

SCIENCE TO SAGE LIFE & LIGHT7




Short intro to Michael Clarage, PhD video Function in the Cosmos
Exploring the Seven Layers of Creation
Karen Elkins
The Dougherty Set by Buddy James Diagrams and Explanations


Cover background by Buddy James

...sent me on the quest to find as many layers in nature after I watch his video (page seven). I knew the number seven was significant but I did not know how much.






From planets in the cosmos to life on Earth, the significance of seven reveals an astonishing connection to all celestial bodies, natural cycles, and even the growth of living beings. It should be no mystery as we dance on the electromagnetic spectrum of light, color and sound vibration. This is a field of color bands and sounds noted on a scale.


Electro-Magnetic Wave




types of electromagnetic waves are:
1.
Gamma Rays: Gamma rays have the highest frequencies and shortest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum. They are produced by nuclear reactions, such as those occurring in stars and during radioactive decay Gamma rays have applications in medical imaging and cancer treatment.
X-Rays: X-rays have frequencies and wavelengths between gamma rays and ultraviolet rays. They are commonly used in medical imaging, such as X-ray radiography and CT scans, and in various industrial applications.
3.
2. Ultraviolet (UV) Rays: Ultraviolet rays have higher frequencies and shorter wavelengths than visible light. They are present in sunlight and play a role in biological processes, such as vitamin D synthesis in the skin However, excessive exposure to UV rays can be harmful and cause skin damage.
Visible Light: Visible light is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that our eyes can detect. It consists of different colors, each corresponding to a specific wavelength and frequency. The colors of the rainbow are a visible light spectrum.
4. Infrared (IR) Rays: Infrared rays have lower frequencies and longer wavelengths than visible light. They are commonly used in thermal imaging, remote controls, and various heating applications
5. Microwaves: Microwaves have even lower frequencies and longer wavelengths than infrared rays. They are used in microwave ovens for cooking and in communication technologies like Wi-Fi and satellite transmissions.
7.
6 Radio Waves: Radio waves have the lowest frequencies and longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum. They are used for various communication purposes, including radio broadcasting, television transmission, and wireless networks.
Understanding these waves is crucial in various fields, from astronomy and physics to medicine, telecommunications, and everyday technology.
Seven Notes in a Musical Scale
In traditional Western music, there are seven distinct notes in a diatonic scale (e.g., C, D, E, F, G, A, B).



As HUEman beings, we are intrinsically connected to the electromagnetic spectrum, a symphony of light that orchestrates life's dance. Nature harnesses this spectrum, as photosynthesis turns sunlight into nourishment, fueling the cycle of life.
Colors are not merely superficial aspects of our world; they are woven into the very fabric of life. Their presence illuminates the changing seasons, reflecting the dynamic nature of existence. The intricate interplay between the light spectrum and life's rhythms underscores our deep connection with the natural world.
Keyboard of life -7 Octave


Life is Light


Seven Colors of the Rainbow
The colors of the rainbow are red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. Seven distinct bands of color.


h u em a n

















different wavelengths of light as various colors, enabling us to navigate our surroundings, recognize objects, and interact with our environment.
2.
Photosynthesis and Plant Growth: Plants utilize the visible light spectrum, particularly the blue and red wavelengths, for photosynthesis. This process converts light energy into chemical energy, sustaining plant life and forming the foundation of the food chain for many living organisms.
3.
Vitamin D Production: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation, a part of the electromagnetic spectrum, triggers the synthesis of vitamin D in our skin. Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption, bone health, and a healthy immune system.
4.
Infrared Radiation: Infrared radiation, with longer wavelengths than visible light, plays a role in heat transfer and thermal imaging. It is used in various technologies, such as remote sensing and thermal cameras.
5.
Communication: Radio waves, microwaves, and other parts of the electromagnetic spectrum facilitate communication through wireless technologies, such as radio broadcasting, television, Wi-Fi, and mobile networks.
6.
Medical Applications: X-rays and gamma rays, part of the high-energy end of the spectrum, have medical applications, such as diagnostic imaging and cancer treatment.
There are seven crystal lattice systems
Cubic or Isometric: These are not always cube-shaped. You'll also find octahedrons (eight faces) and dodecahedrons (10 faces).
Tetragonal: Similar to cubic crystals, but longer along one axis than the other, these crystals forming double pyramids and prisms.
Orthorhombic: Like tetragonal crystals except not square in crosssection (when viewing the crystal on end), these crystals form rhombic prisms or dipyramids (two pyramids stuck together).
Hexagonal: When you look at the crystal on end, the cross-section is a six-sided prism or hexagon.
Trigonal: These crystals possess a single 3-fold axis of rotation instead of the 6-fold axis of the hexagonal division.
Triclinic: These crystals are not usually symmetrical from one side to the other, which can lead to some fairly strange shapes.
Monoclinic: Like skewed tetragonal crystals, these crystals often form prisms and double pyramids.

