NEW SOUTH WALES SYLLABUS
Harry O’Brien
Greg Purcell
ASSESSMENT BOOK
Name: Class Name: 4
0 4 1 7 2 6 3 5 Kilogram MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 1 26-Jul-23 18:51:56
STAGE 2
DRAFT
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University’s objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide. Oxford is a registered trademark of Oxford University Press in the UK and in certain other countries.
Published in Australia by Oxford University Press
Level 8, 737 Bourke Street, Docklands, Victoria 3008, Australia.
© Harry O’Brien and Greg Purcell 2023
The moral rights of the authors have been asserted
First published 2023
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, without the prior permission in writing of Oxford University Press, or as expressly permitted by law, by licence, or under terms agreed with the reprographics rights organisation. Enquiries concerning reproduction outside the scope of the above should be sent to the Rights Department, Oxford University Press, at the address above.
You must not circulate this work in any other form and you must impose this same condition on any acquirer.
ISBN 9780190338206
Reproduction and communication for educational purposes
The Australian Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) allows educational institutions that are covered by remuneration arrangements with Copyright Agency to reproduce and communicate certain material for educational purposes. For more information, see copyright.com.au.
Edited by Kathryn Rowan
Cover illustration by Wesley Valenzuela
Typeset by Newgen KnowledgeWorks Pvt. Ltd., Chennai, India
Illustrated by Gareth Conway, Gregory Baldwin and Daniel Rieley
Proofread by Carly Slater
Printed in China by Golden Cup Printing Co Ltd
DRAFT
Oxford University Press Australia & New Zealand is committed to sourcing paper responsibly.

Acknowledgements
NSW Mathematics K–6 Syllabus © NSW Education Standards Authority for and on behalf of the Crown in right of the State of New South Wales, 2023. NESA does not endorse model answers prepared by the Publisher and takes no responsibility for errors in the reproduction of the Material supplied by NESA.
Acknowledgement of Country
Oxford University Press acknowledges the Traditional Owners of the many lands on which we create and share our learning resources. We acknowledge the Traditional Owners as the original storytellers, teachers and students of this land we call Australia. We pay our respects to Elders, past and present, for the ways in which they have enabled the teachings of their rich cultures and knowledge systems to be shared for millennia.
MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 2 26-Jul-23 18:51:56
Printer FSC logo
Message to teachers
Maths Plus Assessment Book Year 4 is an easy-to-use book for both students and teachers. It provides students and teachers with an assessment book that should easily fit into the whole-school maths assessment policy of most schools.
The book is designed to diagnostically assess students at Year 4 level. Each assessment page is a snapshot of work that addresses the specific outcome from the NESA Syllabus. The book provides students with a variety of opportunities to demonstrate their skills, knowledge and understanding of key concepts in Number and Algebra, Measurement and Geometry, and Statistics and Probability.
The pages in this book can assist with:
• assessing understanding of specific knowledge required by the NESA Syllabus
• diagnosing students’ knowledge to assist with future scaffolding of work
• providing evidence for A–E reporting
• providing meaningful work samples of students’ work and understanding. Supported by discussion, observation, hands-on experiences and teachers’ own observations, these assessment pages can become a useful component in assisting teachers to accurately assess their students.
Answers for the assessment tasks and a Student Book–Assessment Book correlation chart can be found online on the Maths Plus Teacher Dashboard.
A iii
MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 3 26-Jul-23 18:51:56 DRAFT
Harry O’Brien, Greg Purcell
A iv Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206 Assessment Outcomes Page NUMBER AND ALGEBRA Representing numbers Place value to tens of thousands Applies an understanding of place value and the role of zero to represent numbers to at least tens of thousands MA2-RN-01 2 Decimals Represents and compares decimals up to 2 decimal places using place value MA2-RN-02 3 Additive relations Addition strategies Selects and uses mental and written strategies for addition and subtraction involving 2- and 3-digit numbers MA2-AR-01 4 Subtraction strategies Selects and uses mental and written strategies for addition and subtraction involving 2- and 3-digit numbers MA2-AR-01 5 Addition and subtraction number sentences/ missing values Completes number sentences involving addition and subtraction by finding missing values MA2-AR-02 6 Multiplicative relations Multiplication strategies and missing values Represents and uses the structures of multiplicative relations to 10 3 10 to solve problems MA2-MR-01 Completes number sentences involving multiplication and division by finding missing values MA2-MR-02 7 Division strategies and missing values Represents and uses the structure of multiplicative relations to 10 3 10 to solve problems MA2-MR-01 Completes number sentences involving multiplication and division by finding missing values MA2-MR-02 8 Partitioned fractions Partitioned fractions Represents and compares halves, quarters, thirds and fifths as lengths on a number line and their related fractions formed by halving (eighths, sixths and tenths) MA2-PF-01 9 Fractions greater than one Represents and compares halves, quarters, thirds and fifths as lengths on a number line and their related fractions formed by halving (eighths, sixths and tenths) MA2-PF-01 10 Contents MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 4 26-Jul-23 18:51:56 DRAFT
