7 minute read
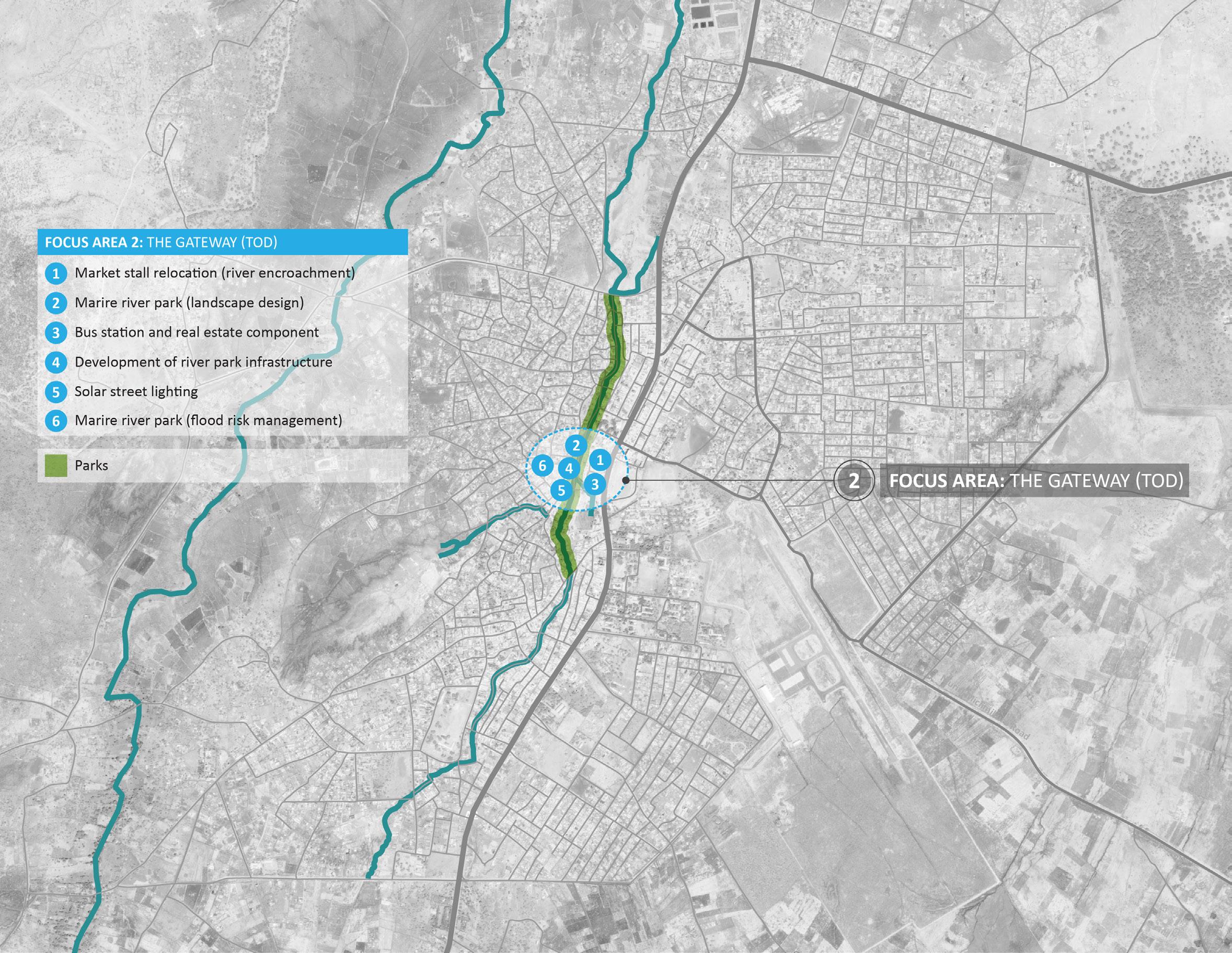
Focus Area 4: Airport
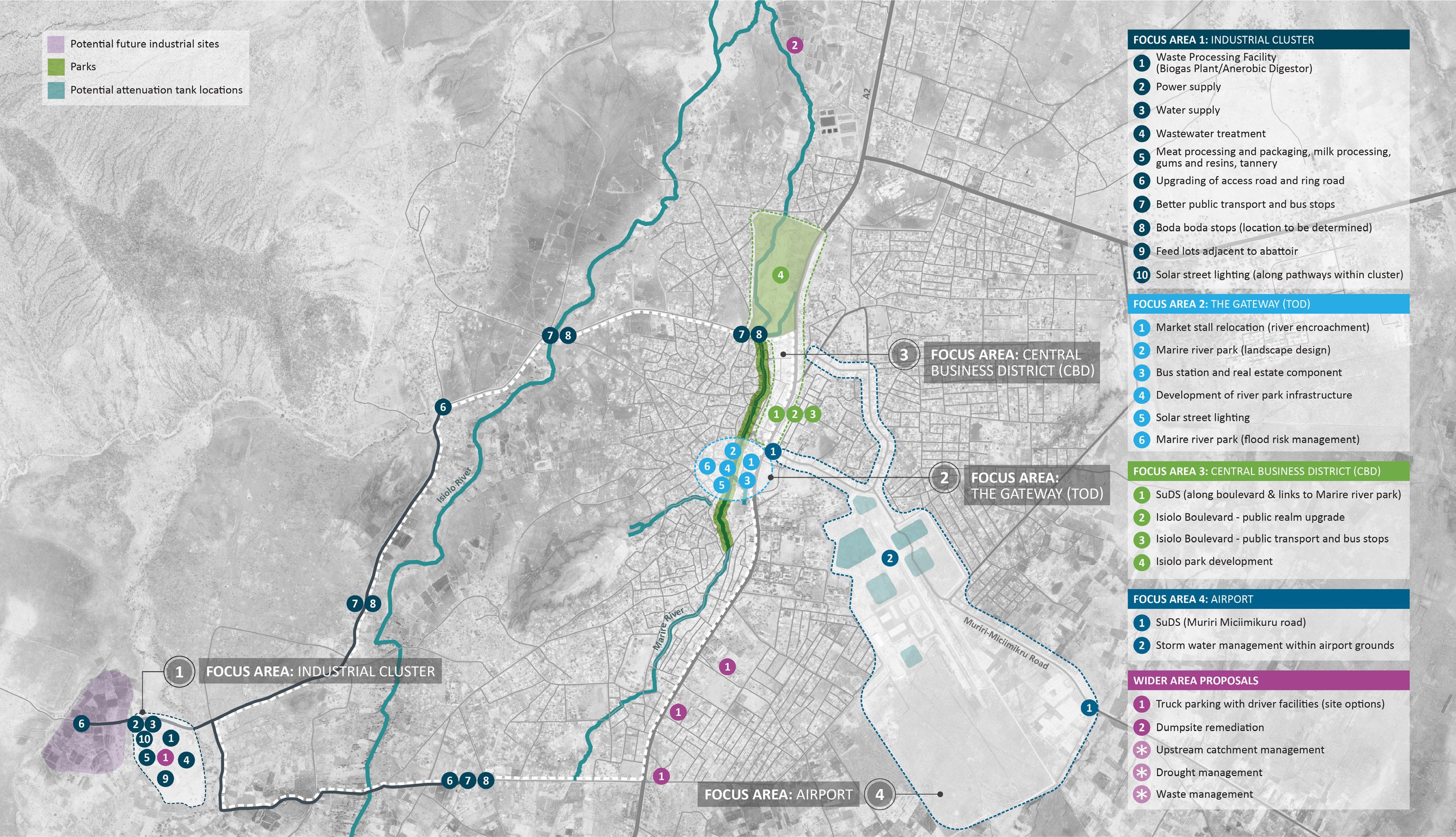
75 ISIOLO URBAN ECONOMIC PLAN
Isiolo Airport aspires to become the international gateway to the wider region, however its operations are affected by seasonal flooding. It is furthermore understood that most of the downstream developments (in the immediate proximity and further downstream) such as in the CBD, are also affected by flooding, potentially caused by the increase in impervious surface within the airport perimeter. The Airport has plans for expansion, the runway is due to be extended and there is a vision which will include additional commercial and light industrial activities within the airport land holding. The consequential reduction in permeable surface is likely to further add to the pressure on storm water drainage in the adjacent lower lying areas. All the above suggests that a broader, coordinated and more holistic vision for the SouthEast sector of Isiolo (outside the airport boundary) could be beneficial to the whole town. The “Airport City” approach could be adopted where mitigation of issues such as storm water drainage are dealt at both site level (within airport ownership) and in the surrounding areas in a coordinated manner. New developments in the future could adhere to a range of coordinated guidelines that improve the drainage and retention performance of plots and buildings whilst an integrated economic vision for the airport neighbourhood could complement the airport expansion plans.
