














อุตสาหกรรมอาหารในเอเชียเป็นหนึ่งในภาคส่วนที่ใหญ่ที่สุด
และมีพลวัตมากที่สุดในโลก โดดเด่นด้วยความหลากหลายทาง
การเติบโตอย่างรวดเร็ว และมีความท้าทายอย่างยิ่ง
สะท้อนถึงความหลากหลายและพลวัตทางเศรษฐกิจของภูมิภาค
แต่ยังต้องเผชิญกับความท้าทายด้านความยั่งยืน ความปลอดภัย
อาหาร และความต้องการของผู้บริโภคที่เปลี่ยนแปลงไป การ
ปรับตัวต่อความท้าทายเหล่านี้ พร้อมกับรับโอกาสต่างๆ ที่เข้า
มา จะมีความสำาคัญอย่างยิ่งต่อความสำาเร็จอย่างต่อเนื่องของ
อุตสาหกรรมอาหารในเอเชีย
ติดตามเทรนด์ล่าสุดของอุตสาหกรรมอาหารโดยเยี่ยมชม Fi
ASIA Indonesia และ Vitafoods Asia! รายละเอียดในเล่ม!
The food industry in Asia is one of the largest and most dynamic sectors globally, characterized by diverse cultural influences, rapid growth, and significant challenges. It reflects the region’s diversity and economic dynamism. The industry also faces challenges related to sustainability, food safety, and changing consumer preferences. Adapting to these challenges while embracing opportunities will be critical for the continued success of the food industry in Asia. Keep abreast on the recent trend of the food industry by visiting Fi ASIA Indonesia and Vitafoods Asia! Read more inside the magazine!

Karuna Chinthanorm Chief Editorial Officer
ADVISORY BOARD
ปราโมทย์ ธรรมรัตน์ PRAMOTE TAMMARATE ifrpmt@yahoo.com
สมคิด รื่นภาควุฒิ SOMKID RUENPARKWOOT somkid-doa@hotmail.com
TEAMWORK
ศุภวัชร์ สุขมาก SUPAWAT SUKMARK ss@media-matter.com
กรุณา จีนถนอม KARUNA CHINTHANOM kc@media-matter.com
อาภาพรรณ ชัฏไพศาล APAPAN CHATPAISARN editor@media-matter.com
บุษยมาศ นาคเกิด BUDSAYAMAS NAKKERD editor@media-matter.com
สิทธิพร ชมภูรัตน์ SITTHIPORN CHOMPURAT journalist@media-matter.com
เบญจมาศ ศรีสุข BENJAMAS SRISUK innolab@media-matter.com
วนัสนันท์ จีนถนอม WANASANAN CHINTHANOM agency@media-matter.com
THU DO innolab.vn@media-matter.com
43/308 หมู่ 1 ถนนจอมทอง
43/308 Moo 1, Jomthong Road, Jomthong, Bangkok 10150 Thailand
TaxID 0105552007301
+66 875171651 F +66 2045 5358 innolab@media-matter.com
http://www.innolabmagazine.com innolabmagazine
The publisher endeavors to collect and include complete, correct and current information in INNOLAB but does not warrant that any or all such information is complete, correct or current. The publisher does not assume, and hereby disclaims, and liability to any person or entity for any loss or damage caused by errors or omissions of any kind, whether resulting from negligence, accident or any other cause. INNOLAB does not verify any claims or other information appearing in any of the advertisements contained in the magazine, and cannot take any responsibility for any losses or other damages incurred by readers in reliance on such content.
TYPES, PURCHASING GUIDELINES, STORAGES AND FUTURE DEVELOPMENT GUIDELINES
CHARACTERIZATION AND CHARACTERIZATION LABORATORY
TO BE BIGGER, BOLDER, AND BRIMMING WITH INNOVATION
POISED TO BOOST NUTRACEUTICAL TREND AND
CPHI SOUTH EAST ASIA 2024: THE SUCCESS OF PHARMACEUTICAL SECURITY IN THAILAND AND ASEAN BEGINS PROPAK ASIA 2024 SURPASSED EXPECTATIONS WITH OVER 68,218 ATTENDEES. BUSINESS DEALS AT THE EVENT EXCEEDED 5 BILLION BAHT














E-mail : thailandlab@vnuasiapacific.com bioasiapacific@vnuasiapacific.com futurechem@vnuasiapacific.com
Tel : +66 2 111 6611 Ext. 241, 243
@thailandlab | @bioasiapacific
Website : www.thailandlab.com | www.bioasiapacific.com


























Multiple funtions incorporated into one unit, resolving issues in various study subjects.
Heidon Trobogear
Friction and Wear Tester
Portable Friction Meter
Tactile Meter
Surface Property Tester
Help Customers:
Improved Product Durability
Enhanced Product Quality
Lower Production Cost
Increase Product Competitiveness
Optimize Product Design



Heidon Three-one Motor (Agitator)
DC Brushless Motor
Feedback
LCD Display
Timer
Safety: Current Limit Circuit and Thermal Protector
Explosion Proof Version Available
Forward/reverse function
Digital tachometer
Low Noise