A v Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206 Assessment Outcomes Page
Geometric measure Position Uses grid maps and directional language to locate positions and follow routes MA2-GM-01 11 Length Measures and estimates lengths in metres, centimetres and millimetres MA2-GM-02 12 Angles Identifies angles and classifies them by comparing to a right angle MA2-GM-03 13 Two-dimensional spatial structure Features of 2D shapes Compares two-dimensional shapes and describes their features MA2-2DS-01 14 Transformations Performs transformations by combining and splitting two-dimensional shapes MA2-2DS-02 15 Area/square centimetres and square metres Estimates, measures and compares areas using square centimetres and square metres MA2-2DS-03 16 Three-dimensional spatial structure Prisms and pyramids Makes and sketches models and nets of three-dimensional objects including prisms and pyramids MA2-3DS-01 17 Volume – cubic centimetres Estimates, measures and compares capacities (internal volumes) using litres, millilitres and volumes using cubic centimetres MA2-3DS-02 18 Capacity Estimates, measures and compares capacities (internal volumes) using litres, millilitres and volumes using cubic centimetres MA2-3DS-02 19 Non-spatial measure Mass/kilograms and grams Estimates, measures and compares the masses of objects using kilograms and grams MA2-NSM-01 20 Time Represents and interprets analog and digital time in hours, minutes and seconds MA2-NSM-02 21 STATISTICS AND PROBABILITY Data Data/graphs Collects discrete data and constructs graphs using a given scale MA2-DATA-01 22 Surveys Collects discrete data and constructs graphs using a given scale MA2-DATA-01 Interprets data in tables, dot plots and column graphs MA2-DATA-02 23 Chance Chance Records and compares the results of chance experiments MA2-CHAN-01 24 MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 5 26-Jul-23 18:51:56 DRAFT
MEASUREMENT AND SPACE
Place value to tens of thousands
1 Place these numbers in the Place Value House in ascending order.
2 Make the smallest number you can using the number cards above.
3 Make the second largest number you can using the same cards.
Round 88 850 to the nearest 10 thousand and then to the nearest 100 thousand.
Make these numbers larger.
12 Make 32 ten times larger.
13 Make 82 one hundred times larger.
14 Make 36 one thousand times larger.
A 2 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206 Applies an understanding of place value and the role of zero to represent numbers to at least tens of thousands MA2-RN-01
307
9 999 37 021 20 456 15
34 207 142 358
6
85 490
608
3
9 2 7
Complete the expanded numbers. 6 5678 = 5000 + 600 + + 7 7685 = + 600 + + 5 8 12 564 = 10 000 + + 500 + + 9 32 456 = + + + + 10 245 316 = + + + + +
327 416 = + + + + +
4 Nearest 10 000 5 Nearest 100 000
11
Thousands Hundreds Tens Ones H O H T O T MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 2 26-Jul-23 18:51:56 DRAFT
1 Label the decimals that are missing from the tape.
Draw a line to connect each hundredth to a place on the 100 cm ruler. 2
rulex metre ruler
Short distances and lengths can be measured using metres and centimetres,
height is 147 centimetres, which can be written as 1 metre 47 centimetres or 1.47 metres.
Complete this chart that shows different ways of recording distances, including the dimensions of the storage container.
14 Draw a line to match the fractions to a place on the number line.
A 3 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206
0 0.1 0.2 0.4 0.5 0.8 1
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
0.48 m 0.25 m 0.33 m 0.70 m 0.91 m 0.65 m
e.g. Amy’s
315 cm 225 cm 159 cm Centimetres Metres and centimetres Decimal notation 3 225 cm 4 3 m 15 cm 5 159 cm 6 1.83 m 7 174 cm 8 1 m 91 cm
1 10 m 1 2 m 3 4 m 90 100 m 0 0.5 1 0.2 m 0.25 m 0.6 m 0.75 m Represents and compares decimals up to 2 decimal places using place value MA2-RN-02 Decimals MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 3 26-Jul-23 18:51:57 DRAFT
Addition strategies
Regroup the addends into tens and ones to add them mentally. The first one has been done for you. 7 36 + 47 becomes +



15 Round each number to the nearest 10 to make an estimate of the answer.
16 Round each number to the nearest 100 to make an estimate of the answer.
Use the jump strategy to answer the questions.
Use any strategies you wish to solve the problems.
Problem


21 Mali walked 560 m, rested for a while and then walked another 306 m. What was the total distance she walked?


22 Goode Cars Pty Ltd sold 643 cars in the first half of the year and 356 in the second half of the year. How many cars were sold during the whole year?
My strategy
A 4 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206 Selects and uses mental and written strategies for addition and subtraction involving 2- and 3-digit numbers MA2-AR-01
5 + 6 =
7 + 9 = 3 3 + 6 = 4 13 + 6 = 5 23 + 6 = 6 33 + 6 =
Solve the addition facts. 1
2
=
=
=
+ =
8 45 + 52 becomes +
9 64 + 57 becomes +
10 75 + 84 becomes
39 + 42 ≈
187 + 302 ≈ 36 + 43 70 + 9 = 79 14 Thous Hund Tens Ones 7 6 4 0 + 1 8 8 9
the
11 Hund Tens Ones 9 8 4 + 4 5 9 12 Hund Tens Ones 4 0 6 + 0 8 4 13 Hund Tens Ones 1 7 9 + 4 7 8
Solve
additions.
