OTHM LEVEL 4 DIPLOMA IN INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
H/650/3385
Unit Title :-Web and Mobile Applications




H/650/3385
Unit Title :-Web and Mobile Applications



• LO-01:-Understand web and mobile application design technology.
• LO-02:-Understand website technologies, tools and software used to develop websites.
• LO-03:-Understand multimedia content creation tools and software.
• LO-04:-Be able to create a website or mobile application to fulfil a set of client and user requirements.

• 1.1 Explain modern web and mobile development technologies and frameworks.
• 1.2 Evaluate the impact of common development technologies and frameworks on design, functionality and management.
• 1.3 Review the impact of website design on search engine results.
• 1.4 Explain how to improve website ranking using search engine optimization (SEO) techniques.

2.1 Explain the concepts of design flexibility, performance, functionality, User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI).
2.2 Evaluate a range of tools, techniques and languages used to design and develop a custom-built website.
2.3 Evaluate the use of a content management system (CMS) for designing and managing a website.
2.4 Explain the considerations, limitations and benefits of website design platforms .

3.1 Describe tools available to create multimedia content for websites.
3.2 Explain regulatory and ethical considerations in creating multimedia content for websites

• 4.1 Design a wireframe document for a website or mobile application to fulfil a set of client and user requirements.
• 4.2 Create a website or mobile application to fulfil a set of client and user requirements.
• 4.3 Identify key performance areas and create a suitable test plan of your website or mobile application.
• 4.4 Evaluate the results of the test plan and overall success of your multipage website or mobile application.

• Commanding verb is Explain which means:-Make something clear to someone by describing or revealing relevant information in more detail.
• Provide an overview of the current technologies and frameworks utilized in modern web and mobile development. Discuss the latest trends and advancements in web development, including front-end and back-end technologies and popular frameworks. Then, delve into the technologies and frameworks commonly used in mobile app development for iOS and Android platforms.

Commanding verb is Evaluate which means Consider the strengths and weaknesses, arguments for and against and/or similarities and differences. The writer should then judge the evidence from the different perspectives and make a valid conclusion or reasoned judgement. Apply current research or theories to support the evaluation when applicable.
Please analyze and assess the influence of commonly used development technologies and frameworks on a project's design, functionality, and management aspects. This evaluation should consider how these technologies and frameworks impact the overall architecture, user interface, performance, scalability, and project maintainability.

1.3
the impact of website design on search engine results.
• Commanding verb is Review which means :-To examine, survey, reconsider a subject, theory or item.
• Evaluate how the visual and structural elements of website design, such as layout, content organization, navigation, and mobile responsiveness, influence the positioning and visibility of a website in search engine results pages.

• Commanding verb is explain which means :Make something clear to someone by describing or revealing relevant information in more detail.
• To enhance the ranking of a website using search engine optimization (SEO) techniques, it is important to focus on several key areas. These include optimizing website content with relevant keywords, improving website loading speed, boosting mobilefriendliness, increasing the number of quality backlinks, and creating valuable and shareable content. Additionally, utilizing meta tags, optimizing images, and improving user experience through clear website navigation is crucial for improving website ranking.
• Commanding verb is explain which means :Make something clear to someone by describing or revealing relevant information in more detail.
• Design flexibility refers to the ability to easily modify and adapt the design of a product or system to meet changing requirements or preferences. It involves creating a design that can accommodate future changes without requiring significant rework.Performance relates to the speed, responsiveness, and efficiency of a product or system. It encompasses aspects such as processing speed, data throughput, and system reliability.Functionality refers to the features and capabilities of a product or system that enable it to perform its intended tasks. It includes all the functions, tasks, and operations that the product is designed to carry out.User Experience (UX) encompasses all aspects of the end-user's interaction with a company, its services, and its products. It focuses on providing a seamless and enjoyable experience for the user, taking into account aspects such as usability, accessibility, and overall satisfaction.User Interface (UI) pertains to the visual and interactive elements of a product or system, including the screens, pages, and visual elements such as buttons and icons that the user interacts with. A well-designed UI enhances the user's ability to interact with the system and facilitates a smooth and intuitive user experience.

2.2 Evaluate a range of tools, techniques and languages used to design and develop a custom-built website
• Commanding verb is Evaluate which means Consider the strengths and weaknesses, arguments for and against and/or similarities and differences. The writer should then judge the evidence from the different perspectives and make a valid conclusion or reasoned judgement. Apply current research or theories to support the evaluation when applicable.
• Conduct an in-depth evaluation of the diverse range of tools, techniques, and programming languages commonly utilized in the process of designing and developing a custom-built website to ensure the selection of the most appropriate and effective options."

2.3 Evaluate the use of a content management system (CMS) for designing and managing a website.
• Commanding verb is Evaluate which means Consider the strengths and weaknesses, arguments for and against and/or similarities and differences. The writer should then judge the evidence from the different perspectives and make a valid conclusion or reasoned judgement. Apply current research or theories to support the evaluation when applicable.
• Considering the integration of a content management system (CMS) for the purposes of designing and administrating a website warrants careful evaluation and consideration.
• Commanding verb is explain which means :Make something clear to someone by describing or revealing relevant information in more detail.
• The passage provides an in-depth examination of the factors that should be considered when choosing a website design platform. It also delves into the common limitations that users often encounter when working with these platforms and highlights the specific benefits associated with each type of platform.


4.1 Design a wireframe document for a website or mobile application to fulfil a set of client and user requirements.
• Commanding verb design which :-A design is the concept of or proposal for an object, process, or system.
• The word, design, refers to something that is or has been intentionally created by a thinking agent, although it is sometimes used to refer to the inherent nature of something – its design.
• Design a wireframe document for a website or mobile application to meet the client's and end users' specific needs and preferences.

• This document should visually outline the layout, structure, and functionality of the website or mobile app, providing a blueprint for the development team to follow.
• It should consider user experience, navigation, interface design, and overall usability.
• The wireframe should effectively communicate the final product's intended look and feel while addressing any specific requirements the client provides.

4.2 Create a website or mobile application to fulfil a set of client and user requirements.
• Commanding verb is Create which means:-Originate or produce a solution to a problem.
• Develop a website or mobile application that meets a specific set of needs and expectations from both the client and the end users.

4.3 Identify key performance areas and create a suitable test plan of your website or mobile application.
• Commanding verb is identify which means:Ascertain the origin, nature or definitive characteristics of something.
• The task at hand is to identify the specific key performance areas, such as load times, response times, reliability, and scalability, and then develop a comprehensive test plan for both websites and mobile applications.
• This will involve detailing the testing criteria, methodology, tools to be used, test scenarios, and success criteria for each performance area.
4.4 Evaluate the results of the test plan and overall success of your multipage website or mobile application.
• Commanding verb is evaluate which means:Consider the strengths and weaknesses, arguments for and against and/or similarities and differences.
• The writer should then judge the evidence from the different perspectives and make a valid conclusion or reasoned judgement.
• Apply current research or theories to support the evaluation when applicable.


• Evaluate the results of the test plan to gauge the effectiveness and achievement of your multi-page website or mobile application.
• This involves reviewing the test outcomes, analyzing user feedback, identifying any issues or areas for improvement, and making datadriven decisions to enhance the overall performance and user experience of the digital product.



• In this section, we review some of the JavaScript libraries designed for modern browsers and smart devices. These libraries exploited the advancement in HTML5, CSS3 and JavaScript and provided an Application Programming Interface (API) for developer to create web-based mobile-friendly applications.
• Lightweight frame-works add structure to a web application and offer a way to handle navigation between different views, and typically split the application into layers implementing the Model-View-Controller (MVC) design pattern.
• These libraries and frameworks are developed using pure JavaScript, so users get interactivity without requiring round-trips to servers and without any additional plugins.
• jQuery is a popular JavaScript library3. jQuery helps in finding and manipulating the Document Object Model(DOM) elements, processing browser events, and dealing with browser incompatibilities.


• jQuery is an extensi-ble library, and thousands of plugins have been created by developers from around the world.
• AngularJS is a toolset for building the framework most suited to application development. It is fully extensible and works well with other libraries. Every feature can be modified or replaced to suit unique development workflow and feature needs.
• AngularJS is often used for creating single-page applications, where only certain portions of the page (sub-views) are updated as a result of the user‘s actions or data being sent from the server.
• Other features include two-way data-binding, reusable components, deep linking, built-in services for backend communication and localization support. Mobile Angular is another User Interface (UI) framework that is built on AngularJS and Bootstrap for mobile-friendly application development.
• Angular Angular 2 (or just Angular) is an open-source JavaScript framework maintained by Google. It is an evolution of its popular predecessor, AngularJS. Apart from JavaScript, Angular applications can be developed in Dart, or TypeScript5.
• The framework makes it simpler to create custom components that can be added to HTML documents and to implement application logic.
• Angular uses data binding extensively, includes adependency injection module, supports modularization, and offers a routing mechanism.

• Whereas Angular JSwas MVC-based, Angular is not. This framework doesn't include UI components.
• Bootstrap is the most popular HTML, CSS, and JS framework for developing responsive, mobile first projects on the web6. It is an open-source library of UI components developed by Twitter.
• The components are built using the responsive web design principles, which makes this library extremely valuable for web applications that needs to automatically adjust its layout depending on the screen resolution.

• Google‘s Material Design libraries is a new library of UI components called Material Design, which maybe come an alternative to Bootstrap. Material Design is optimized for cross-device use and comes with a set of nicelooking UI components.
• Material Design is a unified system that combines theory, resources, and tools for crafting digital experiences. React is an open source library by Facebook for building user interfaces8. It‘s non-intrusive and can be used with any other library or a framework.
• React creates its own virtual DOM object, minimizing access to browser‘s DOM, which results in better performance. For content rendering, React introduces the JSX format,which is a JavaScript syntax extension that looks like XML. Using JSX is recommended but optional.

