




























In a world where the complexities of food security, climate change, and environmental sustainability intertwine more than ever, we are proud to present this special issue of Saudi Sustainability Magazine, dedicated to the passionate and innovative members of the World Food Forum's Near East North Africa Youth Policy Board This unique collaboration highlights the crucial role that youth play in shaping sustainable food systems, particularly within the diverse contexts of the Near East and North Africa (NENA) region.
As the advertising of sustainability continues to evolve, young leaders are emerging as catalysts for change, demonstrating remarkable resilience and creativity in advocating for solutions that are both effective and inclusive. The voices of these young policymakers remind us that the future of our food systems lies in the hands of those who are most affected by them the youth They are not just participants in the conversation; they are empowering their communities and influencing policy discussions to drive meaningful, lasting change.
Throughout this special issue, you will discover a series of articles, interviews, and insights that showcase the dynamic initiatives led by the Youth Policy Board Members. From innovative agricultural practices to community-driven programs addressing food waste, these initiatives embody a commitment to balancing progress with sustainability We invite you to explore their stories, learn from their experiences, and engage in the discourse surrounding sustainable food policies that can benefit both people and the planet.


As we continue to face pressing global challenges including food insecurity, economic disparity, and ecological degradation it becomes ever clearer that collaboration across generations is essential. The youth today are equipped with the knowledge, tools, and passion needed to rethink and redesign the future of food systems By listening to their ideas and supporting their initiatives, we can pave the way for resilient, sustainable, and equitable food systems that nourish our communities and protect our environment for generations to come
We hope this special issue inspires you to join the conversation, embrace innovative strategies, and champion the transformative ideas put forth by the Youth Policy Board Members Together, we can work towards a more sustainable and just world, fueled by the energy and ingenuity of our young leaders
Thank you for being part of this journey towards sustainability Let us move forward together, united by our shared goals and a collective vision for a better future

Dr. Mohammed S. Al-Surf SPSA Founder & President
Saudi Arabia faces the problem of a lack of professionalism and consistency in the emerging field of sustainability in the country. Currently, there are no standardized certifications, professional designations, or credentials for sustainability professionals in the country
This creates issues around consistency in job titles, salaries, and the scope of work for those in sustainability roles. It also limits career progression and credibility for sustainability professionals
To address this problem, SPSA aims to establish a professional membership program with designations and credentials in sustainability
This program will define standard job titles, salary bands, and competency requirements for different roles in the sustainability field. It will provide pathways for career progression through continuous professional development. The program will also establish SPSA as a thought leader in the space and build credibility for the sustainability profession in Saudi Arabia
the lack of professional standards in sustainability creates problems for both employers and professionals in Saudi Arabia. By developing a robust professional membership program, SPSA can help define and elevate the sustainability profession, enabling its members to have successful and impactful careers

Key problems facing sustainability professionals and organizations in Saudi Arabia are:
A lack of awareness about sustainability best practices which limits adoption of sustainability initiatives
The absence of a professional membership organization to support, connect and set standards
Difficulty for organizations in determining and accessing sustainability expertise
Untapped opportunities for global partnerships and collaboration on sustainability issues

Prosperity
Peace
Partnership
Giving priority to the welfare of People of all backgrounds, ethnicity, religion, etc.
Protect our planet's natural resources and climate for future generations.
Ensure prosperous and fulfilling lives in harmony with nature.
Foster peaceful, just and inclusive society.
Implement the agenda through a solid global partnership.
Create a thriving community of sustainability professionals who are equipped with the knowledge, resources, and connections needed to drive positive change towards a more sustainable future in Saudi Arabia
Creating an international multi-sector platform in Saudi Arabia that adopts sustainable measures and collaborates to find solutions to today’s most pressing economic, environmental and socio-political problems Mission:
Established
Members from 92+ Countries

10,000+ Members
































SPSA EDITORIAL
The 10 Commandments of Sustainability are the fundamental principles of creating a sustainable world Knowing these 10 principles is essential for understanding the future of our planet and the actions we can take to ensure its health. To truly understand sustainability, it's important to know the 10 Commandments of Sustainability and how to apply them to our lives
As we continue to witness the effects of climate change and the depletion of natural resources, the importance of sustainability has become more apparent than ever before. The 10 Commandments of Sustainability serve as a guide for individuals and organizations to adopt sustainable practices and reduce their impact on the environment However, before we delve into the specifics of these commandments, it is essential to understand the concept of sustainability and its significance Sustainability refers to the ability to meet our present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs It encompasses economic, social, and environmental aspects and requires a balance between these three pillars By adopting sustainable practices, we can ensure that we leave a habitable planet for future generations and promote a healthier and more equitable world. In this blog, we will explore the 10 Commandments of Sustainability and how they can be applied in our daily lives to create a more sustainable future

Sustainability is a crucial concept that has gained significant attention in recent years. It is a way of living that ensures the well-being of the environment, society, and economy There are ten commandments of sustainability that guide individuals and organizations towards a sustainable future These commandments include reducing, reusing, and recycling resources, conserving water and energy, supporting local businesses, reducing carbon footprint, promoting sustainable transportation, protecting biodiversity, and adopting sustainable practices in daily life By following these commandments, individuals can contribute to a sustainable future and reduce their impact on the environment. It is essential to understand and implement these commandments to ensure a sustainable future for generations to come As global citizens, it is our responsibility to take care of the planet and preserve its resources By incorporating sustainable practices in our daily lives, we can create a better future for ourselves and the planet.
The first commandment of sustainability is to refuse, reduce, reuse, recycle and rot This commandment is crucial in promoting a sustainable lifestyle Refusing is the act of refusing to use an item or service that car harm the environment or deplete our resources For example, the use of single plastic for example is one of the simple ways to practice sustainability Reducing the amount of waste we produce is the first step towards sustainability. We can do this by avoiding buying things we don't need, choosing products with minimal packaging, and using reusable bags, bottles, and containers Reusing items instead of throwing them away is another way to reduce waste For example, we can reuse glass jars as storage containers, use old clothes as rags, or donate items we no longer need Recycling is the final step in this commandment Recycling helps to conserve natural resources and reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills. It's important to ensure that we recycle correctly by separating materials and avoiding contamination. The final R stands for Rot where it basically is focusing on composting and letting food waste rot and benefit the landscape and vegetation By following the first commandment of sustainability, we can make a significant impact on the environment and move towards a more sustainable future

The Second Commandment of Sustainability is "Conserve Resources." This commandment is all about taking care of the earth's natural resources and using them wisely. We need to be mindful of the fact that these resources are finite and that we need to use them in a way that ensures their availability for future generations This means reducing our consumption of non-renewable resources like fossil fuels, conserving water, and protecting biodiversity We can do this by adopting sustainable practices like using renewable energy sources, reducing waste, and recycling We can also support businesses and organizations that prioritize sustainability in their operations. By conserving resources, we not only protect the planet, but we also ensure that we have access to the resources we need to live healthy and fulfilling lives. So, let us make a conscious effort to conserve resources and leave a better world for future generations

The Third Commandment of Sustainability, "Respect Nature," urges us to recognize the importance of the natural world and to take actions to protect it. It reminds us that we are not the only inhabitants of this planet and that we must coexist with other living beings. This commandment encourages us to be mindful of our actions and the impact they have on the environment It asks us to take responsibility for our actions and to make choices that are sustainable and respectful of nature This can include reducing our carbon footprint, conserving water, recycling, and supporting environmentally-friendly practices. By respecting nature, we can help to preserve the planet for future generations and ensure that the natural world continues to thrive. It is our duty to protect the environment and to live in harmony with nature, and the Third Commandment of Sustainability reminds us of this important responsibility

The Fourth Commandment of Sustainability is to preserve biodiversity This commandment is crucial in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem Biodiversity refers to the variety of living organisms that exist on earth. It includes plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms. Biodiversity is essential for the survival of all living organisms, including humans. It provides us with food, medicine, and other resources that are necessary for our survival However, human activities such as deforestation, pollution, and overfishing are threatening the biodiversity of our planet It is our responsibility to protect and preserve the diversity of life on earth We can do this by supporting conservation efforts, reducing our carbon footprint, and promoting sustainable practices By preserving biodiversity, we can ensure a healthy and sustainable future for ourselves and generations to come.

The fifth commandment of sustainability is often overlooked, but it is just as important as the others "Promote Equity and Fairness" is a call to action for us to ensure that everyone has access to the resources they need to live a sustainable life. This includes access to clean water, healthy food, and safe housing. It also means that we need to address systemic inequalities that prevent certain groups from accessing these resources This commandment reminds us that sustainability is not just about protecting the environment, but also about creating a more just and equitable world for all It is important to examine our own privilege and biases and work towards dismantling systems of oppression that perpetuate inequality By promoting equity and fairness, we can create a more sustainable future for everyone.

The Sixth Commandment of Sustainability is to manage waste responsibly. This commandment emphasizes the importance of reducing, reusing, and recycling waste to minimize its impact on the environment Managing waste responsibly involves taking a proactive approach to waste reduction, starting with reducing the amount of waste generated in the first place. This can be achieved by using reusable products, buying products with minimal packaging, and choosing products made from sustainable materials. Reusing items instead of discarding them is another way to manage waste responsibly. Recycling is also an essential part of waste management, as it reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills and conserves natural resources. It is crucial to dispose of hazardous waste properly, such as batteries and electronics, to prevent them from polluting the environment. By managing waste responsibly, we can reduce our impact on the environment and create a more sustainable future for generations to come.

The Seventh Commandment of Sustainability is often overlooked, but it is just as important as the others This commandment urges us to support local economies, which means buying from local businesses and farmers instead of multinational corporations. This not only helps to stimulate the local economy, but it also reduces the carbon footprint of transportation and supports sustainable agriculture By supporting local businesses, we can ensure that our money stays within our community and helps to create jobs and support small businesses It also encourages the growth of sustainable practices, as local businesses are more likely to prioritize ethical and environmentally friendly practices Supporting local economies can also lead to a stronger sense of community and connection to the people and places around us. So, the next time you need to make a purchase, consider supporting a local business instead of a big corporation. It may seem like a small action, but it can have a big impact on the sustainability of our communities

The Eighth Commandment states that we should utilize the Power of Education and Awareness in Creating Sustainable Communities Education and awareness are essential in creating sustainable communities. It is not enough to just know about the issue of sustainability; we need to understand its significance and make conscious efforts to implement sustainable practices. Education provides us with the necessary knowledge and skills to make informed decisions and take action towards sustainability It empowers us to make positive changes in our daily lives and in our communities Awareness, on the other hand, helps us to recognize the impact of our actions and the importance of sustainable practices Through awareness, we can identify the areas where we need to make changes and take steps to reduce our ecological footprint. Education and awareness also play a vital role in inspiring others to join the sustainability movement, creating a ripple effect of positive change. We can spread the message by sharing our knowledge and experiences with others, encouraging them to take action towards a sustainable future Together, we can create a more sustainable world for future generations

As consumers, we have the power to demand transparency from the fashion industry. It is our responsibility to ask for information about the materials used to make our clothes and the conditions in which they were produced By doing so, we can hold companies accountable for their actions and encourage them to make more sustainable choices We should also support brands that are transparent about their practices and are actively working to reduce their environmental impact As the fashion industry is one of the largest polluters in the world, we cannot afford to ignore the impact of our choices. It is time for us to prioritize sustainability over fast fashion and demand transparency from the brands we support. Together, we can create a more sustainable future for the fashion industry
Transparency is a key factor in sustainable business practices It allows stakeholders to hold companies accountable for their actions and ensures that businesses are operating in an ethical manner. Transparent reporting is especially important in the context of sustainability because it allows customers, investors, and other stakeholders to see the environmental impact of a company's operations This includes factors such as greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and waste management By providing this information, companies can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and encourage others to follow suit
Furthermore, transparent reporting can also help companies identify areas where they can improve their sustainability practices. By analyzing data and identifying areas where they are falling short, companies can develop strategies to reduce their environmental impact and become more sustainable This can include investing in renewable energy, reducing waste, and improving supply chain management

Inclusion is a critical element of sustainable development and it's vital this blog concludes with this commandment. It is not just about diversity and representation; it is about ensuring that everyone, regardless of their social status, gender, ethnicity, or religion, has an equal opportunity to participate in decision-making processes that affect their lives and communities Inclusion is about recognizing and valuing the unique perspectives and contributions of every individual, and harnessing their potential to create a more sustainable and just world
Inclusive societies are more resilient and adaptable to change, as they draw on the strengths and skills of all members They also tend to be more innovative and creative, as they foster an environment of collaboration and cooperation In contrast, exclusion and inequality are major barriers to sustainable development, as they lead to social unrest, political instability, and environmental degradation Inclusive policies and practices are, therefore, essential for achieving the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals and building a more sustainable and equitable future for all.
As individuals, we can promote inclusion by challenging stereotypes and prejudices, advocating for marginalized groups, and supporting diversity and inclusion initiatives in our communities As organizations and governments, we can ensure that our policies and programs promote equality and inclusion, and that decision-making processes are participatory and transparent. By working together to promote inclusion, we can create a more sustainable and just world for all.



