VaradayiniShinde,SahilPawar,OPNCalla
1DepartmentofElectronicsandTelecommunications(NBNSinhgadSchoolofEngineering)

2DepartmentofElectronicsandTelecommunications(STESSmt.KashibaiNavaleCollegeofEngineering)
3InternationalCentreforRadioScience
ABSTRACT
Thepropagationofradiowavesisaffectedbymanyreasonsandtheforemostreasonisthemediumittravelsthrough.Thepropertiesofmediumcauseattenuationin thetransmittedsignal.Thispaperexplorestheeffectofdifferentmaterialsonthepropagation.Materialslikemetal,RFabsorber,wood,plastic,PTFEsheet(synthetic plastic polymer) and fiber reinforced plastic (FRP) are placed between two pyramidal horn antennas at X-band (8GHz to 12GHz). Phenomena like reflection, refraction,diffractionandabsorptionaffectthepropagationofwaves.Thepaperpropoundstheeffectofthesematerialsonthesignalreceivedatthereceiverantenna.
KEYWORDS:antenna,X-band,radiowaves,propagation,materials.
I.INTRODUCTION:
Radiopropagationisanimportantaspectinanyradiocommunicationsystem.It isthewayradiowavestravelorpropagatewhentheyaretransmittedfromone point to another It depends on many factors and the choice of radio frequency willdeterminemanyaspectsoftheradiopropagationfortheradiocommunicationsystem.Themediumthroughwhichtheradiowavestravelandthevarious objectsthatmayappearinthepathaffectthepropagationofradiowavesandthe quality of the received signal too.When radio waves travel through a material medium,theyareattenuatedduetothematerial'spermittivityandpermeability Reflection, refraction, absorption and diffraction may take place.The received signalmayalsobeacombinationofseveralsignalsthathavetravelledbydifferentpaths.Thesemayaddtogetherorsubtractfromoneanother Andinaddition tothisthesignalstravellingviadifferentpathsmaybedelayedcausingdistortion ofthereceivedsignal.
Forthispaper,radiowavesarepropagatedthroughdifferentmaterialsattheXband, and the effect of these materials on the waves is recorded and studied. Whenametalsheetisplacedbetweenthetransmittingandreceivingantennas, theradiowavesarereflectedandabsorbed.Thishappensbecausemetalisaconducting material and conducting materials absorb radio and electromagnetic waves.Theattenuationbecauseofmetalisthereforeveryhigh.Thisattenuation affects the power received at the receiver antenna.The second material placed between the two antennas is an RF absorber (absorber).An RF absorber is yet another highly absorbing material. The power received at the receiver, when propagated through the absorber is less and quite similar to that of metal. The thirdmaterialplacediswood.Woodisanon-conductingmaterial.Ithasaminimaleffectonradiowavesandabsorbsradiowavestosomeextent.Theattenuation caused by wood is very less as compared to metal and sponge, the power receivedbykeepingwoodinbetweeniscomparativelymore.Thefourthmaterialplacedisaplasticcontainer Plasticagain,isanon-conductingmaterialand henceitisnotlikelytointerferewiththeradiowaves.Theattenuationcausedby plastic is very less. Power received is more than the conducting materials.The fifthmaterialplacedisaPVCplasticsheet.Theresultantpowerobservedisfairly similartothatofplasticcontainer Lastly,thesixthmaterialplacedisfiber Since fiber is also a non-conducting material, power received when propagated throughitisquitesimilartothatofwood.
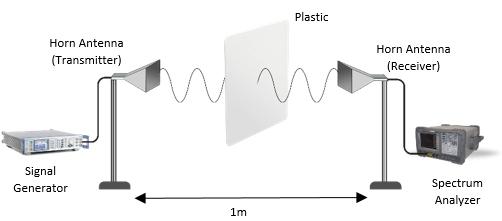
II.EXPERIMENTALSETUP:
Two pyramidal horn antennas are mounted on turntables 1m apart. Both the antennasarefixedatanelevationangleof90˚facingeachother Thetransmitting antennaisfedinputthroughasignalgeneratoroffrequencyrange9kHz-40GHz. Atthereceivingantenna,spectrumanalyzeroffrequencyrange9kHz-13.2GHz isattached.Thematerialisplacedintheexactcenterofbothantennas.Transmittingantennaisappliedafrequencyof8GHzwithpowerof30dBm.Radiowaves aretransmittedinthedirectionofthematerialplacedinthecenter Dependingon the material's property, the radio waves are absorbed or reflected, and these wavesarethenreceivedatthereceiverantenna.8GHzoffrequencyandaspanof 100MHzisappliedtotheanalyzerandthepowerreceivedisrecordedbytheanalyzer.SameprocedureiscarriedoutfordifferentmaterialsatdifferentfrequenciesofX-Band.Thematerialsusedinthisexperimentare:
Figure1:Metal Figure2:Absorber(Sponge)