• Node.js (or Node) is a framework or a library, as well as is a runtime environment9. This framework can be used to develop JavaScript programs that run outside the browser. The Node.js framework includes an API to work with the file system, access databases, listen to HTTP requests, and more.
• Jasmine is an open source framework for testing JavaScript code10. It includes a set of functions that test whether certain parts of your application behave as expected. Jasmine is often used with Karma, which is a test runner that allows you to run tests in different browsers

• Mobile application is a software application designed to run on mobile devices such as smartphones and tablet computers. It is a result of recent technological innovations.
• Mobile applications have appeared because of the convergence of media, information technology, Internet and advanced technologies.
• In addition, for many year s, mobile telecommunications have been under investigation by mobile device manufactures, mobile service providers, application developers, and many researchers in the sphere of information technology (IT) and information systems (IS). However, the most interesting area for research is mobile application evolution .


• Mobile devices and smartphones can be still considered as new ideas in the technology community. Compared to personal computers and laptops, the common mobile smartphones have only been around for a couple of years now.
• This leads to an interesting area of discussion on mobile payments online. In this increasingly digital world, it is not surprising that money will follow suit as well.
• Recent trends show that digital money kept in mobile wallets will soon replace physical cash and even credit cards.
• We can buy most products and services online these days via our laptops and mobile devices. It is easy to link this process to our bank accounts and online payment processors like PayPal.
• SMS payments are currently one of the most popular methods of using mobile phones to pay for goods, services, or even to make per son-toperson payments.
• In order to make SMS payments, a user needs only a phone with SMS capability. That is why many experts believe that because of the simple nature of SMS payments, they will continue to be a prospective area in mobile payments.
There are four specific types of services, which can be made of mobile application.
• Browser Access: The applications, which we use through native browser. For example, m.yahoo.com, www.google.com, m.redbus.in, etc.
• Hybrid Apps – Web: You need to install an application in your device; function of the particular application requires Internet. For example, Social Networking Apps (Facebook, Twitter), Instant Messenger (Skype), E-commerce (Flipkart), Internet Speed Testing (Speedtest), etc.

• Hybrid Apps – Mixed: You need to install the application in your device and function of the application may require Internet.
• For example, there are some games to play alone or to go online for playing with different players (multi player).
• This category also includes medical apps where you can keep a record of your health in order to share with your friends or doctor via internet.
• Native Apps: The applications, which are installed in the device. For example, Reminders, Few Games

Types of software for building mobile application With a small investment, you can create and manage your mobile site or application using one of the platforms listed below:
• Appery.io.
• Mobile Roadie.
• The App builder.
• Good Barber.
• Appy Pie.
• AppMachine.
• GameSalad.
• BiznessApps.
• AppMakr.
• ShoutEm
• The goal for developing mobile application is to provide conditions when maximum number of users use applications for maximum time. This means that the app developed should have the appropriate quality and purpose, so that maximum users across the globe like it.
In this regard, applications should meet the following requirements:
• Conformance to the purposes of users.
• Capability to reach the majority of users Capability to be secure.
• Being user-friendly.
• Supporting continuous improvement and engagement
• Mobile applications can facilitate the development of the society by contributing to resolution of the following problems:
• Quick search of job vacancy.
• Quick communication.
• Considerable cost saving.
• Saving time and increasing productivity.
• Less power consumption because of less computer use.
• Improvement of IT infrastructure in developing countries.
• Entertainment

• The handset manufacturers designed and developed mobile phones of the first-generation. The competition was fierce and trade secrets were guarded.
• They did not want to expose the secrets of their handsets, so they developed the phone software in-house. During this period, the first “time-waster” games started to appear.
• Nokia was famous for putting the video game Snake on some of its earliest phones (1970-ies).
• Because of such things, people started to change their attitude to communication. When prices for mobile phones have dropped and batteries were improved, more people began carrying handy devices
Currently, almost 80% of people are online through mobile devices. Most of these people prefer mobile applications because they are easy in use and perform tasks instantly.
Users become more dependable on mobile application when solving easy tasks like booking movie tickets, checking sport’s scores, buying and selling, or many other similar routine activities. These tasks can be solved by a single click. A mobile app available on apps store has more chances to convert visits into business. That assists to increase rate of sales


Advantages of mobile applications
• Mobile applications help users by connecting them to Internet services, which are more commonly accessed by means of notebook computers. People, especially young, areconstantly using their mobile devices to browse the World Wide Web and if you are not ther e, you are missing the opportunities. There are three main advantages of mobile application:

• Apps are a constant reminder of your business. Mobile apps rein force your brand by increasing your visibility. An app gives a business more presence on a phone than a browser bookmark does because it is always visible on the screen of a phone. This helps building loyalty with customers because your business is around them all the time.

• Apps increase customer engagement. Customers are calling out for mobile apps because they quickly connect them to businesses they most commonly want or need. Businesses are using apps to improve their processes and increase the level of accessibility by customers. The point of mobile apps is to smoothly connect and interact with customers, making it a valuable tool for the modern business.
• Apps reduce costs. Apps reduce costs of SMS messages and paper newsletters. They simplify communications by securely, instantly and directly messaging customers. Apps reduce staff workload by information requests and phone calls

• Mobile applications may also have some bad effect on the society. It includes the following aspects:
• When many Internet based mobile applications are available to teenagers, they are wasting time by using Facebook, Skype, YouTube etc. The young people are in risk when using Internet games or not appropriate applications.
• Most of people use mobile devices everywhere including buses, trains, offices, colleges, universities. It may disturb other people.
• Frequent use of mobile apps is bad for human health.

• One of the greatest challenges is to make your app visible so the at people want to download it.
• If an app is not among the top 50 – 100 across a category in an app store, people will hardly ever download it.
• One of the biggest challenges of mobile applications is their platform capability and limitation.
• In addition to interesting usability of mobile applications, they have some problems connected with platform and limitations.

Let us consider a list of the main problems:
• Small screen size:-On a mobile platform, it is difficult or impossible to view text and graphics like on a desktop computer screen.
• Lack of windows. We can see many windows at a time on a desktop. However, it can hardly be realized on a mobile platform.
• Navigation. Most mobile devices do not have mouse like pointer, so it has limited flexibility in navigation.
• Types of pages accessible. As a rule, mobile platforms do not support all types of file formats.
• Speed. The speed of processing and speed of connectivity of mobile platforms is slow. Size of messages or email. Many devices support limited number of characters in message or email.
• Cost. The cost for cellphones, mobile applications and Internet connection is high

• Fig. 1 a depicts a modern web application architecture. Ideally, no data is read from the DOM, but the application outputs HTML and performs element operations as needed. No data is stored in random objects or the DOM.
• A set of models represents all the data in the application. Views receive change notifications (via events) from models and handle redrawing as appropriate. Views utilize templates to render information as per user interface design.
•

• The model also reads and writes from/to storage (usually a database) using AJAX and server-side scripts. These scripts are written in server-side dynamic languages like PHP or ASP.
• Fig. 1b shows the architecture of a typical AngularJS application. Controllers are written in JavaScript and are the behaviour behind the DOM elements. This makes it easy to test, maintain, and reuse code.

• Services are also written JavaScript and access data or information from the model via AJAX requests (server communication).
• Views are usually HTML-based (including any CSS) and receive information from the model via the controller (as is or after some post-processing).
• Data-binding is an automatic way of updating the view whenever the model changes and updating the model whenever the view changes. Views/templates also provide client-side form validation.
• AngularJS lets developers declare the validation rules of the form without having to write JavaScript code.
• Models provide reads and write access to persistent storage, like a database, and are written in some server-side scripting language (like PHP).

• Single Page Applications (SPA) have more complex state transitions than a server-side application because there are:•DOM events that cause small state changes in views,.model events when model values are changed
• application state changes that cause views to be swapped, global state changes,delayed results from backend CRUD operations via AJAX.
• One of the advantages of using development frameworks is that the above issues are handled or notified seamlessly by the framework and software developer stay focus on the actual business logic and user interface design

Quite popularly referred to, as RoR, Ruby on Rails has emerged as one of the favorites among the web developers today. Since its launch in 2005, RoR is still completely free to use, is open source, and runs on Linux. It is fun to work with and is remarkably quick in getting you through the planning stage and on to the developmental stage. Some of the biggest websites that were built using RoR include Hulu, Airbnb, Basecamp among others.
This is one of the more stable frameworks and is ideal to be used for projects that are of a higher complexity. Using this framework, developers gain the ability to build websites that can change as the business requirements evolve with time. Any business would be inherently dynamic, and developing a website that does not have the ability to change, would not do well for long. It comprises of a set of PHP components, a community, and an application framework which can work really well in tandem to help the websites accomplish their objectives.


One of the most popular and well-known frameworks – Angular.js comes from the digital giant of the day, Google. It is essentially a JavaScript open-source framework that can help you make single web-page applications using an MVC (Model-Controller-View) architectural pattern. It is not really a full stack framework, but you can consider it as a frontend framework which is great for handling your WebPages. If you plan headless commerce development, it is important that you have Angular.js in your toolkit for great results.
An open-source JavaScript library, React.js is maintained by Facebook while being supported by a massive community of react developers. Though it is an e-commerce website development tool, React.js is particularly useful in the development of user interface for the website applications.

A PHP framework is probably best suited when it comes to e-commerce website development and CakePHP is preferred by most developers when it comes to choosing one of the better tools in the written PHP format. A popular framework, CakePHP is created on the MCV (Model-Controller-View) model. What makes CakePHP particularly interesting is that the code for all your older projects may be reused through it. This in turn ends up saving the developers a whole lot of time and money by speeding up the whole process of web development.
This is probably the most popular framework built by Microsoft and has managed to gain the respect of developers from all over the world. Established in the year 2002, Asp.net is especially popular because of its ability to create rich and dynamic websites, web pages, and even web portals. In fact, a great number of companies from the world over prefer Asp.net and deem it as the best technology in website development.

Node.js is decidedly the best when you are looking to build a lightweight, yet highly efficient website. It is uncanny how perfectly well it works with real-time applications that have a huge amount of data running through on distributed devices. Node.js is more than a mere framework. It has the ability to ensure scalability and fast network applications as they are capable of dealing with multiple applications at the same time without compromising on performance.


In it s essence, Yii Framework is strikingly similar to Asp.net. However, the framework is particularly good in developing applications for systems that need a certain repetitiveness in tasks and follows the Rapid Application Development (RAD) concept. This essentially means that the framework enables the developers to get their applications in a ‘good to go’ phase in a really short time. Additionally, it also lends you and easy data migration utility so that you can upgrade or downgrade the application versions on various installations.

