FRCPath Part 2 Surgical Course
Head & Neck Pathology
Consultant Head & Neck Pathologist William Harvey Hospital, Ashford, Kent
Eranga Nissanka-Jayasuriya
Marking Scheme
Case 1
3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0
Case 1
26-year-old, Female, Parotid tumour

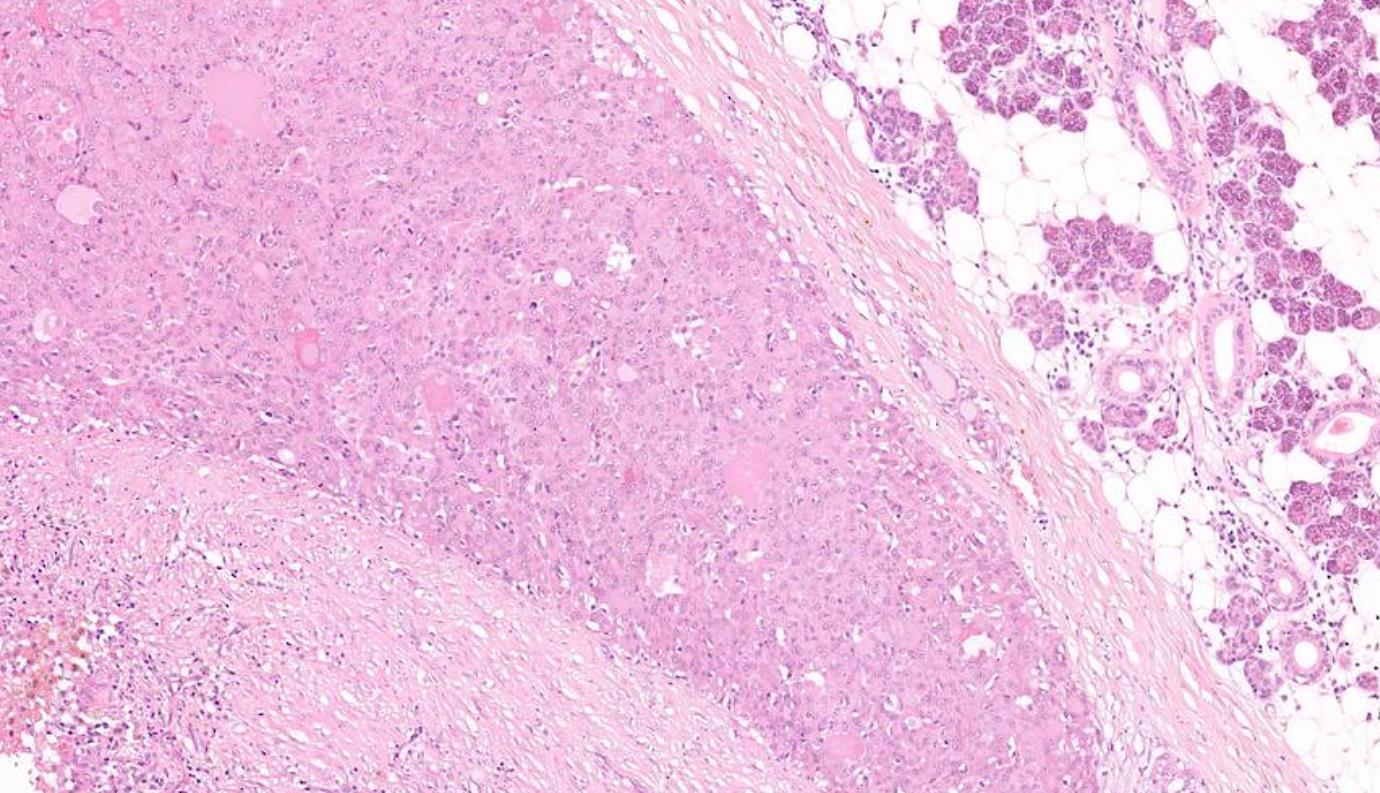

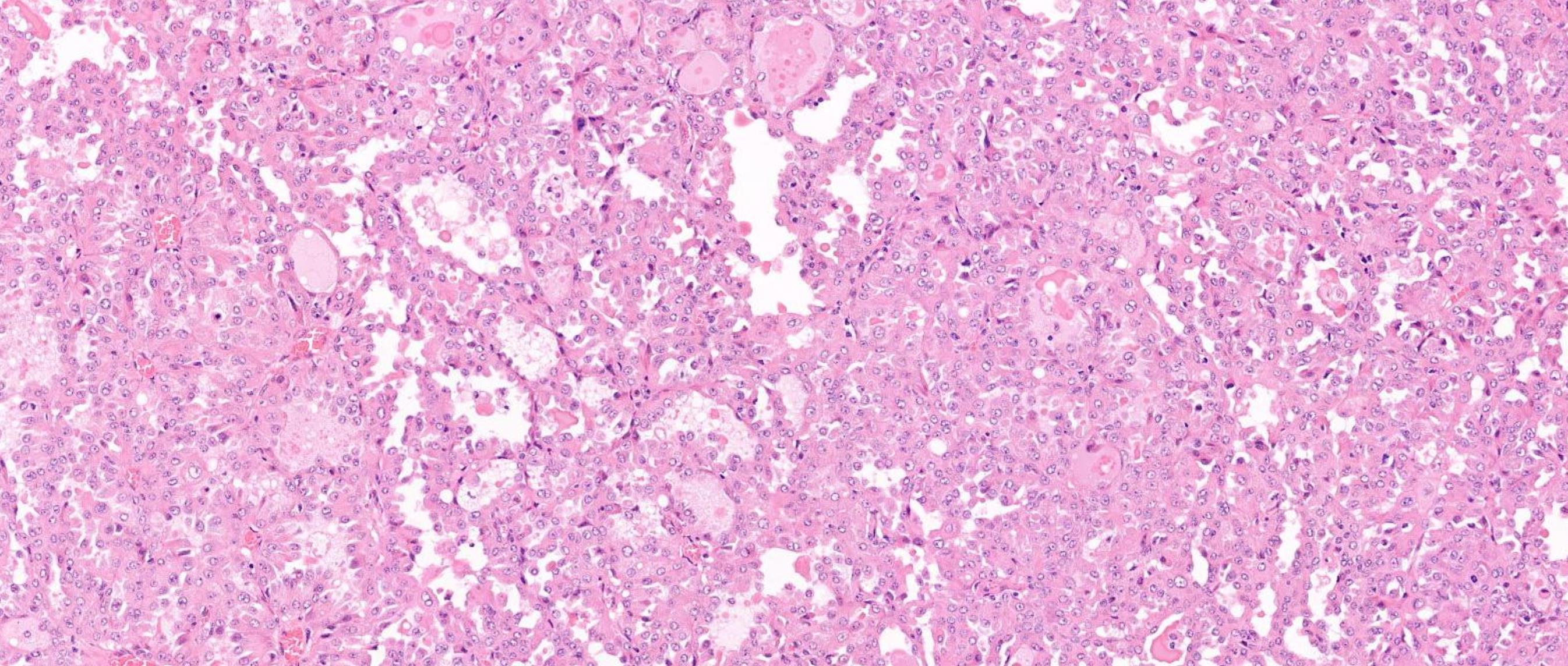

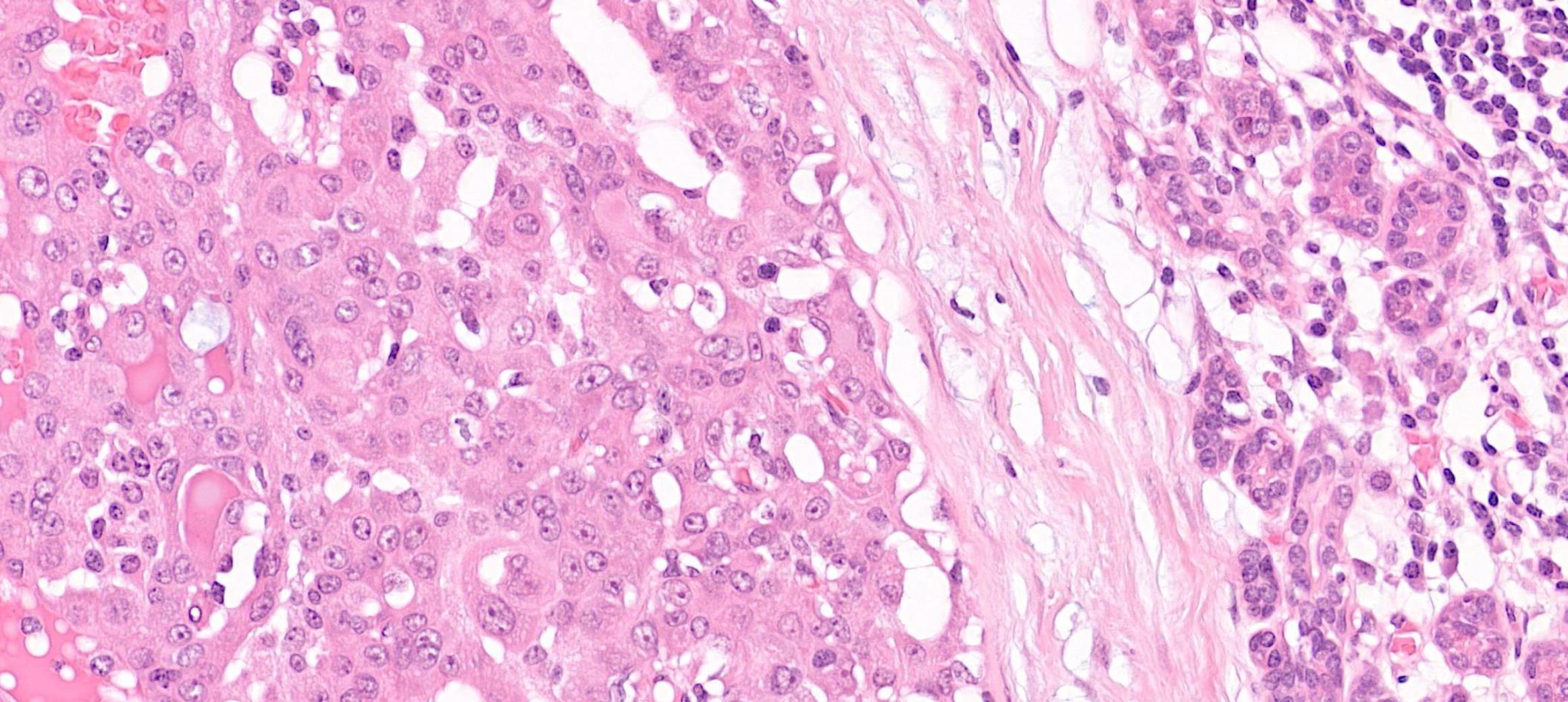
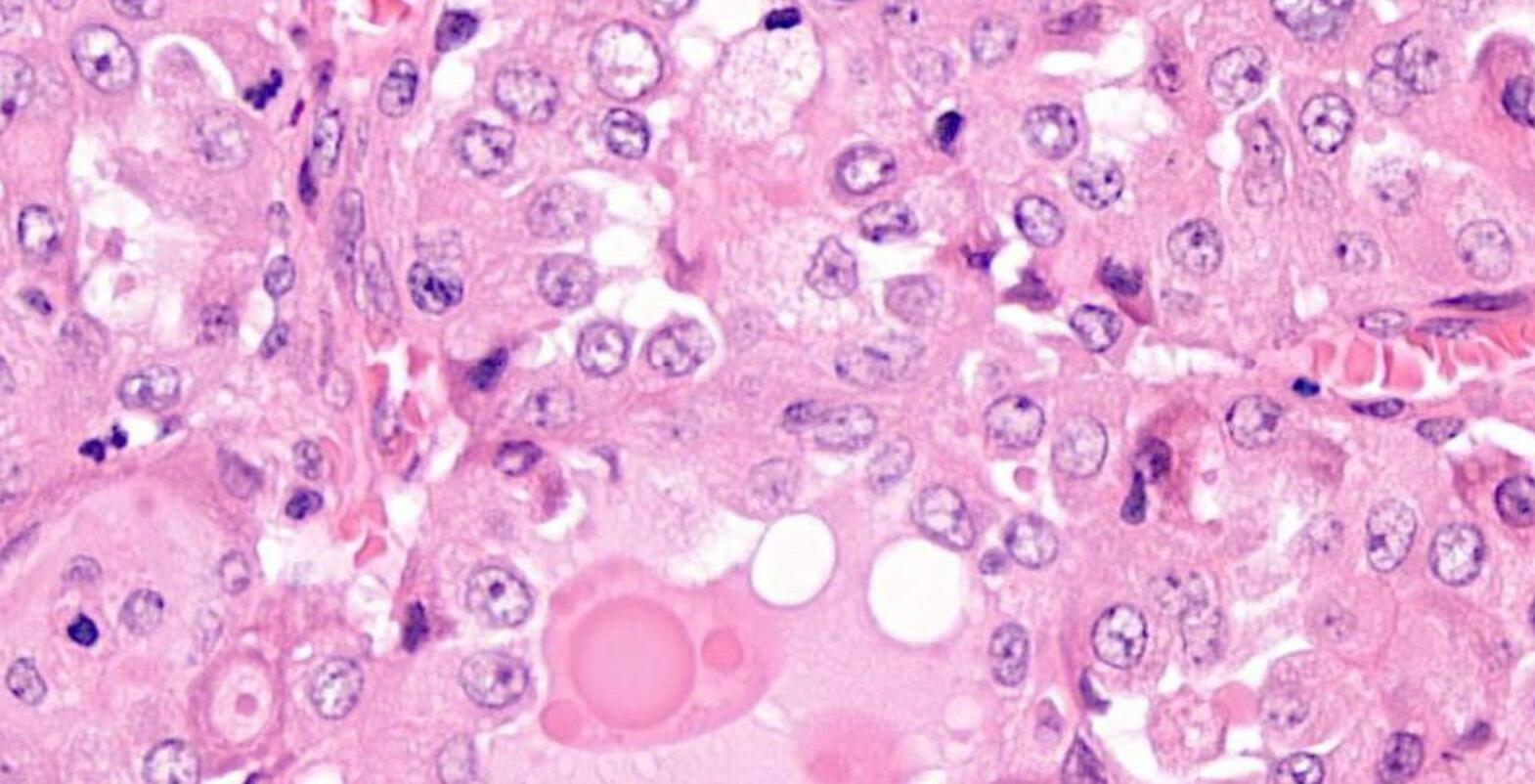
??
Case 1- Salient points • Circumscribed salivary tumour, infiltrative periphery • Papillary cystic, microcystic patterns, hobnailing • Solid sheets of large polygonal cells with granular eosinophilic cytoplasm and vesicular nuclei • Secretory material –colloid-like eosinophilic secretions • Occasional mitotic figures • Work up? PAS, DPAS, • CK7, S100, DOG1, Mammoglobin
Case 1 Diagnosis
Secretory carcinoma
Discussion Differential diagnoses • Acinic cell carcinoma • Secretory carcinoma (previously called MASC) • MEC • 90% -ETV6::NTRK3 fusion -chromosomal rearrangement, t(12;15) (p13;q25) • ETV6::RET, ETV6::MET, ETV6::MAML3 • ETV6 translocation-negative secretory carcinoma. • Similar to Acinic cell carcinoma • But S100+, Mammoglobin+, DOG1-

Mammaglobin







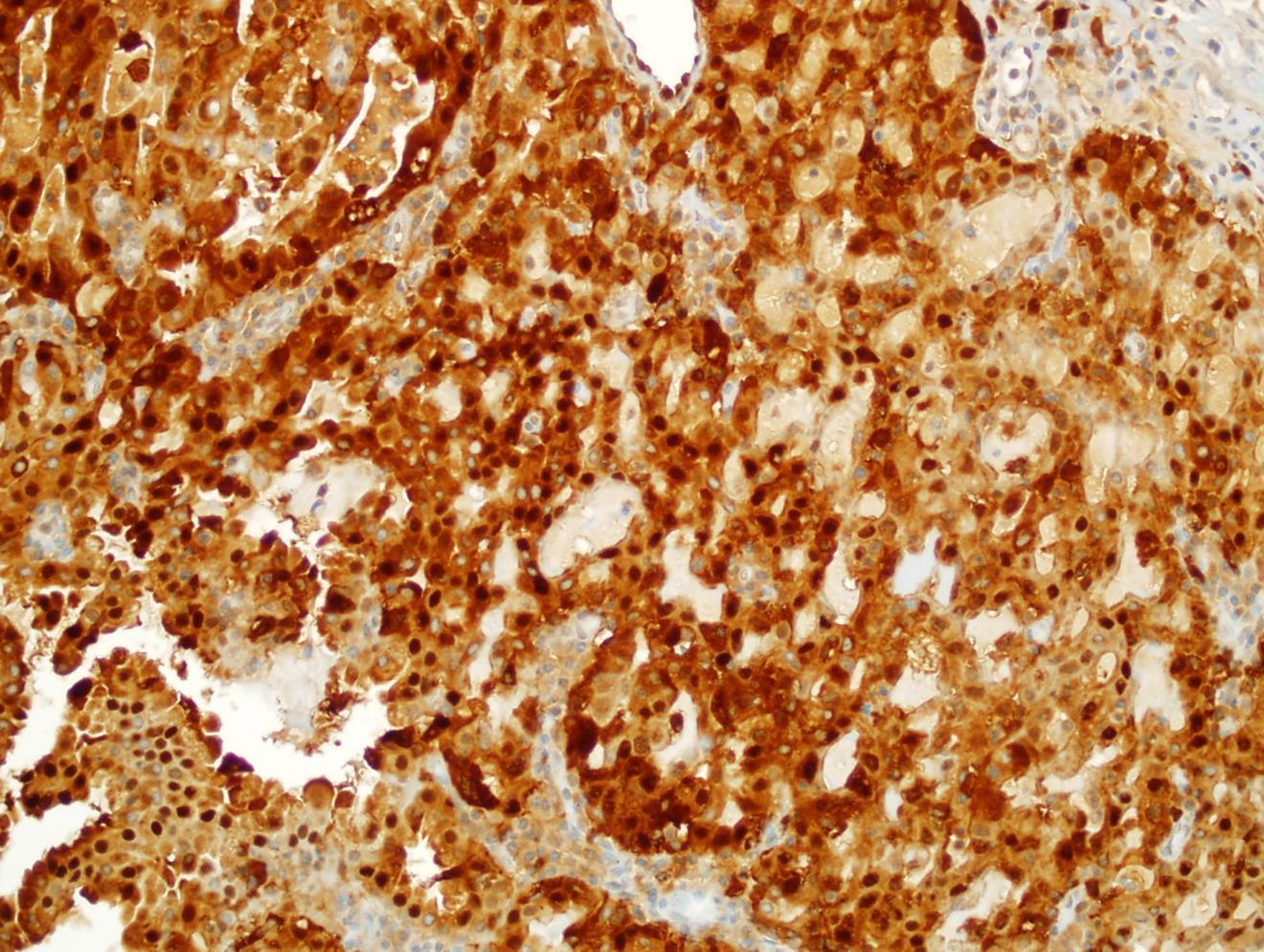

S100
GATA3


ETV6
FISH
WHO
5th ed Essential and desirable diagnostic criteria • Essential: single cell type with vacuolated colloid-like secretory material; no zymogen cytoplasmic granules; IHC positivity for S100 protein, SOX10, and mammaglobin; lack of IHC staining for p40 and/or p63 • Desirable: ETV6 or RET rearrangement demonstrated by FISH, RNA sequencing, or PCR • Low grade • Lymph node metastases are reported in as many as 25% of cases
Case 2 56-year-old, Male Dysphagia And Lump In Pharynx



Case 2- Salient points • Multicystic and solid • Epidermoid, clear cells and mucous cells • Low grade- predominantly cystic • Work up? ABPAS, DPAS • CK7, P63 • Molecular: translocation at t(11;19)(q21;p13) expressing CRTC1::MAML2 fusion gene • DD-papillary cystadenoma, mucous retention cyst
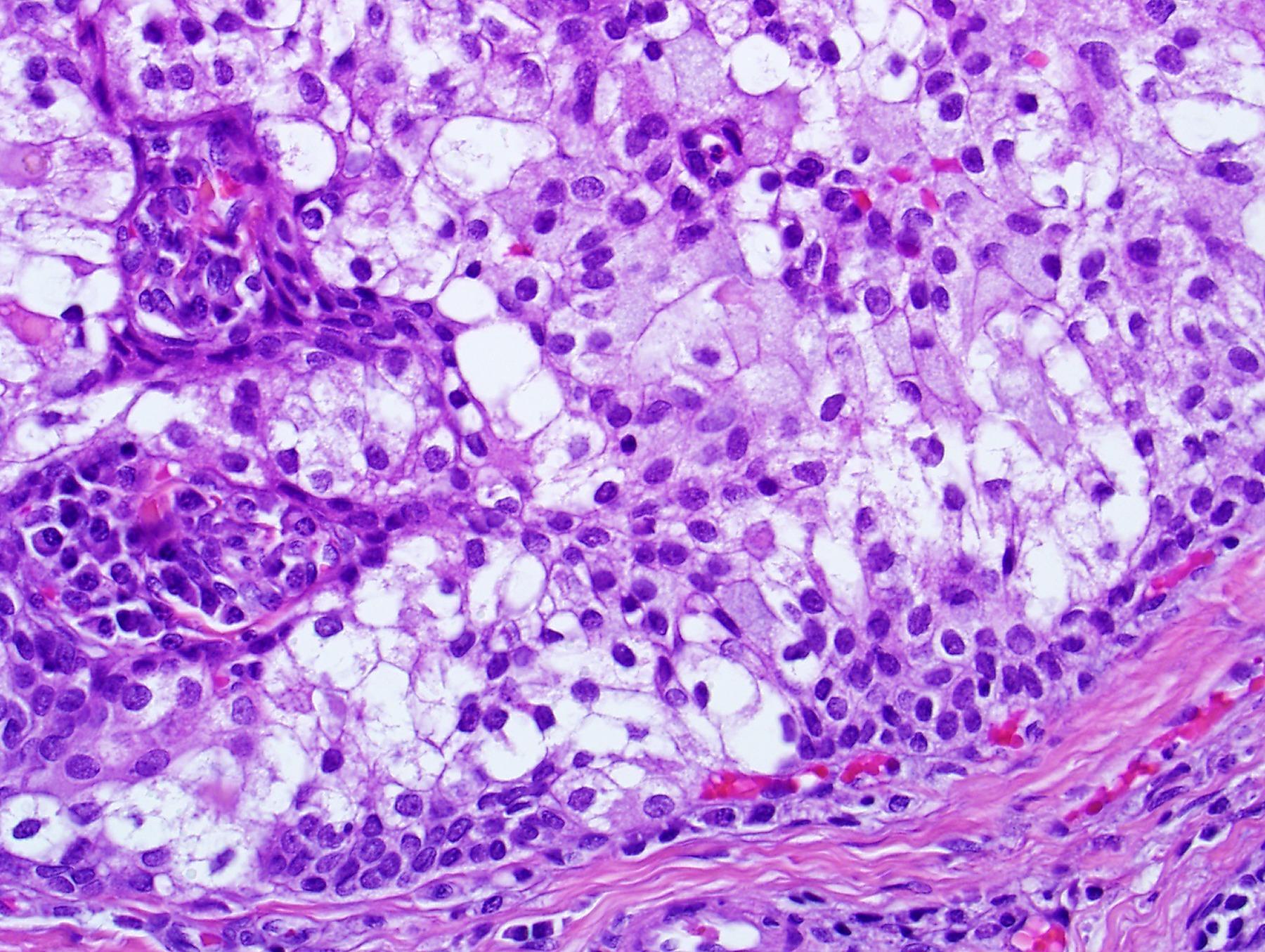
??
Case 2 Diagnosis
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma, low grade
MEC Grading
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1544111
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9529011, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11420454, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25040772
commonest grading system:
-Intracystic component <20% -Neural invasion -Necrosis -Mitoses >4/10 hpf -Ananplasia
Other grading systems:
Selected genetic alterations in salivary tumours Selected Genetic Alterations in Salivary Gland Tumors
Tumor

Acinic cell carcinoma
Alteration
% cases
HTN3-MSANTD3 fusion 95% 5%
NR4A3 fusions
Adenoid cystic carcinoma MYB-NFIB MYBL1-NFIB MYB activation/amplification
Basal cell adenoma/ Basal cell carcinoma
~80%
CTNNB1 or CYLD mutation 40-80% (adenoma) 5-30% (carcinoma)
Clear cell carcinoma EWSR1-ATF1 ~80-90%
Epithelial-Myoepithelial Carcinoma PLAG1 or HMGA2 fusions HRAS mutations ~50%
Low-grade intraductal carcinoma NCOA4-RET ~50%
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma CRTC1-MAML2 CRTC3-MAML2 ~70-80%
Pleomorphic adenoma and carcinoma expleomorphic adenoma PLAG1 or HMGA2 fusions ~60-90%
Polymorphous adenocarcinoma ARID1A-PRKD1
DDX3X-PRKD1
Other PRKD2 and PRKD3 fusions
Salivary duct carcinoma
TP53, HRAS, PIK3CA, PTEN mutations ERBB2 amplification PLAG1 or HMGA2 fusions
Secretory carcinoma
ETV6-NTRK3 ETV6-RET ETV6-MET
~20-50%
90-100%
100%
21-year-old, Female, Lump In Floor Of Mouth.
Case 3

Case 3- Salient points
•
•
•
Pseudocyst lined by compressed rim of foamy macrophages
No epithelial lining
Associated with atrophic minor salivary glands
??
Case 3 Diagnosis
Mucous extravasation cyst (extravasation mucocoele)
• Female 40 years Firm nodule dorsum of tongue. Present for months. Case type Oral. Specimen: Tongue. Macroscopic description: Mucosa 15 x 12 mm with firm tissue to depth of 9 mm.
HN4 Case 4
Immunohistochemistry: None.

