THIS PROJECT IS TO REFLECT ON THE CURRENT ISSUE (HOMELESSNESS IN MALAYSIA), THE DESIGN, HOWEVER, NEEDS TO BE HOSPITABLE TO THE HOMELESS COMMUNITY BESIDES BEING SITE-SPECIFIC AND CONSIDERATE TO THE MALAYSIAN ENVIRONMENT AND CLIMATE.

NorthSide East & South Side WestSide

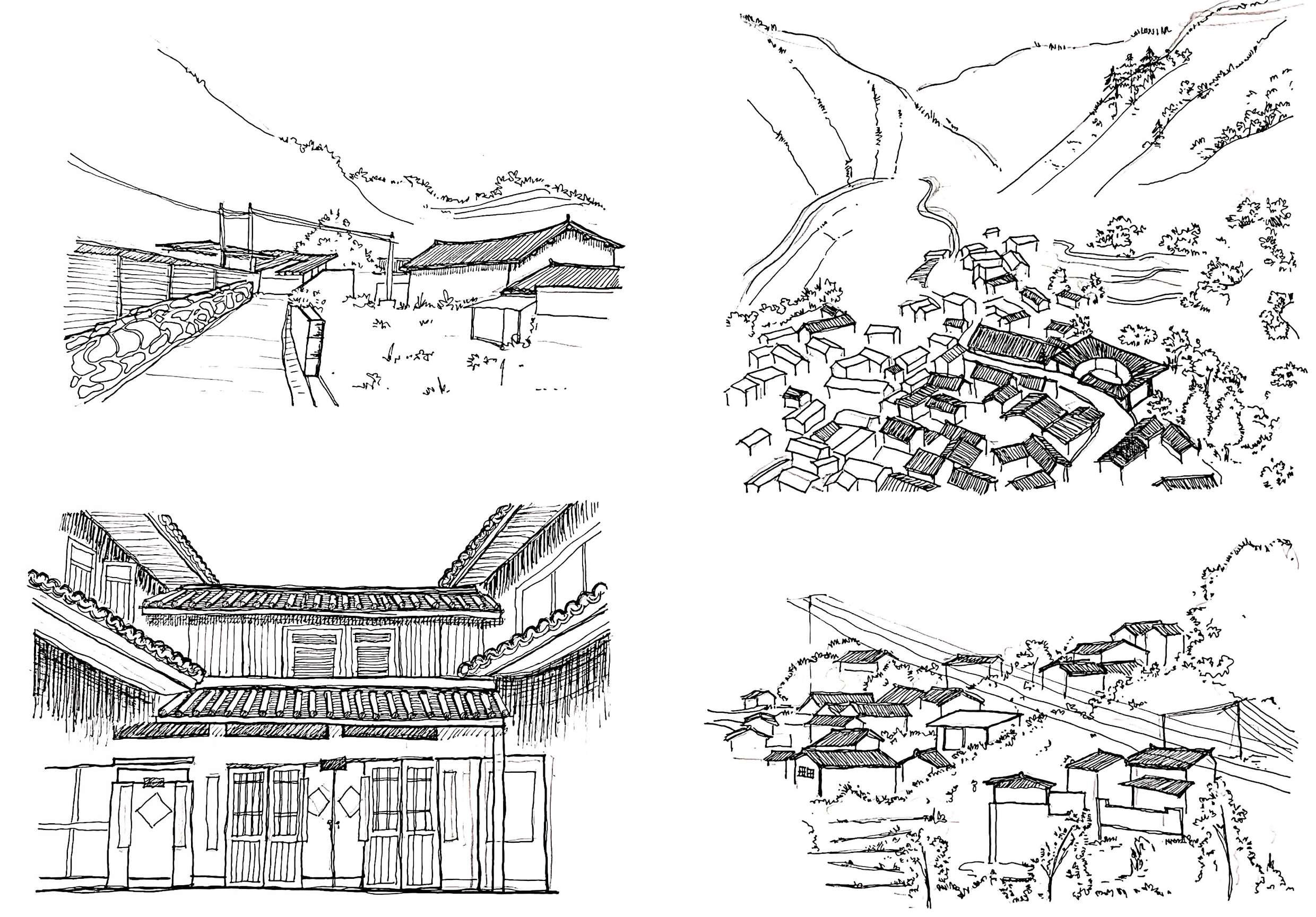
Volunteer team from Tongji University organize activities and coming up solutions to improve the locals' knowledge, living space, and living quality.
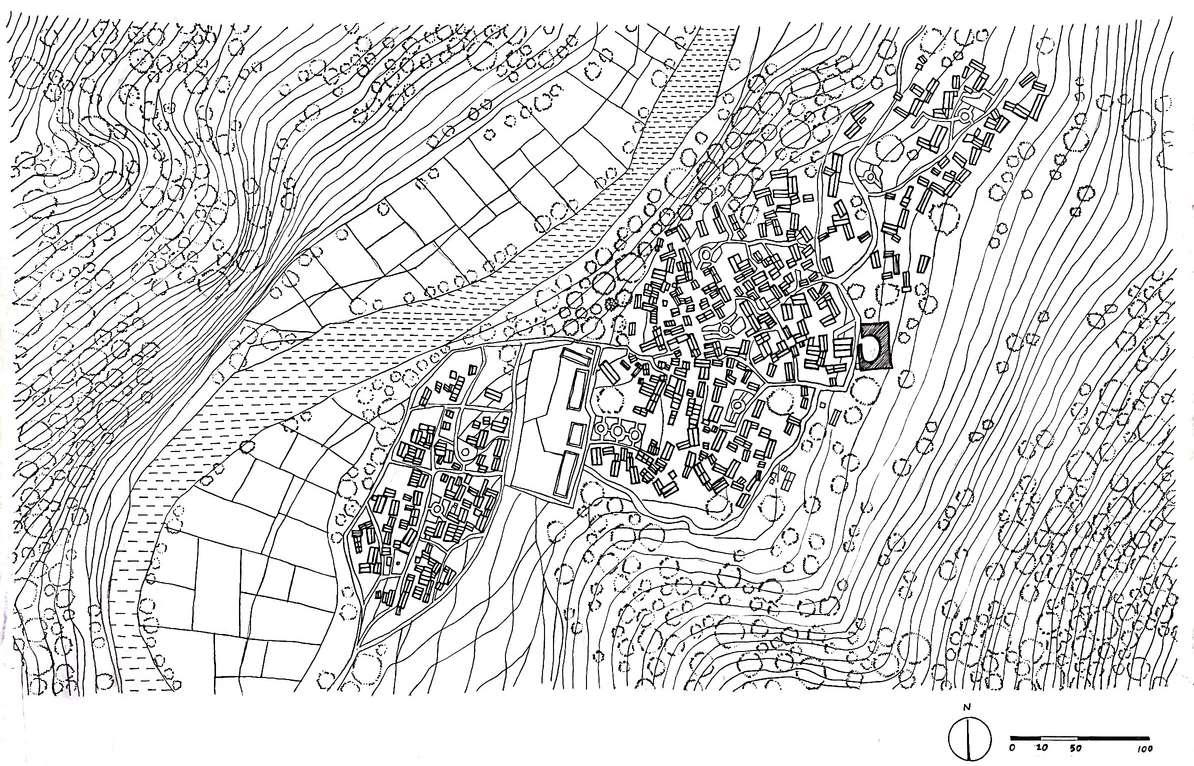
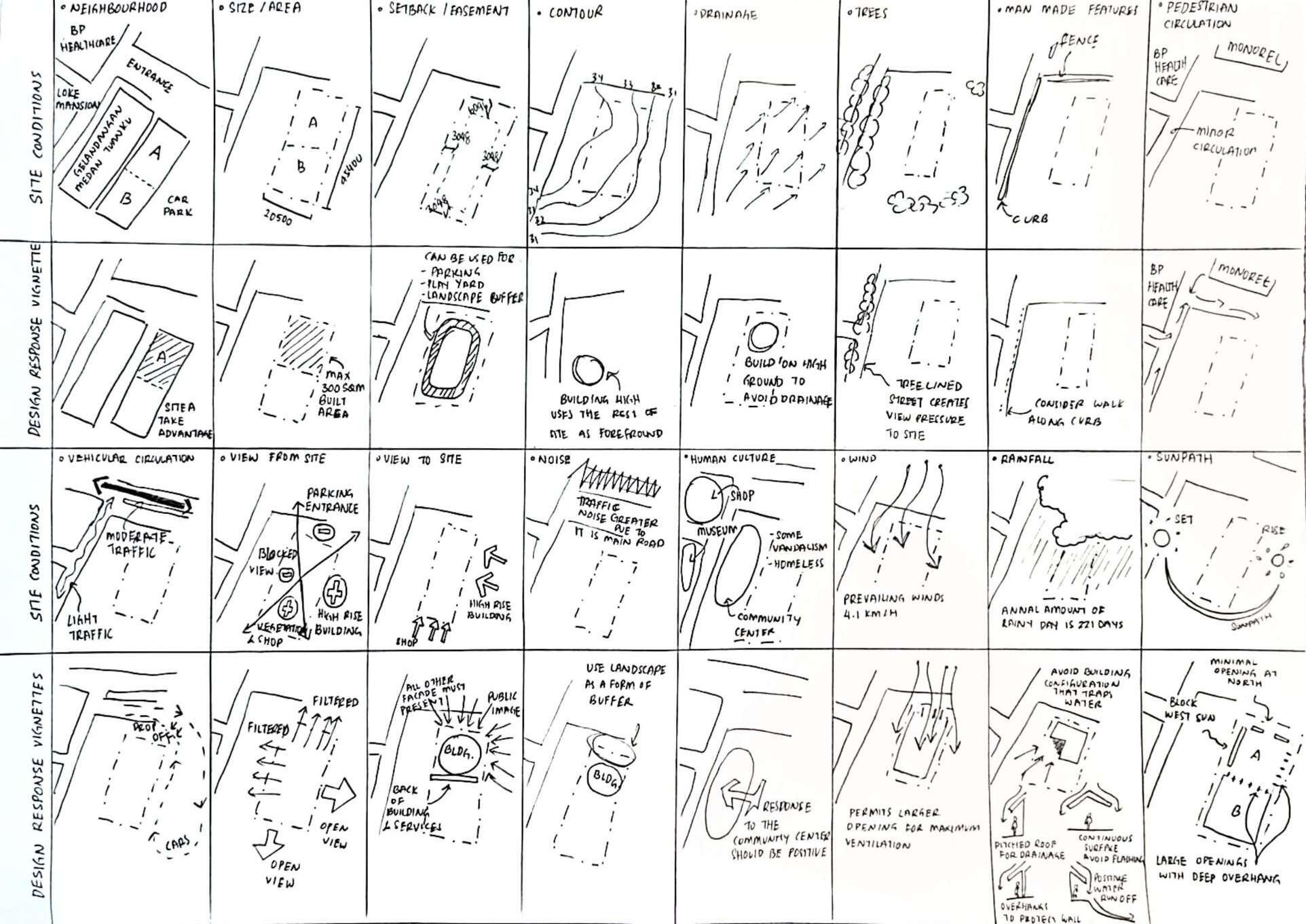
Altitude difference between the upper and lower Yong'an Village is around 300 meters, making the vertical travel distance unreachable
dwe lings dwellings mountains known as negative space as it is where tomb is place left empty to show respect