Welcome to a special edition focused on the creative minds shaping sustainability in the Near East and North Africa (NENA) region! Our region is brimming with young innovators and forward-thinkers who are passionate about creating a greener, more sustainable future. We believe that these bright ideas deserve to be celebrated and supported.
That's why we've launched this initiative to shine a spotlight on youth-led projects that are making a real difference in sustainability From reducing food waste to promoting renewable energy and protecting our environment, these young people are leading the charge toward a more sustainable world. This edition is dedicated to showcasing their inspiring work, sharing their stories, and providing them with the platform they need to keep pushing for change. Together, we can turn innovative ideas into impactful action!
The World Food Forum (WFF) was launched in 2021 by the Youth Committee of the the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), as an independent network of partners. Hosted within FAO, it serves as the premier global platform to actively shape agrifood systems for a better food future, accelerating the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Through youth action, science and innovation, and investment, the WFF forges new paths of action and multi-sector partnerships for agrifood impact at the local, regional and global levels to achieve a more sustainable, resilient, inclusive and hunger-free food future for all.
Within this framework, WFF Global Youth Action was established to harness the passion and power of youth and incite positive action for agrifood systems through youth empowerment It acts as a catalytic movement and driver of youth engagement in food governance, and serves as a knowledge center and innovation lab, fostering and inspiring youth-led solutions.

At the heart of the WFF’s vision is the Youth PolicyBoard (YPB), which governs the WFF Youth Assembly an inclusive, year- round platform that empowers young people to co-create and engage in policy discussions on critical agrifood issues
The YPB’s focuses on addressing policy challenges, developing recommendations on specific agrifood systems topics, and advocating for youth voices and representation in global food governance. Their initiatives range from regional sessions to workshops, consultations and skills development programs.Through these efforts, the YPB seeks to amplify youth voices and push forward the 2030 global agenda by embracing innovation, inclusivity, and sustainability in agrifood systems transformation
By placing youth at the heart of agrifood systems change, the YPB ensures that the next generation is not only heard but also empowered to take meaningful action, contributing to a future where no one is left behind.



The Youth Policy Board is committed to providing a strategic, youth-led vision to the policy-related activities undertaken by the WFF through the Youth Assembly Board members lead the Forum’s work on youth policy positions and coordinate regional activities. Their role is to support and empower youth to engage on food and agriculture topics, enabling their voices to be heard in key international events and processes through active participation in the Youth Assembly and respective outcome documents The Assembly occurs annually, with virtual regional and thematic sessions cumulating in the main, in-person session at the WFF flagship event held every October in Rome, Italy
Established global and regional policy compendia, developed through inclusive consultations with youth groups worldwide, serve as the guiding base for endorsed activities throughout the year. The YPB is responsible for deciding and coordinating the Youth Assembly sessions throughout the year, proposing the agenda and topics, and undertaking the following duties:
Making calls for regular and recurring Youth Assembly sessions in coordination with the WFF Secretariat;
Coordinating the general Youth Assembly meetings at the WFF flagship event in close collaboration with the WFF Secretariat;
Leading the Youth Assembly sessions, including setting themes, topics and questions for consultations and discussions;
Ensuring follow-up of Youth Assembly sessions and drafting final outcome documents

Near East North Africa Youth Policy Board
Member Saudi Arabia
Hanin Alijifri is a dedicated Food and Sustainability Specialist Entrepreneur, and a Clinical Nutritionist, driven by a deep passion for making a positive impact in the fields of food and sustainability Her expertise in nutrition and sustainability allow her to explore innovative approaches to address environmental challenges. The integration of these disciplines is a key aspect of her work towards creating a more environmentally conscious and sustainable future Hanin actively contributes to a positive meaningful change towards sustainability for people and the planet, with the goal of supporting and inspiring others to be an integral part of achieving a nutritional healthier and more sustainable future

Near East NorthAfrica Youth PolicyBoard
Member Algeria
Selma is a dedicated social and climate activist from Algeria, currently pursuing a degree in Political Studies and Human Rights at the American University of Beirut She is the founder of "Together for Blue and Green," a grassroots environmental NGO in Algeria, and a co-founder of the MENA Youth Network. Additionally, Selma serves as a youth board member at ProVeg and the MENA Coalition for Peace, Youth, and Security Her involvement extends to being a Learning Planet Mentor and a former contact point for the Human RightsWorking Group at YOUNGO. Selma's passion for sustainable practices was further developed during her participation as a delegate at the MENA 9th Summer School on Agro-ecology and Sustainable Agriculture Towards Equitable and Justice-based Food Systems, where she applied agricultural knowledge inherited from her grandparents. Currently, she is actively advocating for food security, focusing on the intersection of human rights and environmental sustainability to address these critical issues across the MENA region and beyond

Mohammed Kasim

Near East North AfricaYouth Policy BoardMember، Libya
Bio:
Mohammed A. Mahjoub, a highly accomplished civil engineer and project manager, has over eight years of experience driving sustainable development and climate change adaptation in Libya With a background in agriculture, water and soil conservation, and an ongoing master's degree in Soil and Water Science, Mohammed has made significant contributions at the Norwegian Refugee Council, the United Nations Children's Fund, Roaya, Action Against Hunger, the Agency for Technical Cooperation and Development, and the Center of Judicial Expertise and Research. His dedication to climate change adaptation was recognized through his selection as a delegate at the 28th Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change in Dubai, representing civil society organizations. Mohammed's holistic approach and extensive experience position him as a visionary leader in sustainable engineering and climate change adaptation

Nada Zammel
Near East North Africa Youth Policy Board Member Tunisia
Bio:
Nada Zammel is a passionate human rights advocate and intersectional feminist with a master's degree in Communications from the University of Carthage, Tunisia Hailing from a rural area in Tunisia, she witnessed firsthand the pivotal role of women in agriculture and the discrimination they face. Nada advocates for social justice in Southwest Asia and North Africa, emphasizing the intersection of human rights and climate justice She actively influences policymakers through policy analysis and recommendations to drive meaningful change. Nada is dedicated to raising awareness of these critical issues through an intersectional lens, aiming to empower marginalized communities
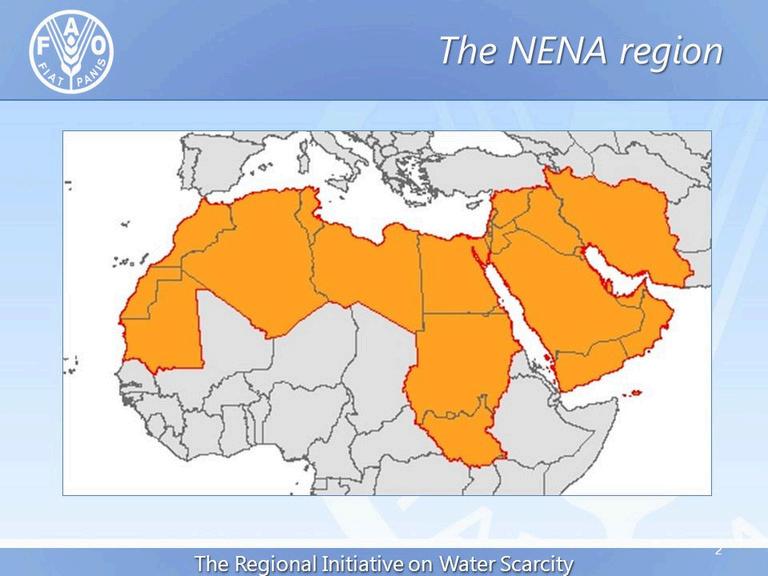
The NENA region, which stands for the Near East and North Africa, encompasses a diverse and strategically significant area characterized by its rich cultural heritage, varying climates, and a complex socio-political landscape. Spanning multiple countries, including Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, Iraq, and the Gulf states, NENA is marked by its historical significance as a crossroads of ancient civilizations and its current role as a focal point for geopolitical dynamics
The region is home to a mix of arid and semi-arid environments, where water scarcity poses significant challenges to sustainable development, agriculture, and food security. Despite these challenges, NENA features a wealth of natural resources, including oil and gas reserves, as well as fertile lands that can be leveraged for agricultural innovation
The NENA region also faces pressing socio-economic issues, including high unemployment rates, youth disillusionment, and political instability, which have been exacerbated by the impacts of conflict, migration, and climate change. As nations in this region navigate these challenges, there is a growing emphasis on fostering resilience and sustainable practices to enhance food security, improve economic opportunities, and promote social cohesion
With its strategic importance and diverse population, the NENA region stands at a crossroads where innovative solutions, regional cooperation, and inclusive policies can help build a more sustainable and prosperous future for its communities.
In the evolving landscape of sustainability, the contributions of youth have emerged as a crucial element in addressing the pressing challenges facing the Near East and North Africa (NENA) region
The Saudi Sustainability Magazine is honored to dedicate a special issue to the World Food Forum (WFF) featuring insights from NENA Youth Policy Board Members This initiative highlights the importance of integrating youth perspectives into sustainability discourse and decision-making, particularly in the context of food systems, environmental protection, and social equity.
The Context of the NENA Region
Youths today are not only inheriting these challenges but are also at the forefront of innovation and change They are leveraging technology, creativity, and grassroots movements to promote sustainable practices in agriculture, waste management, renewable energy, and community development. Their engagement is essential in transforming the narrative around sustainability and ensuring that future generations inherit a healthier planet.
The World Food Forum serves as a global platform that seeks to rally the world’s youth around urgent food and sustainability issues. With its emphasis on dialogue, collaboration, and actionable solutions, the WFF fosters an inclusive environment where young leaders can share their insights, experiences, and innovative ideas This special issue will serve as a reflection of that collaboration, offering a space for NENA Youth Policy Board Members to express their thoughts on sustainability initiatives, food security, and the ongoing struggles faced by their communities
Youth Voices in Action
In this special publication, readers can expect to find a diverse array of articles, essays, and multimedia presentations that capture the essence of youth perspectives on sustainability Topics might include:
Innovative Agricultural Practices: Exploring how young farmers are embracing sustainable farming techniques, such as organic farming, hydroponics, and agroecology, to improve food security and protect natural resources.
Advocacy and Activism: Highlighting the role of youth-led movements in advocating for policy changes that prioritize environmental justice, equitable access to resources, and climate action
Entrepreneurship and Sustainability: Showcasing young entrepreneurs who are developing sustainable business models that not only address local needs but also contribute to broader economic development
Community Engagement: Documenting grassroots initiatives where young people are mobilizing their communities to engage in sustainability practices, from waste reduction campaigns to community gardens







By-Yomna Abdelnasser and Engy Abdelnasser
In March 2024, Egypt faced a sugar scarcity issue due to increase in demand, both, in local and global markets. This scarcity issue has caused Egyptian sisters, Yomna Abdelnasser and Engy Abdelnasser, to think outside of the box in researching and creating a sustainable solution to this issue That’s how Dater, the first brand and factory to produce sugar from date fruit in Egypt, came to life.
The date palm tree is a tree that is native to Egypt and its fruit has been consumed since Ancient Egyptian times. Also, in our present-day, Egypt is the number one country in date production numbers and exports, with 1.8 million tons of date production annually, according to United Nation’s (UN) Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) reports. Unfortunately, food waste takes place in the previous mentioned production as not the whole 1.8 million tons are consumed, with a remainder that gets thrown away or given to livestock as food. What's unfortunate about this information, is that the date palm tree consumes very moderate amounts of water which is very useful in preserving and combating water waste, as opposed to the traditional sugar producing method that extracts sugar from the sugar cane tree The latter process consumes massive amounts of water in its production, contributing to further water waste, in a world where many countries are already suffering from water scarcity and many others are expecting to go through the same crises in the near future. Also, in a world that is currently suffering from global warming and climate change effects, such as drought from icebergs melting in oceans and deforestation due to plants dying from non-suitable growth temperatures, the extraction process of sugar from sugar cane produces huge amounts of carbon emissions and has a carbonfootprint, according to International Sugar Organization(ISO) and Bonsucro Organization.

