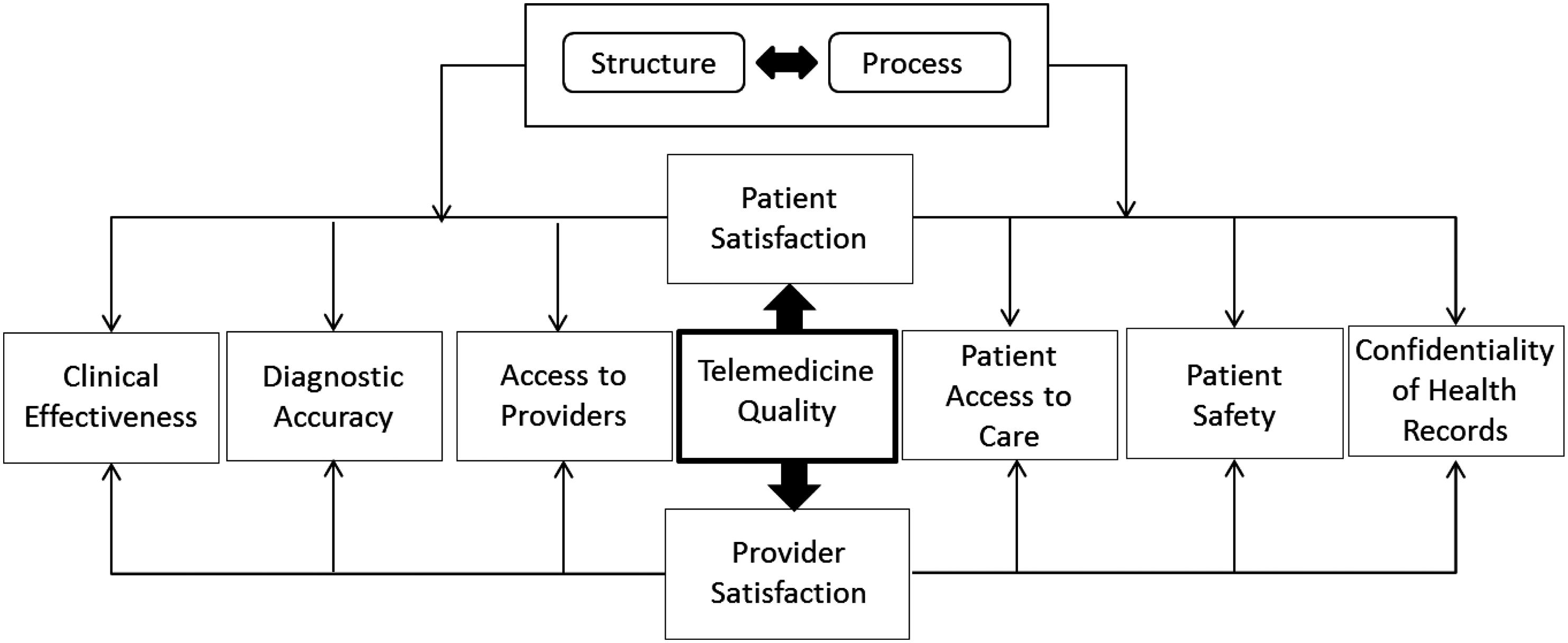
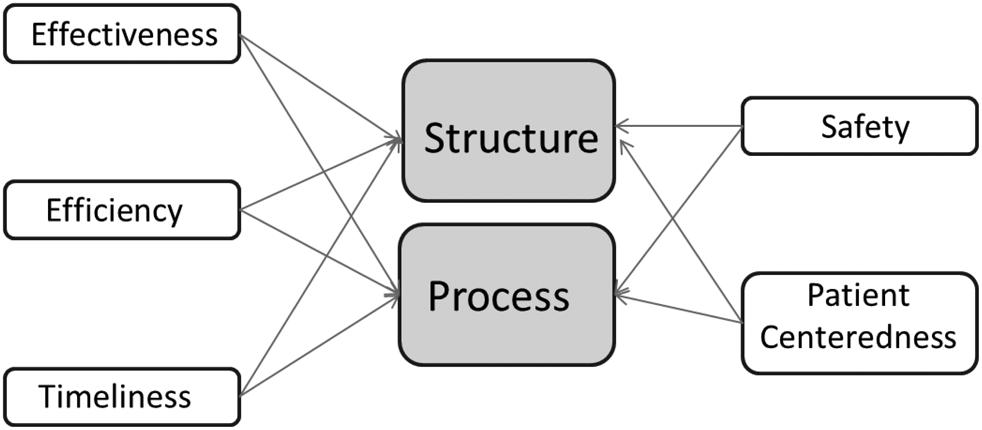
1 minute read
Data Variations
understanding of the context in which the problem or process exists. The ability to treat each subgroup separately makes data analysis more precise. For example, to study nurses’ response times to call lights on a given nursing unit, it may be necessary to break the original data into shifts, as shown in Table 5.1.
In the example in Table 5.1, stratification is used because there is the suspicion of shift-to-shift and unit-to-unit variability, which the data confirms. Stratification allows a more precise analysis of this particular problem. Other stratification factors in healthcare include the following:
Advertisement
◾ Day of the week ◾ Walk-in vs. appointment patients ◾ Salaried vs. non-salaried staff ◾ Geographic locations ◾ Time of day ◾ Specialist vs. primary care physician ◾ Medicare vs. Medicaid ◾ Medicare, Medicaid, commercial, and individual HMO members
To understand the context of data, it is important to understand the sources of variations that could explain disparities in the data. Variations come from many sources and can be attributed to one or more of the following sources:
◾ Human ◾ Equipment ◾ Material ◾ Methods ◾ Environment
Table 5.1 Average Response Time (in Minutes) to Call Lights
Nursing Unit 7:00 AM–3:00 PM 3:00 PM–11:00 PM 11:00 PM–7:00 AM
Unit 4 East 6.9 minutes 14.3 minutes 12.6 minutes
Unit 5 North 2.1 minutes 8.7 minutes 7.3 minutes
Unit 6 West 3.5 minutes 10.8 minutes 8.4 minutes