
Fan KAZEKI
Product Design | Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing, derived from Toyota's 1930 production method aimed primarily at reducing well as response times from suppliers and to to increase efficiency. By receiving goods only companies reduce inventory costs and wastage,
1930 operating model "The Toyota Way", is a reducing times within the production system as customers. Companies employ the strategy only as they need for the production process, wastage, and increase productivity and profit.
KAZEKI=KAZE+KAITEKI
2020.09-2020.12
Industry-University Cooperative Project with EUPA
Collaborated with Laura, LIN

KAZEKI
Product Design ∣ Lean Manufacturing ∣ KAZEKI

04
KAZEKI, a new type of fan that is appropriate for home use in summer.

Frustrated by the fan that cannot keep blowing air to you directly when your family members all need a fresh breeze? Cannot find a comfortable sleeping mode on your fan? or do frequent errors occur often when pressing your fan buttons?
To make a fan for home use, we have redesigned it via Lean manufacturing.



Product Design ∣ Lean Manufacturing ∣ KAZEKI
Fan Grilles Refinement: For Broad and Far-reaching Wind


Instead of strong and straight wind, we have found users prefer the gentle wind which is still strong enough to be diffused further. Thus, we had the fan grille s redesigned.
KAZEKI has the rear grille designed to be concentric for more concentrated intake, and the double-layer front grille, a curved inner layer and a concentrically arranged outer layer, which can create wider-blowing wind. Both of the rear and front grilles are with an angle of inclination to enhance their primary effects.
06
Infrared Sensors Usage: Uninterrupted Coolness
Imagine that your family members and you are gathering in the living room, watching the TV, and a fan at oscillation mode moving from side to side, the airflow hitting on them goes intermittent as the fan oscillates at an even speed, then the wind blowing will not stay long on a single user. This condition might disappoint the users. Considering that users should turn on the oscillation mode while accompanying other people, KAZEKI uses infrared sensors to detect where people locate and decreases its turning speed when it turns to the areas where people are in and increases its speed when there are no people here. Thus, the airflow can go back to the users sooner.
Handle Rethink: For a Better Carrying
Nowadays, most of the fans have their handles on the rear grille, thus, when we are trying to lift the fan, it may hit our calves because the fan will tilt, which is the result from its unstable center of gravity. In this case, additional force is required to have fans in the right position that won’t impede our walking when carrying them.
KAZEKI has its handle integrated into the body part, hence changing the carrying form from “ vertical-lifted” to” horizontal-lifted” will let it be more balanced.

Product Design ∣ Lean Manufacturing ∣ KAZEKI
Control Panel Redesigning: For a Better Operation
The Control panel has lots of types of design, such as buttons, knobs, and even an extra-large button specially designed for people who tend to press the buttons with their toes.
A great control panel has buttons and layouts with both icons’ recognition and operability in well designed. KAZEKI has its buttons in an arc
layout, Buttons with different functions are located on different areas of the dashboard (important: middle/ not too important: side) , the buttons’ diameter also reduces in the same way. We have also tested to find the appropriate button space for the latent need of toes-pressing.
Adequate Wind Mode: For Falling Asleep
People tend to switch their fans to sleep mode or natural wind rather than regular operation at bedtime. But sleep mode and natural wind might keep you from falling asleep especially when you are sensitive to airflow changes, and this situation was confirmed by the user feedback we had collected.
Sleep mode is composed of different airflow volumes and their duration time.
To provide a better fan-using experience, KAZEKI offers two kinds of sleep mode settings, each corresponding to the scenario of whether the air conditioner is turned on at that time.