The previous information, in addition to extensive research and the sugar scarcity issue mentioned earlier in this article, has paved the way for an exceptional sustainable food idea that the Abdelnasser sisters came up with, their venture, Dater.
Dater is the first Egyptian brand and factory to produce sugar from the date fruit. It relies on dates that have been planted in Egypt and consume very insignificant amounts of water, which contribute to global water preservation efforts and ecological friendly approaches. Also, the production process relies on a very simple process that does not emit significant carbon emission and rather emits very insignificant emissions, in an attempt to combat climate change and global warming. Furthermore, the packaging is made out of paper material that is, both, consumer and environmentally friendly as it bio-degrades after 3 years. Furthermore, this production process aims to reduce food waste and preserve the date fruits that get wasted due to lack of consumption. On the other hand, date sugar is rich in antioxidants, fibers, iron, calcium, and potassium, which makes it a health-conscious sugar source. Moreover, it’s safe for consumption by people who suffer from diabetic disorders, making it the perfect sweetener.
The Abdelnasser sisters aim to not only produce Dater for the local market of Egypt, but to also start expanding globally, very soon

Authors Bio:


Yomna Abdelnasser is a political scientist turned investor and entrepreneur She has worked previously in government and international organizations, such as UNWomen She currently runs her factory Dater
Engy Abdelnasser is an assistant lecturer in Political Economy She has worked previously in the field of women economic empowerment with UNWomen and currently teaches Political Economy at The European Universities Egypt (EUE), while co-running the Dater Factory with her sister Yomna
By: Mohamed Zaky Ghozl, Sameh Zaky Ghozl, Amjad Bakri, Nada Muhamed, Omnya Ahmed
NEL was founded on the belief that technology and sustainability are not mutually exclusive, it was born out of observing substantial challenges in Egypt in urban planning and equitable distribution of services and facilities, leading to traffic congestion, inadequate basic services, and environmental degradation At Nature Eye Labs, we are a youth-led organization that runs on the collective passion, creativity, and leadership of young environmentalists, designers, engineers, and innovators Such pressing global issues as climate change, waste management, and sustainable urban development can only be tackled through technology, digital design, and community-driven initiatives. We are aware that youth contribution towards sustainable solution-finding is important, which is where our organization comes into empowering the next generation of societal change. As a youth-led organization, we are proud of the fact that young people take center stage in project leadership and solution design while being vocal champions for sustainability Our team is guided by the core values of inclusion, innovation, and collective impact, with environmental justice and equity for all being our driving force.
With limited resources, but an abundance of collaboration and creativity, we started developing projects aimed at harnessing AI technologies to address urban planning and environmental challenges in Egypt and the MENA region. One of our earliest projects, the Mangrove Mapping, Detection, and Prediction Project, was developed to map, monitor, and protect vital ecosystems along the Red Sea Using satellite imagery and AI, we worked on analyzing the factors contributing to mangrove loss and providing insights on conservation factors.



Our ambitions grew from there as we began exploring the potential of AI in urban planning, developing AI-driven tools like our AI-powered Crisis Management and Urban Planning Platform The platform is designed to address the growing challenges of rapid urbanization and resource inefficiencies in cities leading to infrastructure gaps, traffic congestion, and socioeconomic disparities. Here we came with our platform that uses advanced AI and data analytics to provide real-time insights for optimizing urban planning. Considering geographic, demographic, and environmental data, the platform assists decision-makers in both the public and private sectors in determining the most appropriate locations for services, ensuring service distribution and sustainable urban growth.
Believing in youth empowerment and its vital role in achieving climate justice, we have organized several programs for engineering students to raise their awareness about the importance of tech in tackling climate change We also connected them with esteemed professors from MIT and several leading international institutions and industry leaders fromESRI to get a first look at the recent global trends in sustainability in engineering
Our strong social commitment to achieving net zero has been observed by obtaining the first place at in Banha University Innovation Hackathon (AI in Smart Cities Award), 4th Place in the international Competition of Smart Cities – Egypt, and securing endorsement and expert mentorship from the Ministry of Planning & Economic Development


Moreover, we got the honor of securing funding and mentorship from ITU (International Telecommunication Union) in collaboration with Huawei While our projects have garnered recognition at several international forums, we have only scratched the surface of what’s possible. With the solid passion, drive, and vision we have, we believe that nothing can be done without collaborative efforts, partnerships, and funding to push the boundaries of our work further and get empowered with the right resources. We want to continue developing projects that matter, like our NEL-BOT for ocean cleanup and our AIdriven Urban Planning Platform We want to refine our Smart Carbon Monitoring System to provide actionable data for cities and industries worldwide. We want to continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible in sustainability tech, but we need your help to get there.
As we are still at the beginning of our journey, the work we have set out to accomplish is far from complete We envision to create a more sustainable and equitable world by integrating advanced technologies and urban solutions We aspire to be a leader in using AI and data analytics to address global challenges and improve the quality of life for communities around the world.
Our vision is to create a more sustainable and equitable world by integrating advanced technology with environmental and urban solutions. We aspire to be a leader in using AI and data analytics to address global challenges and improve the quality of life for communities around the world We are dedicated to making a meaningful impact through our projects and capacity-building programs, working towards a brighter and more sustainable future for all.Thank you for joining us on this journey. Together, we can have more influence and build abetter world.
Authors Bio:
1. Mohamed Zaky Ghozl
Mohamed Zaky Ghozl is the Founder and Managing Director of Nature Eye Labs, a youth-led initiative developing AI-driven solutions for environmental sustainability As an SDG Ambassador and mechanical engineer, he merges technical expertise with social impact, driving climate action and empowering youth through innovative tech solutions Recognized by the ITU, Mohamed is committed to advancing global sustainability goals
2. Sameh Zaky Ghozl
Sameh Ghozl is a passionate chemical engineering student and Co-Founder at Nature Eye Labs, currently serving as the Growth Manager. Sameh drives the growth, development, and expansion of NEL, strengthening both internal capabilities and community partnerships to promote sustainability across the MENA region. Moreover, as a Student Researcher, he worked on applied research on air purification and wastewater treatment techniques.
3. Amjad Bakri
Amjad Bakri is the AI Director at Nature Eye Labs, where he leads projects in artificial intelligence and machine learning to advance environmental sustainability With experience in AI engineering and NLP, he has worked with companies like Spiro Carbon Group and EJADA Amjad is passionate about leveraging AI for real-world challenges and enhancing environmental data analysis
4. Nada Muhamed
Nada Muhamed is the Urban Research Director at Nature Eye Labs, where she leads research initiatives at the intersection of urban planning, technology, and environmental sustainability. A graduate of Ain Shams University in Architecture and Urban Planning, Nada leverages her expertise to address urban challenges, focusing on sustainable solutions and data-driven approaches to improve city landscapes.
5. Omnya Ahmed
Omnya Ahmed is the IT Director at Nature Eye Labs, where she leads the development of innovative IT solutions. With a background in software engineering at Orange, she specializes in web development, IT security, and data management Her expertise in IoT, AI, and modern web frameworks drives technological progress at Nature Eye Labs, advancing its sustainability-focused initiatives

By: Rashed Al-Rababah
In today’s world, where environmental degradation and waste accumulation have become significant global challenges, initiatives that focus on recycling and sustainability are more critical than ever. One such initiative making an impact in rural communities is the “Rural Ambassadors for Recycling” project. This community-led project addresses the dual issues of plastic waste management and agricultural development, offering a sustainable, low-cost solution to enhance the livelihoods of rural farmers while protecting the environment.

Rural areas, despite their distance from urban industrial centers, are not immune to the growing problem of plastic waste. Plastic bags, bottles, and packaging materials often find their way into agricultural lands, rivers, and local ecosystems, causing harm to the environment and threatening the health of local communities The lack of waste management systems in many rural areas exacerbates the problem, as plastic waste accumulates over time, contaminating soil and water sources.
At the same time, farmers in rural areas face numerous challenges, including access to modern agricultural tools and technologies that can improve their crop yields. Many farmers in these regions continue to rely on traditional farming methods, which are often inefficient and resource-intensive This creates a perfect opportunity for innovation that not only addresses the waste problem but also supports the agricultural needs of these communities.

The Rural Ambassadors for Recycling initiative was created to address these challenges. The project focuses on educating rural communities about the importance of recycling plastic waste and finding practical ways to repurpose this waste into useful agricultural tools. By transforming discarded plastic into products like irrigation systems, planting containers, and fencing materials, the initiative not only reduces the amount of plastic waste polluting the environment but also provides farmers with cost-effective resources to improve their agricultural practices
Workshops are at the core of the initiative’s strategy. Local farmers and community members participate in hands-on training sessions where they learn how to collect, sort, and recycle plastic waste. These workshops also teach participants how to create simple yet effective tools for use in their farming activities. For example, plastic bottles can be converted into drip irrigation systems, helping farmers water their crops more efficiently, particularly in regions where water is scarce.
One of the most important aspects of the Rural Ambassadors for Recycling initiative is its emphasis on education and community engagement By raising awareness about the environmental impacts of plastic waste and teaching practical recycling techniques, the initiative empowers rural communities to take control of their environmental future The project’s ambassadors are community leaders who advocate for sustainable practices and encourage their neighbour's to adopt recycling as part of their daily lives.
The ambassadors also collaborate with local schools, helping to integrate environmental education into the curriculum. By teaching young people about recycling and sustainability from an early age, the initiative ensures that the next generation will be better equipped to tackle environmental challenges. Involving youth in the project also encourages creativity and innovation, as young people often bring fresh ideas and perspectives on how to repurpose waste


The Rural Ambassadors for Recycling project has had a significant impact on both the environment and the local economy Since its inception, the initiative has helped reduce the amount of plastic waste in participating communities, leading to cleaner, healthier environments. This reduction in pollution has also had positive effects on local agriculture, as cleaner soil and water contribute to better crop yields.
Economically, the project provides a source of income for many participants. Community members who collect and recycle plastic waste can sell the repurposed products, such as irrigation systems and planting containers, to neighbouring farmers and agricultural cooperatives. This creates a circular economy within the community, where waste materials are transformed into valuable resources that support agricultural production. Moreover, the project has helped reduce the costs associated with farming. By providing low- cost, recycled alternatives to expensive agricultural tools, the initiative allows farmers to save money while improving the efficiency of their operations. This is particularly beneficial for small-scale farmers who may struggle to afford modern farming equipment.
The success of the Rural Ambassadors for Recycling initiative has sparked interest from neighbouring communities and environmental organizations. There is growing potential to expand the project beyond its current scope, reaching more rural areas and involving a larger network of community ambassadors. The initiative’s model of combining education, recycling, and agricultural innovation can be adapted to different regions, particularly those facing similar challenges related to waste management and farming.
Future plans for the initiative include scaling up the production of recycled agricultural tools and increasing the number of workshops and training sessions available to rural communities. The project also aims to establish partnerships with environmental NGOs, government agencies, and private sector companies to support its expansion and ensure its long-term sustainability.
Additionally, the initiative envisions the creation of a mobile recycling unit that can travel to remote areas, providing on-site training and waste collection services. This would allow the project to reach communities that are currently underserved and help reduce plastic waste in some of the most isolated regions.
The Rural Ambassadors for Recycling initiative is a powerful example of how community-driven efforts can address pressing environmental issues while supporting local economic development. By transforming plastic waste into valuable agricultural resources, the project not only helps reduce pollution but also empowers rural farmers to improve their livelihoods With its focus on education, sustainability, and innovation, the initiative represents a scalable and replicable model for tackling plastic waste and promoting sustainable agriculture in rural areas around the world.