(food business operator; FBO)
ของอาหารประเภทใดบ้างที่เกี่ยวข้อง
คำ�ว่� “อันตร�ย (hazard)” ต�มคำ�
จำ�กัดคว�มของ Codex Revision 2022
หม�ยถึง “ส�รชีวภ�พ เคมี หรือก�ยภ�พที่ มีอยู่ในอ�ห�ร ที่มีแนวโน้มจะก่อให้เกิดผล เสียต่อสุขภ�พ” จ�กคำ�จำ�กัดคว�มนี้จะเห็น
ว่�สิ่งที่จะก่อให้เกิดอันตร�ยต่อผู้บริโภคไม่ ว่�จะเป็นสิ่งชีวภ�พ เคมี และก�ยภ�พนั้น ขึ้นอยู่กับว่�สิ่งเหล่�นี้อยู่ในอ�ห�รที่มีสภ�วะ อย่�งไร โปรดระลึกไว้เสมอว่�ธรรมช�ติของ
อันตร�ยของอ�ห�รคือเป็นสิ่งที่มองไม่เห็น ไม่ทำ�ให้สี กลิ่น และรสช�ติของอ�ห�ร
เปลี่ยนแปลง จึงทำ�ให้เกิดก�รบริโภคโดยไม่

สภ�วะที่สิ่งเหล่�นี้อยู่ในอ�ห�รเป็นตัวชี้บ่ง ว่�สิ่งเหล่�นี้จะเป็นอันตร�ยของอ�ห�รหรือ ไม่
Pathogen of concern หรือ Microbiological hazard (ซึ่งต่�งจ�ก pathogen ที่ยัง ไม่มีก�รระบุสภ�วะที่เชื้ออยู่ในอ�ห�ร) คือ อะไร ซึ่งส�ม�รถพิจ�รณ�ได้จ�ก 1. ลักษณะสำ�คัญของผลิตภัณฑ์สุดท้�ย (end product characteristics) อันได้แก่ คว�มเป็นกรด-ด่�ง (pH) Water activity (aw)
Table 1 The factors influencing the growth of Clostridium botulinum compare with the key characteristics of canned salted tuna products
Clostridium botulinum
Type A และ Proteolytic B&F (อ้างอิง: ICMSF, Vol. 5, 1996)
The factors influencing the growth of Clostridium botulinum
Type A and Proteolytic B&F (ref: ICMSF, Vol. 5, 1996)
The key characteristics of canned salted tuna products (ref: 4 factories)
1% อุณหภูมิที่สามารถเจริญเติบโต Temperature 10-48°C จัดเก็บและจัดจำาหน่ายที่อุณหภูมิห้อง
Storage and distribute at 25-45°C ความต้องการอากาศ Oxygen
ไม่ต้องการอากาศเลย Strict anaerobe
ภายในกระป๋องมีสภาวะเป็นสุญญากาศ
vacuum
Ensuring food safety for consumers is crucial for food business operators (FBOs). It shall be aware and prioritized. It is the accountability of manufacturers to produce safe food, with no consumers’ demands needed. Therefore, manufacturers shall obtain sufficient knowledge, experience, and data to analyze hazards in certain type of product they are producing.
The term “hazard,” as defined by the Codex Revision 2022, refers to “ a biological, chemical or physical agent in food with the potential to cause an adverse health effect.” According to this definition, whether these hazards pose a risk to consumers depends on
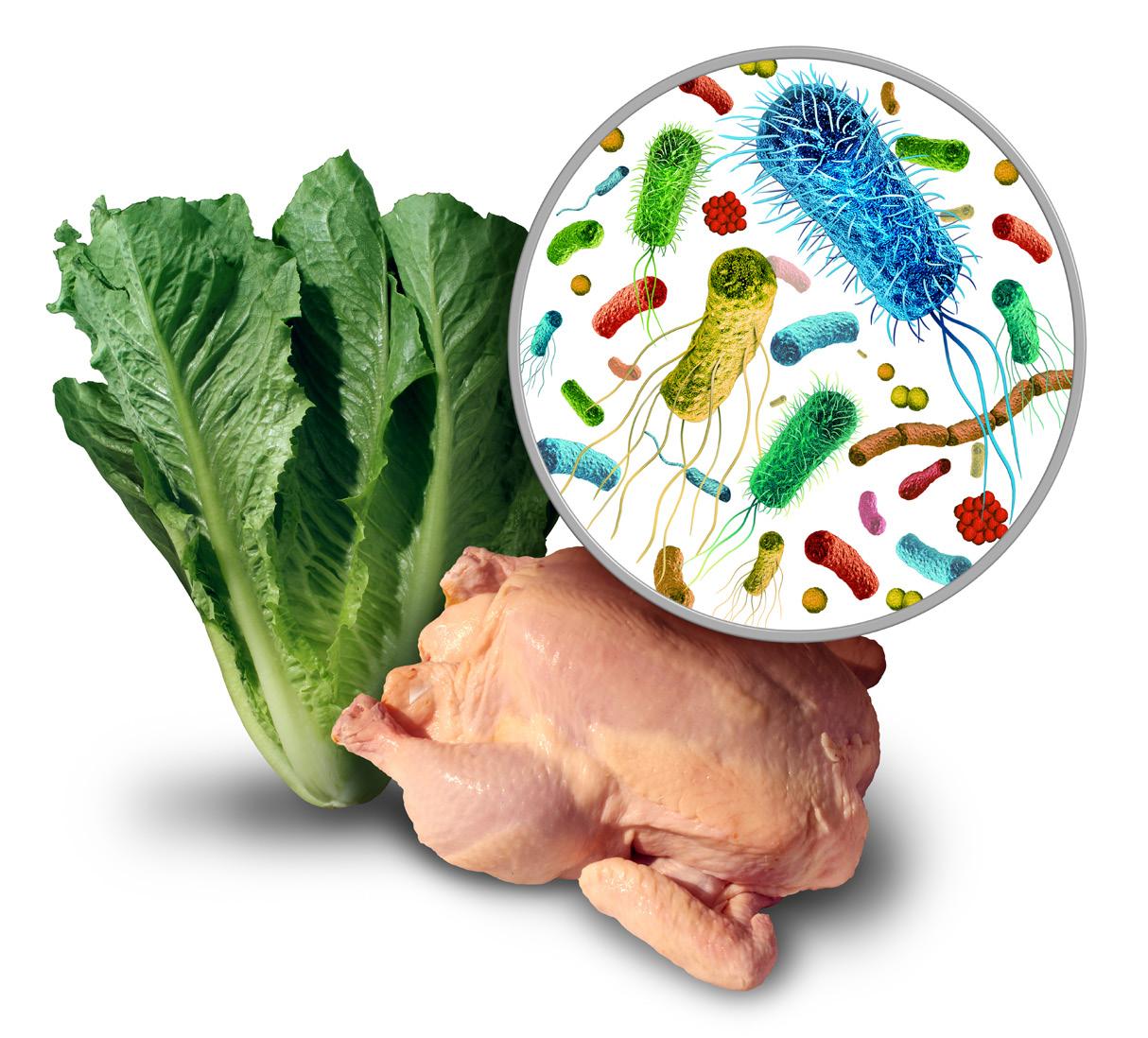
their presence and the condition of the food. Remember, the nature of a food hazard is that it may be invisible and may not alter color, smell, or taste of food. The consumers may unwarily consume it. Therefore, presence of these agents in food indicates whether they pose a hazard. For example, chicken bones in fried chicken drumsticks are not considered as a physical hazard because bones are clearly visible in the product, allowing consumers to consume them cautiously without risk. This is different
from boneless chicken meat products, where any remaining bones would pose a physical hazard because consumers do not expect bones and may inadvertently consume them, it thus poses a risk. Therefore, in such cases, chicken bones are classified as a physical hazard in boneless chicken meat products.
To ensure food safety, particularly concerning biological hazards such as pathogens, food business operators shall have sufficient knowledge to identify pathogens of concern or microbiological hazards (the term ‘pathogens’ is not indicated food condition). This involves considering various factors as follows:
1. End-product characteristics: These include pH, water activity (aw), salt content, packages and packaging processes, sterilization conditions, storage conditions, distribution, including shelf life.