Meteor, a JavaScript based framework enables fast software development and that is exactly why it is so popular. A full stack JavaScript framework, Meteor is composed of a collection of libraries and packages bundled together. The framework needs a lot fewer codes which goes on to indicate that there would be much lesser bugs and a product that would be highly scalable. This is what makes this framework especially beneficial for e-commerce web application development.

This is one of the more stable frameworks and is ideal to be used for projects that are of a higher complexity. Using this framework, developers gain the ability to build websites that can change as the business requirements evolve with time. Any business would be inherently dynamic, and developing a website that does not have the ability to change, would not do well for long. It comprises of a set of PHP components, a community, and an application framework which can work really well in tandem to help the websites accomplish their objectives.
1. Publish Relevant, Authoritative Content
2. Update Your Content Regularly
3. Metadata
4. Have a link-worthy site
5. Use alt tags
Quality, authoritative content is the number one driver of your search engine rankings and there is no substitute for great content—this is especially true when doing SEO marketing. Quality content created specifically for your intended user increases site traffic, which improves your site's authority and relevance. Fine-tune your web writing skills and present yourself as an authority on the topic you are writing about.
Keywords
Identify and target a specific keyword phrase for each authoritative content page on your website.
Think about how your reader might search for that specific page with search terms like:
• online masters in engineering management
• when is the FAFSA deadline?
• what is the difference between engineering and engineering technology?
It is very difficult for a webpage to achieve search engine rankings for multiple keyword phrases unless those phrases are very similar. A single page may be able to rank for both "biomedical engineering jobs" and "biomedical engineering careers". Ranking for "student affairs" and "dean of students" or "gender discrimination" and "violence reporting procedures" with a single page is unlikely.
If you want to rank for multiple keywords phrases with your website, you will need to make a separate webpage for each keyword phrase you are targeting.
Once your keyword phrase is chosen for a given page, consider these questions:
• Can I use part or all of the keyword phrase in the page URL (by using keywords in folders)?
• Can I use part or all of the keyword phrase in the page title?
• Can I use part or all of the keyword phrase in page headings and subheadings?
Answering yes to these questions can improve your search engine ranking. Be natural and user-friendly, though. For instance, you do not want the word "engineering" to show up three or more times in the URL or have the phrase Northern Lights repeated in the page title and also every heading. Readability and usability still trump search engine optimization.
Beyond page URL, title, and headings, content is most influential on search engine rankings. Repeat your keyword phrase several times throughout the page once or twice in the opening and closing paragraphs, and two to four more times throughout the remaining content. Be authoritative. Strategically link to relevant sources and additional information both within your organizations broad website and even to other websites which are useful.
Don't forget to use bold, italics, heading tags (especially an H1), and other emphasis tags to highlight these keyword phrases— but don't overdo it. You still want your language and writing style to read naturally. Never sacrifice good writing for SEO. The best pages are written for the user, not for the search engine


You've probably noticed that we feel pretty strongly about content. Search engines do, too. Regularly updated content is viewed as one of the best indicators of a site's relevancy, so be sure to keep it fresh..
Writing additional content, rich with keyword phrases, on your departmental news blog can also boost your search engine rankings. Blog posts can even be shorter updates about the specific topics you are targeting. Interlink your related CMS webpages and blog posts when it helps give the reader a better picture or additional information about the topic.

When designing your website, each page contains a space between the <head> tags to insert metadata, or information about the contents of your page.
Title Metadata
Title metadata is responsible for the page titles displayed at the top of a browser window and as the headline within search engine results. It is the most important metadata on your page.
For those with a CMS website, the web team has developed an automated system for creating the meta title for each webpage based on your page title. This adds to the importance of using well-thought-out page titles rich with keyword phrases.
Description Metadata
Description metadata is the textual description that a browser may use in your page search return. Think of it as your site's window display a concise and appealing description of what is contained within, with the goal of encouraging people to enter. A good meta description will typically contain two full sentences. Search engines may not always use your meta description, but it is important to give them the option.
Keyword Metadata
Keyword metadata is rarely if ever used to tabulate search engine rankings. However, you should already know your keyword phrases, so it doesn't hurt to add them into your keyword metadata. You'll want to include a variety of phrases. As a general rule, try to keep it to about 3-7 phrases with each phrase consisting of 1-4 words. A great example would be "computer science degree."
A webpage which is content-rich, authoritative, unbiased, and helps visitors learn more about what they are interested in is most likely to attract links from other websites, which improves your search engine optimization.
Improve your authority and credibility by adding relevant links within the text.
For eg: Instead of having "click here" links, try writing out the name of the destination. "Click here" has no search engine value beyond the attached URL, whereas "Michigan Tech Enterprise Program" is rich with keywords and will improve your search engine rankings as well as the ranking of the page you are linking to.
Always use descriptive links by linking keywords it not only improves search engine optimization, but also adds value to your readers, including those with disabilities or who are using screen readers

Always describe your image and video media using alt tags, or alternative text descriptions.
They allow search engines to locate your page, which is crucial, especially for those who use text-only browsers or screen readers.
•
• SEO is a form of online marketing for Web sites. SEO aims to increase traffic to your site by targeting relevant keywords so that your site is listed higher in a search on one of the major search engine sites.
• Because it is a relatively new area, SEO can be misrepresented by dishonest vendors; go to Google and search for the term Keywords, Then look at the bar below the Google logo,and you see something like this: About 928,000,000 results for keywords.
• This means Google has found almost 928 million pages that contain this word. Yet, somehow, it has managed to rank the pages. It’s decided that one particular page should appear first, and then another, and then another, and so on, all the way down to page 928,000,000.


• (By the way, this has to be one of the wonders of the modern world: Search engines have tens of thousands of computers, evaluating 98 billion pages or more and returning the information in a fraction of a second)
• How does Google do it? How does Google evaluate and compare pages? How do other search engines (Yahoo, America Online AOL, MSN...) do the same? We don’t know exactly. Search engines don’t want you to know how they work, but we can explain the general concept.
• When Google searches for your search term, it begins by looking for pages containing the exact phrase. Then, it starts looking for pages containing the words close together.
• Then, it looks for pages that have the pages scattered around. This isn’t necessarily the order in which a search engine shows you pages; in some cases, pages with words close together (but not the exact phrase) appear higher than pages with the exact phrase, for instance.
• That’s because search engines evaluate pages according to a variety of criteria. Search engines look at many factors.


• They look for the words throughout the page, both on the visible page and in the HTML source code. Each time they find the words, they are weighted in some way. A word in one position is worth more than a word in another position.
• A word formatted in one way is worth more than a word formatted in another. There’s more, though. Search engines also look at links pointing to pages and use those links to evaluate the referenced pages: How many links are there? How many are from popular sites? What words are in the link text?
• Figure 2.7 illustrates how a search engine evaluates any Web page and how SEO can benefit the PR in the results of a search for a given keyword or phrase. The two biggest factors in determining a Web page Google PR in the search results are Keyword Relevance and PR.

There are only two types of Websites: content Websites and e-commerce sites. Content sites generally offer unique content such as tips, articles, forums, news, etc.
E-commerce sites sell a product or service. No matter what type of website you own, the basic approach to SEO is the same.
However, performing SEO on an e-commerce website is approached slightly differently than a content site, as there are inherent issues with proper SEO on an e-commerce (store) application.
Content Web sites generally have more textual content than e-commerce Websites, so it is easier to gain organic search referrals. E-commerce sites typically produce fewer organic search referrals unless someone searches for a particular product.

• Still, with proper SEO, e-commerce sites can rank high in search engines and produce excellent organic search referrals.
• Because different visitor groups (target audiences) search differently than other visitor groups, a web designer needs to know what his target audience (Website visitors) is primarily made up of.
• A business professional may search with a different keyword or keyword combination than a home user.
• The web designer needs to know if most users are male or female, how old they are and what sort of occupation they have, if any.
• Although a Web designer does not need to know individually what comprises the target audience, he should attempt to determine the majority. Also, web designers should be aware of their competition.
• He can learn a lot from competitors. When monitoring their competitors, web designers look for several items, such as site layout, content, meta titles, meta descriptions, and meta keywords


• In addition to all the above factors when selecting a hosting company, he focuses on the factors related to SEO; when he looks for a hosting company, makes sure that he can:
• 1. Upload Web pages he created by himself.
• 2. Provide some services and simple tools.
• 3. Use the company’s traffic analysis tool.
• 4. Use a log-analysis tool to show how many people visit his site and how they get there.5. Use his domain name.
• 6. Search engines read URLs, looking for keywords in them, when a Web designer chooses a domain name, he should consider some more important factors:
• 7. Domain names should be short, easy to spell, and easy to remember.
• 8. We should get the .com version of a domain name.Apart from traditional web development tools like HTML and Cascading Style Sheets(CSS), new tools such as Drupal, Joomla, WP, and SEO implementation tools exist.
• “Drupal is open source software maintained and developed by a community of 630,000+ users and developers. It's distributed under the terms of the GNU General Public License (or "GPL"), which means anyone is free to download it and share it with others.
• This open development model means that people are constantly working to make sure Drupal is a cutting-edge platform that supports the latest technologies that the Web has to offer. The Drupal project's principles encourage modularity, standards, collaboration, ease-of-use, and more.”.
• The Drupal SEO Tools module seamlessly integrates a sophisticated all-in-one suite of search engine reporting, analysis and optimization tools into your website. It provides a dashboard that integrates analytics reports with links to webmaster tools and vital Drupal SEO modules .
• Joomla is one of the most popular CMS on the market today. When you choose CMS as a web development SEO could be countable factor more precisely when you select any CMS you should check that how SEO-friendly it is, and how easily it enablesyou to include SEO content to your web pages etc .


