CAN PACKAGING UGANDA'S FOOD INDUSTRY
INVESTMENTS IN AFRICA'S FOOD INDUSTRY

TRENDS IN TEXTURE MODULATION
GLOBAL FOOD SAFETY INCIDENCE












































CAN PACKAGING UGANDA'S FOOD INDUSTRY
INVESTMENTS IN AFRICA'S FOOD INDUSTRY

TRENDS IN TEXTURE MODULATION
GLOBAL FOOD SAFETY INCIDENCE













































FOUNDER & PUBLISHER
Francis Juma
SENIOR EDITOR
Alphonse Okoth
EDITOR
Francis Watari
EDITOR
Nicholas Ng'ang'a
BUSINESS DEVELOPMENT DIRECTOR
Virginia Nyoro
BUSINESS DEVELOPMENT ASSOCIATE
Vivian Kebabe
HEAD OF DESIGN
Clare Ngode
ACCOUNTS
Jonah Sambai
Published By: FW Africa
P.O. Box 1874-00621, Nairobi Kenya
Tel: +254725 343932
Email: info@fwafrica.net
Company Website: www.fwafrica.net
www.foodbusinessafrica.com
www.foodandhospitalitymea.com
www.dairybusinessafrica.com
Food Business Africa (ISSN 2307-3535) is published 6 times a year by FW Africa. Reproduction of the whole or any part of the contents without written permission from the editor is prohibited. All information is published in good faith. While care is taken to prevent inaccuracies, the publishers accept no liability for any errors or omissions or for the consequences of any action taken on the basis of information published.
www.animalfeedmea.com
www.sustainabilitymea.com




Exciting times lie ahead for Uganda’s food and beverage sector as the AFMASS Food Manufacturing Expo makes its highly anticipated debut in the country. Recognized as one of Africa’s premier platforms for food processing, packaging, and agribusiness, AFMASS Food Manufacturing Expo has been pivotal in driving innovation, investment, and industry collaboration across the continent. With its expansion into Uganda, the expo is set to unlock new opportunities, foster economic growth, and strengthen the country’s positioning in Africa’s fast-evolving food and beverage industry.
Scheduled to take place at the Africana Hotel in Kampala from February 11–13, 2025, the expo will serve as a dynamic meeting ground for key stakeholders. Manufacturers, suppliers, policymakers, and industry experts will converge to showcase cutting-edge technologies, explore sustainable production practices, and discuss emerging market trends that are shaping the future of food manufacturing in Africa.
More than just an exhibition, AFMASS Food Manufacturing Uganda edition is a gateway to knowledge exchange and strategic partnerships. Local businesses will have a unique chance to engage with global players, gain insights from industry leaders, and discover solutions that can revolutionize their operations. Whether it’s innovative packaging solutions, advancements in food safety, or efficient supply chain management, the expo promises a wealth of information and networking opportunities for professionals eager to stay ahead in a competitive market.
As we gear up for this milestone event, I also invite you to explore the latest edition of Food Business Africa
magazine—our 66th issue. This edition offers an in-depth look at PepsiCo’s footprint in Africa, detailing the company’s investments, market strategies, and ambitious plans to cater to the continent’s youthful and dynamic consumer base.

Additionally, we dive into the growing trend of texture modulation in beverages. From the velvety creaminess of a well-crafted cappuccino to the refreshing fizz of carbonated drinks and the smooth consistency of premium smoothies, texture plays a crucial role in consumer satisfaction. Our feature unpacks the science behind texture enhancement and how brands are leveraging this trend to create more enjoyable drinking experiences.
Beyond that, this issue highlights key investments in Africa’s food and beverage sector, shedding light on how major brands are positioning themselves for growth. We also examine recent food safety concerns and the regulatory measures being implemented to ensure a safer food ecosystem across the cworld.
Stay ahead of industry developments with expert insights, executive moves, and the latest product launches—all inside Food Business Africa magazine.
I look forward to seeing you at AFMASS Food Manufacturing Uganda edition, where the future of food and beverage manufacturing in East Africa will take center stage. Until then, happy reading!
Alphonce Okoth Senior Editor FW Africa
AFMASS Food Manufacturing Expo Uganda Edition
February 11-13, 2025
Africana Hotel, Kampala, Uganda www.ug.afmass.com
Gulfood
February 17-21, 2025
Dubai World Trade Centre www.gulfood.com
IAOM MEA Regional Milling Forum
Feb 18-20, 2025
Kigali, Rwanda www.iaom-mea.com
PROPAK AFRICA 2025
March 11 - 14, 2025
Johannesburg Expo Centre www.propakafrica.co.za
Green Agric West Africa Expo 2025
25 - 27 Feb 2025
LCCI Conference and Exhibition Center - Lagos, Nigeria www,greenagriexpo.com
African Fine Coffees Conference and Exhibition
2025
26 - 28 Feb 2025
Julius Nyerere International Conference Centre - Dar es Salaam, Tanzania www.afca.coffee/conference/
Future Food Tech
March 13-14, 2025
San Francisco, USA www.futurefoodtechsf.com
Annual Meat Conference
March 24-26, 2025
Orlando, Florida, USA. www.meatconference.com


Sign up today to receive our bi-weekly food, beverage and milling plus packaging industry email newsletters. Never miss breaking news from Africa and the World, twice a week www.foodbusinessafrica.com/signup
IFFA 2025
May 3–8, 2025
Messe Frankfurt, Frankfurt, Germany www.iffa.messefrankfurt.com/ frankfurt
Food Safety Summit
May 12-15, 2025
Donald E. Stephens Convention Centre, Rosemont, Illinois, USA www.food-safety.com/food-safetysummit
AFMASS Food Manufacturing Expo Kenya & Eastern Africa Edition
July 2-4, 2025
Sarit Expo Centre, Nairobi, Kenya www.afmass.com
Africa Future Food Summit
July 2-4, 2025
Sarit Expo Centre, Nairobi, Kenya www.africafuturefoodsummit.com





SOUTH AFRICA – Eskort, South Africa’s leading pork manufacturer, has officially launched a 10,000m² factory extension in Heidelberg, expanding its Gauteng production capacity by 50%.
The factory extension includes state-of-the-art equipment, such as the largest continuous box freezer in Africa, capable of freezing 120,000kg of products to minus 18°C every 24 hours.
The freezing chamber maintains a temperature of minus 41°C, creating optimal conditions for preserving the quality of the pork products.
One of the key features of the expanded facility is the introduction of multi-level picking mezzanine floor systems in the chilled and frozen warehouses.
These systems, the first of their kind in the South African food industry, maximize vertical space by incorporating mezzanine floors for additional levels of storage and picking.
This innovation is set to allow Eskort to handle a high volume of orders efficiently and contribute to overall operational efficiency.
Arnold Prinsloo, Eskort’s CEO, highlighted the core objective of the factory extension, emphasizing the creation of production efficiencies.
“The expansion includes the addition of carcass chillers, a significant increase in deboning lines, and the installation of a large box freezer to accommodate the growing influx of raw material.”
The investment in the factory extension is part of Eskort’s commitment to meeting the rising demand for its products.
The expansion includes new dispatch areas, loading bays, and doubled chilled and frozen cold stores, contributing to improved productivity and cost efficiency.
The company started in 1917 in Estcourt, has evolved over the years, with farmers being shareholders and a focus on antibiotic-free pork production.
INDIA – Anheuser-Busch InBev (AB InBev), the world’s largest beer producer, has committed to investing US$250 million in India’s beverage sector over the next two to three years.
The announcement was made by India’s Union Minister for Food Processing Industries, Chirag Paswan, during the World Economic Forum (WEF) in Davos, Switzerland.
The investment will be spread across various states, including Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, and regions in South India, focusing on expanding AB InBev’s footprint in India’s growing beverage industry.
AB InBev’s investment aims to strengthen India’s food processing industries, creating jobs, enhancing manufacturing capabilities, and contributing to the country’s economic growth.
Paswan emphasized India’s push to attract foreign investments, showcasing the country’s potential for global collaborations.
Platforms like WEF offer India a valuable opportunity
to connect with international investors and demonstrate its business-friendly environment.
Expansion into the energy drink market
Alongside its Indian expansion, AB InBev is making its move into the energy drink market in the United States, a rapidly growing sector.
The company has partnered with 1st Phorm, a sportsnutrition group, to launch a new energy drink brand set to debut in mid-2025.
The beverage will be distributed through AB InBev’s wholesale partners across the U.S. To boost the brand's development, UFC CEO Dana White is collaborating with AB InBev and 1st Phorm.
This strategic partnership demonstrates AB InBev’s commitment to diversifying its beverage portfolio and capitalizing on the increasing demand for energy drinks, marking a significant expansion into a new product category.















Co-located with



No.1 Trade Shows for Food Service, Hospitality & Travel Industry in Africa

HORECA Technologies, Systems & Services





HORECA Equipment, Accessories & Solutions

HORECA Furniture, Decor, Style & Supplies



Specialty Coffee & Tea



Specialty Wines & Spirits


Laundry Equipment & Supplies; Cleaning, Hygiene & Sanitation Products


Fresh & Packaged Foods & Beverages

Bakery, Food & Beverage Ingredients & Commodities
HORECA Design, Engineering & Construction

Varun Beverages Ltd (VBL), the largest bottler of PepsiCo in India, has announced an investment of Rs 412.80 crore (US$48.19 million) in its South African subsidiary, The Beverage Company Proprietary Limited (Bevco).
This move is part of VBL's strategy to strengthen its global presence and enhance operations both domestically and internationally.
Bevco, which holds franchise rights from PepsiCo for South Africa, Lesotho, and Eswatini, manufactures and distributes PepsiCo's licensed products along with its own non-alcoholic beverages in South Africa.
Through the investment, VBL has subscribed to 19.84 lakh ordinary shares of Bevco, increasing its shareholding by 2.42%. The funds will help Bevco repay existing debt and support future business growth.
This investment follows VBL’s acquisition of Bevco in December 2023 for an enterprise value of Rs 1,320 crore (US$154.1 million).
VBL, promoted by the Jaipuria family, controls 90% of PepsiCo's beverage sales volume in India and has been expanding aggressively in Africa.
In 2024, VBL commissioned two new production lines at its Zimbabwe plant to increase production of Aquaclear bottled water and sparkling beverages.
Additionally, the company fully acquired SBC Beverages Tanzania Ltd. and SBC Beverages Ghana Ltd., with investments totaling Rs 1,431 crore (US$169.5 million).
VBL also invested US$50 million in a Pepsi production facility in Kiswishi City, Democratic Republic of the Congo.
In Q3 2024, VBL reported a 24% year-on-year increase in net profit to Rs 6.20 billion (US$73.8 million), driven by strong international market demand, particularly in Africa.
KENYA - Kenya has launched a comprehensive plan to revitalize its sugarcane industry, aiming to address long-standing challenges while lowering sugar prices for consumers.
The initiative targets improvements in the supply chain, production efficiency, and distribution processes, benefiting both farmers and consumers.
Key reforms include the distribution of subsidized fertilizer to increase productivity and farmers' incomes.
President William Ruto highlighted the government's commitment to addressing issues like inadequate funding, poor planting materials, weak research infrastructure, and strained relationships between farmers and millers.
The government has also introduced draft regulations for a quality-based payment system to incentivize farmers to deliver high-quality sugarcane.
These regulations aim to ensure fairness in sugarcane collection and payment processes. A sugar pricing committee, established under the Sugar Act 2024, will oversee pricing and create a bonus system to increase farmers’ earnings.
The Act also creates sugarcane catchment areas to better synchronize milling operations and manage supplies.
The government plans to expand sugarcane growing zones beyond the traditional Western region and establish a centralized database for farmers.
Using Geographic Information System (GIS) mapping, this database will allocate sugarcane fields to specific mills, promoting smart contracting.
To address the quality of planting materials, KES 600 million (US$4.64m) has been approved for the Kenya Sugar Research and Training Institute (KESRETI) to develop improved sugarcane varieties.
Additionally, the government will revitalize five stateowned sugar companies by writing off debts of KES 67 billion (US$518.4M) and settling unpaid farmer dues.
Despite these efforts, challenges remain, including an impending sugar price hike due to a new Sugar Development Levy.