For example, a food-related microorganism (pathogens of concern) of canned salted tuna products, undergone retort sterilization and are distributed at room temperature is Clostridium botulinum. A mesophilic bacterium that produces heatresistant endospores, is considered a pathogen of concern for canned salted tuna products. Refer to Table 1, presenting factors influencing the growth of C. botulinum with the key characteristics of canned salted tuna products. It clearly shows that the product characteristics support growth of C. botulinum. Typical aw range of canned salted tuna products is approximately 0.97-0.99 and pH range is 5.9-6.2. According to Table 1, C. botulinum can grow at aw above 0.935 and pH 4.6 or higher.
In addition, salt content is only 1% in canned salted tuna products. Table 1 indicates that salt concentration of 10% or higher is required to inhibit the growth of C. botulinum Furthermore, headspace purging in the production process is employed to prevent oxidation which can alter product quality attributes - color, odor, and taste. This creates anaerobic environment within the can, favoring growth of strictly anaerobic C.
botulinum. Products are stored and distributed at room temperature as a shelf-stable item with a long shelf life, potentially over a year.
Despite C. botulinum is a slowgrowing bacterium, extended storage periods provide sufficient time to grow and produce dangerous toxins. Room temperature condition supports growth of mesophilic bacteria. Therefore, if there is an error in the sterilization process and some C. botulinum spores survive, the product poses a risk to consumers. Conversely, vegetative pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella, and Escherichia coli, which do not form endospores, are also concerning in food production due to their association with product handling and hygiene practices.
2. Based on recent epidemiological data and scientific reports on foodborne diseases, there are reports of Listeria monocytogenes contamination in various types of ready-to-eat foods, especially in chilled and frozen items. This has led to widespread outbreaks of Listeriosis, causing numerous illnesses and fatalities. DNA analysis techniques, such as DNA sequencing, have revealed that L. monocytogenes can persist in the production environment of various ready-to-eat food manufacturing plants for extended periods, including seafood ready-toeat (>10 years), dairy product and ready-to-eat meat (>12 years). In addition, it is found that Listeriosis is related to L. monocytogenes contamination in the production environment.
Moreover, there are reports of Salmonella contamination from the production environment in lowmoisture ready-to-eat food products such as peanut butter, cereal, chocolate powder, nuts, and sesame seeds. Reports also indicate that contamination of L. monocytogenes and Salmonella in food products occurs after the sterilization process and before the products are packaged.
Therefore, effective control of pathogens contaminating the production environment requires cleaning and disinfection programs. Especially for food contact surfaces as well as non-food contact surfaces, it is to prevent contamination leading to contaminated food products. Furthermore, food operators shall validate cleaning and disinfection procedures of complex machinery and equipment, known as cleaning validation. It is to ensure that the designed cleaning and disinfection procedures effectively eliminate targeted pathogens. Additionally, manufacturers should employ robust environmental monitoring programs to monitor and identify sources of microbial contamination.
To control pathogens and produce safe food, manufacturers shall clearly identify pathogens of concern for each product and determine the control measures at specified production process. For example, C. botulinum in canned food shall be controlled at sterilization process in the retort, while L. monocytogenes and Salmonella shall be controlled at either sterilization process or preventing post-sterilization contamination.


