

IUCN Red Listing of the Atlantic Salmon

Dr William Darwall
Tamara Landscape Partnership Scheme Manager








IUCN International Union for Conservation of Nature
Global authority on the status of the natural world and the measures needed to safeguard it.








What is the IUCN Red List?
Established in 1964, The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species has evolved to become the world’s most comprehensive information source on the global conservation status of animal, fungi and plant species.
The Barometer of Life on Earth
Information about a species range, population size, habitat and ecology, use and/or trade, threats, and conservation actions that will help inform necessary conservation decisions.


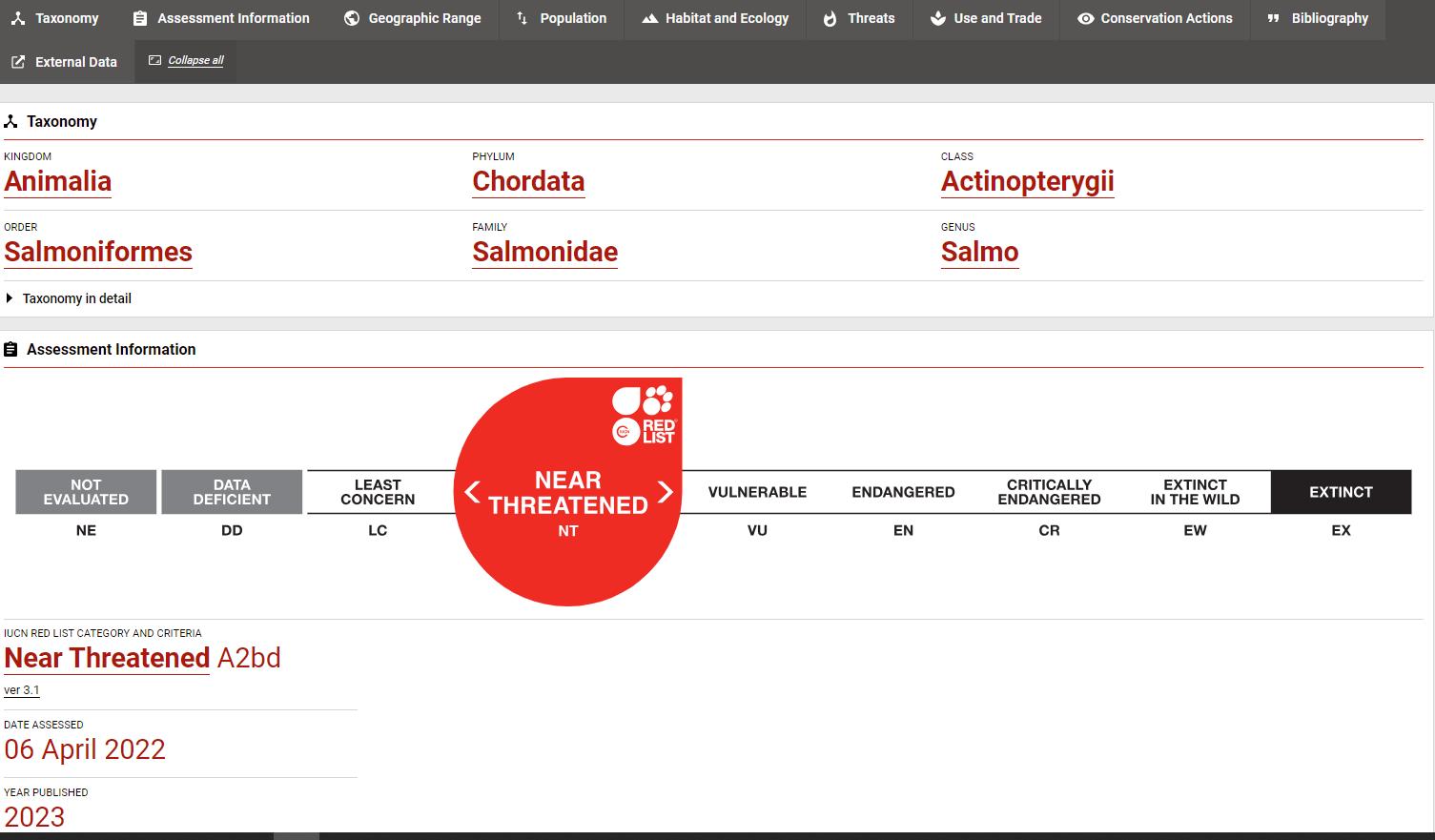
IUCN Red List assessment: an estimate of extinction risk
What is the likelihood of a species becoming extinct in the near future, given current knowledge about population trends, range, and recent, current or projected threats?


Illustration copyright Bob Diven

Why does this matter?
Species extinction rates at least 10 times greater than background rates over the last 500 million years
Driven primarily by human activities


157,000 species assessed to date


IUCN Red List Categories & Criteria
Criteria

Thresholds

Categories






Assessment Process








Who is involved?





Uses of IUCN Red List data
• Data analyses – Red List Index • Conservation planning and priority setting • Influencing funding allocations
















Kunming-Montreal agreement (Dec. 2022)
• Restore 30% degraded ecosystems globally (on land and sea) by 2030
• Conserve and manage 30% areas (terrestrial, inland water, and coastal and marine) by 2030
• Stop the extinction of known species, and by 2050 reduce tenfold the extinction risk and rate of all species (including unknown)


Atlantic salmon assessment – 2022

Global population 39 subpopulations including GB

Global Assessment

Who was involved: IUCN Salmonid Specialist Group
What data were used: Pre Fisheries Abundance Assessment (PFA) data
Red List status: Near Threatened A2bd
“Close to qualifying as a globally threatened species in the near future.”
A2: 23% decline in population over the past 3 generations (15 years) based on:
“b”: index of abundance (PFA)
”d”: actual or potential levels of exploitation





Nominal Catch (Tonnes): source NASCO

GB Sub-population

Who was involved: IUCN Salmonid Specialist Group
What data were used: Pre Fisheries
Abundance Assessment (PFA) data
Red List status: Endangered A4bd
“Very high risk of extinction in the wild”
A4: 63% decline in population estimated for 2010 - 2025 (15 years) based on:
“b”: index of abundance (PFA)
”d”: actual or potential levels of exploitation







GB forecast decline in PFA



What is included in an assessment?


• Overfishing at sea
• Climate Change
Main Threats
• Salmon farms: potential threat – disease, chemical treatments, pollution, feed, escapees
• Pollution: industrial, domestic and agriculture
• River infrastructure: dams, weirs and barriers
• Habitat loss & degradation
• Disease & parasites
• Invasive species: Pink salmon


Conservation Actions
• Convention for the Conservation of Salmon in N Atlantic Ocean (created NASCO)
• Habitat protection through improved land use practices, removal ins-stream barriers
• Invasive species management
• Regulation / removal of commercial mixed stock net fisheries
• Catch and return
• Regulation of water abstraction


Other UK subpopulations
Chalk streams (VU B1ab)
• Restricted range (7,100 km2)
• Over-abstraction of water
• Pollution (sewage & agric.)
• Decline in habitat quality & no. mature fish

Leven (LC)
• River Leven & Loch Lomond
• Reported gradual increase in catches
• Cons Limits – Category 2 (upgraded)











https://www.iucnredlist.org/

© Michel Roggo