USA – U.S. chocolate maker, Hershey Co., has requested approval from the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) to purchase up to 90,000 metric tons of cocoa from the stocks of the ICE exchange, exceeding the current position limit.
This is nearly double the CFTC’s existing limit of 4,900 contracts.
Hershey, which is already well-covered for its cocoa needs in 2025, seeks this increased purchase due to the ongoing cocoa supply shortages.
Cocoa prices have soared in 2024, driven by adverse weather conditions and diseases in Ivory Coast and Ghana, the world’s largest cocoa producers, which together account for more than 60% of global cocoa supply.
The request comes at a time when cocoa stockpiles are dwindling. ICE New York stocks are currently at around 61,000 tons, while London stocks stand at about 21,000 tons.
Production of cocoa is also expected to decline by 14 percent in the 2023-2024 season, down from 4.9 million metric tons in 2022-2023 to an estimated 4.2 million metric tons.
Meanwhile the company has announced key leadership appointments following CEO Michele Buck’s decision to step down, effective June 30, 2026.
Andrew Archambault will take over as president of U.S. confection on February 3, 2025, overseeing brands such as Hershey’s, Reese’s, and Jolly Rancher.
Additionally, Hershey veteran Veronica Villasenor has been promoted to president of salty snacks, succeeding Kristen Riggs, who is leaving the company after two decades.
The company also lowered its annual revenue forecast, although it reaffirmed its 2024 outlook.





KENYA - Kenafric Industries, East Africa’s leading confectionery company, is set for a significant stake sale valued at over US$100 million as private equity firms Amethis and Metier Private Equity Ltd. look to exit their investment.
The two firms, which acquired a 40 percent stake in Kenafric's confectionery and culinary business in 2017, have enlisted South Africa’s Nedbank Group Ltd. to manage the sale, with additional advisory support from I&M Burbridge Capital in Kenya.
This divestment is part of a broader trend of private equity
exits across Africa, driven by improved growth prospects expected in the next 12 to 24 months.
Kenafric, founded in 1987 by the Shah family, has diversified from its initial footwear production into a wide range of products including confectionery, beverages, stationery, and spices.
It is well known for producing over 40 million pieces of gum per month and exporting about 45 percent of its products to markets outside Kenya.
The company operates an extensive distribution network, reaching 40,000 retail outlets with a fleet of 200 motorcycles that serve informal traders and emerging mini-markets.
Kenafric has made strategic moves to expand its market presence, including a partnership with India’s Britannia Industries in August 2022 to acquire Britannia Foods, a struggling biscuit maker.
In December 2024, the Competition Authority of Kenya approved Kenafric’s acquisition of Economic Industries Limited, strengthening its position in the stationery market, where it holds a 12.3% market share.
As private equity activity picks up in Africa, the sale by Amethis and Metier reflects the growing optimism and anticipated exit opportunities in the region.
KENYA – Sasini PLC has reported a KES 562.9 million (US$4.34m) loss after tax for the financial year ending September 2024, ttributed to high production costs, depressed commodity prices, supply chain disruptions, and adverse foreign exchange impacts.
This is a stark contrast to the KES 542.3 million (US$4.2m) profit recorded in 2023.
Despite a 20.4 percent increase in revenues to KES 6.9 billion (US$53.3M), up from KES 5.7 billion (US$44.0m) in 2023, the company’s earnings were significantly eroded by a 45.1 percent surge in operational costs.
The cost of sales rose sharply to KES 6.3 billion (US$48.67m) from KES 4.4 billion (US$33.99m) in the previous year.
Sasini’s tea, avocado, and macadamia segments underperformed during the year, with only the coffee trading unit posting marginal profits.
A persistent tea glut at auction markets, driven by high green leaf production, led to depressed tea prices. The company’s production costs were further exacerbated by increased fertilizer and power costs, as well as lower production volumes.
“Due to the tea glut in the auction, we were unable to secure

long-term contracts with major private buyers as prices remained below production costs,” Sasini said.
This challenge was compounded by the minimum reserve prices set in 2022, which were only suspended in October 2024 by the East African Tea Trade Association.
As part of its business reforms, Sasini closed several revenue and profit lines, increasing costs in the coffee value chain.

– Israeli meat processor Siniora Foods has announced plans to invest US$40 million in a new manufacturing facility in Jeddah, expanding its presence in the region.
The company, which operates in Jordan, Palestine, Turkey, and the UAE, confirmed the project during the Saudi HORECA 2024 exhibition in Jeddah.
The new plant will enhance Siniora’s production capacity for cold cuts and frozen foods, catering to the growing Saudi market.
Aligned with Saudi Arabia’s push for local food production, the facility will focus on producing “Made in Saudi Arabia” products to meet domestic demand.
The Made in Saudi program sees food companies collaborate under one unified brand to deliver significant opportunities for businesses like Siniora Foods to grow and promote their brands and products in Saudi Arabia, its existing markets in Asia and the wider globe
This initiative supports the Saudi Authority for Industrial Cities and Technology Zones (MODON) strategy to drive localization in the food sector.
MODON has reported that the number of food factories in the country has reached 1,300 across 36 cities, reflecting a 31% growth in food industry companies in recent years.
Siniora’s investment follows a US$72 million deal by Nestlé in September, when the global food giant signed an agreement with MODON to establish its first manufacturing facility in Saudi Arabia.
Meanwhile, Saudi Arabia has also intensified efforts to boost food security. The country recently opened a tender for a fish farm on its northern Gulf coast as part of a US$5 billion initiative.
Earlier in May, a unit of the Public Investment Fund (PIF) received approval to launch Saudi Arabia’s first coffee production facility, further strengthening the country’s food production capabilities.
EGYPT – Egypt’s food export sector has experienced remarkable growth, reaching a record US$5.5 billion between January and November 2024—a 17% increase from US$4.7 billion during the same period in 2023.
This represents an additional US$813 million in export value, surpassing the total US$5.068 billion reported for the entire year of 2023.
Arab nations remained Egypt’s largest market, accounting for US$2.936 billion, or 53% of total exports, with a 15% rise in value.
The European Union followed with US$1.083 billion, comprising 20% of total exports and achieving a 33% growth rate.
Non-Arab African countries imported US$464 million (8% of total exports, up 7%), while the United States saw the highest percentage growth, importing US$302 million (5% of the total) with a 40% increase.
Other global markets contributed US$756 million (14% of total exports), reflecting an 8% rise.
Among key importers, Saudi Arabia led with purchases worth US$434 million (up 16%), followed by Sudan at US$363 million, though marking a 20% decline.
The United States ranked third, with imports of US$302 million, up 40%. Libya and Palestine imported US$290 million (+19%) and US$275 million (+26%), respectively.
The Netherlands recorded the highest growth rate, with imports soaring 104% to US$241 million, while Morocco saw an 80% rise to US$201 million.
Key exported products included soft drink concentrates (US$502 million, +5%), flour and groats (US$428 million, +7%), and frozen strawberries (US$364 million, +13%).
Sugar exports dropped 21% to US$357 million, while edible oils surged 169% to US$283 million. Notably, frozen potatoes saw an extraordinary 904% increase, reaching US$204 million.
Over the past decade, Egypt’s cumulative food exports have totaled US$40.5 billion, solidifying its growing influence in the global market.

INDIA – Reliance Consumer Products Ltd (RCPL), the consumer goods arm of Reliance Industries Ltd (RIL), has acquired SIL Foods, a well-known brand in the food sector, particularly for its sauces and condiments.
This acquisition is part of RCPL’s ambitious strategy to expand its footprint in India’s consumer goods market. Since its inception, RCPL has made significant strides, acquiring homegrown brands to strengthen its product portfolio.
SIL Foods, with its trusted legacy, will now leverage RCPL’s extensive distribution network, pan-India presence, and marketing expertise to expand its reach.
While the financial details of the acquisition were not disclosed, the partnership is expected to enhance the brand’s visibility and bring its authentic products to a wider, modern audience.
Ajay Mariwala, Managing Director of SIL Foods, expressed excitement about the merger, highlighting the potential for growth with RCPL’s backing.
Ketan Mody, COO of RCPL, emphasized the company's focus on preserving India’s rich culinary heritage while bringing iconic flavors to consumers in new and innovative formats.
RCPL aims to reach ₹10,000 crore (US$115.73m) in revenue, with acquisitions playing a crucial role in this strategy.
Recent acquisitions include Ravalgaon and Toffeeman confectioneries, Campa soft drinks, Raskik beverages, Sosyo carbonated drinks, and Lotus chocolates.
In the first nine months of FY25, RCPL reported ₹8,000 crore (US$92.47m) in revenue, largely driven by Campa and Independence range products.
Additionally, RCPL is expanding its beverage portfolio, including RasKik Gluco Energy, a functional drink designed for the Indian market, offering affordable, electrolyte-packed options catering to diverse consumer preferences.

Barry Callebaut records 2.7% decrease in sales volume after cocoa prices hikes

SWITZERLAND – Swiss chocolate and cocoa products manufacturer, Barry Callebaut (BC) has reported a 2.7% decline in sales volume, totaling 565,238 tonnes, in the first quarter of fiscal year 2024/25, ending November 30, 2024.
This decrease is attributed to a challenging and volatile market environment, which has impacted short-term customer and consumer demand.
Despite the drop in sales volume, the company experienced a significant increase in sales revenue, reaching CHF 3.45 million (US$3.82bn).
This 53.9% rise in revenue in Swiss francs is primarily driven by Barry Callebaut's cost-plus pricing model, which allowed the company to pass the significantly higher cocoa bean prices onto customers
The surge in cocoa bean prices has been substantial, with terminal market prices increasing by approximately 72% compared to the prior-year period.
Prices escalated from a minimum of GBP 4,355 at the start of the period to GBP 7,708 per tonne by November 30, 2024. This increase is largely driven by hedge fund activity.
In response to these market conditions, Barry Callebaut now anticipates a low single-digit decrease in sales volume for the fiscal year 2024/25, revising its previous forecast of flat cocoa sales volume.
However, the company reaffirms its target for double-digit growth in recurring operating profit on a constant currency basis.
To address the high costs and ensure liquidity, Barry Callebaut has issued a bond worth CHF 300 milliona (US$331m).
The issuance consists of a six-year tranche of CHF 160 million (US$175.97m) and a ten-year tranche of CHF 140 million (US$153.98m).
CEO Peter Feld commented on the situation, stating, "While we focus on short-term operational priorities in the current environment, the significant opportunity to unlock sustainable profitable growth and value creation is evident."
USA - The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has officially banned the use of red dye No. 3, also known as erythrosine, in food, beverages, and ingested drugs.
This decision comes over 30 years after studies linked the additive to cancer in animals. The ban follows a petition filed in November 2022 by advocacy groups, including the Center for Science in the Public Interest and the Environmental Working Group, urging action based on longstanding health concerns.
Manufacturers using red dye No. 3 must reformulate their products by January 15, 2027, for food and beverages, and by January 18, 2028, for ingested drugs.
The ban also applies to imported goods, requiring compliance with U.S. regulations. This move has been hailed as a major victory for public health, with Ken Cook, president of the Environmental Working Group, calling it a “monumental victory” for consumer safety.
Red dye No. 3 is a synthetic color additive used to give a cherry-red appearance to various products, including candies, foods, and drinks.
Though it was banned in cosmetics and topical drugs in 1990 due to its cancer-causing effects in rats, it continued to be used in food and ingested drugs under the Delaney Clause of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, which prohibits color additives linked to cancer.
The FDA’s delay in banning the dye for food use was due to differences in how it interacts with humans compared to rats.
While no direct link to cancer in humans has been proven, the ban aligns with legal requirements. California enacted a similar ban in October 2023.