Types, Purchasing Guidelines, Storages and Future Development Guidelines
เนื้อสัตว์ที่นิยมบริโภคในปัจจุบันได้จ�ก
ก�รตัดแต่งซ�กสัตว์ชนิดต่�งๆ ที่เป็นแหล่ง
อ�ห�ร โดยส�ม�รถนำ�เอ�ส่วนกล้�มเนื้อและ
อวัยวะภ�ยในม�ใช้เป็นอ�ห�รได้ กล้�มเนื้อ
สัตว์ส�ม�รถรับประท�นได้ทั้งแบบดิบและ
สุกต�มคว�มนิยมและวัฒนธรรมประจำ�ท้อง
ถิ่น
เนื้อสัตว์แบ่งออกเป็นกลุ่มใหญ่ต�มสีของกล้�ม ได้แก่
1. เนื้อสัตว์สีข�ว ได้จ�กกล้�มเนื้อของ
ซ�กสัตว์ปีกเป็นหลัก เช่น เนื้อไก่ เนื้อไก่งวง
2. เนื้อสัตว์สีแดง ได้จ�กกล้�มเนื้อของ
หรือสัตว์เคี้ยวเอื้อง
Author info
Nanthanporn Ruchikachorn
Lecturer at School of Culinary Art
Suan Dusit University
Contact
Food Science and Technology Association of Thailand admin@fostat.org
ในกล้�มเนื้อเป็นหลัก โดยเนื้อวัวที่ได้จ�ก
ในกลุ่มผู้บริโภคปริม�ณสูง
กับปริม�ณคุณค่�ท�งอ�ห�ร
5. เนื้อสัตว์ในบรรจุภัณฑ์ย่อยสำ�หรับ
1-2 ที่: เนื่องจ�กก�รขย�ยตัวของคว�ม
เป็นเมืองทำ�ให้ขน�ดครัวเรือนเล็กลงและ ลักษณะก � รบริโภคอ � ห � รของผู้บริโภค
เปลี่ยนแปลงไป บรรจุภัณฑ์ย่อยที่มี Portion
ต่อก�รปรุงหรือท�นขน�ดเล็กจะช่วยอำ�นวย
คว�มสะดวกในก�รรับประท�นอ�ห�รใน
แต่ละมื้อม�กขึ้น
Protein is one of the nutrients that provides energy and affects the development and growth of living things. It is no doubt that the source of complete protein, or in other words, essential amino acids, is meat and meat products. The primary source of meat production is the livestock industry, and raw materials from the mentioned industry can be brought into the product processing industry which is secondary production to increase the products variety and fulfill the needs of consumers.
The meat we consume today is obtained from the part of an animal which can be muscle or offal. Animal muscle can be eaten raw or cooked according to the liking and culture. Animal muscles can be divided into groups based on their color:
1. White meat: It is mainly obtained from the muscles of poultry such as chicken and turkey.
2. Red meat: It is obtained from the muscles of large animals or ruminant animals such as beef, pork, lamb and horse.
Although meat is obtained from different types of animals, all types of meat have similar components which are muscle, connective tissue and fat. The age of the animal and the parts of meat are the factors that affect the taste and the texture of food.
To clarify, if the meat used for cooking comes from a muscle that has a lot of movement such as hip or
leg that has high connective tissue, it will be sticky. However, if it comes from a part that has little movement and low connective tissue such as tenderloin, it will be soft. The meat of wild animals also has a higher connective tissue than animals raised in the livestock industry. The meat of young animal has thick fiber but low connective tissue, so the meat is softer and more delicious than older animals. For example, young chicken and old chicken provide different food textures. Additionally, meat with high fat content is more tender, while meat with low fat content or fat inserted into red meat has less intense taste, and the texture is not as soft as those with high intramuscular fat. The amount of intramuscular fat is an international index for grading the quality of beef. It is mainly determined by the amount of red meat and fat in the muscles. Beef obtained from a specific breed
and a special raising process that produces high levels of intramuscular fat is classified as high-quality and expensive beef.
When choosing meat for cooking, we must consider the part of meat that is proper to food type and cooking duration, in addition, we must consider the color of the meat. Good meat must have a bright color according to its type, however red meat has red pigment that gives it a different color in different oxygen conditions. Therefore, meat sold in a sealed container always has a dark red color because it is not exposed to the air, but when it is taken out of the container, the pigment will react

