Teacher’s Pack





Teacher’sPlanningBook




Teacher’sResource Book



SecondClass Teacher’sPlanningBook

SecondClass Teacher’sResourcesBook
SecondClass Teacher’s Pack








Teacher’sPlanningBook




Teacher’sResource Book



SecondClass Teacher’sPlanningBook

SecondClass Teacher’sResourcesBook
SecondClass Teacher’s Pack




Notetoteachers: Thecontentsshownindicatewhatisincludedinthissampleextract. While we have combinedthe resourcesintoasinglebooklethere,therewillbetwoseparate booksprovidedtoteacherswhoadopttheprogramme–a Teacher’s PlanningBookanda

ThePrimaryMathematicsCurriculum(PMC)hasfive Strands,whichare dividedinto StrandUnits:
Algebra DataandChanceMeasuresNumber ShapeandSpace
● Patterns, Rulesand Relationships
● Expressionsand Equations
● Data
● Chance
● Measuring
● Time
● Money
● UsesofNumber
● Numerationand Counting
● Place Valueand Base Ten
● Setsand Operations
● Fractions
● Spatial Awarenessand Location
● Shape
● Transformation
In MathsandMe,thecontentofeachunitisclearlyconnectedtooneormoreofthe Strands and StrandUnits.
EachoftheStrandUnitscontainsasetofLearningOutcomes.Learningoutcomesareusedtodescribethe expectedmathematicallearninganddevelopment foralllearnersattheendofatwo-yearstage,whendue accountistakenofindividualabilitiesandvaryingcircumstances.
Eachofthelearningoutcomesbeginswiththestem,‘Throughappropriatelyplayfulandengaginglearning experiences,childrenshouldbeableto...’Thisstememphasisestheimportanceofprovidingrichand engaginglearningexperiences.
In MathsandMe alllearningoutcomesarecoveredindepth.Theprogrammehasbeendesignedto includeawide rangeofrich,appropriatelyplayfulandengagingactivitiesandtasks,whichdemonstrate keypedagogicalpractices,andsupportchildrentowardsachievingthelearningoutcomesanddeveloping theirmathematicalproficiency.
The PMCissupported by thePrimaryMathematics Toolkit,whichincludestheProgressionContinua.The progressioncontinuaoutlineasamplelearningtrajectoryofMathematicsatprimarylevel.Theysuggest aseriesof learningexperiences whichchildrenmightengagewithastheydevelopanddeepentheir mathematicalknowledge,skillsanddispositions.Eachcontinuumdescribesthelearningjourneyacrosseleven ProgressionMilestones(a–k)intermsofmathematicalcontent(StrandUnits)andprocesses(Elements).
Takingintoconsiderationtheelevenprogressionmilestones(a–k),thevariousclasslevelsof MathsandMe have beendevelopedaroundcertainmilestones:
JuniorInfants ProgressionMilestonesbandc
SeniorInfants ProgressionMilestonescandd
FirstClass ProgressionMilestonee
SecondClass ProgressionMilestonef
Table2: MathsandMe ClassLevelsandtheProgressionContinua
Thatsaid, MathsandMe recognisesthatchildrenlearnanddevelopatdifferent rates.Therefore,whilethe contentoftheFirstClassbook, forexample,centresaroundsuggestedlearningfromProgressionMilestone e,itisalsoinfluenced by thestatementsinProgressionMilestonesdand f, tocater fortheneedsofallthe children. Teachersare recommendedtoexerciseprofessionaljudgementwhenmakingdecisionsastothe learningactivitiesandtaskswhicharemostappropriate forthechildrenintheirclassroom,andtoadapt accordingly.
ThePrimaryMathematics Toolkitoutlinesmathematicalconcepts.Theseareconsideredtobethe keyideas thatunderpineachlearningoutcome.Itisenvisagedthatchildrenwilldeveloptheirunderstandingofthese conceptsthroughengagingwiththemathematicalprocesses,asoutlinedintheelements.
In MathsandMe,mathematicalconceptsinformthedesignofunits,includingthemathslanguageto focus on,andinfluencetheprogressionofcontentfromoneclasstoanother.
A FocusofLearningidentifiesthepurposeofalessonand/ortheintendedlearningthatwilltakeplace.
In MathsandMe,the FocusofLearningineachlessonechoesthesuggestedlearningexperienceslisted intheprogressioncontinua,i.e.each focusoflearningiseitheranexact replicaofastatement,oris derivedfromoneormorestatements.
The focusoflearningisalsoconnectedtooneofthe fourelementsusingtheabbreviatedtitles.
● Givesand followsdirectionsinvolvinghalfandquarterturns (C)
● Discusses,models,visualisesandpredictshowanobjectwilllookwhen rotatedthroughahalfor quarterturn(R)
● Reasonsaboutalternativewaystoperformthesame rotation(R)
Digitalactivity:Grid References MAM Routines: Reason& Respondwith Write-Hide-Show
Digitalactivity: Turtle Turns MAM Routine: Reason& Respond
Concreteactivity:Predicting Turns MAMRoutine: WriteHide-Show
Pupil’sBookpage62: Turns
Childrendeveloptheirmathsskillsthroughprocessessuch asconnecting,communicating, reasoning,argumentation, justifying, representing,problem-solving,andgeneralising.The PMC(2023)uses fourelementstodefinetheseprocesses,and tocategorisethesuggestedlearningexperiencesgiveninthe progressioncontinua.
● Scissors
● Programmablebottoys, e.g.Bee-Botsorsimilar, andbotmats
The PMCadvocatesthatteachers providechildrenwithrichmathematical learningexperiencesthatareplayfuland engaging,that reflect relevantpedagogical approachesandthatprovideopportunities forchildrentocollaborate,communicate mathematicalthinking,andexpresstheir understandinginmultiplewaysandin variouscontexts.
Table3:An overviewofelementsandabbreviations
In MathsandMe,the focusoflearningineachlessonisclearly connectedtooneoftheseelementsusingtheabbreviated title(seesecondcolumnof Table3).Andwhilethe focusof learningmayincorporatemorethanoneofthesecentral processes,itisthemostprominentelementthatisgiven. ©TheEducationalCompanyofIreland
Inlinewiththelearningoutcomes, mathematicalconceptsandsuggested learningexperiencesintheprogression continua, MathsandMe providesawide rangeofrichandmeaningfullearning experiences foreachlesson.Manyof thesearedesignedaroundthe Maths andMe Routines.
MathsandMe Routines areacollectionofplayful,engagingandinclusiveinteractionsthatpromote mathematicaltalk,thinkingandmodelingamongallchildren.These repeatable routineshave beenchosen astheyareproventoactivatepriorknowledge, fosterproductivedispositionsandprovidevaluable formativeassessmentopportunities forteachers.
Inadditiontosupportingthefive keypedagogicalpractices,whichwillbedescribedindetailinthenext section,the routinesalsosupport formativeassessmentandinclusivepracticesasdemonstratedin Table4.
Doesitsupport/promote…?
Sometimes,Never; TargetBoards
Chapter6ofthe PMCdescribesfive keypedagogicalpractices.Thesepracticesareacknowledgedasessential totheprovisionofqualitymathematicallearningexperiences.
The PMCemphasisesthat‘Dispositionsarenotstaticandcanbenurturedorchanged overtime’andacknowledgesthat‘attitudestoMathematicsandvalues,bothathome andintheclassroom,alsohave astrongimpactonthedevelopmentofthechild’s productivedisposition forMathematics’(p.28).
Thefundamentalaimof MathsandMe is forthechildtocometoappreciatemathsassomething thatispositiveand relevanttothem.Ifthishappens,itismorelikelythattheywillengagewithmaths inameaningfulway. Thisseriesaimstoachievethis by:
● Highlightingthe worldofmathsaroundthechildren −intheirschools,intheirhomes,intheirlives
● Using real-lifeexamples ofmathsinactionandsituationsthatchildrencareabouttomakemaths meaningfuland relevant
● Actively encouragingthepositiveinvolvementof families intheirchild’slearningandmathematical experiences
● Incorporatingfunandentertainingactivities,includingplay, role-playscenariosandengaginggamesto boostenjoymentwhilealso emphasisingcollaborativetasks overindividual work
● Includingtasksthatencourage activeparticipation,exploration,investigation,productivestruggle, risk-taking,creativestrategiesandperseverance,whichwill resultin asenseofpersonalsatisfaction intheiraccomplishments
● Providing scaffolding,encouragementandsupport,includingtimetothinkand reflect
● Enabling childagencyandthechild’s voice.
The PMCstatesthat‘MathematicalmodelinginvolvesusingMathematicstodescribe aproblem-contextanddeterminemeaningfulsolutionstotheproblem…In forming models,childrenmightusephysicalactions,spoken words,objects,images(e.g.graphs, diagramsandpictures),symbolsorwritten words’(p.30).
MathsandMe enablesmathematicalmodelinginmanyways:
● Emphasisingthe importanceofthinkingtime toallowthechildrentomakesenseoftheirthinking
● Using speciallychosenquestionsandtasks toencouragethechildrentomodelmathematically
● Presentingmathsconceptsinmultipleways and/orusingmultiplevisual representationstointroduce thechildrentoawidervarietyofmodelsthantheymighthave encounteredorcreatediflefttotheir owndevices
12 3 9
● Encouragingthechildren tobeindividualandunique inhowthey expressand representtheirideasandthinking
● Promptingthechildrento challengeandtesttheir ownthinking andmodels,and thoseofothers
● Encouragingtheuseof physicalmodels (classroommaterialsandmanipulatives) tosupportmathematicalmodelingintheclassroom,andincluding representationsoftheseintheprintanddigitalmaterials
● Usingavarietyof conceptualandproceduralmodels todemonstratedifferent approachesandstrategiesandencouragechildrentodeveloptheir ownmodels anduniquewaystoapproachcomputationsandtasks.
The PMCdescribesCognitivelyChallenging Tasks (CCTs)as‘richhigher-orderlearning opportunitiesthatshouldappropriatelystretchandchallengechildren’sconceptual understandingastheyencountersignificantmathematicalideasandsituations. Sometimes referredtoas low-thresholdhigh-ceilingtasks,thesetasksshouldprovide allchildrenwiththeopportunitytoaccessMathematics,whileofferingthepotential for deeperengagement’(p.31).
MathsandMe facilitatesCCTsintheclassroom by:
● Incorporatingchallengeslinkedtochildren’scurrentlevelofknowledgeandunderstanding,while providinganappropriatestretch
● Providingtaskswherethesolutionpathwayisnotimmediatelyobvioustothelearnerorwherethe solutionisnot reducedtoasetofstepsandprocedures
● Facilitatingchildrentocommunicateandexpresstheirideasopenly,allowingthemtodiscuss,compare, justifyandevaluatetheirideasorsolutions.
CCTshave beenincorporatedthroughouttheprogrammeanditscomponents.
The PMCdescribesMaths Talkas‘acollaborativeprocesswherechildren’sthinking, strategiesandideasareexpressed,sharedand/orexchanged.Thisallowschildrento reflectontheir ownunderstanding;define,presentandjustifytheirideas;makesenseof andcritiquetheir ownideasandthoseofothers;anddeveloptheirabilitytoexpressand articulatetheirthinking’(p.32).
Ineverylesson, MathsandMe providesideas forMaths Talkactivities,whichbeginwithappropriately challengingandengagingtasks.Bytheir verynaturetheseMaths Talkactivitiesalsoproviderichassessment opportunities,i.e.elicitingcurrentknowledgeandunderstanding,identifyingemergingconcepts.These activitiesemphasisetheprobingand responsiveaspectsofMaths Talk.Allofthe MathsandMe Routines promoteand fosterMaths Talk.Theuseofthese routinessupportsacultureof respectandrisk-taking,where children feelsafetosharetheirthinkingandareencouragedtolistentoandvaluetheideasofothers.
The PMCstatesthat‘Mathematicallearningcanbegreatlyenhancedinaplayenvironment thatisinteractive,engaging,inclusiveandsupportive;andthatprovidesopportunities for exploration,investigation,challenge,creativity,choiceandindependence.Playprovides acontext formathematicalthinkingandthedevelopmentofmathematicallanguageand concepts,withclearpotential forpromotingmathstalk’(p.29).
MathsandMe encouragesplayfulness by:
● Tappingintochildren’sinterestsandcuriositiesthroughengagingthemesand real-lifecontexts
● Suggestingideasandwaystointegratemathematicallearningwithplayfulactivitiesthroughouttheday
● Facilitatingmultiplemeansofexpressionand representation
● Providingopportunities forchildrentoexploreandexperimentwithmathematicalideas
● Fosteringthecreationofasafespace forspontaneity,creativityandimaginativeplaywithmathematics
● Providingaccesstoawide rangeof resources,visualsupportsanddigital resources.
The PMCexplainsthat ‘Assessmentisanintegralpartoflearningandteaching.Itinvolvesteachersand children workingtogethertouseinformationtoinformandsupportlearningandteaching’(p.34).The PMC advocatesthreetypesofassessmentasbeingnecessary‘togainacomprehensivepictureofachild’sprogress andachievement’(p.35).Theseare:
● Intuitiveassessment:Unplanned,unrecorded,andongoing
● Plannedinteractions:Morevisible,maybe recorded,and relatedtolearningoutcomes/competencies
● Assessmentevents:Distinct,visible, recordedevents.
Assessmentisintegratedthroughout MathsandMe.Thelearningexperiencesarestructuredinsuch awaythattheysimultaneouslypromotethedevelopmentofmathsskillsandfluency,andenablethe teachertogather, record,interpret,useand reportinformationaboutachild’sprogressandachievements. Theteachercanthen respondtotheinsightsgatheredfromtheassessmentsandadjusttheirteaching accordingly.
Theprogrammesupportsthethreetypesofassessmentoutlinedinthe PMCinthe followingways:
Intuitiveassessment
● Unitplansprovide comprehensivebackground andrationale information forteachersonallthetopics covered,alongwith guidance andsupportsaroundcommon misconceptions,thus increasingteacherawareness andpreparednesstoobserve and respondtopupils.
Plannedinteractions
● Lessonsaredesignedaround richlearningexperiences linkedtothe focusoflearning andlearningoutcomes.
● Lessonsuseanumberof MathsandMe Routineswhich posequestionsdesigned tostimulateclassroom conversations andtoscaffold learning.The regularityof theseensurethey become familiar,recognisable assessmentopportunities
● Eachlessonplanhighlightsthe learningexperiencebest suitedtogenerating recordableassessmentdata
● Pupil’sBooktasks provide furtherassessmentdata,as doesthe self-assessment feature.
● Mathsjournalling opportunitiesareoutlinedin thelessons.
● Eachunitcomeswitha FormativeAssessment ObservationsSheet for teachers.
Assessmentevents
● The ProgressAssessment Booklet providescheckupquestionslinkedtothe learningoutcomesofeach unit.Thesequestionscanbe usedasaplannedassessment and administeredasa traditionaltest,orusedasthe basisof agrouporwholeclass quiz.
● A comprehensiverecord sheet enableseasyanalysisof assessmentdataatindividual, groupandclasslevel.
Thisguidewillwalk youthroughtheprogramme’s keycomponents,highlightingitsstructure,integrated approach,easeofuse,andthechoicesitofferstobothteachersandchildren.
The MathsandMe yearly overviewisdividedintomonths,thensubdividedinto units.Eachunitiseitheroneortwo weekslongandcoversaspecificareaof learning.Thecontentofeachunitisclearlyconnectedtooneormoreofthe StrandsandStrandUnits.
Review Weeksarealsoincludedinthe yearly overview,providing regular opportunities forchildrento reviewand reflectontheirlearning.
Unitsarethebuildingblocksof MathsandMe.Eachunitisbrokendownintoa numberoflessonplans,and followsasimilarstructure.Theinitiallessonactivates andassesseschildren’spriorknowledge,thesubsequentlessonsdevelopand progressthelearning,whilethefinallessonofeachunitprovidesavaluable opportunityto reviewand reflectviaamenuofoptions.
Let’sStrengthensuggestionsandmaterialprovidesadditionalsupporttochildren,whileLet’sDeepen suggestionsandmaterialprovideadditionalchallengeandextensionopportunities.
● Developsandprogresses thelearning
● Providesopportunities toreviewandreflecton learning FormativeAssessment
Eachlessonalso followsaclearstructure,whichisstraightforwardandeasyto follow, andprovidesflexibility andchoice forteachers.
Warm-up
Eachlessonstartswithwarm-upsuggestionstogetthechildren readytolearn. Theyaretypicallywhole-classactivities,whosepurposemightbeto:
● Provideanintroductiontothemainlesson
● Revisitconceptsthatthecurrentlessonwillbuildupon
● Reviewcontentcoveredpreviously.
Mainevent
Themainpartofthelessonincludesanumberoftasks,throughwhichthe childrenwillachievethe focusoflearning forthelesson.
Thesetasksmaybeconcreteactivities C ,digitalactivities D oractivitiesbased onprinted resources P
Somepointstonoteabout MathsandMe lessons:
● Emphasisonplayfulandengaginglearningexperiences
● Useofdigital resourcestoenhancethelearning
● Useof MathsandMe Routines:see At-A-GlanceGuide
● Support foralllearnersthroughLet’sStrengthenandLet’sDeepen features
● Formativeassessmentopportunitiesthroughout.
Optionalconsolidationandextensionopportunities
Eachlessonendswithachoiceoffurtherlearningexperiencestoconsolidateandextendthechildren’slearning.
To supportteachersinimplementingthe PMC,thecomponentsof MathsandMe have beendevisedtoserve variouspurposesandenhancetheteachingandlearningofmathsintheclassroom,widerschoolandhome environments.
Pupil’sBook
The MathsandMe Pupil’sBookisdesigned foruseafterengagementwith thelearningexperiencesoutlinedinthelessonplans.Itspurposeistwofold: toprovideanopportunitytoconsolidatethenewlearning,andtoprovidea recordofchildren’s work.
The following featuresareincluded:
● TryThis:providesoptional,cognitivelychallengingtasks forpupils
● Let’sPlay:incorporatesplayfulnessintomathsthroughengaginggames andinteractiveactivities
● MathsEyes:encourageschildrentolookaroundthemand recognise mathsinthe real world
● Let’s Talk:providesopportunities forchildrentosharetheirstrategiesand ideas
● Let’sInvestigate:encourageschildrentodevelopcreativestrategies throughactiveparticipationandexploration.