Atlas Copco reports US$16.1B in revenue for FY 2024

SWEDEN – Swedish industrial group Atlas Copco has released its financial results for the fourth quarter and full year of 2024, posting record revenues and stable profitability.
The company reported that orders received amounted to approximately US$15.6 billion, with revenues increasing by 2% to reach a record US$16.1 billion for the financial year 2024.
Operating profit rose by 3% to about US$3.5 billion, resulting in a margin of 21.6%. The adjusted operating margin stood at 21.9%.
Operating cash flow significantly improved to approximately US$2.8 billion.
Additionally, basic earnings per share were US$0.56, and the return on capital employed was 28%.
In the fourth quarter, orders received were around US$3.6 billion, an organic increase of 4%.
Revenues for the quarter reached a record US$4.2 billion, remaining unchanged organically while operating profit for this period was approximately US$910 million, with a margin of 21.8%.
Better still, the adjusted operating profit was about US$911 million, maintaining the same margin.
Profit for the quarter was US$710 million, leading to basic earnings per share of US$0.16.
The company also achieved a record operating cash flow of approximately US$900 million during this quarter.
The Compressor Technique and Vacuum Technique segments experienced slight increases in orders.
However, the Industrial Technique segment saw a decline in orders, primarily due to reduced demand from the automotive industry.
The Power Technique segment reported order growth, partly attributed to recent acquisitions. Service operations expanded across all business areas.
Throughout 2024, Atlas Copco completed 33 acquisitions.
The Board has proposed an ordinary dividend of US$0.27 per share for 2024, to be distributed in two equal installments.
The company anticipates that customer activity will weaken somewhat in the near term.
ICELAND – Icelandic meat and food processing equipment manufacturer Marel has officially merged with American company John Bean Technologies Corporation (JBT), forming JBT Marel Corporation.
The newly combined entity began trading on January 3, 2025, on both the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and Nasdaq Iceland.
The merger integrates Marel’s food processing expertise with JBT’s automation and technology capabilities, strengthening its position in the global food industry.
JBT Marel Corporation will oversee operations across multiple food industry sectors. Brian Deck, now the corporation’s CEO, will lead the meat and poultry division, while Árni Sigurdsson, the former Marel executive and now president, will head the Fish & Retail and Food Service
Solutions branch.
As part of the settlement of its voluntary takeover offer, JBT Marel has begun a compulsory acquisition of all remaining Marel shares not already owned by the new entity.
In accordance with Icelandic law, affected shareholders were notified on January 2, 2025, and the acquisition is expected to be finalized by February 2025.
Additionally, Euronext Amsterdam and Nasdaq Iceland have approved Marel’s request to delist its shares from both exchanges.
January 3, 2025, marks the last trading day for Marel shares on these platforms.
With this merger, JBT Marel Corporation is set to redefine food processing technology, combining automation, expertise, and service to enhance efficiency across the industry.

UK – Tate & Lyle and BioHarvest Sciences have formed a partnership to develop plant-based molecules for sustainable and cost-effective sweeteners in the food and beverage industry.
BioHarvest’s Botanical Synthesis platform facilitates the production of plant-derived ingredients by cultivating specific plant cells.
According to the companies, this method replicates and enhances the phytonutrients found in certain plants, delivering the same health benefits without requiring the cultivation of entire plants.
This approach enables scalable production of non-GMO
ingredients with enhanced nutritional value while using less land and water than traditional farming.
The collaboration aims to create next-generation botanical sweeteners using plant-based molecules.
These sweeteners are designed to replicate the taste of sugar without the aftertaste, providing an affordable and environmentally friendly alternative for healthier food and beverage products.
Tate & Lyle CEO Nick Hampton described the partnership as an opportunity to introduce innovative solutions to the industry.
He highlighted that working with forward-thinking companies like BioHarvest positions Tate & Lyle to lead in the future of food innovation.
BioHarvest CEO Ilan Sobel emphasized the value of Tate & Lyle’s expertise in global food innovation, noting that their regulatory, nutritional, and research capabilities would be essential in bringing plant-based molecules to a wider market.
Chief Technology Officer Yochi Hagay underscored the significance of the collaboration for BioHarvest, stating that it marks a key milestone after more than 15 years of research and development.
He added that Tate & Lyle’s involvement would help scale the technology to meet increasing demand for healthier food options.
This partnership represents a crucial step toward advancing sustainable, plant-based ingredients for a healthier and more eco-friendly future.

DENMARK – Oterra and Icelandic food-tech company Vaxa Technologies have launched Arctic Blue, a natural blue food colour made from spirulina, boasting a significantly lower carbon footprint than conventional alternatives.
Produced in Iceland, Arctic Blue benefits from closed-loop cultivation powered by renewable energy.
Vaxa’s facility, located near a geothermal power plant, uses waste heat and CO₂ to cultivate spirulina in bioreactors, requiring just 1% of the water and land needed for traditional open-pond systems.
This innovative method is estimated to emit 40 times less CO₂ than standard spirulina production.
Arctic Blue also offers improved solubility and a neutral odour, making it easier to use in food and beverage applications.
According to Lotte Jeppesen, Industry Marketing Manager at Oterra, the product retains its vibrant colour and regulatory classification, ensuring seamless integration into existing formulations.
Alongside Arctic Blue, Oterra has introduced its 2025 Colour Trends, aimed at guiding brands, marketers, and R&D teams in the food and beverage industry.
Key trends include Beyond Green, which expands the concept of sustainability beyond the traditional green palette.
Out of the Blue challenges conventional colour choices by introducing bold and unexpected combinations. Vibrant hues such as Peculiar purple and Mystic magenta cater to adventurous consumers who seek novelty and excitement in their food experiences.
True Colours taps into the growing demand for products that promote emotional and physical well-being. Consumers are drawn to functional foods that not only nourish the body but also enhance their mood and lifestyle.
Natural Reality merges AI-driven innovation with the authenticity of real food. As technology reshapes the food industry, this trend highlights the importance of natural ingredients and authentic experiences.
EGYPT – AGF Freezers Ltd., a Canadian company specializing in food freezing and cooling equipment, has launched its new office in New Cairo, Egypt, as part of its ongoing global expansion strategy.
The company’s new facility is designed to strengthen its ability to serve the Egyptian market and improve customer support locally.
Founded in 2010, AGF Freezers combines Canadian engineering with European components and manufacturing capabilities to produce efficient food freezing solutions.
With offices already established in Europe, South America, China, Australasia, and the Middle East/Africa, AGF Freezers serves customers worldwide.
The new office will house a local engineering team capable of offering services such as troubleshooting, scheduled maintenance, retrofitting, and spare parts provision.
Mourade El Hassouni, AGF Freezers’ general manager for the Middle East and Africa, emphasized the importance of the local office in improving response times and customer support.
Beyond its operation in Egypt, the company was recently selected by Imani Harvest Ltd., a major agricultural value-chain company based in Uganda, for its food freezing and processing solutions.
This customer win includes an Individual Quick Freeze (IQF) Tunnel with Sequential Defrost as well as a dewatering shaker and blow off air knife for moisture removal before freezing. AGF will be processing popular fruit products such as mangoes, bananas and jackfruit.
Imani Harvest selected AGF Freezers for the company’s attention to hygienic engineering design and manufacturing construction.
The Sequential Defrost feature will offer significant cost savings as it reduces downtime while processing fruit products on a continuous basis. Installation is expected in Q2 2025.

NETHERLANDS – Louis Dreyfus Company (LDC), a prominent player in the global agriculture and food ingredients market, has signed a binding agreement to acquire BASF’s food and health ingredients business.
LDC’s acquisition includes a production site and stateof-the-art R&D center in Illertissen, Germany, and three application labs outside of Germany.
The Netherlands-based company believes the acquisition will enhance its capabilities in developing applications for various industries.
The financial details of the transaction were not disclosed.
In a statement, James Zhou, LDC’s Chief Commercial Officer, emphasized the potential of the acquisition to transform the company’s role in the food ingredients market.
“This step strengthens our ability to provide solutions for bakery, confectionery, non-dairy, instant foods, personal care, and healthcare products. It represents a step toward evolving from a raw material supplier to a trusted partner for our customers globally,” Zhou said.
The move suits LDC’s strategy to expand its presence in the plant-based sector, while BASF shifts its focus to other priorities.
Through the proposed acquisition, LDC aims to leverage its existing strengths in oils and fats, glycerin and lecithin, as well as its global supply chains.
BASF, a Germany-based chemical company, cited a lack of strategic fit as the reason for the divestment.
The German-based company earlier indicated that the food and health performance ingredients business offered limited operational synergies with its other businesses.
Instead, BASF plans to focus on growth in core areas such as vitamins, carotenoids, and feed enzymes.
“This decision allows us to direct resources toward areas that align with our strategic goals,” said Michael Heinz, a member of BASF’s executive board.


SWITZERLAND - Bühler has acquired advanced puffing technology from CEREX, a Swiss machinery company, to expand its capabilities in the food, pet food, and feed industries.
The technology, initially developed by CEREX, enables Bühler to meet the growing demand for healthier and diverse food products.
It supports the production of snacks, breakfast cereals, bakery goods, confectionery, and dairy items.
The puffing process applies heat and pressure to raw materials with a water content of 10–14% and starch levels of 65–75%, creating lighter, crispier products with enhanced volume and porosity.
This improves the appeal and shelf life of snacks and cereals by reducing moisture content while also enhancing digestibility and enabling the addition of nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and proteins.
Christoph Vogel, Head of Bühler's Human Nutrition Business Unit, noted that the technology provides extensive recipe possibilities and supports innovation in product development to align with evolving consumer preferences.
The system offers energy efficiency, using approximately 60 kilowatt-hours per 100 kilograms of product, compared to 120 kWh in similar systems, and achieves over 95% yield.
Bühler plans to open an Application and Training Center in Uzwil, Switzerland, in 2025 to help manufacturers develop recipes and processes using this technology.
Recently, the company has also unveiled its latest innovation, Stellar technology, designed to accelerate cell growth in biological systems and improve efficiency in food production processes.
This development represents a huge step in combining research with industrial applications, addressing challenges in the food production industry.
Developed in partnership with academic institutions, Stellar technology focuses on enhancing the speed and reliability of cell-based processes.





Abbey
– Ghana's President John Dramani Mahama has appointed Ransford Anertey Abbey as the Acting Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of the Ghana Cocoa Board (COCOBOD).
He assumed office on January 21, 2025 following the resignation of Joseph Boahen Aidoo.
Abbey is a respected media personality and sports administrator, widely known as the host of Metro TV’s morning show, Good Morning Ghana, a platform recognized for its impactful discussions on national matters.
Additionally, he serves as an Executive Council member of the Ghana Football Association and as president of Kpando Hearts of Lions Football Club, contributing significantly to the development of Ghanaian football.
He holds a doctor’s degree in Business Administration (DBA) from SBS Swiss Business School, an MBA in General Management, and certifications in dispute resolution, further solidifies his capacity to provide exceptional leadership for COCOBOD.
President Mahama extended his congratulations to Dr. Abbey, expressing confidence in his ability to provide strong leadership and strategic direction to COCOBOD, a key player in Ghana’s cocoa industry.
KENYA – The Board of Kenya Tea Development Authority (KTDA) Holdings has elected Chege Kirundi as its new national chairman.
Kirundi replaces Enos Njeru, while Eric Chepkwony has been retained as the vice chairman.
Kirundi is currently the board member for Zone Three in Murang’a County and the chairman of Kiru Tea Factory Company PLC.
He holds a degree in law from the University of Nairobi, a Diploma in Law from the Kenya School of Law, and credentials as an advocate of the High Court of Kenya.
Additionally, he is a qualified Notary Public, Commissioner of Oaths, certified Public Secretary, Fellow of the Chartered Institute of Arbitrators (FCIP), and professional mediator.
KTDA is a private company owned by approximately 600,000 smallholder tea farmers across 16 tea-growing counties in Kenya. These farmers are shareholders in 54 tea companies that own KTDA Holdings and its nine subsidiary companies. .