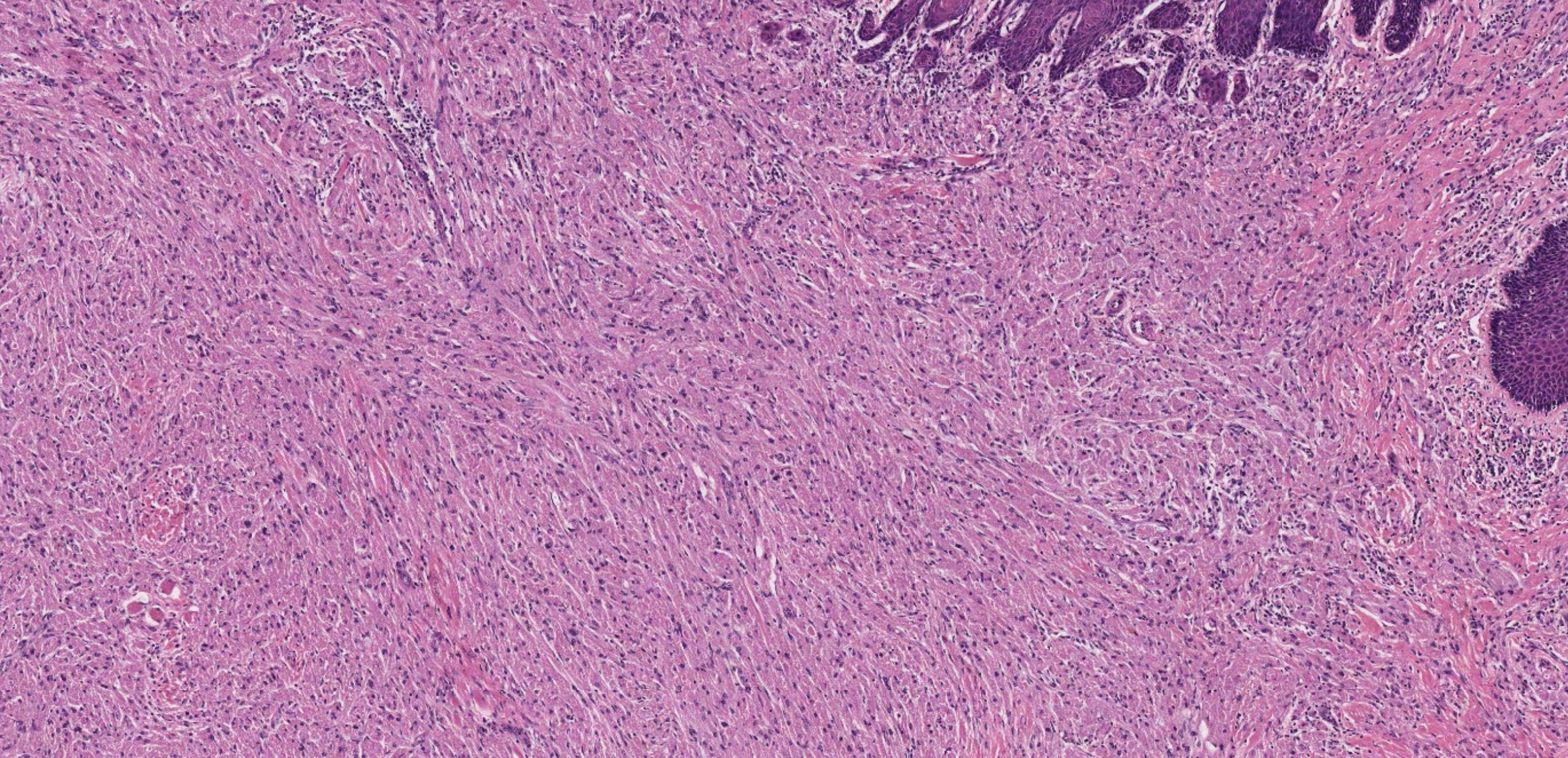

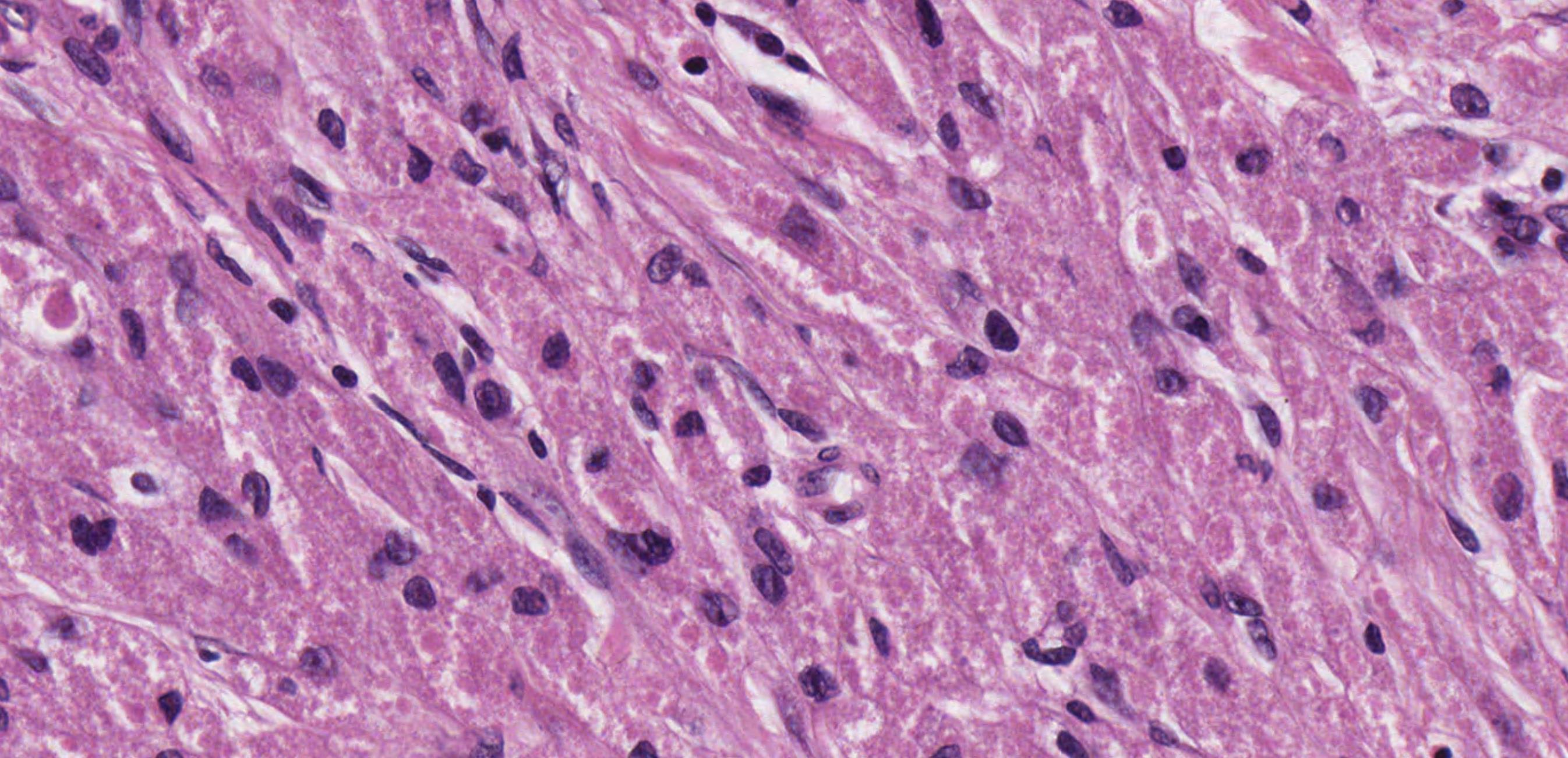

• Nodular mucosa with circumscribed tumour with infiltrative periphery • Large cells with eosinophilic granular cytoplasm • Is surface epithelium normal?
Case 4- Salient points
??
Case 4 Diagnosis
Granular cell tumour
16-year-old, Female, Cyst Associated With Unerupted Lower Wisdom Tooth.

Case 5


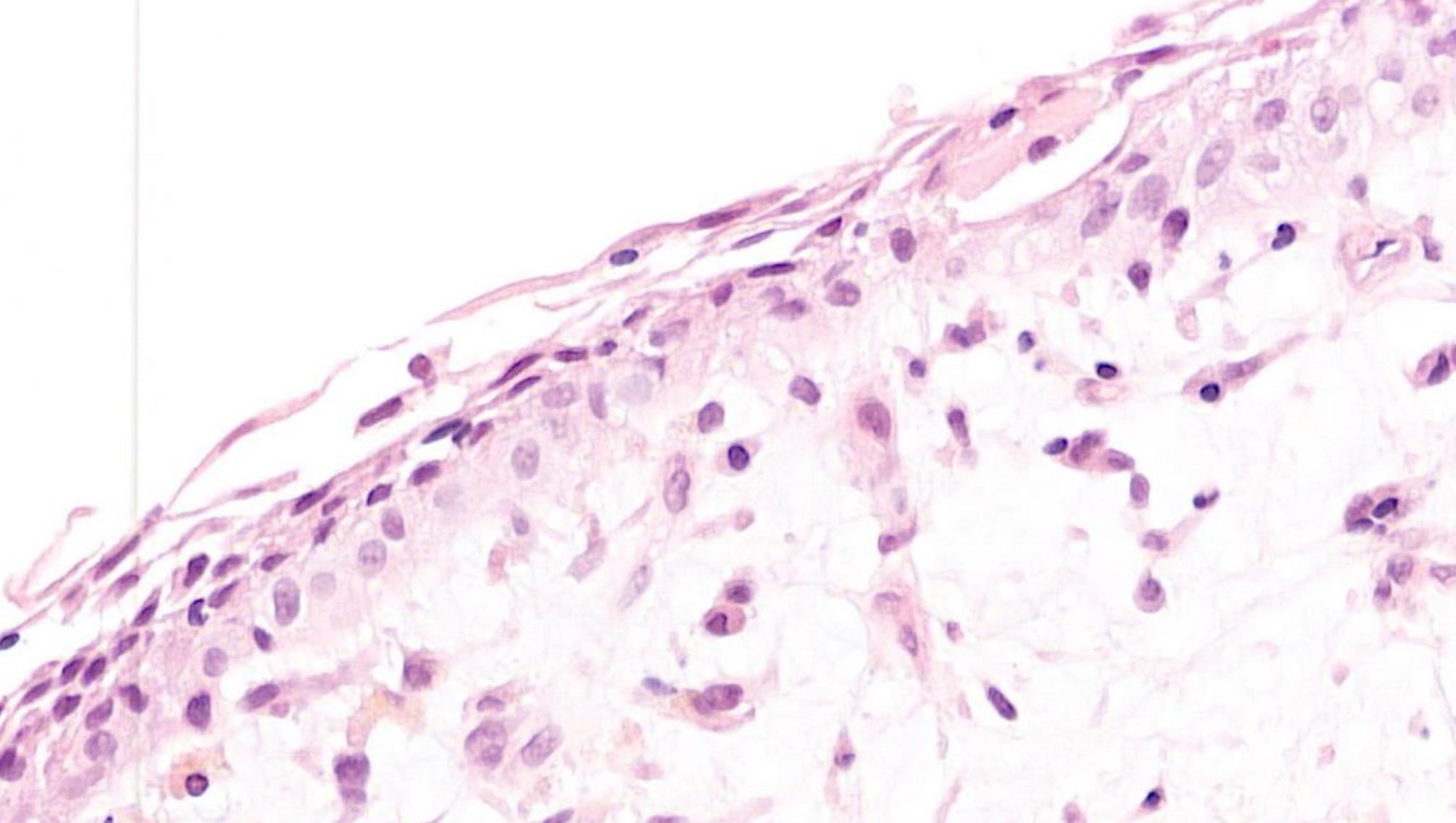
Case 5- Salient points • Non-specific thin squamous epithelial lined cyst • No keratinisation, basal palisading • Largely uninflamed fibrous cyst wall • Location + histology
??
Case 5 Diagnosis
Dentigerous cyst
Common odontogenic cysts & tumours
• Dentigerous cyst • Radicular cyst • Odontogenic keratocyst • Orthokeratinised odontogenic cyst • Ameloblastoma • Radiology is a must- Location, relationship to tooth and nature of radiolucency can give diagnostic cluses

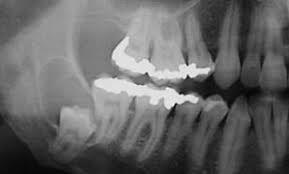
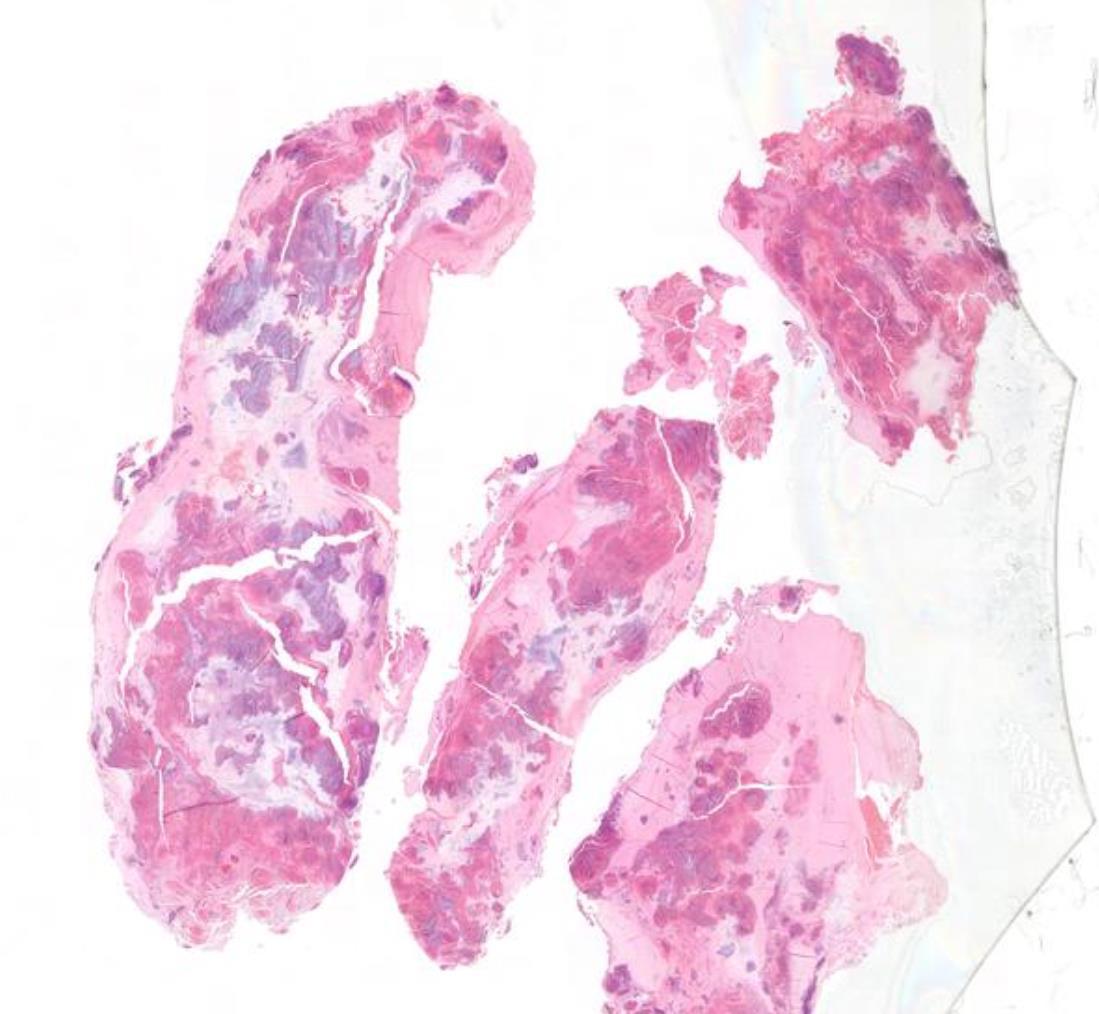
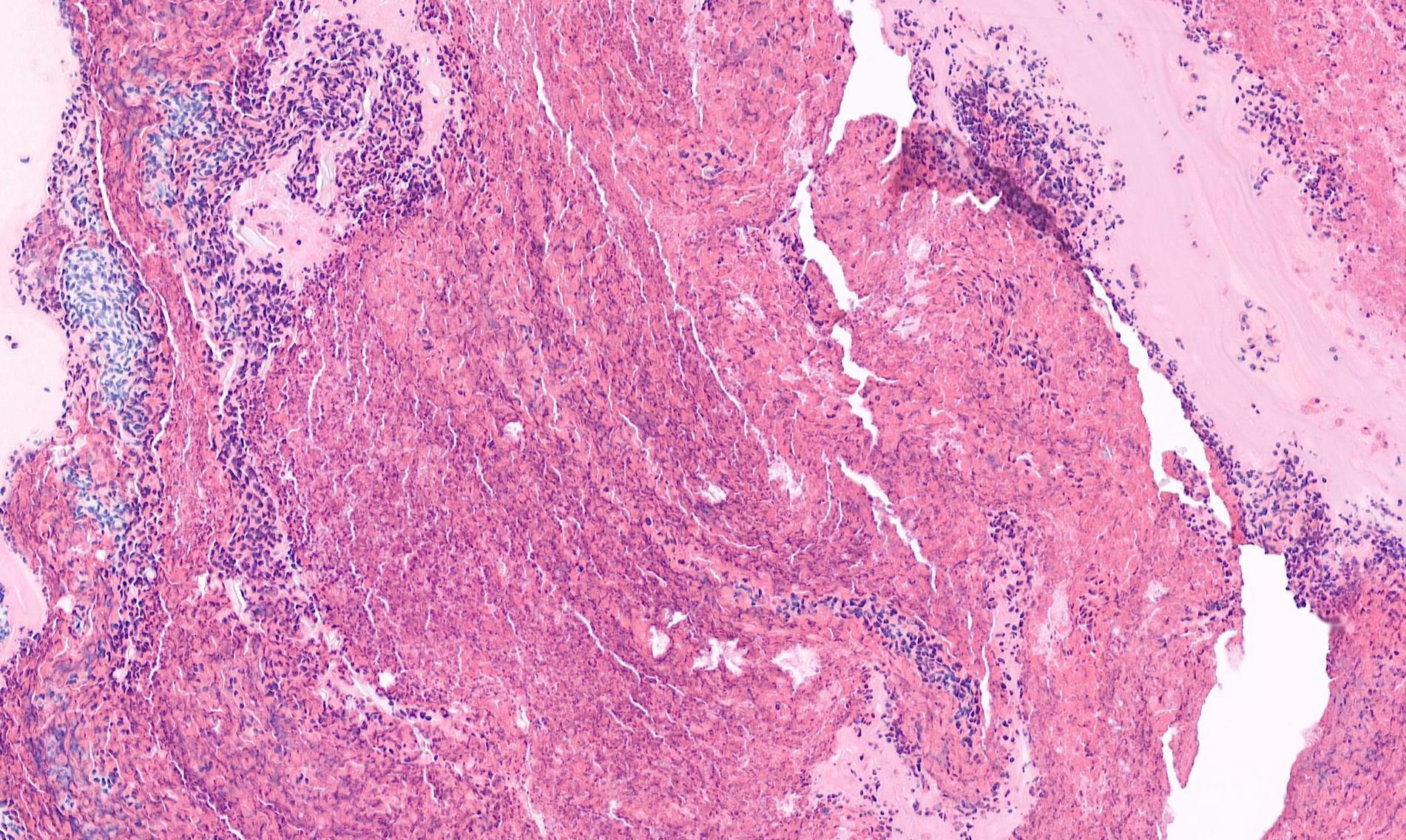
Case 6 28-year-old, Male
Nasal Polyp.


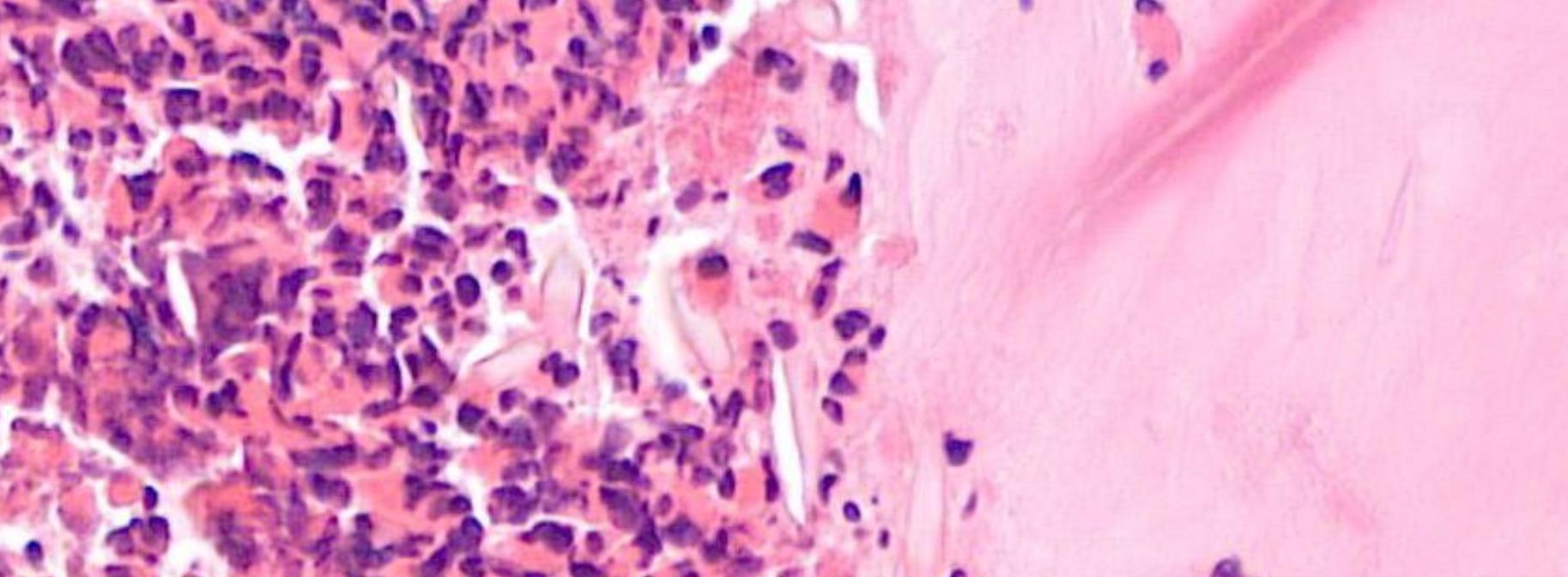

??
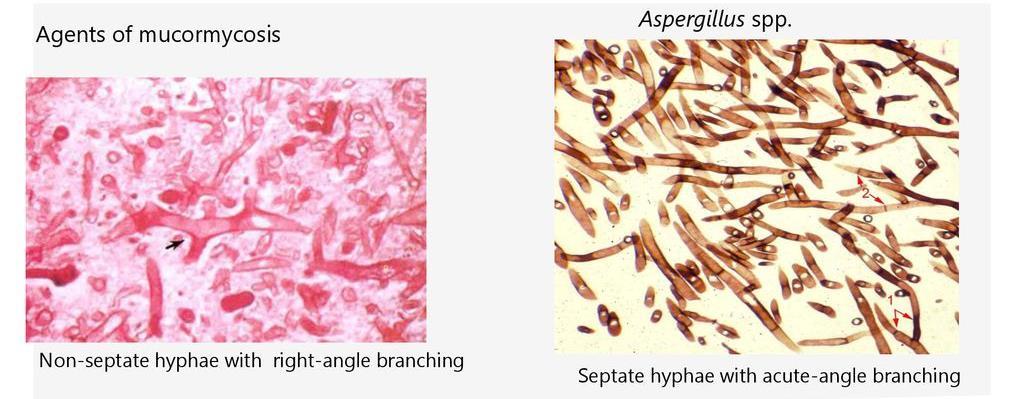
Salient points • Laminated mucin • Degenerate eosinophils • Charcot-Leyden crystals • Fungal hyphae (usually fungal ball)
Case 6 Diagnosis
Allergic fungal rhinosinusitis

Case 7 62-year-old, Female Block From Maxillectomy Specimen.




