OTITIS MEDIA AND ITS MANAGEMENT AMONG G.N.M. II YEAR STUDENTS IN APEX COLLEGE OF NURSING, AT VARANASI
ABSTRACT
OtitisMediaisaninfectionofthemiddleear OtitisMediaisabuild-upoffluidinthemiddleear,aspacebetweeneardrumandinnerear OtitisMediaismorecommon inyoungchildren.
TheawarenessregardingOtitisMediaisneedfornursingstudentstohelpineducationofcommunitypeople. Adescriptivestudywasconductedwhereinstudentsof age group 18-30 years were selected for the study using random sampling method.Atotal 30 students were included in the study Data were collected by using knowledge questionnaires. The 40% respondent having excellent knowledge, 33.33% of the respondents were having good knowledge, and 26.66 % respondent havingaverageknowledgeregardingotitismedia.Asignificantassociationwasfoundbetweendemographicvariablesandknowledge.
INTRODUCTION:
Otitismediaisashorttermmiddleearinfection.It'scomesuddenlyandalong timeintervalitcomesbackwithlessseveresymptoms.Otitismediaismarkedas apain,feverdizzinessandhearingabnormalities.Astudyin1980-1989theotitis mediaresearchcentreatPittsburghwasexaminedtheprevalenceofbacteria.The cultureatcentrewasshowsthattheStreptococcuspneumoniaaredominatedin acuteotitismediacause,Homophilesinfluenzaalsofoundinmanypatients.
OBJECTIVES:
1. Toassessthelevelofknowledgeinnursingstudentsregardingotitismedia.
2. To find out the association between knowledge of students with selected demographicvariablesregardingotitismedia.
3. There will be significance difference between knowledge of students regardingotitismedia.
RESEARCHMETHODOLOGY:
Researchdesignwasconsistedandescriptiveresearchdesignapproachtoassess theknowledgeregardingotitismediaamongG.N.M.IIndyearstudentsin Apex nursingcollegeatVaranasi.Thepopulationselectedforthestudywas30G.N.M. ndII year students.Thesampleswereselectedbyusingnon-probability,purposive sampling technique. The development of tools involved steps of test constructioni.e.preparingtheblueprint,selectionofitems.Contentvalidityofquestionnaire was done and modifications were done according to the suggestion given by experts. Pre testing and reliability of tools were done.The tools were foundtobereliable.
Thedatawerecollectedbyusingstructuralknowledgequestionnaire.Thestructuralquestionnaireconsistingoftwosections;SectionI:demographicdataand SectionII:consistedof20knowledgequestionnairewithmaximumscoreof20.
RESULT:
Theanalysisofdatawasbasedontheobjectivesandhypothesis.Descriptivestatisticswereusedtomean,frequencyandpercentagewithtabularpresentationof data.
Chisquiretestwasusedtotestthehypothesisandsignificancedifferenceinthe levelofknowledgeofstudentsregardingotitismedia.
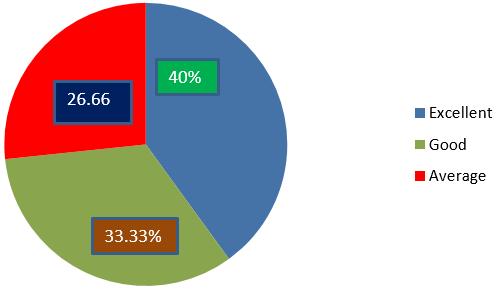
Objective1: Among 30 respondents 12 were having excellent knowledge, 10 having good knowledge andremaining8havingaverageknowledge.
Figure1:PiediagramshowingthelevelofknowledgeofG.N.M.II yearstudentsregardingotitismedia
Figure2:Bardiagramshowingthedistributionofmaleandfemale nd respondentsinG.N.M.II yearstudents
DISCUSSION:
Section-I
DemographicVariables:
Ingendercriteria,themajority73%ofthestudyparticipantsweretofemale,and theremaining27%ofmale.

The religious distribution depicts that majority 94% of the study participants wereHindus,4%Muslims,2%Christiansandremaining0%belongedtoother religions.
