

PROLOGUE
Time has left us history, and also has pushed us to the future. History has gradually withdrawn from our real life, becoming fragile and dilapidated, but increasingly important. The future shields us from the history, but it also endows us to recall the past. The history should become clearer in the years to come.
But the reality is not so. Our lifestyle is erasing the traces of history, and this process is accelerating. The construction of cities seems to be racing against nature. We are striving to build, while nature is rapidly recycling our achievements. When the future gives us more powerful influence, urban designers should make a choice between accelerating creation and mitigating loss.
01 ZEN BORN UNDERGROUND
RELIGIOUS COMPLEX DESIGN
Date: 7/2022-10/2022 Area: 8.87ha Nanjing, China
02 SALVAGE THE HARBOR
COASTAL PUBLIC SPACE DESIGN
Date: 6/2021-12/2021 Area: 18.9ha Helsinki, Finnland
03 OTHER WORKS
SOCIAL RESEARCH
- The Integration Degree of Nanjing International Community ACADEMIC WORK
- Heritage Centered Planning & Design - Nanjing Yuecheng Heritage Park and Museum
GIS APPLICATION


- Green Space Design Based on Ecological Sensitivity Analysis
- "Double Evaluation" of National Territory Development Plan
MANUAL MODEL
- Laser Cutting

- Chess Based on the Contradiction between Modernism and Postmodernism
Date: 9/2020-6/2022
01 ZEN BORN UNDERGROUND
Religious Complex Design

Area: 8.87ha
Type: Summer Workshop
Date: 7/2022-10/2022
Instructor: Tian Li
Keywords: Buddhism, Multi-function, Urban Regeneration
Nowadays, with the rapid development of society, people suffer from spiritual emptiness caused by highly pressured urban life while enjoying rich material life. Thus, the tranquil atmosphere and spiritual purification provided by Buddhist Zen spaces become increasingly important.
The Qingliang Mountain in Nanjing is a small natural mountain. Historically, it was once an important Buddhist site. There were Buddhist buildings in the Ming and Qing Dynasties on the hill, making a robust Buddhist atmosphere. This design aims to create an open public Zen space, and explores the development potential of Qingliang Mountain underground space. Building Zen space underground can protect cultural heritages and avoid suffering from high temperatures.
Under the Qingliang Mountain, this design uses the parameterized technique to integrate the Buddhist Zen space with the daily living space through the combination of carefully designed units, and constructs an underground Zen complex.
Qingliang Mountain, Nanjing, Jiangsu, ChinaNanjing, Jiangsu

Qingliang Platform
Buddhist temples were built on the platform. It was mentioned in many important Chinese poems.
 Military Fortress in The Six Dynasties Buddha Temple in Tang Dynasty Important Place for Literati Tourist Attraction in Modern
Jiangsu, China
Qingliang Temple
A Buddhist temple built in the Qing Dynasty which was the Buddhist Center in Nanjing
Chongzheng Academy The academy was built in the Ming Dynasty with a style of Jiangnan gardens.
Saoye Building
Military Fortress in The Six Dynasties Buddha Temple in Tang Dynasty Important Place for Literati Tourist Attraction in Modern
Jiangsu, China
Qingliang Temple
A Buddhist temple built in the Qing Dynasty which was the Buddhist Center in Nanjing
Chongzheng Academy The academy was built in the Ming Dynasty with a style of Jiangnan gardens.
Saoye Building
Mudule-A





















Mudule-D



COMPOSITION 1 COMPOSITION 2

of




































COMPOSITION 3








After parametric design operations based on the limits of the site boundary, we generate several complexes composed of various units, and select the most appropriate one. The whole complex consists of 2701 units. The large courtyard units are arranged consecutively, with the ends wrapped up by the Buddha Hall space to form the core Zen space. Around the core, spaces are the external service modules and living modules composed of the small exhibition, office, and living space in sequences or units.