Minority ethnic groups including Han, Bai, Hui, and Yi
As the geographical location is deep in valley, the villagers value the significance of the openness of indoor and outdoor public spaces



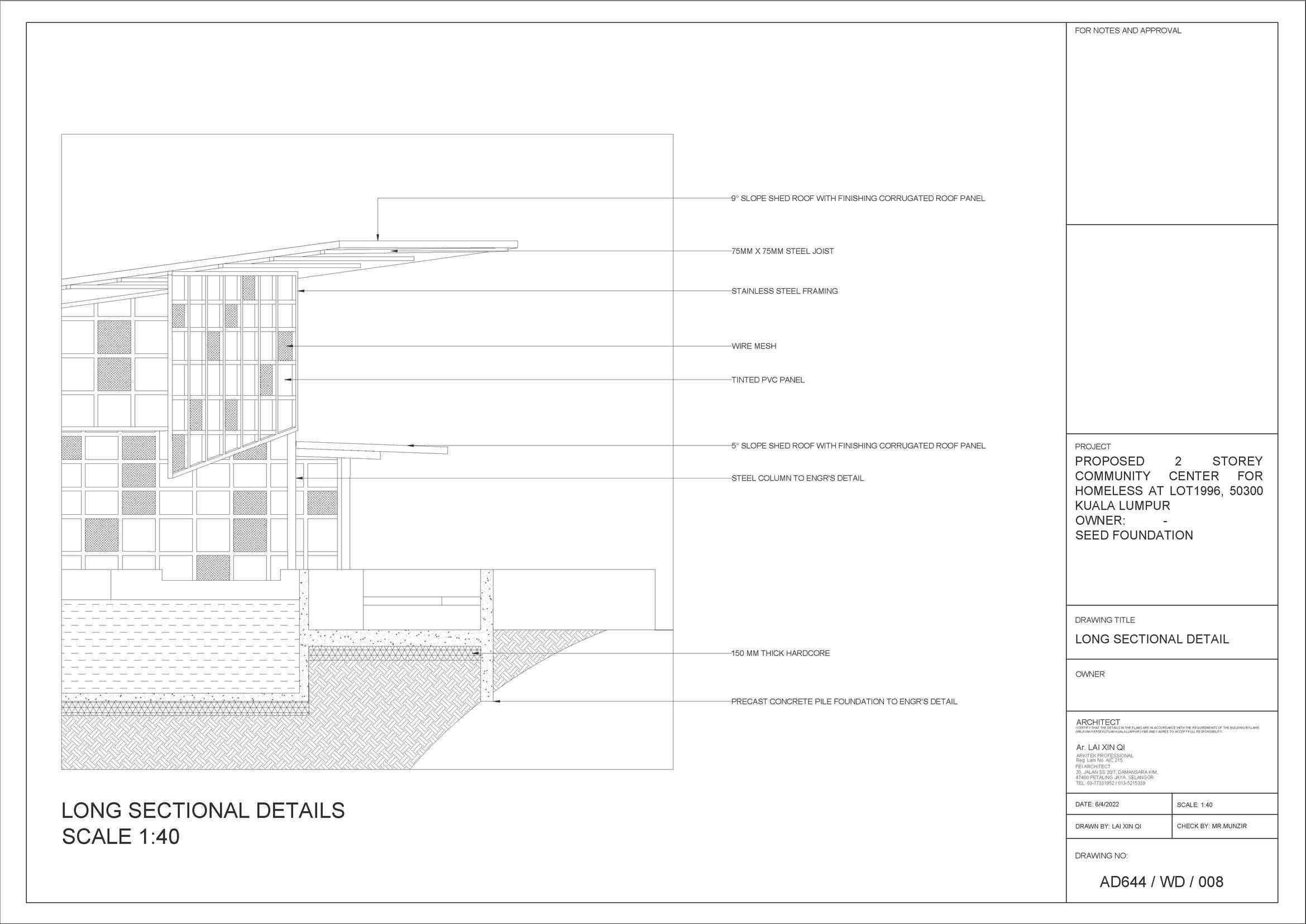
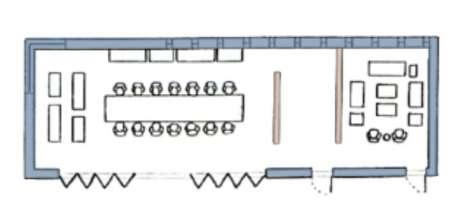
Entrance 'Wu Di Shui' Single storey buildings
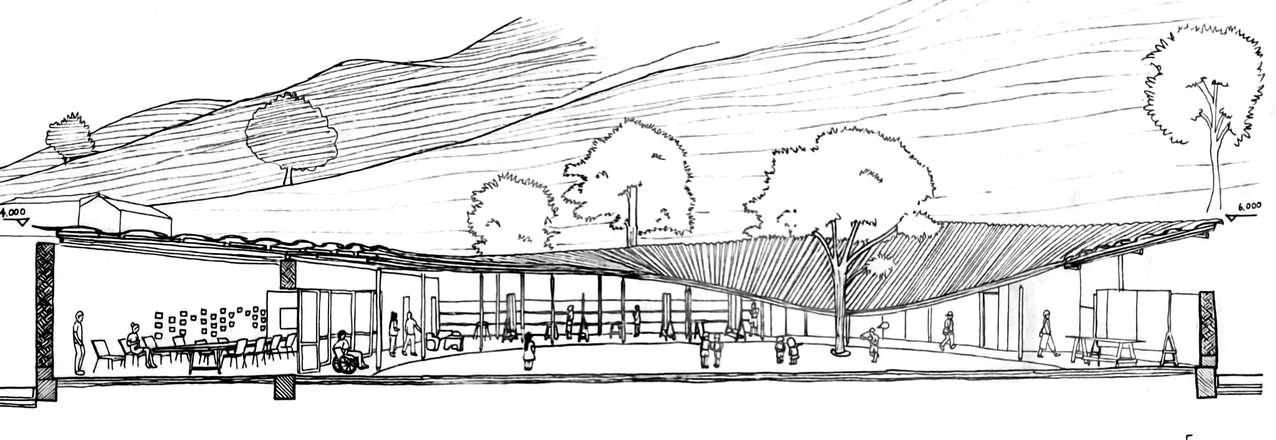
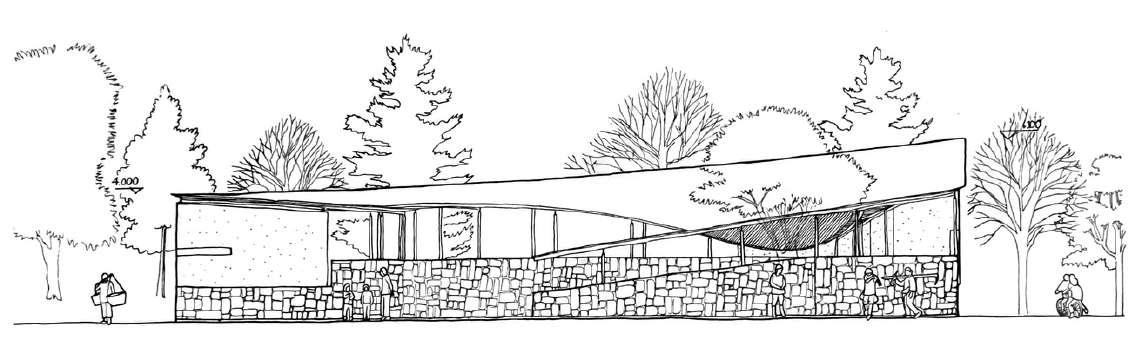
Facade and different perspective of the building being viewed along the approach of the building.


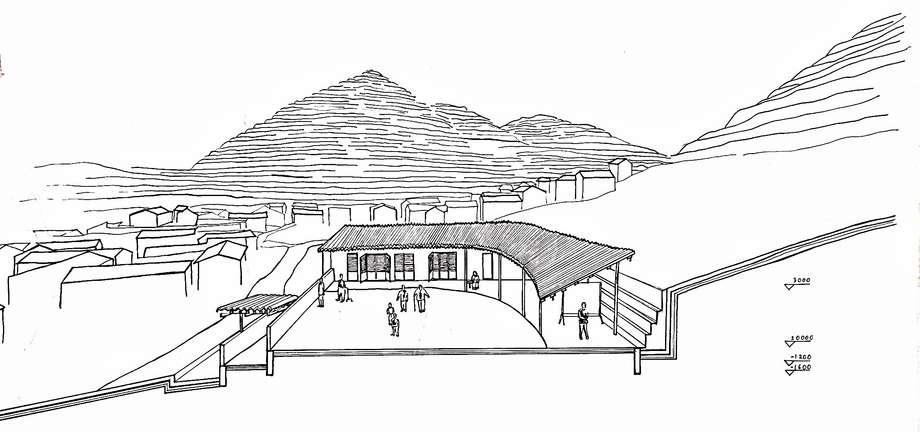
Entrance of site is lowered and narrow to enhance the feeling of openess of the building.


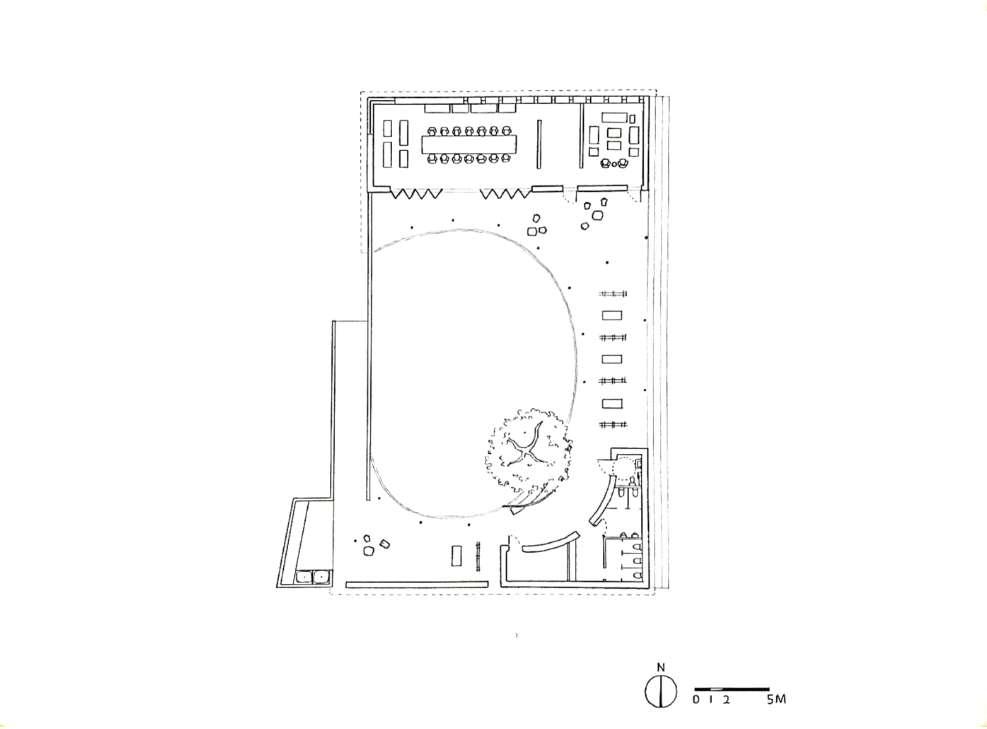
All activities are connected by central courtyard. The central courtyard is the most significancae space shown by its size and placement