Case 7- Salient points
• SCC • Is lymphoid tissue normal- small monotonous sheets, no follicles • Work up- IHC
??
Case 7 Diagnosis
Squamous
cell
carcinoma
and Lowgrade small cell lymphoma (Grade 1 follicular type NHL)
•
Male 14 years
Spontaneous swelling of the lower lip and mucosa generally. Unresponsive to antivirals. No other relevant medical history.
Specimen: Left buccal mucosa.
Macroscopic description: punch biopsy 4x3x3mm.
Immunohistochemistry: D/PAS negative.
Case 8
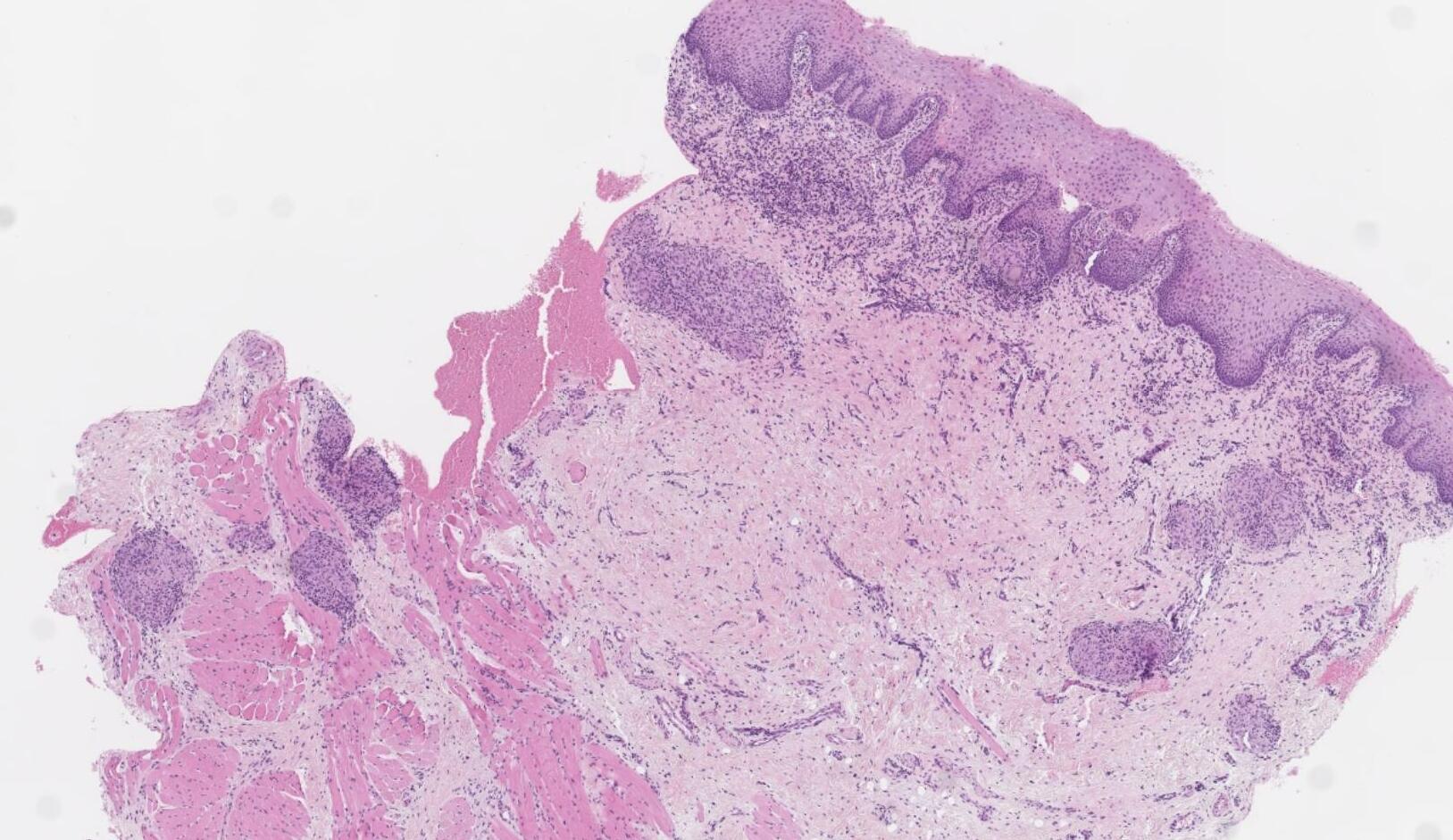

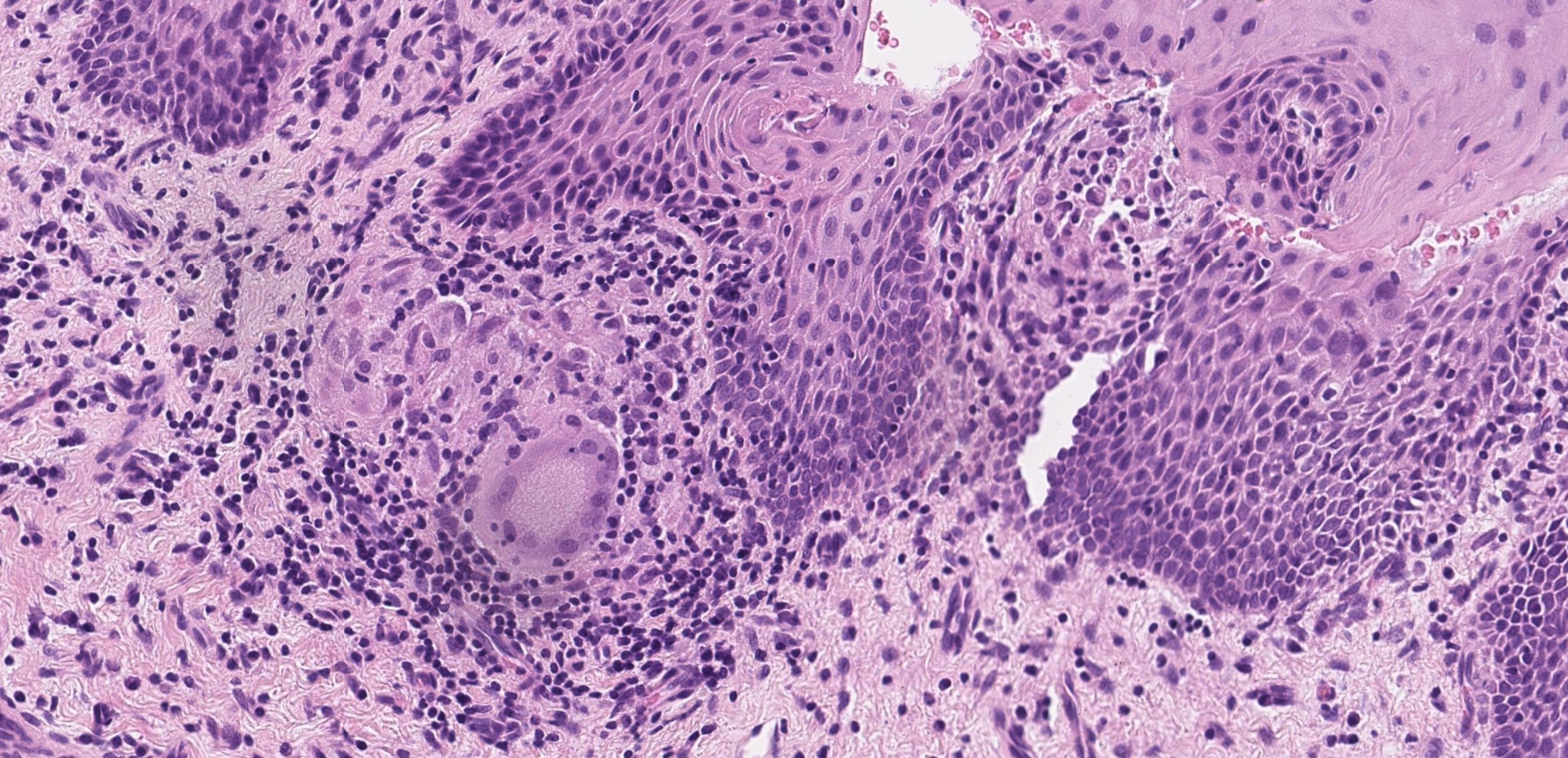
??
Case 8 Diagnosis
Oral granulomatous inflammation likely orofacial granulomatosis
• Cobblestone cheek swelling and lip swelling • Children, young adults • Associated with sarcoidosis and Crohn’s disease (could be the presenting feature before GI symptoms start)
Case 9
38-year-old Female, Cyst Associated With Unerupted Wisdom Tooth.



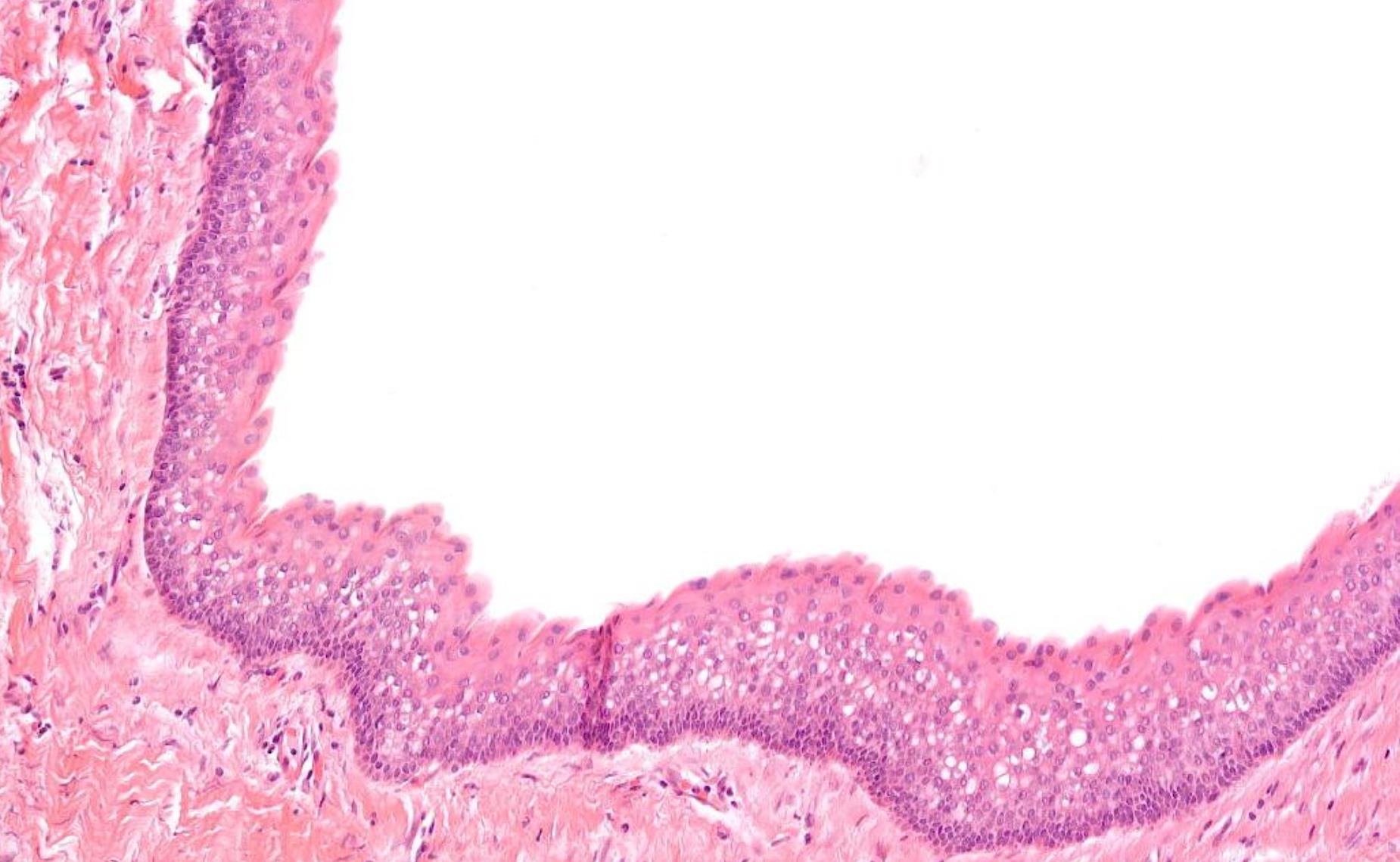
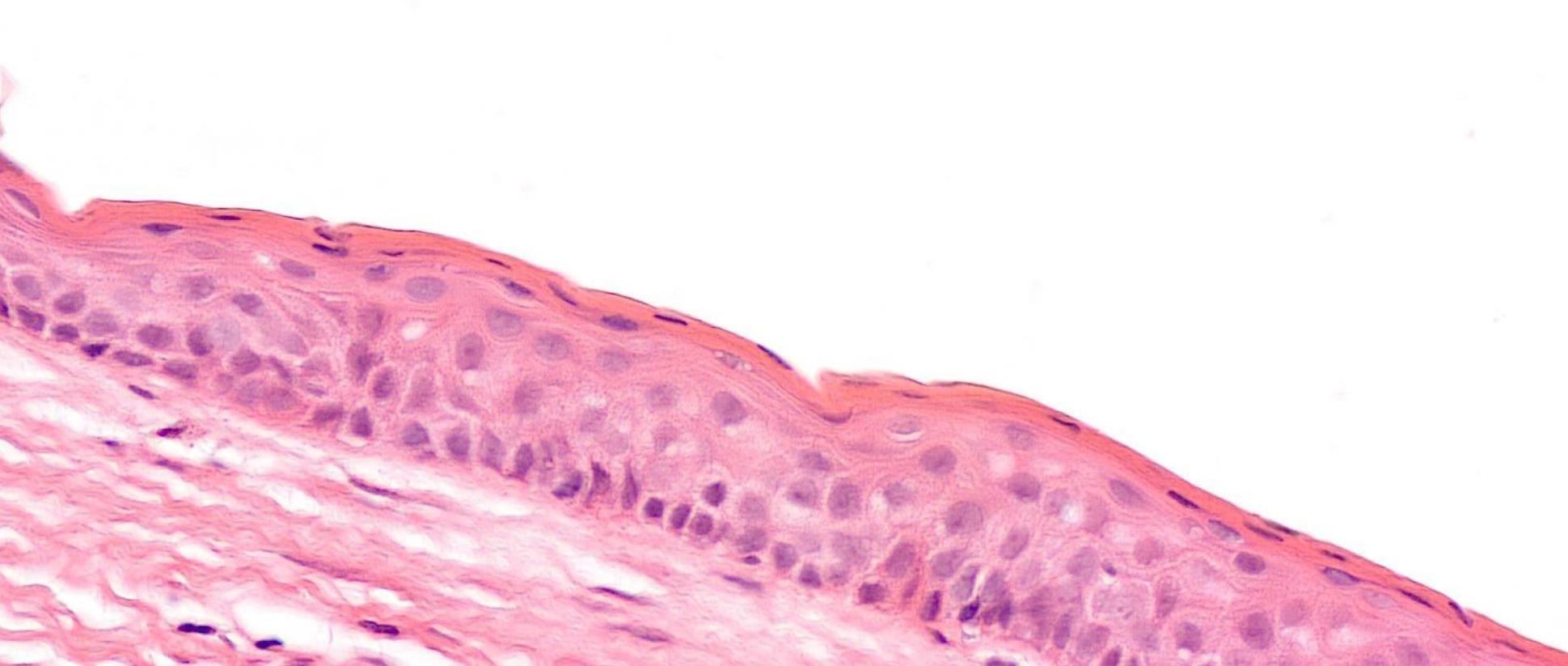


??
Case 9 Diagnosis
Odontogenic keratocyst
Salient points •Basal cell palisading •Corrugated parakeratosis •Focal inflammation –loss of above and “non-specific” features •Consistent loss of PTCH tumour suppressor gene- GorlinGoltz syndrome •Tendency for recurrence
Case 10 66-year-old Excision Of Tumour Tongue / Floor Of Mouth.



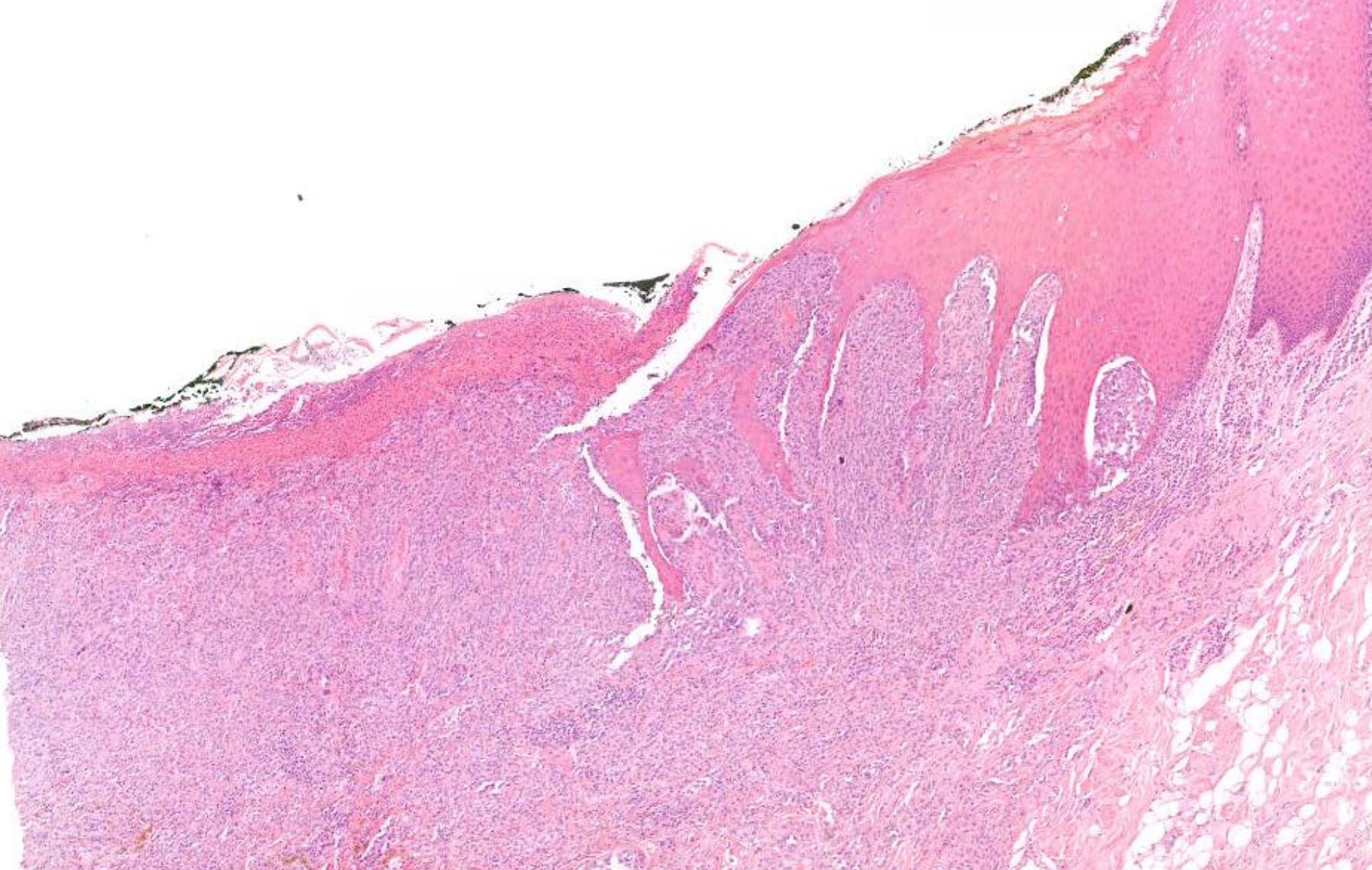


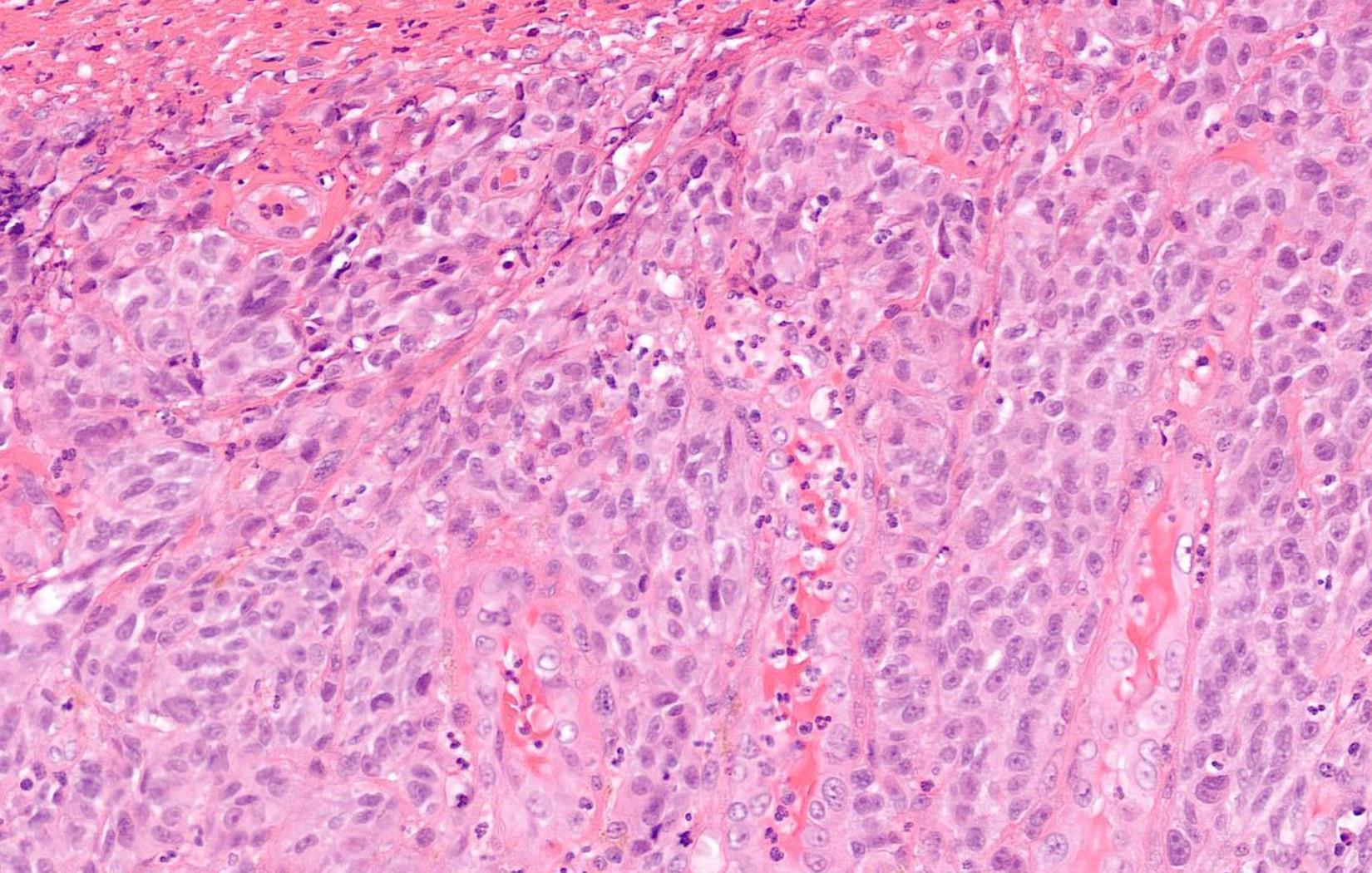



??
Case 10 Diagnosis
Mucosal melanoma
• 80% of head and neck MM- nasal cavity, septum, maxillary sinus • In the oral cavity-maxillary gingiva and palate • Flat pigmented lesions • Tumour cells are polymorphic • Lentiginous/pagetoid growth pattern • All head and neck mucosal MM are T3–4 and stage III-IV • T3 Tumour limited to the epithelium and/or submucosa (mucosal disease) • T4a Tumour invades deep soft tissue, cartilage, bone, or overlying skin • Oral pigmented patches DD • Melanotic macule • Smokers melanosis • Amalgam tattoo • Naevi
Case 11
Numbness Of Face (Distribution Of Infraorbital Nerve) Biopsy From Infratemporal Fossa.