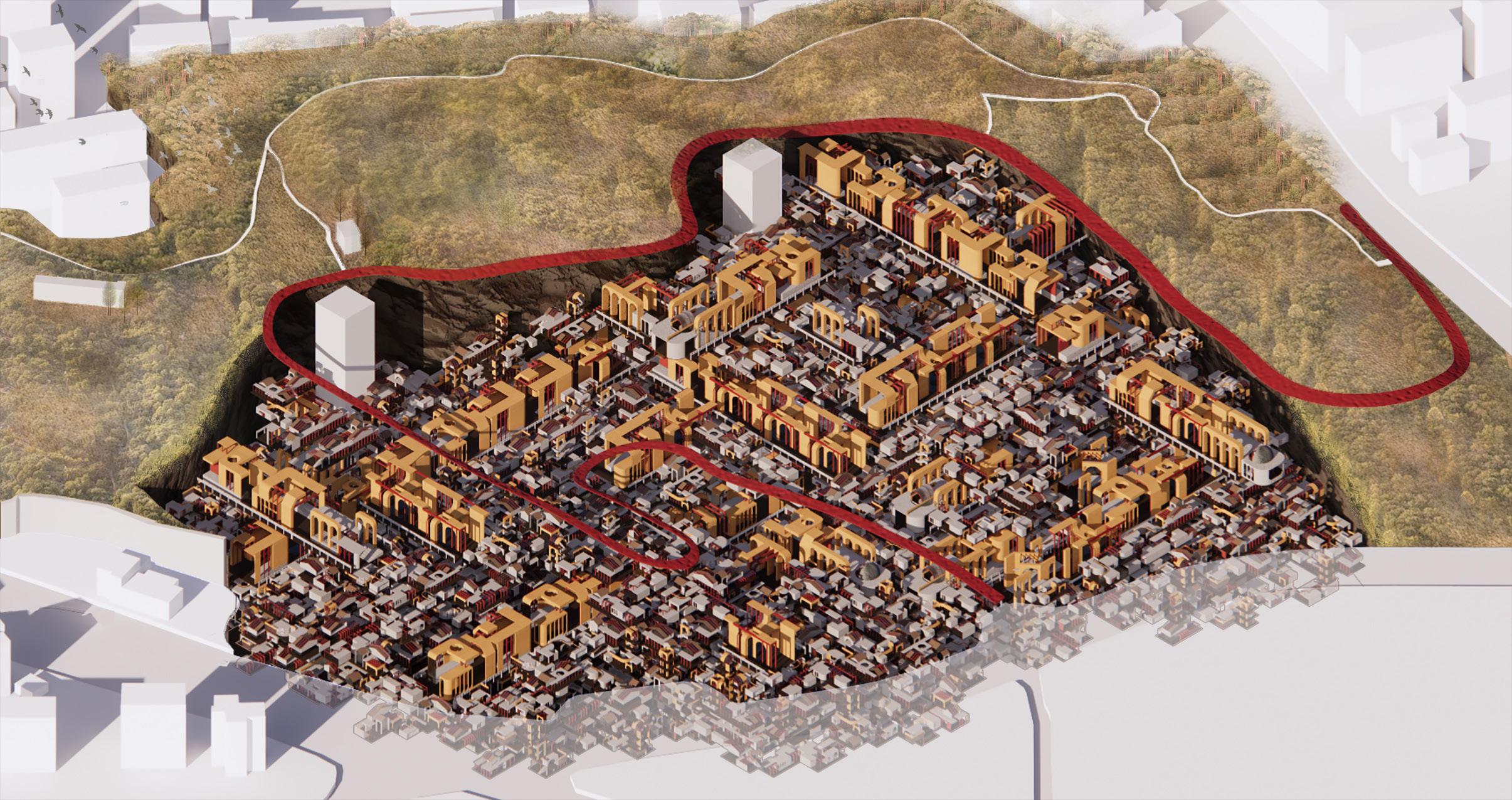
FUNCTION CONFIGURATION

 Residence (839) Courtyard (63)
Vertical Traffic (296) Buddha Hall (22) Exhibition Area (641) Working Area (840)
Residence (839) Courtyard (63)
Vertical Traffic (296) Buddha Hall (22) Exhibition Area (641) Working Area (840)





02
SALVAGE THE HARBOR
Coastal Public Space Design
South Harbor, Helsinki, Finland
Area: 18.9ha
Type: Competition Date: 9/2021-6/2022
Instructor: Wenfei Zhang
Keywords: Rain Flood, Terrain, Revitilization
Helsinki South Harbor was once the transportation center of Helsinki, a port city. The construction of the West Port and the port of Vuosaari has reduced the transportation function of the South Port. South Harbor, located in the city center, is now losing its vitality.In addition, the sea level is rising caused of climate warming, and the Baltic Sea is also affected. Helsinki South Harbor is facing the risk of being submerged.
The project aims to transform the coastal public space of Helsinki South Harbor into an open space with strong accessibility, comfort, and attraction. At the same time, terrain design is used to cope with the sea level rise in the future to 2100.
To integrate the local characteristics of Helsinki into the design, we extracted the sea ice phenomenon along the coast of Helsinki. We made a topology of the sea ice morphology to generate the terrain used in the design.