Author Bio:
I have led and coordinated environmental initiatives, including the "Rural Ambassadors for Recycling," which focuses on transforming plastic waste into agricultural solutions. My experience includes working with rural communities to raise awareness about recycling, developing sustainable practices, and contributing to pollution reduction I am dedicated to fostering environmental sustainability and innovation in underdeveloped areas through practical recycling solutions
r rababah97@gmail com Region and Country: Ajloun, Jordan




By: Priyadarshan Reddy G

In Octo of the country g g p g g oup of volunteers passionate about nature and preserving the coastal beauty of Kuwait, the movement has since grown into a well-known community effort As the environmental issues in Kuwait became more pressing, Kuwait Eco Warriors stepped up to not only raise awareness but actively engage in cleaning up the coastlines, with a vision to inspire change across the community.
The motto of Kuwait Eco Warriors, “Go Green, Go Clean,”encapsulates the core of our mission.We believe that environmental conservation is a shared responsibility, and taking action today will ensure a sustainable future for generations to come. Our focus is not just on cleaning the beaches but also on instilling a mindset of environmental stewardship within the local community.Through consistent efforts and unwavering commitment, we aim to create a cleaner, greener Kuwait
Kuwait Eco Warriors has become a beacon of environmental action in Kuwait We have completed189 weeks of beach cleanups, with 123of those weeks conducted consecutively without a break. Our cleanups span across several beaches including Fahaheel, Mangaf, Abu Halifa, Fintas, Mahboula, Doha, Al-Bida, Shumaymeh, and Flamingo Beach. Every week, our diverse team of volunteers gathers to clear trash and plastic waste that litters the shores, posing a threat to marine life and the local ecosystem.

What sets our organization apart is the dedication of our volunteers. Our team consists of around 60 members representing a variety of nationalities, including individuals from India, the USA, Egypt, Canada, the Philippines, Kuwait, Palestine, and Sri Lanka This diverse group reflects the universal appeal of environmental causes and the shared desire for a healthier planet, regardless of cultural backgrounds or nationalities Together, we have collected approximately 20 tons of trash, a staggering testament to both the magnitude of the problem and the effectiveness of consistent cleanup efforts
The Kuwait Eco Warriors is fundamentally a community-driven initiative. Our work relies heavily on the enthusiasm and commitment of volunteers who dedicate their Fridays to making a tangible difference.While beach cleanups are the primary activity, we also see this as a platform to educate and engage the broader community, particularly the younger generation.
We have organized several children's beach cleanups, which aim to foster environmental consciousness from an early age. These cleanups not only involve children in the physical task of cleaning beaches but also serve as an educational experience. By learning about the harmful effects of plastic pollution on marine life, children become more aware of their role in protecting the environment These events are crucial in shaping the mindset of future generations who will ultimately inherit the responsibility of safeguarding our planet


Our efforts have not gone unnoticed on the global stage. In 2022 and 2023, KuwaitEco Warriors collaborated with the World Cleanup Team, a partnership that allowed us to connect our local mission with a global movement. We also organized a major cleanup campaign at the Abu Halifa grounds, highlighting the power of collective action in tackling environmental challenges Additionally, we have worked closely with organizations like the UK Embassy in Kuwait, Emerson Company, the Kuwait Malayikical Association, and the Dive Earth team These collaborations have helped amplify our message and expand our reach, drawing more people to our cause
Our association with World Clean Day has been another milestone in our journey.Through this partnership, we align our local efforts with a global day of action that sees millions of people participating in environmental cleanups worldwide. This allows Kuwait Eco Warriors to contribute to a much larger, international initiative, fostering a sense of global solidarity for environmental conservation.
Beyond physical cleanups, Kuwait Eco Warriors has also been active in promoting awareness about sustainable practices. Our online campaign, “Go Green, Go Clean,” focuses on reducing the use of plastic and promoting alternatives like bamboo toothbrushes, reusable bags, and eco-friendly products This campaign complements our cleanups by addressing the root of the problem excessive plastic use and encouraging more sustainable consumption habits
We believe that awareness is just as important as action Through social media platforms, particularly our Kuwait Eco Warriors Instagram page, we regularly update the community about ongoing cleanups, share environmental tips, and highlight the importance of reducing plastic waste. By engaging with the public online, we hope to inspire more individuals to make environmentally conscious choices in their daily lives.


Kuwait Eco Warriors is proud of the progress we’ve made over the past few years, but we understand that the journey toward a cleaner environment is ongoing As long as there is pollution on our beaches, we will continue our mission Our team remains committed to organizing cleanups every Friday, no matter the weather or circumstances With a growing community of volunteers and the continued support of our partners, we are confident that we can achieve even more in the future At its heart, Kuwait Eco Warriors is a symbol of what can be achieved when a community comes together with a shared purpose. Our work is a reminder that every small action contributes to a larger impact. Together, we are not just cleaning beaches; we are paving the way for a more sustainable and eco-conscious future for Kuwait.





By-Leila Rossa Mouawad
“Buzuruna Juzuruna” which translates in Arabic to “our seeds our roots”,is a Lebanese nonprofit organization that has been active since 2016. It was founded when young Lebanese, Syrian and French farmers decided to join forces in saving one common treasure: heirloom seeds. Today, the organization supports sustainable agriculture with a core focus on preserving heirloom seeds passed down through generations. This type of seed is more resilient and resistant to pests and diseases as it is adapted to the local climate. Heirloom seeds secure the autonomy of farmers, unlike hybrid ones produced by large corporations that have control over the global seed market.They also offer a higher nutritional value, which boosts the immunity and health of consumers.
Buzuruna Juzuruna was the first heirloom seed agro-ecological farm in Lebanon Since its establishment, the organization has succeeded in saving many varieties from extinction, often starting from just a handful of seeds Its library currently hosts more than 1000 varieties of cereal, fruit and vegetable seeds, many of which yield rain-fed crops that are adapted to the region’s water scarcity
One of the founders notes that this amount of seeds is enough to plant an area three times the size of Lebanon
In the 2 hectare farm, managed by 18 employees and their families, 80% of the diversely cultivated land is used to produce seeds. Those seeds are later on preserved in the library, exchanged, generously donated or sold at affordable prices. The remaining 20% of the land is used to grow crops that are sent to the local market. One key destination for example is the Badaro UrbanFarmers Market, where farmers get to interact directly with consumers in the heart of the city.


In addition to its diverse agricultural fields and highly valued seed library, the Buzuruna Juzurunafarm in Saadnayel Lebanon also includes a training center, plant nurseries, animal farm, and a section for composting and formulating organic fertilizers and repellents from crops and their residues The farm’s small building is constructed with locally sourced material including clay, hay and wood The farm is equally equipped with solar panels to fulfill its energy needs This mixture of eco-friendly approaches facilitates thermoregulation and helps the farm adapt to and mitigate climate change
In a country where almost 90% of food is imported, boosting the autonomy of farmers becomes a priority. This in turn directly contributes to the nations's food sovereignty. Buzuruna Juzurna is just one among many other small initiatives such as Nohye El Ard, Les Racines Du Ciel, Turba Farm, the Agricultural Movement in Lebanon, Hobob and many others working on the same issue. These initiatives are part of a growing network in the country, changing conventional farming through seed sharing and communal education as an act of resistance and independence.


is a researcher at the American University of Beirut - Nature Conservation Center Through her educational background in forestry and extensive experience in communication, Leila represented youth in international forums and supported scientists in communicating their complex messages to a wider audience. Leila is also passionate about nature photography and highlighting the hidden beauty in the world's tiniest creatures.

By: Farah Salma, & Malak Yacout

In today's turbulent world, volunteers stand as guardians of our humanity. They mend hearts, uphold values, and nurture morale, serving as beacons of compassion and examples of altruism. The Volunteer Circle began with a belief in liberating volunteering from traditional constraints, a belief that has blossomed into a thriving community of thousands. For the people by the people, this non-profit social enterprise is revolutionizing volunteering across the MENA region through an innovative AI-powered platform, offering personalized, skill-based opportunities for volunteers while providing essential human resources solutions to organizations, start-ups, and academic and corporate institutions.
Over the past seven years, The Circle has transformed the landscape of volunteering taking it from sporadic, occasional acts to a well-oiled system that's easily accessible. It is a vision about altering the way we use our time and effort on the personal level, improving the capacity of organizations and transforming how volunteering is perceived from being solely charity-based to a dynamic and robust system of skillbased contributions It’s no longer an underutilized resource, but rather a powerful engine for economic advancement, sustainable development, career growth, and personal well-being.

Volunteering has long been associated with personal growth and community contribution, but The Volunteer Circle takes it further. Internal surveys show 81.9% of volunteers reporting improved well-being, 79.8% experiencing increased confidence, and 83% seeing progress in their development goals, which showcases structured volunteerism's impact on career growth and mental health improvement By 2024, The Volunteer Circle had placed 120 volunteers into jobs across various sectors, demonstrating the potential of volunteerism as a bridge to employment. Data from volunteer evaluations shows 91% of volunteers gained soft skills that increased their employability, and 70.87% felt their CVs were strengthened by their volunteer experiences.
Beyond individual benefits, The Volunteer Circle’s impact extends to entire communities. In 2023 alone, the organization saved local communities over $17,000 in resources by connecting skilled volunteers to areas of need. Volunteers also made a tangible impact by touching 35,620 lives, preserving 342 trees, supporting 30 differently-abled individuals, and 324 lifeline calls, showcasing the profound and life-saving impacts volunteers can have when properlymobilized Their dedication serves as a source of hope in times of distress and builds a mutually beneficial relationship between volunteers and the community, where both sides gain and grow together.


The Volunteer Circle is not limited to a single cause or sector. In 2023, volunteers contributed to 11 different sectors, including environment and nature conservation, arts, sports, culture, education, health, and animal welfare.
In a region marked by economic instability, rising unemployment, and decreasing resources, the need for organized volunteer support has never been greater. The Volunteer Circle addresses these needs head-on, providing a lifeline for individuals and communities facing hardship in the MENA region, by offering tech-powered solutions that are both scalable and impactful
The Volunteer Management Membership, a signature service by The Volunteer Circle since April 2021, allows organizations to access volunteers on demand, ensuring timely and effective deployment to areas of need.
Another key offering, the Volunteer Leadership Training offers organizations tools to recruit and retain top talent. Built on the experience of over 300 partner organizations, this accessible online course equips organizations with strategies to meaningfully engage volunteers.
Additionally, the Volunteer Advisory Service provides personalized consultancy in areas like Volunteer Management, Impact Measurement, and Community Building to help organizations create sustainable volunteer programs.
The Career Circle, launched to meet the demand for skilled talent, connects volunteers with job opportunities, transforming volunteerism into a gateway to employment. It helps organizations hire individuals who have demonstrated dedication and skill through their volunteer work
For entities in need of a readily available marketplace, The Volunteer Circle’s Whitelabel Technology provides a platform tailored to specific needs, matching supply and demand under the organization’s brand.