We are made of crystalline light

crystal lattice systems ... it’s pure geometry


Law of octaves in chemistry
Law of octaves in chemistry generalization made by the English chemist J.A.R. Newlands in 1865 that, if the chemical elements are arranged according to increasing atomic weight, those with similar physical and chemical properties occur after each interval of seven elements. The chemical elements are arranged according to increasing atomic weight, those with similar physical and chemical properties occur after each interval of seven elements.


electronic Absorption Spectra



Ratio
7 7 7
The Divine Ratio of Seven
Seven, often associated with the divine and perfection, resonates throughout the natural world. The spiral of the nautilus shell follows the Fibonacci sequence, featuring seven spiral arms, mirroring the beauty of the stars in the Milky Way galaxy. Nature's underlying order speaks to the universal principle of seven as an expression of divine symmetry.



7 7 7



6 6 6
4 4 4 5 5 5





CascadingSElectro-Magnetic ignature
“All matter is crystalline, all matter is frozen light.”
~ Walter Russell Liquid crystalline water is our living rainbow.“
Dr. Mae-Wan Ho




Micro to macro




Human Embryo Development


Embryo parts, Body parts, Glands, Brain divisions, Inner ear parts, Retina parts, Heart cavities, Body systems, Bodily functions
1
Fertilization: The process begins with the fusion of the sperm and the egg (ovum) during fertilization, resulting in the formation of a zygote a singlecelled embryo.
2
Cleavage: After fertilization, the zygote undergoes rapid cell division through a process called cleavage. The zygote divides into multiple cells called blastomeres. During this stage, no overall growth in the embryo's size occurs.
3
Morula: As cell division continues, the blastomeres rearrange and compact, forming a solid ball of cells known as the morula.
4.
Blastula: The morula undergoes further cell divisions, creating a fluid-filled cavity called the blastocoel. The structure that forms at this stage is called a blastula. In mammals, it is also referred to as a blastocyst, with distinct inner cell mass and trophoblast cells.
5
Gastrulation: During gastrulation, the blastula undergoes significant changes in cell movement and rearrangement. Three primary germ layers ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm are established, setting the foundation for the development of different tissues and organs.
6.
Organogenesis: Organogenesis is the stage where the three germ layers start to differentiate and give rise to specific organs and tissues. Cells continue to divide and migrate to their respective positions, forming the rudimentary structures of the developing organism.
7.
Fetal development: After organogenesis, the developing organism is referred to as a fetus. During this stage, the organs and systems become more refined and mature. The fetus continues to grow and develop until birth.
the 7 Senses?
Your senses are a neurological process that organizes sensation from your environment and makes sense of it. Our sensory network processes by receiving, interpreting, and organizing input.






YOUR SENSES ARE ELECTRIC WHAT GIVES YOU A CHARGE





Matter, light and energy are the same they are one.
Walter Russell



The Seven Stages of Life's Symphony

In various spiritual and philosophical traditions, there are interpretations of the human life journey that involve seven stages, each characterized by distinct qualities and experiences. These stages often symbolize growth, self-discovery, and transformation While different belief systems may have their interpretations, here's a generalized outline of the seven stages of the human life cycle.


Infancy: This stage encompasses early childhood, from birth until around the age of 2 or 3. Infancy is marked by complete dependency on caregivers, rapid physical growth, and the development of basic motor and cognitiv skills
Early Childhood: This stage typically spans from ages 3 to 6. Early childhood is characterized by exploration, curiosity, and the development of language and social skills Play and imagination play significant roles in learnin during this phase.
3.
Middle Childhood: Middle childhood ranges from ages 7 to 12. It is a period of increasing independence, cognitive development, and formal education. Children begin to form friendships, discover their interests, and develop a sense of self.