The Citrus Growers’ Association of Southern Africa (CGA) has appointed Dr. Boitshoko Ntshabele as its new Chief Executive Officer, effective February 1, 2025.
He takes over from Justin Chadwick, who will retire in March after leading the association for 25 years.
Dr. Ntshabele has a robust background in academia, private enterprise, and public service. For the past five years, he has served as Director of Biosecurity at the Department of Agriculture, Land Reform and Rural Development.
He also held leadership positions at Onderstepoort Biological Products and was the Minister Counsellor for Agriculture at South Africa’s Embassy in Belgium from 2015 to 2019.
CGA advocates for the citrus industry’s critical role in agriculture and its contribution to the South African economy, representing more than 1,560 citrus growers across South Africa, Eswatini, Zimbabwe, Botswana, and Namibia.
The CGA commended his “successful track record in management, policy development, international engagement, and negotiation,” highlighting him as a knowledgeable advocate for local citrus growers.
INDIA – PepsiCo India has appointed Nitin Bhandari as Vice President and General Manager for India and South Asia Beverages.
Bhandari will succeed George Kovoor, Senior Vice President and General Manager for India Beverages, who is set to retire on March 31, 2025.
Based in Gurugram, Bhandari will focus on driving growth, enhancing consumer engagement, and strengthening relationships with stakeholders and local communities.
Bhandari is a seasoned professional with nearly two decades of experience at PepsiCo, holding various leadership positions across India, Southeast Asia, and the Pacific.
Most recently, as Vice President and Chief Growth Officer for PepsiCo India, he spearheaded transformational initiatives across India, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and Nepal.
Prior to this, he managed PepsiCo’s operations in the Philippines, Malaysia, and Singapore.
Bhandari has achieved several milestones, including launching successful e-commerce ventures across Asia, revitalizing PepsiCo’s food business in Thailand, and developing innovative marketing strategies for Mountain Dew in India.


United Spirits appoints Praveen Someshwar as new
INDIA – United Spirits Limited (USL) has appointed Praveen Someshwar as the company’s new Managing Director and CEO, effective April 1, 2025.
He takes the CEO role from Hina Nagarajan, who is set to assume a global role within the Diageo Group.
Someshwar will work closely with Nagarajan as CEO-Designate until March 31, 2025, to ensure a smooth handover.
Nagarajan, who has led USL for nearly four years, will resign as Managing Director and CEO on March 31, 2025.
During her tenure, Nagarajan played a pivotal role in steering USL’s growth and consolidating its position as a key player in India’s beverage industry.
Someshwar brings over two decades of experience in leadership roles across various industries.
For the past five years, he has served as the Managing Director and CEO of HT Media, where he oversaw a portfolio of prominent brands, including Hindustan Times and Mint.
Previously, he spent 24 years at PepsiCo, managing roles in general management, finance, and strategy across India and the Asia-Pacific region.
NAMIBIA – Namib Mills Investment Group has appointed Christo Ellis as its new Chief Executive Officer.
Ellis takes on the leadership role at a pivotal moment as the group focuses on expanding its footprint and strengthening its operations.
He brings a wealth of knowledge and expertise to the group with over 30 years of experience in the food processing industry.
“This extensive experience allows me to identify opportunities for improvement and ensure we deliver quality products that meet consumer expectations,” he stated.
Under Ellis’ leadership, Namib Mills is expanding its export activities, with pasta and instant porridge reaching markets in South Africa, Zambia, and Botswana.
The group, a cornerstone of Namibia’s agribusiness sector, comprises Namib Mills, Namib Poultry, and Feedmaster, playing a vital role in food production and distribution across the region.
The group, a cornerstone of Namibia’s agribusiness sector, comprises Namib Mills, Namib Poultry, and Feedmaster, playing a vital role in food production and distribution across

Algerian beverage manufacturer, Hamoud Boualem hashas expanded its Slim line of fruit-flavored soft drinks to include an apple-flavored variant, “Slim Pomme” in a 240ml aluminum


Astral Foods has launched a new Southern Style Crumbed Chicken range under its Earlybird Farm brand, offering convenience with resealable packaging.
The new product line includes pre-cooked crumbed chicken thighs and strips that can be baked in the oven or air-fried, catering to consumers seeking quick, high-quality meal options.
www.astralfoods.com



Coca-Cola has introduced Fanta Pomme, an apple-flavored soft drink, containing 102 kcal (5% daily value) per 250ml, with 52mg of salt (1% DV), no fat, and 25g of sugar (28% DV). It is partially
The ingredients include water, sugar, CO2, acidity regulators (INS 330, INS 331(iii)), artificial flavor, coloring (INS 150d), preservatives (INS 211), and sweeteners (INS 950, INS 955), all of which are food-



Danone has launched the Delice Aux Morceaux De Cerise, a product made with fresh whole milk that is fortified, containing 5.6% king's love preparation and pieces, along with black carrot concentrate and a king's love flavor similar to natural.
The product also includes sugar, cream, yogurt lactic acid, tapioca starch, and the cereal preservative E202. It contains 2% fat and may have traces of gluten and nuts.
www.delicedanone.com




Sunpac has launched the Sela Bladder and Kidney Teabags, designed to support bladder and kidney health. The tea, made with African traditional herbs, utilizes buchu for its renowned cleansing properties for both the bladder and kidneys.
The tea bags offer a convenient and easy way to incorporate this health-boosting tea into daily routines.
www.sunpac.co.za





Shoprite has launched its Homegrown Apricot Fruit Jam, produced in collaboration with Jacobs Jam Company.
The jam, made in the Ceres Valley, contains 35% apricot pulp and is free from artificial colors and preservatives. It is certified halal and kosher parev, and the packaging is recyclable, including both the tub and lid.
www.shoprite.co.za






In this article, we explore how PepsiCo is seeking to capture a bigger share of the African market by adapting its strategies with the diverse and dynamic needs of Africa, and where competition is heating up from local companies, as well as established global giants.
By Francis Watari
PepsiCo, the maker of the its namesake brand Pepsi, is a globally recognized leader in the food and beverage industry, with a diverse portfolio that includes other iconic brands such as Lay’s (snacks), Gatorade (energy drinks), Tropicana (juices), and Quaker (oats).
In Africa, the company’s brands also include Ceres (juices), Simba (snacks), Weetabix (breakfast cereals) and many others, as the global major has over the last five years turned its focus onto the African continent, where despite a population of boom that is expected to double to more than 2.5 billion people, global giants continue to grapple with low consumption of packaged food and beverage products.
While its global footprint spans over 200 countries, PepsiCo’s operations in Africa showcase a unique blend of innovation, sustainability, and community engagement.
Pepsi, one of the flagship products of PepsiCo, plays a significant role in the company's strategy and operations across Africa. As the beverage landscape on the continent evolves, PepsiCo is leveraging its iconic brand to capture market share, respond to consumer preferences, and drive growth – while also seeking new opportunities in the snacks, juice and breakfast cereals aisles.
PepsiCo has a long history in Africa, dating back to its initial entry into South Africa in 1948 through a partnership with New Age Beverages (NAB). However, in 1985, the company withdrew its operations in protest of the former White minority government’s apartheid policies. At the time, it had a 25 percent share market while NAB had 75% ownership, according to the
company. Using the South African nation as its base, PepsiCo ventured northwards, launching operations in Kenya, Uganda, and Tanzania in the East and Nigeria in the west.
Throughout the region, PepsiCo’s approach was much like its main competitor, Coca-Cola’s: outsource bottling operations to independent bottlers. According to Euromonitor, the drink giants find this strategy attractive as they get to largely retain control over beverage production, sacrificing some margin but satisfying investors by reducing direct exposure to the volatility of distribution costs – especially in Africa, where costs are high and complexities in the market can be daunting.
PepsiCo has been diversifying its operations to capture a larger share of the soft drink market. Africa is home to a rapidly growing population and an emerging middle class that is reshaping consumption patterns. Over the past twenty years, household spending in Sub-Saharan Africa has grown 150% faster than the population. Landry Signé at the Brookings Institution forecasts that total household consumption in Africa will reach US$2.1 trillion by 2025 and US$2.5 trillion by 2030. This presents a significant opportunity for Pepsi as consumers seek out affordable and accessible food and beverage options.
In South Africa, for instance, the soft drinks market is projected to grow at an annual compound rate of 5.3%, reaching approximately 1.537 billion units by 2027. Despite facing fierce competition from Coca-Cola and local brands, Pepsi aims to increase its market share through strategic initiatives and partnerships.
Following its exit in 1985, the U.S. food and

beverage giant made a comeback to the African market in 1997 with an investment into snack company, Simba (Pty) Ltd in South Africa. Launched in 1957 by Leon Greyvenstein, Simba was already a household name by the time PepsiCo was acquiring it in 1995. Leveraging its extensive market reach, PepsiCo was able to introduce its other globally acclaimed snack brands such as Lays and Doritos into the South African market and by early 2000s, the company was controlling 63% of the country’s potato chips market.
Driven by slowing growth in the American home market and a desire by CEO Ramon Laguarta to give PepsiCo a greater global presence. However, pushed the company into seriously considering strategies to grow into the sub-Saharan Africa market.
In 2019, PepsiCo decided to upscale its South African success by acquiring Pioneer Foods, a larger food processing company based in South Africa but with a market reach estimated to span 80 countries. The US$1.7 billion acquisition

of Pioneer Foods completed in March of 2020 is one of the largest deals made by PepsiCo outside of the US.
With the acquisition, PepsiCo not only got access to Pioneer Foods’ distribution facilities, but also its local executives, who can continue to guide the merged company’s growth. It also lay its hands on a range of widely popular products such as Sasko (bread), White Star (maize meal), Ceres and Liqui-Fruit (juices), Bokomo and Weet-Bix (breakfast cereals) and more. This significant investment catapulted the company to one of South Africa’s largest food and beverage producers, with 29 manufacturing plants across the 9 provinces of the country, with operations across the bakery, milling, snacks, grains, beverages, foods and fruit processing categories.