323
6
369 17 422 + 56 = 18 353 + 45 = 19 234 + 130 = 20 465 + 324 = MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 4 26-Jul-23 18:51:57
E.g.
+ 46 becomes 323 + 40 +
=
DRAFT
Jump strategy Partition the second number into its place-value set to subtract the numbers. For example, 189 56 becomes 189 50 6 =
Use the jump strategy or any strategy you wish to solve the subtractions.
16 Round each number to the nearest 100 to make an estimate of the answer.
Separate the numbers into place value parts in order to subtract.
Solve the problems below.
Problem
19 Mia had a bag of 376 marbles. If she lost 123 of them, how many would be left?
20 There were 4233 buttons in a jar and the owner gave away 516. How many buttons were left in the jar?
21 Alex had 6264 sheep. If she sold 1341, how many would she have left?
Working Answer
A 5 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206
1 37 6 = 2 40 5 = 3 38 23 = 4 43 20 = 5 32 16 = 6 43 24 = 7 82 35 = 8 85 27 = 9 428 100 = 10 143 24 = 11 183 35 =
the subtractions.
Solve
133. 12 Hund Tens Ones 7 8 4 4 6 9 13 Hund Tens Ones 9 7 3 6 2 7 14 Hund Tens Ones 1 7 2 4 0 8 15 Thous Hund Tens Ones 7 6 4 0 4 7 8 9
1878 1107 ≈
Selects and uses mental and written strategies for addition and subtraction involving 2- and 3-digit numbers MA2-AR-01 Subtraction strategies 17 58 35 – 18 87 45 –67 43 –60 20 4 7 40 3
MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 5 26-Jul-23 18:51:57 DRAFT
Calculate the missing numbers in the number sentences.
Find the missing numbers in these equivalent number sentences.
16 8 – 3 = 21 −
Solve the problems below.
19 Maxwell scored 276 points in the first game and 325 in the second. How many points did he score altogether?
20 Zia had a bag of 375 marbles. If she gave away 150, how many did she have left?
21 How far did Joni travel if her trip to Sydney was 695 km and the flight to Brisbane was 754 km?
22 The sticker book contained 573 stickers. If the teacher used 125 of them, how many are left?
Use your knowledge of addition and subtraction to find the missing digits.
27 Write a problem of your own to match the number sentence provided.
A 6 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206
− 14 = 16 3 − 17 = 15
1 − 16 = 18 2
=
5 − 13 = 19 6 − 18 = 11
4 − 15
17
8 78 = 42 + 9 62 = 38 +
7 85 = 56 +
84 = 38 + 12 73 = 45 +
10 96 = 47 + 11
14 19 + 8 = + 18 15 18 + 7 = + 12
13 17 + 6 = + 14
17 9 – 4 = 32 − 18 7 – 5 = 41 −
Completes number sentences involving addition and subtraction by finding missing values MA2-AR-02 Addition and subtraction number
values 23 5 7 8 + 2 8 3 9 25 9 8 4 6 2 6 24 4 4 + 5 7 8 9 1 26 7 8 5 2 8 5 5
sentences/missing
= MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 6 26-Jul-23 18:51:57
485 − = 252
DRAFT
Complete the multiplication facts.
Multiplication strategies and missing values
Multiply the tens, then the ones to solve the following multiplications. For example, 26 × 3 becomes 20 × 3 (60) plus 6 × 3 (18) = 78.
Complete the number sentences that describe the family number facts.
Solve the word problems.
15 Hai saved $35 per month for 7 months. How much did he save?
16 Keira planted 6 rows of trees with 14 seeds in each row. How many seeds did she plant?
17 Waru had 7 boxes of toys with 15 toys in each box. How many toys did he have?
Find the missing numbers in each number sequence.
A 7 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206
6 × 3 = 2 7 × 4 = 3 8 × 5 = 4 6 × 6 = 5 4 × 7 = 6 6 × 8 = 7 7 × 9 = 8 8 × 7 =
1
9 29 × 5 = 10 36 × 8 =
11 56 7 8 12 48 6 8 13 9 3 14 80 8 × 8 = 56 7 × = 56 ÷ 8 = 7 56 ÷ = 8 6 × 8 = × 6 = 48 48 ÷ 8 = 48 ÷ = 8 × 3 = 27 3 × = 27 ÷ 9 = 3 27 ÷ 3 = 10 × = 80 × 10 = 80 ÷ 10 = 8 80 ÷ 8 =
18 3 × 7 = 19 5 × = 30 20 7 × = 42 21 3 × + 2 = 20 22 × 4 + 6 = 30 23 5 × 9 + = 50 24 8 × 6 = 12 × 25 9 × = 100 − 28
Represents and uses the structures of multiplicative relations to 10 3 10 to solve problems MA2-MR-01 Completes number sentences involving multiplication and division by finding missing values MA2-MR-02
MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 7 26-Jul-23 18:51:57
DRAFT
Division strategies and missing values
This area model is not finished but it can still be used to help identify multiplication facts.
Use the model to complete these facts.
1 5 × 6 = 3 30 ÷ 5 =
2 6 × 5 = 4 30 ÷ 6 = Complete these divisions related to the model.