The future of volunteering in the MENA region is promising, with The Volunteer Circle leading the charge. As it evolves to meet the needs of volunteers and organizations, the platform redefines what it means to volunteer today.
The Volunteer Circle Research Initiative, launched in 2023, aims to fill the regional gap in volunteerism data. By publishing research such as Volunteering: The New Wealth of Students, the organization provides insights into how volunteering drives social change and economic mobility.
Looking ahead, the mission remains clear: to make volunteering accessible, impactful, and targeted Whether through job matching, leadership training, or innovative tech solutions, the platform is committed to empowering individuals, organizations and communities alike to create lasting social change. There has never been a better time to be bold in our service and compassion. How will you use these resources to achieve your goals and create positive change in your community?



Authors Bio:
Farah Salma: Farah is an advocate for community empowerment and social change With a Master's in Sciences from Lebanese University, she leads Strategy and Growth at The Volunteer Circle, a social enterprise in Lebanon dedicated to empowering communities and fostering social change through volunteerism Farah promotes inclusivity, well-being, personal growth, and sustainable development, drawing inspiration from nature, art, and mindfulness.
MALAK YACOUT: Malak is a marketing graduate, aspiring entrepreneur, and avid traveler. From Tanzania to Egypt, Malak has plenty of volunteering experience prompted by her drive to understand different cultures. Malak has supported business start-ups and small organizations in achieving their goals. She hopes to bring about the satisfaction of volunteering to people in the MENA through The Volunteer Circle.
By-Chaymae Mouhiyedine


What if bees disappear...?
This question, as alarming as it may seem, deserves our attention.Indeed, these pollinating insects are responsible for 75% of our crops and 90% of wild plants.According to the Global Goals organization, bees are considered the most important creatures on the planet [1], a world without bees would mean, among other things, the disappearance of chocolate and coffee. A difficult prospect to imagine, isn't it?
The perils facing honeybee colonies are both multifaceted and severe Among the most alarming is Colony Collapse Disorder (CCD), where worker bees abruptly desert the hive, leaving the queen and brood in peril. Additionally, varroa mites—a parasitic scourge—undermine bee health, while environmental hazards, including wildfires, pose further threats. Variations in temperature, humidity, and exposure to pesticides; compound these challenges, adversely impacting bee well-being. Conventional beekeeping techniques, reliant on manual inspections, disrupt hive tranquility and fall short of providing comprehensive, continuous oversight. In scenarios involving remote or extensive apiaries, such inspections become increasingly impractical, rendering hives susceptible to undetected issues until it is too late. Addressing this issue is extremely important and urgent
RevoBee’s team has developed a paradigm-shifting electronic device seamlessly integrating Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) addressing the challenges faced by modern apiculture Traditional beekeeping methods are often invasive and inefficient, leading to stress on bees and difficulty detecting issues early RevoBee state-of-the-art technology monitors the hive conditions, detects threats like varroa mites and environmental hazards, and provides real-time data to beekeepers.



By: Bendjedid Rachad Sanoussi, Amal Belarabi, Khadidjath Adekpedjou, Medoune Ndour Tounkara
Green Leaf AI is revolutionizing the way we address crop diseases, particularly in date palm trees, by harnessing the power of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning Our mission is to improve early detection and management of crop diseases, ensuring better yields and more sustainable agricultural practices, particularly for smallholder farmers Date palms are a critical agricultural asset for local farmers, providing a significant source of income and sustenance. However, these crops are highly susceptible to diseases, which can devastate yields and impact the livelihoods of farmers Traditional methods of disease detection are often reactive and inefficient, leading to substantial crop loss and economic hardship.
At Green Leaf AI, we are using AI to enable rapid and accurate identification of diseases, helping farmers take timely preventive measures to protect their crops. Our goal is to improve crop yields, reduce pesticide use, and promote sustainable agricultural practices Indeed, we work to provide early disease detection in date palm trees Our solution includes an application that captures images of the trees, which are then analyzed by our AI model to identify early signs of disease The app offers real-time alerts and recommendations, enabling farmers to take preventive measures This approach reduces crop loss, minimizes pesticide use, and enhances overall yield and sustainability.


We are contributing to several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through its innovative approach to sustainable agriculture Our AI-powered solution enhances food security and sustainable agriculture (SDG 2) by improving the health and yield of date palm crops, which reduces crop losses and boosts productivity We support good health and well-being (SDG 3) for farmers and consumers, promoting safer agricultural practices by minimizing the need for chemical pesticides Our commitment to driving innovation in the agricultural sector aligns with industry, innovation, and infrastructure (SDG 9), fostering a culture of innovation through collaborations with research institutions and universities Additionally, our focus on sustainable farming practices aligns with responsible consumption and production (SDG 12), while also contributing to climate action (SDG 13) by reducing the environmental impact of farming and enhancing climate resilience Finally, by protecting and preserving vital date palm crops, we support life on land (SDG 15), maintaining biodiversity and supporting local ecosystems.
Our innovative project, Création d’une base de données ouvertes sur les maladies des dattiers pour améliorer la recherche et la formation, focuses on building a comprehensive, open-access database of date palm diseases The lack of accessible data and technical expertise often limits farmers' ability to identify and treat crop diseases, which can lead to decreased yields and negative economic impacts. Through collaborations with local farmers, we collect images of date palm diseases and make this dataset available for AI-based disease identification systems. This open data initiative is designed to empower farmers by providing them with the tools and knowledge they need to improve crop health and productivity


Achievements and Collaborations
Green Leaf AI has garnered recognition and support through various platforms We showcased our solution at the Africa Smart City Forum (ASCF) 2024 in collaboration with the Mohammed VI Polytechnic University (UM6P). Our participation in the Expo of Innovation Smart City (SInov-City) at ASCF2024, where Green Leaf AI was one of the 10 startups chosen to exhibit, allowed us to present our technology to a wider audience of stakeholders and innovators.
Additionally, we participated in the ClimateLaunchpad Morocco Bootcamp in July 2024, which helped refine our solution. Later, we achieved second place in the prestigious Falling Walls Lab Morocco 2024, where we presented our project "Breaking the Wall of Crop Disease Detection with Artificial Intelligence." Our focus on AI and machine learning enables the early detection and effective management of date palm diseases, supporting more resilient and sustainable farming practices

With the support of partners like La Communauté d’Afrique Francophone sur les Données Ouvertes (CAFDO), Green Leaf AI is working to further expand our open data initiative, which will serve as a valuable resource for researchers, agricultural experts, and local communities across the region. Indeed, this project aims to improve the early detection of diseases in date palm leaves by building an open database In collaboration with farmers, we are collecting images of diseased date palms to be used in AI systems for effective disease identification and treatment This will help smallholder farmers increase yields and reduce economic losses. https://www.cafdo.africa/?p=806. We are playing a key role in fostering innovation in sustainable agriculture by promoting data accessibility and AI-driven disease detection


Name of Contributors:
Bendjedid Rachad Sanoussi: Founder & Chief Technology Officer
Amal Belarabi: Co-Founder & Head of Business Development
·Khadidjath Adekpedjou: Co-Founder & Food Technology and Human Nutrition Officer
·Medoune Ndour Tounkara: Data Scientist
By: Bendjedid Rachad Sanoussi, Amal Belarabi, Khadidjath Adekpedjou, Medoune Ndour Tounkara
The climate change is not only an environmental topic but also a matter of social and economic justice. Threats like increased temperatures, erratic weather conditions, droughts, and floods impact everyone However, the most affected are the underprivileged and marginalized communities in the world who, in fact, are found to have the smallest contribution to the global emissions. The disparity has caused the birth of the climate justice movement, which protests that the climate crisis be addressed through the prism of equity and that the solutions are fair and inclusive as well


It is a fact that some of the developed nations have been the ones who have been causing the bulk of the greenhouse gas emissions However, the developing world, especially the South, is the one which is suffering the most. Small-scale farmers, coastal communities and Indigenous people are among the groups that are affected the most because of the loss of job opportunities, the decline of their health and the shortage of the basic food items due to natural calamities caused by global warming. Since we are calling for immediate and concrete actions to mitigate climate change, it is only through the acknowledgement of this inequality and the subsequent collective effort towards compensatory climate justice, sustainable development and policy change that leverage the voice of the less privileged, whereby we will be surely doing these people justice

Author: Salma NAJI

Salma NAJI is an agro-engineering student specializing in sustainability and environmental protection. She collaborates with international organizations and participates in MENA events, focusing on climate justice and empowering marginalized communities Driven by a passion for sustainable agriculture, she seeks to address global challenges like food security, water scarcity, and the impacts of climate change Njsalma21@gmail com +212693748208 (00212693748208)
Agro-engineering student North Africa, Morocco

Agriculture is especially the field of activity that experiences direct environmental impetuses. Farmer around the world are confronting climate change which brings about erratic rainfall, soil degradation, and crop failure resulting in food insecurity. For example, rural farmers in African and Middle Eastern countries regions that are already suffering from water scarcity are disproportionately affected Lossless climate justice is a course of action to protect the farmers of such a circumstance, emphasizing these measures the utmost important being of course, the policies and projects that enable shifting the habits reducing carbon emissions, moving towards a vegan diet, and microgripping Reduction of these emissions would in effect cut global warming causing better weather patterns and thus less water shortages.
At the center of the concept of climate justice is the principle that those who suffer the most from the crisis should make decisions on the solutions adopted. Indigenous peoples, women, youth, and rural communities frequently have critical information on sustainable farming techniques and environmental conservation By involving them in decisions, we ensure that the climate policies respect the perceptions of various communities and at the same time attend to practical necessities. Besides that, empowerment denotes empowering the communities with capacities to discover their own funds, technologies, expertise thus they can adapt and mitigate their climate change. For example, programs that support women farmers or train youth in renewable energy can drive local sustainable development, creating long-lasting benefits
The global move to renewable energy and the adoption of sustainable practices will happen Nevertheless, this revolt and subsequent transition should also keep in mind the old workers and changing the job markets for the betterment of the environment. Green employment, social security systems, and retraining programs are fundamental to realizing the joint objectives of environmental preservation and social cohesion.
The idea behind a "just transition" is the one that checks that the communities can make the convert to a green economy and at the same time, it respects their rights and dignity, provides new chances for those affected by the climate disaster, etc. The instance of taking an integrated approach is indispensable.
Climate justice is a concept that stretches much further than its traditional environmental concern it is the securing of equal opportunities to urge the creation of a balanced and inclusively run global society that does not confine anybody to the shadows of a marginally secure future In fact, enrichment can be gained from the integration of community development and environmental justice into collective undertakings, such as mitigating or adapting to climate change (how) one can deal with each of them Moreover, climate rescue and social movements for racial equality have oblique influences on one another. For this reason, the present rapacity is severe. For the triumph in the phase of real climate justice

By: Raghad Fathaddin
Sangha Estidama Hub, launched in 2021 in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, aims to create a system that nurtures the human spirit by promoting a wellbeing economy. This model puts planetary wellbeing focusing on both people and the environment at the heart of decision-making and as a measure of economic progress. Sangha believes that the state of the world is a direct reflection of the state of its people. Hence, to address 21st-century challenges, especially climate change, Sangha emphasizes that the root cause of the issue lies within humanity itself
The PERMA program is one of Sangha’s core initiatives designed to equip future leaders with the tools and mindset to lead well and sustainable lives Based on the PERMA model of positive psychology, which focuses on Positive Emotion, Engagement, Positive Relationships, Meaning, and Accomplishment, this workshop aims to help individuals or governments measure and improve personal and collective wellbeing. The interactive 5-session workshop covers topics like identifying and managing emotions, boosting creativity, enhancing communication skills, and fostering positive relationships. Participants also learn about personal growth, and how to let go of limiting beliefs. Nature-based learning, like planting activities, is integrated into the workshop to strengthen participants’ connection with the environment.
Unlike traditional programs, Sangha takes a holistic approach by combining personal, emotional, and environmental education It teaches participants not only that they are part of nature but also that they are nature By fostering self-respect, the program encourages respect for the environment This method focuses on cultivating emotional intelligence and mindfulness, thereby enabling individuals to build sustainable systems and communities. Sangha’s programs have already reached over 100 participants, aged 4 to 40, across SaudiArabia, including Jeddah, Riyadh, and Al Ula.