Figure3:Plastic
III.OBSERVATIONS:
Figure4:Wood

Figure:5FRP

Figure:6PTFE

Experiments of different materials at different frequencies are carried out.The observationsareasfollows:
Frequency Metal RFAbsorber(Sponge) Plastic
8GHz -29.36dBm -29.44dBm -1.87dBm
9GHz -19.13dBm -19.34dBm 1.97dBm
10GHz -12dBm -13.81dBm 3.18dBm
11GHz -18.79dBm -19.34dBm 3.5dBm
12GHz -22.24dBm -22.47dBm 1.14dBm
Frequency Wood FRP PTFEsheet
8GHz 0.43dBm 1.11dBm 1.65dBm
9GHz 1.85dBm 2.84dBm 2.69dBm
10GHz 2.64dBm 3.47dBm 3.65dBm
11GHz 1.8dBm 3.49dBm 4.09dBm
12GHz 0.16dBm 3.06dBm 2.06dBm
IV.CONCLUSION:
Radiowavesarepropagatedthroughdifferentmaterials.Attenuationcausedby metalandRFabsorberonthepropagationofwavesisobservedtobequitesimilar Metalisaconductingmaterialandhenceitabsorbsandreflectsmostofthe waves. However, the effect of wood, plastic, PTFE and FRPis observed to be comparativelylesssincetheyarenon-conductingmaterials.
REFERENCES:
I. T Tongboonsong,A.Boonpoonga,K.Phaebua,T LertwiriyaprapaandL.Bannawat, "AStudyofanX-bandFMCWRadarforSmallObjectDetection,"20219thInternationalElectricalEngineeringCongress(iEECON),2021,pp.579-582,doi:10.1109/ iEECON51072.2021.9440348.
II. E.S.Malevich,M.S.Mikhailov,A.A.VolkovaandK.Y Kozhevnikov,"ExperimentalResearchofX-bandRadioWavePropagationinForestVegetation,"2019International Youth Conference on Radio Electronics, Electrical and Power Engineering (REEPE),2019,pp.1-4,doi:10.1109/REEPE.2019.8708757.
III. M. Cheffena and T Ekman, "Modeling the Dynamic Effects of Vegetation on
RadiowavePropagation,"2008IEEEInternationalConferenceonCommunications, 2008,pp.4466-4471,doi:10.1109/ICC.2008.838.
IV J.H.TarngandK.M.Ju,"Effectofmetallow-partitionsonradiopropagationinan office," Proceedings of 1994 3rd IEEE International Conference on Universal PersonalCommunications,1994,pp.135-139,doi:10.1109/ICUPC.1994.383035.
V M.A.Karam,A.K.Fung,E.MouginandA.Lopes,"Electromagneticwaveinteractionwithconiferoustrees:theoryandexperiment,"AntennasandPropagationSociety Symposium 1991 Digest, 1991, pp 1386-1389 vol 3, doi: 10 1109/ APS.1991.175108.
VI. Q.Wangetal.,"RangeandHeightMeasurementofX-BandEMPropagationinthe MarineAtmosphericBoundaryLayer,"inIEEETransactionsonAntennasandPropagation,vol.67,no.4,pp.2063-2073,April2019,doi:10.1109/TAP.2019.2894269.
VII. K.SalayongandT Lertwiriyaprapa,"Studyofelectromagneticabsorbermadebynatural rubber," 2015 IEEE Conference on Antenna Measurements & Applications (CAMA),2015,pp.1-2,doi:10.1109/CAMA.2015.7428183.
VIII. M. Plonus, "Theoretical investigations of scattering from plastic foams," in IEEE TransactionsonAntennasandPropagation,vol.13,no.1,pp.88-94,January1965, doi:10.1109/TAP.1965.1138379.