Adolescence: Adolescence typically covers ages 13 to 19. It is a period of significant physical, emotional, and psychological changes. Adolescents seek to establish their identities, form deeper social connections, and grapple with questions of purpose and belonging
Early Adulthood: Early adulthood spans from ages 20 to 39. This stage is marked by significant personal and professional growth, pursuing education, building careers, forming long-term relationships, and starting families. 5.
Middle Adulthood: Middle adulthood extends from ages 40 to 64. It is a phase of consolidation, where individuals may focus on their careers, family life, and personal goals This stage is often associated with increased wisdom and self-assurance.
Late Adulthood: Late adulthood covers ages 65 and beyond It is a phase of reflection, retirement, and potential physical and cognitive changes. Individuals may focus on leaving a legacy and finding meaning in their lives.
Great Divides'
Micro to macro

Seven Layers of Skin:

The skin is composed of three primary layers: the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue). However, it is not traditionally associated with seven layers.
1.
In the human body 7 major glands
Pituitary Gland: Often referred to as the "master gland," it controls several other glands and regulates hormone production.
2.
Thyroid Gland: Produces hormones that regulate metabolism and play a crucial role in growth and development.
3.
Adrenal Glands: Situated on top of the kidneys, they produce hormones like cortisol and adrenaline that help the body respond to stress and regulate metabolism.
4.
Pancreas: Produces insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar levels.
5.
Ovaries (in females): Produce estrogen and progesterone, which are involved in reproductive functions and menstrual cycles.
6.
Testes (in males): Produce testosterone and are involved in the development of male reproductive organs and secondary sexual characteristics.
7.

Pineal Gland: Produces the hormone melatonin, which regulates sleep-wake cycles and other biological rhythms.

These are just a few examples of glands in the human body. There are many other glands and organs that contribute to the intricate system of hormone production and regulation, which ultimately influences various aspects of human life and health.
Chakras evolution of self inner to outer spaces





Human Energy Centers
1.
Muladhara (Root Chakra) - Saturn: Muladhara is located at the base of the spine and is associated with stability, grounding, and basic survival instincts. Saturn, as the planet of discipline and structure, aligns with the foundational and grounding nature of this chakra.
2.
Svadhisthana (Sacral Chakra) - Jupiter: Svadhisthana, located in the lower abdomen, is related to creativity, pleasure, and emotional wellbeing. Jupiter's expansive and benevolent energy is seen as harmonizing with the creative and joyful aspects of this charka
3.
Manipura (Solar Plexus Chakra) - Mars: Manipura, situated in the upper abdomen, is associated with personal power, willpower, and selfconfidence. Mars, as the planet of action and assertiveness, is aligned with the energetic and self-motivated qualities of this chakra.
4.
Anahata (Heart Chakra) - Venus: Anahata, located at the heart center, is connected to love, compassion, and harmony. Venus, as the planet of love and beauty, resonates with the qualities of this chakra, promoting loving relationships and emotional balance
5.
Vishuddha (Throat Chakra) - Mercury: Vishuddha, located at the throat, is linked to communication, expression, and self-truth. Mercury, as the planet of communication and intellect, aligns with the expressive and communicative aspects of this chakra.
6
Ajna (Third Eye Chakra) - Moon: Ajna, situated between the eyebrows, is associated with intuition, inner wisdom, and spiritual insight. The Moon, as a symbol of emotions and intuition, aligns with the qualities of this chakra.
7.
Sahasrara (Crown Chakra) - Sun: Sahasrara is located at the crown of the head and represents spiritual connection and enlightenment. The Sun, as the center of our solar system and a symbol of light and consciousness, aligns with the transformative and illuminating nature of the crown chakra
The Bodies Electric Circuit
"The torus field, a fundamental electromagnetic phenomenon, finds intriguing correspondence in Earth's atmospheric composition, which is organized into seven distinct layers. In parallel, the human energy system exhibits a comparable stratification through its seven chakras This intriguing congruence suggests a deeper resonance between macrocosmic and microcosmic energetic architectures.
Just as the Earth's atmosphere is composed of troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere, ionosphere, and magnetosphere, the chakra system consists of seven energy centers - Root, Sacral, Solar Plexus, Heart, Throat, Third Eye, and Crown. Each layer, whether terrestrial or energetic, serves unique functions crucial to their respective systems
The torus field mirrors this intricate layering. Its dynamic flow, akin to the exchange of energy between Earth's atmospheric strata, exhibits simultaneous upward and downward movement This property, observed both in the natural world and the human energy body, suggests a fundamental symmetry in the way energy circulates within complex systems.
Furthermore, much like the neural impulses in the human body that facilitate the transmission of charged particles, the torus field acts as a conduit for the flow of information across energetic pathways, aligning with the nuanced functioning of each chakra. This intricate interplay resonates with the layered complexities of both the chakra system and Earth's atmospheric strata, underscoring the profound interconnectedness between our microcosmic existence and the macrocosmic realm."