• WordPress SEO Plugin is automatically optimizing WP blog for Search Engines. It has following features:
• 1. Support for custom post types
• 2. Advanced canonical URLs
• 3. ONLY Plugin to provide SEO integration for WP e-Commerce sites
• 4. Support for CMS-style WP installations
• 5. Automatically optimizes your titles for search engines
• 6. Generates META tags automatically
• 7. Avoids the typical duplicate content found on WP blogs

• Search engines are important tools that facilitate Internet users’ ability to search for information about public relations and find advertised goods and services that appear in search engine results. The most popular search engines include Google, Bing, and Yahoo.
• The working process for all search engines is sep-rated into three main parts. The first step is crawling, which sends bots and spiders to get information from websites and web-pages by running along connected networks.
• From that process ,pages are indexed by separating collected information to record it as a search engine database and rate the webpages that have been collected. In the last step, the engine shows the search results of any keywords that searchers have utilized.
• Pare search has found that, in determining its priority order, Google will consider many factors, such as keywords in any part of the webpage, popularity, number of competing and qualifying web--sites, etc.
• SEO is improving websites’ search engine rankings, resulting in higher (i.e., earlier) ranking through search engines due to organic searches that lead to earlier placement on SERPs.
• It is a process that helps websites work better together with search engines; it is also a good technique that helps increase the quantity and quality of website visitors and can be applied to improve online marketing efforts.
• SEO is also a technique to promote websites because it supports buyers and sellers by helping them meet more easily.

• On-page optimization is the most important part of the searchingbehaviour of users because they usually type keywords or sen-tenses into the search box to begin the search process. Therefore, during website improvement and development, it is necessary to mix keywords into the improvement process.
• This should be planned from the beginning when the domain is registered: the developer should research keywords by looking at records to select suitable keywords to register the domain name and create a sub-domain. The content of the sub-domain should feature keywords in the URL and should not use a hyphen (-)more than three times in the URL. It should be shortbecause the shorter it is, the more capability it has to quickly capture large amounts of data from search engines.
• Structure optimization refers to the standard of the web-Site development determines the HTML standard for the document, beginning with the header. It’s the most important step; you should always incorporate keywords in the title tag. Next isthe Meta tag, which contains a description of the website.

• The meta tag, which should be no longer than 150 characters, is alsoimportant because it appears on SERPs.
• If the meta tag is longerthan 150 characters, the SERPs will remove the excess andreplace it with an ellipsis.
• The body tag should also be properly planned for keyword distribution based on other factors and its determinedproportion of keyword density.
• Proper keyword density proper-time should range from 5–20%, which means that when all key-words are included, every 1 to 5 words should be a keyword.
• It should stress headers H1, H2, and H3 and stresskeywords in the content by formatting them differently from therest of the text, such as in a different size or in bold. Other partsthat should contain keywords include illustrations.

• Every figureshould contain a keyword in an alt tag, including using keywordsas anchor text.Link optimizations, both internally and externally, link pride--termined layers of documents on the website, which should notconsist of more than four layers.
• Apart from that, developers must create and determine both internal links and external linksand should take care not to miss any links, which would result in users being unable to find documents.
• External links should connect only to quality websites with content that applies to the the website of origin is credible and original. If the website is known to the public and has a high Page Rank (PR) to avoid a low page ranking, it should not link to junk or illegal websites orignore search engine rules.
• Other factors that can be controlled in websites are the size ofany document files on the webpage. Their ideal size is around100 kb to maximize loading speed and quickly show results; it should also always create a new webpage andcontent.
• It should never link to a dead website that doesnot add anything new. SERPs prefer large websites with significantamounts of in-depth material.
• Similarly,registered websites whose domain has existed for along time are preferred over new domains; however, regardlessof the domain’s age, the website content should be continually updated.


• In addition, developers should create site maps to enableusers to quickly and easily surf to any part of the website andimprove files that support Robot.txt to facilitate finding itthrough search engines.
• If we want to emphasize Google users,we should set up Google Analytics to support the website. Developers must ensure they do not use spam keywords when improving internal factors. In the meta keyword and content, developers should avoid overusing the keywords in the H1tag.
• On the other hand, documents with no keywords, low-key-word density, or keywords that do not lead users to the content,do not yield good results for the webpage. When incorporating mixed media, whether flash pages, video clips, or scripts, search engines may not know what internal content they link to; therefore, they should be tagged with keywords that enable users and search engines to find their destination.

• When creat-A static page is better than a dynamic page; keywords should never be in the same colour font as the background.
• Additionally, the site should never utilize documents that placekeywords beneath the figures, including putting keywords veryclose to the margin of the papers or creating invisible text. Usingsingle-pixel links to relate to other documents is also a thingto avoid.
• The matter in the webpage should duplicate the content ofother websites; or, better yet, it should contain original content,which is always better than copying documents from other sitesand protects the website from possible copyright and intellect-Dual property infringement claims

With off-page optimization, there are many factors that the devel-oper and web admin cannot control; nevertheless, they can still try to create the best possible environment to ensure it brings users to their page. Page rank (PR) originated with the Google search engine.
Although website owners cannot directly add page rank, they can create an environment or situation that has backlinks or a suit--able link proportion.
Although links will directly result in a pagerank for any website, those with many links will earn a high PR and have the best opportunity to appear on the first page of SERPs.
• If a website has several backlinks,its results will be positive but will not rise rapidly in the SERP sunless it has many website visitors. If the links come from sites that are already highly ranked, that would bebest.
• Anchor text is best when it contains keywords, but it should not be so keyword-dense that it becomes spam. In addition, alink that has existed for a long time is better than a new one.
• Anchor text should always be kept the same. If well-known websites with high PR refer to a website, more is better.



• However, most references to other websites do not produce good results because they would be deducted from the original site’s PR.
• The frequency of keywords from websites that are referred to should be appropriately high and relate to the original website’s content.
• Submitting one’s webpage to a directory website is a factor that results in improved ranking order.

• The most well-known directory website is DMOZ, on which many search enginesrely.
• Therefore, it is important to submit passages to DMOZ; in addition, keeping passages on and performing indexing from DMOZ, as well as including other credible websites, is best.
• The best scenario for a website is when several directory websites contain content and perform indexing on it. The age and size of the website are also factors here: old is better than new, and big is better than small.
• Regarding the number of website visitors, more is best, including-in time or duration spent on the website, which shows the popularity of and interest in the website.
• If the site features a book-marking, it would help ensure future payments for the domain, because a domain that has existed for many years gets more attention than one that is renewed every year.



• There are many rules to be avoided, such as websites that contain no links from any other website; similarly, buying advertisements unrelated to the website matter and having primarily new links will cause negative results.
• Long-duration links yield more positive results. In addition, linking to websites that have been hacked or prohibited produces a negative result. Finally, leasing a stable host leads to a positive result.


• Google has a set of guidelines of what you can do and what you shouldn’t do to make your website Google friendly.
• If you violate any of those guidelines either intentionally or even because you didn’t know about them, you risk getting a ‘Google penalty,’ and this means your website will be removed from Google or your rankings will dramatically drop.

• Techniques that search engines recommend as part of a good design. White hat SEO is a term used to describe the process of optimizing your website without violating any rules.
• It refers to the SEO techniques following the SEO guidelines set by the search engines.
• It means it uses approved search engine optimization techniques to improve a site's ranking on search engine results pages (SERP).
• Unlike Black Hat SEO, it mainly focuses on the human audience instead of a search engine. People who are looking for long-term investment on their websites rely on white hat SEO techniques.

• Techniques that search engines do not approve and attempt to minimize the effect of.
• These techniques are also known as spamdexing. It refers to the SEO techniques which are not in accordance with the SEO guidelines set by the search engines.
• These techniques exploit the weaknesses in search engines to get higher rankings for websites on the search engine results pages (SERP).
• It mainly focuses on search engines and not on the human audience. People who are looking for a quick financial return on their website rather than a long term investment use black hat SEO techniques.

Always follow a White Hat SEO tactic and do not fool your site visitors. Be honest, and you will get something more.
It ensures the excellent quality of the web pages.
It provides the availability of helpful content on the web pages
It ensures that the users should create web page content, not just for search engines.
It provides that the content a search engine indexes and subsequently ranks is the same content a user will see

✓ Attempting ranking improvements that are disapproved by the search engines.
✓ Redirecting users from a page built for search engines to one more humanfriendly.
✓ Redirecting users to a page different from the page the search engine ranked.
✓ Serving one version of a page to search engine spiders/bots and another version to human visitors. This is called the Cloaking SEO tactic.

✓ Using hidden or invisible text or the page background color, using tiny font size, or hiding them within the HTML code such as "no frame" sections.
✓ Repeating keywords in the metatags and using unrelated keywords to the website content. This is called metatag stuffing.
✓ Calculated keywords within a page to raise the keyword count, variety, and density of the page. This is called keyword stuffing.
✓ Creating low-quality web pages containing very little content but are instead stuffed with similar keywords and phrases. These pages are called Doorwayor GatewayPages.
• 1)Keyword Stuffing
• 2) Cloaking
• 3) Hidden Text
• 4)Doorway Pages
• 5)Article Spinning
• 6)Duplicate Content


• The search engine analyzes the keywords and key phrases on the web pages to index the websites.
• To exploit this search engine feature, some SEO practitioners increase keyword density to get a higher ranking which is considered a black hat SEO technique.
• A keyword density between two to four percent is considered optimal; increasing keyword density beyond that will irritate your readers and affect your ranking.
• Cloaking is a method which gives search engines the impression that a website carries content that is different to what users actually see. Visitors see a user friendly, visually appealing website which may, for example, contain little text and plenty of graphic or multimedia elements.
• Cloaking is a black hat SEO technique where a website shows one version of a URL, page, or piece of content to the search engines for ranking purposes while showing another to its actual visitors.
❑ The text which search engines can view but readers can't is known as hidden text.
❑ This technique incorporates irrelevant keywords and hides text or links to increase keyword density or improve internal link structure.
❑ Some ways to hide text are setting the font size to zero, using CSS to set text off-screen, creating white text on a white background, etc.


▪ The poorly written pages rich in keywords but don't contain relevant information and focus on the links to redirect users to an unrelated page are called doorway pages.
▪ Black hat SEO professionals use these pages to pass on user traffic to unrelated sites.

▪ It involves rewriting a single article to produce its different copies so that each copy looks like a new article.
▪ The content of such articles is repetitive, poorly written, and has low value for the visitors.
▪ In this technique, such articles are regularly uploaded to create the illusion of fresh articles.

