2 minute read
Rânula e Cavidade Bocal Ranula and the oral cavity
Rute Pereira 1 , Inês Serras 2 , Inês Sousa 3
1 Internato Geral, CHUAlgarve - Portimão
Advertisement
2 Interna da Formação Específica de Pediatria, Serviço de Pediatria, CHUAlgarve - Portimão 3 Assistente Hospitalar de Pediatria, Serviço de Pediatria CHUAlgarve
agnesesa@gmail.com
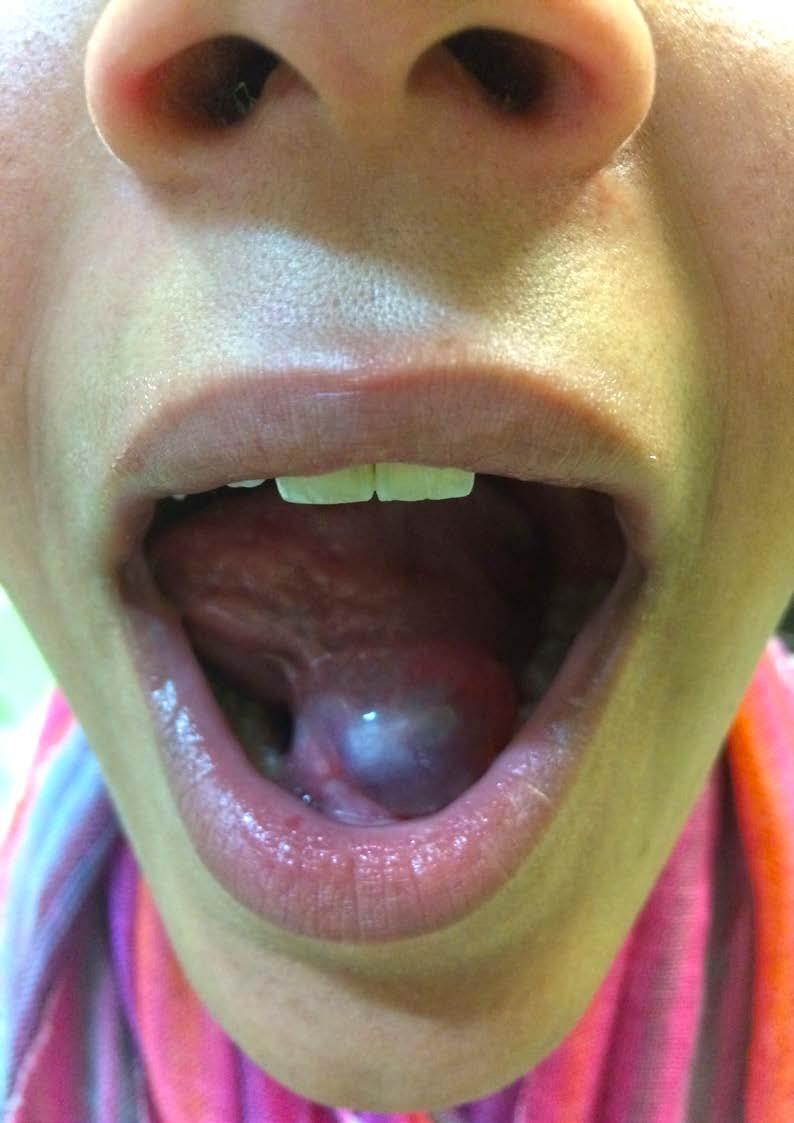
Rânula, substantivo feminino, segundo o dicionário Priberam da Língua Portuguesa, “tumor sublingual”. Terá origem, o termo rânula, no latim rana, ou seja rã, por se assemelhar macroscopicamente ao ventre desse animal.
Apesar de, por vezes e erradamente, ser chamada de quisto - formação cavitária dotada de um epitélio que lhe define as características - a rânula é, na verdade, um pseudoquisto, uma vez que não tem revestimento epitelial. Trata-se, então de uma colecção de saliva ao nível do pavimento da cavidade bucal, que se apresenta como uma tumefacção mole, com origem, na grande maioria dos casos, na glândula sublingual e, excepcionalmente, na glândula submandibular. Esta colecção é extraglandular e extraductal e, na prática, comporta-se como um mucocelo localizado no pavimento da boca, ou a nível cervical, resultante do extravasamento de líquido mucoso para os tecidos moles circundantes a um ducto excretor da glândula salivar, numa zona de obstrução ou sujeita a trauma.
Caso a rânula tenha um trajecto posterior ao longo dos planos fasciais do pescoço, poderá estender-se até ao espaço parafaríngeo. No caso de ter origem na glândula submandibular e caso se estenda através de um ponto fraco no músculo milo-hioideu, até ao triângulo submandibular, tratar-se-á de uma rânula mergulhante.
O tratamento da rânula é bastante discutível, mas a base para a evicção (ou redução) da recorrência passa pela exérese da glândula sublingual. Este caso clínico da Figura, referenciado para a Cirurgia Maxilo-Facial, corresponde a rapariga de 12 anos com história prévia de punção simples. Rânula, per the dictionary Priberam of the Portuguese Language, “tumor sublingual”. It will have origin, the term rula, in the Latin frog, or frog, for resembling macroscopically to the belly of this animal.
Although, erroneously, called a cyst - a cavity formation endowed with an epithelium - the ranula is a pseudocyst as it has no epithelial lining. It is, essentially, a collection of saliva on the floor of the buccal cavity a soft swelling, which originates, in the great majority of cases, in the sublingual gland and, exceptionally, in the submandibular gland. This collection is extraglandular and extraductal and, in practice, behaves like a mucocellus located on the floor of the mouth, or at the cervical level, resulting from the extravasation of mucous fluid to the soft tissues surrounding the excretory duct of the salivary gland, as a consequence of obstruction or trauma. If the ranula has a posterior path along the fascial planes of the neck, it may extend to the parapharyngeal space. If it originates in the submandibular gland and extends through a weak point in the myloyoid muscle, until the submandibular triangle, it will be a plunging ranula.
The treatment of the ranula is debatable, but the basis for avoiding (or reducing) recurrence depends on the excision of the sublingual gland. On the case at band the image belongs to a 12 years old girl with a previous history of a simple needle puncture, that was refered to Maxillofacial Surgery.