Birkland



Earths magnetosphere

Seven Layers Of The Human Aura

An artist's rendering of the structure of Earths magnetosphere wikipedia
1) Bow shock.
2) Magnetosheath.
3) Magnetopause.
4) Magnetosphere.
5) Northern tail lobe
6) Southern tail lobe.
7) Plasmasphere.


The Seven "Heavens" refers to the layers of our atmosphere.
1. troposphere
2. stratosphere
3. ozone layer
4. mesosphere
5. thermosphere
6. ionosphere
7. exosphere

Heaven’s cascading scale of cosmic light
Beltrami Vortex







art by James Sorenson

vibration

Harmonic Patterns in the wake
Asplanets revolvewithinour galaxywecross differentplanets pathsatdifferent timesoftheyear. Theserevolutions weavea geometricpattern inthesky creatingdifferent frequencies.











W a l t e r R u s s e l l — P e r i o d i c T a b l e

Sun: The Sun is associated with the vibrational frequency of 126.22 Hz. The corresponding musical note is B.
Moon: The Moon is associated with the vibrational frequency of 210.42 Hz. The corresponding musical note is G.
Mars: Mars is associated with the vibrational frequency of 144.72 Hz. The corresponding musical note is D.
Mercury: Mercury is associated with the vibrational frequency of 141.27 Hz. The corresponding musical note is C#.
Jupiter: Jupiter is associated with the vibrational frequency of 183.58 Hz. The corresponding musical note is F.
Venus: Venus is associated with the vibrational frequency of 221.23 Hz. The corresponding musical note is A.
Saturn: Saturn is associated with the vibrational frequency of 147.85 Hz. The corresponding musical note is D#

There were seven classical planets visible to the naked eye: Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, the Sun, and the Moon
“Science of Light” or Hindu Astrology




Hindu thought teaches us that the individual human being is a reflection of the universal Being and explains how we can link the two together for overall well-being and for ultimate Self-realization. This connection is mirrored in the discipline of Vedic astrology, or Jyotish, the science of light, which shows how the influences of the stars and planets at a cosmic level affect the movement of our personal human lives through our karma and our dharma.
Modern physics is recognizing our human activities are interrelated with those of the cosmos, both on subtle and vast levels. Modern medicine is slowly accepting the existence of powers of life and intelligence in nature that we cannot reduce to mere chemistry and which we are an integral part of.
Wonder7
EARTH

ys of the Week:
s the most well-known example e week consists of seven days: day, Wednesday, Thursday, ay, and Sunday.
time place
In ancient times, there were seven known seas, typically referred to as the Mediterranean Sea, Red Sea, Black Sea, Adriatic Sea, Aegean Sea, Caspian Sea, and Persian Gulf.


Schumann Resonance 7.83 Hz
The fundamental frequency of the Schumann Resonance is around 7.83 Hz. This frequency is often associated with the natural electromagnetic field of the Earth and is sometimes referred to as the Earth's "heartbeat" or "resonant frequency." It is believed to have a calming and grounding effect on living beings.
7 OF BIOLOGY

stages rhythms
Seven-day Cycles in Biological Rhythms:
Some biological processes in plants and animals, such as circadian rhythms, can exhibit cycles with periods close to seven days.

Seven Life Stages of Insects:
In the life cycle of some insects, they go through seven distinct stages: egg, larva, nymph, pupa, pre-adult, sub-imago (a stage of incomplete development), and imago (adult).

Seven and the Planetary Growth:
The planetary growth cycle reveals seven stages, tracing the formation of celestial bodies. From the accretion of dust and gas to the finalization and migration, the seven stages of planet formation echo the stages of human life, hinting at the interconnectedness of the universe and the microcosm within.
Moon Cycle
Cycles