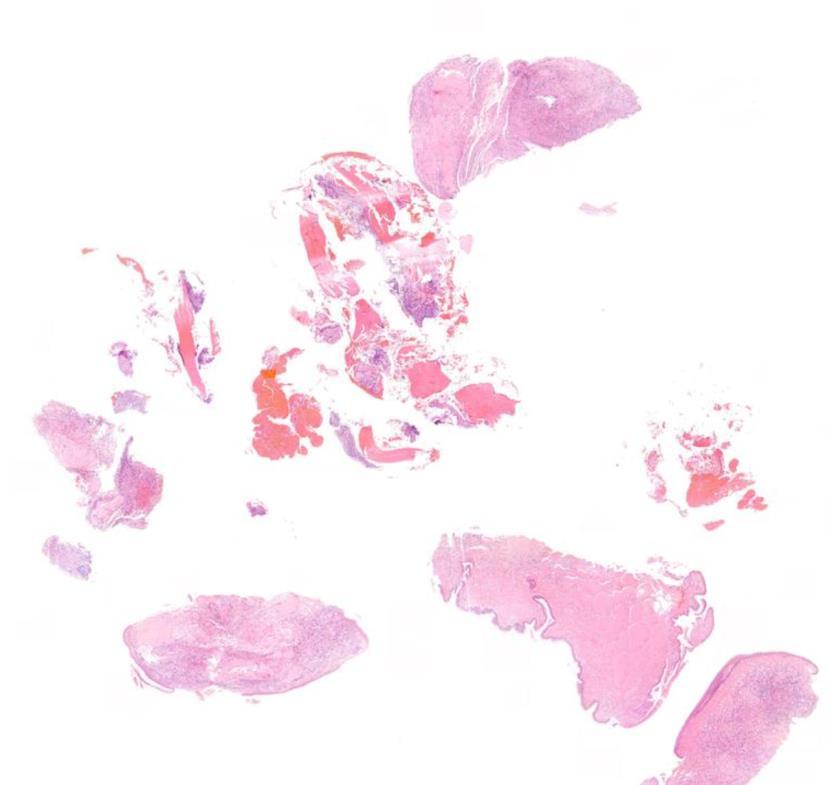


??
Case 11 Diagnosis Amyloidosis
Salient points • Deposition of hyalinised eosinophilic material in stroma •Congo red +++ •Consider type •? Assoc with plasma cell dyscrasia –Kappa and lambda check plasma cells at edge of lesion •Systemic investigations for AL ? Myeloma, H&N AL commonest •AA / hereditary
Case 12 55-year-old, Male Lump In Parotid.




??
Case 12 Diagnosis
Acinic cell carcinoma
Notes • Lymphoid
• ACC • MEC • Prognostic factor- better
indicator • ACC can undergo HG transformation
stroma
prognostic
• Female 24 years
Lesion left forehead with a 6-8 week history of recurrent headaches. ? cause.
Specimen: Skull. Macroscopic description: Disc of bone covered on one surface by elevated soft tissue. Cut sections reveal a central bone cavity filled with granular material. -
Case 13




??
Case 13 Diagnosis
Langerhans cell histiocytosis
• Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) is a clonal neoplastic proliferation of myeloid dendritic cells expressing LC phenotype • Single system/ multisystem involvement • cranial and facial bones, skin, gingiva, or cervical lymph nodes • intra-osseous ill-defined unilocular radiolucency with gingival involvement and tooth mobility. • >99% survival for unifocal disease LCH cell clusters are diagnostic, but caution is needed in lymph nodes because paracortical dendritic/LCs are indistinguishable from sinus-based LCH cells.
Case 14
42-year-old, Female Lump In Neck.
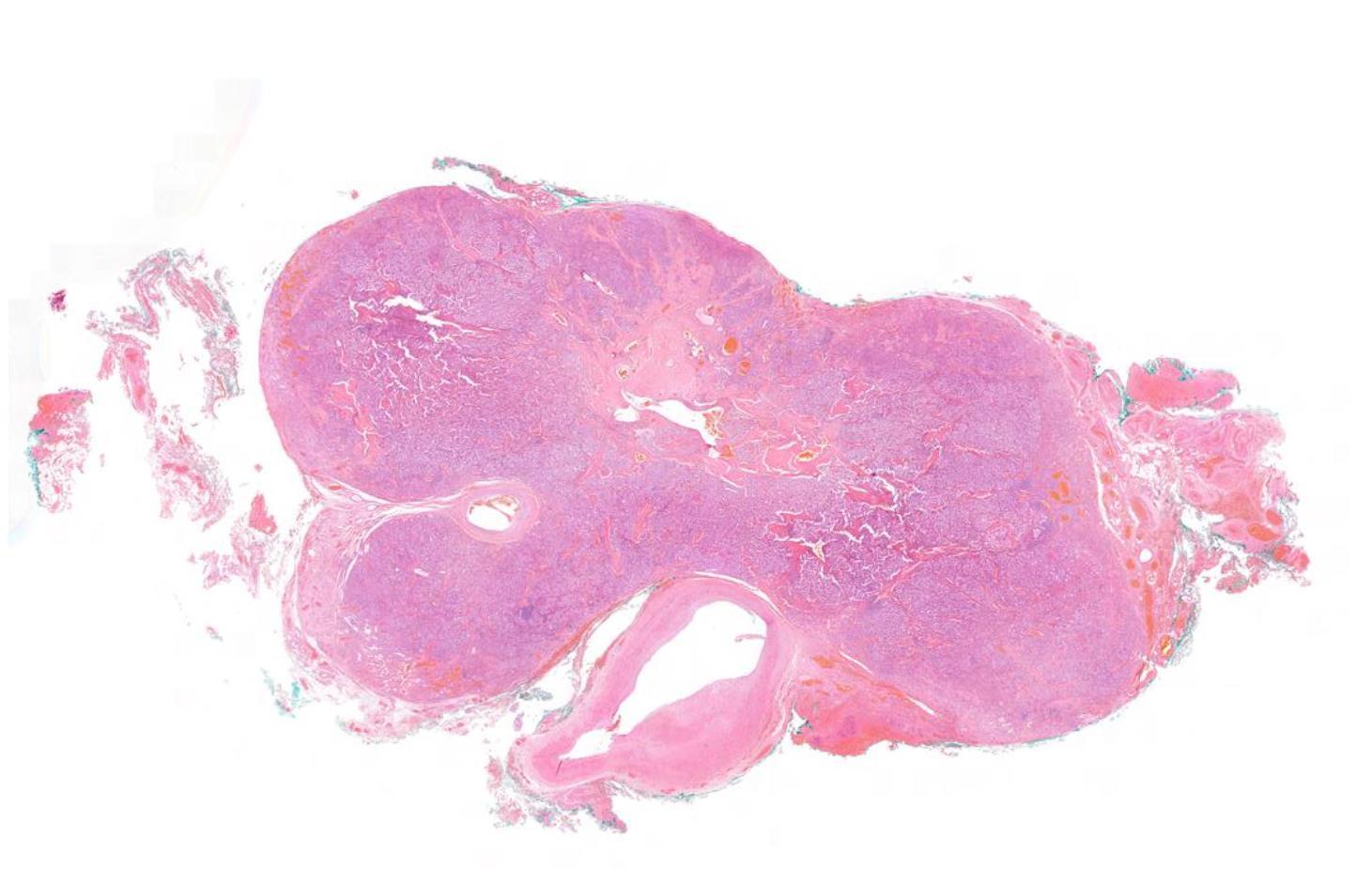


??
Case 14 Diagnosis
Carotid body tumour
• Well differentiated non-epithelial neoplasms derived from paraganglion cells of the autonomic nervous system. • Hereditary predisposition- 40% • Hereditary paraglanglioma syndrome • Germline mutation in SDHD (47%), SDHB (30%), SDHC (16%) • 3-4% risk of metastasis DDThyroid- medullary carcinoma Laryngeal neuroendocrine tumours Parathyroid tumours
HN15
60-year-old, Male Epistaxis, Numbness Of Cheek And Proptosis.



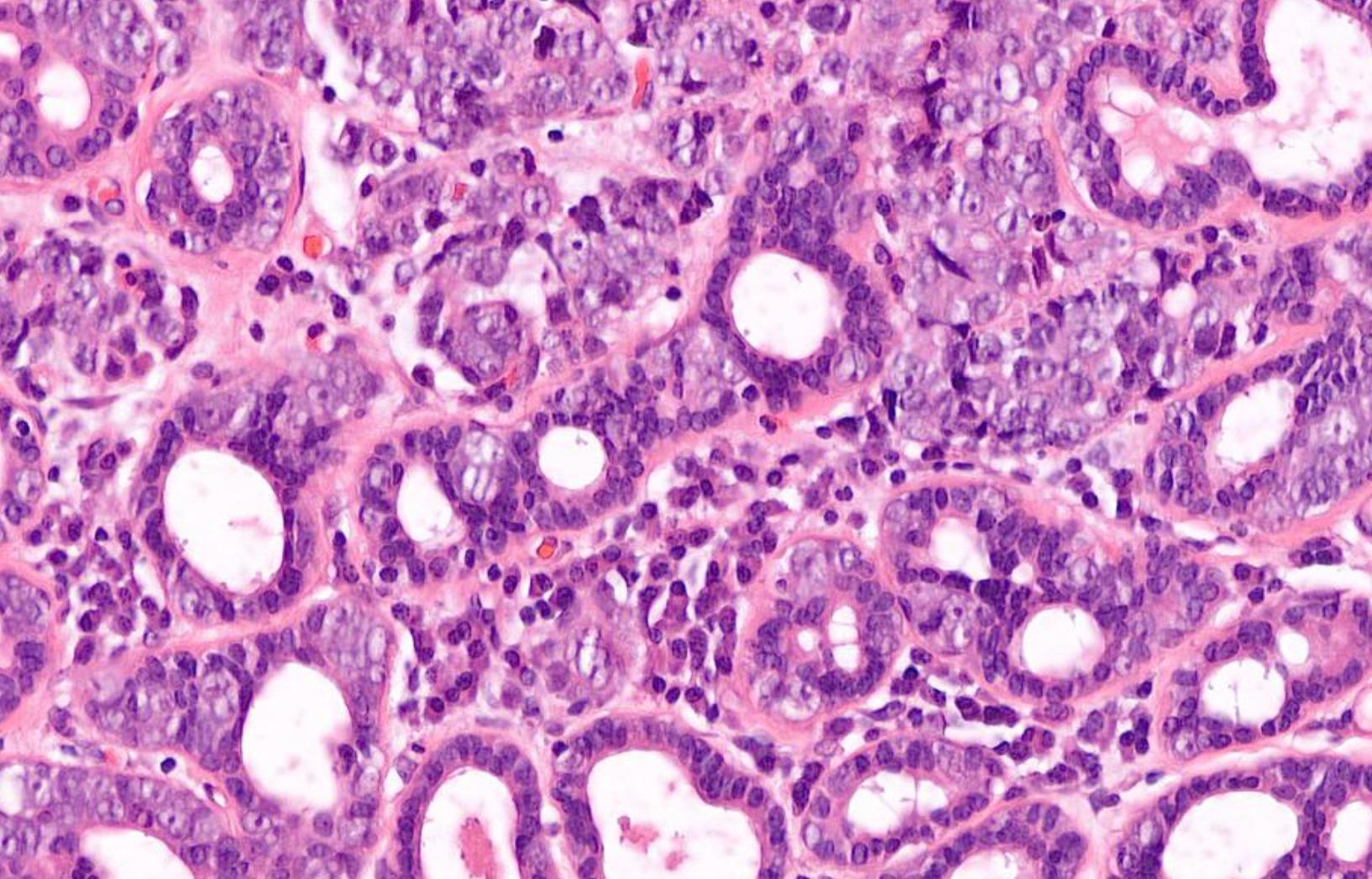
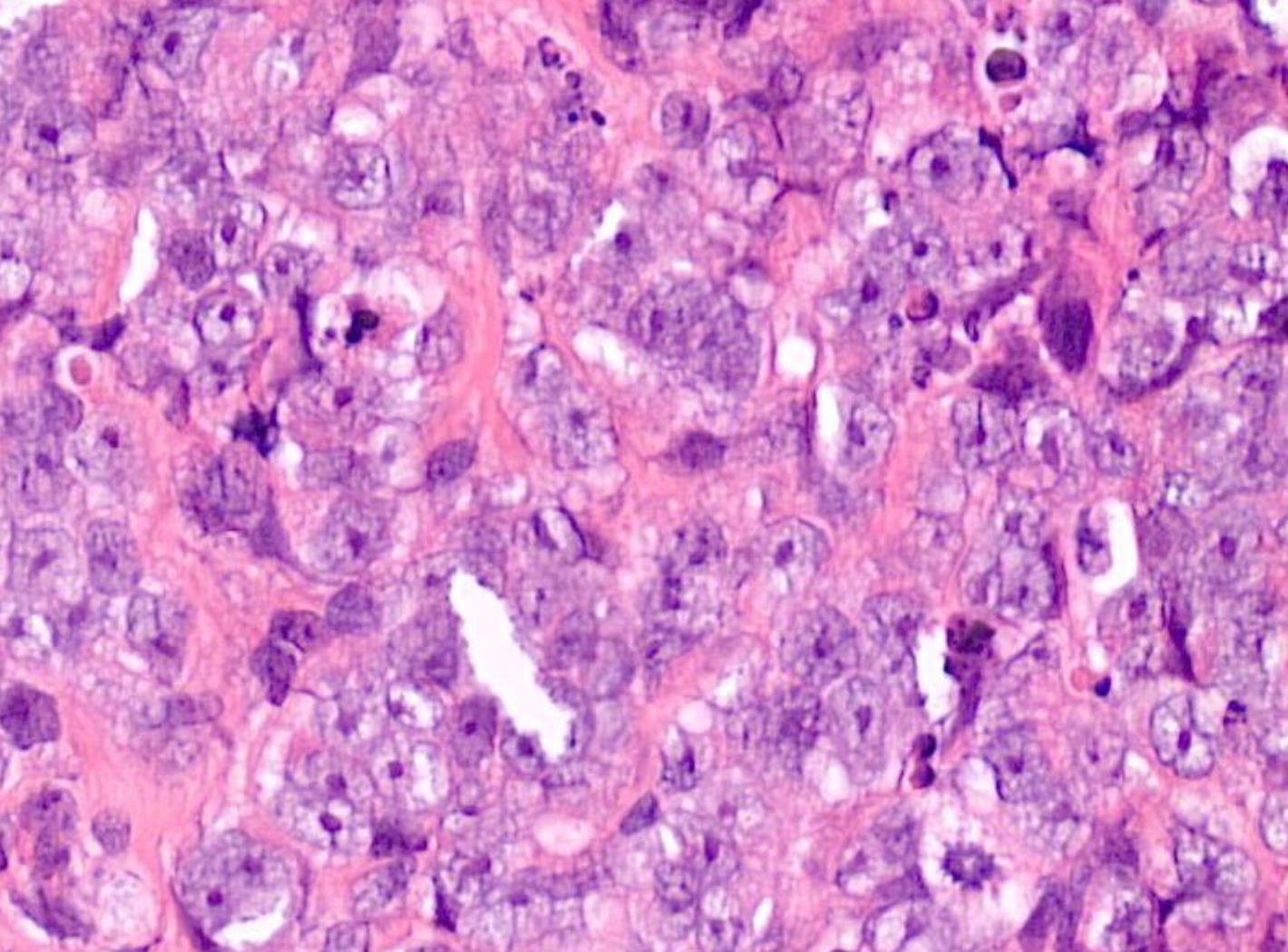
??
Case 15 Diagnosis
Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma (SNUC)
Sinonasal round blue cell tumours broad variants •Epithelial •Mesenchymal •Neuroectodermal •Haematolymphoid pancytokeratin p63 (or p40) synaptophysin chromogranin S100 desmin CD45 CD99
Epithelial • non-keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma (NKSqCC) • non-keratinizing nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NKNPC) • basaloid squamous cell carcinoma (BSqCC) • NUT midline carcinoma (NMC) • lymphoepithelial carcinoma (LEC) • adenoid cystic carcinoma (solid pattern) (AdCC) • small cell carcinoma, neuroendocrine type (SmCCNET) • HPV related multiphenotypic sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma • SMARCB1/SMARCA4- deficient CA • sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma (SNUC)
Neuroectodermal • Olfactory neuroblastoma (ONB) • Ewing sarcoma/peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumour (ES/pPNET) • Malignant mucosal melanoma (MM) Haematolymphoid • Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma (NK/TCL); • Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and other B- and T-cell lymphomas; • Extramedullary myeloid sarcoma (myeloid sarcoma; MS) • Plasmacytoma Mesenchymal • Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) • Synovial sarcoma (SS) • Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma • Also metastases from other sites should be considered
Case 16
16-year-old, Male Epistaxis, Biopsy Of Mass, Upper Part Of Nasal Cavity.



??
Case 16 Diagnosis
Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
• Puberty onset • Essential and desirable diagnostic criteria • Essential: male patient; posterior nasal cavity/nasopharynx location; numerous vessel types and sizes, some with muscular walls; stromal stellate fibroblasts with variably collagenized stroma • Desirable: ß-catenin and androgen receptor + in stromal cells

Case 17 71-year-old, Female Large Cystic Lesion Posterior Mandible.



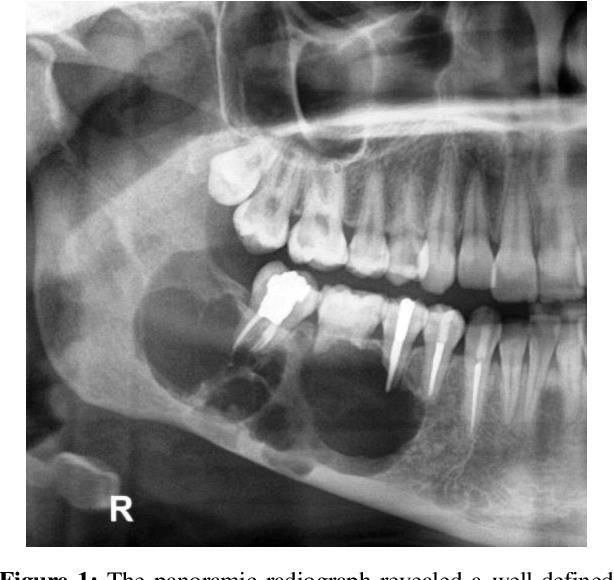
??
Case 17 Diagnosis Ameloblastoma
Case 18
28-year-old, Female Palatal Swelling.
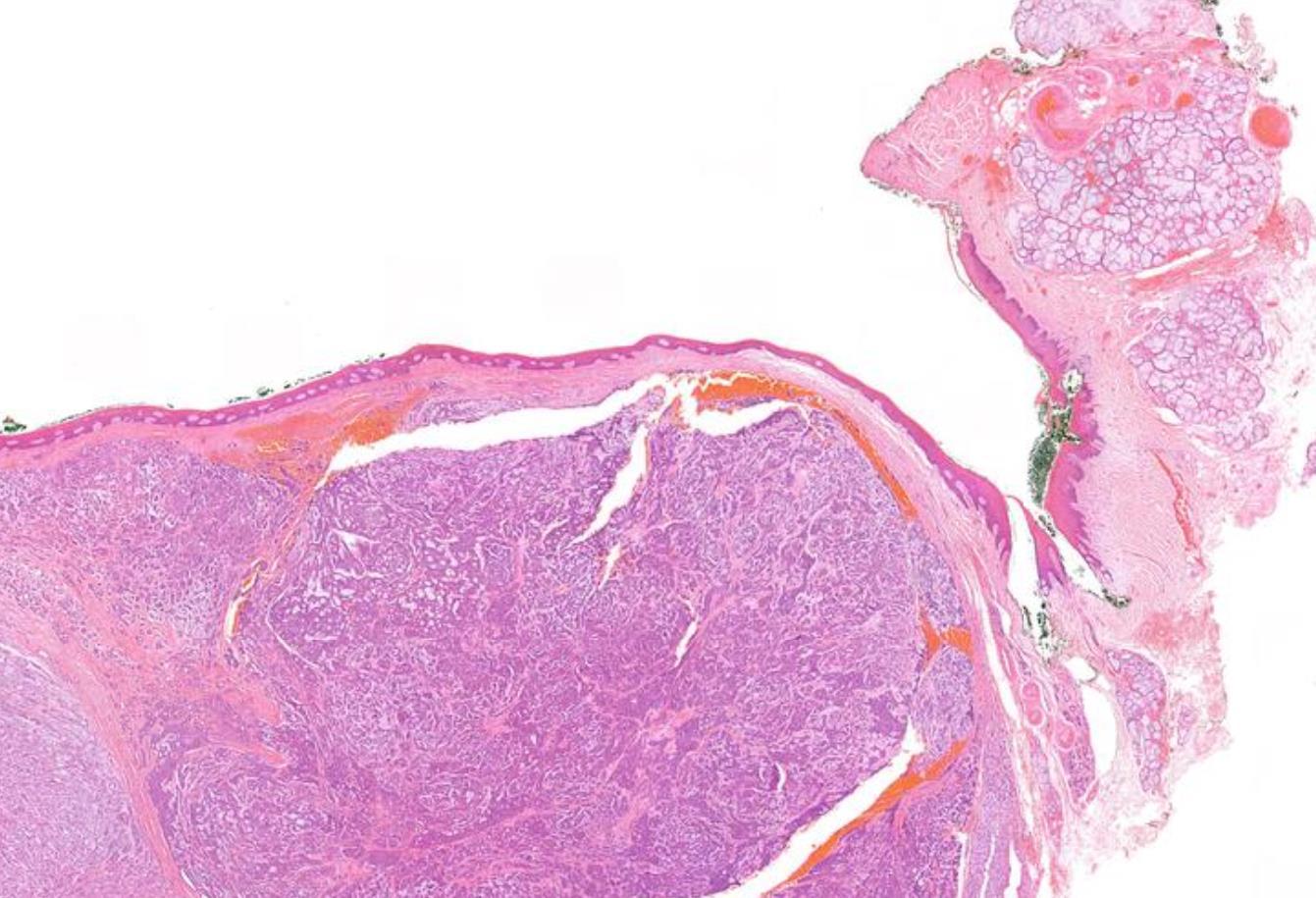




??
Case 18 Diagnosis
Polymorphous adenocarcinoma (PLGA)
Case 19
Male 64 years, Left parotid gland mass.