ThePupil’sBookalsocomeswiththe followingadditional resourcestosupportlearning:a MWBwithan opennumberlinetemplate,adoubletenframe,achoiceoftwospinners forusewithgames,placevalue arrow cardsandplacevaluecut-outcounters.
The MathsandMe Home/SchoolLinksBook recognisestheimportanceofthe familyinthechild’slearning.Includedinthebookare‘Dear Family’notes for eachunit,whichprovidetipsonhowtosupportthechild,practicalactivitiesto becompletedathome,andQRcodesthatlinktodigital resourcessuitable for homeuse.Theactivitiesinthisbookhave beencreatedtobeapproachableand open-endedto facilitatechild-ledinvestigationandplayfullearning.
The MathsandMe teacher’s resourcematerials have beensplitintotwobooks:the Teacher’s PlanningBookandthe Teacher’s ResourcesBook.
The Teacher’s PlanningBookprovides comprehensiveteachingandplanning supportmaterialsinlinewiththe PMC.A yearly overview,unitplanswithshort-term planningandlessonplansareallincluded.
● The YearlyOverviewmapsouttheunits andstrandunitscovered overthecourse ofthe year.
● TheUnitPlansincludetheshort-term plan(fortnightlyplan)andadditional informationuseful forplanning,suchas commonmisconceptionsandmodelsand representationsused.