Figure 30 - Development Framework plan showing Focus Area 4 - Airport
Focus Area 4: Sequencing
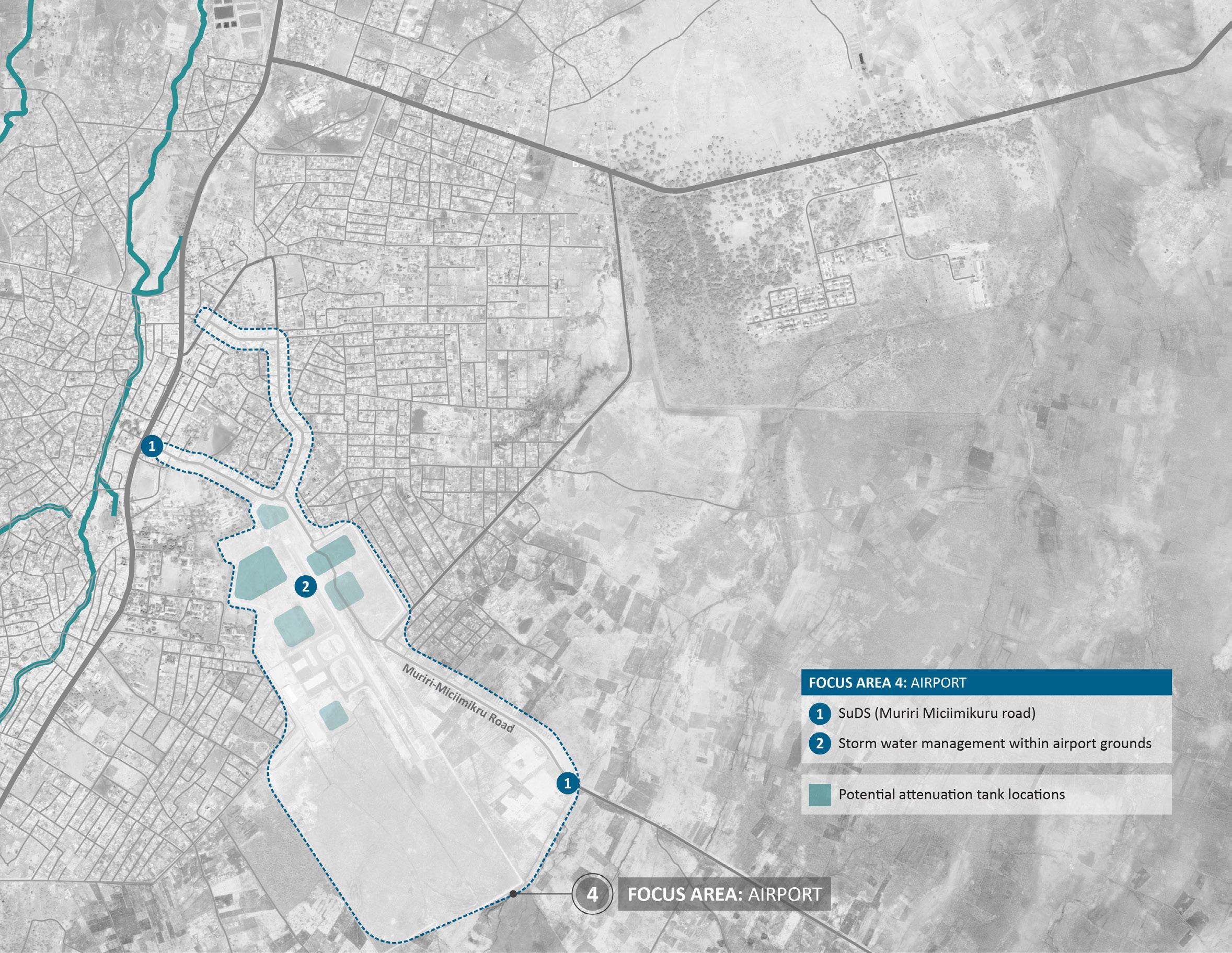
1. Sustainable Urban Drainage systems (SuDS) - in order to manage storm water run-off events that occur from the airport area of the Town it is proposed to introduce SuDS infrastructure along the roads leading into the Town. This will alleviate potential flash flooding through reducing peak water flow by means of attenuation and retention. 2. Storm water management within airport grounds - by managing the water flow from the airport. This will be done through a combination of providing on site retention, then releasing it slowly into the SuDS infrastructure provided within the existing roads rights of way.
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT PLAN 76
AIRPORT SuDS (Muriri Miciimikuru Road) 1
The proposals include a coordinated approach to storm water drainage, namely underground tank storage within the airport perimeter and introduction of SuDS, such asswales, raingardens, retention ponds etc) along the streets between the airport and the CBD. The potential re-use of the retained stormwater is an important opportunity in such a water starved region and an important resource to be capitalised upon from both the airport and Isiolo Town.
Sub-Components Estimated Cost Impacts (Benefits) Delivery Mechanisms
› Airport onsite storm water management with underground water retention tanks › Integration of SuDS to reduce and mitigate surface water run-off in streets between Airport and CBD area › Permeable paving and surfaces within the airport and along the
Town streets where appropriate › Upgrade of drainage › Adding street trees and planting to support