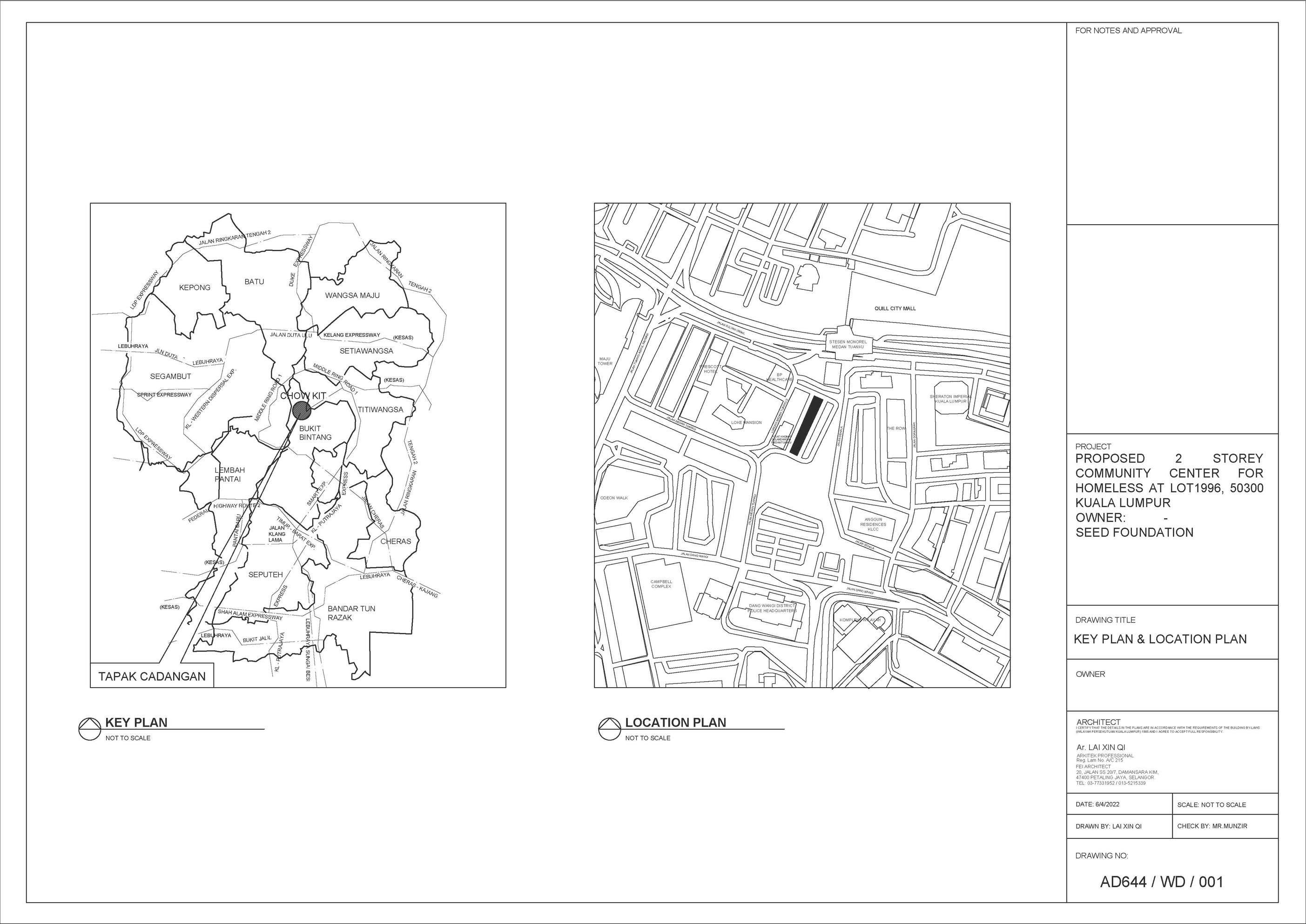
 Located in Yunlong County of Yunnan Province, Yong'an Village, Dali, China
Located in Yunlong County of Yunnan Province, Yong'an Village, Dali, China
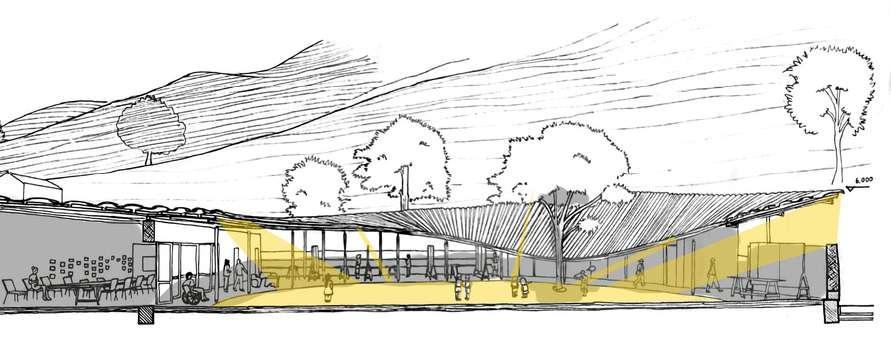

Wind
Shading from morning to evening


Natural Light expose to the space
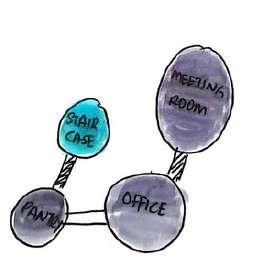
Bubble diagram Services




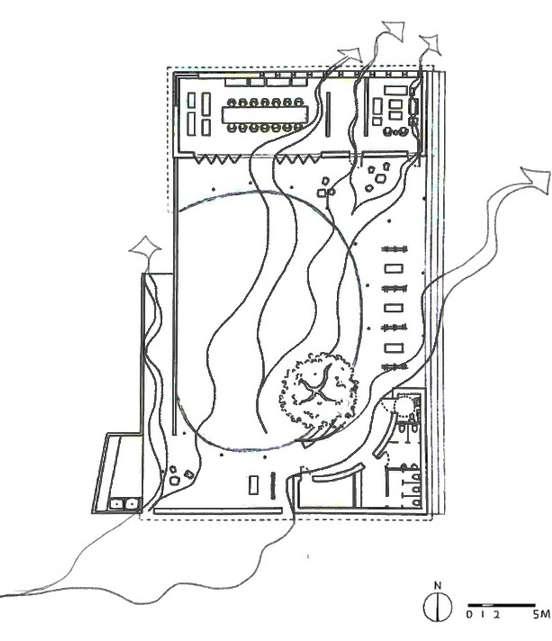
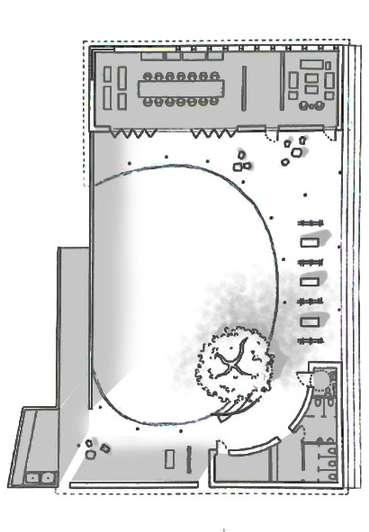
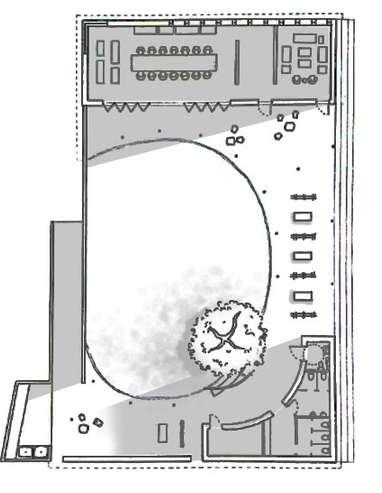



HorizontalElements
No elevated & depressed base plan so that its disabled friendly





Overheadplane
VerticalElements
Hall&Office
4planesclosure isolates a space from the site
Singleverticalplane separates the space into two functions - hall & offices

Verticallinearelements (columns)
Singleverticalplane (divider)
Parallelplanes on both sides gives a strong directional quality

U-shapedplane which have an orientation facing the inner courtyard




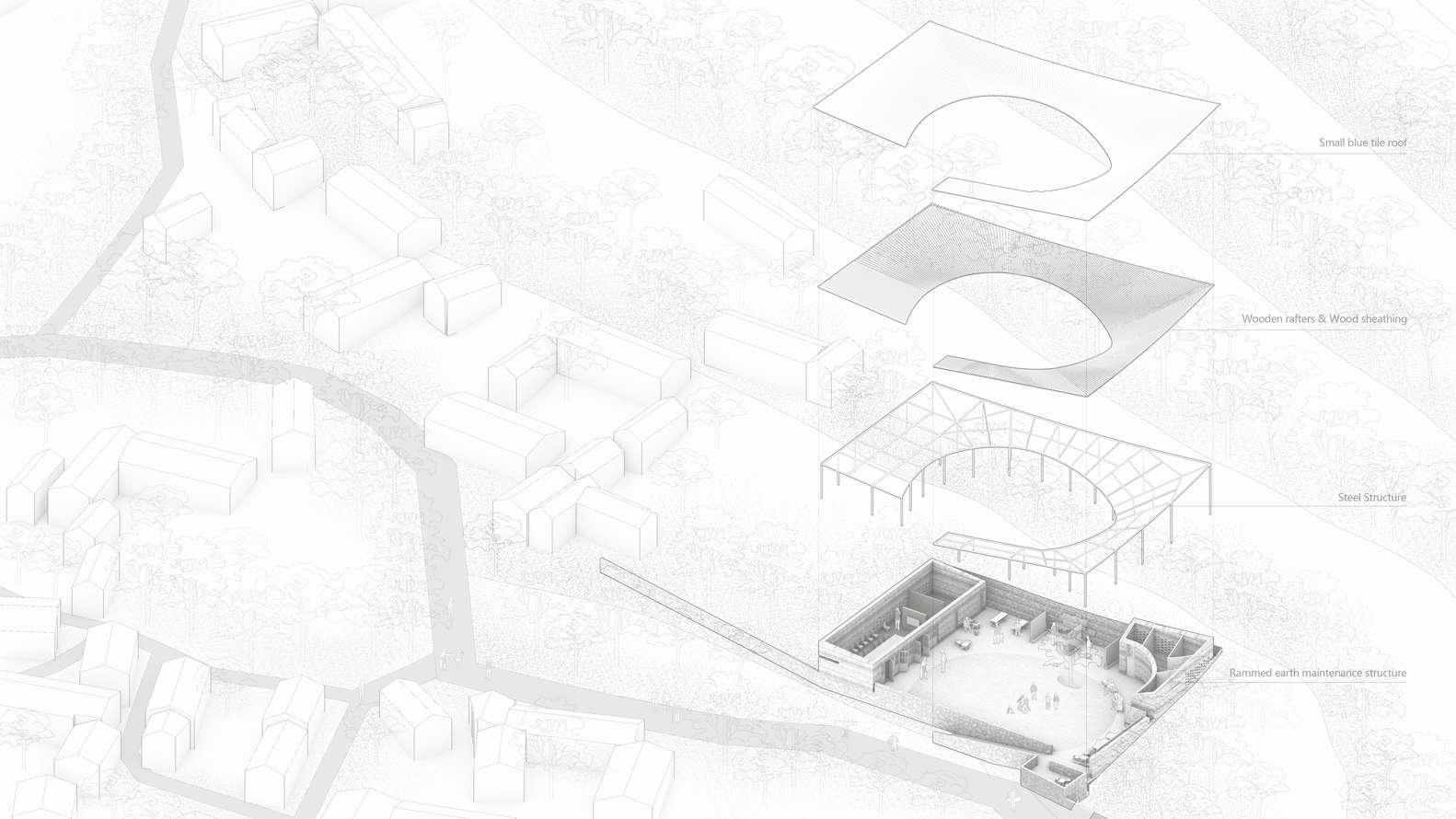
Roof
Material used:
Local terracotta clay tiles
Type of roof:

Straight-grained single-sloped curved roof

Architecture Influence
Feel more familiar with the materials
Consistent with the villagers house
Advantages:
Environmentally-friendly material
Energy efficient
Low maintenance
Cost efficiency
Sustainable
Material used:
Steel
Type of column:
Stepped steel columns with thinner ends details
Architecture Influence
Steel columns were connected by high efficiency hinge joint to strengthen its loading capability Creating an interesting contrast with the rammed earth wall.
Material used:
Rammed earth

Rubble masonry
Red sandstone
Type of wall:
Rammed earth wall
Dry Rubble Masonry wall
Architecture Influence
Responding to the local site culture


Advantages:
Superior thermal mass
Temperature and noise control
Strength and durability
Low maintenance
Load bearing and pest deterrence
Floor
Material used:
Rubble masonry
Red sandstone
Type of floor:
Dry Rubble Masonry outdoor decking
Dry Rubble Masonry floor finishes
Architecture Influence
Elaborated the localized characteristic of the construction process.
Construction details:
The hyperboloid form of the roof was generated through algorithmic geometry
It could drain water effectively
This construction method can be easily taught to the villagers through simple mathematic.


Disadvantages:
Difficult installation
Heavyweight Brittle
Construction detail:
To minimize the usage of nonstandard building components and derived the coordinate points required for form-finding process targeting the arc steel beam and arc length data.
The lightweight steel structures had injected an impression of industrializations onto the community center.

Construction detail:
The content of rammed earth wall material contained red sandstone which could be found on site



This construction method has largely eliminated the use of machinery
Disadvantages:
High cost
It doesn’t provide long-term insulative benefits.
Limited to low-rise buildings and square shapes.
Construction detail:
The outdoor decking and floor finishes are adopting the dry rubble masonry
The brown rubbles were made from sandstone collected from the riverbed in lower village.

Advantages:
Stronger and more durable Light in Weight
Cost-effective Environment Friendly Energy Efficiency
Disadvantages:
High Maintenance Fireproof Treatment Fabrication Error
Advantages:
Durable and strong
Does not bend swell ,warp and splinter
Weather resistant
Disadvantages:
Low flexural resistant Difficult to repair Takes more time to build
HorizontalElements
Circulation&UserExperience
Overheadplane
VerticalElements
Noelevated&depressedbase plansothatitsdisabledfriendly

Hall&Office
4planesclosure isolatesaspacefrom thesite


Singleverticalplane separatesthe spaceintotwofunctions-hall&offices

Innercourtyard
Verticallinearelements (columns)
Singleverticalplane (divider)

Inner courtyard
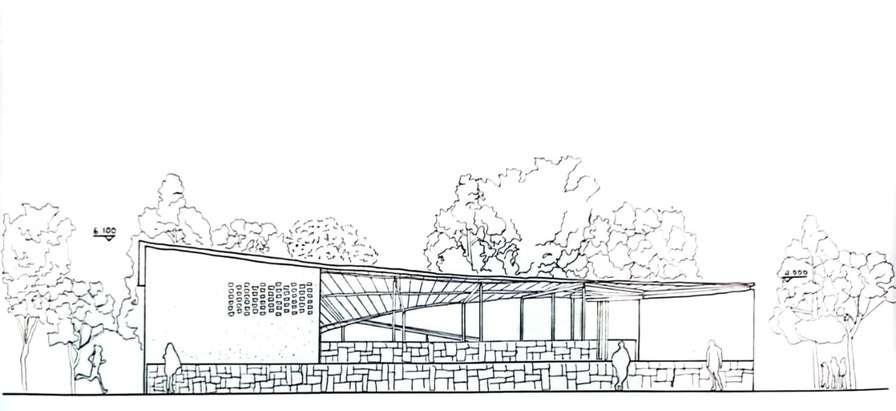
SouthELevation
Kitchen
Plan





PublicWashroom
4planesclosure



 West Elevation
East ELevation
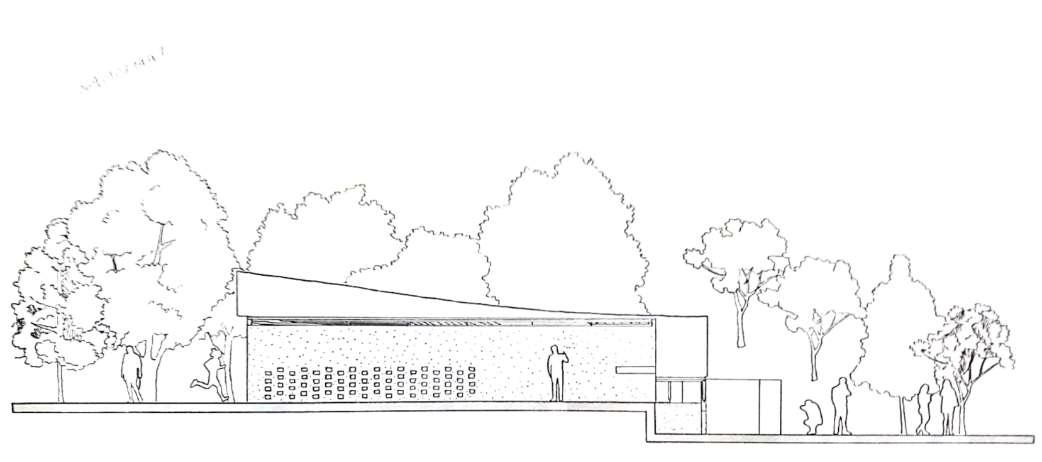
West Elevation
East ELevation








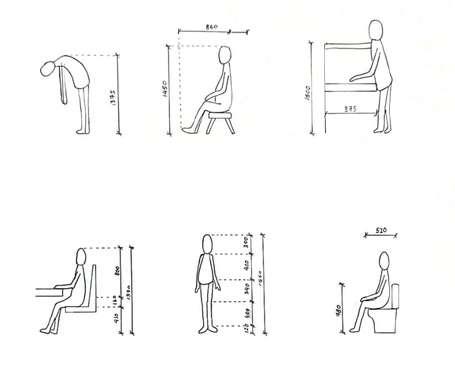
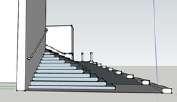
Staircase is a structure connects 2 vertical distance
Number of treads: not exceed 16 in a single flight Dimension:

- Tread: less than 255mm
- Riser: not more than 180mm

Minimum headroom is not less than 2m measured vertically from any point over the full width of the stairs Tread and riser's dimension must be constant within a staircase to prevent users from tripping and falling
Landing
An area of a floor near the top or bottom step of a stair
An intermediate landing is a small platform that is built as part of the stair between main floor levels
FUNCTION
allow stairs to change directions allow the user a rest
Clearance
Stairway headroom
Stair overhead clearance is the vertical distance measured between the outer edge of the stair tread surface
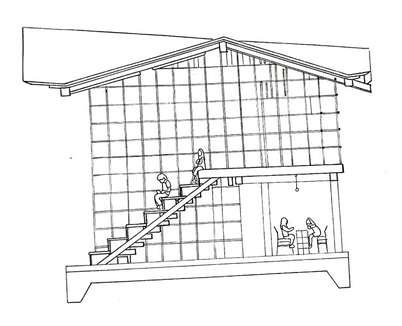
Architect: Arthur Erikson
Reason of the staircase design is Ericksons father lost both of his legs in the First World War, which deeply impacted his son's designs The intension of Erickson is to make public spaces accessible and enjoyable
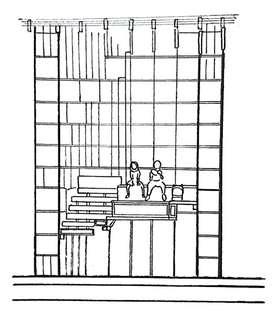

Staircase Design



Advantage
Everyone is able to use the staircase and ramp
Disadvantage
The stairs are all the same colour, which he says can make it difficult for a visually impaired person to tell where one step begins and the next one ends hard for stroller be pushed having lots of landing which makes more turns for OKU too steep too long distance which will be difficult for OKU people with poor stamina
Ways to improve the staircase
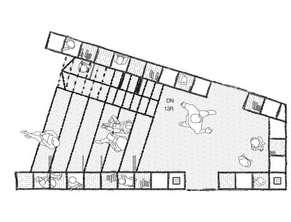
Architect:OrientOccidentAtelier
Theuseofthelocalconstructionmethodologiesenabledcost-savingsandempoweredpeople with ocalskilstohelpbuildwithefficiency.
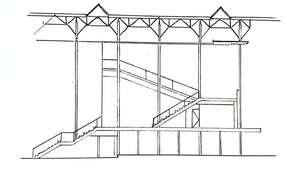
Staircase Design
DoubleTreadScalestaircasedesign
Placement of staircase
Entrance Advantage
People allow to walkthrough with suitable steps
Another side can be used as sitting area
Aesthetic
Disadvantage
Complex construction progress Need large area
Architecture Influence
The design utilizes vernacular methodologies and material