5 30 ÷ 2 = 7 30 ÷ 3 =
6 30 ÷ 4 = 8 30 ÷ 10 =
Kedra has 24 building blocks that she is sorting into groups.
17 How many groups of 2 can she make?
18 How many groups of 3 can she make?
19 How many groups of 4 can she make?
20 How many groups of 6 can she make?
21 How many groups of 8 can she make?
22 What would happen if she tried to make 5 groups?
24 ÷ 5 = groups and a remainder of
Problem
23 $64 was to be shared equally among 4 people. How much did each person receive? ÷ =
24 Navaya’s bracelet was $96. If she is going to pay it off over 4 weeks, how much will she pay each week? ÷ =
A 8 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206
9 20 ÷ = 5 10 35 ÷ = 7 11 28 ÷ = 4 12 36 ÷ = 6 13 ÷ 5 = 8 14 ÷ 4 = 9 15 × 6 = 96 − 36 16 4 × 9 = × 6
Calculate the missing numbers in these division number sentences.
Represents and uses the structure of multiplicative relations to 10 3 10 to solve problems MA2-MR-01 Completes number sentences involving multiplication and division by finding missing values MA2-MR-02
and division
14 ÷ 3 = remainder 26 15 ÷ 4 = remainder 27 16 ÷ 3 = remainder 28 50 ÷ 8 = remainder 29 25 ÷ 4 = remainder 30 36 ÷ 7 = remainder MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 8 26-Jul-23 18:51:58
Use multiplication
facts to solve the number sentences. 25
DRAFT
Partitioned fractions
Shade then record equivalent fractions for the ones given.
Compare the fractions with related denominators to decide whether the statements are true (t) or false (f).
17 How many eighths equal one whole?
18 How many fifths equal one whole?
A 9 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206
Represents and compares halves, quarters, thirds and fifths as lengths on a number line and their related fractions formed by halving (eighths, sixths and tenths) MA2-PF-01
= = = = 10 1 2 1 1 2 4 2 1 2 8 3 8 1 4 10 1 2 5 1 2 is greater than 1 8 6 1 4 is equal to 2 8 7 3 4 is less than 7 8 8 1 2 is equal to 4 8 9 1 5 is less than 1 10 10 4 5 is greater than 7 10 11 3 5 is equal to 6 10 12 8 10 is equal to 4 5 13 1 6 is greater than 1 3 14 2 3 is equal to 2 6 15 5 6 is greater than 2 3 16 4 6 is equal to 2 3 0 7 8 1 6 8 5 8 4 8 3 8 2 8 1 8 0 1 3 4 1 2 1 4 0 1 9 10 8 10 7 10 6 10 5 10 4 10 3 10 2 10 1 10 0 1 4 5 3 5 2 5 1 5 0 1 5 6 4 6 3 6 2 6 1 6 0 1 2 3 1 3
4 MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 9 26-Jul-23 18:51:58 DRAFT
Fractions greater than one
Represents and compares halves, quarters, thirds and fifths as lengths on a number line and their related fractions formed by halving (eighths, sixths and tenths) MA2-PF-01
Write the mixed numerals displayed by the shaded shapes below. 1
3
4
Shade the shapes to display the mixed numerals.
Add the missing mixed numerals to the number lines.
Connect each mixed numeral to a place on the number line.
Change these fractions into mixed numerals.
A 10 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206
=
=
=
= =
2
6 2 3 2 3 2 3
5
7 2 4 1 4 1 1 1 4 1 3 4 2 2 4 2 3 4 3 1 4 4 3 2 4 2 8 2 3 1 3 1 1 1 3 3 2 3 2 3
9 1 2 10 1 2 3 11 1 1 4 12 2 1 2 13 2 1 4 14 3 1 4 15 3 2 3 4 2 3 0 1
16 5 4 = 18 3 2 = 20 6 4 = 17 5 3 = 19 7 4 = 21 4 3 = 2 2 3 1 1 4 MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 10 26-Jul-23 18:51:59
DRAFT
Eight children—Hanny, Kim, Than, Sam, Logan, Mila, Gina and Eliana—put their houses on the map above by putting their initial in their house, e.g. H is Hanny’s house.

Answer true (t) or false (f).
1 Gina’s house can be found at grid reference C3.
2 Eliana’s house can be found at grid reference G3.





3 Than’s house can be found at grid reference D5. 4 The library can be found at grid reference F3. 5 There are three railway stations.


6 There are two schools.
7 A restaurant can be found on the corner of Cook Road and Ocean Road.