• The content copied from a website to publish on another website as the original content is known as duplicate content.
• This black hat technique is known as plagiarism.

• Use a maximum of ten to fifteen meta keywords for a single page.
• Use a comma to separate the meta keywords and don't leave space between them.
• Don't repeat any meta keyword or phrase.
• Incorporate the most important words at the beginning of your meta keyword list.
• They should be specific and relevant to the page, i.e. they should accurately reflect what you are talking about on the page

✓ A search engine algorithm is a complex algorithm used by search engines such as Google, Yahoo, and Bing to determine a web page’s significance.
✓ Search engines collect essential data, which allows them to almost instantly choose whether a site is a spam or relevant data.
✓ Relevant sites receive high rankings in search engines, and spam or irrelevant sites receive exceptionally low rankings.

❑ A search engine penalty is an action taken against a website participating in deceptive or black hat SEO techniques.
❑ Google's definition of a "penalty" is some manual action taken against a site, opposed to the automated consequence of an algorithm or quality filter.

❑ Definition:
o The act of supplying a URL to a search engine in an attempt to make a search engine aware of a site or page.
❖ Search engine submission” refers to the act of getting your website listed with search engines. Another term for this is search engine registration. However, getting listed does not mean that you will rank well for particular terms. It simply means that the search engine knows your pages exist.
❖ Search engine submission is crucial if you want your website to be found and indexed by major search engines such as Google and Bing. Being indexed means your site will be visible in the search results, which is great for increasing organic search traffic, leads and sales.

✓ At a minimum, submitting to a search engine involves adding the URL of the site or page that will be under consideration.
✓ Search engines sometimes ask for additional contact information, including name and/or email address.
✓ Policies for adding URLs vary among various search engines.
✓ Some search engines only ask for the main URL of a site, claiming that the rest of the site will be spidered; others require the submission of individual pages.
✓ Variation also exists concerning how often URLs may be added. Some engines have tried to discourage bulk submissions to minimize spamming.
✓ Submitting sites/pages can be done manually or in an automated manner.
✓ Manual submission involves going to each “Add URL” page and filling out the form fields individually.
✓ Automatic submission involves filling out information only once; a software program uses the necessary information to submit to many search engines.
✓ Confusing search engine submission with search engine optimization is a common mistake. The mere act of submitting does nothing to optimize the pages in question and achieve higher rankings. Submitting poorly-optimized pages can do more harm than good.


1. Get your content seen
✓ In the past, seeing your social content has been all about working the algorithms to get your content into people’s feeds. Now, people are taking a more active approach to find the content they want rather than just scrolling through the content presented.
✓ So, the focus on discoverability is not new. Social SEO requires a shift in thinking about how people discover your content. When people search for information on social platforms, you want them to find your content.

❑ Raised Authority:
✓ Business listing aids in developing an online identity.
✓ Search engines find the listed websites creditable, thereby increasing your website's authority.
✓ Business listing sites offer backlinks to your website that stress search engine crawlers to put value in the website.
✓ Online business listing involves details of your business like Name, address, phone number, website link, social media profile links, city, country, a brief description of your business Etc. This plays an essential role in increasing the authority of your site.

❑ Boost Traffic:
✓ Being a part of business listing sites generates reference backlinks, boosting website traffic.
✓ Adding your website to a business listing website demands a complete business profile. This helps search engines to drive relevant traffic to your website by ranking you higher on search engine pages when people search for your niche.
✓ Most customers use third-party sites to find relevant companies serving their needs nearby their location. Hence, business listing sites help to draw potential customers in relevant locations and play a major in boosting SEO.
Inbound Links:
Various local business listings allow you to add a link to your business website.
This link helps to improve the ranking of your website on search engines.
This happens because of these inbound links, which add authority to your website when indexed by search engines.

▪ The short definition of off-page SEO is covering search engine tactics outside a website.
▪ Off-page SEO often correlates with linkbuilding activities, but there are far more tactics to implement if you want to enjoy a competitive advantage.
▪ There are tactics like brand building, content marketing, social media, and anything that can be part of your offpage SEO strategy.


➢Search engine submission
➢ Social Bookmarking
➢ Classified submission
➢ Forum Marketing
➢ Directory Submission
➢ Article Submission
➢ PDF Submission
➢ Social Networking
➢ Business Listing
➢ Blog submission
➢ Video Marketing

✓ With Google constantly changing its algorithm, the SEO community still believes that off-page SEO plays a significant role in a web page's ability to rank.
✓ While search algorithms and ranking factors are constantly changing, the consensus within the SEO community is that the relevance, trustworthiness, and authority that effective off-page SEO affords a website still play a major role in a page's ability to rank.

✓ As Google considers many off-page SEO factors while ranking a web page, it is rather challenging to rank only on the merit of good Content.
✓ Above all, good content is a highly subjective topic and taking a stand based on assumptions could hamper the trustworthiness of Google.
✓ That is why the founder Larry and Sergey introduced the PageRank metric that helped Google value the inbound links before ranking a page.
✓ Much water has flown in the last 20+ years, and the PageRank algorithms have been perfected to make the results incredibly better than they were in the early days.
✓ Website owners should aim for a combination of High-Quality Content + Authority Backlinks from Trustworthy Sites.
On-page search engine optimization happens within site, while off-page SEO happens outside the site. If you write a guest post for another blog or leave a comment, you’re doing off-page site promotion.




❑ The primary goal of technical SEO is to assist Google's bots in successfully crawling, interpreting, and indexing your website's pages.
❑ For example, creating an extensive XML sitemap and making your site mobilefriendly are only some tactics used to help web spiders filter and categorize your pages based on their content.
❑ Technical SEO strategies cover everything that impacts the crawling and indexing of the website. Search engine spiders crawl websites from time to time to index new content on the site.
❑ Any technical issues on site can prevent search engine spiders from carrying out their work. This is when technical SEO comes to play.
❑ Issues like slow website speed, broken links, and canonicalization errors are all technical issues and can be fixed using technical SEO.
➢ Page speed measures the time it takes for content on a particular webpage to load. It is easy to confuse this term with other words related to site optimization, like "site speed," which refers to the average loading time of more than one sample page on a given site.
➢ Many factors determine page speed, including server quality, file sizes, image compression, Etc.


• Mobile optimization involves tailoring websites or applications to ensure a seamless and user-friendly experience on mobile devices. It encompasses design, performance, and functionality adjustments to accommodate the constraints and capabilities of smartphones and tablets.
The primary role of mobile optimization is to enhance the user experience for visitors accessing a website or application on mobile devices. It involves responsive design, efficient use of resources, and adapting content to fit smaller screens, touch interactions, and varying network conditions.

User Experience: Mobile optimization improves user satisfaction by providing a smooth and intuitive experience on smaller screens.
SEO Ranking: Search engines prioritize mobile-friendly websites, impacting search rankings and visibility.
Increased Engagement: Optimized mobile experiences lead to higher engagement, lower bounce rates, and increased conversions.
Wider Accessibility: With the proliferation of mobile devices, optimization ensures broader accessibility, reaching a larger and more diverse audience.

Competitive Advantage: Mobile optimization is essential for staying competitive, as users increasingly prefer mobile devices for online activities.
Load Time and Performance: Optimized mobile sites load faster, contributing to better performance and user retention.
Adaptation to Trends: As mobile usage trends evolve, optimization allows businesses to adapt quickly to changing user behaviors and expectations.
Your website needs to accommodate the needs of the user. Having a simple clear intention on all pages will help the user interact with what you have to offer. What is the purpose of your website?
Are you imparting practical information like a ‘How to guide’? Is it an entertainment website like sports coverage or are you selling a product to the user?
There are many different purposes that websites may have but there are core purposes common to all websites;
Describing Expertise
Building Your Reputation Generating Leads Sales and After Care
Simplicity is the best way to go when considering the user experience and the usability of your website. Below are ways to achieve simplicity through design.
Colour has the power to communicate messages and evoke emotional responses. Finding a colour palette that fits your brand will allow you to influence your customer’s behaviour towards your brand. Keep the colour selection limited to less than 5 colours. Complementary colours work very well. Pleasing colour combinations increase customer engagement and make the user feel good.
Typography has an important role to play on your website. It commands attention and works as the visual interpretation of the brand voice. Typefaces should be legible and only use a maximum of 3 different fonts on the website.
Imagery is every visual aspect used within communications. This includes still photography, illustration, video and all forms of graphics. All imagery should be expressive and capture the spirit of the company and act as the embodiment of their brand personality. Most of the initial information we consume on websites is visual and as a first impression, it is important that high-quality images are used to form an impression of professionalism and credibility in the visitors’ minds.

Navigation is the wayfinding system used on websites where visitors interact and find what they are looking for. Website navigation is key to retaining visitors. If the website navigation is confusing visitors will give up and find what they need elsewhere. Keeping navigation simple, intuitive and consistent on every page is key.
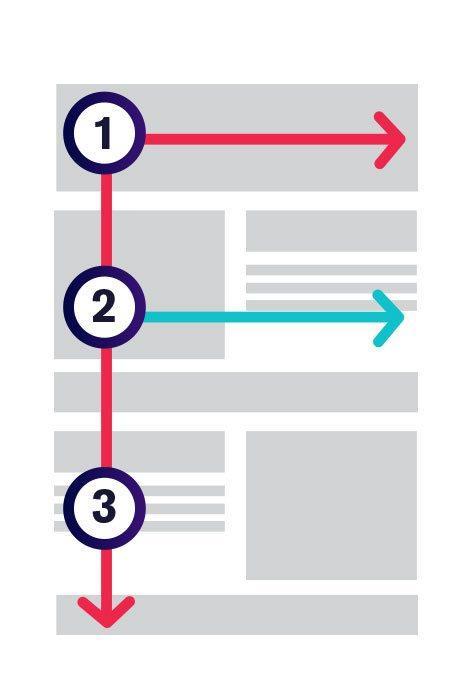
The F- based pattern is the most common way visitors scan text on a website. Eye-tracking studies have found that most of what people see is in the top and left areas of the screen. The F shaped layout mimics our natural pattern of reading in the West (left to right and top to bottom). An effectively designed website will work with a reader’s natural pattern of scanning the page.