??
Case 19 Diagnosis
Extranodal marginal zone lymphoma (MALT)
•H&N 2nd most common site after GI tract •Small lymphocytes and marginal zone cells •Monocytoid cells with abundant pale cytoplasm are sometimes present •Remnants of reactive follicles are
sometimes with follicular colonization.
formed lymphoepithelial lesions
common,
Well-
• Positive for CD20, CD22, PAX5), usually IgM, occasionally IgG or IgA, and rarely IgD, CD43 or TBX21 (T-bet)
• Negative for CD5, CD10, BCL6, CD23, cyclin D1, SOX11, and EBV
• Immunoglobulin light chain monotypia of B cells or plasma cells
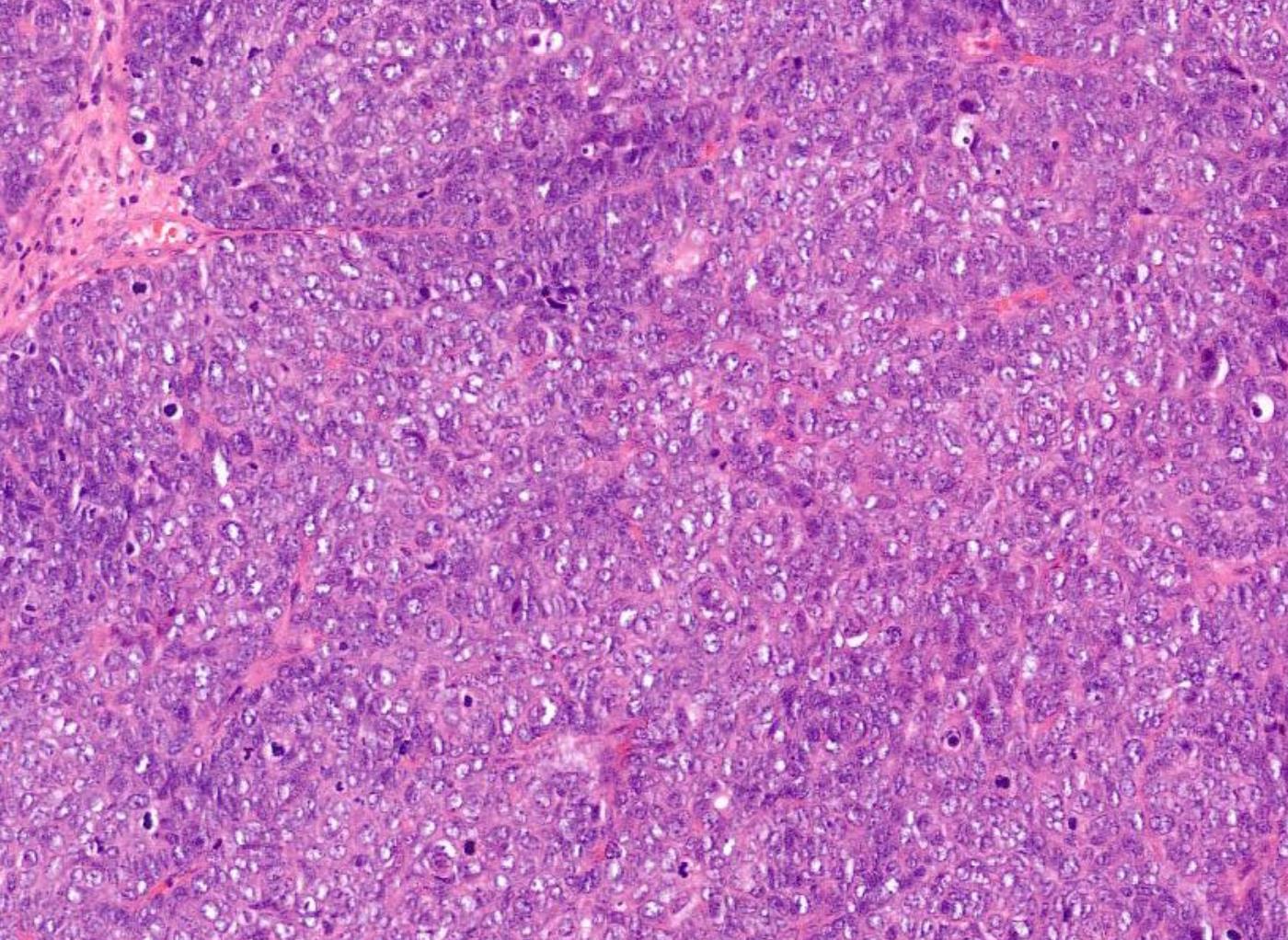
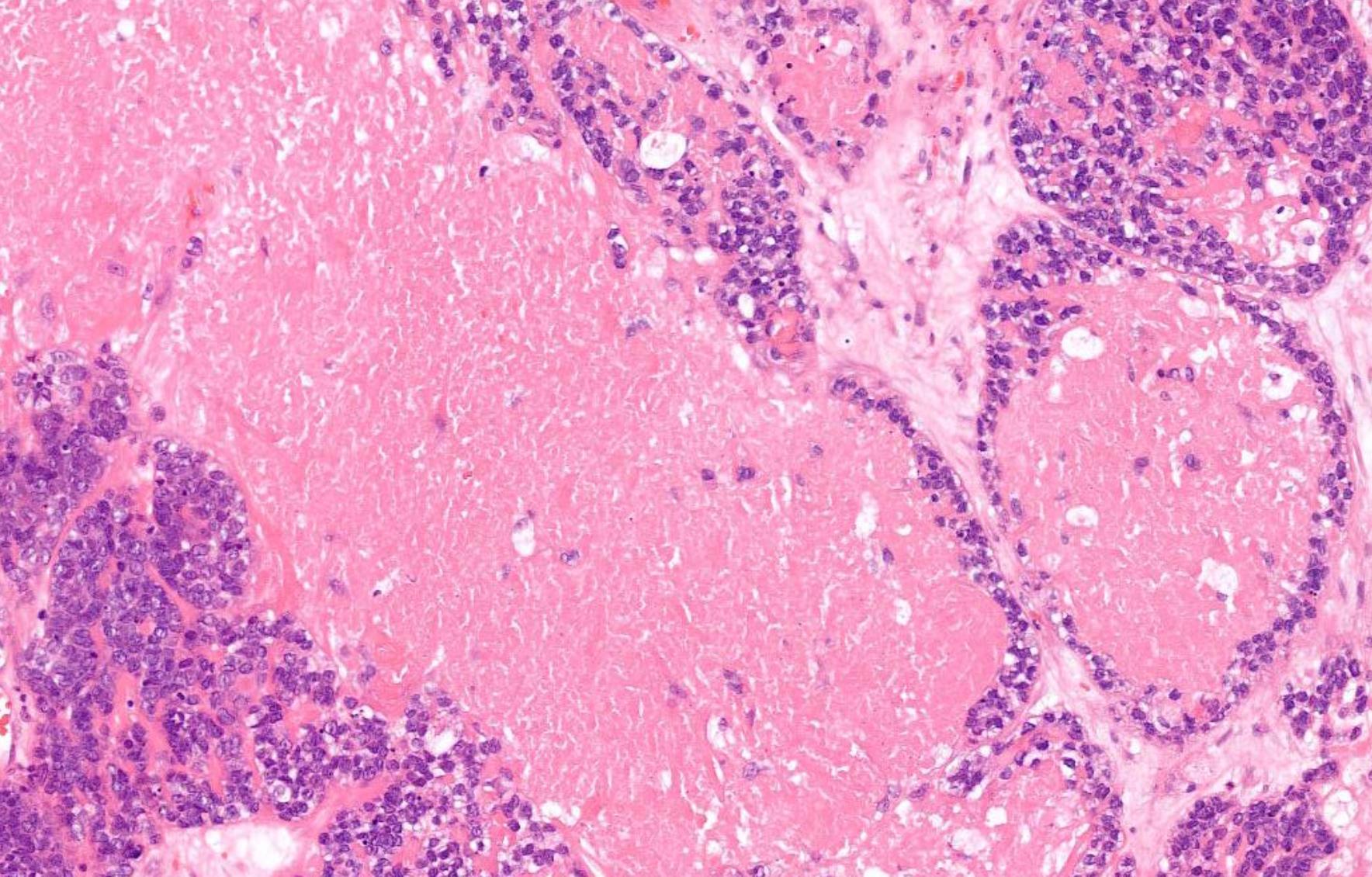
Case 20 34-year-old, Male Nasal Tumour.
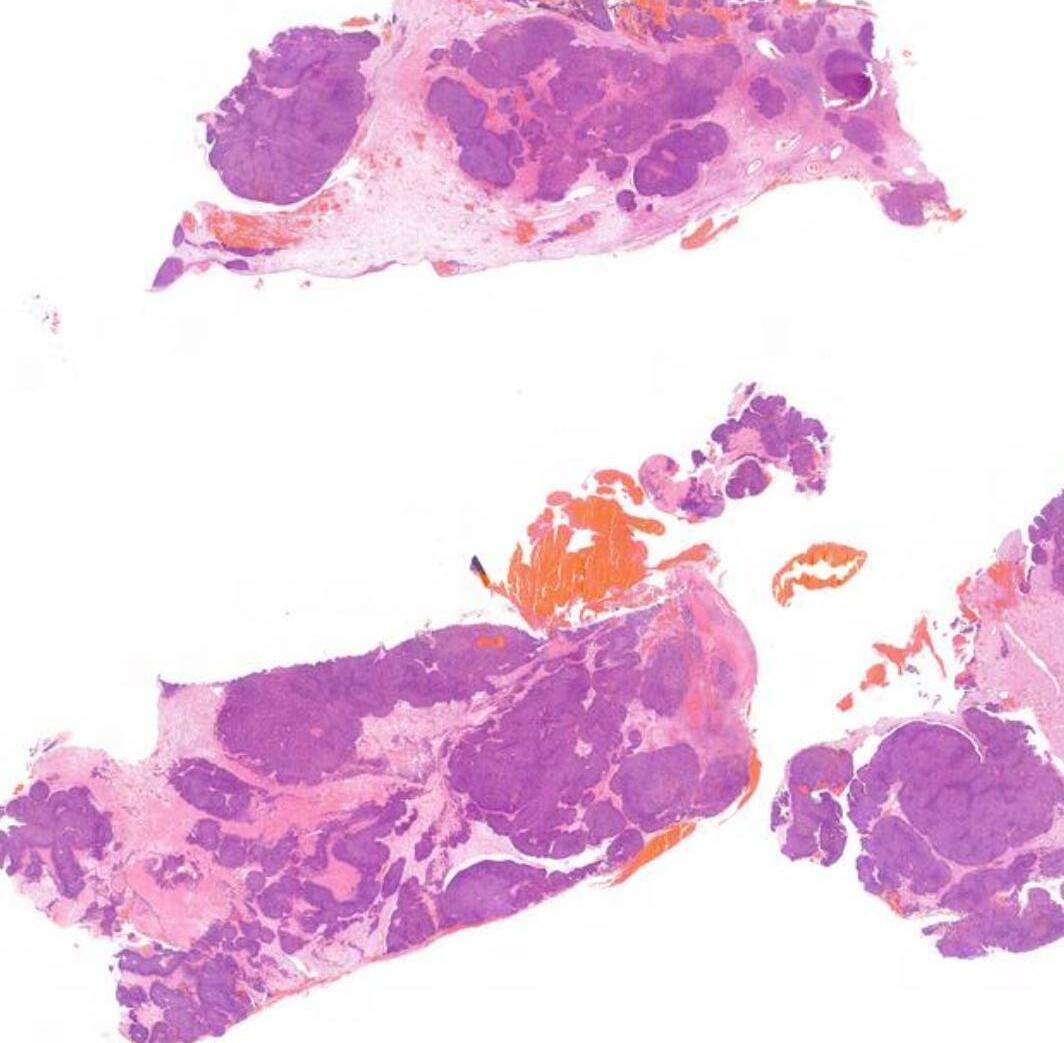


??
Case 20 Diagnosis
NUT midline carcinoma
More common in young adults
Foci of abrupt keratinization
Pancytokeratin+, p63+, p40+, NUT1+ t(15;19); BRD4-NUT gene fusion
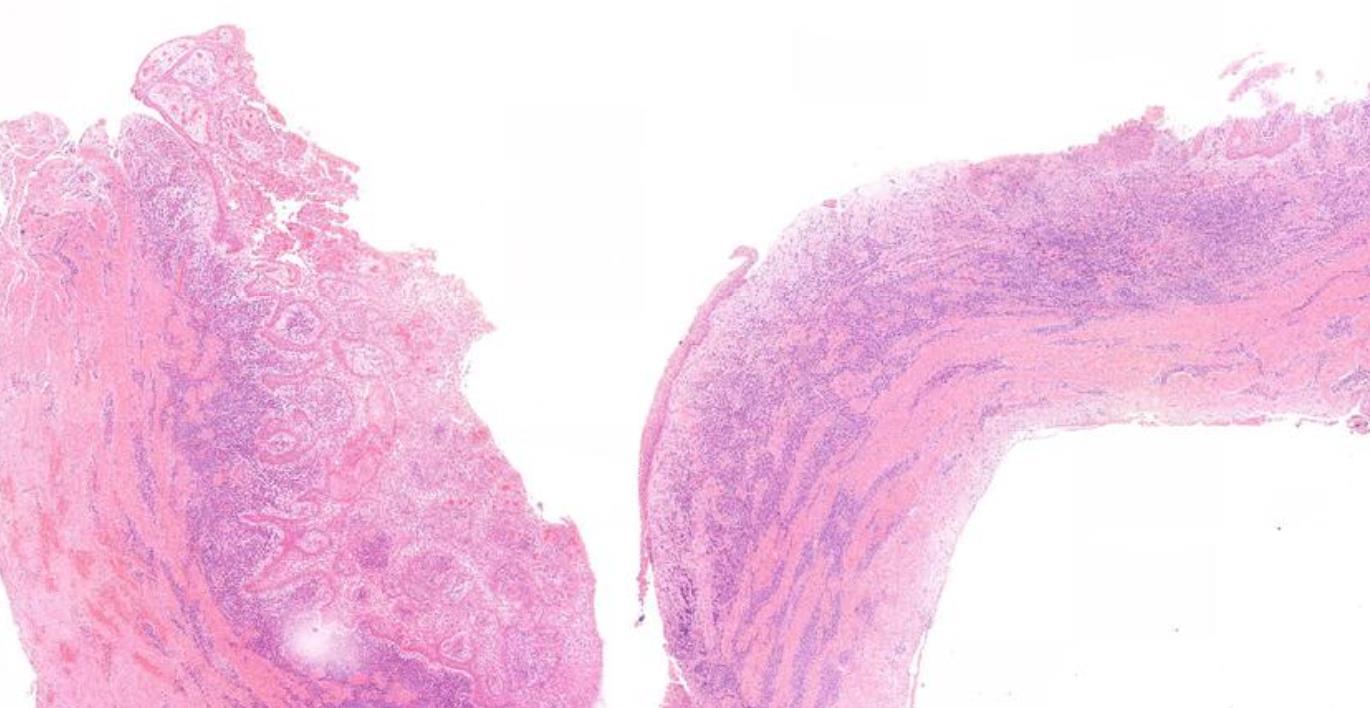
Case 21
Cyst From Apex Of Non-Vital Incisor Tooth



??
Case 21 Diagnosis
Radicular cyst
Case 22
19-year-old, Female Lymph Node Post Auricular Area.
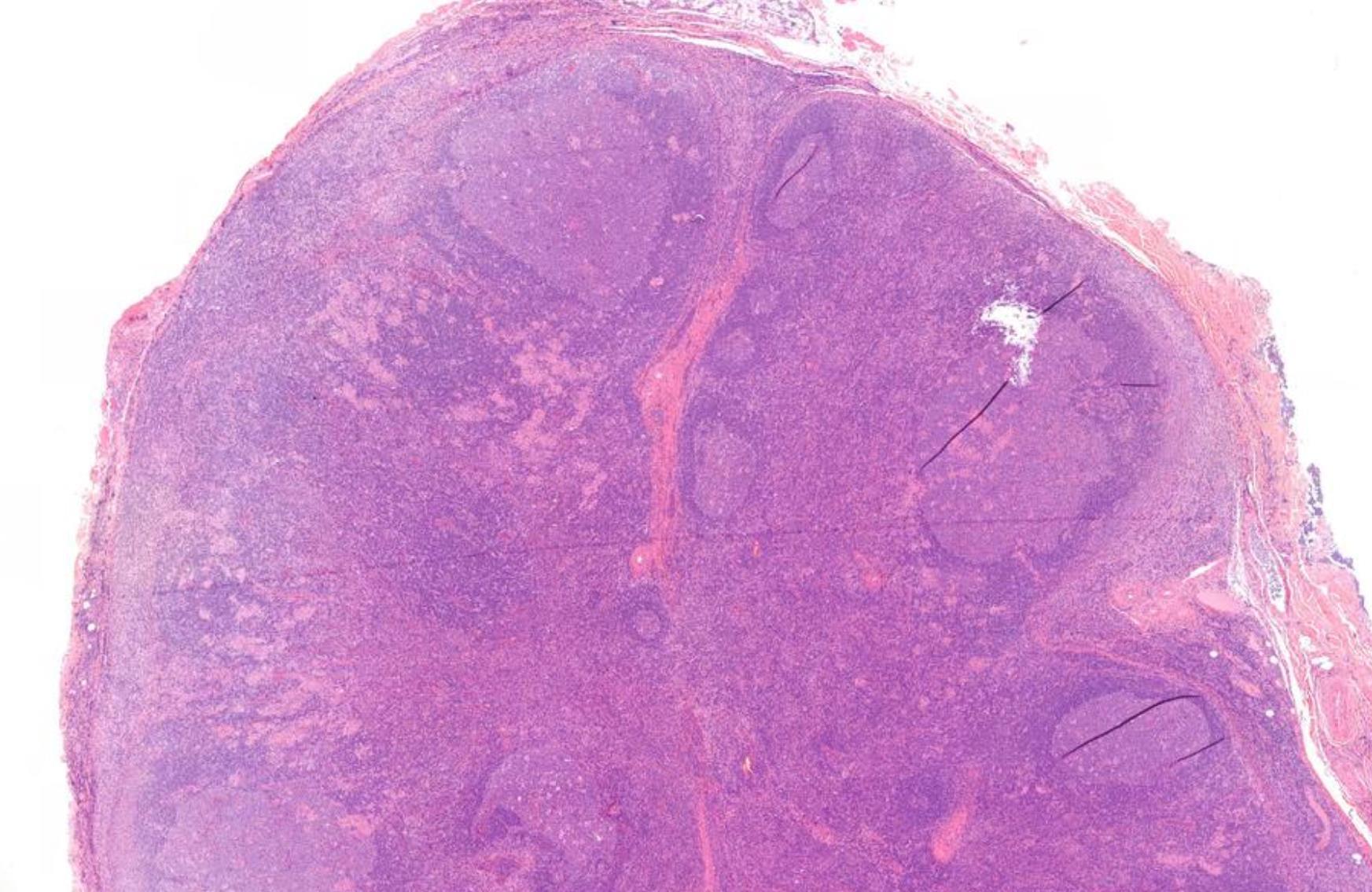


points Classic Triad •Reactive follicular hyperplasia, •Perifollicular / interfollicular epithelioid histiocytes -granulomas •Aggregates of monocytoid B cells.
Salient
??
Case 22 Diagnosis
Toxoplasmosis lymphadenitis
Case 23
22-year-old Female. Lymph Node From Neck.

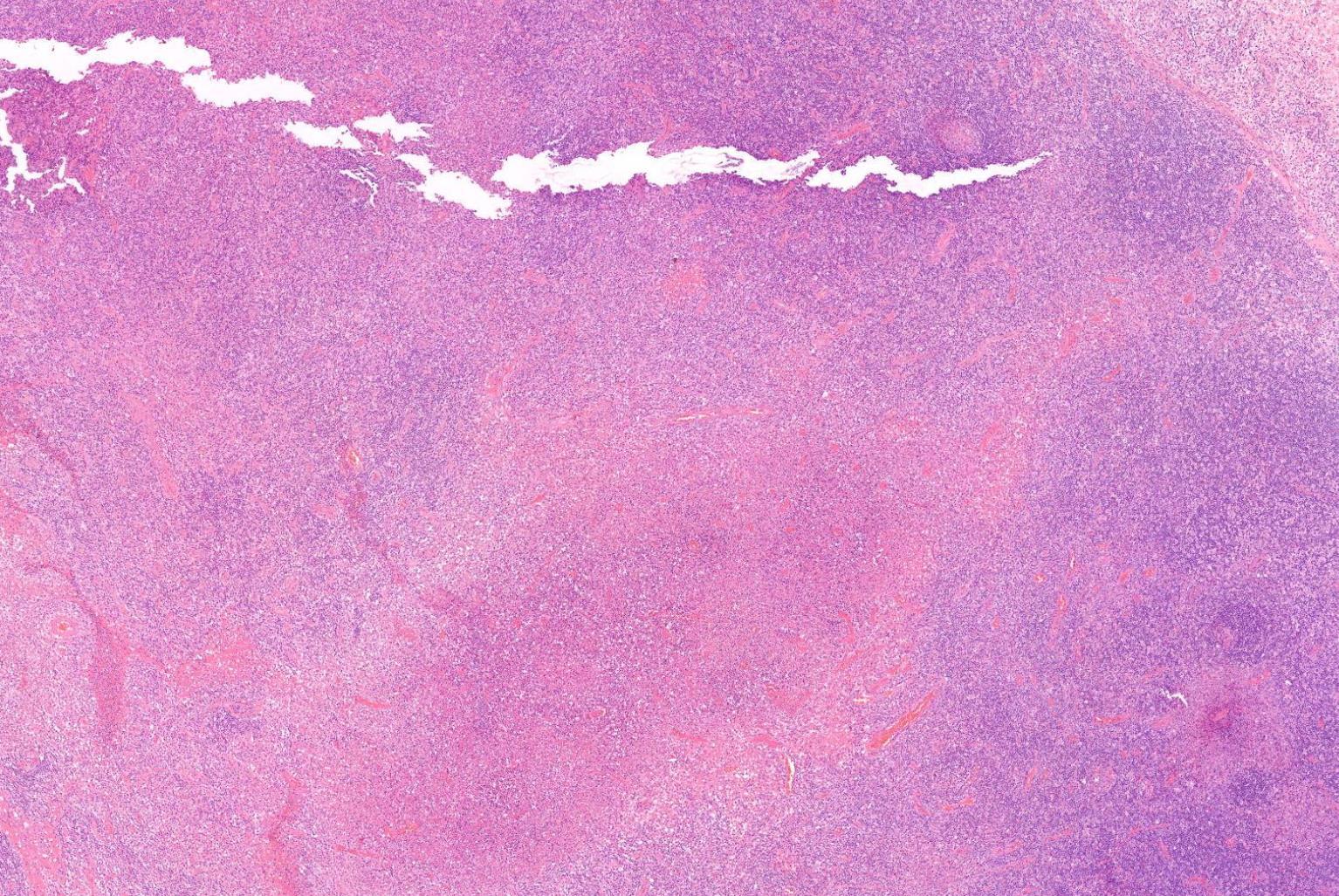

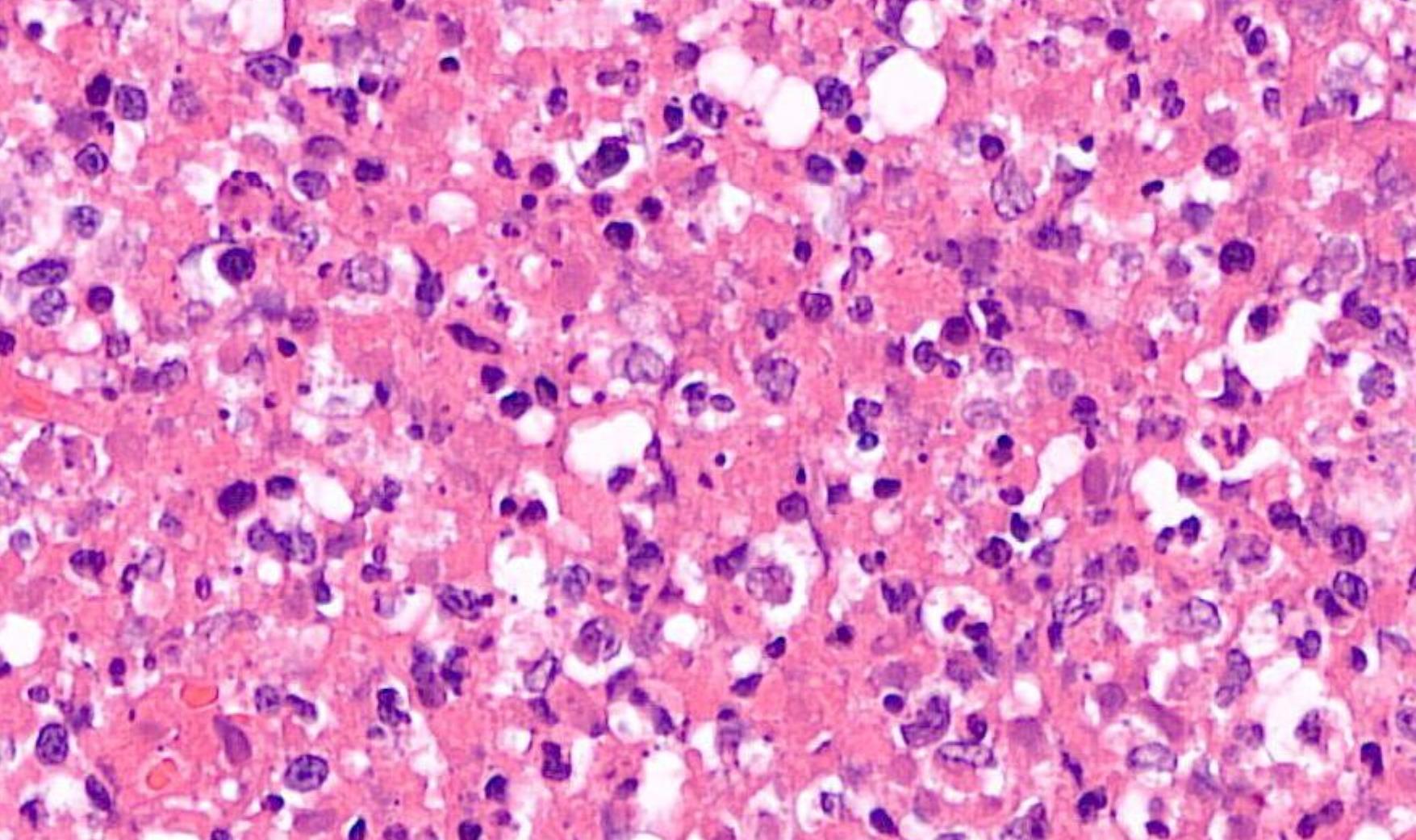
??
Case 23 Diagnosis
Kikuchi Fujimoto disease (Kikuchi histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis)
• Self-limiting, unknown etiology • Young adults of Asian origin • Histologic patterns: proliferative, necrotizing, and xanthomatous. • DD- infectious lymphadenitis, autoimmune lymphadenopathy (primarily systemic lupus erythematosus), and lymphoma • Histomorphologic diagnosis • Thehistiocytes+lysozyme,myeloperoxidase,CD68,CD163, andCD4. • ThelymphocytesCD3-positiveTcellsdemonstratinga predominanceofCD8comparedwithCD4,veryfewCD20positiveBcells.Plasmacytoiddendriticcells-CD123+
Case 24 55-year-old, Male Parotid Swelling