SuDS implementation and add aesthetic appeal › £292/m3 an indicative cost based on prices from the UK for standard geocellular attenuation cells. The drainage system for the airport will include other elements. This will be confirmed following concept and detailed design process › Improved storm water management both at source and downstream › Improved drainage for surface water run-off › Reduced flooding events within the Town / CBD › Improved land value around the airport › Typically, Public funded projects › Potentially: multilateral partnership among
Kenya Airport Authority,
Water authority, and
Municipality
Challenges Data Gaps Time Frame Phasing Project Priority
› Coordination and buy-in from variable stakeholders › Funding › Land ownership › Pre-feasibility and feasibility studies › Site survey is required › Short to medium term › Urban
Development
Proposals supporting
Economic Growth (infrastructure) › Airport Authority within their boundary › Municipality in all public Right of Ways
Operations & Maintenance
77 ISIOLO URBAN ECONOMIC PLAN
Figure 31 - Airport flood alleviation and water treatment; concept proposal

ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT PLAN 78
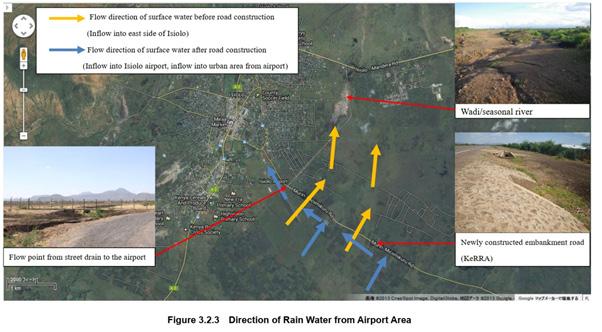
It is well recognised by the local government that the inland water from the airport is one of the biggest factors of flood in Isiolo Town.29 The hard surfaces and the paved areas at Isiolo international airport reduce the amount of infiltration and this has been exacerbated by the development of the construction of a new airport access road, which is raised on a bund and hence directs water to the west and into Isiolo Town.