with oxygen and turn it into bright red color. If the greenish color appears, it means that the meat is degraded by microorganisms, the mucus and bad odor may occur also. The good quality meat must be moist and firm.
The meat of animals has high moisture content, so it has a short shelf life and needs to be stored at a low temperature. For a short-term storage, it can be stored at temperatures above freezing but should not be longer than 5 days because the microorganisms still active. To maintain the best quality, meat should be stored at temperatures below 0 degrees Celsius which the meat will be hard and will be difficult to cut, so it should be trimmed and divided for cooking before freezing. If meat with high moisture content is frozen and brought out to melt and alternating several times, both flavor and texture will be lost.
Processing is another way to extend the shelf life of meat. It also causes by-products with different odors, flavors, and textures. There are various processing methods. You can use one or several methods at once. The popular meat processing techniques include:
Salt: It is used in drying/smoking. The products are ham, bacon, sun-dried meat and dry sausages.
High temperature: It is used for food made from canned meat.
Fermentation: It is used with salt. The products are fermented pork and sour sausage.
Since the signing of the Paris Agreement in 2015, many countries around the world have been discussing the solution to address climate change. Awareness is being raised towards the global climate crisis. In the food sector, the livestock industry is considered a large industry that produces greenhouse gases, However, many related products emerge to solve the problem such as vegan diets, plant-based meat and cultured meat. Nevertheless, demand for traditional meat products continues
to trend upwards. The demand in 2023 is 30% higher than 2018, and demand trends change according to the situation. Current trends in meat foods can be summarized as follows:
1. Ready-to-cook or ready-to-eat meat: As the social norm is changed and the household size is smaller, so the food consumption pattern is changed also. The Products that help make daily life easier are becoming more popular. The examples are:
Frozen crispy fried chicken: It can be heated using an oven or air fryer oven for about 4 minutes.
Frozen teriyaki chicken skewer: It can be heated using a microwave or air fryer oven for about 3 minutes.
Sous vide chicken breast: It can be heated using a microwave. It can be eaten with salad or combined with other food.
2. Meat with new flavors: The change of favoring causes the demand of unique, varied and tasty meat. This can be achieved by adding flavors that are characteristic of each nation or adding spices that are popular at that time, for example,
Mala dried pork leg: It’s a pork leg stewed in a Chinese-style malaflavored sauce and packed in readyto-eat container. It can be heated using a microwave for about 3-5 minutes. It can be eaten as a side dish or snack.
Western-style ham/ Chinese-style processed meat: It’s used for cooking or eaten as an appetizer.
3. Healthy meat: The consumers want products that facilitate their busy lifestyles. Besides, the products should be healthy and nutritious, as well as have sustainable food production. For example,
Frozen chicken meat that the chicken was naturally raised without added hormones. Consumers are safe from drugs or residues used during the farming process.
Low sodium bacon. It can replace regular high-sodium bacon and it is suitable for children or those who control their sodium intake.
4. White meat: Poultry meat
consumption tends to increase and replaces red meat consumption because it has a short production time, and it is popular among people who consume high amounts of protein such as people who exercise and build muscle as well as health-conscious consumers. White meat is low in fat when compared to red meat and it is considered cheap when compared to its nutritional value.
5. Meat in individual packages for 1-2 servings: The expansion of urbanization affects the size of household and consumption characteristics. A small package containing Portion for cooking or eating in small sizes. It will help facilitate eating more at each meal.
In addition to the various trends mentioned above, there is another trend in distribution channel strategy. Because of the digital transformation, especially during the global outbreak of new strains of virus, the entire world enters the digital transformation at a rapid pace. Especially in Asia, it was found that various product distribution channels change from offline to online distribution even fresh food that has a short shelf life. The most important factor in this trend is the infrastructure that supports transportation. It can lower operating costs, respond to the purchasing needs of consumers, and cause the circular economy.
Therefore, entrepreneurs who are in the meat or processed meat business and interested in expanding the business, It is necessary to clearly define the target customers and choose marketing strategies that are appropriate for target customers whether product strategy, distribution channel strategy or promotional strategies based on statistical information about trading, import-export, consumer behavior and in-depth product market trends. These are guidelines for new products development or distribution channel strategies. You can use a single strategy or combine many marketing strategies to build a competitive advantage. However, pricing strategy should be carefully considered to prevent price erosion.
สตาร์ช (starch) เป็นหนึ่งในองค์ประกอบหลักในอาหารที่ให้คุณค่าทางโภชนาการแก่ทุกมื้ออาหารของมนุษย์และสัตว์

ในที่นี้ ขอเรียกสต�ร์ชง่�ยๆ ว่� “แป้ง” ซึ่งก็คือพอลิเมอร์ของน้ำ�ต�ลกลูโคสที่ต่อกัน เป็นส�ยย�วๆ ประกอบด้วยพอลิเมอร์ 2
แบบ คือ พอลิเมอร์ส�ยตรง (amylose) และส�ยกิ่งแขนง (amylopectin)
�และเปลี่ยนสภ�พเป็น
ปร�กฏก�รณ์เช่นนี้เร�เรียกว่�
ของแป้งสุก” หรือ “Retrogradation” มี คุณสมบัติที่เก�ะตัวกันแน่นและรีดน้ำ�ออก
เมื่อ
คงตัวอยู่ได้ เช่นเดียวกับขนมจีน ขนมชั้น
และขนมไทยต่�งๆ ก็อ�ศัยคุณสมบัติในก�ร
คืนตัวหรือก�รจับตัวกันของพอลิเมอร์ส�ยตรง
จนเกิดเป็นเจลที่มีคว�มยืดหยุ่นต�มต้องก�ร
Starch is a primary nutrient that provides nutritional value to every meal consumed by humans and animals. It is derived from staple plants that are major sources of starch, such as rice, corn, wheat, potatoes, and cassava. When extracted from seeds, roots, or underground stems, it yields starch granules, along with proteins, fats, and various minerals.
Starch is a long-chained polymer of glucose molecules. It consists of two types of polymers: amylose (linear polymers) and amylopectin (branched polymers). When we cook starch, millions of tiny starch granules swell, become translucent, and increase in viscosity. However, if we let the cooked starch cool down overnight or store it in the refrigerator, it becomes opaque, water is separated, and it turns into a gel or solid mass. For example, coconut milk mixed with corn starch, used in sticky rice with mango, is solidified and loses its original texture when stored in the refrigerator.
Some foods, such as rice noodles, Pad Thai noodles (Sen Chan), or Thai steamed rice flour dumplings (Khao Kriab Pak Moh), are made from cooked rice starch that forms delicious, soft gel-like sheets when steamed. Even when hot broth is poured over, the noodles remain intact. Similarly, Kanom Jeen noodles, Thai layer cake (Kanom Chan), and Thai sweets rely on the retrogradation properties of straight-chain polymers, forming a gel with the desired elasticity. This phenomenon is known as “starch retrogradation.” Polymers are tightly packed, expelling water from their structure. Once this occurs, it is difficult to separate the polymer chains by heating (thermo-irreversible). For example, if retrogradation occurs in yogurt starch, whey separation will occur. In chili or oyster sauces, lumps may form in the bottle or water may separate at the neck of the bottle. In bread, retrogradation causes hardness and dryness after being stored for
several days.
However, in many types of food, retrogradation is highly desirable, especially when using starch with high amylose content. In fried foods like fried chicken or banana fritters, it results in a crispy texture that lasts longer and reduces oil absorption. In gummy jellies, this starch is used instead of gelatin for halal and vegetarian food to prevent melting and deformation in a hot environment. In cheese, it makes a firmer texture, partly replacing milk proteins. It ensures that cheese retains its shape after baking. In crispy snacks, it helps create a firm and crisp texture that doesn’t break easily. In rice noodles and Khanom Jeen, it aids forming sheets and strands effectively.
For over a hundred years, starch textbooks around the world have stated that “starch retrogradation is irreversible or difficult to.” Rice flour dumplings or noodles formed in this process remain in their original sheets or strands, regardless of soaking in hot water over time. They may soften and break into small pieces that settle at the bottom. This is different from carrageenan jelly, agar used in coconut jelly or culture media, and gelatin. When these gels are heated and cooled, they solidify into gels, but when reheated, they melt into a liquid and solidify into gels again when cooled, repeating the process.
With advances in biotechnology, a new type of starch has emerged in the world. It transforms ordinary
potato starch into something with extraordinary properties. This is the world’s first starch that redefines the phenomenon of starch retrogradation. It is highly safe, non-GMO, and not a food additive. Thus, it is a clean label ingredient, and an e-number is not required.
This remarkable starch, when cooked, behaves like ordinary starch - cooling into opaque white gel. But when reheated, it instantly transforms into a clear liquid. Upon re-cooling, it returns to an opaque white gel, alternating back and forth as if it were not starch. Only certain hydrocolloids, such as gelatin, carrageenan, and agar, can exhibit such properties. This phenomenon is known as “thermo-reversibility. Through this innovative approach, starch is reorganized at the molecular level using a special enzyme