08
Market Research
Investigate fans’ information such as price, main functions, and sales volume at both physical and online stores. Make a cross-comparison between those information and the consequences of contextual inquiry to find out a better location in the fan market for the subsequent design process.
Main function analysis of fans on the market
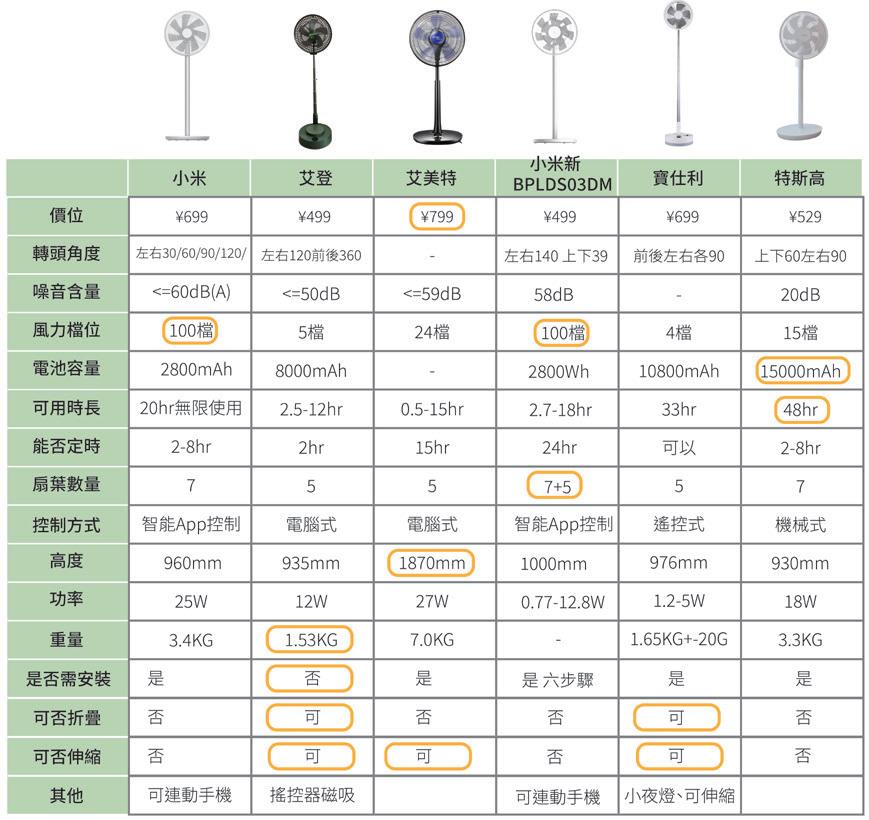
∣Ready to use out of the box
∣collapsible for storage
∣light and portable
∣Height-convertible telescopic pole
Left and Right Up and Down 360° Left and Right 120° Up and Down 39° Left and Right 140° Up and Down 180° Left and Right 180° Up and Down 60° Left and Right 90° 20hr 100 5 100 24 4 15 YES NO YES YES YES YES NO YES NO NO YES NO YES NO YES NO YES YES NO Cellphone linkage Magnetic remote control Cellphone linkage Night light Smart application Computerized Smart application Computerized Remote control EdonAirmate Xiaomi-B PorseriTesgao Price Oscillation Angle Noise Level Mode of Operaion Battery Capacity Endurance
Number
Control
Height Power Weight Installation Requirement Collapsible Telescopic pole Other
Timer function
of Blades
Method
10
Contextual Inquiry
The contextual inquiry requires us to go into the actual environment to gain an in-depth understanding of usage requirements via observation and interview. After this, we can find insight into those potential issues and latent needs.
Usage Requirements :
Living Room|Sense of loss caused by windless section when in oscillation mode
Bedroom|Comfortable and gentle wind
Kitchen|Cool strong wind

Children|Safety concern
Men|String wind, easily install and dismantle
Women|Pleasant natural wind