site train station proposed train station subway station train route planned train route subway route highway tram line ship route for passenger ship route for freight water level, 2050 water level, 2100 historical architecture urban axis



“Our
“Vuosaari
easily handle a
MAPPING OF THREE PROBLEMS IN SITE SCALE PROBLEM ANALYSIS







[Poor Accessibility]




THE DERIVATION OF THE PLAN STRUCTURE OF SITE PLAN

Relocate the road to expand the coastal area and to connect outside green space.
Create an overall three-level elevation difference to tackle the flood issues.




Create continuous hard ground to provide bicycle lanes.
Response to flooding by smallscale topographic change.


Connect outside green space and invite green inside.
Waterfront platforms provide better accessibility to the sea.



Existing Bicycle Lanes
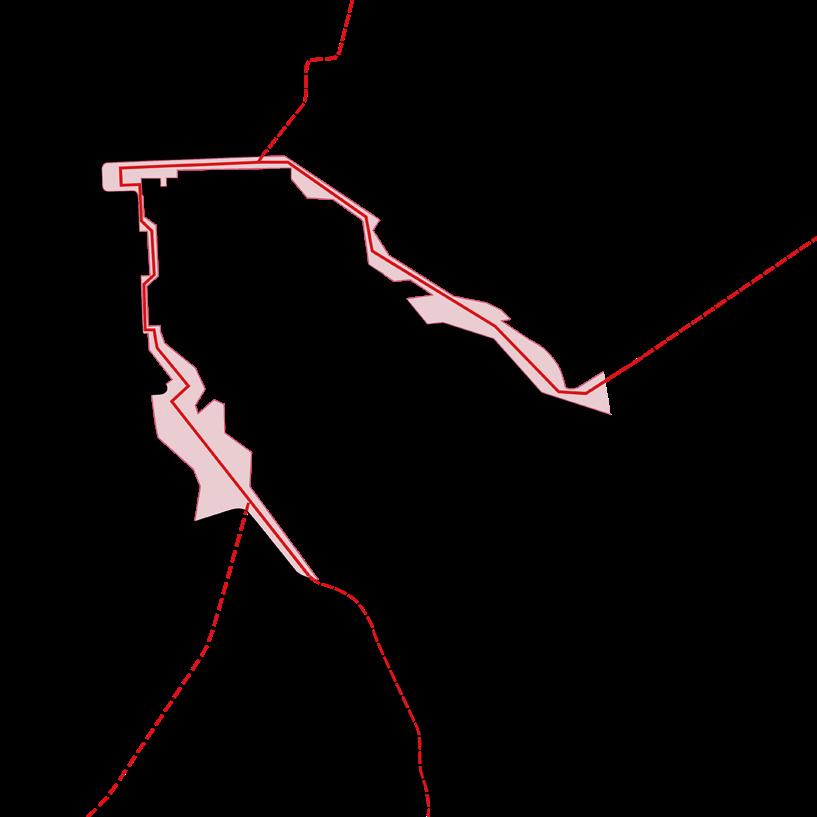

Proposed Bicycle Lanes Connection of Ecology Hard Ground



Green Space
Floating Island
Seriously Flooded Area
Slightly Flooded Area



































1.Helsinki Market Square
2.Havis Amanda
3.Helsinki Market Hall
4.Sandy beach
5.Marine trestle
6.Square connected
7.Port of Helsinki

8.Small ship wharf
9.Indoor
10.Green
11.Floating
12.Type
SEA LEVELS IN PRESENT AND FUTURE SCENARIOS





[Sea level before




in
level in 2050 after
[Sea level in
after
SEA LEVELS OF DIFFERENTS TERRAINS AFTER DESIGN







[Normal
in
in
level in 2050]
level in 2100]
IMPORTANT AREA DETAIL RENDERING

In the southwest of the site is an important landscape, Tahtitorninvouri Park, which is separated from the coast by a driveway. This design will build an elevated green square to connect Tahtitorninvouri Park with the coast. An underpass tunnel will be used to maintain the driveway's continuity and improve the beach's greening continuity.