Plant growth follows a well-defined cycle that involves several stages. These stages, though not always precisely seven, represent the major phases of a plant's life cycle. The specific number of stages can vary depending on the type of plant, environmental conditions, and other factors. Here is a generalized overview of the typical stages of plant growth:
1.
Germination: The life cycle of a plant typically begins with germination. During this stage, a seed absorbs water and swells, initiating metabolic processes within the seed. The seed coat cracks, and the embryonic plant (embryo) emerges from the seed, usually as a small root (radicle) and a shoot (plumule).
2.
Seedling: The seedling stage starts with the emergence of the shoot above the soil surface. As the shoot grows, it develops the first true leaves, which are characteristic of the plant species During this stage, the seedling relies on stored nutrients from the seed until it develops a functional root system and can photosynthesize to produce its food.
3.
Vegetative Growth: In the vegetative growth stage, the plant's primary focus is on establishing a strong root system and developing a robust vegetative structure, including stems, leaves, and branches. Photosynthesis becomes the primary means of energy production as the plant actively grows and increases in size.
4.
Flowering Initiation: This stage is crucial for plants that produce flowers. Environmental cues, such as changes in day length or temperature, trigger the transition from vegetative growth to reproductive growth. The plant begins to allocate energy toward the production of flowers and seeds
5.
Flowering and Pollination: Flowers are produced during this stage, and pollination occurs. Pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, or wind, transfer pollen between flowers, enabling fertilization and seed production.
6.
Fruit and Seed Development: After successful pollination and fertilization, the flowers transform into fruits that house the developing seeds. The fruit provides protection and aids in seed dispersal, ensuring the propagation of the plant.
7.
Seed Dispersal and Germination: Once the seeds are mature and ready for dispersal, they are released from the fruit and spread through various mechanisms, such as wind, water, or animals. The cycle then repeats as the dispersed seeds find suitable conditions for germination and the start of a new plant life cycle.
Seven Cycles of Earth
The Earth, our blue oasis in space, unfolds a tapestry of seven cycles that shape our world. The seven continents that span the globe offer diverse ecosystems, habitats, and climates. Furthermore, the Earth's geological processes, represented by the seven tectonic plates, orchestrate the dynamic dance of continents over millennia
Seven Continent of Earth

Seven Layers of Earth
1. North America
2 South America
3. Australia
4. Asia
5. Africa
6. Antarctica
7. Europe

Eco-systems
While there isn't a strict consensus on the exact number of biomes, many ecological classifications recognize several major biomes on Earth. One common classification system identifies the following seven biomes:
1. Taiga (Boreal Forest): The taiga is a coniferous forest biome with cold winters and mild summers. It stretches across northern regions, including Canada, Russia, and Scandinavia, and is dominated by evergreen trees like spruce, pine, and fir.
3
Tundra: The tundra biome is characterized by cold temperatures, low precipitation, and permafrost (permanently frozen soil). It is found in the Arctic and Antarctic regions and is home to hardy plant and animal species adapted to harsh conditions.
2. Temperate Deciduous Forest: This biome is characterized by temperate climates with distinct seasons. It is found in regions such as the eastern United States, Europe, and parts of Asia. Trees in these forests shed their leaves during the winter.
4.
Grassland (Prairie, Steppe, and Savanna): Grasslands are vast areas dominated by grasses and other herbaceous plants. They are found in regions with moderate rainfall but not enough to support extensive tree growth. Examples include the North American prairies, the African savannas, and the Eurasian steppes.
6
5. Rainforest: Rainforests are lush, biodiverse biomes with high rainfall and warm temperatures year-round. Tropical rainforests are found near the equator, while temperate rainforests are found in cooler regions like the Pacific Northwest of North America.
7.
Desert: Deserts are dry biomes with very little rainfall and extreme temperature variations between day and night. They can be hot deserts, like the Sahara in Africa, or cold deserts, like the Gobi Desert in Asia.
Aquatic (Freshwater and Marine): Aquatic biomes include both freshwater (rivers, lakes, and wetlands) and marine (oceans, seas) environments These biomes are home to a diverse array of aquatic


Seven Metals:



WHAT ARE THE SEVEN SCIENCES?



These seven major Universal Laws explain how energy, frequencies, and vibrations “work.” These laws, which are as real as the law of physics, dictate “the rules to the Game of Life” and how to consciously create the life we want.
Principles
Seven Hermetic Principles
1. The principle of mentalism
“The All is Mind; the Universe is Mental.”
2. The principle of correspondence
"As above, so below; as below, so above.” [...] This principle embodies the truth that there is always a correspondence between the laws and phenomena of the various planes of being and life.”
3. The principle of vibration
"Nothing rests; everything moves; everything vibrates."
4. The principle of polarity
"Everything is dual; everything has poles; everything has its pair of opposites; like and unlike are the same; opposites are identical in nature, but different in degree; extremes meet; all truths are but half-truths; all paradoxes may be reconciled."
5. The principle of rhythm
"Everything flows, out and in; everything has its tides; all things rise and fall; the pendulum-swing manifests in everything; the measure of the swing to the right is the measure of the swing to the left; rhythm compensates."
6. The principle of cause and effect
"Every cause has its effect; every effect has its cause; everything happens according to law; chance is but a name for law not recognized; there are many planes of causation, but nothing escapes the law."
7. The principle of gender
"Gender is in everything; everything has its masculine and feminine principles; gender manifests on all planes.”