Product Design ∣ Lean Manufacturing ∣ KAZEKI
Customer Value Analysis
Customer value analysis is used after competitor analysis and contextual inquiry to obtain the satisfaction and importance of nowadays fan product design features. What we need to find are those features with high importance but low satisfaction: the so-called “blue ocean” of this product.
Blue Ocean of Fan:
∣New fan-using experience such as coolness, gentle sleep mode airflow.
∣Improving user experience of oscillation mode.
∣Humanized operation about buttons, storage, and carrying.
Wind-Blow Experience
A|Low noise volume.
B|Non-disturbing oscillation mode.
C|Concentrated airflow.
D|Airflow that is wider-blow but gentle.
E|Variety of air volume modes.
F|Enough wind power.
G|Maintain coolness when using oscillation mode.
H|Continuously wind-blow while using oscillation mode.
I|Non-disturbing oscillation mode while sleeping
J|The variation in air volume

doesn’t cause trouble for falling asleep.
K|One fan matches every space requirement.
L|Explicit buttons indication
M|Quickly adjust to desired wind mode.
N|One-handed adjustable fan pitch.
O|Press buttons without bending over
P|Buttons can be pressed accurately and effortlessly.
Q|Explicit and reasonable buttons position.
R|Easily moving
S|Easy installation.
T|Durable components.
U|Remote control storage design.
V|Space-saving while using.
W|Space-saving storage method
X|Grilles that do not get dirty easliy.
Y|Easy-to-clean grilles.
Satisfaction
Importance
Operation Installation Dismantling Other
12
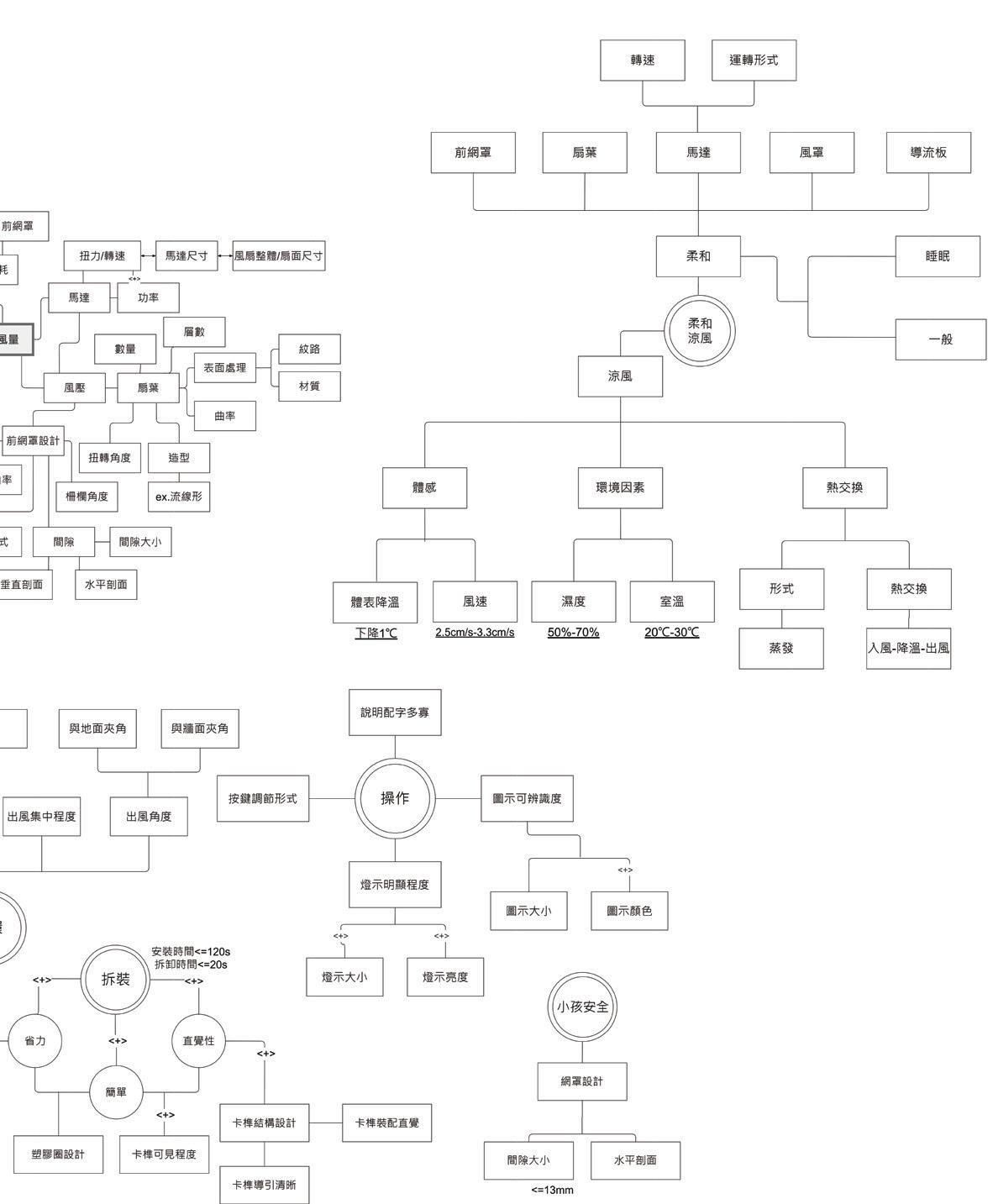
Causal Mapping