Visual hierarchy is the arrangement of elements in order of importance. This is done either by size, colour, imagery, contrast, typography, whitespace, texture and style. One of the most important functions of visual hierarchy is to establish a focal point; this shows visitors where the most important information is.

An effective website has both great design and great content. Using compelling language great content can attract and influence visitors by converting them into customers.

Grids help to structure your design and keep your content organised. The grid helps to align elements on the page and keep it clean. The grid-based layout arranges content into a clean rigid grid structure with columns, sections that line up and feel balanced and impose order and results in an aesthetically pleasing website.
Waiting for a website to load will lose visitors. Nearly half of web visitors expect a site to load in 2 seconds or less and they will potentially leave a site that isn’t loaded within 3 seconds. Optimising image sizes will help load your site faster


More people are using their phones or other devices to browse the web. It is important to consider building your website with a responsive layout where your website can adjust to different screens.
HTML makes up the layout and structure for your website. This language is dynamic and allows you to create a beautiful website using less code. HTML is used to create a starting point for the website and is what most of your static pages start from. A better way to understand this language is to consider it as the skeleton that is holding your website together.
CSS is the language developers can use to style a website. The style sheet language describes how your website is presented and its layout. CSS is used hand in hand with HTML to add colors, backgrounds, layouts, font sizes, and more. This language is a core technology web developers use to design and build websites.
Java is the most popular web programming language. It is used to develop website content, games, apps, and software. Java is used in the production of most Android apps. Studies have shown over 15 billion devices are using Java in some form or other. Java language is portable and can be run on multiple software platforms.
JavaScript is used in many aspects of web development. Web developers use this language to add interactive elements to their websites. User engagement is important to your business, and your web developer should be incorporating JavaScript elements in your design
Python is one of the easiest languages to use and work with. Python can create a framework for basically any website need. This language uses simple and straightforward syntax, making it easy for web developers to work with and explain to their users. Some familiar sites that are using this language are Pinterest and Instagram.
SQL is a database query language that is used when your website is computing large amounts of data. Using SQL allows you to gather data from different databases and use it to cater your website to your target audience. This language is not used alone; instead, it is paired with others to get the most out of your customer database and website development.
PHP is often used on data-heavy websites or for app development. This is an open-source language that can be easily modified to meet the needs of your business or website. Large websites like WordPress and Facebook use PHP to manage and process their data.
.NET (pronounced dot net) is a framework that provides programming guidelines that can be used to develop a wide range of applications from the web to mobile to Windowsbased applications. The .NET framework can work with several web programming languages such as C#, VB.NET, C++, and F#. At Grand Circus, we use C# as well as MVC. .NET has a huge collection of predefined class libraries (pre-written code) that has support for simple and complex data structures.
Angular is a TypeScript-based open-source front-end application platform led by the Angular Team at Google and by a community of individuals and corporations. Angular is a complete rewrite from the same team that built AngularJS. Angular is a platform that makes it easy to build applications with the web.
Angular combines declarative templates, dependency injection, end to end tooling, and integrated best practices to solve development challenges. Angular empowers developers to build applications that live on the web, mobile, or the desktop.


A content management system, often abbreviated as CMS, is software that helps users create, manage, and modify content on a website without the need for specialized technical knowledge.
In simpler language, a content management system is a tool that helps you build a website without needing to write all the code from scratch (or even know how to code at all).
Instead of building your own system for creating web pages, storing images, and other functions, the content management system handles all that basic infrastructure stuff for you so that you can focus on more forward-facing parts of your website

WordPress is a good example of a content management system.
Let’s start with creating a piece of content. Without a content management system, you’d need to write a static HTML file and upload it to your server (sounds complicated, right?).
With a content management system like WordPress, you can just write your content in an interface that looks a good bit like Microsoft Word
WordPress is a good example of a content management system.
Let’s start with creating a piece of content. Without a content management system, you’d need to write a static HTML file and upload it to your server (sounds complicated, right?).
With a content management system like WordPress, you can just write your content in an interface that looks a good bit like Microsoft Word

On a more technical level, a content management system is made up of two core parts:
A content management application (CMA) – this is the part that allows you to actually add and manage content on your site (like you saw above).
A content delivery application (CDA) – this is the backend, behind-thescenes process that takes the content you input in the CMA, stores it properly, and makes it visible to your visitors.
Together, the two systems make it easy to maintain your website.






















Your website needs to accommodate the needs of the user. Having a simple clear intention on all pages will help the user interact with what you have to offer. What is the purpose of your website?
Are you imparting practical information like a ‘How to guide’? Is it an entertainment website like sports coverage or are you selling a product to the user?
There are many different purposes that websites may have but there are core purposes common to all websites;
• Describing Expertise
• Building Your Reputation
• Generating Leads
• Sales and After Care
Simplicity is the best way to go when considering the user experience and the usability of your website. Below are ways to achieve simplicity through design.
Colour has the power to communicate messages and evoke emotional responses. Finding a colour palette that fits your brand will allow you to influence your customer’s behaviour towards your brand. Keep the colour selection limited to less than 5 colours. Complementary colours work very well. Pleasing colour combinations increase customer engagement and make the user feel good.
Typography has an important role to play on your website. It commands attention and works as the visual interpretation of the brand voice. Typefaces should be legible and only use a maximum of 3 different fonts on the website.
Imagery is every visual aspect used within communications. This includes still photography, illustration, video and all forms of graphics. All imagery should be expressive and capture the spirit of the company and act as the embodiment of their brand personality. Most of the initial information we consume on websites is visual and as a first impression, it is important that high-quality images are used to form an impression of professionalism and credibility in the visitors’ minds.

Navigation is the wayfinding system used on websites where visitors interact and find what they are looking for. Website navigation is key to retaining visitors. If the website navigation is confusing visitors will give up and find what they need elsewhere. Keeping navigation simple, intuitive and consistent on every page is key.

The F- based pattern is the most common way visitors scan text on a website. Eye-tracking studies have found that most of what people see is in the top and left areas of the screen. The F shaped layout mimics our natural pattern of reading in the West (left to right and top to bottom). An effectively designed website will work with a reader’s natural pattern of scanning the page.

Visual hierarchy is the arrangement of elements in order of importance. This is done either by size, colour, imagery, contrast, typography, whitespace, texture and style. One of the most important functions of visual hierarchy is to establish a focal point; this shows visitors where the most important information is.
An effective website has both great design and great content. Using compelling language great content can attract and influence visitors by converting them into customers.

Grids help to structure your design and keep your content organised. The grid helps to align elements on the page and keep it clean. The grid-based layout arranges content into a clean rigid grid structure with columns, sections that line up and feel balanced and impose order and results in an aesthetically pleasing website.

Waiting for a website to load will lose visitors. Nearly half of web visitors expect a site to load in 2 seconds or less and they will potentially leave a site that isn’t loaded within 3 seconds. Optimising image sizes will help load your site faster

More people are using their phones or other devices to browse the web. It is important to consider building your website with a responsive layout where your website can adjust to different screens.
1. HTML
HTML makes up the layout and structure for your website. This language is dynamic and allows you to create a beautiful website using less code. HTML is used to create a starting point for the website and is what most of your static pages start from. A better way to understand this language is to consider it as the skeleton that is holding your website together.
2. CSS
CSS is the language developers can use to style a website. The style sheet language describes how your website is presented and its layout. CSS is used hand in hand with HTML to add colors, backgrounds, layouts, font sizes, and more. This language is a core technology web developers use to design and build websites.

Java is the most popular web programming language. It is used to develop website content, games, apps, and software. Java is used in the production of most Android apps. Studies have shown over 15 billion devices are using Java in some form or other. Java language is portable and can be run on multiple software platforms.
JavaScript is used in many aspects of web development. Web developers use this language to add interactive elements to their websites. User engagement is important to your business, and your web developer should be incorporating JavaScript elements in your design
Python is one of the easiest languages to use and work with. Python can create a framework for basically any website need. This language uses simple and straightforward syntax, making it easy for web developers to work with and explain to their users. Some familiar sites that are using this language are Pinterest and Instagram.
SQL is a database query language that is used when your website is computing large amounts of data. Using SQL allows you to gather data from different databases and use it to cater your website to your target audience. This language is not used alone; instead, it is paired with others to get the most out of your customer database and website development.

PHP is often used on data-heavy websites or for app development. This is an open-source language that can be easily modified to meet the needs of your business or website. Large websites like WordPress and Facebook use PHP to manage and process their data.
.NET (pronounced dot net) is a framework that provides programming guidelines that can be used to develop a wide range of applications from the web to mobile to Windows-based applications. The .NET framework can work with several web programming languages such as C#, VB.NET, C++, and F#. At Grand Circus, we use C# as well as MVC. .NET has a huge collection of predefined class libraries (prewritten code) that has support for simple and complex data structures.

Angular is a TypeScript-based open-source front-end application platform led by the Angular Team at Google and by a community of individuals and corporations. Angular is a complete rewrite from the same team that built AngularJS. Angular is a platform that makes it easy to build applications with the web. Angular combines declarative templates, dependency injection, end to end tooling, and integrated best practices to solve development challenges. Angular empowers developers to build applications that live on the web, mobile, or the desktop.
A content management system, often abbreviated as CMS, is software that helps users create, manage, and modify content on a website without the need for specialized technical knowledge.
In simpler language, a content management system is a tool that helps you build a website without needing to write all the code from scratch (or even know how to code at all).
Instead of building your own system for creating web pages, storing images, and other functions, the content management system handles all that basic infrastructure stuff for you so that you can focus on more forward-facing parts of your website

WordPress is a good example of a content management system.
Let’s start with creating a piece of content. Without a content management system, you’d need to write a static HTML file and upload it to your server (sounds complicated, right?).
With a content management system like WordPress, you can just write your content in an interface that looks a good bit like Microsoft Word
WordPress is a good example of a content management system.
Let’s start with creating a piece of content. Without a content management system, you’d need to write a static HTML file and upload it to your server (sounds complicated, right?).
With a content management system like WordPress, you can just write your content in an interface that looks a good bit like Microsoft Word
On a more technical level, a content management system is made up of two core parts:
A content management application (CMA) – this is the part that allows you to actually add and manage content on your site (like you saw above).
A content delivery application (CDA) – this is the backend, behind-the-scenes process that takes the content you input in the CMA, stores it properly, and makes it visible to your visitors.
Together, the two systems make it easy to maintain your website.