These seven apparently different substances of matter are but different states of motion of the one substance.
They are the seven tones of an octave; and there are ten octaves of seven tones each. In the last four octaves are many mid-tones, each one registering its own state of motion. Man calls these various states of motion of the one substance by many names, and they appear to be many substances. The apparent difference between the many is due solely to difference in motion and not to substance. Many states of motion are possible but there are not two substances in the universe. There is only one substance. There can only be one substance. As all states of motion are measurable and are under the absolute control of mind, and as man is mind, man may, with dawning knowledge of causes, change any one state of motion into any other state of motion, and by so doing transmute any one substance into any other one. The granite rock may become gold, or radium, at the will of man."

Walter Russell, The Universal One

Walter Russell - periodic table



The Dougherty Set

Lenses within lenses
the universe is lenticular and harmonies are secreted out of pinches. The chaotic, stochastic, and harmonic all have a place of orientation within 1st principal fundamental emergent properties. The cascading effect of initial conditions is ever present. The rib like alignment of conjugating "SpaceTime" plasma flows exhibit lenses within lenses. All of which are phase conjugate, as in Golden ratio scales of golden ratio
Perhaps multiple nested scales of fresnel lenses focuses light as seen here in the diagram of #thedoughertyset ....
A Fresnel lens is a succession of concentric rings, each consisting of an element of a simple lens, assembled in proper relationship on a flat surface to provide a short focal length. The Fresnel lens is used particularly in lighthouses and searchlights to concentrate the light into a relatively narrow beam At the micro, plank or sub plank scales of the atomic nucleus the Dougherty set predicts particles to be nothing more than overlapping lenses which are all composed of the spherical nature of light.


White light fragments and freys into many different types of waves including helicon waves. When spheres overlap, (lensing the white light) it produces birkeland currents When the lensing happens as does on the heliopause a toroidal forest of vortices is formed creating the domino cascade of helical wave nesting and wave interference this is the magneto hydro dynamic geometry of #thedoughertyset

It is interscalar geometry! It also lays out the qualitative and quantitative structures we see in our daily lives ie reality. Using the magnetohydrodynamic geometry of #Thedoughertyset you can see that the field creates the form. The entire toroidal forest cascade seen here is just the repetition of one simple inverse square bessel function. This is how the universe dynamically delivers her goods. It is a process Crystal or a flow.
The Dougherty Set



As one can see this arrangement naturally produces the magnetosphere and the magnetopause of the earth. It also goes so far as to be predictive as to where and why the planets are where they align and spin axis or tilt is also explained and accounted for via the vortexture that the repetition of this bessel function produces.
L i f e o u t o f s o u n d
These sound bodies come into the earth in the forms of large nested z pinche. They then circulate the toroidal Van Allen belts and build up resonance via cyclicity repetition and recursion. This is what the earth eats is sound and the earth speaks to her children and they speak the same language as the heavens. Creatures on earth pop out of the always singing web they make the noises of the web and do the exact dance of the web it's the vortexture.
Every dance is telling us something about the hierarchical strings, every marking on every creature is telling us strange phenomenon in association with the universe.

This is because of the azimuthal or wrap around currents being in counter rotation along cylindrical sheaths creating twin layers or twin sheets. All Cosmic filaments or power lines from one galaxy to another even local solar systems Interstellar and Galactic currents move in this manner and use the descriptive super geometry shown here known as #thedoughertyset. After Donald Scott did a review of the Dougherty set he said this model matches his model and goes deeper into the complex geometries that his model predicts. The name of his model of a birkeland current is a force free field aligned current which is a Bessel function!
The Dougherty Set

The Dougherty Set
within the filaments of birkeland currents!!
AKA, a gaussian Bessel filament. Nature creates such "patterns within patterns" by many recursions of a simple rule, for example, to produce a snowflake. Computer programmes also make fractals by looping through the rule repeatedly, famously producing the abstract Mandelbrot set.
By Buddy James


The Dougherty Set

Above is a mapped out image of the first fundamental filament of magnetohydrodynamic geometry. There is an infinite amount of these fractal filaments that create the frequencies of us. Perturbations in the ether create nested geometric platonic solids and more as they gyroscopically expand and contract within the toroidal cores. The concentric layering of different shells like the mantle and the core on the earth and other planets correspond with the breathing of the geometry as it opens and closes. This allows for creatures on Earth to get larger as well as smaller due to expansion and contraction IE compression and rarification.

er, Interdisciplinary and EU advocate es presents a primer metry is embedded U Model of . Welcome a fresh ed to decode this ponent in ing the Electric


https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-r7vweFUJdM
by Buddy James



Seven Deadly Sins:




Seven Heavens
In religious or mythological cosmology, the seven heavens refer to seven levels or divisions of the Heavens. The concept, also found in the ancient Mesopotamian religions, can be found in Judaism, Christianity, and Islam; a similar concept is also found in some other religions such as Hinduism. Some of these traditions, including Jainism, also have a concept of seven earths or seven underworlds both with the metaphysical realms of deities and with observed celestial bodies such as the classical planets and fixed stars.


