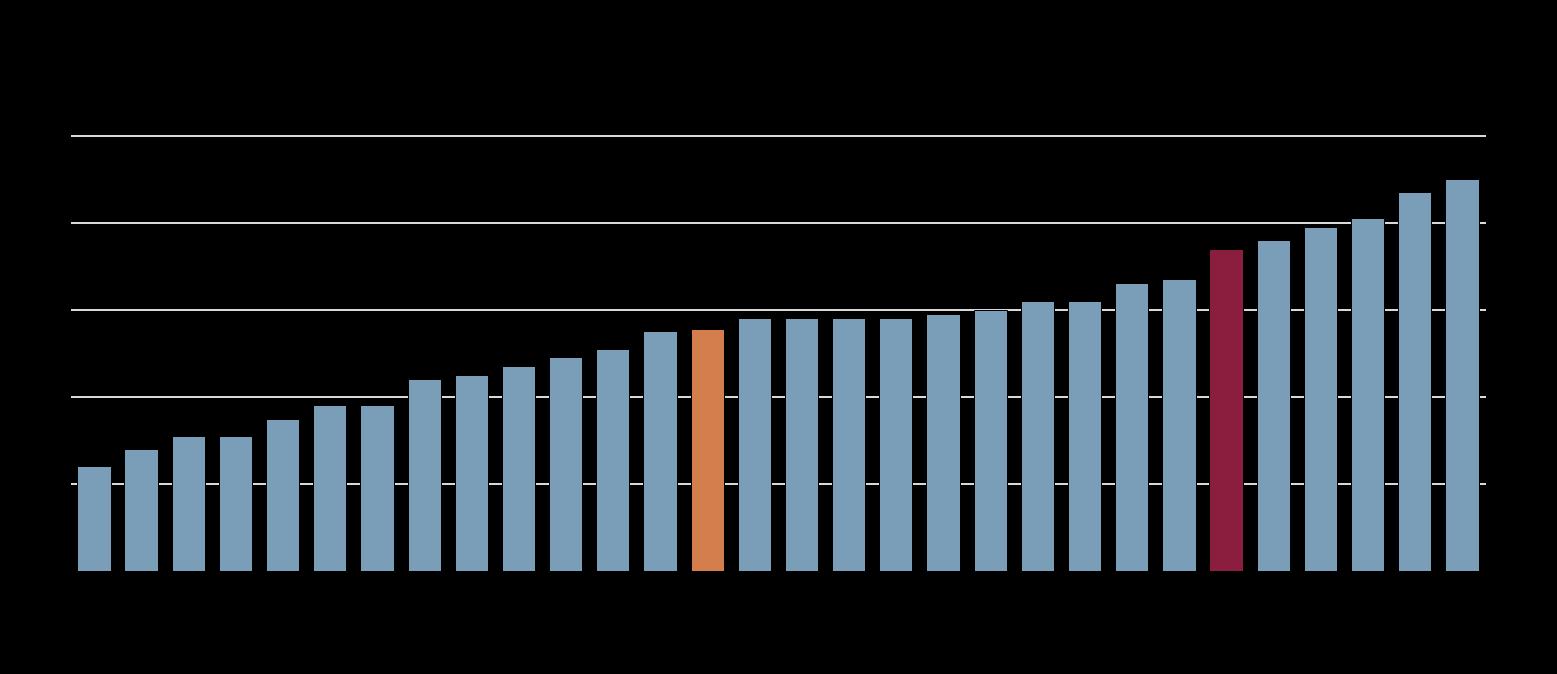
Note: Greenhouse gas emissions include those from the land use/land use change and forestry sector (LULUCF).
Source: OECD Environment database; OECD Population database; OECD calculations.



Fiscal
Step up fiscal consolidation to rebuild fiscal space and prepare for rapid population ageing
Enhance skill provision at all stages of the learning cycle, foster domestic innovation capacity and improve the business environment
Housing Green
Improve housing affordability by strengthening supply and through targeted support to lowincome households, and develop the private rental market
Price carbon emissions more consistently across the economy, strengthen incentives to accelerate housing renovations and increase low- carbon transport
Productivity
For more information


Disclaimers:
The statistical data for Israel are supplied by and under the responsibility of the relevant Israeli authorities. The use of such data by the OECD is without prejudice to the status of the Golan Heights, East Jerusalem and Israeli settlements in the West Bank under the terms of international law. This document and any map included herein are without prejudice to the status of or sovereignty over any territory, to the delimitation of international frontiers and boundaries and to the name of any territory, city or area.