Less Steep More handra ls Adding co ors to staircase
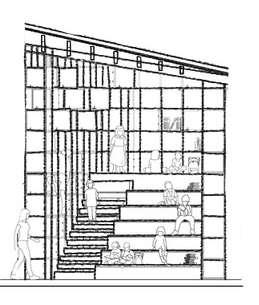
"Local kids explore the uses of the new uses of space by action – they climb Griddy as though it is a jungle gym"
Wall of staircase
The wall is a double layer steel frame with local wood plates allowing storage and even vertical circulation
Riser: 180mm
Thread: 500mm
Heght : 2500mm
Width : 4750mm
Each flght has 7 - 14 steps
Characteristic historical elements form an exciting combination with new oak and steel additions, and a warm coour palette of reds and oranges


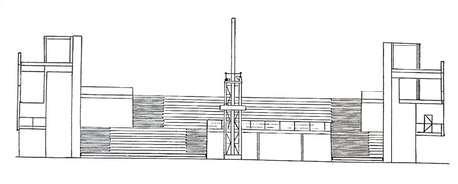
Structure of staircase
Glass Steel Architecture Influence
People allow to sit and walkthrough the stairs

Another side can be used as sitting or meeting area
Placement of staircase Hall Center
The interior is varied, playful and innovative. There is a diversity of atmospheres for meeting, collaboration, and concentrated work

Dimension PLAN
Riser: 150, 300mm

Tread: 220 440 mm
Heght : 3450mm
Wdth : 38800 56800mm
Each flght has 6 - 23 steps
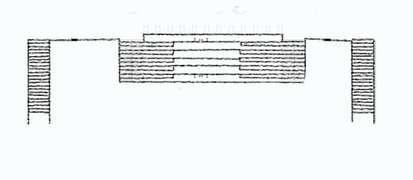
A method of escape in the event of a fire or other emergency that makes the stairwells inside a building inaccessible Brickwal Constant


Recommended standard of escape stair

Door swing to be in direction of escape (Push)
Door swing to be in outside if travel on stair
Minimum Distance Between:
*Not recommended by JBPM because a person's rhythm of walking down steps is broken Exits


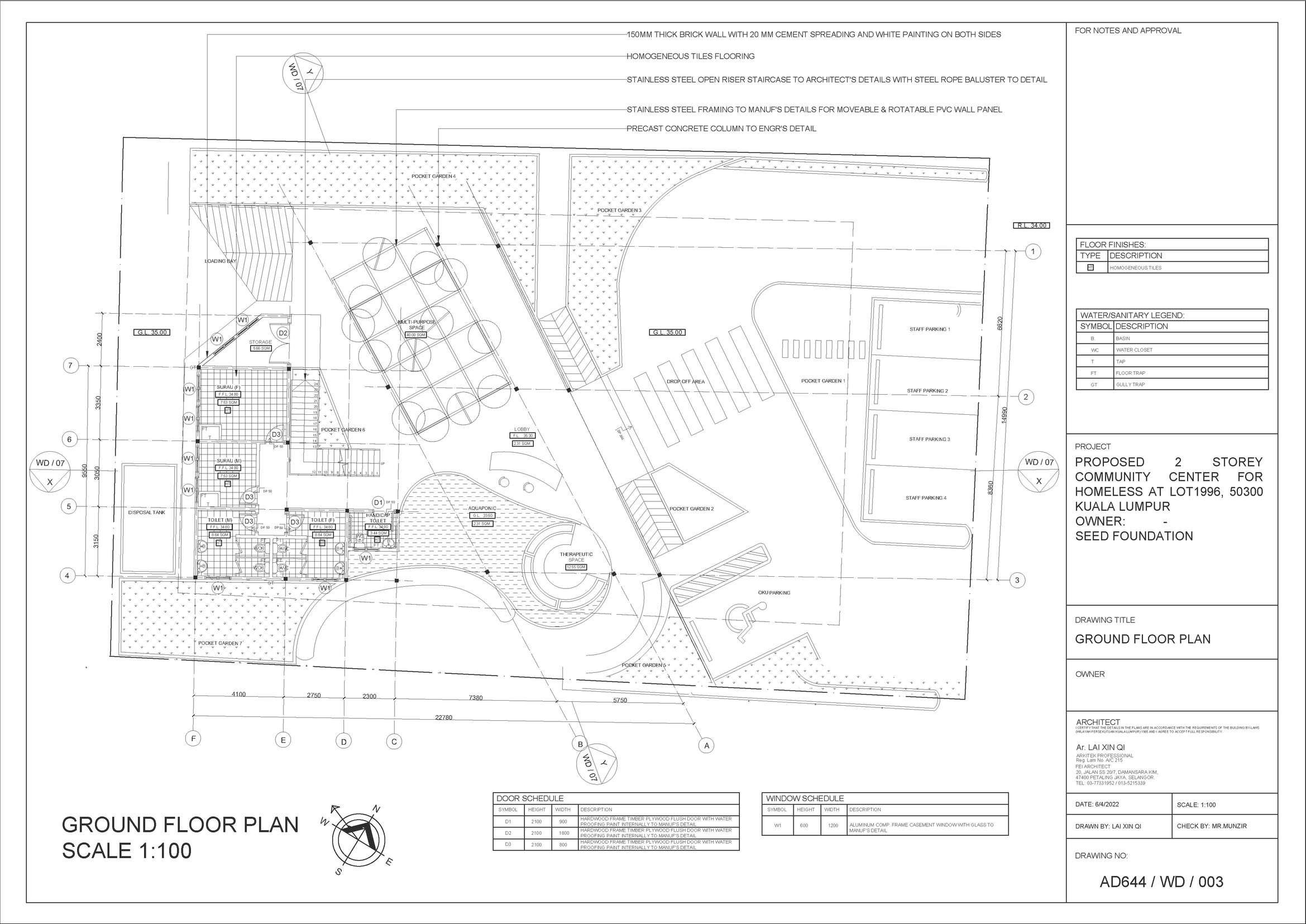
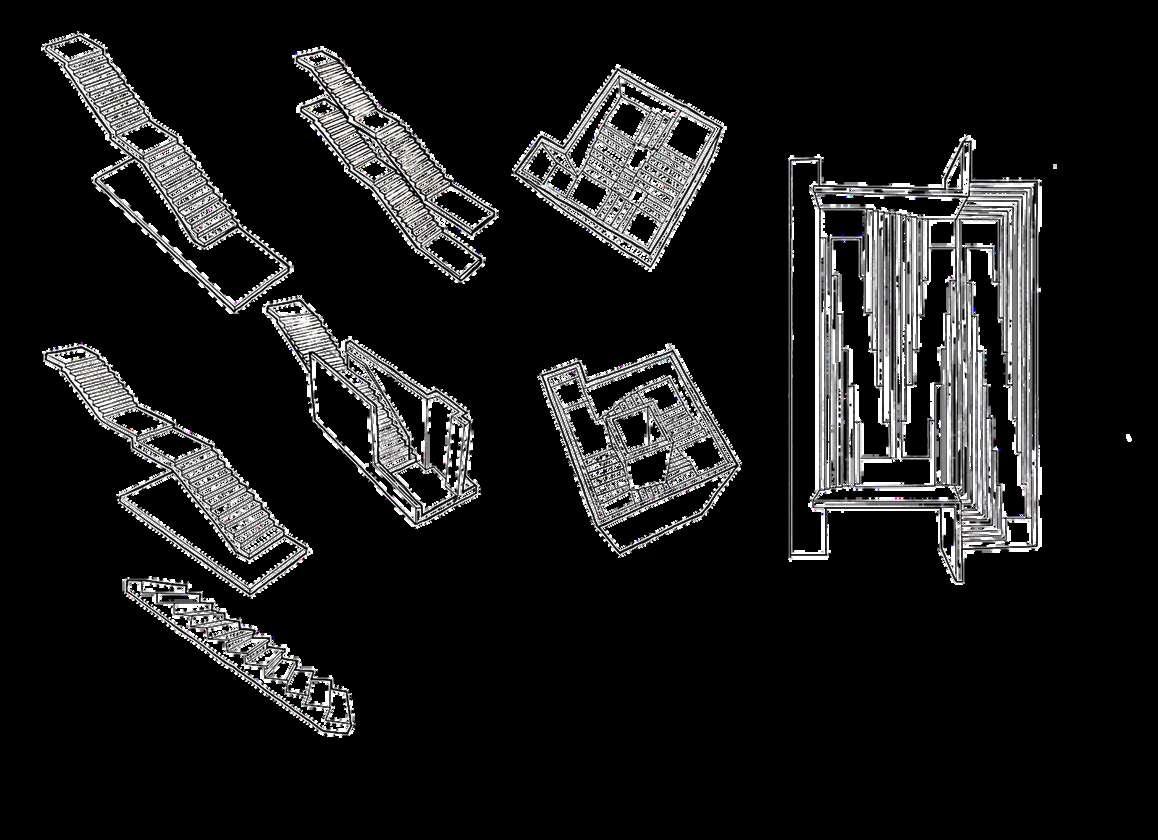
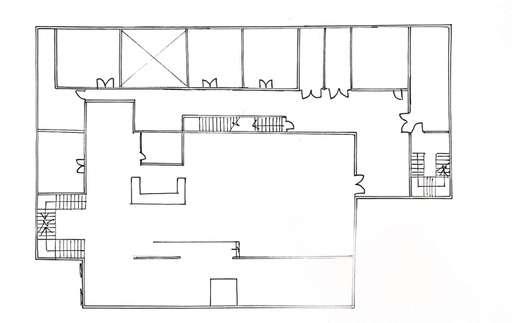
Ground Floor Plan
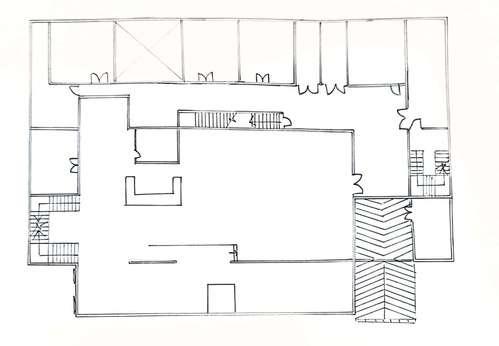
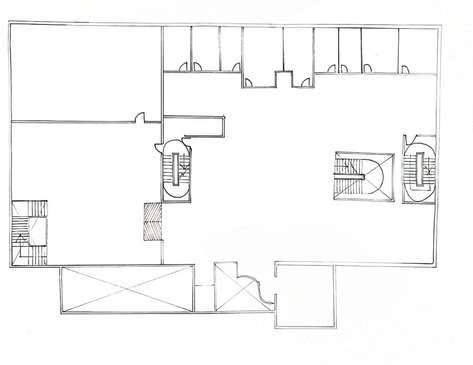