The significance of the number 7 is found in various religions and cultures around the world. While not all religions attribute the same significance to the number 7, it is a common theme in many of them. Here are a few examples:

Christianity: As mentioned earlier, the number 7 holds great symbolic significance in Christianity, particularly in the context of the Bible. It is associated with completeness, perfection, and divine significance.
Judaism: In Jewish tradition, the number 7 is also significant. For example, the seventh day of the week is the Sabbath, a day of rest and worship The seven-branched menorah is a symbol of Judaism, and there are references to seven in various Jewish rituals and traditions.
Islam: While the number 7 is not as prominently featured in Islam as it is in Christianity and Judaism, it does hold some significance. For example, in Islamic tradition, there are seven heavens or levels of paradise.
Hinduism: In Hinduism, the number 7 is considered sacred and often appears in religious texts, rituals, and cosmology. There are seven chakras, seven days in a week, and seven sacred rivers, among other references
Buddhism: In some Buddhist traditions, the number 7 is considered auspicious and symbolizes completeness. For example, the Buddha is said to have taken seven steps at birth, and there are references to seven jewels or treasures in Buddhist teachings.
Zoroastrianism: In Zoroastrianism, the ancient religion of Persia, there are references to seven divine beings or archangels called the "Amesha Spentas."
Chinese Culture: In Chinese culture, the number 7 is considered lucky and is associated with good fortune. It is often used in rituals and symbolism, such as the Seven Stars of the Big Dipper.
Native American Religions: Some Native American tribes also attach significance to the number 7 in their spiritual practices and ceremonies. These examples demonstrate that the significance of the number 7 is not limited to a single religion but is a recurring theme in various religious and cultural contexts, often symbolizing completeness, perfection, and spirituality.



Seven in the Bible
The first use of the number 7 in the Bible relates to the creation week in Genesis 1. God spends six days creating the heavens and the earth, and then rests on the seventh day. This is our template for the seven-day week, observed around the world to this day. The seventh day was to be “set apart” for Israel; the Sabbath was a holy day of rest (Deuteronomy 5:12).
Thus, right at the start of the Bible, the number 7 is identified with something being “finished” or “complete.” From then on, that association continues, as 7 is often found in contexts involving completeness or divine perfection. So we see the command for animals to be at least seven days old before being used for sacrifice (Exodus 22:30), the command for leprous Naaman to bathe in the Jordan River seven times to effect complete cleansing (2 Kings 5:10), and the command for Joshua to march around Jericho for seven days (and on the seventh day to make seven circuits) and for seven priests to blow seven trumpets outside the city walls (Joshua 6:3–4). In these instances, 7 signifies a completion of some kind: a divine mandate is fulfilled.
Interestingly, man was created on the sixth day of creation. In some passages of the Bible, the number 6 is associated with mankind. In Revelation “the number of the beast” is called “the number of a man ” That number is 666 (Revelation 13:18). If God’s number is 7, then man’s is 6. Six always falls short of seven, just like “all have sinned and fall short of the glory of God” (Romans 3:23) Man is not God, just as 6 is not 7
Series of seven things crop up often in the Bible. For example, we find seven pairs of each clean animal on the ark (Genesis 7:2); seven stems on the tabernacle’s lampstand (Exodus 25:37); seven qualities of the Messiah in Isaiah 11:2; seven signs in John’s Gospel; seven things the Lord hates in Proverbs 6:16; seven parables in Matthew 13; and seven woes in Matthew 23
Multiples of 7 also figure into the biblical narrative: the “seventy weeks” prophecy in Daniel 9:24 concerns 490 years (7 times 7 times 10). Jeremiah 29:10 predicted the Babylonian Captivity would last for seventy years (7 times 10). According to Leviticus 25:8, the Year of Jubilee was to begin after the passing of every forty-ninth year (7 times 7).
Sometimes, the symbolism of 7 is a great comfort to us: Jesus is the seven-fold “I AM” in the Gospel of John. Other times, it challenges us: Jesus told Peter to forgive a wrongdoer “seventy times seven” times (Matthew 18:22, NKJV). And then there are passages in which the number 7 is associated with God’s judgment: the seven bowls of the Great Tribulation, for example (Revelation 16:1), or God’s warning to Israel in Leviticus 26:18.
Speaking of the book of Revelation, the number 7 is used there more than fifty times in a variety of contexts: there are seven letters to seven churches in Asia and seven spirits before God’s throne (Revelation 1:4), seven golden lampstands (Revelation 1:12), seven stars in Christ’s right hand (Revelation 1:16), seven seals of God’s judgment (Revelation 5:1), seven angels with seven trumpets (Revelation 8:2), etc. In all likelihood, the number 7 again represents completeness or totality: the seven churches represent the completeness of the body of Christ, the seven seals on the scroll represent the fullness of God’s punishment of a sinful earth, and so on. And, of course, the book of Revelation itself, with all its 7’s, is the capstone of God’s Word to man. With the book of Revelation, the Word was complete (Revelation 22:18).
In all, the number 7 is used in the Bible more than seven hundred times. If we also include the words related to seven (terms like sevenfold or seventy or seven hundred), the count is higher. Of course, not every instance of the number 7 in the Bible carries a deeper significance
Sometimes, a 7 is just a 7, and we must be cautious about attaching symbolic meanings to any text, especially when Scripture is not explicit about such meanings However, there are times when it seems that God is communicating the idea of divine completeness, perfection, and wholeness by means of the number 7.