8 Mila’s house is south of Logan’s house.
9 Logan’s house is south of Mila’s house.
10 Gina’s house is west of Wharf Street.
11 Ocean Road runs from east to west.
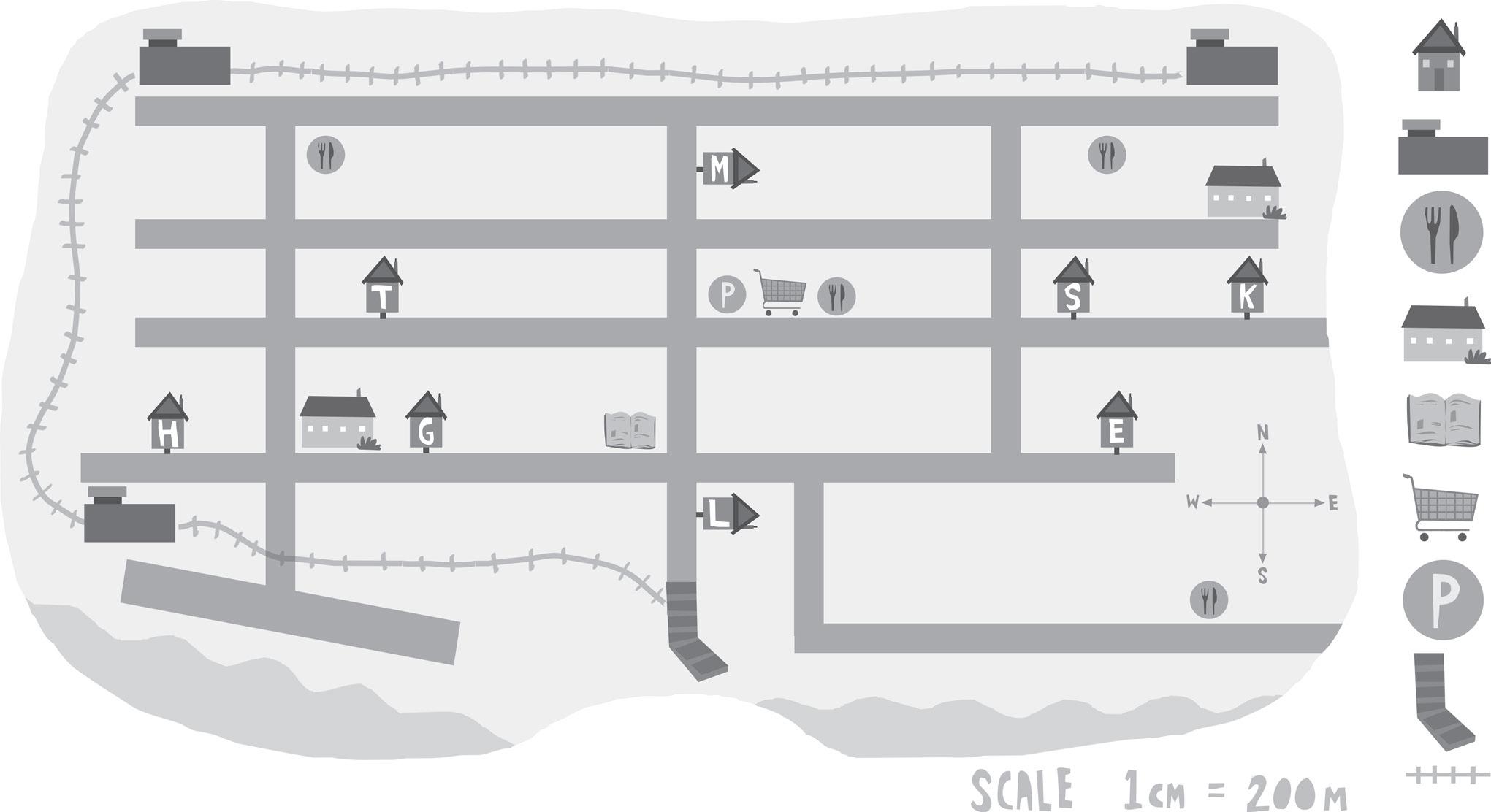

A 11 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206 Uses
MA2-GM-01 Position
grid maps and directional language to locate positions and follow routes
House A 1 2 3 4 5 B C D E F G H Railway station Restaurant School Library Shopping Post office Wharf Railway SCALE 1 cm = 200 m OCEAN
BANANA
COOK ROAD WHARF STREET SHORT STREET LONG STREET PALM
PACIFIC
CLIFF BEACH
PACIFIC
MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 11 26-Jul-23 18:51:59
ROAD
ROAD
ROAD
DRIVE
ROAD
ISLAND
DRAFT
Measure the length of these lines in millimetres. Write the answers on the lines.
5 Measure and record the length and width of each rectangle. Calculate each rectangle’s perimeter and record it on the shape.
Each model has been built with centicubes. Calculate and record the length, width and height of each model in centimetres.
A 12 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206
1 2
4
3
=
cm ____ cm ____ cm
cm
cm Convert the millimetres
6 20 mm = cm 7 90 mm = cm 8 60 mm = cm 9 50 mm = cm 10 40 mm = cm 11 30 mm = cm Convert the centimetres
metres. 12 400 cm = m 13 600 cm = m 14 700 cm = m 15 300 cm = m 16 500 cm = m 17 800 cm = m
metres, e.g. 168 cm = 1.68 m. 18 155 cm = m 19 162 cm = m 20 198 cm = m 21 175 cm = m
Perimeter
____
Perimeter = ____ cm ____
____
into centimetres.
into
Use decimal notation to convert the centimetres into
24 length height width Measures and estimates lengths in metres, centimetres and millimetres MA2-GM-02 Length 10 millimetres = 1 centimetre 100 centimetres = 1 metre length cm width cm height cm length cm width cm height cm length cm width cm height cm MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 12 26-Jul-23 18:52:00 DRAFT
22 23
Answer the questions.