It further gave the company access to operations in Namibia, Botswana as well as a foothold into Kenya, where Weetabix East Africa, a subsidiary of Weetabix UK, is a leading breakfast cereals manufacturer and distributor. PepsiCo acquired a 60% stake in Weetabix UK in 2016.
The PepsiCo SSA region was further beefed up in January of 2020 when PepsiCo acquired Ethiopian snacks manaufacturer, Senselet, from Netherlands-based Veris Investments. Founded in 2015, Senselet Foods has a leading market position in Ethiopia with its Sun Chips brand that is produced from locally sourced potatoes.
In 2007, Varun Beverages, one of the largest bottlers of PepsiCo products outside the United States, entered Africa when it acquired the PepsiCo franchise in Mozambique. Since then, it has expanded operations into Zambia, Morocco, Zimbabwe, South Africa and more recently, the Democratic Republic of Congo, where it has already commissioned a Pepsi production facility at Maluku SEZ near Kinshasa.
In 2023, Varun Beverages consolidated PepsiCo’s presence in South Africa with the acquisition of South Africa’s Beverage Company (BevCo) for US$159 million.
Following the acquisition, Bevco is PepsiCo’s sole licensed bottler in South Africa, Lesotho, and Eswatini while also holding distribution rights for Botswana and Namibia. This partnership allows Pepsi to leverage BevCo's established manufacturing facilities and distribution networks, enhancing its ability to reach consumers effectively.
Beyond the South African region, PepsiCo has greatly expanded its reach in East and West Africa. In 2009, PepsiCo partnered with Seven Up Bottling Company (SBC). Launched in 1960 by Lebanese national Mohammed El-Khalil, the company, one of PepsiCo’s bottling franchises, controls over 40% of Nigeria’s beverage drinks market.
From its 9 bottling facilities in Nigeria, the company also exports its PepsiCo products to the rest of the west African
region. A 10th bottling facility is in neighboring Ghana to serve the rapidly expanding Ghanian market. In July 2021, the company celebrated its 60 years of operations in Nigeria with the launch of a new look and identity.
SBC has also been bold enough to re-introduce the Pepsi brand in Kenya and Tanzania (since 2001). Today, the 350ml bottles of Pepsi, 7Up, Mirinda, and Mountain Dew are ubiquitous in the country and can be found in Mwanza, a considerable distance from the company’s base in Dar es Salaam. With the success of the Pepsi brand in Tanzania, SBC in 2013 invested into a new US$28 million bottling facility at the heart of Kenya’s capital Nairobi, to take on market leader Coca-Cola.
To further cement its operations in the continent, the New York based food and beverage giant created the PepsiCo subSaharan Africa region to oversee its foray into the market with an estimated population of 1.14 billion.
When it comes to the cola wars, Coca-Cola has long been the dominant player in Africa. However, Pepsi is increasingly seeking new ways to take the lead across the continent.
Markets such as Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Nigeria and Ghana, the sounds of the cola-wars are gathering steam, as the two soda giants square off with each other for the consumer’s wallet.
Case in point: as airline passengers exit the arrivals section at Entebbe International Airport in Uganda, one will not fail to notice the two huge advertising boards by both Pepsi and Coca-Cola, with the two barely ten meters apart. The same awaits each passenger, as each exit from Uganda at the airport, with wall adverts by each of the majors, next to each other, as one exits the passport check-in, towards the lounges and dutyfree shops. Further, you will not fail to notice the hundreds, perhaps thousands, of Pepsi ads as you transverse the city of Kampala and other major towns across Uganda.
However, the beverages giant is no longer just taking a keen look at Coca-Cola only. Family-owned bottling companies such as the Bakhresa Group, METL Group and Jambo Group (Tanzania), Trade Kings Group (Zambia), AJE Group, Monarch Beverages and others (West Africa), Hariss International (Uganda), Kevian and Bidco Africa (Kenya), among hundreds of others across Africa, continue to grab a stake into the rising demand for soft beverages across the continent.
The continent’s young population, growing urbanization, and rising disposable incomes make it an attractive market for consumer goods. However, cultural diversity, economic disparities, and infrastructure gaps require tailored approaches. By aligning its products, marketing strategies, and sustainability initiatives with the continent’s unique needs, PepsiCo ensures that Pepsi remains a refreshing choice that resonates with African consumers for generations to come.
PepsiCo has demonstrated a deep understanding of these nuances, ensuring that Pepsi not only appeals to Africa’s diverse tastes but also aligns with its cultural values and aspirations.
Pepsi understands that African consumers care more about price and availability than subtle differences in taste. While Coke has traditionally targeted the middle and upper classes with higher prices, Pepsi focuses on affordability. Pepsi offers larger and cheaper bottle sizes that are within the budgets of low-income customers.
Pepsi utilizes a different distribution strategy that gets their products to more consumers. Rather than relying solely on formal distribution channels and major retailers, Pepsi utilizes small shops, kiosks, and street vendors across Africa. By partnering with these ubiquitous small businesses, Pepsi ensures wide distribution even in remote areas and informal settlements.
A third factor is the aggressive marketing strategy employed by Pepsi. They have targeted younger, “aspirational” consumers with promotions, endorsements with celebrities and musicians popular in Africa, and social media campaigns. Pepsi understands that many African youth see their products as more modern and global.
Additionally, Pepsi is hugely becoming active in local community activities through sports sponsorships and other community events. For example, in football, Africa’s most beloved sport, features prominently in Pepsi’s marketing efforts. By sponsoring major tournaments and collaborating with local football stars, Pepsi has become a trusted name among fans.
PepsiCo’s commitment to Africa goes beyond selling products; it extends to supporting local economies.
The company sources key ingredients like sugar, maize, and potatoes from African farmers, ensuring that its operations benefit local communities.
As of 2022, PepsiCo was procuring more than 1.5 million tonnes of local maize, wheat, potatoes, oats and raisins every year and employs approximately 13,000 people in 70 warehouses and 45 production facilities on the continent. This approach not only reduces supply chain costs but also empowers smallholder farmers and promotes sustainable agriculture.
Additionally, PepsiCo has actively been funding community projects aimed at building sustainable food systems, ensuring freshwater availability and creating local employment opportunities. For example, PepsiCo launched the R600 million Kgodiso Development Fund in 2022 to help transform the food system in South Africa.
PepsiCo’s operations in Africa stand at a crucial moment, as the global drinks major seeks to be more engrained in the continent, beyond its famous drink, Pepsi. The company is increasingly creating a competitive edge aimed at capturing a larger share of Africa’s food and beverages market.
Through strategic partnerships like those with Varun Beverages, strategic acquisitions and a focus on localized product offerings and marketing strategies, PepsiCo aims to strengthen its position in this dynamic market. As it navigates challenges while capitalizing on growth opportunities presented by a burgeoning middle class and changing consumer preferences, Pepsi’s adaptability will be key to its success on the continent. FBA




By Alphonse Okoth
Uganda, strategically positioned as the economic gateway to the Great Lakes region of Africa, is becoming a regional powerhouse in agriculture and food production. The country's diverse climatic conditions and fertile land have fostered the growth of key agricultural sectors, making Uganda a leader in agricultural commodities across Eastern Africa.
Its position within the Great Lakes region, comprising Rwanda, the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), South Sudan, Burundi, western Kenya, and northern Tanzania, enhances its access to both regional and international markets. As a result, Uganda’s food, beverage and milling industry is booming, driven by a young and dynamic population, increasing urbanization, and shifting consumer preferences toward packaged and processed foods.
Uganda’s agricultural sector is the backbone of its economy, contributing approximately 23% to its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and employing around 68% of the population, according to the Uganda Bureau of Statistics (UBOS). The country’s agricultural dominance in the region is crucial for its own economic stability and positions Uganda as a leading supplier of food and raw materials to neighboring countries in the East African region.
Uganda is recognized as a leader in the production of several key agricultural commodities critical to the food security of the East African region. For instance, Uganda is a large milk producer in East Africa, with an annual production of over 3.85 billion litres in 2023, an increase from 2.51 billion litres in 2018, according to the Uganda Dairy Development Authority – however, due to limited local consumption of dairy products, the country has become the largest exporter of value-added dairy products in Eastern Africa.
This growth reflects the increasing productivity of Uganda's dairy sector, which has seen the national dairy herd rise from 13 million heads in 2013 to 16.7 million in 2023. The sector provides vital livelihood support for millions of Ugandans, especially smallholder farmers who form the backbone of the dairy industry.
Maize, barley, and rice are also among Uganda’s key cereal crops, with the country being one of the leading producers of maize in Eastern Africa. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) reports that Uganda produces around 3.6 million metric tons of maize annually, most of which is
consumed domestically. At the same time, a portion is exported to neighboring countries like South Sudan and Rwanda. The availability of large quantities of maize, a staple crop, not only meets local demand but also bolsters regional food security.
In addition to cereals, Uganda's meat industry is critical in food security and regional trade. The country is known for its high-quality beef, particularly from the indigenous Ankole long-horned cattle, which are highly valued in East Africa.
Uganda is also a significant producer of poultry and fish, with fish farming in lakes such as Lake Victoria contributing to the country’s increasing fish exports, particularly to international, and increasingly, regional markets. Fish exports from Uganda reached US$153 million in 2021, a considerable growth compared to previous years (Uganda Bureau of Statistics, 2021).
Uganda's agro-processing and manufacturing sectors have experienced significant growth, driven by increasing demand for packaged food, beverage and milled products. According to a report by Agroberichten Buitenland, the food processing industry is projected to reach US$10.6 billion by 2027, reflecting a robust expansion in this sector.
The manufacturing sector, particularly food processing, has been a key contributor to this growth. Between 2014 and 2018, the sector grew at an average annual rate of 5.5%, with food processing alone accounting for 40% of manufacturing output, reports Martin Fowler – Senior agricultural adviser, USAID.
Some of the major multinationals with manufacturing
THE COUNTRY IS KNOWN FOR ITS HIGH-QUALITY BEEF, PARTICULARLY FROM THE INDIGENOUS ANKOLE LONGHORNED CATTLE, WHICH ARE HIGHLY VALUED IN EAST AFRICA.
operations in Uganda Coca-Cola (Coca-Cola Beverages Uganda (CCBU), PepsiCo (Crown Beverages), Diageo (Uganda Breweries Limited) and AB InBev (Nile Breweries). These giants have continued investing into the country, especially in the last 10-15 years, as the country sought to be self-reliant on processed and packaged food products, while reducing its reliance on imported products from the region and beyond. However, nearly fourty years since the end of the debilitating wars and instability of the 1970s and early 1980s, entrepreneurship is thriving in Uganda, as local family-owned businesses and regional companies jostle for the consumer, with the likes of Kakira Group, Mukwano Group, Bidco Uganda, Harris International rising to the occasion, as they increasingly instrumental in this transformation, catering to local and international markets.

NUMBERS
3.85B
LITRES OF MILK PRODUCED IN 2023
The non-alcoholic beverage market in Uganda has experienced significant growth, driven by evolving consumer preferences and a shift toward healthier, less intoxicating options. According to Statista, in 2023, the market reached US$587 million, marking a substantial increase from previous years.
This surge is attributed mainly to the younger generation's changing attitudes toward alcohol, which has led to a higher demand for alternatives such as juices, bottled water, and other nonalcoholic beverages. Consequently, the market has seen an influx of local and international brands diversifying their product offerings to meet this demand.
Apart from the two soda giants, Coca-Cola and PepsiCo, the soft beverages market has seen the emergence of intense competition of other companies in the sector, with Harris International, Yaket International and others crowding the market with their locally formulated and manufactured products.
Uganda's alcoholic beverage market is undergoing significant transformations, driven by evolving consumer preferences and increasing competition from local producers. Historically
dominated by large corporations, the sector now features a growing number of local companies producing spirits and wines tailored to the tastes of Uganda's younger, more diverse population.
The Ugandan spirits market was valued at approximately US$1.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach US$2.8 billion by 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.8% during this period, according to IMARC.
Despite this growth, the industry faces challenges due to a significant proportion of unregistered producers. According to the Uganda Alcohol Industry Association, approximately 65% of alcohol producers in the country operate without official registration.
In response to these challenges, local producers focus on quality and product innovation to appeal to a growing market. For instance, Uganda Breweries Limited, a leading beer manufacturer in Uganda, has expanded its product line to include locally produced spirits, catering to the diverse preferences of Ugandan consumers.
Uganda’s dairy industry is experiencing remarkable growth, positioning the country as a key player in the East and Central African


dairy market. As of 2023, Uganda’s national dairy herd has expanded to 16.7 million cows, a significant increase from 13 million in 2013. This expansion is reflected in milk production, which reached 3.85 billion liters in 2023, up from 2.51 billion liters in 2018. Despite this growth, Uganda’s per capita milk consumption remains relatively low at 63 liters per year, far below the World Health Organization’s recommended 200 liters per capita.
The growth of the dairy sector is fueled by increased processing capacity, with the production of milk, yogurt, cheese, and ice cream gaining importance. These dairy products cater to the growing domestic demand and are increasingly being exported to neighboring countries. This positions Uganda as one of the leading dairy exporters in the region. Uganda’s dairy industry plays a vital role in food security and rural livelihoods, providing employment opportunities across the value chain, including production, processing, and distribution.
With recent investments by Jesa Farm Dairy and Benni Foods, joining earlier investments by the likes of Pearl Dairy, Amos Dairy, Lakeside Dairy, Rainbow Dairy and other players, the dairy industry in Uganda offers the most diversified range of products, ranging from packed milk, yoghurt, cheese, ice cream, milk powder and casein, bether than any other country in the region.
Local brands like Lato Milk have expanded their portfolios beyond traditional dairy products into other sectors. In 2021, Lato Milk launched two soft drink brands: Lato Vitaz, a juice fortified with essential nutrients to boost the immune system, and Lato Gluco Power-B, catering to consumers seeking energy-boosting options. The firm also produces a range of premium baby food products.
The meat industry is another significant sector in Uganda’s agricultural economy, with beef, poultry, and pork playing key roles. Uganda’s Ankole long-horned cattle are iconic, serving as a source of milk and meat.
However, the rising demand for pork has attracted global attention. Uganda is now recognized as the largest pork consumer in Africa and the second-largest global pork

consumer after China. On average, each Ugandan consumes 3.5 kg of pork annually. This shift in consumption patterns has led to an increase in pig farming, with the number of pigs growing from 1 million to 7.1 million in recent years.
Small-scale farmers are crucial to Uganda’s meat industry, especially in the pork segment—an estimated 1.1 million households rear pigs, contributing significantly to food security and rural livelihoods. The pork value chain, including production, processing, and distribution, employs millions of Ugandans, making it a key economic growth and social stability sector.
Uganda is the second-largest coffee producer in Africa, following Ethiopia, with coffee being the country’s most significant export commodity. The coffee industry predominantly comprises smallholder farmers who cultivate robusta coffee, Uganda’s primary coffee variety. In 2023, Uganda exported over 6 million bags of coffee, further solidifying its position as a global coffee exporter. The coffee sector supports approximately 1.7 million smallholder farmers, many of whom rely on coffee as their primary source of income.
Uganda’s robusta coffee is highly sought after internationally, contributing to the country’s reputation as the second-largest exporter of this variety worldwide. Major players in Uganda’s coffee industry include Olam Uganda Ltd, Ugacof (U) Ltd, Kyagalanyi Coffee Ltd, and Touton Uganda Ltd, all of which promote Ugandan coffee internationally. The coffee industry contributes to the country’s economy but also helps promote Uganda’s agricultural potential globally.
The future of Uganda’s food industry is bright, with strong growth prospects driven by agricultural abundance, rising consumer demand for processed foods, and substantial investments in the sector. As the country continues to leverage its strategic advantages, it will become a key player in the global food market, creating new opportunities for businesses, farmers, and consumers.