About the Author:
As Founder & CEO of Sangha Estidama Hub, Planetary wellbeing & wellbeing economy specialist. I focus on sustainable development and human progress through wellbeing and environmental initiatives. With experience in Saudi Arabia, the UK, and France, I’ve partnered with organizations like UNESCO, WHO, and the World Bank A Y20 Saudi Delegate (2022), I hold degrees from Southampton and King’s College


By: Mohamed Shokry

The Horn of Africa nation has struggled with state and institutional building for over two decades and has succeeded in the establishment of federal member states and public institutions, which show a gradual recovery of country’s governance and state building.
Somalia has been subjected to conflicts for about 30 years, accompanied by climatic disasters that included prolonged droughts, recurrent floods, epidemics, and seasonal locust invasions. Those combined weather and climate-related disasters have impacted the lives of millions of people in the country, resulting in mass displacement, loss of livelihoods, food insecurity, and a higher unemployment rate.
Somalia has experienced more than 30 climate-related hazards since 1990, including 12 droughts and 19 floods. This exposed the country’s limited capacity for disaster risk management and the vulnerability of the people to these recurrent crises. With poor and fragmented early warning systems in the country, climatic disasters, particularly floods, droughts, and locust invasions, continue to affect the people every year and result in the loss of livelihoods and the destruction of infrastructure
An early warning system is a vital tool for proper disaster risk reduction and management in the country to disseminate and better communicate with affected communities in the disaster-prone areas to create resilience pathways and help them cope with and withstand climatic shocks. Early warning systems in the country aren’t enough to disseminate the most needed information to the right people, which poses a greater gap in the early warning mechanism. The country’s early warning system is faced by fragmented and uncoordinated platforms provided by different agencies, accompanied by poor dissemination and communication channels.
Millions of people in Somalia are at risk for not receiving early warning information about forecasted or anticipated disasters; thus, this cost lives livelihoods, and damages properties, infrastructure, and ultimately create mass displacement and a dire humanitarian catastrophe.

Early warning systems in Somalia are currently provided by several institutions, both government and international partners, through multiple and fragmented platforms, though their effectiveness and outreach can be questionable.
The warnings are provided via online systems to the different concerned partners and organizations, with a focus on weather, rainfall, floods, droughts, cyclones, and locust outbreaks The current EW providers are described below:
ICPAC-IGAD Climate Prediction and Application Center is a regional climate and information center accredited by the World Meteorological Organization to provide climate information services to 11 EastAfrican countries, including Somalia. The center is mandated to deliver several climate services that are intended to enhance the resilience of the people affected by climate change and extreme weather events Climate forecasting, early warning, and climate information dissemination are some of the services provided by the center
FEWS NET is a leading provider of early warning and analysis on acute food insecurity around the world. FEWS NET provides timely and evidence-based warning information and analysis of food security Monitoring and forecasting agro-climatic conditions is also among the products that FEWS NET produces. This information is publicly available through its website and network.
SWALIM: FAO’s Somalia Water and Land Information Management (SWALIM) is a key contributor toSomalia’s land and water information. It is one of the main sources of climate and water data that stakeholders rely on It produces weekly and monthly updates and early warning products on rainfall, floods, droughts, cyclones, and weather


SODMA: The National Multi-Hazard Early Warning Center in the Department of Disaster Risk Management under the Somalia Disaster Management Agency (SoDMA), is the country’s mandated entity in disaster warning activities. Its main tasks are the coordination of disaster risk management activities in the country. One of the center’s primary responsibilities is to regularly create climate information products, such as forecasts for temperature and rainfall, early warnings for cyclones, floods, and droughts, and projections on desert locust movement and diseases
MOEWR: The Department of Hydrometeorology in the Ministry of Energy and Water Resources, FederalGovernment of Somalia, is responsible for producing forecasts on river water level and rain forecasts with flood and drought monitoring.
Information Management Center, Puntland: This center, officially known as the InformationManagement Center for Water and Land Resources, was established by the government of Puntland in partnership with FAO-SWALIM through the Integrated Land and Water Resources Management Project (ILWRM). The center’s mission is to provide information about water and land resources to government ministries, international development organizations, and academic institutions. It provides early warning and forecast products on rainfall and droughts as well


Weak institutional capacity: The country’s capacities, both federal and state institutions, that are involved in early warning activities are weak or insufficient to provide timely and accurate information to the people. Limited monitoring stations and forecasting models, a small number of experts and professionals, and a lack of local strategies and plans for proper early warning systems are key challenges facing Somalia’s early warning and early action landscape.
Limited resources: One of the main pressing challenges for better early warning system implementation in Somalia is limited resources across the involved institutions. The government is currently funded by external partners for its programming, and the private sector, which is a dominant entity in the country, doesn’t invest in these areas.
Lack of coordination between different agencies: The current service providers in the early warning sectors are coordinated. Different warnings and alerts are produced each week and month based on the variety of dates they separately receive and disseminate. The forecasts provided are the same because of a lack of coordination among the providers.
Inadequate data and information: since the 1990s, the country’s data regarding weather and water has been lost due to destroyed stations across the country. Since then, the country has been dealing with fragmented and detached data, which can’t help the decision-making process of providing accurate advisory outlooks and forecasts.
Poor communication and dissemination of information: most of the early warning alerts and information don’t directly reach the affected people as they are not disseminated via the right media or channels. Information is produced and visualized on websites that are not available to people in disaster-prone areas
Fragmented platforms: the current platforms aren’t coordinated but fragmented with loads of different information and data, which may lead anyone seeking the right insights regarding early warning information in the country.

An effective early warning system saves lives, economies, and infrastructure and mitigates the impacts of disasters or climatic shocks while ultimately developing proactive and early preparedness measures in the community for an incoming threat. In Somalia, improving the country’s early warning system is vital for its capacity to cope with the recurrent and repetitive drought and flooding that affect millions of people in the country and cause lots of economic and property loss
The following points are the proper inputs to improve Somalia’s early warning systems:
Coordinated and systematic platforms where service providers are harmonized.
Establishment of water and weather monitoring stations and forecasting models
Capacitating or empowering local institutions and individuals with skills and resources
Improving communication and dissemination channels where remote people are easily reached or targeted
Political will from the government and interest from the private sector.
Considering the above-explained points will eventually solve the current challenges that Somalia’s early warning sector is facing.


Written by: Mohamed Shokry
I am a passionate Agriculture and Climate Professional from Somalia I advocate for sustainable land management through permaculture, agroforestry and climate-smart agriculture. I leverage my M&E expertise and data storytelling skills to design impactful projects in Somalia's agriculture, livelihoods, climate change, and disaster risk reduction sectors. My proven track record includes leading complex initiatives focused on food security, climate resilience, and sustainable resource management, with a focus on climate-smart agriculture practices.


Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) is one of the most popular and widely grown vegetables in the world due to its wide adaptability and versatility. The estimated world production of tomato is about 89.8 million Mg from an area of about 3,170,000 ha. It is the most extensively consumed vegetable crops in the world (Grandillo et al. 1999). It can be eaten raw in salads or as an ingredient in many dishes, and in drinks (Alam et al. 2007) Tomatoes and tomato-based foods are an ample source of nutrients, and has many health-related benefits to the body. In regions where it is being cultivated and consumed, it constitutes an essential part of people’s diet.
In addition, Tomato production is a source of income for most rural and peri-urban producers in Africa. Despite all the numerous benefits of the crop, numerous challenges, especially those in Africa, are making its production unprofitable in most developing countries. The challenges faced by producers relates to in production Such as poor seeds or Pest infestation, diseases, post-harvest, and marketing.

During the colonial period, Arabs, Italians and Indians introduced number of vegetable crops, including tomatoes, into Somalia for their daily needs and to a lesser extent for commercial purposes. Improved production practices and crop handling extensively grew among the casual laborers utilized by Italians and Asians in Somalia during the colonial era Thereafter, the trained laborers were attracted to the tomato cultivation for its profitability. This led to the deletion of the above-mentioned mistaken idea and considered the tomato to be the best vegetable crop used with different purposes. Tomato was not only a welcome food, but also became an important source of income for many households throughout the country.
Fruits and vegetables play an important role in Somalia’s national economy They potentially offer for the country favorable long-term opportunities for exportation and foreign exchange earnings. For instance, Bananas used to be a major exported crop before the civil war. The home-grown and most prevalent fruits and vegetables are the main source of vitamins. Particularly striking is the rich content of vitamin C in guava, papaya and mangoes, higher than the level of Vitamin C in grapefruits and lime, which are conventionally regarded as main source of vitamin C Furthermore, the three fruits, especially papayas, also contain plenty of vitamins A. The table below shows the nutritional value of fruits grown in Somalia in comparison with other important food crops.
Horticultural crops, as above-mentioned, are not only a welcome food, but also an important source of income In addition, the return per hectare from horticulture is higher than that of other crops such as maize or sorghum.


Puntland Locates in the north-eastern part of federal government of Somalia and mainly arid areas apart from some parts of Sanag region parts that are sub-humid areas with a relatively considerable precipitation Since the collapse of Somalia central government in 1991, this part, Puntland state of Somalia, of the country areas has been in a perpetual drought and subsequently faced with a acute food insecure.
Puntland’s agriculture sector is second in the economy of the state. The sector contributes approximately 15% of GDP and about 35% of the export earnings. Moreover, through links with manufacturing, distribution and service-related sectors, agriculture indirectly contributes a further 30% of the country’s GDP
Also, agriculture is also important because it is the main activity in the rural areas where over 80% of the population are located, and got involved, in one way or the other, in the sector Correspondingly, even in the urban areas, agricultural related activities provide the main source of livelihoods. One other reason for giving priority to agriculture is that the majority of the Puntland population are food insecure. Estimates available indicate that about 80.6% of the population lacks access to adequate food and, even the little they get, is of poor quality. The incidence and prevalence of food insecurity is more severe due to persistent droughts for the last two years 2015 and 2016. And that is mainly predicated upon due to the, despite agriculture being the only sustainable and secure sector to tackle the recurring droughts, dwindling support of donors-cum-international organizations, specially FOA who has been major source of provision ever since the collapse of the central government.


In Puntland, tomato is grown almost all over the regions, mostly under irrigation (furrow, drip or Surface one), and sometimes, but limited due to the average rainfall which is mostly below normal, under rain fed conditions. Farmers prefer growing tomato because it grows fast, covers large area with little investment, has a high demand in the market, and last of all has a reasonably good yield and a good return. Yet, the average yield of tomato in Puntland has remained low, and on that note, Somali Agricultural Research and Consultancy proposes to conduct the study of/addressing the aforementioned disadvantageous challenges for tomato production in Puntland to subsequently propose Potential Solutions.