1 Does box A contain a straight angle?
2 Which box contains a right angle?
3 Which box contains an acute angle, which is an angle smaller than a right angle?
4 Which box contains an obtuse angle, which is an angle larger than a right angle?
5 A reflex angle is greater than a straight line. It is almost a full circle. Which box shows a reflex angle?
Draw another arm to create an angle that matches the description.
6 Right angle
7 Acute angle
8 Obtuse angle
Acute angles are less than a right angle. Obtuse angles are greater than a right angle.
9 Which of the shapes above are made up of right angles?
10 Which of the shapes above is made up of three acute angles?
11 Which of the shapes above is made up of angles that are all larger than right angles?
A 13 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206 Identifies angles and classifies them by comparing to a right angle MA2-GM-03 Angles
A B C D E
A B C D E arms vertex turn MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 13 26-Jul-23 18:52:00
DRAFT
Features of 2D shapes
Use the letters on the shapes to answer the questions.
1 Which shape is an octagon?
2 Which shape has 6 sides and 6 angles?
3 Which shape is a rhombus?
4 Which shapes have 4 right angles?
5 Which shape is a trapezium?
6 Polygons are shapes that have 3 or more straight sides and 3 or more angles. Are all the shapes L to S polygons?
7 Which shapes are quadrilaterals?
8 Which shapes are parallelograms?
9 Name each polygon and record the number of sides and angles each shape has.
Name Sides Angles
Name Sides Angles
10 Explain how to tell the difference between a rhombus and a trapezium.
A 14 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206 Compares
two-dimensional shapes and describes their features MA2-2DS-01
N M O Q R S L P MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 14 26-Jul-23 18:52:00
DRAFT
1 equilateral triangles combine to make a .
2 trapeziums combine to make a .
3 combine to make a rhombus.
4
Trace over parts of the hexagon’s diagonals to show how 3 rhombuses can combine to create a hexagon.
What shapes combine to form the following shapes, e.g. squares and triangles?
5 L-shape A _____________________________________________
6 triangle B _____________________________________________
7 trapezium C _____________________________________________
8 trapezium D _____________________________________________
9 hexagon E _______________________________________
10 hexagon F _______________________________________
11 trapezium G _____________________________________
12 hexagon H ______________________________________
13 trapezium I ______________________________________
14 pattern J ________________________________________
15 Draw lines on the star to make it into 4 triangles and a square.
A 15 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206
Transformations
Performs transformations by combining and splitting two-dimensional shapes MA2-2DS-02
A B C D E F G H I
J MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 15 26-Jul-23 18:52:01
DRAFT
Area/square
centimetres and square metres
A base unit for measuring area is a square centimetre (cm2), which can be viewed as a square with 1 cm sides.
1 Below each shape record the area in square centimetres (cm2). The shapes are drawn on 1 cm grid paper.
cm2 cm2 cm2 cm2 cm2
2 Calculate the area of these right-angle triangles drawn on 1 cm grid paper by following these steps:
• Transform each triangle into a rectangle.
• Calculate the area of the rectangle.
• Halve the rectangle’s area to get the area of the triangle.
cm2 cm2 cm2 cm2
3 Calculate the area of these rectangles in square centimetres (cm2).
Rectangle = 4 cm2
Triangle = 4 cm2
A 16 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206
Estimates, measures and compares areas using square centimetres and square metres MA2-2DS-03
1 cm 1 cm 1 cm 1 cm
Area =_____ cm2 6 cm 3 cm Area =_____ cm2 7 cm 4 cm Area =_____ cm2 5 cm 3 cm Area =_____ cm2 9 cm 2 cm MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 16 26-Jul-23 18:52:01
DRAFT
Draw a line to match each object to its net.
Record the number of faces, vertices and edges there are on each 3D object.
7
Draw a line to match the views to a model.
A 17 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206
Rectangular
Cylinder Pentagonal
Triangular
1 2 3 4 5
prism
prism
prism Square pyramid
6
8 Faces Vertices Edges Faces Vertices Edges Faces Vertices Edges 9 10 11 Top view (T) Front view (F) Side view (s) T F F F F S S S S T T F S T T
Makes and sketches models and nets of three-dimensional objects including prisms and pyramids MA2-3DS-01
Prisms and pyramids
MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 17 26-Jul-23 18:52:02 DRAFT
Volume – cubic centimetres
Calculate the volume of each model built with cubic centimetres.
Start by working out how many are in the bottom layer and then multiply that number by how many layers there are.
Record the volume of each object made from cubic centimetres.
12 Which model had the smallest volume?
13 Which model had the greatest volume?
14 Which models had the same volume?
A 18 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9 10 11
cm3 cm3 cm3 cm3 cm3 cm3 • bottom layer = 4 • 3 layers • 3 x 4 = 12 cm3 Model Cubes per layer Number of layers Volume cm3 1 2 3 4 5
Estimates, measures and compares capacities (internal volumes) using litres, millilitres and volumes using cubic centimetres MA2-3DS-02
MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 18 26-Jul-23 18:52:02 DRAFT
Colour the measuring beakers to the level that matches the capacity of the containers.