Timeline JS is a KnightLab project for very easily creating sophisticated timeline projects that you can embed in your own website or blog. The interface takes you through each step of the process. It relies on Google Spreadsheet for inserting your data for the timeline, and will give you a starter template that you fill in.
You can insert images and videos into your timeline, but they have to be hosted elsewhere, like YouTube. You can also host images on hosting sites like PostImage.org, or Imgur.
Storymap JS is a tool for creating location-based slide-show stories. As the user clicks the next button, they are taken to the next scene in the story, which can incorporate photos, videos, or text. The tool can also be used with a very large image (called a gigapixel) instead of a map. But the resolution of the image needs to be extremely large to work.

Juxtapose JS is a tool for creating before-and-after photo sliders that can be embedded on any website or blog. The photos have to be hosted elsewhere. You can use a photo hosting service like PostImage.org, or Imgur.
SoundCite is a tool for adding sound to specific pieces of text. The text appears highlighted with a small play button. When pressed, the sound will play as the user reads the text. The Soundcite page has an example that better illustrates how it works.
Sounds (.mp3) must be hosted on your own server, or uploaded to SoundCloud.

ThingLink is an image annotation tool that allows you to put markers on top of an image. When clicked, these markers will display an info window with text, photos, video, or audio clips.
Canva is an online service that allows you to create graphics, presentations, and infographics. Canva is also a nice way to get starter templates that you build upon, or draw inspiration from. Many designs are free, but some graphics cost $1 each. Storage of your project is limited without a fee.
Infogram is an online service that allows you to create infographics using a simple drag-and-drop interface. The graphics are much nicer looking than most, even professional, data visualization programs would produce, but the capabilities are limited to simple datasets. The best way to use this is to let the graphic lead the data format (start with what you want to visualize) because you’ll quickly find its limitations. Infogram is free for most basic charts, with subscription fees for power users.
Chart Blocks is an online tool for easily creating charts and customizing them in a draw-and-drop interface. The price is free up to 30 charts.

DataVisu.al is an online tool for making charts. You upload spreadsheet data and adjust a few sliders to customize the look of the chart. The basic version, which allows you to save low-resolution versions of your chart with their brand stamped on it, is free.
Palladio is an online tool for creating a few different chart types. The tool is free, but limited to only a few very specific types of charts: a map, a gallery, a graph-node view, and a table view. You upload a spreadsheet of data, but the spreadsheet needs to be in a specific format. Their website has an example template to work from.
11. Verse Verse is an online service that allows you to annotate videos with other videos, or allow the user to make choices about what to see next. The service is free up to 30 minutes of video storage per month.
12. Klynt
Klynt is a software tool that you can purchase and install on your computer which allows you to create and edit interactive video experiences. Think choose-your-own-adventure videos. As the viewer watches, they are presented with options of what to see next, and depending on what they click, they are taken to the next segment of the story.

Tumult Hype is piece of software that you download and install on your Mac, which allows you to create web animations that can be embedded on websites. The software is timeline based, but exports HTML5/JavaScript code that can be integrated within existing sites. The software also supports creating an entire website from the ground up, but wasn’t specifically designed for this purpose. The software costs $50.
Pageflow is a web service for creating multimedia “scrollytelling” types of stories. The pricing is 8,50€/month.
Odyssey is a web tool that allows you to create interactive stories that have some kind of locational element to them.
The tool uses CartoDB as backend. It can be a little technical, even though it tries to walk you through the process, and some coding knowledge can be helpful.
Envato Marketplace is a series of websites where creative artists can sell templates of their work for nominal fees.
This is a great way to get samples for websites, WordPress themes, audio loops, motion graphic projects, or even just simple design graphics. Often students use these as starting points for inspiration on projects. The costs vary, but most items are under $20.
17. WordPress.com
WordPress.com gives you a free website which can be used as either a blog or portfolio. The free version is limiting, however, and for about $3/month you can get a custom domain name and tools to add custom design to your site.
It is important to note that WordPress.com is different than WordPress.ORG. WordPress.COM is a commercial service that makes it easy to build websites, while WordPress.ORG is free and open-source software that allows you to create a WordPress site on your own server. For most people, .COM will be a much easier, turnkey solution for building a website.
18. Theme X (WordPress)
Theme X is a WordPress theme that allows a high level of customization and multimedia integration to a WordPress site. Though various extensions, the theme offers a drag-and-drop interface for creating customized pages. The theme costs about $70.
19. WordPress.com
WordPress.com gives you a free website which can be used as either a blog or portfolio. The free version is limiting, however, and for about $3/month you can get a custom domain name and tools to add custom design to your site.
It is important to note that WordPress.com is different than WordPress.ORG. WordPress.COM is a commercial service that makes it easy to build websites, while WordPress.ORG is free and open-source software that allows you to create a WordPress site on your own server. For most people, .COM will be a much easier, turnkey solution for building a website.
20. Theme X (WordPress)
Theme X is a WordPress theme that allows a high level of customization and multimedia integration to a WordPress site. Though various extensions, the theme offers a drag-and-drop interface for creating customized pages. The theme costs about $70.
Tilda.cc is an online platform for building webpages that is geared toward storytelling. It uses design modules called “blocks” that allow you stack and build great-looking stories without coding. The service is free for one site, but limits to 50 pages.
SquareSpace is one of the most popular options for students building their portfolios. It’s highly customizable, but comes pre-packaged with great-looking themes for turnkey website designs. The cost is about $12/month
Exposure.co is a platform for photographers to create visuallyoriented website portfolios. It’s free to start.

• Patents
• Protect certain novel, useful and nonobvious inventions having a utilitarian function
• Copyrights
• Protect creative expression in a fixed medium
• Trademarks
• Confer exclusive rights in any word, symbol or device that serves to identify the source or origin of goods or services
• Trade secrets
• Protect commercially valuable information whose contents are secured from public knowledge and disclosure

• Patent examples
• Hardware technology, media on which game is recorded, and software that enables game to perform its functions
• Copyright examples
• Software, artwork, storyline, characters, props, costumes, text, dialogue, sound effects, music
• Trademark examples
• Business name of the developer and publisher, game title, mascots (Mario and Sonic), designs, unique packaging
• Trade secret examples
• Confidential know how used to program, budgets, secret projects, contract terms

• Works Protected
• Inventions and processes protected by utility patents can be “any new and useful process, machine, manufacturer or composition of matter, or any new or useful improvement thereof…”
• So-called “method” patents are utility patents that cover computerized processes and functions
• The design of physical objects, such as the Xbox, can be protected separately by a design patent

• Standards
• To qualify for utility patent an invention must be:
1. New
2. Useful
3. Nonobvious
• Nonobviousness requires that the invention be sufficiently different from known technology and knowledge so as not to be obvious to a person with ordinary skill in the field of the invention.
• Ownership
• In general, the inventor is the owner of the patent
• The inventor may assign rights to the invention to others, such as the inventor’s employer, through written agreement
• They may be multiple inventors in group works
• Registration is essential to secure patent rights
• Exclusive Rights
• The patent owner can exclude others from making, using or selling the patented invention or objects embodying the patented invention

• Duration
• A utility patent is granted for 20 years from the date the application is filed
• Patents issued prior to June 8, 1995, exist for 17 years from the date the patent is granted
• The patented invention may be freely copied once the patent expires

• Works Protected
• Almost any recorded original expression such as:
• Literary works
• Musical works (including lyrics)
• Dramatic works (including music)
• Pantomimes and choreographic works
• Pictorial, motion picture, graphic and sculptural works
• Sound recordings
• Architectural works
• Works Not Protected
• Ideas, titles and names, facts

• A copyright has 2 requirements:
1. Originality and “fixation in a tangible form”
• To be original, the work must not have been copied by the author and have a small level of creativity
2. The fixation requirement is met if the work is recorded in any medium such as:
• Text, videotape, photograph, sound recording, or CD
• Ownership
• Ownership of a copyright belongs to author or authors of the work
• The author is generally the creator of the work, but certain works made under contract as “works for hire” are owned by the person contracting for the work
• Registration is not required but confers enforcement rights
• Exclusive Rights
• A copyright owner has five exclusive rights:
1. Reproduction right (copy, duplicate or imitate)
2. Modification right
3. Distribution right
4. Public performance right
5. Public display right
• Moral rights are granted to visual artists to prevent improper attribution and protect the integrity of the work

• Duration
• For works created by an individual or individuals after January 1, 1978, the copyright lasts for the life of the author plus seventy years
• Copyrights in anonymous works and works made for hire exist for a period of 95 years from the date of first publication or 120 years from the date of creation, whichever is sooner

• Works Protected
• Any word, symbol, name, slogan, picture, design, shape, color, sound or smell that serves to identify the source or origin of goods or services can be a trademark
• A service mark is a trademark applied to services instead of products
• Standards
• A trademark must be capable of distinguishing the owner’s goods or services from the goods or services of others
• The relative enforcement strength of a trademark is determined on the basis of the degree of such differentiation:
1. Arbitrary or coined
2. Suggestive
3. Descriptive
4. Generic
• Ownership
• A trademark is owned by the first party to use it in connection with the goods or services
• Registration is not essential but establishes important enforcement rights
• Exclusive Rights
• A trademark owner has the exclusive right to use the trademark in connection with specific goods or services
• Subsequent users of the same or similar mark are deemed infringers

• Duration
• A trademark continues as long as it remains in use
• Federal registrations are subject to renewal every ten years


• Works Protected
• Each state has its own laws, but many have adopted versions of the Uniform Trade Secrets Act
• The UTSA provides that information that derives “independent economic value” from not being publicly known and whose secrecy is properly guarded is protected from unauthorized use by others

• Standards
• Trade secrets must have commercial value and remain secret
• There is no requirement that they be recorded and there is no provision for registration
• Unlike patents and copyrights, trade secrets can include ideas that have no current utility or application

• Ownership
• An employer generally owns trade secrets developed by employees and by independent contractors hired to develop or create such information
• Exclusive Rights
• The owner of a trade secret can maintain it as long as secrecy is properly maintained
• The owner of IP rights can transfer all rights by written assignment or a portion of rights by a written license
• Rights transfer between an employee or independent contractor is dependent on:
• The nature of the rights transferred
• The existence of an enforceable agreement between the parties setting forth the terms of any such transfer

• Existing patents, copyrights and trademarks can be searched
• Trade secrets cannot be searched, but violation generally requires intentional theft
• Copyrights are only violated if there is actual copying of the protected work
• Patent infringement does not require intent or even knowledge of the patent
• The standard of infringement for trademarks is whether there is a “substantial likelihood of confusion” between trademarks among intended consumers
• HTML is a language for describing web pages.
• HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language
• HTML is not a programming language, it is a markup language.
• A markup language is a set of markup tags.
• HTML uses markup tags to describe web pages.