By Alphonse Okoth
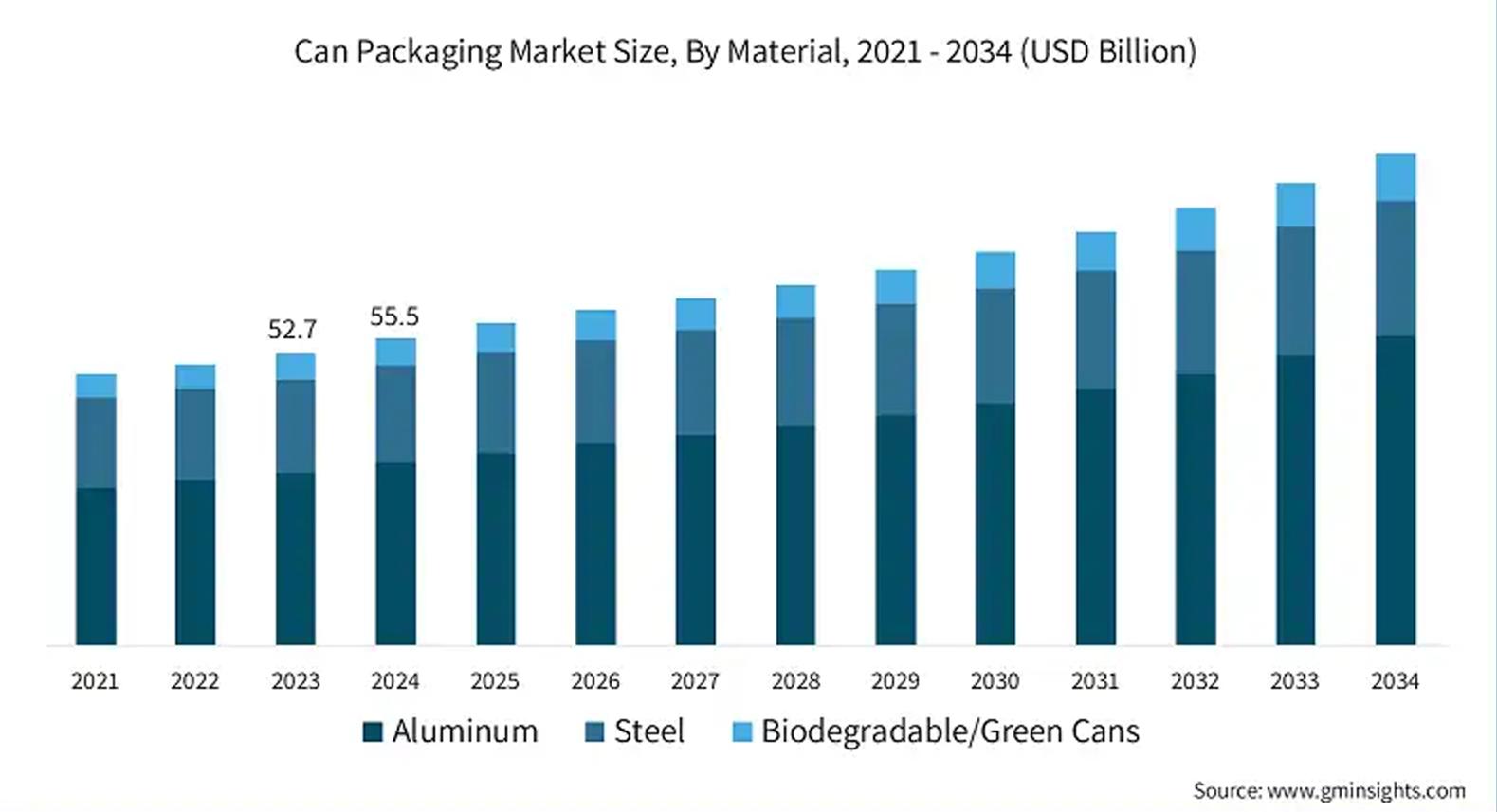
The global can packaging market, valued at US$55.5 billion in 2024, is expected to grow at a steady pace of 4.8% annually through 2034. This growth is fueled by changing consumer preferences, the growing demand for sustainable solutions, and rapid technological advancements. These trends push manufacturers to rethink packaging, striving to meet the demand for eco-friendly, efficient, and convenient options.
Over time, can packaging has evolved significantly, driven by material, design, and technology innovations. These developments address environmental challenges, enhance user experiences, and improve functionality. Industries like food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and chemicals are leading the charge in adopting these breakthroughs. This article explores the key innovations reshaping the can packaging industry.
Sustainable and innovative materials
Sustainability is the driving force behind many of today’s packaging innovations. Manufacturers increasingly turn to reusable, refillable, and recyclable materials, focusing on ecofriendly options like recycled aluminum and biodegradable coatings. Aluminum is becoming more popular due to its recyclability and lower environmental impact than plastics.
For example, Coca-Cola has introduced aluminum bottles that combine sustainability with a premium aesthetic. The company aims to incorporate 35% to 40% recycled material in its packaging by 2035, though its reduced sustainability targets—cutting the goal from 50% by 2030—have drawn criticism from environmental advocates.
Beyond Coca-Cola, other companies are also innovating in sustainable packaging. Amazon, for example, is testing biodegradable delivery bags made from plant-based materials in Valencia, Spain. These bags are designed to replace traditional fossil-fuel-based plastics and have received positive customer feedback.
As the packaging industry evolves, the focus shifts from an all-or-nothing approach to sustainability. Experts predict that by 2025, strategies will become more nuanced, considering factors like material sourcing, production methods, and endof-life disposal.
Smart packaging: Engaging consumers in new ways
Digital technology is revolutionizing the packaging industry into
a dynamic and interactive medium. Companies are elevating packaging beyond its traditional role by incorporating QR codes, near-field communication (NFC) chips, and advanced sensors. Smart packaging enables consumers to access realtime information such as product freshness, traceability, and nutritional details, creating a more informed and engaging shopping experience.
One standout example of this innovation is Heineken, which has integrated NFC-enabled tags into its beer cans. These tags allow customers to access exclusive content, such as personalized promotions, behind-the-scenes brand stories, or interactive games through their smartphones. This initiative has enhanced customer engagement and fostered brand loyalty by offering unique digital experiences tailored to individual preferences.
Moreover, smart packaging technology is improving food safety and waste reduction. Sensors embedded in packaging can monitor temperature changes or detect gas emissions, indicating the freshness of perishable products. This is particularly valuable in the food and beverage sector, where shelf life and quality are critical.
In the pharmaceutical industry, smart packaging is used to improve patient medication adherence. Packaging equipped with digital reminders or tracking systems ensures patients take their prescriptions on time, reducing the risks associated with missed doses.
As digital technology becomes more cost-effective, even small and medium-sized businesses can leverage these innovations. Furthermore, integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning could enable packaging to analyze consumer behavior and preferences, delivering hyper-
personalized experiences.
Functional designs: Combining aesthetics and practicality
Modern can packaging blends visual appeal with practical utility. Innovations like customizable shapes, resealable lids, and ergonomic designs enhance both the aesthetics and functionality of packaging. Ergonomic designs ensure that packaging is easy to open, handle, and store, improving the overall user experience.
Craft beer brands like Sierra Nevada have embraced unique packaging formats, helping to establish a strong brand identity. Offering variety packs with different beer styles caters to diverse consumer preferences and highlights creativity in packaging.
Convenience has become a cornerstone of innovation in the food packaging industry, addressing the diverse needs of modern consumers. Beyond traditional canned goods offering unparalleled shelf stability, brands incorporate user-friendly features like easy-open tabs and resealable options to enhance accessibility. For instance, Del Monte’s introduction of peeloff lids has made their canned goods more convenient for a broader demographic, including children and older people, demonstrating how thoughtful packaging can improve usability without compromising product integrity.
Other companies are also in charge of innovative solutions. Campbell’s Soup has implemented easy-open lids, eliminating the need for can openers and making their products more accessible to a wider audience. Similarly, Hormel Foods has
added pull-tab lids to their canned meats and chilli products, a feature designed to aid consumers with limited hand strength. These advancements reflect a growing industry trend toward designing packaging with inclusivity in mind.
Microwaveable and ready-to-eat packaging options are also gaining popularity. Tetra Pak’s aseptic packaging technology allows products like soups and sauces to be stored without refrigeration and heated directly in the packaging, offering unparalleled convenience and extended shelf life. Meanwhile, Uncle Ben’s Ready Rice pouches provide a quick meal solution, enabling consumers to heat and serve rice in just 90 seconds. These developments cater to time-conscious consumers seeking practical meal options.
Brands are also excelling in single-serve and portable packaging. Chobani’s yogurt cups with attached spoons make on-the-go snacking seamless, while Kraft Heinz offers snack packs like cheese and crackers in resealable containers, ensuring both freshness and ease of use. These designs appeal to busy consumers looking for quick, portable solutions without sacrificing quality.
Flexible and stand-up pouches are also transforming packaging norms. Planters Nuts utilizes resealable stand-up pouches to maintain freshness and allow convenient storage. In contrast, Tropicana’s single-serve juice pouches with attached straws cater to younger consumers, reducing spills and enhancing portability.
These examples highlight the packaging industry’s


dedication to convenience, showing how thoughtful designs can improve product accessibility, cater to diverse lifestyles, and enhance the overall consumer experience. As brands continue to innovate, convenience packaging is set to remain a



key driver of market differentiation and customer satisfaction.
Intelligent packaging: Revolutionizing food safety and quality control
Intelligent packaging transforms how industries ensure product safety, quality, and freshness. By incorporating advanced technologies that monitor external and internal conditions, intelligent systems provide real-time insights into product integrity. This innovation is particularly impactful in sectors like food, pharmaceuticals, and perishable goods, where quality assurance is critical.
One of the most widely adopted features in intelligent packaging is freshness indicators. These visual or digital cues change color or display alerts based on the product's freshness, allowing consumers and retailers to quickly assess whether an item is safe to consume. For example, in the seafood industry, freshness indicators detect spoilage caused by temperature fluctuations during transportation and storage.
Similarly, time-temperature integrators (TTIs) are becoming a standard in the supply chain for perishable goods. These devices track the cumulative exposure of products to temperature changes, providing data that can predict shelf life. TTIs are especially beneficial in cold chain logistics for dairy, meat, and frozen products, where maintaining optimal temperatures is crucial to prevent spoilage.
In the pharmaceutical industry, intelligent packaging has made significant strides in ensuring drug efficacy and patient safety. Packaging equipped with electronic sensors can monitor storage conditions like humidity, temperature, and light exposure, which are critical for maintaining the stability of certain medications. Some systems even feature alerts to notify users if the product has been exposed to harmful
conditions.
Emerging technologies like RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags and NFC (Near Field Communication) chips are taking intelligent packaging to the next level. These innovations enable detailed traceability throughout the supply chain, allowing manufacturers and consumers to access information about a product’s origin, handling, and storage conditions. For instance, smart wine bottles equipped with NFC chips enable customers to verify the authenticity of the product and access details about its vintage and provenance.
Intelligent packaging is also contributing to sustainability efforts. By reducing food waste through accurate freshness tracking, these systems help consumers and businesses avoid discarding products prematurely. Additionally, the data collected from intelligent packaging can be used to optimize logistics and storage, further minimizing resource wastage.
While can packaging is embracing innovation, it faces several challenges. Development costs are a major barrier, as new materials and smart technologies require significant investment. Additionally, raw material shortages, especially in aluminum, tin, and steel, impact production schedules and drive up costs.
Recycling remains a complex issue, especially with the integration of smart packaging features like NFC chips and QR codes, which can complicate recycling. Moreover, supply chain disruptions, as seen during the COVID-19 pandemic, can further hinder production.
Finally, encouraging consumer adoption of new packaging methods can be challenging. Despite growing interest in sustainable packaging, studies show that consumer behavior often doesn’t align with expressed preferences, making it difficult for companies to justify the investment in new solutions without clear evidence of demand.
Despite these obstacles, the can packaging industry continues to innovate, focusing on sustainable, functional, and intelligent packaging. Overcoming these challenges will require collaboration between manufacturers, consumers, and policymakers to create packaging solutions that are both efficient and eco-friendly. FBA