● TheLessonPlansoutlinethe focusof learning,learningexperiences,equipment needed,andmathslanguagethatwillbe focusedon.Fromthere,eachlessonisbrokendowninto WarmUpactivities,theMainEventandOptionalConsolidationandExtension Possibilities.
The Teacher’s ResourcesBookincludesalladditionalmaterialsoutsideofplanning.A rangeofphotocopiable materials(PCMs)are featuredhere,includinggeneralPCMs,Let’sStrengthenSuggestions for Teachers,Let’s StrengthenPCMsandLet’sDeepenPCMs.
The MathsandMe ProgressAssessmentBooklet featuresassessmentsthat covereachunit.Assessmentscomeinthe formofcheck-upquestionswhichare linkedtothelearningoutcomesofeachunit.Thebookletisdesignedinsucha waythatitcanbeeasilyusedaftereachunit,orduringeach review week.




The MathsandMe digital resourceswillbringmathstolife forchildren,andenhanceclassroomlearning by encouragingparticipationandpositiveengagement.The resourcesaredesignedtocater fordifferentlearning stylesandcontributetothewide rangeofrichandplayfullearningexperiencesintheprogramme.
Innovative,intuitiveandeasytonavigate,the MathsandMe resourceshave primarilybeendeveloped asteachingtools fortheinteractivewhiteboard(IWB)andcanbeusedinconjunctionwiththechildren’s mini-whiteboards(MWBs)whereappropriate.
Supportingthepedagogicalpracticespromotedinthe PMCandproviding variedlearningopportunities forchildren,the resources reflectthelesson’s focusoflearning,promoteMaths Talk,incorporatemathematicalmodeling andallow for formativeassessment.Many resourceshave beenspecifically designedaroundthe MathsandMe Routines,suchasConceptCartoon, Three-Act TaskandQuickImages.
Digital resourcesaccompanymostlessons. To provideguidance fortheintegrationofdigital resourcesin theclassroom,theyare referencedindetailthroughoutthelessonplans foreachunit,withsuggestions for discussionanddifferentiation.The resourcesincludethe following:
Animations
Featuringtheprogrammecharacters–Mia,Jay, Lexi,DaraandMontythedog –theanimationsbringmathstolife withcolourfulstories,songsandfun scenarios relevanttochildren.



Videos
Immersiveandinterestingvideoswithdetailedconceptexplanationsandmeaningfulexamplesofmaths inactioninthe real world.



Awide rangeofdigitalactivities–includingposters,slideshowsandinteractivegames–tosupport teachingandconsolidatelearning,encourageMaths Talkandpromoteactiveparticipation.