Draw a causal mapping so as to determine the follow-up experiments.
Causal mapping centered around the target function, write down detail related to the target function item by item, included material, mechanism, and principle used.
Product Design ∣ Lean Manufacturing ∣ KAZEKI



14
Research and Testing
Four experiments are taken in this project: air intake and exhaust experiment, wind somatosensory experiment, carrying experiment, and operation experiment.
Flow Simulation

How can we create a wider-blowing wind without losing its wind-blowing distance?
In this process, we use Solidworks Flow Stimulation to test the effect of different kinds of grilles on airflow, including influences on wind distance and wind diffusion. Then select a pair of the better effect as the final design.
Preliminary sketches of the grilles →
Front grille, final version:
∣ Double-layers design consists of a curved inner layer and a concentrically arranged outer layer, both with an angle of inclination for a wider-blowing wind.
∣ The curved inner layer is designed to lower the wind resistance by making the grille shape match the rotational inertia that blades make.

∣ The concentrically arranged outer layer acts as an inducer of wind, causing the wind to blow wide.


Rear grille, final version:
∣Rear grille as an air-inlet section, is designed to be concentric arrangement with an angle of inclination for more concentrated intake.
∣The concentrically arranged rear grille is designed to be in the form that can balance the wind aggregation and volume of air intake.
∣By using the rear grille to gather air, air intake volume increases and thus can have the exhaust being increased either.
Solidworks Flow Simulation∣Wind Distance
Solidworks Flow Simulation∣Exhaust Wind
Product Design ∣ Lean Manufacturing ∣ KAZEKI
Experiment-Somatosensory
Regarding the feedback that “sleep mode is not comfortable,” we took an in-depth inquiry with the fan users and noticed it will disturb people to fall asleep if there are obvious changes in the airflow volume.
Present sleep modes were referenced so as to configure a more comfortable and properer sleeping wind.
First, we made 6 different sleep modes (Group AGroup F1) with various permutations of air volume and time allocation. Then having the subjects simulated falling asleep and gave some feedback about the experience of each mode.