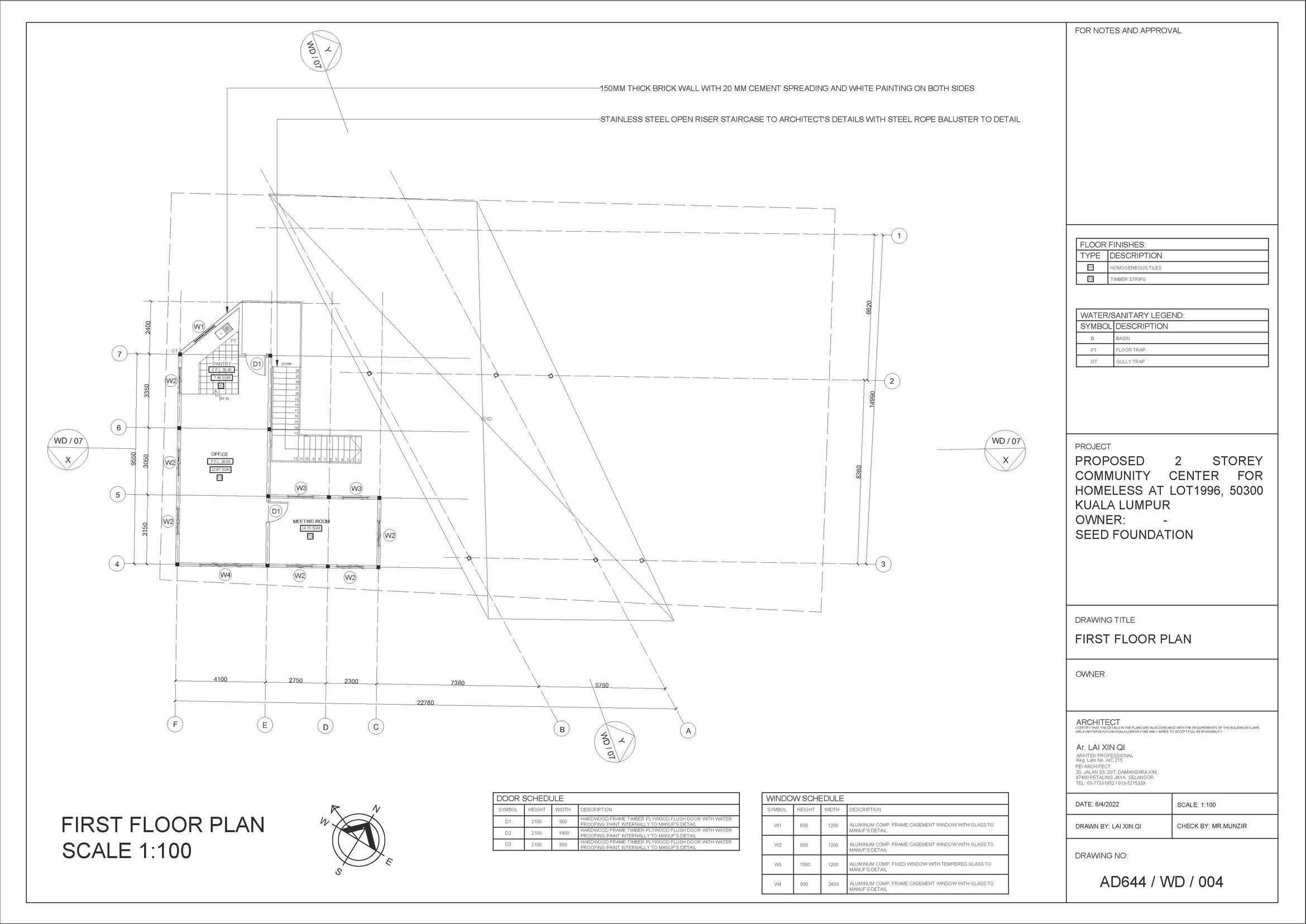
First Floor Plan
Escape staircase is located at the opposite side of the entrance
The escape door will be opened when the door knob is rotated and the door is pushed at the same time

The fire alarm will ring when the door is opened
The escape door opening direction is pushed from the staircase so that the escape can be done smoothly
Some staircases cannot be considered as escape staircases
Problem 01: Different layout of staircase
between Ground Floor Plan & First Floor Plan

Solution 01: Standardize the staircase layout


Problem 02: The exit is leading to the switch room
Solution 02: Create another exit
Problem: Obstruction near escape door Solution: Remove any obstruction near the escape door - to prevent any injuries made during emergency - provides fast exit in case of emergency



Inside staircase B
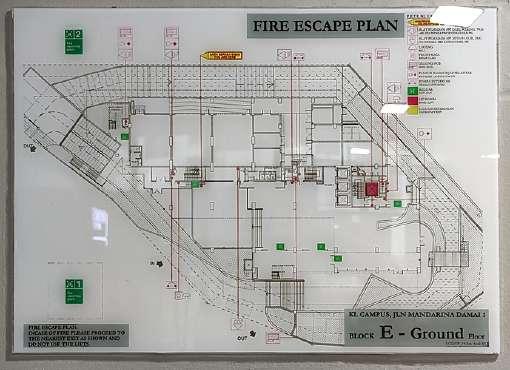
Ground Floor Fire Escape Plan 6th Floor Fire Escape Plan
Fire escape stairs with 15m radius
No of steps in one flight: 9
Location of excavation floor plan: In front of elevator
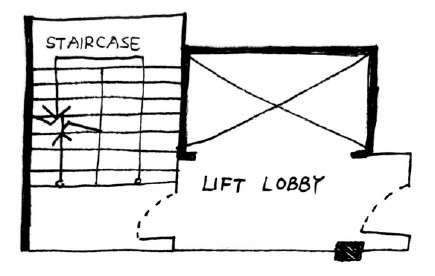
Ventilation system used: Permanent ventilation opening with minimum of 1 m² to outside


Ground Floor Fire Escape Plan
Fire alarm bell & manual call point can be found in front of staircase




Fire resistance door swing outward on ground floor for faster escape
Fire alarm bell & manual call point near the stairs


Fire resistance door swing inward on 6th floor according to direction of escape




Staircase B with permanent ventilated opening
3rd Floor Fire Escape Plan
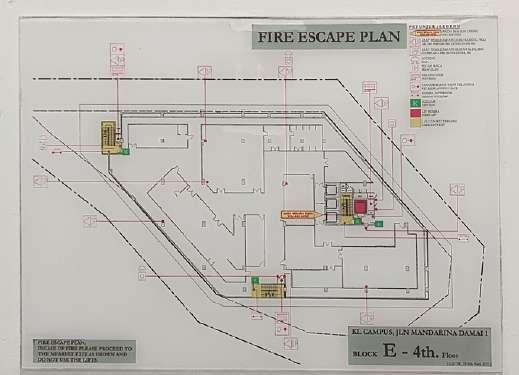


Fire escape stairs with radius 15 meter


External escape staircase: A & C
Internal escape staircase: B

No of steps in one flight: 11
Fire resistance door swing inward on 4th floor following the direction of escape
Ventilation system used: Supply only pressurization ventilation system
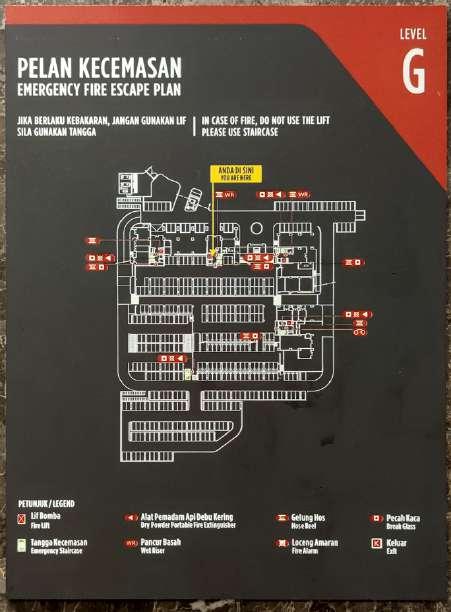
Fireman's switches
Fireman Intercom
Fireman switches & fireman intercom can be found in every level

Elements in the escape main shaft Hose reel
Location fire escape main shaft in UCSI Block E. Emergency light system
Wet riser next to fire resistance door inside fire escape shaft