Acomprehensivesetofbespokeinteractivemathstoolsandmanipulatives,includingMoney,Shapes,Clock, NumberSquare,Place Value,Dice,Spinnerandlotsmore!
Teacherscanaccessthe MathsandMe digital resourcesvia www.edcolearning.ie,whereadedicated websitewillhosttheprogramme’s keycomponents.Witheasy-to-usefilteringtosupportclassroom teachingandlessonplanning, mathsandme.ie willincludeinteractivee-books,digital resources,editable planningdocumentsandprintables(suchasMathsLanguageCards,ManipulativesCut-OutsandAssessment RecordSheets).
To supporthome/schoollinksandstationteachingintheclassroom,abankofdigital resources–suchas animationsandinteractivegames–willbemade availableviaafreePupil/ParentApp.
Unit9: Locationand
rmPlanUnit9:Locationand Tr ansformation (J anuary: We eks1&2)
MathsandMe:2ndClass–Shor tTe
Aw arenessandLocation; Tr ansformation;Shape
ShapeandSpace>Spatial
Ed
CMLearningExperiencesAssessment
IntuitiveAssessment: re spondingtoemerging misconceptions
Assessment Interactions: re spondingtoinsights gleanedfromchildren’s re sponsestolearning experiences
AssessmentEvents: informationgathered fromcompletionofthe unitassessmentinthe ProgressAssessment Bookletpagexx
Strand(s)>Strandunit(s)
LearningOutcome ( s )T hroughappropriatelyplayfulandengaginglearningexperienceschildrenshouldbeabletousespatialknowledge fo rthepurposesoforientationandnavigation;visualiseandmodellocation usingsymbolicco-ordinates;understandthatshapesandlinesegmentscanbe re flected, ro tatedandtranslated.
Fo cusofLearning(withElements)
D Notice& Wo nderL1,6
D Think-Pair-ShareL1,7–8
D Re ason& Re spondL1–8
C P CapturetheCountersL2
D Wr ite-Hide-ShowL2,3
C BuildIt!SketchIt! Wr iteIt!L1,4
C Predicting Tu rnsL3
C MakingRightAnglesL5
C Sy mmetryStationsL6
D ConceptCartoonL7
C MovingShapesL7
C ExploringandCreating Te ssellationsL8
C Solving Te ssellatingPuzzlesL8
Print re sources Pupil’sBookpages61–67 Home/SchoolLinksBookpages23–24 PCMxx
DifferentViews: Re cognisesthe re lationshipbetweendifferentmodesof re presentingpositionandlocation(bird’s-eyeview ve rsus streetview)(R)
Location: Identifiesanddescribesthegenerallocationofanobjectusingagridsystem(U&C);Exploresgrid re fe re ncesinthe contextofbarriergames,orotherplayfulactivities(A&PS)
Tu rns: Givesand fo llowsdirectionsin vo lvinghalfandquarterturns (C );Visualisesandpredictshowanobjectwilllookwhen ro tated throughahalforquarterturn(R); Re asonsaboutalternativewaystoper fo rmthesametransformation(R)
Directions: Givesand fo llowsdirectionsin vo lvingturnsandsimpledistancesorlandmarksinthecontextofsimpleplans/grid maps/aerialphotosof fa miliarenvironments (C ); Re cordsdirectionsasaseriesofsimplesteps (C );Devisesandanalyses ro uteson maps,plansorgridsthatsatisfycertainconstraints(A&PS)
RightAngles: Exploressquareandnon-squarecornersintheenvironment,identifyingsquarecornersasrightangles(U&C)
Re flections: Discusses,modelsandvisualises re flectionofshapes(U&C);Completesmissing re flections,ofshapesorimages (C)
WhatMo ve ?: Discusses,models,visualisesandpredicts re flection, ro tationandtranslationofobjects,imagesandshapes(U&C); Re asonsaboutalternativewaystoper fo rmthesametransformation(R)
Te ssellations: Exploresandcreatessimpletessellations(U&C);Explorestessellationswhereasingleshapeis re peated(A&PS); Examinestessellationsandidentifiesifshapesha ve been re flected, ro tatedand/ortranslated(U&C)
Re viewand Re flection: Re viewsand re flectsonlearning(U&C)
Ke y: Elements: (U&C)UnderstandingandCommunicating; (C )Communicating;(R) Re asoning;(A&PS)ApplyingandProblem-Solving.
LearningExperiences: C concreteactivity; D digitalactivity; P activitybasedonprintedmaterials, fo llo we d by lessonnumbers.
CM:CuntasMíosúil: pleasetickwhen yo u ha ve completedthe fo cusoflearning.
Lesson
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
ProgressionContinua
MathsLanguage
Equipment
InclusivePractices
See‘SecondClass MathsandMe ProgressionContinuaOverview’ foradetailedbreakdownofhowallprogression continuaarecovered.
See‘SecondClass MathsandMe MathsLanguageOverview’andindividuallessonplans.
See‘SecondClass MathsandMe MathsEquipmentOverview’andindividuallessonplans.
● SeeLet’sStrengthenandLet’sDeepensuggestionsthroughoutlessonplans.
● SeeUnit9Let’sStrengthenSuggestions for Teachers.
● SeeUnit9Let’sStrengthenPCM.
Integration
● SeeUnit9Let’sDeepenPCM.
Seeindividuallessonplans.
● Locationand TransformationisthesecondShapeandSpaceunitin MathsandMe.Itisacombinedunit, exploringthetopicsofSpatial AwarenessandLocationand Transformation.
● Whilethechildrenhave exploredsimplemapsandgridspreviously,thisisthefirsttimethattheyare introducedtousingagridsystemandgrid references,i.e.lettersalongthehorizontal,numbersalong the verticaland referenceswhichareexpressedasanorderedpair(e.g.F2).Ingridsystemsandgrid references,theobjectislocatedintheareaorspacecreated by theintersectinglines.
● Inlaterclasses,theywillbeintroducedtopairsofcoordinates,e.g.(6,4),asanotherwayto representlocation. Inthecoordinatesystem,thelocationoftheobjectisaspecificpointattheintersectionofthelines.
● Turns:Whiletheprimary focusofthisunitisonfull,halfandquarterturns,ifappropriate,challengesome childrentoalsoexploretheeffectsofthreequarterturns.
● Theprogressioncontinua forlevelsd,e, f, g,andh refertotwospecifictypesofsymmetry:linesymmetry, introducedatleveld,and rotationalsymmetry,not formallyexploreduntillevelg.Therefore,in Maths andMe forSeniorInfantsto2ndClass,thechildrenwillonlybeexploringlinesymmetry.Aslinesymmetry isalso referredtoas reflectiveormirrorsymmetry, MathsandMe usestheterm‘mirrorsymmetry’,both tohelpcreateadistinctionbetweenthechildren’sunderstandingofthistypeofsymmetryandtheirlater understandingof rotationalsymmetry,andtoemphasisetheimportanceofincorporatingtheuseof mirrorsasanessentialpieceofequipmentwhenexploringthisconcept.
● Whilethecardinalpoints(north,south,eastand west)arenotexplicitiytaughtinthisunit,ifthese directionsariseorganicallyfromthepupils’ owndiscussionanddirections,theyshouldbeacknowledged andincorporated.
● Patterns:Thisunitalsoprovidesopportunitiestodevelopunderstandingofsomepatterntypes, e.g.symmetrical,tessellating,inpreparation forUnit11 Patterns.(Seealsointhesameunit: Patterns: SupportingLearning).
The overarchingthemeofthisunitis TheZoo.Thisthemeprovidesa real-lifecontextthechildrencan identify(i.e.triptothe zoooranother family-friendlydestination)andusesimplemapstonavigate.
Forachildtobeabletoflexiblyvisualiseposition,directionandtheeffectsofmovementand transformationonshapesandobjects,theymusthave ampleexperienceofmanipulatingthephysical representations.Therefore,experienceswithconcretematerialsandequipmentarevitalandshouldbe enabledasmuchandasoftenaspossible.
Thechildrenmay:
● Confuserightandleft(eveniftheyhave beenusingthesedirectionssinceSeniorInfants), particularlywhentheorientationoftheobjectisdifferenttotheir ownorientationandclockwise/ anti-clockwise.*
● Struggleto rememberthatinagrid reference,thelettercomesfirst.
● Struggletovisualiseandidentifyhalfandquarterturns.(Makingaturn yourself requirestheability tovisualise yourselffromabove as youturnafractionofacircle,clockwiseoranti-clockwise.It mayhelp forthechildrentoinitiallyuseacut-out,withobviousfront,backandsides,thatcanbe physicallyturned).*
● Struggletoidentifyrightanglesifthelinesmakingtheangleareorientatedanyotherwaythan horizontaland vertical.
● Incorrectlyassumethatwhereashapeishalved,thatthisisalsoalineofsymmetry.*
● Createaduplicate/repeatimage(seebelow)whentryingtocreateamirrorimage.*
*SeetheUnit9–Let’sStrengthenSuggestions for Teachers forspecificinterventionstoaddressthese misconceptions.
● 3-Dandaerial representationsofvariousobjectsandshapes
● Gridsandgrid referencestoaidlocation
● Physicalandpictorial representationsofobjectsthatcanbeturned
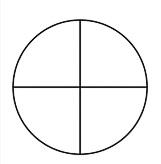
● Circlesdividedintohalvesandquartersto representturns
● Curvedandstraightarrowsgoing/turningbothleftandright
● Physicalandpictorial representationsof2-Dand3-Dshapes
● Physicalandpictorial representationsofobjectswithrightangles
● Physicalandpictorial representationsofshapesthatcantessellate
● Recognisesthe relationshipbetweendifferentmodesof representingpositionandlocation(bird’s-eye view versusstreetview)(R)
Digitalactivity:The Zoo(1)
MAM Routines:Notice& Wonderwith
Think-Pair-Share/Reason& Respond
Digitalactivity:DifferentViews
MAM Routine: Write-Hide-Show
Concreteactivity:CubeConstructions
MAM Routine:Buildit!Sketchit! Writeit!
Pupil’sBookpage61:DifferentViews
● bird’s-eye/aerialview,streetview
D Digitalactivity:TheZoo(1)
MAM Routines:Notice& Wonderwith
Think-Pair-Share
● Lotsofcubesandcuboids,bothconnecting (interlockingcubes,magneticblocks, polydrons,megablocks,Lego,etc.)and notconnecting(baseten, woodenbuilding blocksandnumber rods)
● Geometricsolids
Recordthechildren’s responsestobothquestionson theboard.
Displaytheposterand,usingThink-Pair-Share,ask:
● Whatdo younotice?Whatdo you wonder?
D Digitalactivity:TheZoo(1)
MAM Routine: Reason& Respond Displaytheposterandaskorclicktoplay thequestionsbelow. Whenever appropriate,askthechildrentogive reasons fortheir responses(s), forexample, toexplainwhyorhowtheythinkthis.
● Whatdoesthispostershow?
● Thisisa zoo;whatcluestellusthis?
● Namesomethings youthink you recognise.
● Whereisthisviewfrom?
● Whydo youthinkthisissometimescalledan aerialview?
● Whydo youthinkthisissometimescalleda bird’s-eyeview?
● Whatistheoppositetoanaerialorabird’s-eye view?(astreetview)
● If we couldseethisasastreetview,what would youexpecttosee?
● Whenmightabird’s-eyeoranaerialviewbe better?
● Whenmightastreetviewbebetter?
Optional:UsingGoogleMaps,locatetheschoolusing itseircode.Lookattheschoolfromthedifferent availableviewpoints(aerialview,streetviewfront, streetviewbehind,etc.).Thechildrencouldalsodo somethingsimilarwiththeir ownhomes(whenat homeorinschooliftherearesufficientdevices available).
D Digitalactivity:DifferentViews
MAM Routine: Write-Hide-Show Playtheinteractivegame,inwhichthechildren mustmatchtheaerialimageswithcorresponding street-viewimages.
C Concreteactivity:CubeConstructions