By Francis Watari
As global economies mature and growth slows in traditional markets, forward-thinking investors are turning their eyes toward Africa's rapidly growing food and beverage sector. With a growing population, the demand for food and beverages continues to increase. According to Statista, about 1.3 billion people live in Africa and this number is expected to increase to about 2.5 billion by 2050, presenting a golden opportunity for those willing to invest in Africa's food and beverage industry.
One key driver of this growth is the continent's youthful population. Experts predict the continent will hold this title of "youngest region" well into the future, with a median age hovering around 25 years by 2100. Africa's youth population itself is projected to reach a staggering 850 million by 2050, and by 2063, young people will make up half of the continent's massive 2 billion working-age population.
As incomes rise, so does the demand for quality food and beverages. Urbanization is also playing a significant role, with more African consumers demanding convenient and diverse food products, which opens the door for international food and beverage companies.
The demand for processed and packaged foods, beverages,
and convenience foods is soaring, driven by urbanization and the rise of the middle class. Additionally, Africa's agricultural potential remains largely untapped, offering opportunities for investment in food processing and supply chains to meet domestic and export needs.
In 2024, the continent recorded a sizeable number of investments in the increasingly lucrative food and beverage industries as companies aimed to expand their consumer base. This article will highlight some of the notable investments in Africa's beverage, meat, and dairy industries in 2024, highlighting top trends driving the sectors.
Perhaps one of the most notable investments occurred in the soft drink market, attributed to increasing consumer demand for non-alcoholic beverages. Companies such as Coca-Cola and PepsiCo are leading the charge, with a focus on expanding their production capabilities and distribution networks.
Coca-Cola, currently ranked the world's most valuable brand by Brand Finance has been at the core in revamping the soft drink industry. In September, Coca-Cola Beverages Africa (CCBA) announced expansion of its Nigerian operations, committing US$1 billion over the next five years to the
expansion of production facilities, improving supply chain logistics, and enhancing the company's retail presence across the country.
Additionally, the company plans to invest US$175 million in Kenya over the next five years aiming to accelerate its systems expansion in the region. The company has also invested US$50 million in a new bottling line in Namibia, set to produce 27 000 bottles an hour, boosting production capacity by 30%. During the year, the beverage company also launched a US$27 million production line in Uganda with a capacity of 67,000 bottles per hour, reinforcing its commitment to the African market.
On the other hand, PepsiCo has not been left out in terms of growing its market share. The company, through its subsidiary Varun Beverages Ltd (VBL), has made strategic acquisitions seeking to regain its popularity in Africa. The India-based PepsiCo franchisee started the year on a high note, completing the acquisition of South Africa-based Beverage Company BevCo and its subsidiaries for US$158.28M.
The Pepsi maker consolidated its presence in the continent with the full acquisition of SBC Beverages Tanzania Ltd. (US$154.5M) and SBC Beverages Ghana Ltd. (US$15M). In October, the company announced a US$50 million investment in a production facility in Kiswishi City, Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC).
The alcoholic beverage sector was not left behind in capturing the surging demand for beverages, especially in the premium category. Beverage giants such as Diageo, AB InBev, and Heineken made significant investments in the alcoholic beverage sector through their subsidiaries. Diageo invested over US$63.21 million to expand its production facilities and facilitate community-based projects such as facilitating access
1.3 BILLION PEOPLE LIVE IN AFRICA AND THIS NUMBER IS EXPECTED TO INCREASE TO ABOUT 2.5 BILLION BY 2050 ACCORDING TO STATISTA.
to clean water and promoting sustainable manufacturing practices.
Meanwhile, Heineken committed to reducing its carbon footprint with a US$119.58M investment in the returnable bottle glass program in South Africa. In Rwanda, the brewer invested US$32M to expand its subsidiary Bralirwa Plc. The brewer also revealed plans to invest US$33.1 million in Egypt and acquire Ethiopia-based Komari Beverage.
On the other hand, AB InBev - the world's largest brewer, invested US$80 million for the upgrade of its Zambian Breweries' production plant. The company also boosted its operation in Nigeria, helping its subsidiary International Breweries Plc, to repay an outstanding US$379.9 million loan. Other notable investments include a US$31.5 million investment by Ethiopian-owned Kegna Beverages.
Africa has been increasingly recording an increase in

demand for animal products due to urbanization, which has a considerable impact on food consumption patterns in general and specifically on the demand for meat.
Data from The Regional Strategic Analysis and Knowledge Support System (ReSAKSS) indicate that since 2000, Africa's meat production has experienced significant growth, nearly doubling from 11.59 million metric tons to 19.88 million metric tons by 2020. The continent now contributes approximately 6 percent to global meat production, a notable increase from 4.5 percent two decades ago.
In 2024, the sector recorded some remarkable investments as the industry players aim to meet the rising demand. In November, Brazil-based meat producer JBS signed a memorandum of understanding with Nigeria, allocating US$2.5 billion to the construction of six meat-processing facilities in the region. With a population exceeding 220 million, Nigeria's meat market is one of the largest in Africa, with an estimated annual consumption of over 1.5 million metric tonnes of various types of meat. The country also commissioned an ultra-modern fish hatchery in Calaba, capable of producing 20 million fingerlings and 12 million juveniles annually.
In the South, South Africa's leading pork manufacturer Eskort officially launched its 10,000m² factory extension in Heidelberg, expanding its Gauteng production capacity by 50%. The factory extension includes state-of-the-art equipment, such as the largest continuous box freezer in Africa, capable of freezing 120,000kg of products to minus 18°C every 24 hours.
The dairy industry in Africa has long been characterized by a significant production gap compared to other regions, with major challenges including low milk yields per cow, poor infrastructure, limited access to quality feed and inconsistent market access. Small-scale farmers do most dairy production in Africa with limited technical knowledge and access to market information.
However, the dairy industry is increasingly attracting significant investments as producer countries seek to bridge the gap between production and demand. Algeria, one of the

top dairy producers in Africa, entered into a US$3.5 billion agreement with Qatari-based agricultural company Baladna for the development of what the government termed as the 'world's largest integrated dairy farming and production project'. The project will cover 117,000 hectares and will be segregated into three hubs, each comprising an arable farming operation, a dairy and beef farming operation, and a powdered milk manufacturing facility.
Japan also allocated a US$55,240 grant to the New Horizon Association for Social Development (NHASD) to facilitate the construction of a dairy facility in Balat, Egypt. Since 1994, Japan has contributed over US$10 million to support 179 projects across various sectors in Egypt.
Local governments are also playing a huge role in pushing the reawakening of the dairy industry. Cameroon has unveiled a comprehensive development plan valued at US$500.2 million to boost national milk production by 2035. The plan aims to increase milk production from less than 200,000 tons to 1,146,600 tons over the next 11 years (2024-2035).
The Tanzania Agricultural Development Bank (TADB), in collaboration with the Ministry of Livestock and Fisheries, also launched a US$47 million initiative to empower smallholder


dairy farmers and enhance milk production through strategic partnerships and innovative practices. Tanzania also inaugurated a US$217,000 refurbished dairy research facility at the Tanzania Livestock Research Institute (TALIRI), set to producing improved forage, advancing grassland research systems, and providing advisory and educational services to smallholder dairy farmers.
Nigeria, the most populous country in the continent, also revealed plans to invest approximately US$4.32 million in the construction of 60 Milk Collection Centres (MCC) across the country. Fan Milk Plc, a subsidiary of multinational company Danone, also opened a yoghurt production line in Ibadan, Oyo State, to produce its FanYogo Yoghurt Drink.
"Currently, Nigeria spends US$1.5 billion annually on importing dairy products due to a production deficit. Nigerians consume an average of 1.6 billion litres of milk and its products, but domestic production is insufficient to meet this demand," highlighted Alhaji Kashim Shettima, the Vice President of the Federal Republic of Nigeria.
With a growing population, the demand for dairy products is forecast to continue with an upward trajectory, presenting an opportunity gap for investors. The milk market in Africa is projected to grow by 8.65% (2025-2029) resulting in a market volume of US$33.79bn in 2029, according to Statista.
The global emphasis on health and wellness is significantly influencing food trends in Africa. There is a growing demand for organic, non-GMO, and nutrient-dense foods. Superfoods like moringa, baobab, and chia seeds are gaining popularity for their health benefits, and there is an increasing focus on clean eating and functional foods that promote overall well-being.
In addition, about 84% of consumers surveyed in Kenya, Nigeria, and Ghana are actively looking for minimally processed snacks with added nutrients. Countries are also implementing strategies like imposing sugar tax on beverages to address the ongoing health concerns associated with sugar consumption.
With increasing tourism activity in the African landscape, the demand for authentic African foods that offer a taste of local culture is experiencing a boom. People love local and authentic flavours. Ingredients like baobab, sorghum, and fonio are becoming popular. Enjoy craft beers with African spices, snacks with cassava flour, and fruit juices with local fruits.
A 2022 report revealed that 67% of Ghanaian consumers actively seek out products featuring local ingredients. To cater to this demand, brands must prioritize authenticity in their offerings. Collaborating with local chefs and influencers who embody the cultural essence of the brand can further amplify its authenticity and appeal to consumers seeking a taste of home. This trend goes beyond taste preferences; it is about creating sensory experiences that evoke nostalgia and a sense of belonging.
Busy lives mean people want convenient foods like frozen meals, single-serve drinks, and meal kits. The market for easy meals is expected to grow 8.5% each year from 2023 to 2028. Brands can capitalize on this by launching personalized meal kit subscriptions tailored to individual dietary needs and allergies. Offering customized portion sizes and ingredient options ensures meals perfectly match.
Convenience and hassle-free solutions build brand loyalty and encourage regular consumption. Businesses can also adopt e-commerce platforms such as Glovo and The Bar by Diageo to enhance customers' shopping convenience. This trend is going up because more people have smartphones and better internet access.
Africans are more concerned about how their food choices affect the environment. They want products that are sourced sustainably, made ethically, and create less waste. Brands can capitalize on this by diversifying their plant-based product portfolios and collaborating with suppliers and food technologists to create innovative offerings. Highlighting the health, environmental, and ethical benefits of these products is crucial for resonating with conscious consumers who are increasingly seeking alternatives to traditional animal-based products.
The year 2024 was pivotal for Africa's food and beverage industry, showcasing its resilience and potential as a driver of economic growth and innovation. The sector demonstrated remarkable progress from strategic acquisitions and foreign investments to infrastructure commitments and sustainability initiatives. Businesses that understand the highlighted driver trends and adapt accordingly will be positioned to take advantage of the evolving consumer preferences across the continent. FBA
By Alphonse Okoth
Food safety took center stage in 2024 as nations worldwide faced contamination outbreaks, regulatory overhauls, and renewed efforts to protect consumers. From tragic poisoning incidents in Africa to global bans on hazardous additives, the year underscored the ongoing struggle to maintain safe food systems.
In a heartbreaking crisis, nearly 900 people in South Africa suffered food poisoning between September and November, with at least 22 children losing their lives. Investigators traced the contamination to snacks laced with organophosphates, highly toxic pesticides. The tainted products were primarily sold in informal convenience stores, known locally as spaza shops, raising concerns about regulatory oversight in smallscale retail.
The government responded swiftly. President Cyril Ramaphosa ordered the closure of affected spaza shops and mandated a nationwide registration program to ensure all vendors meet basic safety standards. "We must protect our children and ensure that what is sold in our communities meets strict safety regulations," Ramaphosa stated.
The crisis highlighted a broader issue across Africa—food
safety enforcement remains fragmented, often failing to reach informal markets that serve millions daily. At the annual Food Safety Summit in Johannesburg in May, experts called for standardized testing and better training for small retailers to prevent future tragedies.
On the West African coast, Cape Verde grappled with a mysterious health crisis affecting nearly 1,000 tourists over three years. Visitors reported severe stomach infections caused by bacteria such as Shigella and Salmonella. The outbreaks dented the country’s tourism industry, prompting authorities to tighten hygiene regulations in hotels and restaurants. The incident underscored the need for stronger food safety protocols in regions reliant on international visitors. "Tourism is our economic lifeline, and food safety must be a priority," said a Cape Verde tourism official.
A major food safety scandal unfolded in India when Hong Kong’s Center for Food Safety detected ethylene oxide—a carcinogenic chemical—in Indian spice exports. Popular brands like MDH and Everest faced global recalls, forcing countries to reassess safety standards for imported spices.