WHY THE LAYERS?

C o n c e p t f r o m V i d e o
Our atmosphere has seven or eight distinct layers before it meets the magnetosphere which itself has seven or eight layers.
If you believe nothing else in the Universe is alive, or stars are not conceived and born, or Love and Yearning are not powerful forces for galaxies and stars and cells all based upon precisely zero

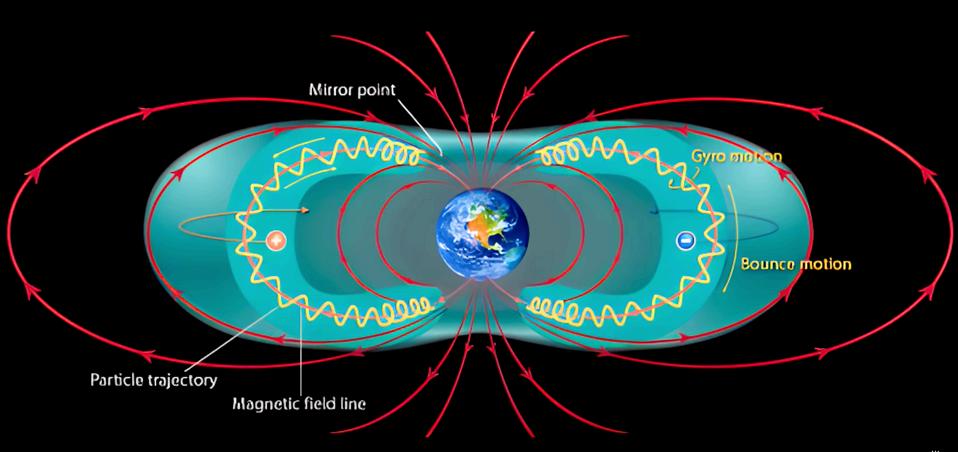
The function of these layers complete our connection to the solar wind. Otherwise, it would crash onto the surface of the Earth creating a mix of ceramic and molten glass. U N I V E R S E I S R S


OUR FIRST QUESTION SHOULD BE, WHAT FUNCTION DOES THIS SERVE?


WATCH THE VIDEO

Thunderbolt ProjectMore videos about our electric universe

https://sciencetosagemagazine.com/michael-clarage-ph-d-the-living-cosmos/
ELECTRIC IDEAS


Creation
IN THE WAVE LIES THE SECRET OF CREATION.
WALTER RUSSELL
E A R E O N E
WE ARE THE WAVE





PARTICLES OF LIGHT




WE LIVE IN THE WAVE & CURRENTS
“To every thing there is a season, and a time to every purpose under the heaven: A time to be born, and a time to die; a time to plant, and a time to pluck up that which is planted.” King Solomon




AIR - LAND - SEA



COLLECTIVE BRAIN
NETWORKS AND CIRCUTS




DENDRITES TO NERVOUS SYSTEMS SAME




RHYTHM CURRENT



RIBS TO SPINES FORMULA
Seven Cervical Vertebrae: In humans and some other mammals, the neck, or cervical region of the spine, typically consists of seven vertebrae.