MAM Routine:Buildit!Sketchit! Writeit! Distributethecubesandcuboidstotheclass.The childrenshouldusethesetoconstructsmallmodels ofvariouscolours.Theyshouldthensketchand colourbothabird’s-eye/aerialviewandastreetview oftheirmodel.
Optional:
● Thechildrencouldphotographtheirmodelsfrom thetwodifferentviewpoints.Thephotoscould thenbeusedasamatchingactivity forothers.
● Groupscouldswaptheirsketchesandbuildeach other’s models.Cantheymatchthesketchtoits 3-Dmodel?
P Pupil’sBookpage61: DifferentViews
Thechildrenmay benefitfromthe additionalsupportof the3-Dgeometric solidstocomplete activityC.
Trythis! Forthebird’s-eyeviewoftheclassroom,the childrencoulduseasquaredcopypage,PCM1− 1cmSquareGrid,PCM2−2cmSquareGridand/or PCM3−ClassroomCut-outs.
Let’sStrengthen:
Thechildrenmaybenefitfromtheadditional supportofthePCMslistedabove.
Let’sDeepen: Challengethechildrentodrawtheclassroommap withoutanyextrasupport.
Integration Giventhatthe overarchingtheme forthisunitisThe Zoo,therearelotsofopportunities forcross-curricularintegration,e.g.Language English:languageand vocabularydevelopmentusing thethemeofthe Zoo;LanguageGaeilge:Ainmhí; Science TechnologyandEngineering:animallife; Geography:animalconservation,animals/habitats aroundthe world;Music:listeningand respondingto TheCarnivaloftheAnimals.
MathsJournal Thechildrencouldchooseother objectsintheclassroomtosketchinaerialandstreet view.
Locationand TransformationDisplay Setupa displayintheclassroom,towhichthechildrencan contributelabelledexamplesoftheir own work/ constructionsfromthisunit.
GamesBank Play‘DirectionsTic-Tac-Toe’.
Digitalactivity:Grids MAM Routines: Reason&
Respondwith Write-Hide-Show
Digitalactivity:The Zoo(2) MAM Routine:
Reason& Respond
Digitalactivity:WhereAmI? MAM Routines:
Reason& Respondwith Write-Hide-Show
Game:CapturetheCounters
Unit9:
D Digitalactivity:Grids
MAM Routines: Reason& Respondwith
Write-Hide-Show
Lookattheimage,whichshowsagridof2-Dshapes.
Ask:
● Whatshapecan youseeat/inthetop/bottom/ middle/left/right/centre?
Thechildrenshould recordtheir responsesontheir MWBs.
Whilethechildrenhave exploredsimplemaps andgridspreviously,thisisthefirsttimethat theyareintroducedtousingagridsystemand grid referencesasawayto representlocation, e.g.F2,A3.
D Digitalactivity:TheZoo(2)
MAM Routine: Reason& Respond Displaytheposterandaskorclicktoplaythe questionsbelow. Wheneverappropriate, askthechildrentogive reasons fortheir response(s),e.g.toexplainwhyorhow theythinkthis.
● Whatisthiscalled?(amap)
● Whatisthisamapof?(the zoo)
● Whereistheentrance?Can youdescribeits locationanotherway?
● Whereisthegiraffe?Can youdescribeitslocation anotherway?
● Pickananimal. Tell yourpartnerwhereitis. Swap and repeat.
● Whydoesthemaphave gridlinesonit?
● Howcould youusethisgridtodescribethe
locationoftheentrance?
● Inwhichcolumnistheentrance?(column C)
● Inwhich rowistheentrance?(row 1)
● Howmight we usethisletterandthisnumberto describetheentrance?(grid referenceC1)
● Doesthegridmakeiteasierormoredifficultto explainthelocation?
Thechildrenmaybenefitfromusingamnemonic tohelpthem rememberthatingrid references thelettercomesfirst,e.g.LcomesbeforeNin thealphabet,soletterbeforenumber;Ccomes beforeRinthealphabet,socolumnbefore row.
Forextrapracticeusinggrids,seeLet’s StrengthenPCM.
D Digitalactivity:WhereAmI?
MAM Routines: Reason& Respondwith
Write-Hide-Show
Displaytheimage.Chooseananimalor featureon thegrid.Thechildrenshouldwritethegrid reference forthisontheir MWBsto recordthelocation.
Let’sStrengthen:
Thechildrenmaybenefitfromtheadditional supportofPCM4–Mapofthe Zoo,onwhich theycan‘draw’theirindex(‘pointing’)finger alongthecolumnsand rowstoidentifythegrid reference.
C P Game:CapturetheCounters! Play‘CapturetheCounters!’fromtheGamesBank. DistributecopiesofPCM5–LocationGridand Spinnersandcounterstotheclass.
Locationand TransformationDisplay Whatnew examplescouldbeadded?
MathsJournal Thechildrencould recordintheir mathsjournalwhattheydidinthemainpartofthis lesson.
Read TreasureMap by StuartJ.Murphyisabout agroupofchildrentryingtofindhiddentreasure.
GamesBank Playadifferentgridgame,e.g. ‘Line’emUp!’
Integration Geography:map workandmapping skills;PE:orienteering.
● Givesand followsdirectionsinvolvinghalfandquarterturns (C)
● Discusses,models,visualisesandpredictshowanobjectwilllookwhen rotatedthroughahalfor quarterturn(R)
● Reasonsaboutalternativewaystoperformthesame rotation(R)
D
D C P
Digitalactivity:Grid References MAM Routines: Reason& Respondwith Write-Hide-Show
Digitalactivity: Turtle Turns MAM Routine: Reason& Respond
Concreteactivity:Predicting Turns MAMRoutine: WriteHide-Show
Pupil’sBookpage62: Turns
● Scissors
● Programmablebottoys, e.g.Bee-Botsorsimilar, andbotmats
D Digitalactivity:Grid References MAM Routines: Reason& Respondwith Write-Hide-Show Lookattheimage,whichshowsagridof3-Dshapes withgrid references.Ask/say:
● WhatshapeislocatedinA1?B3?,etc.
● Writethelocationof…(specifyoneofthe shapes)on your MWB.
Assesswhetherthechildrencancorrectlyuseand interpretgrid references.
D Digitalactivity: Turtle Turns MAM Routine: Reason& Respond Usetheinteractivetooltoturntheturtleandask thequestionsbelow. Wheneverappropriate,askthe childrentogive reasons fortheir response(s), for example,toexplainwhyorhowtheythinkthis.
● Whatanimalisthis?(turtle)
● Whatviewoftheturtleisthis?(aerialor bird’s-eyeview)
● Watchcarefully.Describewhathappensnext.
Usethecontrolpaneltomaketheturtledoahalf turn,clockwise/totheright.Ask:
● Theturtleisnow facingtheoppositedirection. Hedidahalfturntohisright.Anotherwaytosay thisisthathedidahalfturnclockwise.Whatdoes clockwisemean?
● Can yousketchhowhemovedon your MWB?
● Watchcarefullyagain.Describewhathappens thistime.
Usethecontrolpaneltomaketheturtledoahalf turn,anti-clockwise/totheleft.Ask:
● Theturtleisbackwherehestarted.Hedida halfturntohisleft.Anotherwaytosaythisis thathedidahalfturn,anti-clockwise.Whatdoes anti-clockwisemean?
● Can yousketchhowhemovedon your MWB?
● Watchcarefullyagain.Describewhathappens thistime.
Usethecontrolpaneltomaketheturtledoaquarter turn,anti-clockwise/totheleft.Ask:
● Theturtledidaquarterturntohisleft.Another waytosaythisisthathedidaquarterturn, anti-clockwise.
● Can yousketchhowhemovedon your MWB?
● Iftheturtlewantsto returntowherehestarted, howmusthemove?Can yousketchiton your MWB?
● Whatotherturnscouldtheturtledo?
C Concreteactivity:Predicting Turns
MAM Routine: Write-Hide-Show
Thepurposeofthe followingactivities is forthechildrentovisualiseandpredict theendpointsofturns,andtothenmake theturntochecktheirpredictions.Itisnotnecessary todoallofthelistedactivities,sochooseoneor morethatbestsuittheneedsof yourclass, dependingonthe resources available.
Placea MWBoneachofthe foursidesofthe classroom,eachwithadifferentshapedrawnon it, forexample, oval,parallelogram,hexagonand rectangle.Say/ask:
● Makeaprediction:If youstand facingthe hexagonandthenmakeaquarterturn,clockwise, whatshapewill youbelookingatthen? Writeit on your MWB.
● Showme.
● Nowdoit:Standup.Holdbothhandsstraightout infrontof you,pointingtowardsthehexagon. Makeaquarterturn,clockwise.Whatshapeare youlookingat?
Repeatwithotherdirections,includinghalfturns andthreequarterturns,bothclockwiseandanticlockwise.Ask:
● IfIstart facingthehexagonandIfinish facing the oval,howmightIhave turned?
● Istheremorethanonewaytodothis? Explainwhy.
Forvariety,thisactivitycouldalsobedoneinanother space(e.g.theyardorthePEhall).Identify fourmain features.Thechildrencouldwritetheinitialletterof these featurestoindicatewheretheypredictthey will faceafterturning.
Let’sDeepen:
Challengethechildrentomakeand/orvisualise threequarterturns.
Predicting Turns2
Thechildrenshouldcutoutananimal(e.g.the turtle)fromPCM6–AerialViewof ZooAnimalsand placeitonPCM4–Mapofthe Zoo. Youcangive theinstructionsornominatechildrentodoso, for example:
● Makeaprediction:If youturntheturtleahalf turn,anti-clockwise,whatwillitbe facing? Write iton your MWB.
● Showme.
● Nowdoit: Turntheturtleahalfturn,anticlockwise.Whatisit facing?
Repeatwithotheranimal representationsandother instructions.
Let’sDeepen:
Challengethechildrentomakeand/orvisualise three-quarterturns.
Describing Turns
Workinginpairs,onechilddescribestotheotherhow toturnananimalandtheycheckthatitwasdone correctly. Swap roles.
ProgrammingaBot
Ifaprogrammablebottoyis available,ask:
● Howdo we programmethebottodoaquarter turn,clockwise/anti-clockwise? Writethe instructionson your MWB.Checktoseeif you were correct.
● Howdo we programmethebottodoahalfturn, clockwise/anti-clockwise? Writetheinstructions on your MWB.Checktoseeif you were correct.
● Howdo we programmethebottodoafullturn, clockwise/anti-clockwise? Writetheinstructions on your MWB.Checktoseeif you were correct.
Placethebotinaparticularpositiononthebotmat. Ask:
● Howdo we programmethebottoturnto face…(namea featureonthemat)? Writethe instructionson your MWB.Checktoseeif you were correct.
Writesometurninputsontheboard.Ask:
● Whatwillthebotbe facingif we inputthese instructions? Writetheansweron your MWB. Checktoseeif you were correct.
Repeatwithother features.
Let’sDeepen:
Challengethechildrentosuggestalternative waystoperformthesameturns,e.g.threequarter turnsclockwiseisthesameasaquarterturnanticlockwise;twohalfturnsclockwiseisthesameas afullturnanti-clockwise,etc.
P Pupil’sBookpage62: Turns
StartEndStartEndStartEnd Inwhatdirection,andbyhowmuch,mightIhaveturnedeach shape,ifitlooksthesameattheendasitlookedatthestart?
Integration Science, Technologyand Engineering:computationalthinking,codingand programming;energyand forces,turninggearsand cogwheels.
Locationand TransformationDisplay Whatnew examplescouldbeadded?
GamesBank Playadifferentgridgame,e.g. ‘Towerof3’.
● Givesand followsdirectionsinvolvingsimpledistancesorlandmarksinthecontextofsimpleplans/ gridsmaps/aerialphotosof familiarenvironments (C)
● Recordsdirectionsasaseriesofsimplesteps (C)
● Devisesandanalyses routesonmaps,plansorgridsthatsatisfycertainconstraints(e.g.theshortest route,nocrossing roads, avoidingobstacles)(A&PS)
Digitalactivities:SameButDifferent– Turns/ TurningShapes MAM Routine: Reason& Respond