1 2 3
200 mL 250 mL 350 mL 500 mL 280 mL 600 mL
4 Place the containers on the grid in ascending order.
Name Millilitres
Use millilitres and then litres and millilitres to show two different ways of recording how much is in the sets of measuring beakers.
5
Convert these millilitres into litres.
7 2000 mL = L
8 5000 mL = L
Convert these litres into millilitres.
6
9 2250 mL = L
10 5750 mL = L
A 19 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206
L = mL 12 5 L = mL 13 4.5 L = mL 14 1.250 L = mL 500 mL 50 mL 100 mL 150 mL 200 mL 250 mL 300 mL 350 mL 400 mL 450 mL 500 mL 50 mL 100 mL 150 mL 200 mL 250 mL 300 mL 350 mL 400 mL 450 mL 500 mL 50 mL 100 mL 150 mL 200 mL 250 mL 300 mL 350 mL 400 mL 450 mL 1000 mL 100 mL 200 mL 300 mL 400 mL 500 mL 600 mL 700 mL 800 mL 900 mL 1000 mL 100 mL 200 mL 300 mL 400 mL 500 mL 600 mL 700 mL 800 mL 900 mL 1000 mL 100 mL 200 mL 300 mL 400 mL 500 mL 600 mL 700 mL 800 mL 900 mL 1000 mL 100 mL 200 mL 300 mL 400 mL 500 mL 600 mL 700 mL 800 mL 900 mL mL or L mL mL or L mL Estimates, measures and compares capacities (internal volumes) using litres, millilitres and volumes using cubic centimetres MA2-3DS-02 Capacity 350 mL 200 mL 300 mL 250 mL MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 19 26-Jul-23 18:52:03 DRAFT
11 3
Mass/kilograms and grams

200 g 50 g 250 g 500 g 100 g
1 Place the grocery items in ascending order.
Use a scaled measuring device like kitchen scales to measure these items.
Change the fractions of a kilogram into grams.

DRAFT
Convert these grams into kilograms.
9 4000 g = kg 10 6000 g = kg 11 9000 g = kg
Convert these kilograms into grams.
12 5 kg = g 13 7 kg = g 14 2.5 kg = g
Answer true or false.
15 1 kg 200 g is heavier than 11 2 kg
16 1 kg 600 g is less than 2 kg
A 20 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206 Estimates,
MA2-NSM-01
measures and compares the masses of objects using kilograms and grams
Apple Atrawberry Potato Pineapple Tomato
Name
6 7 8
Grams
grams grams grams grams kg kg kg grams grams grams 3 4 1 2 1 4
2 4 3 5 MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 20 26-Jul-23 18:52:04
Draw the hands on the clock faces to display the matching time. 1
7 o’clock half past 2 a quarter to 3 : :
Write the digital time using am or pm for the following clocks, e.g. 2:35 pm.
6 7 8 9
Place these race times in order from shortest to longest.
10 54 sec 48 sec 39 sec 50 sec
11 41 sec 52 sec 29 sec 38 sec
12 65 sec 57 sec 60 sec 58 sec
Calculate how long it is until the next hour.
15 If the time is 2:52 am how many minutes is it to 3 am? minutes
16 If the time is 8:45 pm how many minutes is it to 9 pm? minutes
17 If the time is 9:25 am how many minutes is it to 10 am? minutes
18 If the time is 6:15 am how many minutes is it to 7 am? minutes
19 If the time is 10:10 pm how many minutes is it to 11 pm? minutes
Answer true or false.
seconds
minute

A 21 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206
2 3 4 5
120
2
15
a quarter
1 3 5 1 0 2 0
20 60
= 1
21 12 hours = 1 day 22 5 days = 1 week 23 48 hours = 2 days 24
seconds =
minutes 25
minutes =
hour
1
10 sec 1 min 5 sec 1 min 15 sec
2 min 45 sec 3 min 15 sec 2 min 30 sec Represents and interprets analog and digital time in hours, minutes and seconds MA2-NSM-02 Time MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 21 26-Jul-23 18:52:04
Afternoon Evening Morning Evening 13
min
14
DRAFT
Data/graphs
Sam said that most children in his class liked the colour green the best.
The children held up signs naming their favourite colours to see if Sam was correct.