HTML markup tags are usually called HTML tags
• HTML tags are keywords surrounded by angle brackets like <html>
• HTML tags normally come in pairs like <b> and </b>
• The first tag in a pair is the start tag, the second tag is the end tag.
• Start and end tags are also called opening tags and closing tags.

• HTML Document = Web Page
• HTML documents describe web pages, it contain HTML tags and plain text
• Structure of the web page: <html> <head> information of the web page</head> <body> content display on browser </body> </html>

• Web Browser
• The purpose of a web browser (like Internet Explorer or Firefox) is to read HTML documents and display them as web pages.
• The browser does not display the HTML tags, but uses the tags to interpret the content of the page

• We use a plain text editor (like Notepad) to edit HTML. This is the best way to learn HTML.
• However, professional web developers often prefer HTML editors like FrontPage or Dreamweaver, instead of writing plain text.
• When you save an HTML file, you can use either the .htm or the .html extension.
• With new software it is perfectly safe to use .html.
• HTML Elements: An HTML element is everything from the start tag to the end tag: Start tag *
content
* <p> This is a paragraph </p> <a href="default.htm"> This is a link </a> <br />

• HTML Element Syntax
• An HTML element starts with a start tag / opening tag and ends with an end tag / closing tag
• The element content is everything between the start and the end tag
• Some HTML elements have empty content
• Empty elements are closed in the start tag
• Most HTML elements can have attributes

Nested HTML Elements
• Most HTML elements can be nested (can contain other HTML elements).
• HTML documents consist of nested HTML elements.
Empty HTML Elements
• HTML elements without content are called empty elements. Empty elements can be closed in the start tag.
• <br> is an empty element without a closing tag

Example:
• <html>
• <body> <p>This is my first paragraph</p> </body>
• </html>
Explain:
• The <html> element defines the whole HTML document.
• The <body> element defines the body of the HTML document.
• The <p> element defines a paragraph in the HTML document

HTML Attributes
• HTML elements can have attributes
• Attributes provide additional information about the element.
• Attributes are always specified in the start tag.
• Attributes come in name/value pairs like: name="value“.
• Attribute values should always be enclosed in quotes
Example
• <a href=“http://www.w3schools.com”>This is a link </a>
Attribute Value Description
class class_rule or style_rule The class of the element
id id_name A unique id for the element
style style_definition
An inline style definition
title tooltip_text A text to display in a tool tip
• Below is a list of some attributes that are standard for most HTML elements:

HTML Headings

•Headings are defined with the <h1> to <h6> tags.
•<h1> defines the largest heading.
•<h6> defines the smallest heading.


Example
Browsers automatically adds an empty line before and after headings.
•<h1>This is a heading1</h1>
<h2>This is a heading2</h2>
<h3>This is a heading3</h3>




• Example <html> <body>
<h1>This is heading 1</h1>
<h2>This is heading 2</h2>
<h3>This is heading 3</h3>
<h4>This is heading 4</h4>
<h5>This is heading 5</h5>
<h6>This is heading 6</h6> </body>
</html>

• HTML Rules (Lines)
• The <hr /> tag is used to create an horizontal rule (line).
• Example:
<html><body>
<p>The hr tag defines a horizontal rule:</p>
<hr />
<p>This is a paragraph</p>
<hr />
<p>This is a paragraph</p>
</body></html>

• Optional Attributes of the <HR> tag:
<HR Align=”directtion” Width= “Value” Size=value color=#rrggbb>
• Example:
<HR Align=CENTER Size=12 Width=100% color=RED>
<HR Align=CENTER SizeE=6 Width=50% color=GREEN>
<HR Align=CENTER Size=3 Width=25% color=BLUE>
<HR Align=CENTER Size=1 Width=10% color=YELLOW>
Comments can be inserted in the HTML code to make it more readable and understandable. Comments are ignored by the browser and are not displayed.
<html><body>
• <!--This comment will not be displayed-->
• <p>This is a regular paragraph</p> </body></html>


• HTML Paragraphs:
• Paragraphs are defined with the <p> tag
• Browsers automatically adds an empty line before and after paragraphs.
• Example: <html><body>
<p>This is a paragraph.
<p>This is a paragraph.
<p>Don't forget to close your HTML tags!</p> </body></html>

• HTML Line Breaks:
• Use the <br /> tag if you want a line break (a new line) without starting a new paragraph.
• The <br /> element is an empty HTML element. It has no end tag.
• <br> or <br />
• Example: <html><body> <p>This is<br />a paragraph<br /> with line breaks</p> </body></html>

• HTML Text Formatting:
• HTML uses tags like <b> and <i> for formatting output, like bold or italic text.
• These HTML tags are called formatting tags.
• Example:
<html><body>
<p><b>This text is bold</b></p>
<p><big>This text is big</big></p>
<p><i>This text is italic</i></p>
<p>This is<sub> subscript</sub> and <sup>superscript</sup></p>
</body></html>
<b> Defines bold text
<big> Defines big text
<em> Defines emphasized text
<i> Defines italic text
<small> Defines small text
<strong> Defines strong text
<sub> Defines subscripted text
<sup> Defines superscripted text
<u> Deprecated. Use styles instead

• HTML Styles: The style attribute is a new HTML attribute. It introduces CSS to HTML.
• The purpose of the style attribute is:
• To provide a common way to style all HTML elements.
• With HTML styles, styles can be added to HTML elements directly by using the style attribute, or indirectly by in separate style sheets (CSS files)..
• Examples
• style="background-color:yellow"
• style="font-size:10px"
• style="font-family:Times"
• style="text-align:center"
• Some the attribute always use:
• Background Color
Ex: <body style="background-color:yellow">
• The style attribute defines a style for the <body> element.

Font
<p style="font-family:courier new; color:red; font-size:20px">
– The style attribute defines a style for the <p> element.
Text Alignment
Ex: <h1 style="text-align:center">
– The style attribute defines a style for the <h1> element.

• HTML Fonts: <FONT Face=”fontName1, fontName2, fontName3” size=”value”
color=”#rrggbb”>
content
</FONT>
• Example: <p> <font size="2" face="Verdana"> This is a paragraph. </font> </p>
Attribute Example Purpose
size="number" size="2" Defines the font size
size="+number" size="+1" Increases the font size
size="-number" size="-1" Decreases the font size
face="facename" face="Times" Defines the fontname
color="colorvalue" color="#eeff00" Defines the font color
color="colorname" color="red" Defines the font color

• The Right Way to Do It
<html> <body> <p style="font-family:verdana;font-size:80%; color:green">
This is a paragraph with style. </p> </body> </html>

• HTML Color Values: HTML colors are defined using a hexadecimal (hex) notation for the combination of Red, Green, and Blue color values (RGB).
• The lowest value that can be given to one of the light sources is 0 (hex 00). The highest value is 255 (hex FF).
• Hex values are written as 3 double digit numbers, starting with a # sign.



• HTML Color Names:
• The W3C HTML and CSS standards have listed only 16 valid color names: aqua, black, blue, fuchsia, gray, green, lime, maroon, navy, olive, purple, red, silver, teal, white, and yellow.

To change the color scheme of web page you use Body tag.
• [1]V. Syr yamk in , V. Shidlovsky. Correlation-extremal direction-finding systems (Tomsk State University publishing house, 2010)
• [2] S.V. Shidlovskii, J. Comp. Sys. Sci. Int 45, 282 (2006)
• [3] D.V. Shashev, MATEC Web Conf. 79, (2016)
• [4] D.V. Shashev, S.V. Shidlovskiy, J. Phy: Conf. Ser. 881, (2017)
• [5] Mobile app. [Electronic resource] URL: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mobile_app
• [6] J. Rocheleau. 6 Safety Steps To Making Secure Mobile Transactions. URL:
• http://www.hongkiat.com/blog/secure-mobile-paymen t-tips/
• [7] Types of mobile application. URL:
• http://softwaretestinggarbage.blogspot.ru/2012/10/types-of-mobile-application.html
• [8] Gr. Smith. 10 Excellent Platforms for Building Mobile Apps. URL: http://
• http://mashable.com/2013/12/03/build-mobile-apps/#XycLK6j7ZkqA
• [9] Yo. De. What is the goal of the mobile app development? URL:
• https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-goal-of-the-mobile-app-development
• Internet World Stats (2015) World Internet Users Statistics [Online] http://www.internetworldstats.com/stats.htm
• 2. Aufray, J., 2009. Master International Business & Marketing, IDRAC Lyon (2009)
• 3. Duermyer, 2017. https://www.thebalance.com/can-you-reallymake-money-with-affiliate-marketing-1794168
• 4. Oliveira, A., 2017. A Four-Step Guide To Creating Your Digital Marketing Plan, https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbesagencycouncil/2016/11/17/afour-step-guide-to-creating- your-digital-marketing-plan
• 5. McDonald, M.,2012. Market Segmentation: How to do it, how to profit from it, John Wiley & Sons.
• 6. Stern, C.W. and Deimler, M.S., 2006. The Boston Consultancy Group on Strategy: Classic concepts and new perspectives, John Wiley & Sons.
• 7. Chaffey, D. and Ellis-Chadwick, F., 2015. Digital Marketing Strategy, Implementation and Practice, 6th edition. Financial Times/ Prentice Hall, Harlow.