Digitalactivity: Zoo Routes MAM Routines: Reason& RespondwithBuildit!Sketchit!
Writeit!
Pupil’sBookpage63:Directions
● Programmablebottoys,e.g.Bee-Bots orsimilar,andbotmats
● journey, route
D Digitalactivities:SameButDifferent–
Turns/TurningShapes
MAM Routine: Reason& Respond
Playthetwoslideshowsandaskthechildrento propose reasons forwhytheimagesarethesameand whytheyaredifferent.
D Digitalactivity:Zoo Routes
MAM Routines: Reason& RespondwithBuildit!
Sketchit! Writeit!
DistributeacopyofPCM7–DirectionCards toeachchild.Displaytheimageandsay:
● ImagineMiaisattheentranceandwantstovisit thelionsfirst.Use yourDirectionCardsor your MWBtoshowthedirections.
● ImagineJayisattheentranceandwantstovisit thepenguins,buthealsowantstogotothecafé onthewaytothepenguins.Use yourDirection Cardsor your MWBtoshowthedirections.
● ImagineLexiisattheentranceandwantsto visittheelephants,butshealsowantstogo tothetoiletonthewaytotheelephants.Use theDirectionCardsor your MWBtoshowthe directions.
● Chooseananimalbutdon’tsayit aloud.Use yourDirectionCardsor your MWBtoshowthedirectionsto getto yourchosenanimalfromtheentrance.Ask yourpartnerto follow yourdirections−didthey gettothecorrectanimal?
Let’sStrengthen:
Thechildrenmaybenefitfromadditional supportssuchasprogrammablebottoysif available,and/orPCM4−Mapofthe Zoo.
Let’sDeepen:
Challengethechildrentocompare routesandto identifythemostefficient routearoundthe zooto seeasmanyanimalsaspossible.
P Pupil’sBookpage63: Directions
Pleasenotethatabottoyis not requiredtocomplete thepage.Thegoalis forthe childrentointerpretthe directionstoidentifywhere thebotwillendup.
Let’sStrengthen:
Thechildrenmaybenefitfromadditional supports,suchasusingtheirfingertomove along thegridasdirected,usingasmallitem(e.g.a sharpenerorrubber)tophysicallymove alongthe gridorthebotcut-outfromPCM6.
Let’sDeepen:
Challengethechildrentouseinstructionsthat includethreequarterturns.
Bottoys workonthepremisethatthe directions/commandsareinputtedfirst andthena‘go/play’ buttonispressed toexecutethedirectionsasinputted. If available,thechildrencouldexplore aprogrammablebottoy, e.g.Bee-Bot inadvance,butthisisnot required.
Alternatively,onlineinteractivetoolscan alsobeused forthechildrentovirtually explorehowbottoys work. Forexample, thisonlineBee-BotEmulatorlets you programmeavirtualBee-Botandcould bedisplayedontheIWB: edco.ie/55ma
ThereisalsoaBee-Botapp, availableto downloadfreefromtheAppleAppStoreor GooglePlayStore,withseveraloptionsand levelsofdifficulty.
Anotheroptionistocreate‘kid-bots’!Achild inthegroupassumesthe roleofabotand thereforecanonlymove asdirected by their group.Theotherchildreninthegrouphave to ‘programme’thekid-bot by providingalistof directions(e.g. forwards, forwards,turnright, forwards,etc.)togetthemsafelyfromwhere theyare,totheirseat.This works really well onatiledfloor.
Botplay Ifaprogrammablebottoyis available:
● Childrencouldusethebottodeviseandsolve their ownproblems.
● Design your ownclassbotmat(seePCMs8and9
−Blank 14 cmSquareGrids).Usingalargesheet ofpaper,drawhorizontaland verticallinesto createagridwith15×15cmspaces.Using PCMs8and9,thechildrencancreatetheir own 14 × 14 cmscenethatcanbegluedorattached withstickytapetoasquareontheclassgrid.
● Workingindividuallyoringroups,thechildren couldchooseatheme(e.g. zoo,pet farm, farm, treasureisland)anddesignahuntwithobstacles tobe avoided.Otherchildren/groupscouldbe askedto workoutpossible routes.
● Thedesignsand/or routescouldbe recordedin theirmathsjournals.
Locationand TransformationDisplay Whatnew examplescouldbeadded?
GamesBank Chooseagridgametoplay.
● Exploressquareandnon-squarecornersintheenvironment,identifyingsquarecornersasrightangles (U&C)
D D C P
Digitalactivity:SameButDifferent–Corners
(1) MAM Routine: Reason& Respond
Video:SquareCorners MAM Routine:
Reason& Respond
Concreteactivity:MakingRightAngles
Pupil’sBookpage64:RightAngles
● squarecorner,rightangle
● Teachingclocks
● Geoboards
● Programmablebottoys,e.g.Bee-Bots orsimilar
● Stickytape
● Markers
D Digitalactivity:SameButDifferent–Corners(1)
MAM Routine: Reason& Respond
Playtheslideshowandaskthechildrentopropose reasons forwhytheimagesarethesameandwhy
theyaredifferent.Ifnotsuggested,promptthe childrento refertothenumberandtypeofcorners (i.e.squarecornersornot)oneachshape.
D Video:SquareCorners
MAM Routine: Reason& Respond
Playthevideo.Wheneverappropriate,allowthe childrentoanswerthequestionsposedandgive reasons fortheir response(s), forexample,explain whyorhowtheythinkthis.Thechildrenshould maketheir ownsquarecorner/rightanglealong withthevideoandusethistofindrightanglesinthe classroom,onshapes,etc.
C Concreteactivity:MakingRightAngles
Thepurposeofthe followingactivitiesis forthe childrentoexploreandcreaterightanglesusingthe available resources.Itisnotnecessarytodoallofthe listedactivities,sochooseoneormorethatbestsuit theneedsof yourclass,dependingonthe resources
available. Youwillneedteachingclocks,geoboards andelasticbands,abottoy, stickytapeandamarker.
TeachingClocks: Challengethechildrentousea teachingclocktomakerightangles. Relatethese dynamicangles(changing/movingasopposedtothe staticanglesof2-Dshapes)tomakingquarter,half andfullturns.
Teachingtip:
Otherthan3o’clockand9o’clock,thetimes thatmakerightanglesontheclockmay notbeonesthechildrencaneasilyidentify. Therefore,the focusshouldbeoncreating whatlookslikearightangleandthen checkingitwiththeirsquarecornerfinder.
Let’sDeepen:
Challengethechildrentoexplainthe relationship betweenmakingthreerightanglesontheclock andthefractionofaturnthatthismakes.
Geoboards: Useageoboardandelasticbandsora geoboardapptomakeshapeswithrightangles.Isit possibletomakeashapewithone/two/three/four/ fiveormorerightangles?
Bot Toy: Ifaprogrammablebottoyis available, attachamarkertoitwithstickytape.Ask:
● Howcan youprogrammethebottodrawaright angle?
● Whatabouttworightangles?
● Whataboutashapewith fourrightangles?
Allowthechildrentimetoexploreandinvestigate theshapestheycanprogrammethebottoytodraw.
P Pupil’sBookpage64: RightAngles
Locationand TransformationDisplay Whatnew examplescouldbeadded?
Play Searchonlinetoplayinteractivegames, suchas Tetris.
Mathseyes Identifyexamplesofrightangles intheclassroomorlocalenvironment. Recordthe examples foundinthemathsjournals.
GamesBank Chooseagridgametoplay.
Focusoflearning(withElements)
● Discusses,modelsandvisualises reflectionofshapes(U&C)
● Completesmissing reflectionsofshapesorimages (C)
D D C P
Digitalactivity:SameButDifferent–Corners(2)
MAM Routine: Reason& Respond
Digitalactivity: Reflections
MAM Routines:Notice& Wonder withThink-Pair-Share/Reason& Respond
Concreteactivity: SymmetryStations Pupil’sBookpage65: Reflections
● Plasticmirrors(oneperpair)
● Tangrams(onesetperpair)
● Pentominoes,patternblocks,andanyother available 2-Dshapes(bothsymmetricalandnon-symmetrical)
● Pegboardsandpegs
● Geoboardsandelasticbands
● Scissors
● Paintandpaintbrushes
● Cubes(e.g.interlockingcubes)
● reflection,mirrorsymmetry,linesofsymmetry,flip
D Digitalactivity:SameButDifferent–Corners
(2) MAM Routine: Reason& Respond
Playtheslideshowandaskthechildrentopropose reasons forwhytheimagesarethesameandwhy theyaredifferent.Whilethisisasimilar resourceto
theoneusedinthepreviouslesson,onthisoccasion, ifnotsuggested,promptthechildrento refertothe cornersasanglesandtoidentifytheanglesasright angles,ornot.
D Digitalactivity: Reflections
MAM Routines:Notice& Wonderwith Think-Pair-Share/Reason& Respond
Displaytheposter.UsingThink-Pair-Share,ask:
● Whatdo younotice?Whatdo you wonder?
Recordthechildren’s responsestobothquestions ontheboard.Allowthechildrentheopportunityto respondto(agree/disagreewithorquery)others’ responses,butdon’tconfirmor rejectanyofthe ideas.Noteany‘wonderings’thatcouldbecomethe basis forasubsequentmathsinvestigation.
Distributeatangramsetandamirrortoeachpair. Displaytheposterandaskorclicktoplaythe questionsbelow. Wheneverappropriate,askthe childrentogive reasons fortheir response(s), for example,toexplainwhyorhowtheythinkthis.
● Whatisthesameaboutalloftheseimages?
● Whatisdifferent?
● Whatdo we calltheimageoftheshapeseenin themirror?(reflection)
● Whattangrampieceslooksimilartothisone when reflectedinamirror?
● Whatpieces wouldlookdifferent?
● Ifthesideofthesquarewastouchingthemirror, whatshapemightbevisible?(rectangle)
● Tryit. Were youcorrect?Explainwhy.
● Iftheparallelogramwastouchingthemirror, whatshapemightbevisible?(irregularhexagon)
● Tryit. Were youcorrect?Explainwhy.
● Whatothershapepiecescould youexplorewitha mirror? Trythem.
Distributepentominoes,patternblocksoranyother available2-Dshapes available(bothsymmetricaland non-symmetrical)toeachpair/group.Ask/say:
● Usingonlyoneshapeandthemirror,can you maketwoshapesappear?How?
● Can youmakeonlyoneshapeappear?How?
● Can youmakethemappearadifferentway?
● Isitadifferentshape?If yes,whatshapehas nowappeared?
● Can youplacethemirrorontheshapesothatthe reflectionmatchestheotherhalfoftheshape?
● If youcandothis, we cansaythatthisshapehas alineofsymmetry.Whichshapeshave linesof symmetry?
● Arethereanyshapesthathave morethanone lineofsymmetry?Whichones?Wherearethe linesofsymmetry?
C Concreteactivity: SymmetryStations
Organisetheclassinto fourorfivegroups,depending onnumbers.Choose fourorfiveoftheactivities below, dependingonthechildren’sneedsandthe available resources,andallocateanactivityto eachgroup.Afteranappropriateamountoftime (e.g. 10−20minutes),thegroupsshould rotateto anewstation.Thesestationscouldbeusedonjust onedayor overbothdays.Thefullinstructions for eachactivityare availableonPCMXX− Symmetry Stations.ThePCMcanalsobeprintedandcutupso thattheinstructions foreachactivityare available attheappropriatestation.(Ifsettingupstationsis not feasible, youcouldchoosetodooneormore activitieswiththewholeclassatthesametime.)
● Station1−Cuttingand Folding2-DShapes. Equipmentneeded:2-Dshapes,paper,scissors andruler foreachchild.
● Station2− PentominoesPieces.Equipment needed:pentominopieces,paper/copyandruler foreachchild.
● Station3– Pegboard Symmetry.Equipment needed:mirror,pegboardandpegs foreachpair.
● Station4– PatternBlocks Symmetry.Equipment needed:mirror,patternblocksand MWBperpair.