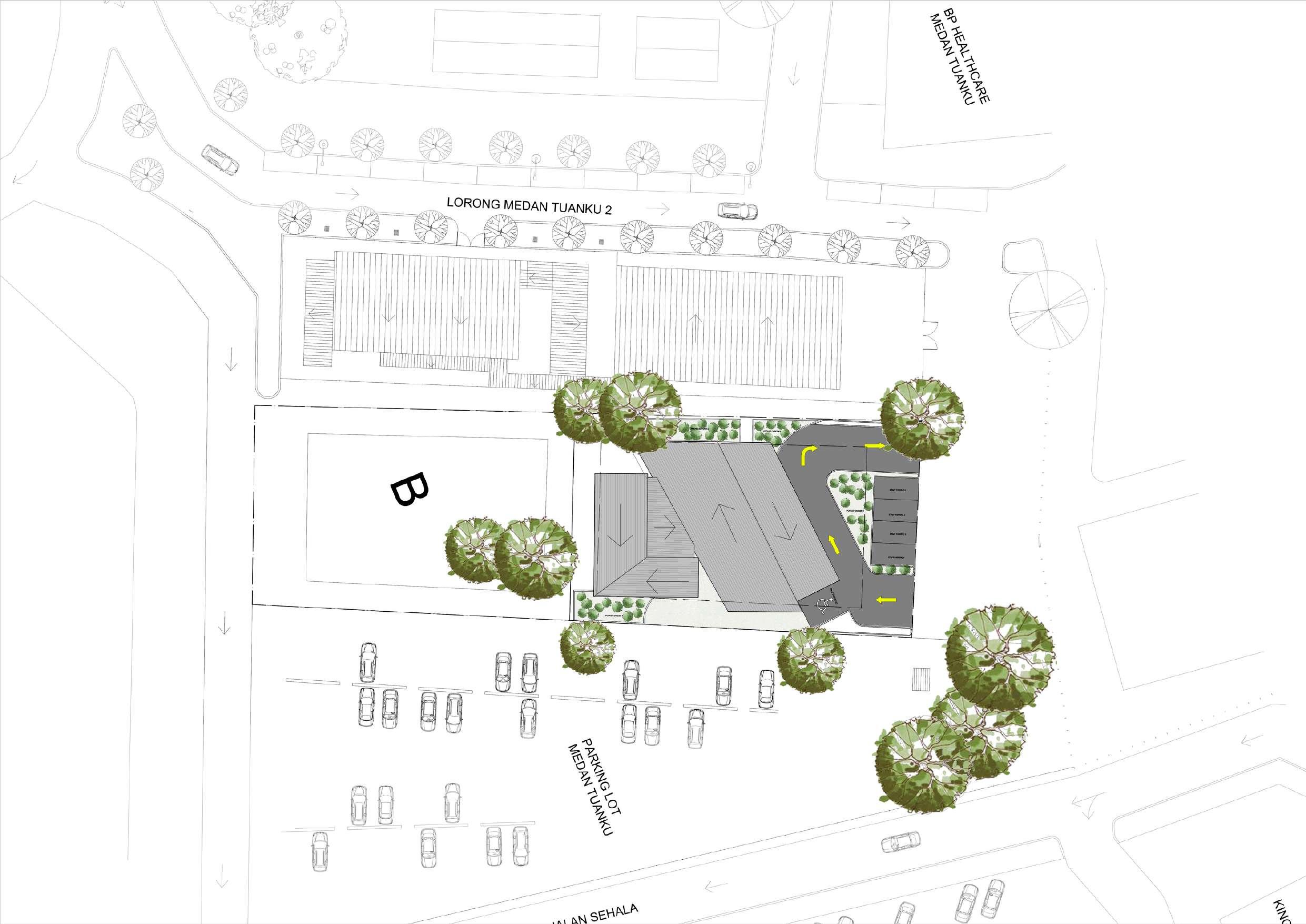
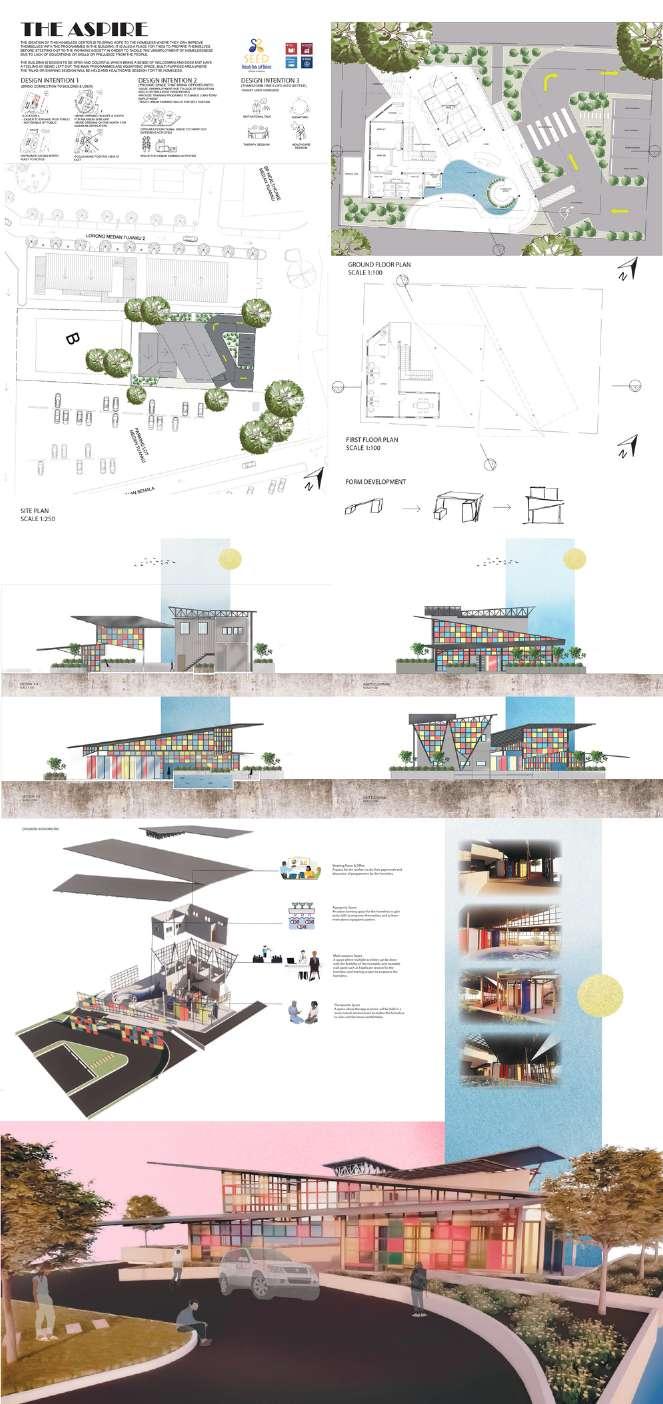
DESIGN INTENTION 1: SITE (BRING CONNECTION TO BUILDING & USERS)
DESIGN INTENTION 2: BUILDING TYPOLOGY (PROVIDE SPACE THAT BRING OPPORTUNITY)
Issue: Unemployment due to lack of education/skills or prejudice from people
DESIGN INTENTION 3: BUILDING PROGRAMME (TRANSFORM ONE'S LIFE INTO BETTER)

Target users: Homeless
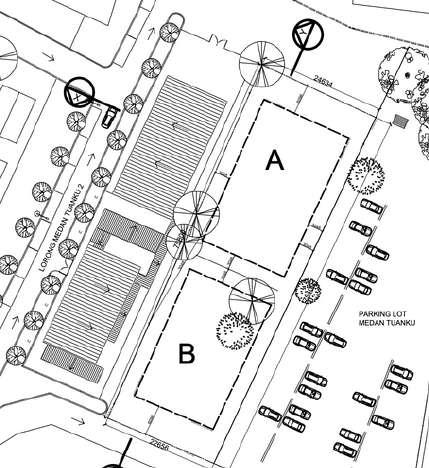
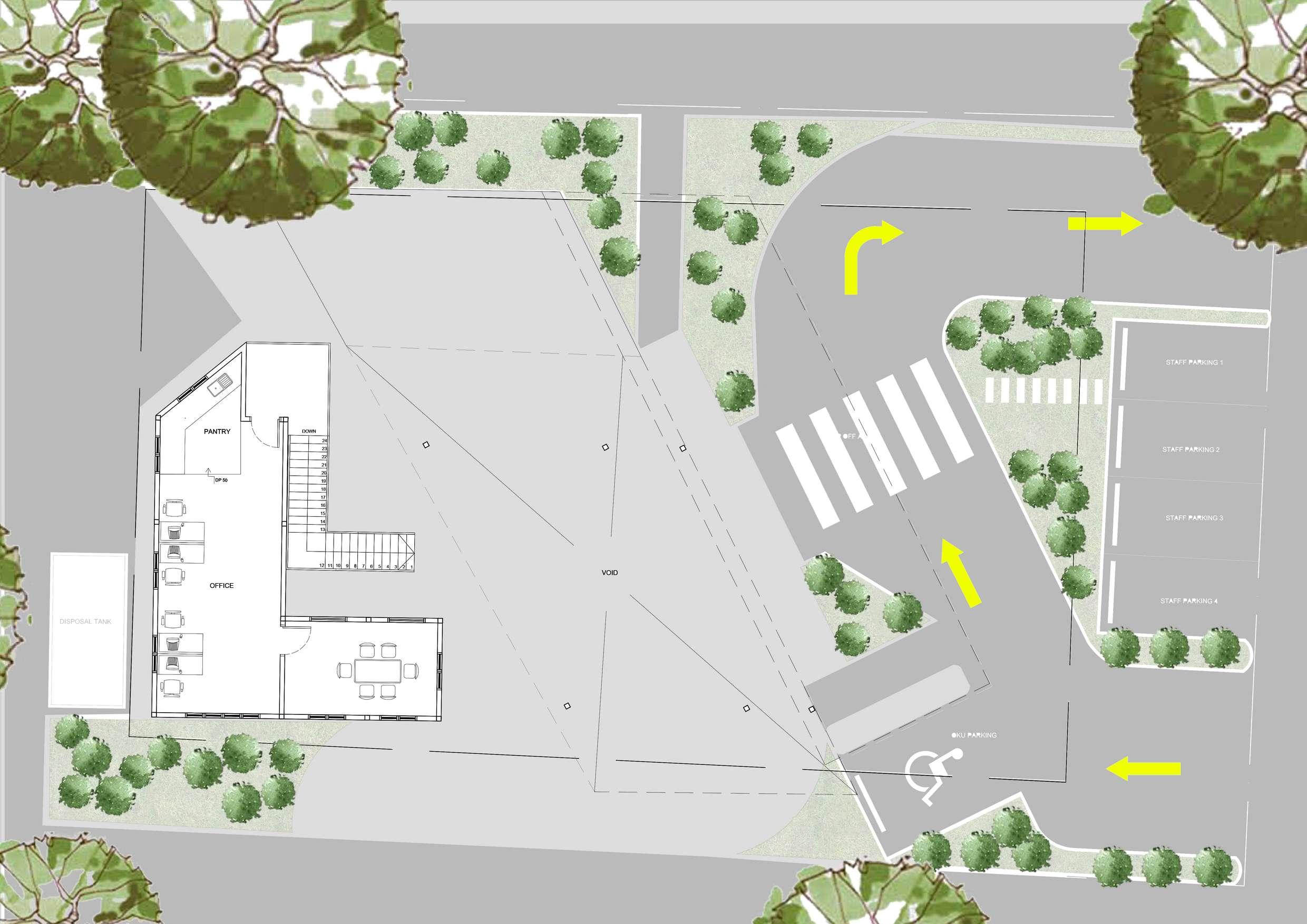
Location A

- easier to engage with the public
- noticeable by public



- Provide training programmes to enable long-term employment
- Teach urban farming skills for self sustain
- more opening on the East & South for more sunlight
- more opening at the North for maximum ventilation
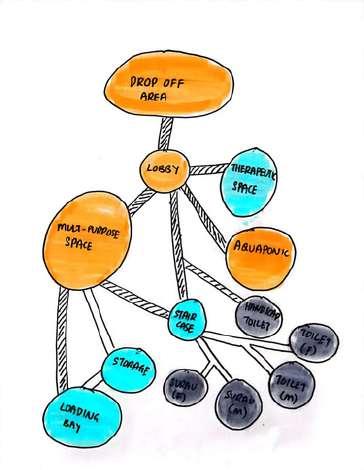
Open multifunctional space to carry out different activities
Aquaponic Therapeutic space
- entrance locate at the North
- easy to notice by public


Space for urban farming activities
Healthcare space Motivational talk
- focus more positive view on the East



- The plant is to show that the nature is blending with the building to allow the users have a sense of comfort


- The steps are to show the success of the homeless from different stages of their life
- The openings are to respond the site where the building should maximize the ventilation from the North
- The walls are to respond the site where the building should maximize the sunlight from the East and South
- The overall model is to show that the community center is a gathering space
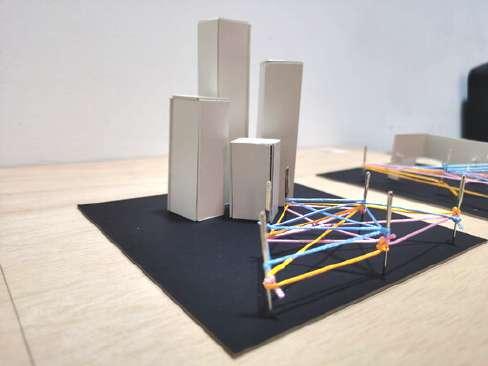