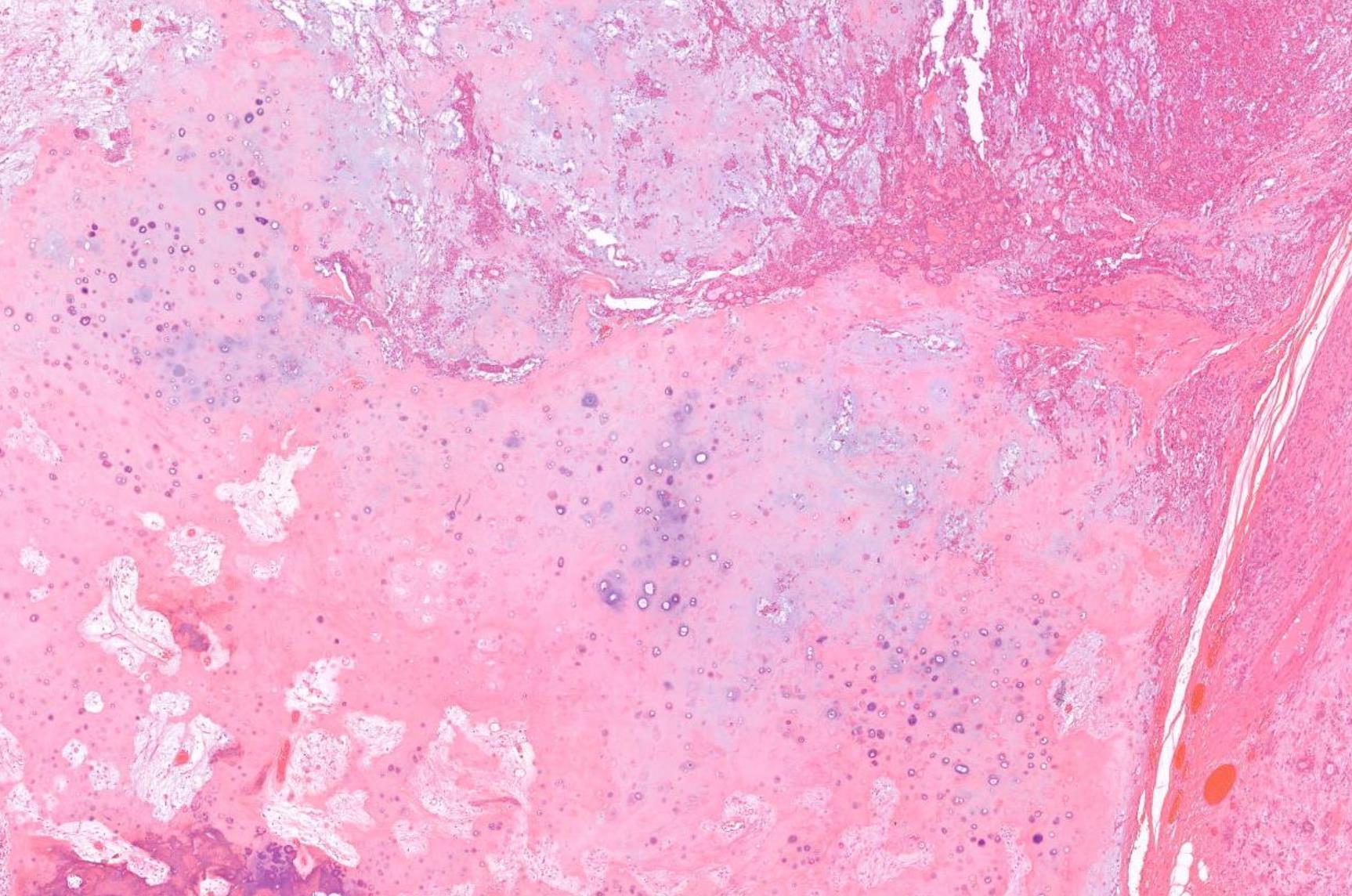
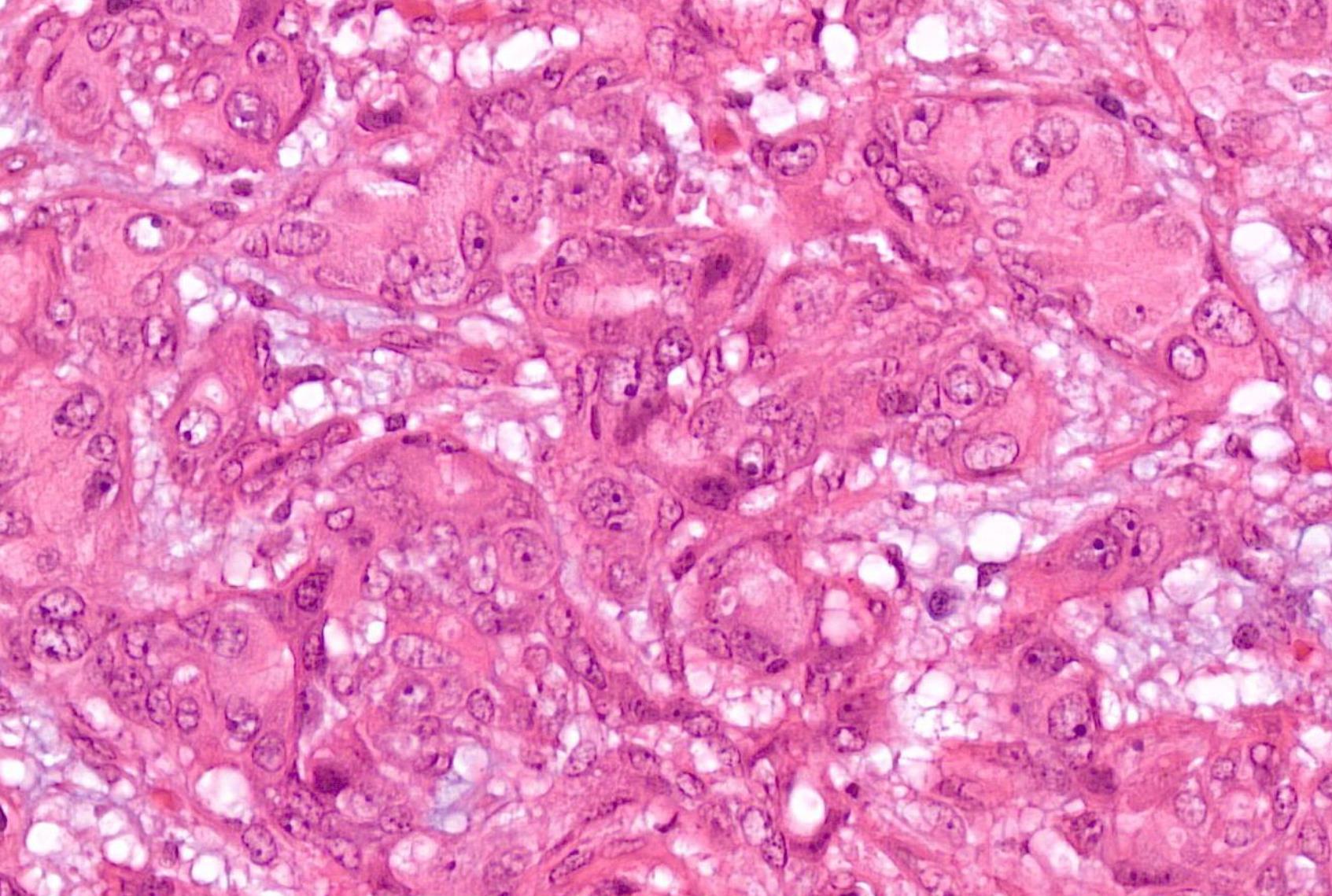

??
Case 24 Diagnosis
Pleomorphic adenoma with ossification and atypia
Case 25 79-year-old, Male Parotid Swelling.





??
Case 25 Diagnosis
Warthin tumour with Small lymphocytic lymphoma
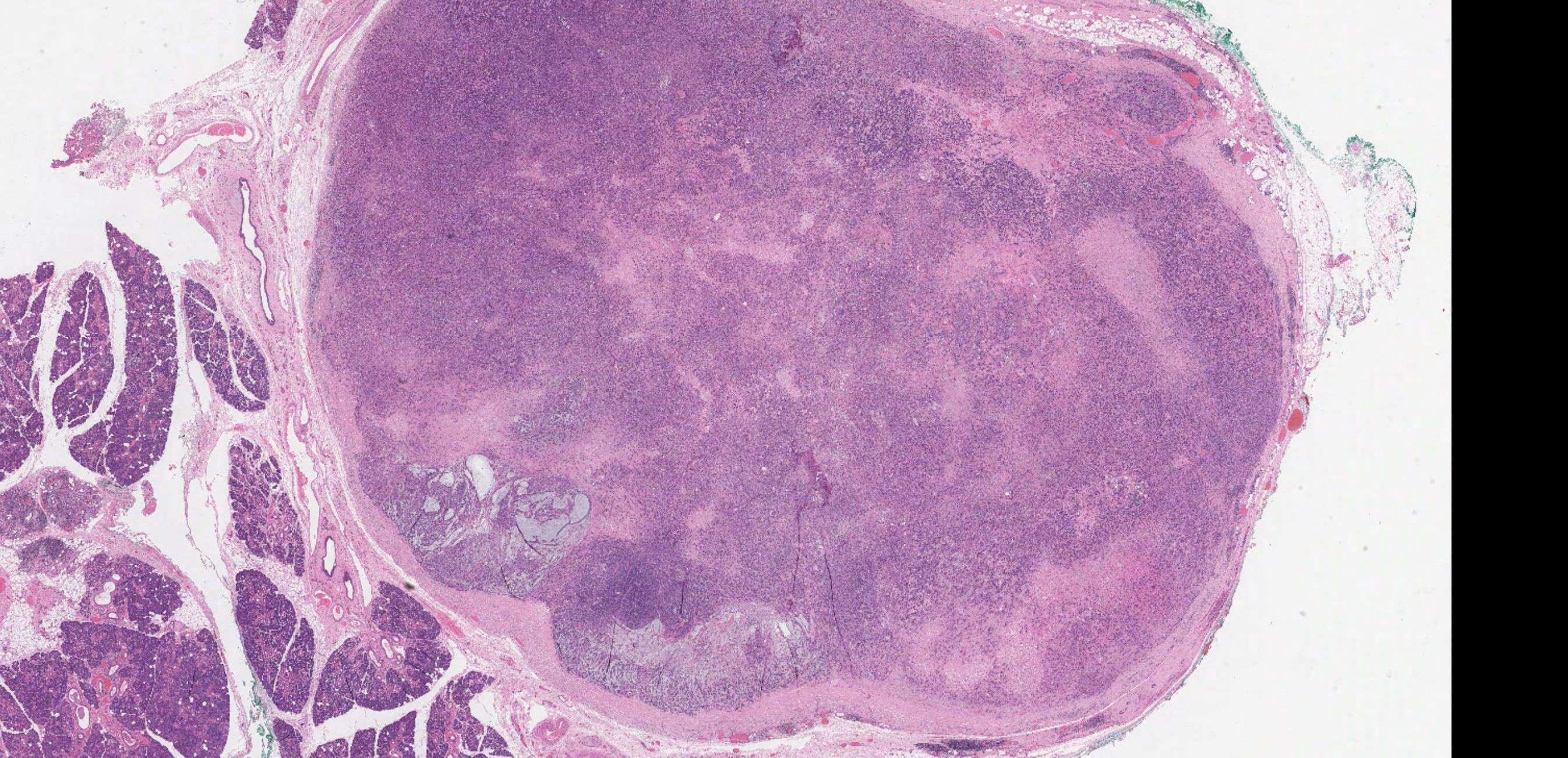
Case 26 46-year-old, Female Lump On Gum.