● Station5–Geoboard Symmetry.Equipment needed:mirror,geoboardandelasticbands perpair.
Unit9: Locationand Transformation
● Station6– SymmetricalArt.Equipmentneeded: paper,paintandpaintbrush foreachchild.
P Pupil’sBookpage65: Reflections
Let’sStrengthen: Thechildrenmay benefitfromthe ongoingsupportof mirrors forallofthese activities.
Challengethechildrentojustifyhowtheyknow theirmirrorimageisaccuratewithoutusinga mirror.
Locationand TransformationDisplay Whatnew examplescouldbeadded?
Read Read Let’sFlyaKite by StuartJ.Murphy, whichisabouttwosquabblingsiblingslearningabout symmetrywhentheirbabysitterhelpsthembuildand flyakite.
Play Playorusesomeonlineinteractive resources,includingpatternblockorgeoboardapps, tocreateasymmetricalpattern:
edco.ie/33xy edco.ie/9a6p
Integration Art:construction,print,painting, drawingvarioussymmetricalshapes,completing reflectionimages;History: feastsand festivals, looking forlinesofsymmetryinart,imagesand patternsassociatedwithvariouscultural feasts, e.g.Hanukkahandthemenorah,Diwaliand rangoli patterns.
GamesBank Play‘Mirror Patterns’.
● Reasonsaboutalternativewaystoperformthesametransformation(R)
Digitalactivity:How WasItMoved?
MathsandMe Routines:ConceptCartoon withThink-Pair-Share
Video: Transformation MathsandMe Routine: Reason& Respond
Concreteactivity:MovingShapes
Pupil’sBookpage66:WhatMove?
● slide/translation,turn/rotation,flip/reflection
D Digitalactivity:How WasItMoved?
MathsandMe Routines:ConceptCartoon withThink-Pair-Share
DisplaytheConceptCartoonand,usingThink-PairShare,askthechildrenthe followingquestions,and togive reasons fortheiranswerswhereappropriate:
● Whatdo younotice?Whatdo you wonder?
Clicktohearthecharactersproposetheirideasand, usingThink-Pair-Share,ask:
● Whatdo youthink?
● (Pointingataspecificcharacter)Do youagree withtheiridea?Explainwhy?
● Do youthinksomethingdifferent?Whatdo you think?Whydo youthinkthis?
Ifappropriate, recordthechildren’s responses tothesequestionsontheclassboard.Allowthe childrentheopportunityto respondto(agree/ disagreewithorquery)others’ responses,butdon’t confirmor rejectanyoftheideas.
D Video: Transformation MathsandMe Routine: Reason& Respond
Playthevideo,pausingwhensuitabletoallow childrento respond,giving reasons fortheiranswers asappropriate.
C Concreteactivity:Modeling Turns,Flipsand Slides
Distributethe availableshapestothe children,includingpentominoes, tangrams,patternblocks,if available.Instructthe childrentotracearoundashape,move it,andthen tracearounditagain,fillingintheshapeinits‘after position’.
If required,PCMXXMovingShapescouldalsobe usedtoaddstructuretothisactivity.
Let’sDeepen:
IfusingPCM,pairsofchildrencould work togetherwherethefirstchildmovesashapeand recordsitonthePCMandthesecondchildtriesto workouthowtheshapewasmoved.
Afterwards,askthechildren:
● Wasiteasyto workouthowtheshapes were moved?
● Were thereanyshapesthatmadeiteasieror moredifficultto workouthowtheshapes were moved?Whichones?
● Whatisitabouttheseshapesthatmadethem easier/difficult?
Teachingtip:
Itcanbemoredifficulttoidentifyhowa regularshape(e.g.circle,equilateraltriangle, square, regularhexagon)wasmovedthanan irregularshape.
P Pupil’sBookpage66: WhatMove?
● Exploresandcreatessimpletessellations(U&C)
● Explorestessellationswhereasingleshapeis repeated(A&PS)
● Examinestessellationsandidentifiesifshapeshave been reflected, rotatedand/ortranslated(U&C)
Digitalactivity:SameButDifferent–MovingShapes MathsandMe Routine: Reason& Respond withThink-Pair-Share
Concreteactivity:ExploringandCreating Tessellations
Concreteactivity:Solving TessellatingPuzzles Pupil’sBookpage67: Tessellations
Equipment
● Pentominoes,tangrams,patternblocks, andanyother available2-Dshapes(both tessellatingandnon-tessellating)
● tessellate,tessellations,cover, withoutgaps, repeat
D Digitalactivity:SameButDifferent–Moving Shapes MAM Routine: Reason& Respondwith Think-Pair-Share
Playtheslideshowandaskthechildrentopropose reasons forwhytheimagesarethesameandwhy theyaredifferent.
C Concreteactivity:ExploringandCreating Tessellations
Thepurposeofthe followingactivities is forthechildrentoexploreandcreate tessellationsusingthe available resources.Distribute pentominoes,tangrams,patternblocksand/or assorted2-Dshapestotheclass.
ShapesthatDo/DoNot Tessellate: Tellthechildren tousepatternblocks,pentominoes,tangramsor2-D shapestocoverthesurfaceofacopyorbook.Ask:
● (Usingseveralshapesofthesametypeandsize) Whichoftheseshapestessellate?Explainwhy.
● Whatshapesdonottessellate?Explainwhy.
● Isthereanyshapethatdoesnottessellatewith itselfbutdoestessellatewithadifferentshape?
● Putsomeidenticalshapesina rowall facingthe samedirection.Dotheytessellateif youslide themintogether?(Forexample:Inpatternblocks thesquares,hexagons,parallelogramscanallbe slidintogethertotessellate.)
● Ifnot,cantheybeturned/rotatedorflippedto tessellate?(Forexample:Inpatternblocksthe halfhexagons/trapezoidsandtrianglesmust be rotatedahalfturnorflippedup/downto tessellate.)
Thechildrencouldalsocreatedrawntessellations intheirmathsjournals by tracingaroundshapes, movingthemand re-tracingthem.Askthechildren toidentifywhichdrawnshapesareexamplesofa slide,flipor rotation/turn.
C Concreteactivity:Solving TessellatingPuzzles Itisnotnecessarytodoallofthelistedactivities,so chooseoneormorethatbestsuittheneedsof your class,dependingonthe resources available.
ZooAnimals: Thechildrenshouldusethetangrams, pentominoesand/orpatternblockstocomplete puzzlesof zooanimal representationsand/orto createtheir own representationsof zooanimals. PCMs 10 and11–ShapeAnimalscontainvarious puzzlesthatcanbecompleted.
Let’sStrengthen:
ThechildrenmaybenefitfromusingthePCMs12 and13−ShapeAnimals,whichhave internallines as wellastheoutline.
Let’sDeepen:
Challengethechildrentocreatetheir own puzzles,i.e.tomakeapicture,tracetheoutline onlyandchallengeanotherchildtocomplete theirpuzzle.
DigitalZooAnimals: Therearemanyfreeonline gamesandpuzzlesthatcanalsobeused.
Fortangrams,gotothe followinglinksbelowand choosetocompleteanyoneofthegivenpuzzles, someofwhichinclude zooanimals:
● (Chooseanimaloptionsatthebottomof thescreen.) edco.ie/fyha
● Forpentominoes,goto: edco.ie/fr2r
Forpatternblocks,gotothelinksbelowandchoose tocompleteanyoneofthegiventemplates,someof whichinclude zooanimals:
● edco.ie/y8hb
● edco.ie/498h
● edco.ie/w5tk
P Pupil’sBookpage67: Tessellations
Teacher’s ownchoicefromanyofthelessonwarm-ups.
Usethismenuofactivityideastochoosehowbesttostructurethislastlessonoftheunittosuit yourneeds andtheneedsof yourclass.
Classroomposter: Reviewand Reflect UseThink-Pair-Sharealongsidetheprompt questionsto reviewtheunit.
Individualchildrencouldpresentexamplesoftheir owndrawings/work/constructionstotheclass,and talkaboutwhattheyhave learned.
Askthechildrentoexplainthe following words, perhapsusingexamplesordrawingsontheir MWB: bird’s-eye(aerial)view,streetview,journey, route, fullturn,halfturn,quarterturn,clockwise,anticlockwise, rotation, rotate,squarecorner,right angle,tessellate, reflection/flip,mirrorsymmetry, linesofsymmetry,flip,slide/translation.
CompletequestionsXXonpageXX.Alternatively, thesecanbelefttodoaspartofabigger review duringthenext review week.
● Playorusesomeoftheonlinedigital resources referencedintheunit,including Tetris.
● PlayagamefromtheGamesBank.
Identifychildrenwhomightbenefitfromextra practicewithsomeofthe keyconceptsorskills inthisunit.ConsulttheUnit9Let’sStrengthen Suggestions for TeachersandLet’sStrengthenPCM.
STEAMactivitiescombiningmathsandart:There arelotsofvisualartsactivitiesthatexplorethese concepts, forexample:
● Symmetricalart:Provideeachchildwithhalfa pictureoftheir own face(oracelebrity’s face) andaskthemtodrawtheotherhalf.
● Tessellations:Createatessellatingpicture,using geometricshapes.
Searchonline forotheractivitiesthat wouldsuit your class.
● Go forawalkaroundtheschool.Wherecan youseeexamplesofrightangles,tessellations, reflections/mirrorsymmetry? Take photos to record.
● Makeamapoftheyard/playgroundorschool. YoucoulduseGoogleMapsandstreetviewto help you.
SelectoneoftheCCTsontheLet’sDeepen PCM.Displaythetaskontheclassboard.Encourage thechildrento worktogetheringroups.
6 5 4 3 2
k angaroo
elephant
polarbear
k angaroo
polarbear elephant
Cuttingand Folding2-Dshapes
Needed:2-Dshapes,paper,scissors, ruler
1. Tracearoundthe2-Dshapes.Cut themoutand foldtheshapes.Draw theline(s)of symmetryalongthe fold lineusingaruler.
2. Sorttheshapesinto:
● nolinesof symmetry
● 1lineof symmetry
● 2ormorelinesof symmetry
Whatcouldyouusetocheck thatyou arecorrect?
PentominoesPieces
Needed:pentominopieces,paper/ copy,ruler
1. Usingonly1pieceeachtimeandthe mirror,make2pentominoesappear. Whichpieceslook exactlythesamein themirror?
3. Foldagainandpresscarefullytoprint thedesignontheoppositehalf.Open back up. ©TheEducationalCompanyofIreland
Pegboard Symmetry
Needed:mirror,pegboard,pegs,per pair
1. Startbyputtingalineof pegsdown alongthecentreof thepegboard.
2. The firstchildmakesapatternwith thepegsontheirsideof thecentre line.
3. Thesecondchildmakesthemirror imageontheirside.Usethemirrorto check.
4. Swapandrepeat.
Geoboard Symmetry
Needed:mirror,geoboard,elastic bands,perpair
1. Startbyputtinganelasticbanddown alongthecentreof thegeoboard.
2. The firstchildmakesashapewiththe bandsontheirsideof thecentreline.
3. Thesecondchildmakesthemirror imageontheirside.Usethemirrorto check
4. Swapandrepeat.
2. Placethemirroracrossthemiddle of eachpentominopiece,bothways. Whatpiecesappear‘whole’again? Whatdoesthattellusaboutthose pieces?
3. Tracearoundthepentominopieces thathavelinesof symmetry.Drawthe line(s)of symmetryusingaruler. Whichpieceshavemorethanonelineof symmetry?
PatternBlocks Symmetry
Needed:mirror,patternblocks, MWB,perpair
1. Startbydrawingalinedownalong thecentreof theMWB.
2. The firstchildmakesapatternwith thepatternblocksonthetheirsideof thecentreline.
3. Thesecondchildmakesthemirror imageontheirside.Usethemirrorto check.
4. Swapandrepeat.
SymmetricalArt
Needed:paper,paint,paintbrush, perchild
1. Foldthepaperinhalf andopen back up.
2. Paintadesignononehalf only.
4 3 2 I