The Scope of study will be Puntland sate of Somalia. Specifically, of the nine regions of the state, Bari and Nugal Region will be studied as far as the Challenges exist on tomato production is concerned. The SARC has the capacity and the expertise required to conduct the research.
The objectives of the task is as follows:
To identify factors effected/that causes the decline (are you sure its in decline or never took off the ground) of tomato production in Puntland.
To find out potential solutions for the beefing up of tomato production in Puntland
To identify opportunities and constraints towards tomato production in Puntland
To estimate the expected improvements in tomato production for producers, market participants and consumers as a result of expanded production, marketing and consumption of more tomato.

find out reliable information about the challenges of tomato production in Bari and Nugal Regions. The focus of the study will be as follows:
Data collection throughFocus group discussions aimed at on the farmers, sellers, seed suppliers and agricultural cooperatives.
Household interview of the individual farmers, especially small-scale ones, will be targeted.
Key informants’ interview; agricultural professionals such as agricultural agronomists, environmentalists from the Ministry of Agriculture and Irrigation, Somali Agricultural Research and Consultancy, experts in crop sciences selected from research institutions and cooperatives.
What are the major key constraining factors along its value chain (challenges) tomato growers?
Examine the trend of productivity, quality and earnings increased for the last 10 years?
If so, what is the harvest/yield rate of the tomato production in the investigated areas?
What are the major challenges farmers face during production of tomato?
What is the rate of Smallholder tomato farming in Puntland in comparison to total crop production?
In Puntland, tomato has a significant role in meeting local and nutritional food necessity, generation of income, and job creation. In that note, a large segment of Puntland population is are living in farming settlements of all regions. They mostly depend on subsistence farming characterized by traditional practices. In farming settlements, preliminary information’s indicates that is faced with a myriad of constraints along its value chain. These consist of agronomic limitations like incidence of pest and diseases and physiological syndromes (cracking, sunburn or scald); Environmental and industrial constraints such as climate variations, varieties,
Finally, institutional limitations such as poor post-harvest machineries and knowhow and inadequately organized rural and urban market infrastructures that sanction volatile price instability. Therefore, I will identify the fundamental constraints and proposes strategic interventions to improve tomato competitiveness along the value chain in Puntland.
The Puntland agricultural settlements have a great potential for market-oriented farming. The climate and fertility of agricultural zone locations allow farmers to grow and subsequently harvest multiple horticultural crops amongst which is tomatoes; both traditional and recently introduced improved varieties. The main market towns of Puntland which have satisfactory absorption capacities enable farmers to easily sell their commercial produce and hence, providing them with the opportunity to gain a sustainable income which in turn will enable them to contribute provision of basic needs for their families. Therefore, I will identifies the fundamental constraints and proposes strategic interventions to improve tomato competitiveness along the value chain in Puntland

Written By: Mohamed Warsame



By: Azza Kamal Mohamed Hassan
Food security in Sudan is a critical issue, exacerbated by ongoing conflict, economic instability, and environmental challenges. The recent outbreak of war in April 2023 has deepened these issues, displacing millions and further disrupting agricultural activities, food distribution networks, and market access. Despite these obstacles, there are promising strategies and innovative solutions that can help improve food security in the country. This article explores general approaches and solutions relevant to Sudan’s unique context
Food Security Challenges
Sudan faces severe food security issues due to a combination of factors:
Ongoing War: The conflict that erupted in April 2023 between the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) and the Rapid Support Forces(RSF) has displaced millions of people across the country, exacerbating food insecurity. This has severely disrupted the planting season, destroyed infrastructure, and blocked humanitarian aid routes. Agricultural production in war-torn areas has drastically declined, and market access has become increasingly limited, leading to skyrocketing food prices and leaving entire communities on the brink of famine.
Conflict in Other Regions: In addition to the ongoing war, long-standing conflicts in regions like Darfur, South Kordofan, and Blue Nile continue to affect agricultural activities. These regions, which are essential for food production, have seen widespread displacement and violence, further reducing food availability.
Economic Instability: Economic challenges, including high inflation and currency devaluation, have led to soaring food prices and limited purchasing power for many Sudanese families. The economic situation also affects food distribution networks and access to essential resources.
Environmental Factors: Sudan experiences prolonged droughts and erratic rainfall patterns that negatively impact agriculture The arid and semi-arid regions struggle with water scarcity, which affects crop yields and livestock productivity. Additionally, desertification and land degradation further exacerbate food security issues.

Promoting sustainable agricultural practices is crucial for enhancing food security. Techniques such as conservation agriculture, which includes minimal tillage, crop rotation, and organic farming, can improve soil health and boost crop yields. Introducing drought-resistant crop varieties and improving irrigation methods can help farmers adapt to changing climatic conditions and mitigate the impact of water scarcity.
Technological innovations offer significant potential for addressing food security challenges:
Solar-Powered Irrigation Systems: These systems provide a reliable water source for irrigation, reducing dependency on conventional water sources and enhancing agricultural productivity.
Mobile Agricultural Apps: Apps that offer weather forecasts, pest control advice, and market prices can help farmers make informed decisions and optimize their farming practices.
Community-based solutions are essential for addressing food security: Community Seed Banks: These banks help preserve local crop varieties and ensure farmers have access to quality seeds, which is crucial for maintaining agricultural diversity and resilience.
Local Food Storage Solutions: Building community storage facilities can reduce post- harvest losses and ensure a steady food supply throughout the year, helping to stabilize food availability.
Addressing the needs of displaced populations is vital: Food Aid and Agricultural Support: Providing immediate food aid, establishing temporary agricultural support programs, and integrating displaced individuals into local food production systems can help mitigate the impact of displacement on food security.

Engaging youth and local communities in food security efforts is crucial for building resilience and fostering innovation. Programs that involve young people in agriculture, technology development, and community planning can drive new solutions and enhance the effectiveness of food security initiatives. Local participation in these efforts helps ensure that solutions are tailored to specific needs and conditions
Conclusion
Improving food security in Sudan requires a comprehensive approach that combines sustainable agricultural practices, technological innovations, community-based solutions, and support for displaced populations By addressing current challenges and leveraging these strategies, Sudan can make significant progress toward achieving food security and building a more resilient food system.
Author: Azza Kamal Mohamed Hassan
Bio: Azza Kamal Mohamed Hassan holds a Bachelor's in Food Science and Technology and a Master's in Total Quality Management and Excellence (Food Safety). She is a certified Lead Auditor for FSSC 22000 and a Shift Supervisor at Al Rawabi Dairy Company Azza also serves as a Youth Representative Observer for the World Food Forum. Mobile:00971588860047 Email:azzakamal1993@gmail.com



By: Ahmed Al Sorani , Syria
The project aims to address the critical shortage of animal feed in rural regions, Syria, where limited water resources and ongoing conflict have severely impacted livestock-reliant communities. By implementing a sustainable barley sprouting system using water-efficient hydroponic techniques, the project provides a reliable, low-cost feed source. This initiative will improve livestock health, increase income for affected families, and enhance food security. The intended outcome is a resilient, self-sustaining agricultural practice that empowers local communities to rebuild their livelihoods.




In rural areas around the world, livestock farming and agriculture are foundational to life and local economies. However, these communities are increasingly facing challenges due to climate change, water scarcity, and economic crises that impact many rural regions. In this context, the idea of using hydroponic barley sprouting systems as an innovative solution to provide sustainable animal feed emerges as a promising approach. This concept relies on growing barley in controlled environments using water-efficient techniques, thereby enhancing feed production without requiring large amounts of water, which is essential for traditional farming methods. This idea has significant potential to bring about substantial changes in rural agriculture if adopted widely.
One of the major challenges faced by rural areas is water scarcity. In regions suffering from water shortages, traditional farming for feed production becomes unsustainable. Traditional agriculture relies heavily on large quantities of water, which has become a scarce resource due to climate change. In this regard, hydroponic systems offer an effective alternative by using recycled water and significantly reducing consumption. By controlling the amount of water used in farming, these systems can ensure sustainable agricultural production even in the driest regions. This makes them an attractive solution for rural areas grappling with limited water resources.
Additionally, farmers in rural areas face multiple economic challenges. The high cost of imported feed and heavy reliance on external markets exacerbate poverty pressures on these communities Relying on local, sustainable sources of feed, such as barley grown in hydroponic systems, can alleviate the financial burden on farmers.These systems are not only cost-effective to operate but can also provide high-quality nutrition for animals, improving their health and productivity. When livestock are healthy and productive, it positively impacts the income of farming families, contributing to their economic stability.
Another advantage of this idea is its suitability for rural implementation. Although hydroponic technology might seem complex at first glance, simple training and limited resources can enable farmers to manage these systems themselves. Rural farmers may sometimes lack technical training and knowledge of modern agricultural practices, but with appropriate support from NGOs or government bodies, these obstacles can be overcome Providing local training programs for farmers on how to effectively use and maintain hydroponic systems can enhance their capacity to be self-reliant rather than waiting for external aid.

The potential positive impact of this idea on food security cannot be overlooked Livestock farming is a critical part of the rural food system, with many people in these areas depending on animal products like milk and meat. Improving livestock health through sustainable and high-quality feed contributes to enhanced food security for individuals and communities. Increased production of meat and dairy not only improves local nutrition but also opens up opportunities for better marketing of agricultural products, leading to broader economic development
It is also important to note that hydroponic systems can be replicated in various rural contexts around the world. Whether regions face water scarcity due to dry climates or political and economic challenges, this system offers an adaptable solution. Its ability to provide sustainable solutions in volatile environments, such as conflict-affected rural areas, makes it a viable option not only for addressing feed shortages but also for achieving greater stability in these communities.
With all these benefits, the success of this idea depends significantly on the collaboration of various stakeholders. This initiative requires broad support from civil society organizations, government bodies, and agricultural experts to ensure its successful implementation The role of educational institutions in training farmers and providing research on improving hydroponic systems is crucial for the sustainability of this solution. Furthermore, external funding from donors may be necessary in the initial stages of the project to provide essential equipment and resources.
In conclusion, the idea of using hydroponic barley sprouting systems in rural areas represents an innovative and practical solution to the problem of animal feed shortages. This solution offers significant opportunities to enhance food security, promote economic sustainability, and adapt to environmental challenges in rural areas. By effectively addressing the need for sustainable feed, this approach can contribute to transforming agricultural practices and improving the resilience of rural communities.



By: Adiba Mohmed Asif Patel , UAE

In the rapidly changing global environment, the Near East and North Africa (NENA) region faces growing challenges in securing sustainable food systems. With a large youth population and increasing pressures from climate change, water scarcity, and land degradation, the region is at a critical juncture To tackle these issues, research and development (R&D) efforts must be at the forefront of driving sustainable solutions that ensure food security and climate resilience
Through a collaborative approach, combining technological advancements and policy innovation, R&D can help transform the region’s agricultural landscape while creating opportunities for youth engagement and economic growth.

In NENA, agriculture is a key sector, contributing to both economic stability and food security However, the region is highly vulnerable to environmental and geopolitical risks R&D serves as a crucial tool in addressing these vulnerabilities by fostering innovative approaches to agricultural practices, resource management, and climate adaptation.
For instance, one of the primary challenges in the region is water scarcity. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the NENA region is home to 12 of the world’s most water-scarce countries. R&D initiatives focused on water-efficient technologies, such as drip irrigation and desalination, are helping to improve water management practices, reducing the reliance on traditional, inefficient methods.
Moreover, the region’s harsh climate conditions, including frequent droughts and temperature extremes, make it necessary to develop climate-smart agriculture (CSA) techniques. R&D in this area has resulted in the creation of drought-resistant crop varieties, improved soil management techniques, and innovative farming practices that can withstand the effects of climate change


Youth play a vital role in driving innovation and sustainability across the NENA region Collaborations with organizations like the World Food Forum and the NENA Youth Policy Board are essential in ensuring that young people are actively involved in the region’s R&D efforts. Their energy, creativity, and technological savvy are key assets in addressing the unique challenges of the region.
The World Food Forum, for instance, brings together young professionals, policy makers, and innovators to engage in discussions and activities aimed at creating sustainable food systems. By providing platforms for youth to contribute their ideas and research, these collaborations empower the next generation of leaders to take charge of the future of food security and climate resilience in their communities.
Youth-led startups in the region are already making significant strides. Innovative agritech companies are using technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), big data, and blockchain to improve supply chain transparency, optimize resource use, and increase crop yields These innovations are not only contributing to food security but also creating job opportunities for the region’s growing youth population


For R&D efforts to be truly effective, they must be supported by strong policy frameworks. Governments across the NENA region have a critical role to play in fostering an environment conducive to innovation. This includes investing in research institutions, incentivizing sustainable agricultural practices, and ensuring that policies align with both local needs and global sustainability goals.
Policy-driven support for sustainable agriculture can take many forms, including subsidies for green technologies, improved access to credit for farmers adopting sustainable practices, and regional collaborations that address cross-border environmental challenges such as desertification and water shortages. Countries like Morocco and Egypt are leading by example, implementing national strategies that prioritize sustainable agriculture and climate resilience.
Additionally, regional collaboration is vital to address shared challenges. Organizations such as the Arab League and the African Union are promoting cross-border cooperation on R&D initiatives, allowing for the sharing of knowledge, resources, and best practices This regional approach ensures that innovative solutions can be scaled up and adapted to local contexts, benefiting multiple countries in the region.
Looking forward, the continued investment in R&D is crucial to the future sustainability of the NENA region. By integrating cuttingedge technologies with traditional agricultural knowledge, the region has the potential to become a leader in sustainable food systems. However, this will require ongoing collaboration between governments, the private sector, research institutions, and civil society.
To achieve long-term success, R&D must prioritize climate resilience, food security, and youth engagement This involves not only developing innovative technologies but also ensuring that these solutions are accessible and scalable for smallholder farmers, who make up a significant portion of the region’s agricultural workforce.
Finally, a key factor in ensuring the sustainability of R&D efforts is education. By investing in agricultural education and training programs, countries in the NENA region can equip the next generation of farmers, researchers, and policy makers with the skills they need to implement and sustain innovative agricultural practices



Research and development are essential to addressing the critical challenges facing the Near East and North Africa in the areas of food security and climate resilience. Through the active involvement of youth, the integration of innovative technologies, and strong policy support, the region can create a sustainable future that balances economic growth with environmental stewardship. By fostering collaboration and investing in R&D, the NENA region has the opportunity to transform its agricultural systems and ensure food security for generations to come.