"The world trusts Indian spices, and this incident is a wake-up call for the industry to implement stricter quality controls," said India’s Food Safety and Standards Authority spokesperson. The scandal eroded consumer confidence and forced exporters to tighten monitoring of pesticide residues in food products.
2024 saw significant regulatory reforms aimed at strengthening food safety. The U.S. FDA officially banned Red No. 3, a synthetic dye linked to cancer in animal studies, requiring food and pharmaceutical companies to reformulate products by 2027. This move, hailed by consumer advocacy groups, aligns with previous restrictions in the European Union and reflects a broader trend toward reducing synthetic chemicals in food.
Meanwhile, China lifted restrictions on frozen fruit imports but imposed stricter inspection rules to prevent contaminated shipments. Concerns over pesticide residues and bacterial contamination drove the changes, with new regulations requiring exporters to provide detailed reports on agricultural chemical usage. Non-compliance now results in immediate bans or fines.
In Europe, the European Union introduced regulations limiting harmful chemicals in food packaging, targeting bisphenol A (BPA) and per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). European food manufacturers must transition to safer alternatives, prompting innovation in sustainable packaging materials. While industry leaders welcomed the regulation, some small manufacturers expressed concerns about the costs of reformulating packaging processes. Beyond these headline reforms, governments worldwide increased penalties for food safety violations. Australia introduced tougher fines and potential criminal charges for food fraud. Canada’s Food Inspection Agency expanded its recall authority, enabling swifter removal of
unsafe products. Brazil and Japan also introduced policies to improve transparency in food labeling and tighten regulations on supply chains.
The events of 2024 served as stark reminders of the deadly consequences of food safety lapses. On June 7, the World Health Organization marked World Food Safety Day under the theme "Food Safety: Prepare for the Unexpected," emphasizing the need for countries to act proactively rather than reactively.
These developments reinforce the importance of consumer awareness—checking labels, understanding risks, and demanding accountability from food producers. Meanwhile, governments and industry players must collaborate to strengthen regulations, especially in weak oversight regions.
Experts advocate for increased investment in food safety education, advanced testing technologies, and stronger international collaboration. Initiatives such as blockchainbased traceability and AI-powered contamination detection are gaining traction as tools to enhance global food safety networks. Sustainable agricultural practices, including reducing pesticide reliance and adopting organic farming methods, are also emerging as long-term solutions to food safety challenges.
Consumer engagement is another key focus. Governments are launching educational campaigns to help the public recognize food safety risks and make informed choices. Social media platforms are also used to quickly disseminate food recall information, ensuring prompt public awareness of potential dangers.
The global momentum toward stricter food safety regulations, technological advancements, and increased consumer awareness sets the stage for a more resilient and transparent food industry in the years ahead.

By Francis Watari
The way a beverage feels in your mouth—its texture—can make or break your drinking experience. We often talk about flavor and aroma, but the texture is equally vital in making drinks enjoyable. Think about a milkshake's smooth creaminess, the soda's light crispness, or the rich foam of a cappuccino. These sensations don’t just happen; beverage manufacturers carefully design them.
In today’s competitive market, brands are striving for great taste and textures that enhance the overall sensory experience. The right texture can influence how we perceive sweetness, freshness, and quality. Moreover, texture modulation helps brands cater to diverse consumer preferences, from healthconscious individuals seeking low-calorie options to those craving indulgent, creamy beverages.
This article delves into the science and art of texture modulation in beverages, exploring how innovative ingredients, advanced technologies, and reformulations shape the drinks we love.
The role of ingredients and additives
Creating the perfect texture starts with choosing the right ingredients. Hydrocolloids like xanthan gum, pectin, guar gum, and carrageenan help thicken, stabilize, and improve mouthfeel without affecting flavor. For instance, The CocaCola Company uses a blend of pectin and xanthan gum in its fruit-based beverages to create a more natural, pulpy texture, replicating the experience of fresh juice.
Emulsifiers such as lecithin and Polysorbate 80 play a crucial role in blending oil and water-based ingredients, ensuring a smooth, uniform texture. This is particularly vital for plant-based dairy alternatives like Oatly and Silk, where these additives help recreate traditional dairy milk's rich, creamy consistency, enhancing the overall drinking experience.
Beyond plant-based milk, emulsifiers are also essential in other beverage categories. For example, in coffee creamers such as Nestlé’s Coffee-mate, mono- and diglycerides stabilize the mixture, preventing separation and ensuring a velvety mouthfeel. Similarly, emulsifiers in protein shakes like Premier
Protein and Muscle Milk help distribute protein particles evenly, avoiding sedimentation and improving drinkability.
In soft drinks and flavored waters, emulsifiers such as gum arabic and sucrose esters incorporate fat-soluble flavors, ensuring a consistent taste from the first sip to the last. This technique is widely used in citrus-flavored beverages like Fanta and Mountain Dew, where oils from fruit peels must remain suspended in the liquid.
Beverage type and temperature
Carbonated drinks, like Pepsi or Red Bull, must remain light and refreshing, avoiding excessive viscosity that could dull their crispness. Meanwhile, dairy and plant-based beverages benefit from a rich, creamy texture achieved with stabilizers. Functional drinks like protein shakes face the challenge of avoiding grittiness while maintaining a satisfying mouthfeel. Brands like Muscle Milk and Soylent use maltodextrin and other stabilizers to ensure a smooth, enjoyable texture.
Temperature also plays a significant role. A warm latte, for example, must remain stable and creamy without separating, while an iced coffee should maintain its texture even as it cools. Starbucks relies on carrageenan and pectin to keep lattes consistent at different temperatures.
Consumer demands for clean labels
Today’s consumers want healthier, more transparent ingredient lists. According to a 2023 Innova Market Insights report, 65% of global consumers read ingredient labels before purchasing beverages. In response, brands are shifting away from synthetic additives and opting for natural alternatives.
Take Bolthouse Farms, for example. The brand uses pea protein and oat fiber to maintain texture in its protein smoothies without relying on artificial stabilizers. Similarly, Tropicana has introduced pulpy juice options that cater to consumers who prefer a more natural mouthfeel.
A growing trend in beverages is including real ingredients—such as fruit pieces, seeds, or cereal—to enhance texture naturally. According to Mintel’s 2023 study, 40% of consumers enjoy drinks with varying textures. This has led to brands like Innocent Smoothies incorporating chia seeds and fruit pulp into their beverages to create a more interactive drinking experience.
In the clean-label realm, hydrocolloids derived from natural sources are gaining popularity. For example, pectin, derived from fruits, and

guar gum, a natural thickener from guar beans, are both clean-label-friendly and capable of providing the desired thickness and smoothness. This trend extends to plant-based emulsifiers like lecithin from sunflower, replacing synthetic emulsifiers to appeal to health-oriented consumers. Using such natural ingredients, companies create beverages that resonate with health-conscious audiences while delivering on texture and mouthfeel.
Juices with inclusions (for example, pieces of fruit or cereal) not only provide a unique texture experience, but they can also provide functionality (for example, protein and fiber or make the drink more filling) and attract 36% of consumers, according to a survey done by Mintel (2018) using a base of 1,552 Internet users over the age of 18 who bought any juice in the three months before the survey, in the United States.
Reformulating beverages to reduce sugar, fat, or salt presents a challenge: these components contribute to the mouthfeel, so removing them can significantly alter the sensory experience. Sugar provides viscosity and body, fat enhances creaminess, and salt balances flavors.
CONSUMERS WANT HEALTHIER, MORE TRANSPARENT INGREDIENT LISTS, WITH 65% OF GLOBAL CONSUMERS READING INGREDIENT LABELS BEFORE PURCHASING
To compensate, manufacturers use taste and texture modulators. PepsiCo’s Tropicana Light, for example, uses fruit fibers and stevia-based modulators to maintain sweetness and texture without sugar calories. Similarly, Nestlé has developed fat mimetics, such as protein- or polysaccharide-based structures, to restore the creamy texture lost when reducing fat in its products.
Emerging technologies like 3D printing are revolutionizing beverage texture. In high-end coffee markets, this technology creates custom foam layers, adding depth to lattes and cappuccinos.
Nestlé has explored 3D-printed foam structures to enhance aeration in its ready-to-drink coffee lines, offering a unique sensory experience. Additionally, 3D printing is being tested in the craft beer industry, where brewers experimented with structured foam designs that enhance the aroma and presentation of specialty beers.
Other innovations, such as microencapsulation, allow manufacturers to control how ingredients are released in the mouth, creating dynamic textures that evolve as you drink. This is being explored in sports nutrition beverages, where layers of flavor and texture can change during consumption.
Companies like Gatorade and Powerade are developing microencapsulated electrolyte beads that burst at different intervals, providing a more engaging drinking experience. Similarly, dairy-free yoghurts and probiotic drinks incorporate microencapsulation to protect live cultures, ensuring optimal release and stability over time.
Another cutting-edge technology is high-pressure processing (HPP), which modifies beverage textures while
maintaining freshness and extending shelf life. This technique is used in cold-pressed juices and plant-based milks, where it enhances smoothness without the need for excessive stabilizers. Brands like Suja and Innocent have adopted HPP to deliver fresher, silkier textures while preserving nutritional integrity.
Texture modulation is no longer just a technical consideration; it’s a powerful tool for shaping consumer perception and building brand loyalty. As clean-label trends dominate, manufacturers will explore bioengineering techniques to refine textures even further. The future may see beverages tailored to individual preferences, offering personalized textures catering to sensory experiences.
As Dr. Emily Carter, a food scientist at the Institute of Beverage Innovation, explains, “Advancements in bioengineering and precision fermentation will allow us to create textures that mimic traditional dairy without artificial additives, making plant-based beverages more appealing to mainstream consumers.”
Similarly, consumers are becoming more sophisticated in their expectations. They want drinks that not only taste good but also feel premium. Texture is now a key differentiator, and brands that master it will have a competitive edge.
For brands looking to stand out, mastering texture modulation isn’t just about science—it’s about delivering a delightful, memorable drinking experience that keeps consumers returning for more. Whether it’s the velvety feel of a smoothie, the crisp refreshment of a soda, or the creamy foam of a cappuccino, the texture makes a drink genuinely satisfying. FBA

