Sponge City concept can be applied in the airport area. The sponge city concept is about integrating urban water management into the urban planning policies and designs. The infrastructure systems will collect, convey and store stormwater. In addition, it will provide a water treatment element that can provide a new water source that can be reused for irrigation or other activities. › Solutions to include bunds and detention basins to slow down and store water on the surface.
› Covered underground attenuation storage tanks such as geocellular storage systems or oversized pipes that can be installed with pollutant separators that removes attached pollutants and highly contaminated substance such as free-floating oil, hydrocarbons and heavy metals. › Buried stormwater storage within Airport grounds to store water from roofs areas to be reused in airports activities such as air conditioning, landscape irrigation, washing paved areas, toilet flushing. Industrial area planned as part of airport expansion - potential for water re-use.
› Proposed Road along southern airport perimeter to include space for storm water storage within road design. › Existing drainage culvert has limited capacity this should be rehabilitated to incude additional storage in shallow bunded areas. › Retrofit SuDS features along Muriri Miciimikuru road to intercept runoff and convey it away from the Isiolo Town.
Figure 32 - Direction of rain water from airport area
Challenges Data Gaps Time Frame
› The implementation of sponge city concept requires appropriate planning and legal frameworks in place to implement and maintain the system. › The airport challenges in implementing Green
Infrastructure strategies mainly include those related to wildlife attraction, climate change, antiicing/deicing compounds, and land use limitations. › Long-term operability (i.e. maintenance requirements) › Funding › Feasibility study for rainwater harvesting: how would water be used, what is the cost benefit, minimum storage volumes Long term
29 Isiolo Flood Management Plan
79 ISIOLO URBAN ECONOMIC PLAN
Case Studies:


Transitioning to Sponge Cities: Challenges and Opportunities to address Urban Water Problems in China Qingdao has developed the concept of a sponge city into an implemented process of urban planning and construction management. The implementation of the sponge city should be an integrated system of grey and green infrastructures that reduce the runoff and pollution from the source, control the runoff and pollution inline and treat the runoff at the end of the pipe. Rivers and lakes can also be used as water quality channel for pollution removal and establish aquatic habitats. The sponge city concept in Qingdao, China comprises 5 components for the terminal area. It includes swales, greenland, water storage, bioretention pond and wetland. Bioretention ponds and wetlands have been used to provide water purification space. Plant species have been selected to provide effective particles removal. Plants are essential for facilitating the effective removal of pollutants in wetlands and bioretention systems, particularly nitrogen. The vegetation also maintains the soil structure of the root zone. The plants roots loosen the soil and creates macropores, which maintain the long-term infiltration capacity of bioretention systems. Pollutant removal equipment has been added to 3 bodies of water to ensure clean water. The “gas-floating-biochemical-filtration” integrated equipment is used to assist wetland purification, physical removal of N, P, organic matter and solid suspensions, and to provide an additional level of water treatment.
30 http://www.sdslimited.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/Edinburgh-Airport-Case-Study.pdf 31 http://www.wateractive.co.uk/case_studies/below_the_surface_edinburgh_airports_calm_despite_the_storms 32 http://www.sdslimited.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/Geolight-Brochure-2016.pdf Edinburgh Airport - Edinburgh, UK30 Scotland’s Largest underground surface water drainage system has been installed as part of Edinburgh Airport expansion. It is designed to store 7,000m3 of surface water during heavy storms. The water is collected visa gravity network of slot drains and 660m long 1500mm diameter pipes before reaching to the SDS GEOlight attenuation system.31 A number of oil interceptors are used along the gravity network to clean the water before it enters the GEOlight tank to reduce maintenance requirements. The water stored within the GEOlight attenuation system can be pumped as required to a network of standpipes for irrigation or can be discharged to the drainage system at a controlled manner.32



Schiphol Airport - Amsterdam Just past the edge of the runway, there’s a series of hedges and ditches laid out like interlocking diamonds. Falls PnP - Roodepoort, South Africa A detention pond reduces stormwater peak flows while supplying a sump with stormwater used for irrigation