Written by: Adiba Mohmed Asif Patel

By: Chaima Ayari
In an era where environmental concerns are more pressing than ever, innovative solutions to waste management are crucial. The Advanced Waste-to-Energy Conversion System (AWTECS) represents a groundbreaking approach in this field, tackling the dual challenges of hazardous waste disposal and sustainable energy production. This pioneering project is not only designed to reduce environmental contamination but also aims to transform waste management into a cleaner, more efficient process.
Hazardous waste is a significant environmental and health concern. Traditional methods of disposal, such as landfilling and incineration, often come with their own set of problems. Landfills can leach harmful chemicals into the soil and groundwater, while incineration can release toxic pollutants into the air. AWTECS addresses these issues by offering a more sophisticated solution.
The AWTECS system utilizes advanced technologies to convert hazardous waste into energy in a controlled and environmentally friendly manner. By integrating state-ofthe-art waste treatment methods with energy production processes, AWTECS ensures that hazardous materials are neutralized while simultaneously generating valuable resources.


At the heart of the AWTECS technology is a multi-stage conversion process that effectively deals with various types of hazardous waste. Here’s a brief overview of how it operates:
1.
Waste Collection and Pre-Treatment: Hazardous waste is first collected and pretreated to prepare it for conversion This step may involve sorting, shredding, or chemical treatment to make the waste more suitable for processing.
2.
High-Temperature Processing: The pre-treated waste is then subjected to hightemperature processing in specialized reactors. These reactors operate at temperatures high enough to decompose hazardous materials into less harmful compounds. This process not only neutralizes toxic substances but also breaks them down into simpler molecules
3.
Energy Recovery: During the high-temperature processing, the breakdown of waste materials produces a range of by-products, including gases and heat. AWTECS captures these by-products and converts them into usable energy. The gases can be utilized to generate electricity, while the heat can be harnessed for industrial applications or district heating.
Emission Control: One of the critical aspects of AWTECS is its robust emission control system. Advanced filters and scrubbers ensure that any potentially harmful emissions are captured and treated before being released into the atmosphere. This system minimizes the environmental impact of the conversion process, making it a cleaner alternative to traditional waste management methods.
Residue Management: After conversion, the remaining residues are carefully managed These residues are typically transformed into inert materials or used in construction, reducing the overall volume of waste that requires disposal. 5.
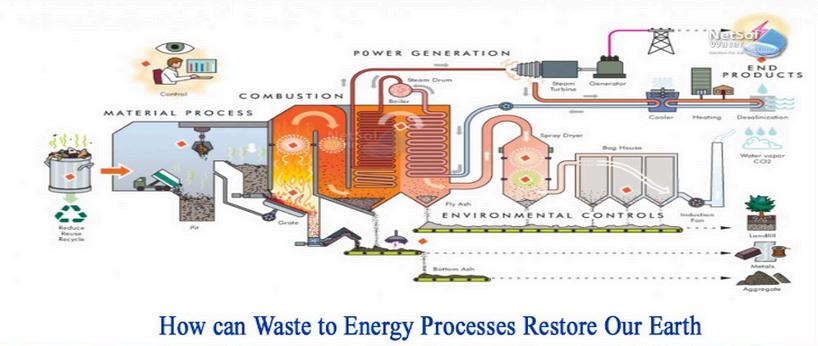

Hazardous waste poses a formidable challenge due to its potential to cause severe environmental and health issues. Traditional disposal methods, such as landfilling and incineration, often fail to adequately address the risks associated with hazardous materials. Landfills can lead to soil and groundwater contamination, while incineration can release toxic emissions into the atmosphere AWTECS provides a more advanced and environmentally responsible solution.
At the core of AWTECS is a sophisticated multi-stage process designed to convert hazardous waste into usable energy. The system begins with the collection and pretreatment of waste, which involves sorting and processing to prepare the materials for conversion Next, the waste undergoes high-temperature processing in specialized reactors, where it is decomposed into less harmful substances. This process not only neutralizes toxic compounds but also generates gases and heat, which are then harnessed to produce electricity and heat energy.
A key feature of AWTECS is its robust emission control system. Advanced filters and scrubbers capture and treat any potentially harmful emissions, ensuring that the conversion process remains environmentally friendly. Additionally, the remaining residues are managed in a way that reduces the volume of waste requiring disposal, often turning them into inert materials or usable by-products.

AWTECS Facility: A high-resolution photograph of the AWTECS plant showcasing its advanced reactors and clean, modern design

The AWTECS project offers several significant benefits, both environmentally and economically:
Reduced Pollution: By converting hazardous waste into energy rather than disposing of it through traditional means, AWTECS helps reduce pollution The advanced emission controls ensure that the conversion process is as clean as possible.
Sustainable Energy Production: The energy generated through the AWTECS process contributes to a more sustainable energy grid. By turning waste into electricity and heat, AWTECS supports clean energy initiatives and reduces reliance on fossil fuels
Reduced Landfill Use: With AWTECS, there is less need for landfills, which are often associated with environmental contamination. This reduction in landfill use not only helps protect land and water resources but also extends the lifespan of existing landfills.
Economic Efficiency: The ability to generate energy from waste adds economic value to what would otherwise be considered a liability. This transformation creates new revenue streams and can lead to job creation in the waste management and energy sectors.
The benefits of AWTECS extend beyond its innovative technology. Environmentally, the system significantly reduces pollution by minimizing the risks associated with hazardous waste disposal By converting waste into energy, AWTECS lessens the need for landfills, protecting land and water resources from contamination. Moreover, the energy generated contributes to a more sustainable energy grid, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and supporting clean energy initiatives.
Economically, AWTECS creates new opportunities. The transformation of waste into energy adds value to materials that would otherwise be a liability. This process not only generates revenue but also has the potential to create jobs within the waste management and energy sectors. The integration of waste management with energy production represents a forward-thinking approach that aligns economic benefits with environmental stewardship.

The Advanced Waste-to-Energy Conversion System (AWTECS) represents a significant advancement in waste management technology. By addressing the challenges of hazardous waste disposal and contributing to sustainable energy production, AWTECS stands at the forefront of environmental innovation.
As more industries and municipalities adopt this technology, the potential for a cleaner, more sustainable future becomes increasingly attainable. AWTECS not only offers a solution to the pressing problem of hazardous waste but also paves the way for a more efficient and environmentally friendly approach to waste management.
In the evolving landscape of environmental technology, the Advanced Waste-toEnergy Conversion System (AWTECS) stands as a beacon of innovation. This cuttingedge project is designed to tackle the complexities of hazardous waste management by transforming waste into sustainable energy By addressing both environmental contamination and energy generation, AWTECS represents a significant leap toward a cleaner and more efficient future.


In a small town shadowed by the towering mountains, there was a growing concern about the nearby waste disposal site. Once a simple landfill, it had become a source of toxic leaks and pollution, threatening the health of the community and the surrounding environment. But as the years went by, the town’s leaders became determined to find a solution.
Enter the Advanced Waste-to-Energy Conversion System (AWTECS). The project, initially a distant concept in environmental circles, was soon brought to life in their town. The facility’s construction was met with skepticism, but hope began to build as the massive reactors and high-tech equipment took shape. The day the facility was inaugurated, the town's residents watched with a mixture of curiosity and anxiety Inside the plant, the process began waste was carefully sorted and fed into the reactors. The high temperatures and advanced technology neutralized the hazardous compounds, while the energy generated from this process was harnessed to power homes and businesses.
Months later, the results were astounding. The once-toxic landfill was now a site of clean energy production The town's air and water quality improved dramatically, and the new source of energy contributed to a more sustainable future. The success of AWTECS not only transformed their waste but also brought the community together, showing that innovation could turn even the darkest challenges into a bright opportunity.
AWTECS
The implementation of the Advanced Waste-to-Energy Conversion System (AWTECS) represents more than just a technological breakthrough; it embodies a commitment to local empowerment and sustainable practices. As communities face increasing waste management challenges, AWTECS serves as a model for integrating advanced technology with grassroots solutions
The AWTECS initiative starts with engaging local communities in the waste management process. By involving residents in waste sorting and pre-treatment, the project creates a sense of ownership and responsibility. Educational programs are implemented to inform the community about the importance of proper waste disposal and the benefits of the AWTECS system.
In addition to environmental benefits, AWTECS generates economic opportunities for local residents. The construction and operation of the facility create jobs, from plant operators to maintenance staff. Furthermore, local businesses benefit from the sustainable energy produced, which can lead to lower energy costs and new commercial opportunities
Looking ahead, the AWTECS initiative plans to expand its model to other communities facing similar waste management issues. By sharing their success stories and best practices, they aim to inspire other regions to adopt similar technologies The goal is to create a network of communities empowered by advanced waste-to-energy solutions, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient future.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the AWTECS project is a testament to the power of innovation in addressing some of the most challenging environmental issues of our time. As we look toward the future, it is technologies like AWTECS that will lead the way in creating a more sustainable and cleaner world.

Contributors
Dr. Emily Carter
Environmental Engineer and Project Lead
Dr Emily Carter is a leading expert in waste management technologies with over 15 years of experience in environmental engineering She has spearheaded numerous projects aimed at reducing environmental impact through innovative technologies Contact: emily carter@awtecs com
John Mitchell
Community Outreach Coordinator
John Mitchell specializes in community engagement and education related to environmental initiatives His work focuses on bridging the gap between advanced technologies and local communities to ensure effective implementation. Contact: john.mitchell@awtecs.com
Sophia Lee
Technical Specialist
Sophia Lee is a technical specialist with expertise in waste-to-energy systems. She provides support and maintenance for AWTECS technology, ensuring its efficient and reliable operation. Contact: sophia.lee@awtecs.com


The "Your Story Matters" section of the Saudi Sustainability magazine is a compelling platform committed to sharing the experiences and initiatives of individuals and organizations who are driving positive change towards a sustainable future in Saudi Arabia. Serving as a powerful medium for inspiration and education, this section features in-depth interviews, success stories, and thought-provoking narratives that shed light on the innovative solutions and sustainable practices being implemented across various sectors in the Kingdom.
From stories of individuals leading impactful environmental projects to businesses adopting sustainable strategies, "Your Story Matters" showcases the diverse range of efforts taking place to address environmental, social, and economic challenges in Saudi Arabia. It aims to create a sense of pride and motivation, encouraging readers to contribute to the sustainability movement and find ways they too can positively impact their communities and the environment. Through this section, Saudi Sustainability magazine reinforces the idea that every individual's story matters and plays a crucial role in shaping a sustainable future for the country.

Share your story with us and showcase your sustainability efforts to the world.
Sharing your story can be in any of the following formats:
Company Profile
Success Story Awards and Achievements
Case Studies
Reports Research
Photos and much more.
Submit your interest to info@spsaonline.net