•

??
Case 26 Diagnosis
Peripheral ameloblastoma
• Female 74 years 18 year history of submandibular swelling that has recently increased in size.
Specimen: submandibular gland.
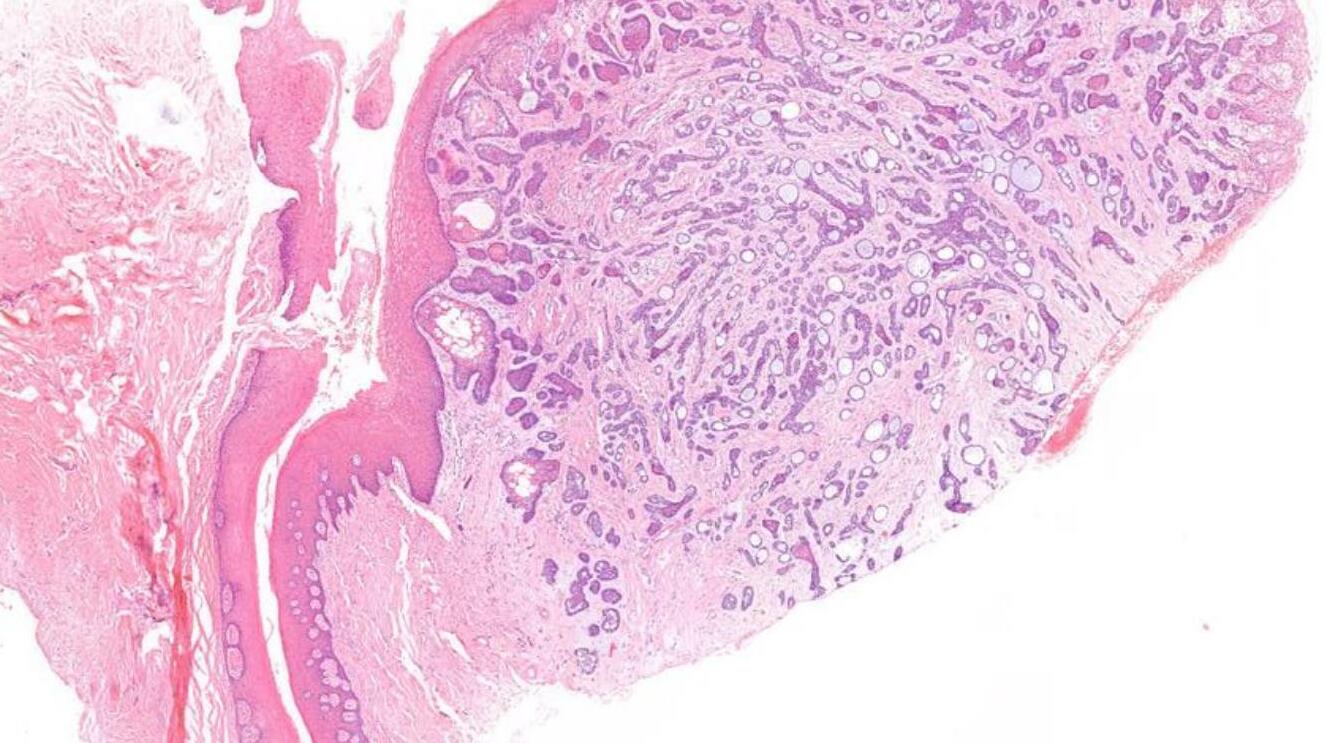
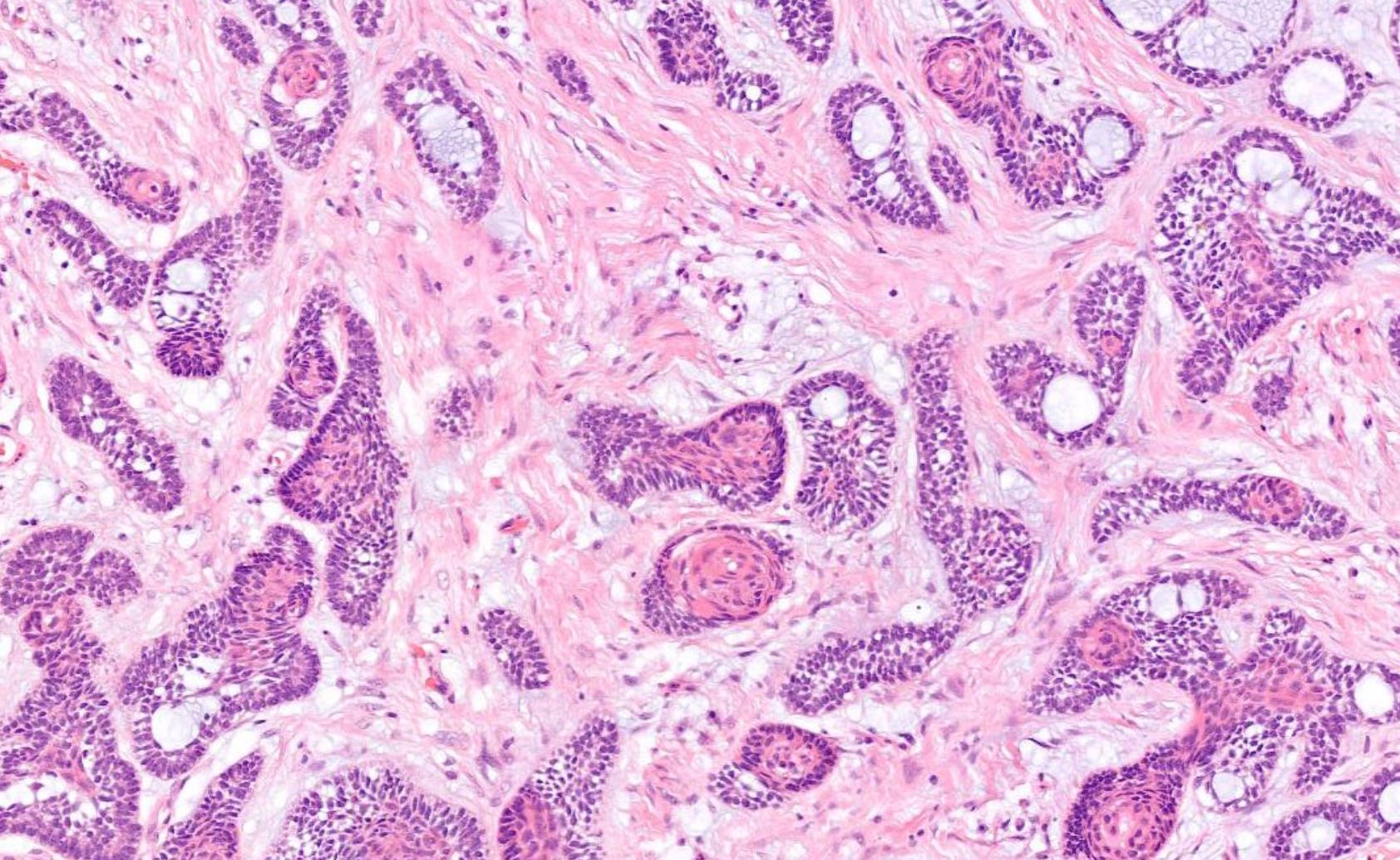
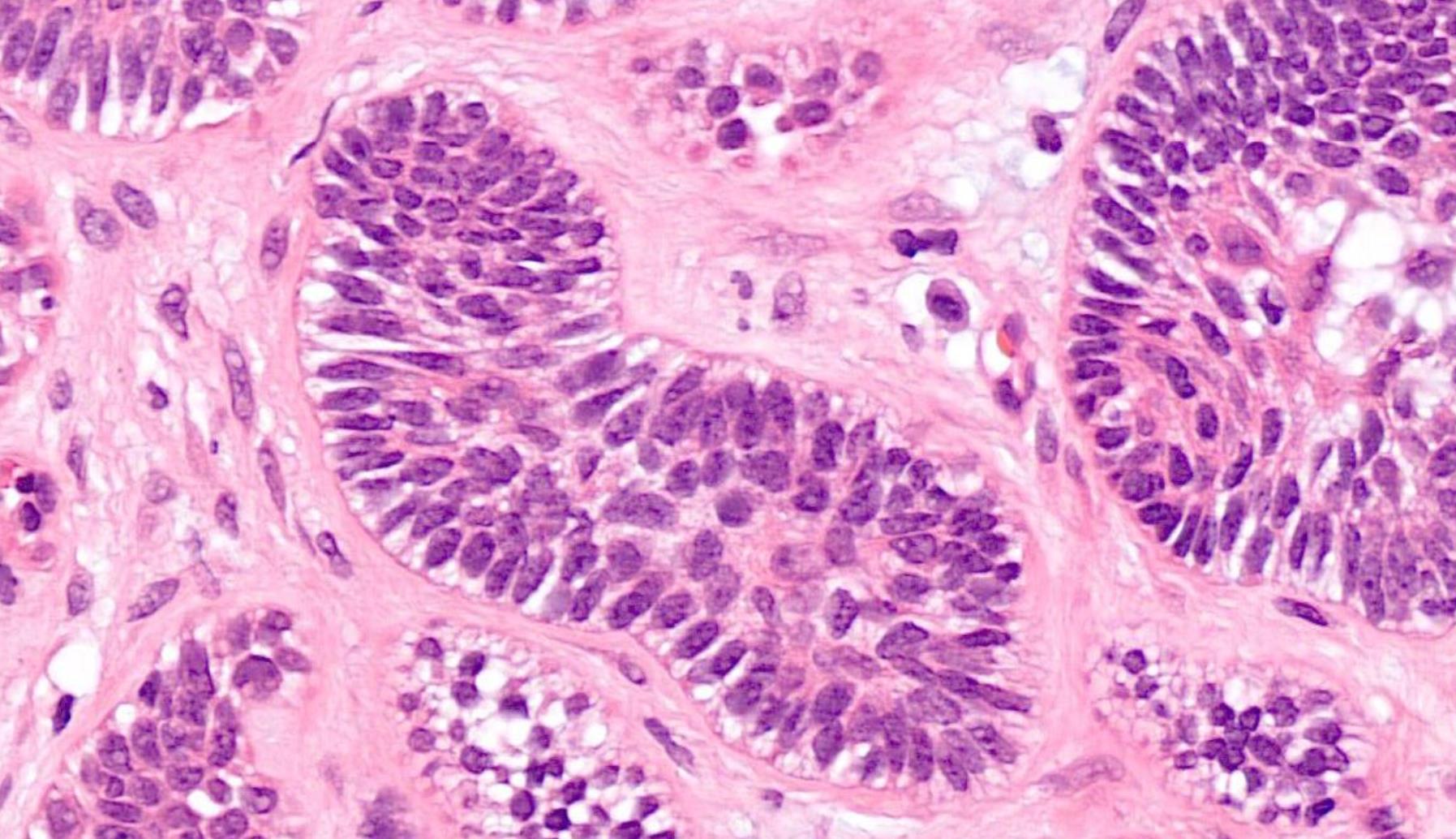
Case 27
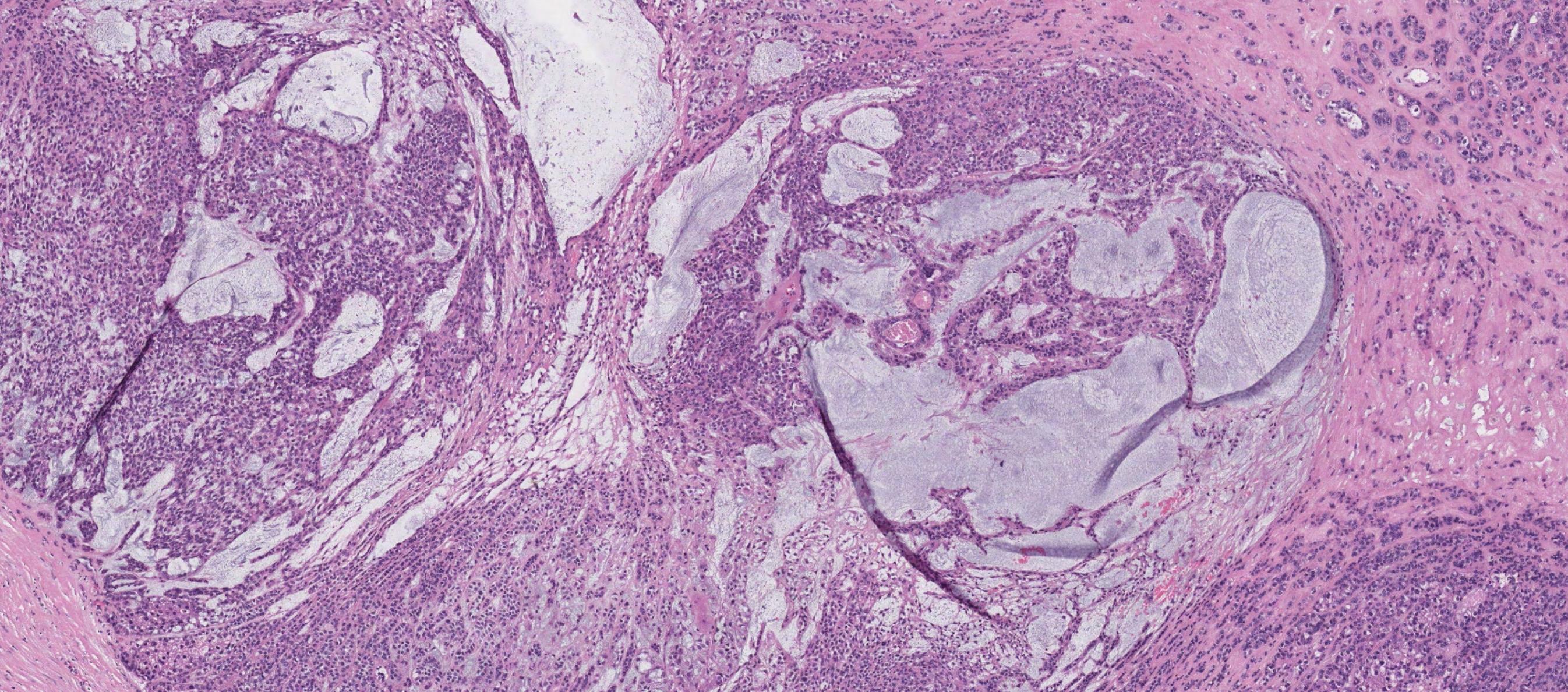
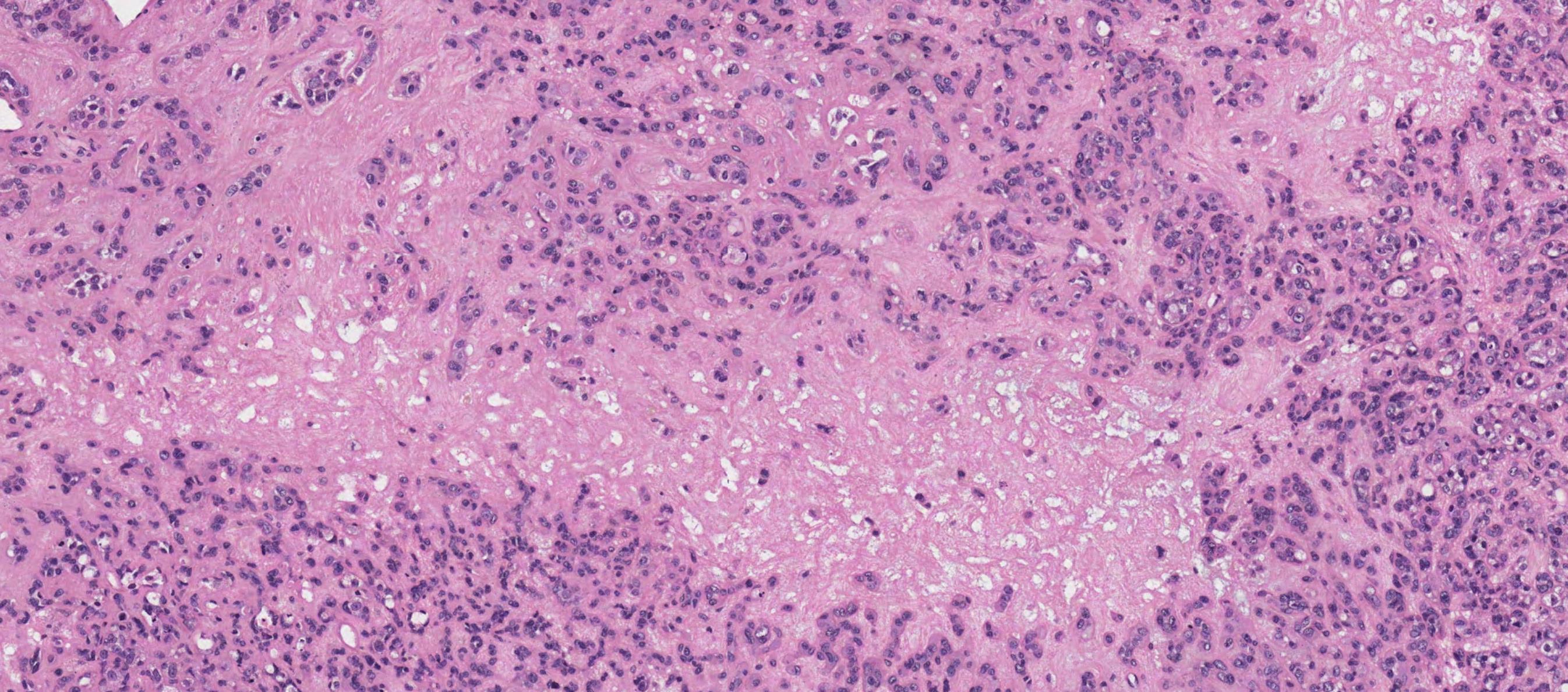
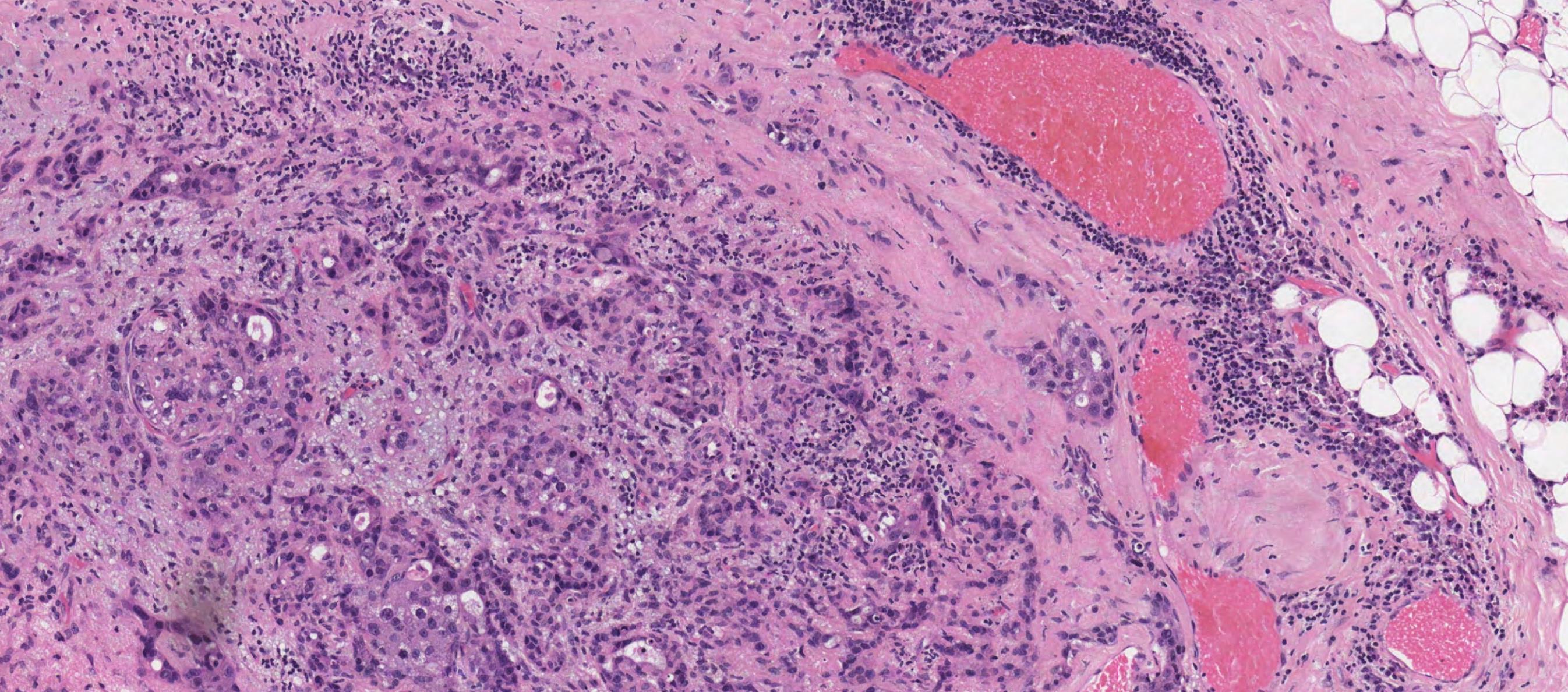
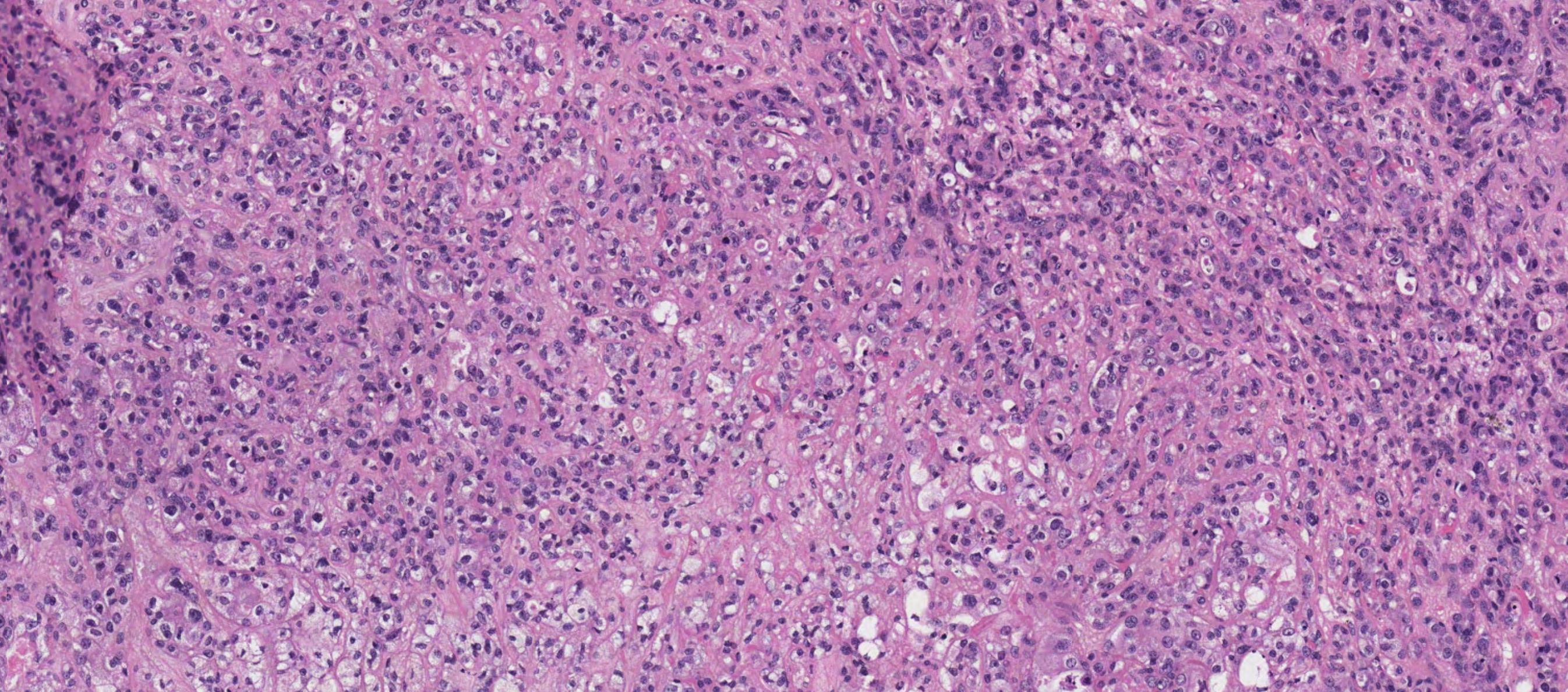
??
Case 27 Diagnosis
In-situ carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma
Case 28
39-year-old, Male White Patch Buccal Mucosa, Smoker.
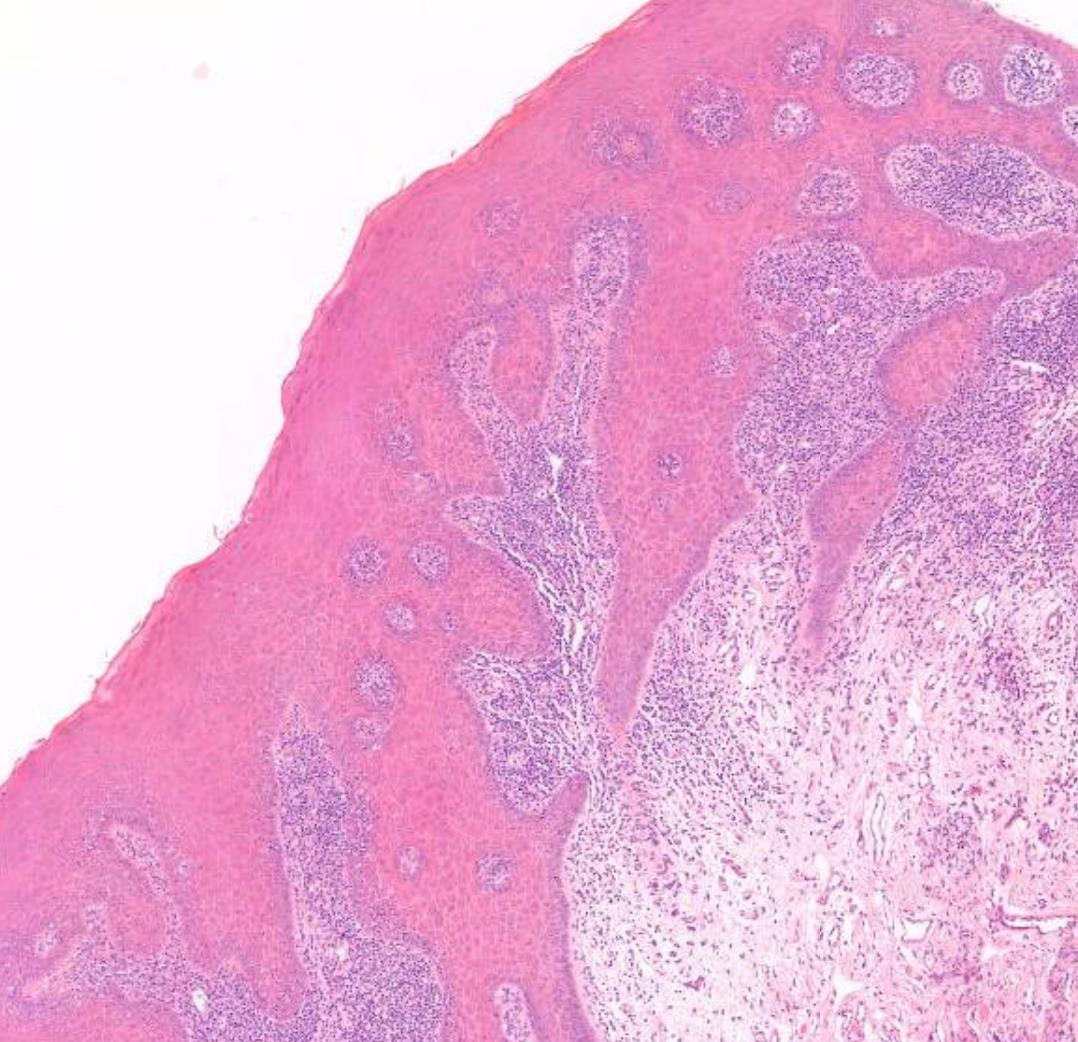
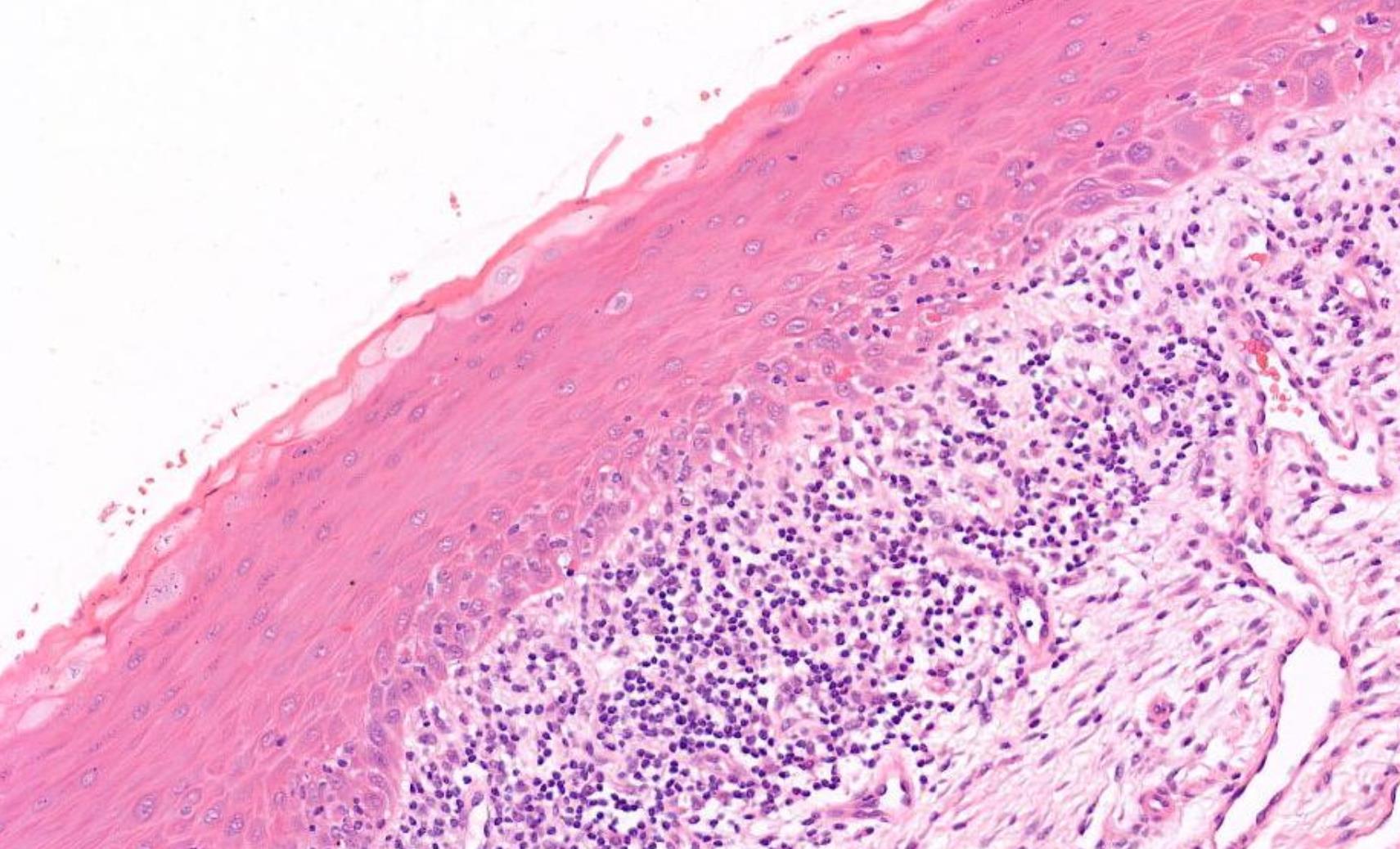

??
Case 28 Diagnosis
Lichenoid mucositis –lichen planus or lichenoid reaction
Case 29
57-year-old, Male White Patch Buccal Mucosa, Smoker.


??
Case 29 Diagnosis
Chronic hyperplastic candidosis
HN30
45-year-old M, Previous Multiple Excisions Of Nasal Tumour, Further Resection.
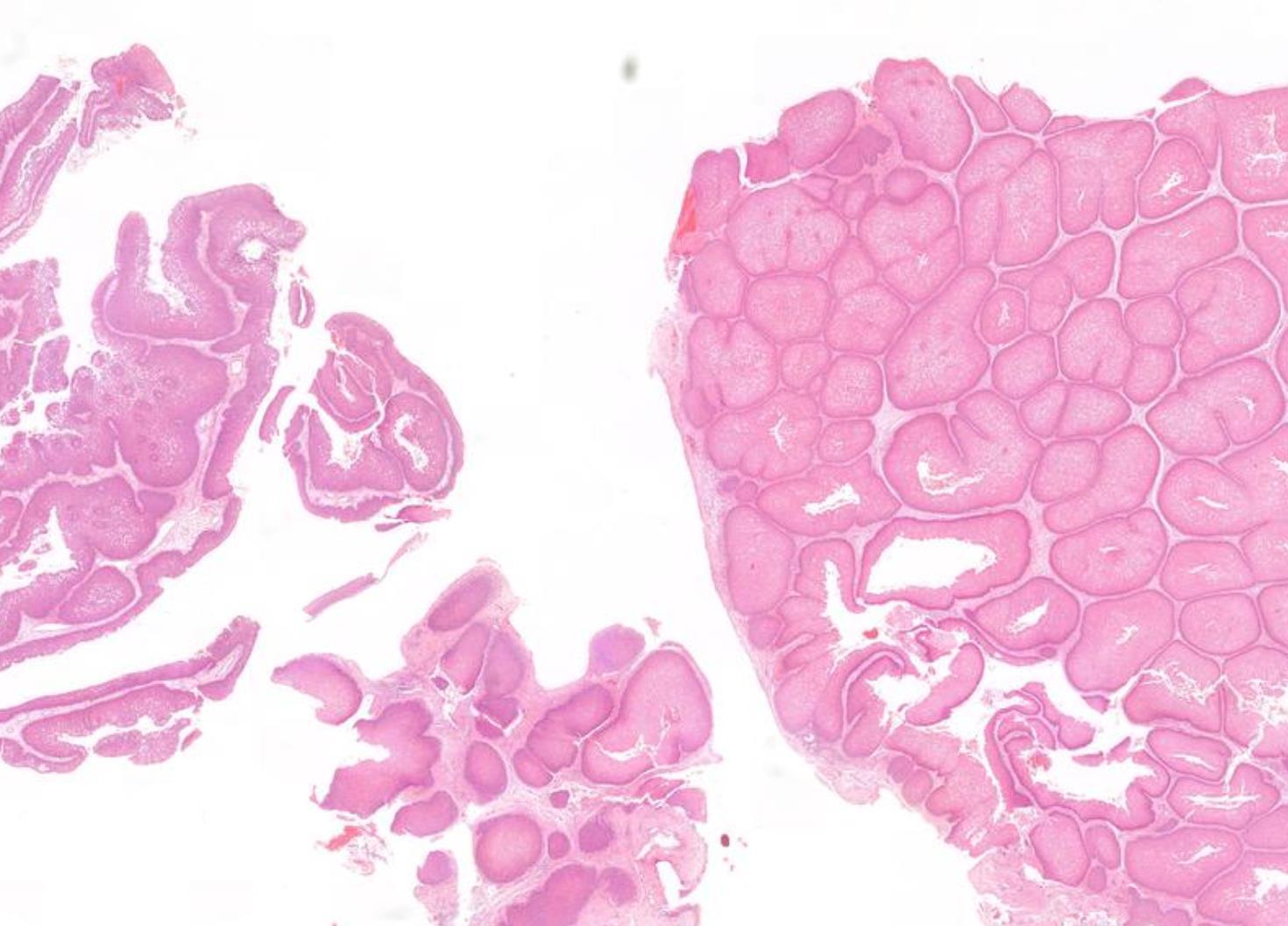

