2 minute read
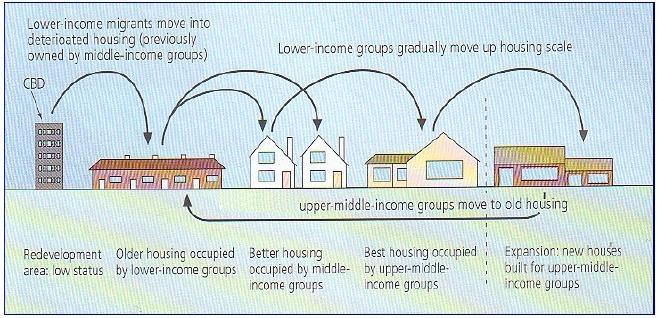
Figure 5 Process of transformation
Figure 5 Process of transformation
2.2 Modern Concern about Preserving Built Heritage
Advertisement
The notion of heritage as artefacts and structures from the past, as well as regulations connected to their preservation, have grown in parallel with modernity, making this a vital requirement and obligation of modern society. The purpose of this protection has been identified as humanity's cultural legacy since the seventeenth century, and this has increasingly expanded to cover not just old landmarks and historical works of art, but also complete ideas for a range of new values developed in recent decades.
For instance, in its medium term programme of 1989, UNESCO defined the full scope of such heritage (25 C/4, 1989:57) in the following:
“The cultural heritage may be defined as entire corpus of material signs - either artistic or symbolic - handed on by the past to each culture and therefore to the whole of humankind. As a constituent past of the affirmation and enrichment of cultural identities as a legacy belonging to all humankind, the cultural heritage gives each particular place its recognizable features and is the storehouse of human experience. The presentation and the preservation of the cultural heritage are therefore a cornerstone of any cultural policy.”
Weather, the ageing process, and consumption through usage are all factors that contribute to the destruction of constructed heritage. Buildings can also be altered as a
result of changes in function, taste, or fashion. Apart from it, many historic structures and pieces of art are in risk of being damaged as a result of natural disasters. Aside from that, numerous historical structures are under jeopardy as a result of violent conflicts, purposeful destruction, and demolition by humans.
One of the primary problems and duties of modern civilization is the preservation, restoration, and conservation of heritage, as well as regulations connected to their protection. These concepts and policies have arisen as a result of a process. The current conservation movement has been highlighted.
2.2.1 Impact of Technology
Technology-driven civilizations and industrial progress have had a significant influence on traditional communities, leading to the emergence of the concept of tradition and cultural preservation. Modern architectural practice has resulted in the loss of individuality in structures, since the rise of industrial society showed a total rejection of past references.
2.2.2 Saving Cultural Identity
Technology was crucial in the revitalization of the urban environment, serving as a medium for the advancement of new ideas and interactive communication. The enormous
population growth in major cities, on the other hand, has had the opposite impact.
Anthony M. Tang, the former New York City Landmarks Preservation Commissioner, stated the following in an interview published in Heritage magazine, “We have become an urban civilization. In the process we are becoming the civilization of the disappearing cultural roots as the rapid expansion of the modern metropolis renders widespread devastation of architectural patrimony. What does it mean when we lose one handsome familiar building? When an express way cutting through the city centre