Inagecriteria,themajority82%ofthestudyparticipantswereto18-22yearsof
KEYWORDS:Study,Knowledge,Student,Assess,OtitisMedia,Management. Copyright©2022,IERJ.Thisopen-accessarticleispublishedunderthetermsoftheCreativeCommonsAttribution-NonCommercial4.0InternationalLicensewhichpermitsShare(copyandredistributethematerialinany mediumorformat)andAdapt(remix,transform,andbuilduponthematerial)undertheAttribution-NonCommercialterms.

agegroup,16%to23-26years,1%to27-30yearsandremaining1%toabove30 years.Thus,thestudyrevealedthatmostoftheparticipantswere18-22yearsof agegroup.
Aspertheeducationaldistributionofthestudyparticipantsonly44%werehavingIntermediateeducation,34%Graduate,1%Post-graduateand21%werehaving other courses. Thus, the study revealed that most of the 44% participants werehavingeducationlevelofIntermediate.
Theinformationsourcedistributiondepictsthat62%ofstudyparticipantsgets information from college teacher, 24% from Internet, 9% from other while remaining5%throughNewspaper Thus,thestudyrevealsthatmajorityofstudy participant'ssourceofinformationisCollegeteacher
Section-II
KnowledgeRegardingOtitisMedia:
Theresultshowsthatmajority33.33%ofthesampleswerehavingGoodknowledge,26.60%Averageknowledgeandremaining40%hadexcellentknowledge regardingotitismedia.
CONCLUSION:
Theresearchershaveconductedastudyonotitismedia.Theresultshowedthat 33.33% were having good knowledge, 40% excellent knowledge and 26.60% averagelevelofknowledgeregardingotitismedia.Thisconcludesthatmoreeducation and awareness is needed among the nursing students regarding otitis media.
REFERENCES:
I. LidaAnneSilvetri,AngelSilvetri,AnneKaushik,”NCLEX-RN”,4thedition,2014, Elsevier,Indiaprivatelimited,pageno.458.
st
II. B.T Basavanthappa,NursingResearch,I ed.pageno.127-133.
III. B.K.Mahajan,MethodinBiostatisticsforMedicalStudentsandResearchWorkers, 6thed.pageno.30-33.
st
IV J.P Baride,A.P KulkarniandR.D.Mazumdar,ManualofBiostatistics.I ed.page no.41-46.
V EmmettSD,KokeshJ,KaylieD(November2018)."ChronicEarDisease".TheMedicalClinicsofNorthAmerica.102(6):1063–1079.
VI. Ruben,RobertJ;Schwartz,Richard(February1999)."Necessityversussufficiency: the role of input in language acquisition". International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology 47(2):137–140.
VII. CokerTR,ChanLS,NewberrySJ,LimbosMA,SuttorpMJ,ShekellePG,TakataGS (November2010)."Diagnosis,microbialepidemiology,andantibiotictreatmentof acuteotitismediainchildren:asystematicreview".JAMA.304(19):
VIII. PrincipiN,BianchiniS,BaggiE,EspositoS(February2013)."Noevidenceforthe effectivenessofsystemiccorticosteroidsinacutepharyngitis,community-acquired pneumonia and acute otitis media". European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & InfectiousDiseases.32(2):151–60.
IX. Erasmus T (2012-09-17). "Chronic suppurative otitis media". Continuing Medical Education.30(9):335–336–336.
X. RosenfeldRM,SchwartzSR,PynnonenMA,TunkelDE,HusseyHM,FicheraJS,et al.(July2013)."Clinicalpracticeguideline:Tympanostomytubesinchildren".Otolaryngology–HeadandNeckSurgery 149(1Suppl):S1-35.
XI. WallaceIF,BerkmanND,LohrKN,HarrisonMF,KimpleAJ,SteinerMJ(February 2014)."Surgicaltreatmentsforotitismediawitheffusion:asystematicreview".Pediatrics.133(2):296–311.
XII. YilmazS,KarasalihogluAR,TasA,YagizR,TasM(February2006)."Otoacoustic emissionsinyoungadultswithahistoryofotitismedia".TheJournalofLaryngology andOtology 120(2):103–7
XIII. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Otitis_media
XIV https://www mayoclinic org/disease condditions/ear-infection/symptomscourse/syc-20351616
XV https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/disease/861
XVI. https:emedicine.meddscape.com/article/994656-overview
XVII. https://www.healthline.com
XVIII.https://kidshealth.org
XIX. https://www.nature.com
XX. https://www.stanfordchildrenes.org