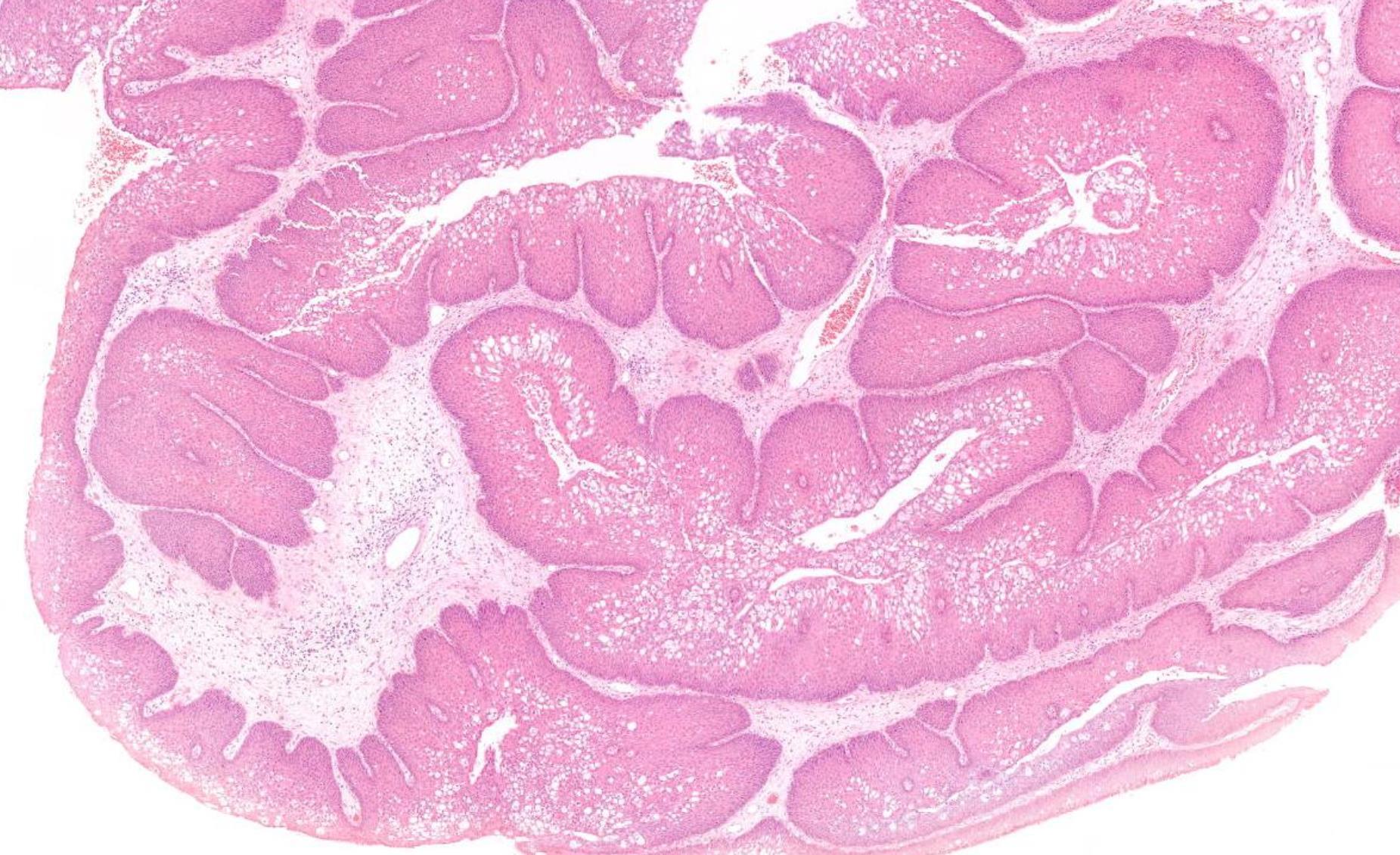
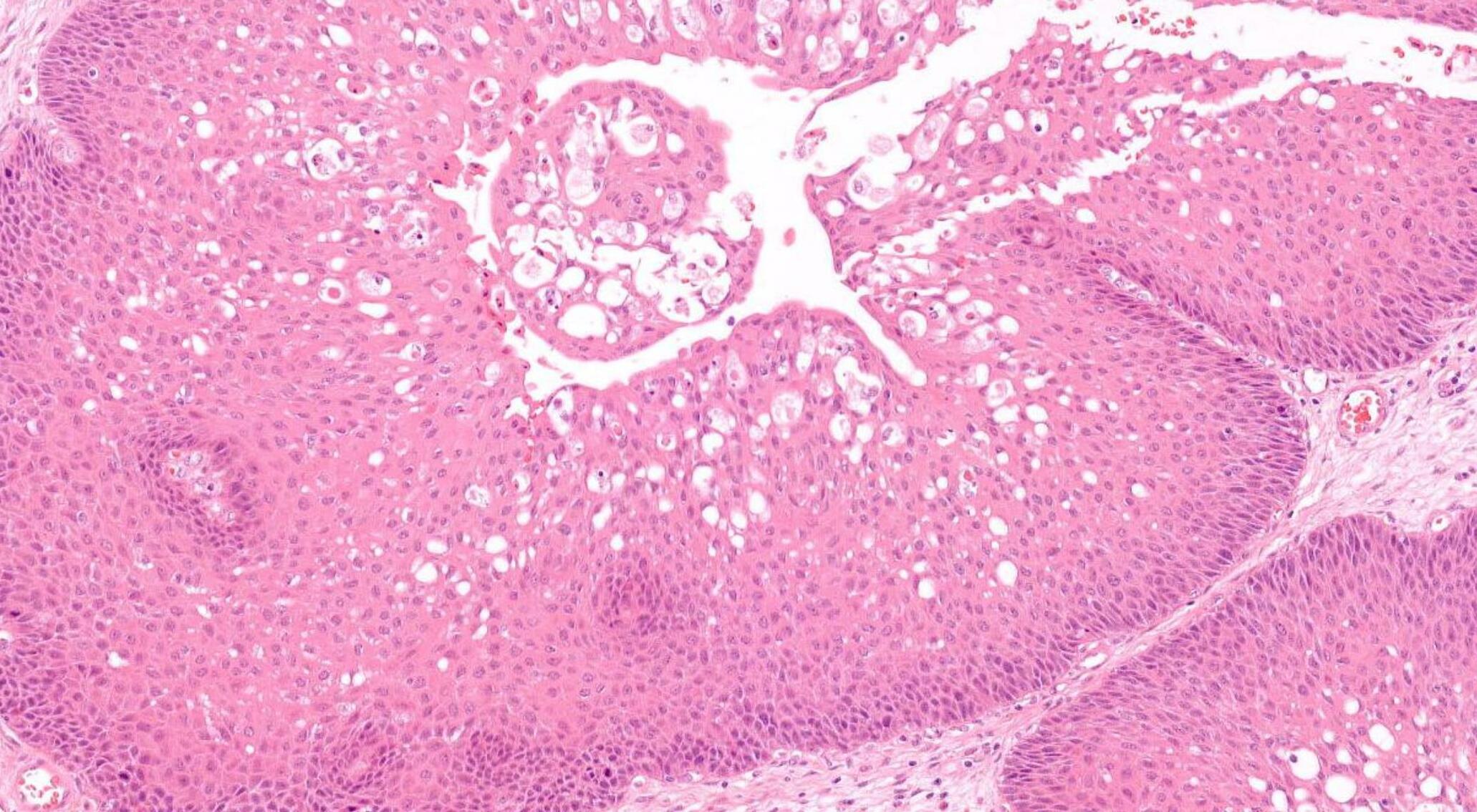

??
Case 30 Diagnosis
Squamous cell carcinoma arising in sinonasal inverted papilloma
Case 31
•
Female 56 years Slow growing lesion left neck from dorsal root C3. ? Nerve. Left posterior triangle. Present 20 years. Case type Combined. Specimen: Neck. Macroscopic description: Five bosselated nodules of soft tissue collectively measuring 55 x 45 x 15 mm. Immunohistochemistry: S100 positive.
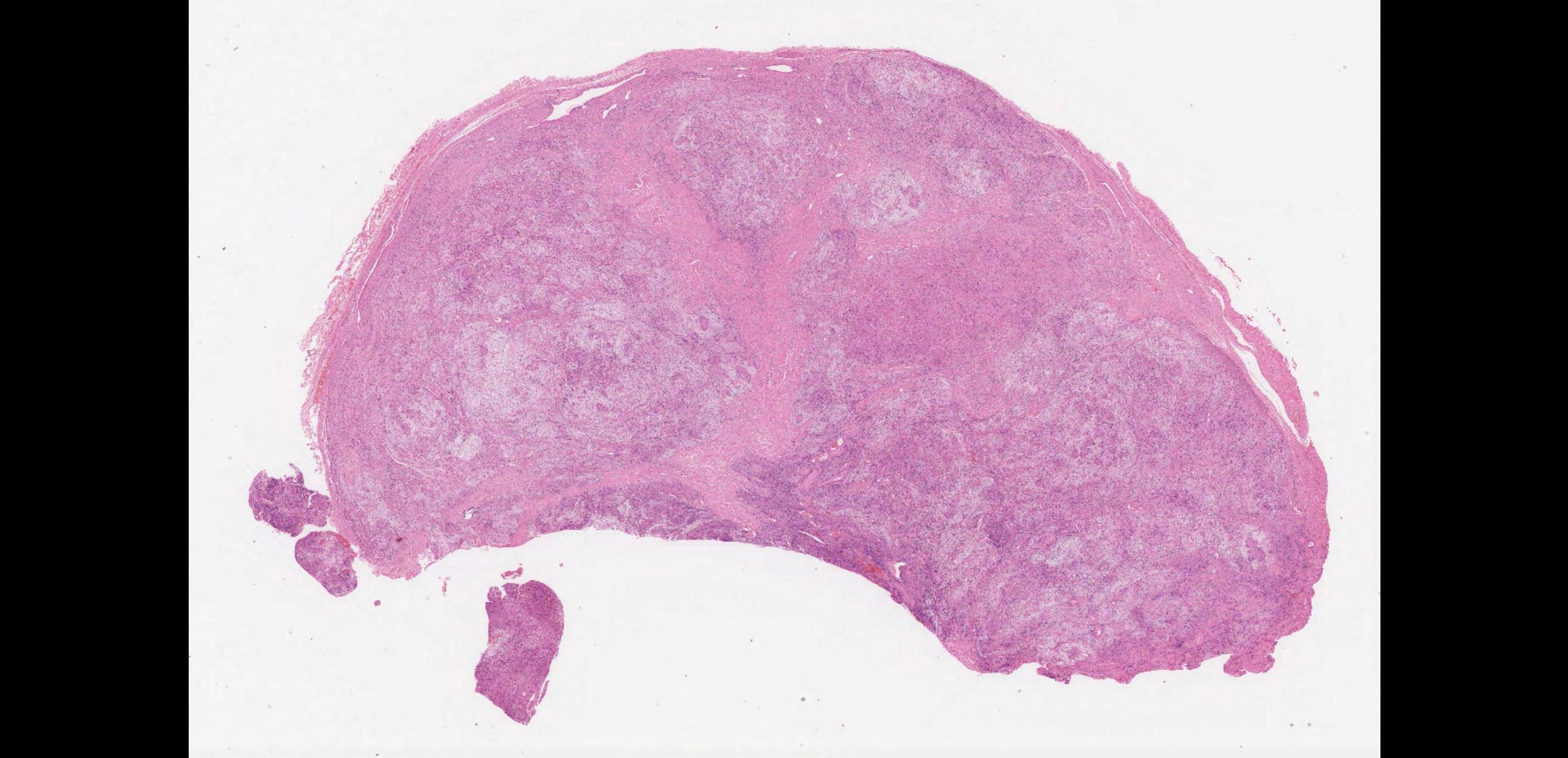



??
Case 31 Diagnosis
Ancient schwannoma
• Male 58 years
Leukoplakia present 3/12. Specimen: Incisional biopsy right side of tongue.
Macroscopic description: Mucosa 11 x5 x3mm.
Immunohistochemistry: none.
Case
•
32
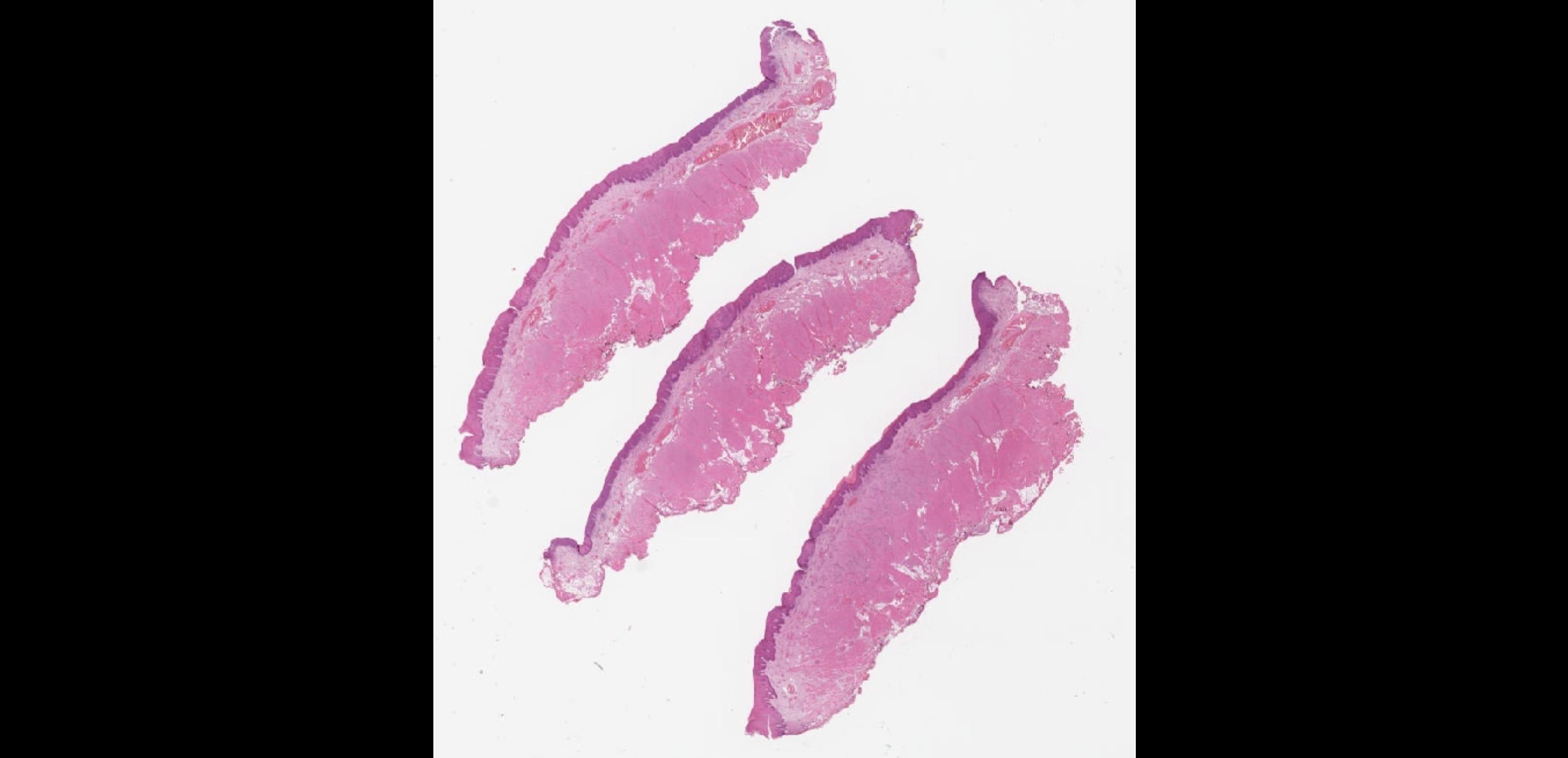
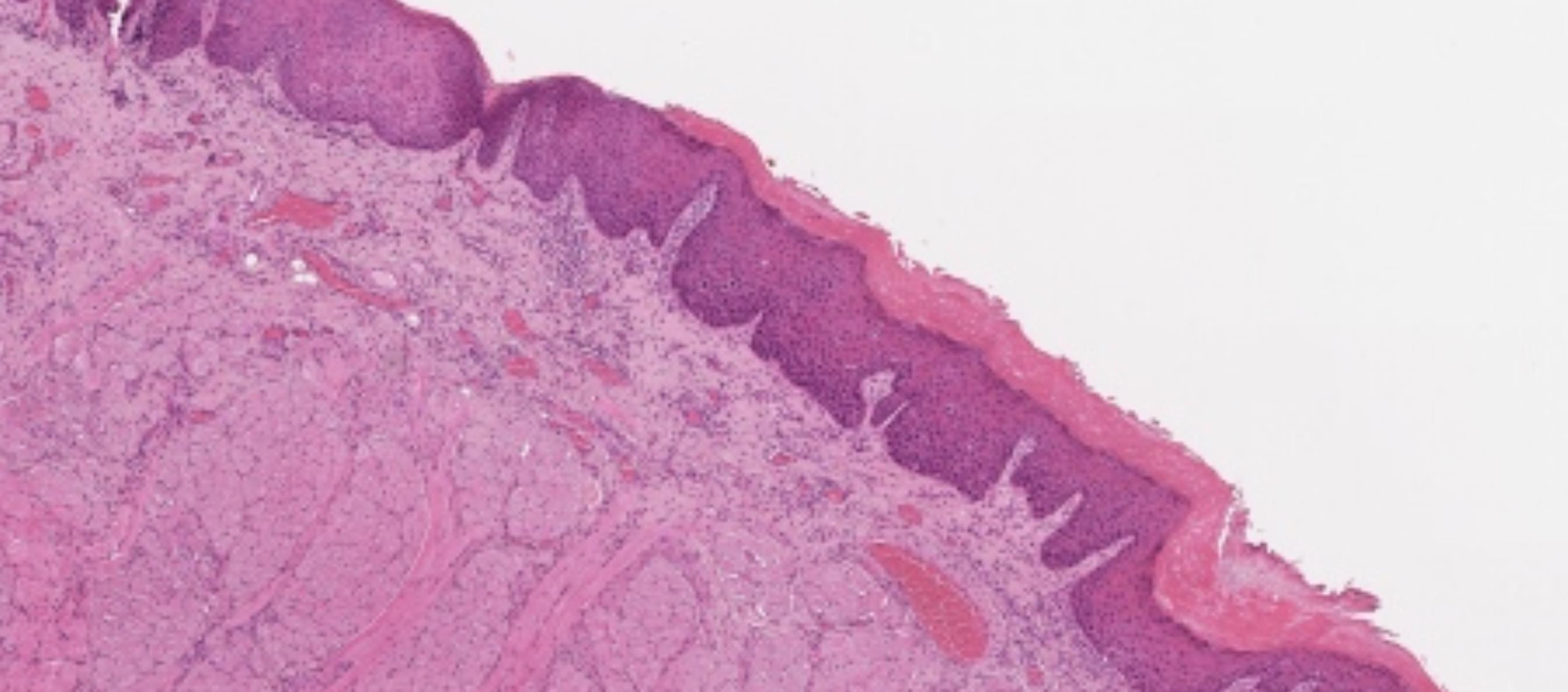
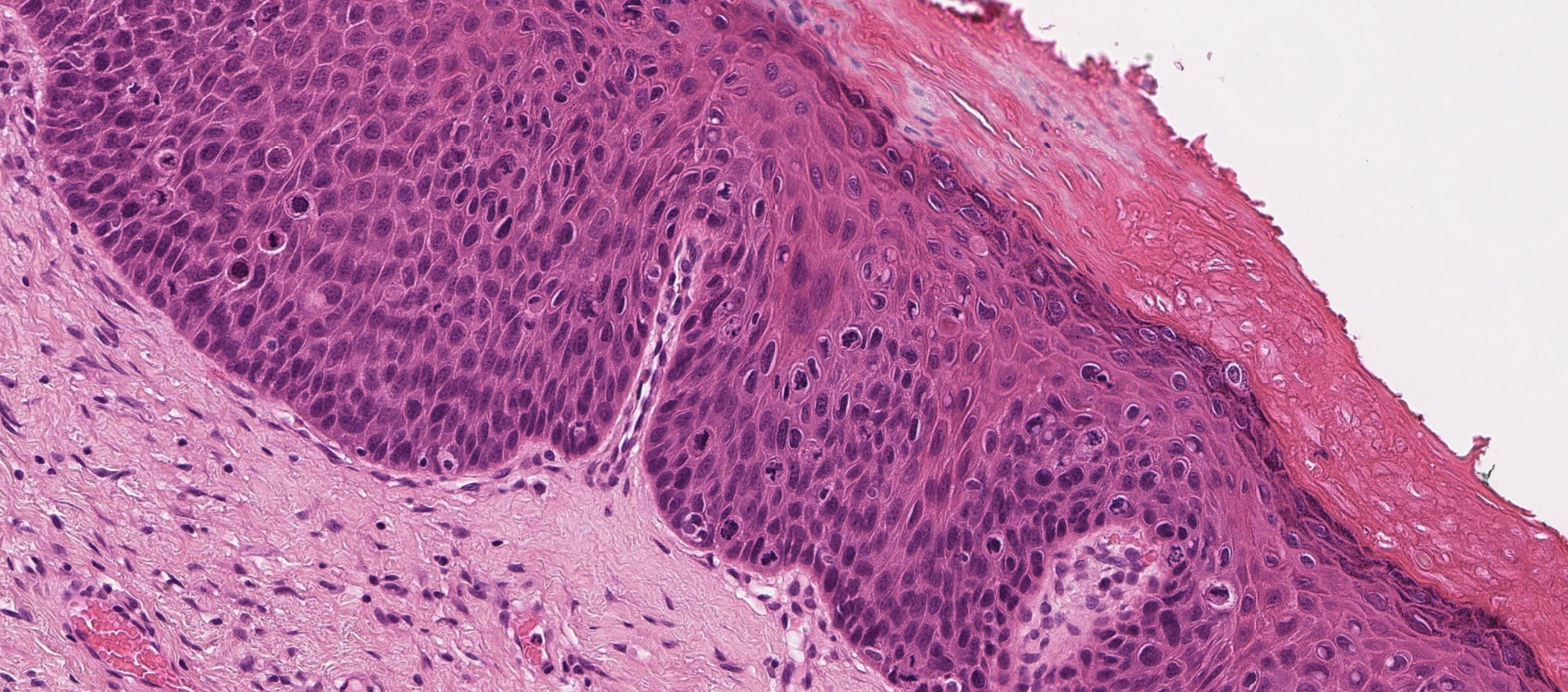
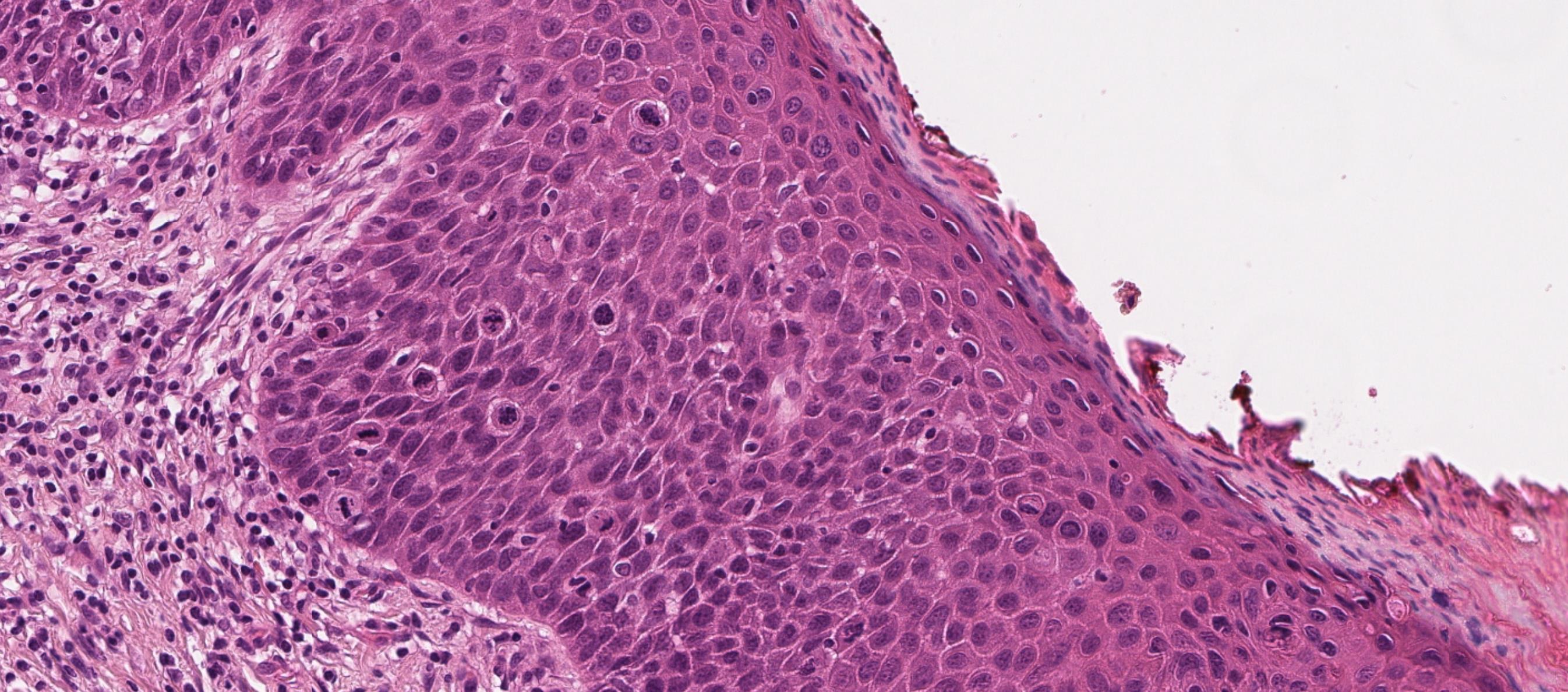
??
Case 32 Diagnosis
HPV related Oral intraepithelial neoplasia (Koilocytic dysplasia)


































































































































