Unlike regular starch molecules that are tightly packed during retrogradation and cannot unwind, this starch can unwind when heated and rebind upon cooling, similar to typical retrograded starch. However, it does not form as tight and strong as agar or gelatin. It provides sufficiently firm texture to be mixed into various foods, transforming soups or sauces into thick liquids or soft gels. The texture is closer to fat compared to currently available fat replacers. It is capable of melting like real fat at around 50°C. Rather than just providing greasiness, this innovation breaks the limitations of starch as a natural polymer, propelling it to the next level.
1. Gel Formation: Starch that has been fully cooked through boiling can change from a liquid to a gel state upon cooling, and remains stable when stored in a refrigerated environment overnight. The gel formation rate and the texture’s firmness depend on the amount of starch,
specific modifications to the starch, and environmental conditions.
2. Reversibility: Once gelled, the starch can revert to its original liquid state. This contrasts with conventional starches that cannot revert to a liquid state once gelled or undergo retrogradation. This reversibility is due to the specific molecular structure of the modified starch, which allows for reversible bonding and can transform back into a liquid when heated to temperatures above 50°C.
3. Stability: Gels formed from reversible starch are generally stable across various pH levels and can maintain their properties under diverse storage conditions.
4. Texture and Mouthfeel: This starch provides a smooth and consistent texture and can enhance the mouthfeel of various food products effectively.
Applications in the Food Industry:
Reversible starch is utilized in innovative ways in the food industry, such as converting soups or sauces into thickened or soft gel-like textures. It offers a texture that closely resembles fat, more so than existing fat replacers. It can melt like real fat at around 50°C, not just providing fat-like properties but also overcoming the limitations of traditional starches, which are
products have textures and flavors that are nearly indistinguishable from their full-fat counterparts. Additionally, it supports the development of fusion cuisine and molecular gastronomy, showcasing the remarkable capabilities of thermo-reversible starch.
This starch provides a unique texture that melts and solidifies according to temperature, mimicking fat and providing creamy texture when broken down by saliva enzymes in the mouth. Unlike other hydrocolloids like gelatin, which can switch phases but cannot be digested in the mouth like starch. This is why when eating Xiao Long Bao made with gelatinbased soup, the soup feels greasy and leaves sticky residue on lips, requiring to be served hot. However, the soup retains such high heat that it can scald the mouth, leading to lawsuits in China.
Furthermore, the starch facilitates the production of diverse foods or caters to specific consumer groups representing the significant markets, such as:
- Halal foods for Muslim communities in Malaysia, Indonesia, and the Middle East.
- Vegetarian or vegan foods in India, a large and noteworthy market.
- Foods in China, where concerns about gelatin and mad cow disease are rising.


This new type of starch significantly contributes to the food industry by creating novel foods, including Xiao Long Pao (soup dumplings), Liu Sha Pao (lava buns), black sesame dumplings, cheese-stuffed sausages, chili sauce-filled sausages, cream cheese, yogurt, low-fat margarine, and low-fat cream salads. These
- Replacing hydrogenated shortening, which contains transfats that cause cancer, or reducing saturated fat content in bakery products, margarine, and black sesame glutinous rice balls.
Thermo-reversible starch thus offers new choices and innovations with high safety, helping expand and create new market opportunities for the food industry to grow sustainably.