- The multiple thread like network is to show multiple activities can be done in a community center
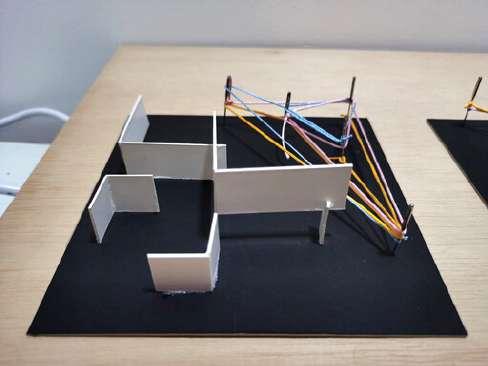
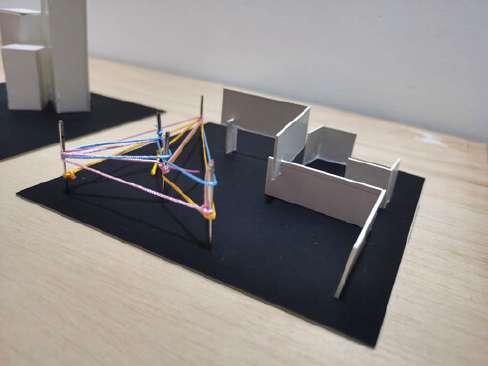
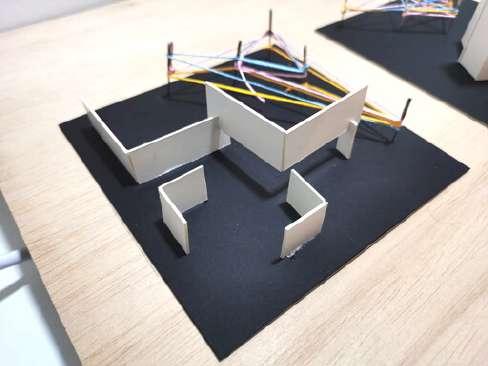
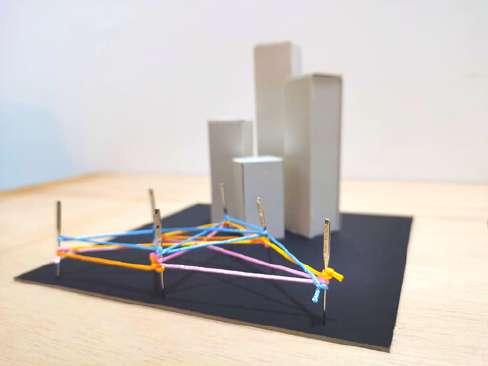
- The elevated structure is to represent the spaces in the building will be differentiate with different leveling for public and private spaces
- The multiple thread like network is to show a network of knowledge and people focusing on improving the lifestyle of the homeless
- Through the knowledge and help given, the homeless can improve their life through stages by stages represented by the increment of leveling
- As an overall, the improvement of the successfulness in homeless will reduce the rate of homelessness and make a better city


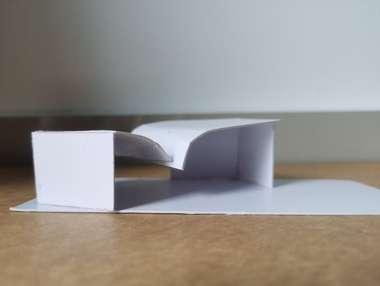


- Slanted roof for rainwater collection
- Double height volume for main programme
- Large opening for sunlight and ventilation
- 2 separate roof as butterfly roof for rainwater collection and differentiation of spaces for services space and main programmes space
-- 3 separated shed roofing to differentiate each zoning / spaces and creates a dynamic
- Giving a sense of growth of the homeless from stages to stages
SCALE 1: 250

GROUND FLOOR PLAN
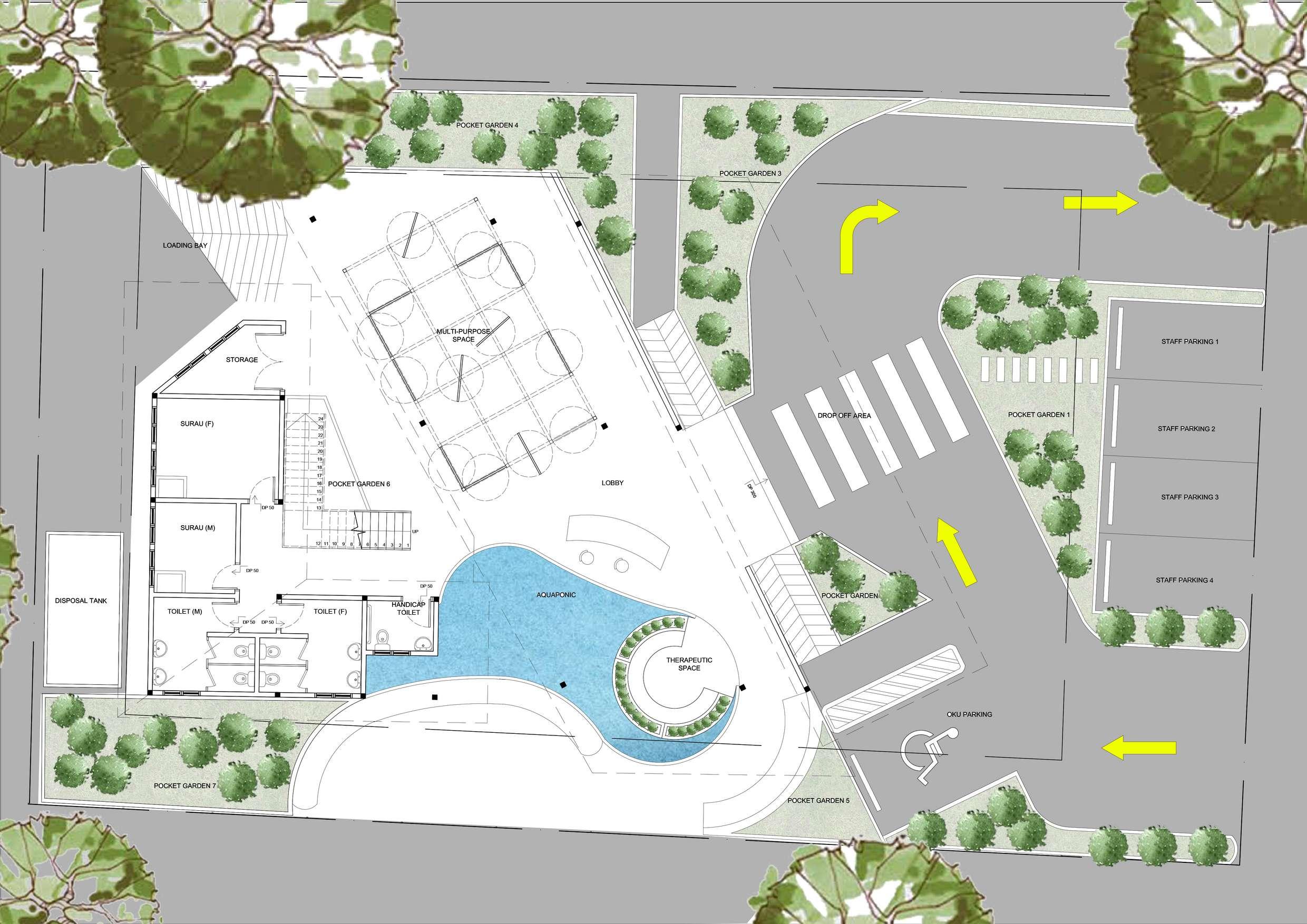
SCALE 1: 100

SCALE 1: 100

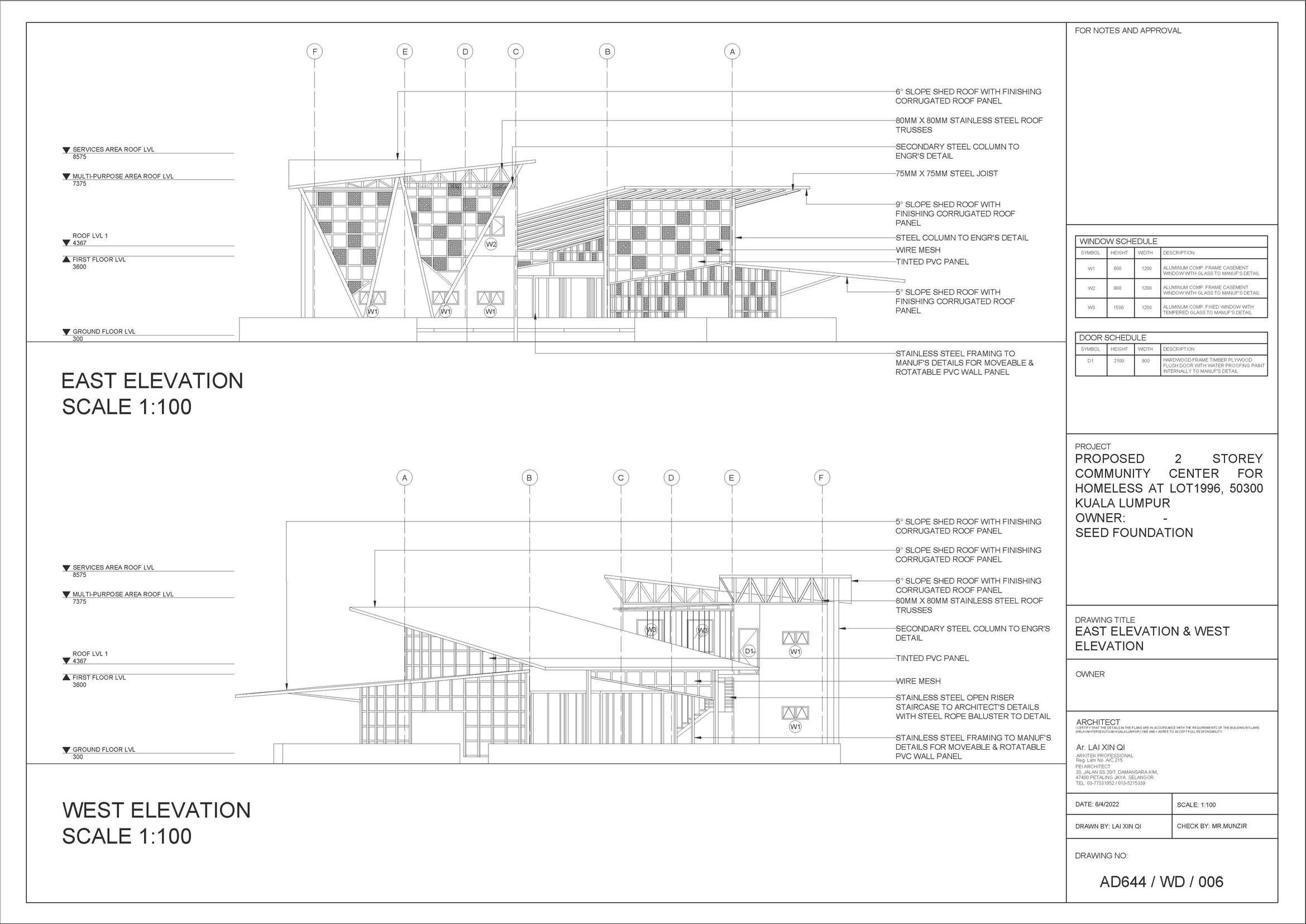
NORTH ELEVATION

SCALE 1: 100
EAST ELEVATION
SCALE 1: 100










 SCAN HERE TO LOOK AT THE PRESENTATION BOARD
SCAN HERE TO LOOK AT THE WALKTHROUGH VIDEO
SCAN HERE TO LOOK AT THE PRESENTATION BOARD
SCAN HERE TO LOOK AT THE WALKTHROUGH VIDEO