The green park on the site's north side has varied terrain, including rolling green space and interlaced footpaths combined with green space in the shape of broken ice. In addition, there are floating islands on the shore, which cannot be submerged while the sea level changes, and also simulate sea ice in shape.

 [Green Square Connected with the Tahtitorninvouri Park ]
[Green Park in the North of the Shore]
[Human Visual Perspective Drawing From Green Square]
[Human Visual Perspective Drawing from Upper Greenland]
Green Square Undercrossing Roadway Green Square Coastal FootpathTahtitorninvouri Park
Floating Island Coastal Footpath with Greenland Upper Greenland with Interlaced footpath Urban Area
[Green Square Connected with the Tahtitorninvouri Park ]
[Green Park in the North of the Shore]
[Human Visual Perspective Drawing From Green Square]
[Human Visual Perspective Drawing from Upper Greenland]
Green Square Undercrossing Roadway Green Square Coastal FootpathTahtitorninvouri Park
Floating Island Coastal Footpath with Greenland Upper Greenland with Interlaced footpath Urban Area
Social Research: The Integration Degree of Nanjing International Community
Abstract:
With the rapid process of social globalization, the international community has become an essential carrier of many social phenomena in Nanjing. Cultural differences lead to of separation between immigrants and between immigrants and aborigines to certain degrees. Concerning such phenomena, this report combines and analyzes the status quo and internal determinants of the degree of integration of international communities from the perspective of integration and provides suggestions for constructing integrated international communities.
Technical Roadmap: Research background
Internationalization of the international community
Policy support Mixed residence Lack of research
Site selection
Typical international community in Nanjing
Youth Olympic Village Nanxiu Village Dongfang Tianjun
Model building
Social integration indicators
Spatial integration Economic integration Social integration Cultural integration
Investigation and analysis
living space
Activity space
Residential status Income status Education status
Working status
Social participation Social relations Public Service
Identification Cultural adaptation City comment
1. Spatial Integration
Analysis of living and activity space

Living space Activity spaceSite Youth Olympic Village Nanxiu Village Dong fang Tianjun
2.Economic Integration
Example of analysis results: residential status

Site Olympic Village Nanxiu Village Dongfang Tianjun
Access to housing Form of Living
3.Social Integration
Example of analysis results: social participation










Site Olympic Village Nanxiu Village Dongfang Tianjun gain community sevices join community activity
4.Cultural Integration
Example of analysis results: cultural adaptation
Rent Dormitory Purchase Live alone Share Family
Summary of economic integration
Based on the questionnaire survey results, we can judge that Nanxiu Village, where housing purchase occurs, has the highest degree of integration in living conditions, followed by Dongfang Tianjun, where people live with their families.
Regarding working conditions, we analyzed the occupation and enterprise type of residents, the highest degree of integration is among the residents of Nanxiu Village, who take Chinese students in their social network. And the second is the residents of the Youth Olympic Village who work with Chinese colleagues.







Summary of social integration
Few or no
Occasional Often
Regarding social participation, the integration of foreign residents in Dongfang Tianjun and Nanxiu Village is significantly higher than in Youth Olympic Village.To a certain extent, it is affected by their living style and occupation
Few or no Occasional Often
In social relations, we mainly collect data on the number of Chinese friends of non-Chinese residents. The overseas students in Nanxiu Village have more Chinese people in social network.
In terms of access to public service facilities, the Youth Olympic Village has the highest degree of integration, which may be because the Youth Olympic Village was initially built as a city node.
Summary of cultural integration
Optimization strategy
Main conclusions Problems Optimization strategy
The integration evaluation indicators in the research and analysis part refer to the EU social integration indicators.
Site location

Area:9.5ha
Korean families
Tianjun
Non Chinese resident
Summary of spatial integration
Based on the questionnaire survey results, non-Chinese residents tend to gather in apartments under the premise of foreign students or international apartments. At the same time, the environment of pure commercial housing can promote the integration of residential space to a greater extent than apartments.

Site Olympic Village Nanxiu Village Dongfang Tianjun Language Mastery Communication barriers
Summary and Optimization Strategies
Few or no Primary Mastered
From the perspective of cultural adaptation, the integration degree of Nanxiu Village is higher than that of the Youth Olympic Village and Dongfang Tianjun. Students have the highest cultural adaptability, followed by company employees, housewives and children have the least.
High
Low General
Both social evaluation and identity recognition levels show that Nanxiu Village has a higher integration degree than Dongfang Tianjun and Youth Olympic Village. This is affected by the acceptance of community services and participation in community activities.