(biopharmaceuticals)
ผลิต สกัด หรือผลิตแบบกึ่งสังเคราะห์จากต้นกำาเนิดชีวภาพ
หรือส่วนผสมเชิงซ้อนของสารเหล่านี้
การทดสอบคุณสมบัติของยาชีววัตถุ คืออะไร
ย�ชีววัตถุเป็นโมเลกุลที่มีคว�มซับซ้อน
สูง ต้องมีคุณภ�พสูงเพื่อคว�มปลอดภัย
และประสิทธิภ � พในก� รใช้ง � นในมนุษย์
และต้องมีคว � มคงตัวของผลิตภัณฑ์
สุดท้ � ยม � กกว่ � ก � รทดสอบคุณสมบัติ (characterization) ของย�ชีววัตถุเป็น
ขั้นตอนสำ�คัญในก�รพัฒน�และก�รผลิต
ย�ชีววัตถุ ผลิตภัณฑ์ขั้นสุดท้�ยจะจำ�แนก
คุณสมบัติจ�กคว�มซับซ้อนและลักษณะ วิวิธพันธ์ุเฉพ�ะตัว (intrinsic complexity and heterogeneity) ซึ่งจำ�เป็นต้องมี
ดีควรได้รับก�รตรวจสอบและควบคุมใน ระหว่�งกระบวนก�รผลิต
ลำ�ดับขั้นตอนก�รทำ�ง�นหล�ยชุดจะนำ� ม�ใช้เพื่อทดสอบคุณสมบัติเชิงวิเคร�ะห์เพื่อ คุณภ�พของผลิตภัณฑ์ตลอดกระบวนก�ร เหล่�นั้น เนื่องจ�กย�ชีววัตถุมีคว�มซับ ซ้อน ก�รทดสอบคุณสมบัติของส�รจึงไม่ใช่แค่ก�รทดสอบเพียงครั้งเดียว
Author info
INNOLAB team innolab@media-matter.com
Source: Provital at PCHI 2024
Biopharmaceuticals, also known as a biological medical products or biologics, is any pharmaceutical drug product manufactured in, extracted from, or semi synthesized from biological sources. Different from totally synthesized pharmaceuticals, biologics include vaccines, whole blood, blood components, allergenics, somatic cells, gene therapies, tissues, recombinant therapeutic protein, and living medicine used in cell therapy. Biologics can be composed of sugars, proteins, nucleic acid, or complex combinations of these substances, or may be living cells or tissues. They (or their precursors or components) are isolated from living sources—human, animal, plant, fungal, or microbial. They can be used in both human and animal medicine.

What is biopharmaceutical characterization?
Biopharmaceuticals are highly complex molecules which require high quality for safety and efficacy in human uses and need more stability of the final product. Biopharmaceutical characterization is critical step of biopharmaceutical development and manufacturing. Biopharmaceutical final product is characterized by intrinsic complexity and heterogeneity, which drives the need for a deeper knowledge of the structural features that can have huge impact on the stability, efficacy and safety of the final drug. The desired level of quality for well-characterized products, should be monitored and controlled during the manufacturing processes.
A series of workflow for analytical characterization should be applied for product quality throughout those processes. Because of the complexity of biopharmaceuticals, their characterization is never performed through a single assay, more techniques are usually required to monitor all the critical features to ensure their quality. Characterization testing is an understanding of the physical and chemical properties of biopharmaceutical materials. During drug development, these properties

can have an impact on the product’s performance, ability to be processed, stability and appearance.
The analytical characterization of biopharmaceutical is still challenging for biotech industry to meet the requirements. Conventional methods, such as chromatography and electrophoresis, are routinely used because they are easy to use, robust, and cost effective.
Current trends for characterization are in-depth and well characterized. Current advances in instrumentation can help to follow those trends and characterize very complex heterogeneity. Mass spectrometry is the most powerful instrument among
them, which provides high resolution, accurate, and confident data with rich information from primary structure (intact mass and peptide mapping) to high order.
Why biopharmaceutical characterization is important? Biopharmaceutical characterization is important because it allows scientists to monitor those features that ensure drug efficacy and safety. The characterization step allows manufacturers to improve biopharmaceutical production from the very early phases and to follow a
quality by design approach — not only in the design of the biotherapeutics but also in the production process.
For example, some features may indicate cellular stress during upstream processing and monitoring allows for quick correction of the culture conditions, resulting in a better yield and an overall better quality of the product. For this reason, there is a growing interest in bringing analytical techniques closer to the bioprocess pipeline or even integrating them so that real-time monitoring of the critical features can improve both process and product.
is biopharmaceutical characterization important for the discovery, development, and manufacture of biologic?
The importance and significance of characterization for biopharmaceuticals arises from the complexity of the product. it is important to first understand how different stresses impact
the assembly. Characterization helps to define the range of contaminants and their effect on product function. This understanding can be used as a signature of the molecule’s behavior in all aspects of development and manufacturing. Characterization of a biologics for a certain target in drug discovery phase can help identify treatments for other disorders. characterization to some extent also helps understand and manage the risk involved with manufacturing and cost attached to clinical trials.
A wide range of analytical techniques are required during the development and manufacturing of biologics. These approaches are necessary for the continuous assessment of biologics, helping to identify and characterize post-translational modifications (e.g., glycosylation), structural heterogeneity, stability,
conformation, etc. Biopharmaceutical drug developers are able to evaluate and adjust the upstream and downstream bioprocesses involved in biomanufacturing and implement changes as required to ensure efficiency of the process and purity of the final product.