1 Use tally marks to show favourite colours.
Blue Red Green Yellow Black Orange Pink
2 Construct a column graph showing the tally results.
3 Which colour is the most popular?
DRAFT
4 Which colour is the least popular?
5 Which colours were equally popular?
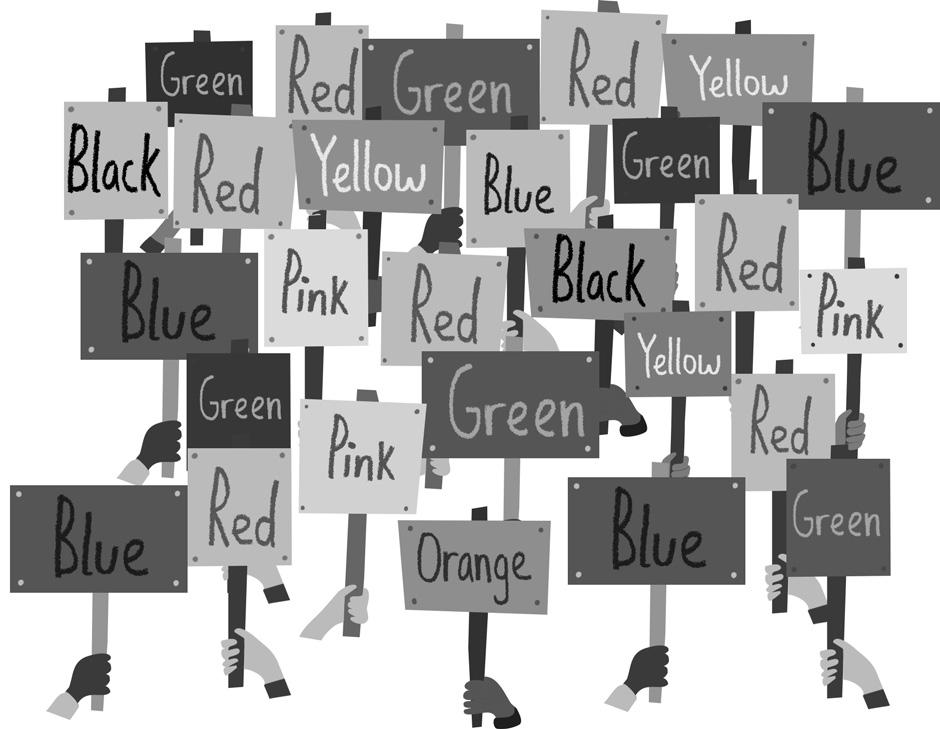
6 How many more children like red than green?
7 Class 4P collected data about the types of pets they have. Use the data shown on the tally mark grid to create a dot plot that displays that data.
Fish Birds Dogs Cats Rabbits Horses
Our class pets Fish Birds Dogs Cats Rabbits Horses
A 22 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206 Collects discrete data and constructs graphs using a given scale MA2-DATA-01
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Colours Blue Green Black Pink Red Yellow Orange Favourite colours Number of children
MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 22 26-Jul-23 18:52:04
1 Conduct a survey to find: Which is the most popular sports team among Year 4 students? Predict 6 teams you think might be mentioned.
2 Conduct your survey and record the results on the grid using tally marks. Team Tally
3 Show how your data could be displayed on a column graph. Most Popular Sports Team
Numbers
Teams
4 How accurate were your predictions?
5 Which game was represented the most?
6 Was there a result that surprised you? What was it?
7 If a new sports store was to open near your school, what merchandise would you recommend they stock?
A 23 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206
Collects discrete data and constructs graphs using a given scale MA2-DATA-01 Interprets data in tables, dot plots and column graphs MA2-DATA-02 Surveys MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 23 26-Jul-23 18:52:04
DRAFT
Here are the contents of Catherine’s marble bag.
R = red, B = blue, G = green, Y = yellow, P = pink, O = orange
Write yes or no to answer the questions below.
1 Is Catherine more likely to pick a red marble than an orange marble?
2 Is Catherine more likely to pick a yellow marble than a blue marble?
3 Is Catherine less likely to pick a yellow marble than a green one?
4 What is the most likely colour that Catherine will pick out of the bag?
impossible certain H H T H H ? DRAFT
5 Circle the label above that best describes the chance of the dice landing on 2.
6 Will the next toss of the coin above definitely be a head?
7 Explain why or why not.
A bag of 10 red marbles and 1 yellow marble
8 What is the most likely colour to be drawn from the bag?
One marble was drawn from the bag and not returned.
9 Is it certain that you could still draw a yellow marble from the bag?
10 Explain why.
A 24 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206
R Y B Y B P G R P G R G B R B R O B Y G R
R R R Y R R R R R R R
likely
1 out of 6 Records and compares the results of chance experiments MA2-CHAN-01 Chance MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 24 26-Jul-23 18:52:05
DRAFT
A 25 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206 MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 25 26-Jul-23 18:52:05
DRAFT
A 26 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206 MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 26 26-Jul-23 18:52:05
DRAFT
A 27 Oxford University Press ISBN 9780190338206 MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 27 26-Jul-23 18:52:05
ASSESSMENT BOOK PRACTISE, MASTER, ASSESS
Maths Plus NESA Syllabus / Australian Curriculum Edition, Year K to 6 is a whole-school program based on the NSW Education Standards Authority Mathematics K–6 Syllabus for the Australian Curriculum.
Maths Plus follows a graded and spiralling approach, allowing teachers to revisit concepts throughout the year. It provides students with opportunities to sequentially develop, practise and master their skills and knowledge in the content strands of the Australian Curriculum: Mathematics:
• Number
• Measurement
• Statistics
• Algebra
• Space
• Probability
The Assessment Books feature post-tests to assess the concepts and skills developed in the Student Books and Mentals and Homework Books. Answers can be found online on the Maths Plus Teacher Dashboard.
www.oxfordowl.com.au
Oxford Owl is the home for Oxford Primary professional resources.
Printer FSC logo

ISBN 978-0-19-033820-6
9 780190 338206
us at oup.com.au or contact customer support at oup.com.au/help 4 STAGE 2
visit
MP_NSW_AB4_38206_TXT_3PP.indb 28 26-Jul-23 18:52:05
DRAFT





