Regarding spatial equity, most international communities passively provide space for the integration of local and foreign residents, lacking consideration of the integration needs of migrant groups. From the economic and social aspects, the integration of non-Chinese residents is primarily affected by their occupations and enterprises. From the cultural aspect, the degree of integration of non-Chinese residents depends on the demand for social relations and the degree of cultural barriers.
Area:14ha
Area:0.5ha
overseas students
Nanxiu village
Employees of international enterprises
Youth Olympic village
Although there is a certain degree of integration difference in residential space due to different housing types, the equal use of public space is essential to promote integration.The public areas of different sizes, types, and service objects provided by various communities are used by residents of various countries simultaneously.

Optimization strategies:
1. Create a diversified environment. Hold Sino foreign exchange activities according to the immigration background of various international communities, and create more space for quick social events.
2. Promote community renewal. Create residential and public spaces that meet the needs of migrant groups.
3.
service facilities. Implant public service facilities within the 15-minute life circle.
Academic Work: Heritage Centered Planning & Design - Nanjing Yuecheng Heritage Park and Museum Mapping Overview















This design promotes Yuecheng Site’s potential, making it an open heritage park. The Site is relatively low in openness. To invite visitors, the design forms a wedge-shaped open green space, having the Qinhuai River and the Zhonghua Gate to its north, echoing other iconic heritages in the cityscape. Another key of the project, the Yuecheng Heritage Museum, locates at the center of the Heritage Park to the Zhonghua Gate, providing a panoramic view. The southeast and northwest sides of the site are mainly equipped with supporting functions such as residential buildings, commercial blocks, and archaeological research institutes. The buildings’ architectural forms were influenced by old Nanjing's styles, mainly sloping roofs. The junction between housing and the site park is the commercial street. The courtyard-style architectural layout restores Nanjing's historical memory.



Generation of structure

The Heritage Museum locates on the axis of the Heritage Park. The design adopts landscaping elements, so the park’s green space can be continued in the museum. In addition to the exhibition space provided inside the museum, it is an excellent sight-viewing platform. Visitors can have panoramic views of the Heritage Park, Zhonghua Gate, and Nanjing Porcelain Tower in any exhibition hall area.
 Zhonghua Gate
Porcelain Tower
Yuecheng Site Yudai River
Zhonghua Gate
Porcelain Tower
Yuecheng Site Yudai River
GIS Application: Green Space Design Based on Ecological Sensitivity Analysis






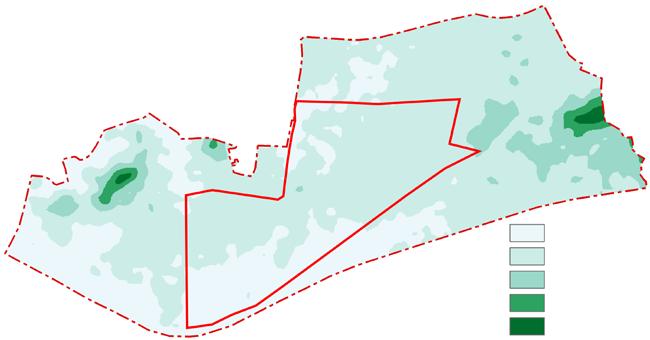
The project is an urban design for a new town center of an area of 160ha in Nanjing, China. ArcGIS is used to analyze the site's green space, water, elevation, and slope for ecological protection in planning urban green space and selecting the area with high environmental sensitivity to set green space.




Manual Model: Laser Cutting

GIS Application: "Double Evaluation" of National Territory Development Plan

Evaluation Process:
Importance of ecosystem service Sensity
Importance of
protection
water
Water

Suitability of agricultural production
Suitability of urban construction
Manual Model: Chess Based on the Contradiction between Modernism and Postmodernism
This project is a chess game based on the topological form of two groups of modernist and post-modernist architectures. We learn the differences between the two architectural trends during the production process.

The shape of the chess pieces is carved with rubber stamps, then turned over with silica gel, and finally watered with drops of glue to shape to sense the architectural shape by hand.
The chessboard is also the display cabinet and storage box of chess pieces, with built-in drawers. The internal chess pieces can be observed on the surface of the acrylic. The production process of the chessboard is laser cutting and manual assembly.