Writethelocationof eachshape:
Pick:Whatyouwanttodo,whatyouwanttouse,andwhoyou’dliketo dothesewith!

Aerialviews:
Jaystackedsomeshapepieces. Colourthepicturetoshowthattherewas abluetriangleatthebottom, withayellowsquareontopof that andaredcircleontopof theyellowsquare.
TurningCogwheels:
If themedium-sizedcogwheelisturnedclockwise, thesmallestcogwheelwillturn__________ andthelargestcogwheelwillturn_________________. If themedium-sizedcogwheelisturnedanti-clockwise, thesmallestcogwheelwillturn__________ andthelargestcogwheelwillturn_________________.
Makeasetof Tetrominoes:

Tetrominoesarelikepentominoesexceptthateachoneismadeupof 4squares connectedalongatleastoneside.Thereare5differenttetrominoesinaset.
UsePCMXXBlank 2cmSquareGridstomakeasetof tetrominoes.
Ask yourself:
● Howcanyoutellthatyoumadeatetromino?
● Howdoyou knowthateachoneisdifferent?
● Howwillyoucheck thatonetetrominoisnotthesameasanother?
● The5tetrominoshoesareoftengivenletternameslikethepentominoes;what letternameswouldyougiveyourtetrominoes?
Box Symmetry:
Use2mirrorsandstandthemup,atright anglestoeachother,onyourdesk. (Think:Whatcouldyouuseto keepthem uprightandtogetheronyourdesk?)
Place1shapeclosetothemirrors;whatdo younotice?Howmanyshapesdoyousee? Nowuse2shapes.Howmanyshapescan yousee?
Completethetableopposite. Whatpattern(s)doyouspot?
Class Teachers: Usetheseactivitiesalongsidethespecifiedlessons,tostrengthentheunderstandingof children,as required.Manyoftheseactivitiescouldalsobeusedasastation.
SpecialEducation Teachers: Usetheseactivitiestosupportchildren(pre-teachingor re-teaching)inin-class and/orwithdrawalsessions.
Somechildrenmaystillconfuserightandleft,particularlywhentheorientationoftheobjectisdifferenttotheir ownorientation.
Assesstheirunderstandingwithavarietyofquestions:Put yourlefthandup,Put yourright footout,etc.Ifthereisconfusion, explorevariousrightandleftmnemonics,andencouragethechildrentochooseastrategythat works forthem.
Arrangethechildreninpairsto faceeachother.Askthemto raisetheirrighthand,touchtheirleftear,etc.Ask:
● Whatdo younotice?
● Can youexplainthis?
Clockwise&Anti-clockwise
Somechildrenmaystillconfuseclockwiseandanti-clockwise.
Provideeachchildwithapaperplatewiththecentremarkedandtwocurvedarrowsindicatingtheturndirections.Elicitfromthe childrenthedirectionindicated by eacharrow andlabelthemaccordingly.
Ask/say:
● Hold yourplateasifitisasteeringwheel. Turnitclockwise.
● Now returntocentre. Turnitanti-clockwise.
Repeatasnecessary,checking forcorrectmovements.
Use/reusethesuggestedactivitiesinLesson3as reinforcement.
Somechildrenwillbenefitfromtheadditionalsupportofa referencecircle.
Useormakeapapercircle, foldinhalfandhalfagaintodivideitintoquarters.Askthechildrentocolourineachquarterina differentcolour.Thiscirclecouldbeplacedundertheanimalcut-outs(fromthePCM)astheyarebeingturned.
Somechildrenmayincorrectlyassumethatwhereashapeishalved,thatthisisalsoalineofsymmetry.
Explorethisfurtherusingirregularshapes.
Usingapaper rectangle,draw alinetodivideitinhalfthroughitsdiagonal.Ask:
● Howhave Idividedthe rectangle?(inhalf)
● Isthisalineofsymmetry?Explainwhy.
Checktoseeifthechildrencan foldit overexactly,and/or by placingamirroralongthesupposedlineofsymmetry.Doesthe createdimagemirrorormatchtheoriginalshapeused?Ifnot,thenthislineisnotalineofsymmetry.
Somechildrenmaycreateaduplicate/repeatimagewhenaskedtocreateamirrorimage.
Encouragethechildrento recognisethatthecolourandtypeofobjectthatisclosesttothelineofsymmetryononesideshouldalso beclosesttothelineofsymmetryontheotherside,i.e.thatthingsthat were ‘totheleftof’inthefirsthalfwillnowbe‘totheright of’inthesecondhalf,andvice versa.
Title
Numberof players: 4
Youneed:
Howtoplay:
Variation:
MWB,marker
Deepen:
Playaspairs,2against2.Ineachpair,one personisthewriterandtheotheristhe describer.
OntheMWBawriterdrawsa3 × 3grid.
The firstdescriberwilldescribetothe firstwriter wheretowritetheir firstX.
Theseconddescriberwilldescribetothesecond writerwheretowritetheir firstO.
Playcontinuesuntilonepairhaswritten3ina row.
For2players:Player1describestoPlayer2 wheretoplacePlayer1’sX.Player1describes toPlayer1wheretoplacePlayer2’sO.
Thecentrespacecannotbeuseduntilboth writershavewritten2XsorOs.
Usealargergrid(e.g. 4 × 4).
Thedescriberswearblindfoldsandhavetotryto visualisethemoves.
Title
Numberof players: 2–6
Youneed: PCMXXLocationGrid&SpinnerTemplates, paperclip,pencil,36counters
Howtoplay: Layacounteroneachof thespacesof the locationgrid.Eachplayerinturnspinsboth spinnersandusestheletterandnumbertotake acounter fromthatsquareof thegrid.If the counterisalreadytaken,thatplayermissesago. Continueplayinguntiltimeisuporallthe countershavebeentaken.
Thepersonwiththemostcountersattheend winsthegame.
Variation: The firstpersonwith10counterswinsthegame.
Deepen: CapturetheCoins!Placeamixtureof 36coins onthegrid.Thepersonwiththemostmoney(in cents)attheendwinsthegame.
Numberof players: 2
Youneed:
Howtoplay:
Strengthen:
Deepen:
Selectionof differentcolouredcubes,MWB,mirror
Tostart,drawastraightlinedownthroughthe middleof theMWB,whichwillbecalledthe ‘mirrorline’.
Eachplayer,inturn,sticks5differentcoloured cubestogetherandlaysthemdownonthe MWB,touchingthemirrorline.Player2makesa mirrorimageof Player1’spatternandlaysthat downontheothersideof themirrorline.
Theplayerscheck thatthesecondpatternis correctbyplacingamirroronthemirrorline facingthe firstpattern.
If correct,Player2scoresapoint.If notcorrect, nopointsarescored.Keepswappingrolesuntil thetimeisup.
Thepersonwiththemostpointsattheendwins thegame.
Startwithonly3or 4 cubes.
Use2ten frames,bothvertical.The firstplayer laysouttheirownchosenpatternof cubesand cubecoloursintheten frame.Thesecondplayer createsasecondpatternthatmirrorsthe first.
Day1,Lesson1: DifferentViews
● Recognisesthe relationshipbetween differentmodesof representingposition andlocation(bird’s-eyeview versusstreet view)(R)
Day2,Lesson2: Location
● Identifiesanddescribesthegenerallocation ofanobjectusingagridsystem(U&C)
● Exploresgrid referencesinthecontextof barriergames,orotherplayfulactivities (A&PS).
Day3,Lesson3: Turns
● Givesand followsdirectionsinvolvinghalf andquarterturns (C)
● Discusses,models,visualisesandpredicts howanobjectwilllookwhen rotated throughahalforquarterturn(R)
● Reasonsaboutalternativewaystoperform thesame rotation(R)
Day4,Lesson4: Directions
Day5,Lesson5: RightAngles
● Givesand followsdirectionsinvolving simpledistancesorlandmarksinthecontext ofsimpleplans/gridsmaps/aerialphotosof familiarenvironments (C)
● Recordsdirectionsasaseriesofsimple steps (C)
● Devisesandanalyses routesonmaps,plans orgridsthatsatisfycertainconstraints(e.g. theshortest route,nocrossing roads, avoidingobstacles)(A&PS)
● Exploressquareandnon-squarecornersin theenvironment,identifyingsquarecorners asrightangles(U&C)
Days6and 7, Lesson6: Reflections
● Discusses,modelsandvisualises reflection ofshapes(U&C)
● Completesmissing reflectionsofshapesor images (C)
Day8,Lesson7: Whatmove?
● Discusses,models,visalisesandpredicts reflection, rotationandtranslationof objects,imagesandshapes(U&C)
● Reasonsaboutalternativewaystoperform thesametransformation(R)
Day9,Lesson8: Tessellations
● Exploresandcreatessimpletessellations (U&C)
● Explorestessellationswhereasingleshape is repeated(A&PS)
● Examinestessellationsandidentifiesif shapeshave been reflected, rotatedand/or translated(U&C)
Day 10,Lesson 9: Reviewand Reflect
● Reviewsand reflectsonlearning(U&C)