According to the evaluations that we collected, group C and group F1 are screened out, and each of them derived another two groups (Group C1-3, Group F1-3).
In the second experimental stage, several subjects told us “I think this wind mode is suitable if I turned on the air conditioner at the same time, ” and “I think this mode will work excellent if the weather is approaching fall. ” Therefore, We decided to let KAZEKI have two types of sleep patterns, divided by whether an air conditioner is used (Group C2 and Group F3).
The sleep patterns are shown in the figure below.
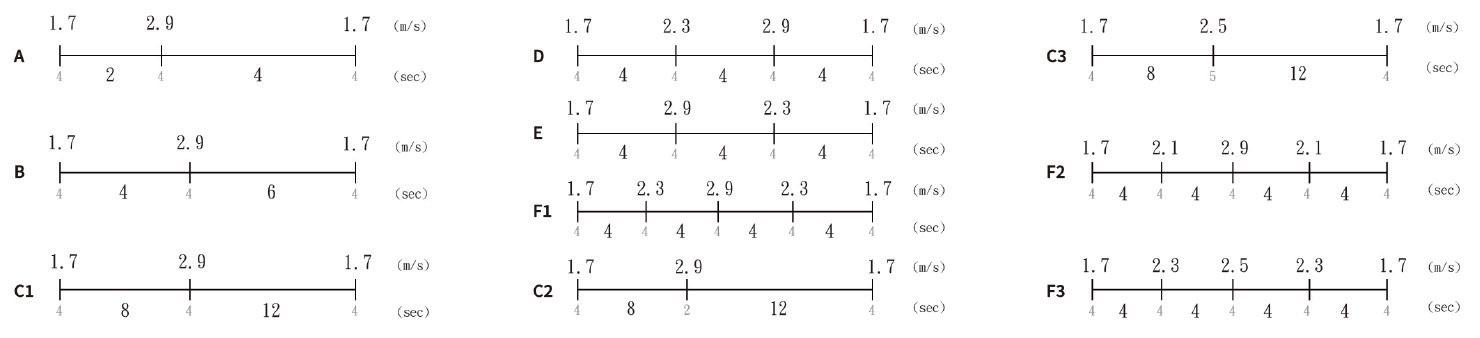
Description Experiment Procedures 10 Testing Groups∣Air Volume x Time Allocation Wind Speed / Air Volume Duration / Transition Duration (m/s) 1.7 2.3 2.9 2.9 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 (sec) ∣1st experimental stage ∣2nd experimental stage ∣Final Decision A B C1 D E F1 C1 C2 C3F1 F2 F3 C2 F3
Format
16
Experiment-Handle

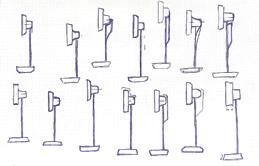

Traditional fan handles will cause inconvenience when users try to lift the fan. In the carrying experiment, we tried several handle shapes with modeling clay and put them on a fan to simulate the carrying scenario. However, it seems inappropriate no matter where the handle is placed. This situation makes us start to think that why there must be a “handle.” So we tried to integrate the “carry function” into



the main body design. After testing, we found that “lifting horizontally” is more effort-saving than lifting vertically, furthermore, It is still intuitive for first-time users that the carrying function is integrated into the main body, that is, a fool-proof design, although this design is quite different from the traditional ones. That’s KAZEKI's handleless carrying design.

Product Design ∣ Lean Manufacturing ∣ KAZEKI
Experiment-Buttons‘ Icon
The button icons and ways it works are somewhat confusing for users, for example, fans with a lot of wind modes but can only be adjusted in one way / one direction, once you press too many times by mistake, the only thing you can do is keep pressing.
Hence, we redesigned 13 distinct groups of button interfaces for the subjects and asked them for comments on those layouts according to their
intuitiveness of icons, positional arrangement of buttons, etc.
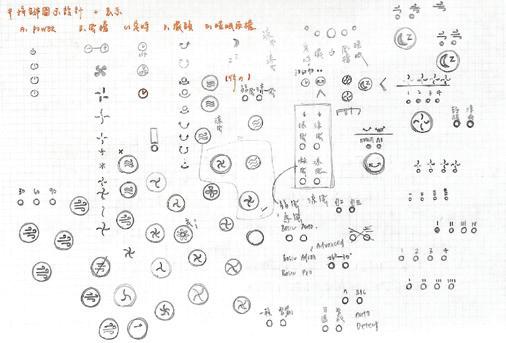
In the first experimental stage, we screened out group A and group B, then extend another two groups of each with their same concept, and group B became our final decision after the second experimental stage.

Group B interface design features:
∣Arc-shape buttons layout: According to the feedback, the arch arrangement is more beautiful than the other groups where the buttons are placed horizontally since it corresponds to the shape of the fan base.

∣Buttons’ size and position result from their usage frequency: We enlarge and center the frequently used button to make it easier for the user to press.

A B
18


















