Biopharmaceutical characterization for biologic products
Bioactive compounds are analyzed using various methods, such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS). NMR analysis provides quantitative data and structural characterization of a product. However, NMR possesses a relatively low sensitivity and is used to profile major constituents. Several chromatographic tools such as ion exchange, affinity and gel filtration chromatography are used to purify recombinant protein-based biopharmaceutical products.
Biopharmaceutical Characterization Laboratory (BPCL) has been set up in King Mongkut's University of Technology Thonburi (KMUTT) since January 2020 according to the national need. The establishment has been supported by KMUTT, Thailand Center of Excellence for Life Sciences (TCELS), and National Vaccine Institute (NVI) in supporting research and development as well as production of biopharmaceutical products. For the first launched of biopharmaceutical characterization services, BPCL focused on glycoprotein analysis in compliance with ISO/IEC 17025 and international standards.
BPCL has been launched the first set of biopharmaceutical characterization services including analyses of peptides, proteins, oligonucleotides, oligosaccharides, protein aggregates, product impurities, cell, production seeds, as well as the specific characteristics of bio therapeutics and vaccines. Their technical specialists have the expertise to take biologics from research and product development through characterization and quality control tests, and into clinical trials for safety and efficacy testing.
BPCL provides one stop services for characterization of Biopharmaceutical products including.
- Protein characterization
- Microbial & cell culture characterization
- Viral characterization
- DNA & RNA characterization
- Bioactive ingredient characterization
Tests includes pharmacopoeia methods and methods used sophisticate scientific equipment such as MALDI-TOF/MS, Q-TOF/MS, LC/MS-MS, CD-spectrometer, surface plasmon resonance (SPR), NGS as well as bioassays (ADCC, CDC).

Author info พชร สังข์ทอง
Potchara Sungtong Director, Business Development
Food & Beverage Technology, DKSH Management (Thailand) Limited potchara.s@dksh.com 063 858 6581
ของจุลินทรีย์ซึ่งอาจส่งผลต่อความสมบูรณ์ของผลิตภัณฑ์และความปลอดภัยของผู้ป่วย
ทำาความเข้าใจการทดสอบประสิทธิภาพ
ของสารต้านจุลินทรีย์ USP <51>
ก � รทดสอบประสิทธิภ � พของส � ร
ต้�นจุลินทรีย์ USP <51> เป็นวิธีก�รที่
ออกแบบเพื่อทดสอบประสิทธิภ�พของส�ร
ต้�นจุลินทรีย์ในผลิตภัณฑ์ย�ละล�ยน้ำ�ที่ไม่
ผ่�นก�รฆ่�เชื้อที่มี Water activity (a w ) ≥0.6 ก�รทดสอบนี้ทำ�ให้มั่นใจได้ว่�ส�ร
ต้�นจุลินทรีย์ในผลิตภัณฑ์ส�ม�รถยับยั้งก�ร เติบโตของจุลินทรีย์ที่อ�จปนเปื้อนระหว่�ง
หรือหลังกระบวนก�รผลิต
นี้ได้หลจุลินทรีย์ส�ม�รถเข้�สู่ผลิตภัณฑ์เหล่�
คือ 0, 1, 7, 14, และ 28 วัน USP ได้จัดหมวดหมู่ผลิตภัณฑ์ย � ละล�ยน้ำ�ที่ไม่ผ่�นก�รฆ่�เชื้อออกเป็น 4 กลุ่ม
กัน และต้องตรงต�มเกณฑ์ก�รทดสอบ
สุขภ�พของผู้บริโภคและรักษ�ชื่อเสียงของ
แบรนด์ ก�รทดสอบประสิทธิภ�พและก�ร
ทดสอบแบบท้�ท�ย (challenge test)
ของส�รต้�นจุลินทรีย์มอบข้อมูลพื้นฐ�นท�ง
วิทย�ศ�สตร์สำ�หรับก�รใช้ส�รกันเสีย เพื่อ
ให้แน่ใจว่�ผลิตภัณฑ์ยังคงปลอดภัยสำ�หรับ
ก�รใช้ง�นตลอดอ�ยุก�รเก็บรักษ�ที่กำ�หนด ผู้ผลิตต้องเลือกส�รกันเสียอย่�งระมัดระวัง โดยพิจ�รณ�จ�กสูตรของผลิตภัณฑ์ ก�ร
No less than (NLT) 1.0 log reduction from the initial calculated count at 7 days, NLT 3.0 log reduction from the initial count at 14 days, and no increase from the 14 days’ count at 28 days
No increase from the initial calculated count at 7, 14 and 28 days
In the highly regulated pharmaceutical industry, ensuring the safety and longevity of non-sterile aqueous products is paramount. Antimicrobial preservatives are crucial in preventing microbial contamination, which can compromise product integrity and patient safety. These preservatives help maintain the stability and efficacy of pharmaceutical products throughout their shelf life and during use, particularly for products that may be repeatedly exposed to potential contaminants. The USP <51> Antimicrobial Effectiveness Test (AET) is an essential tool in this context, providing a standardized method to evaluate the effectiveness of antimicrobial preservatives in pharmaceutical formulations.
The USP <51> Antimicrobial Effectiveness Test is a protocol designed to test the effectiveness of antimicrobial compounds in non-sterile, aqueous pharmaceutical products with a water activity (aw) of ≥0.6. This type of testing ensures that the antimicrobial compounds present in the product are capable of inhibiting the growth of microorganisms that may be introduced during or after the manufacturing process.
Microorganisms can be introduced to these products in various ways, such as reusing a container which requires multiple openings. Even just-washed hands aren’t sterile, so it is inevitable that microbes will be introduced. This test provides evidence that the antimicrobial compounds can inhibit those microbes over a specified period.
The procedure involves inoculating the product with specific strains of bacteria, yeast, and mold recommended by USP and monitoring the reduction in microbial count at designated intervals of 0, 1, 7, 14, and 28 days.
USP has categorized non-sterile aqueous products into four categories which are tested at different intervals and have to meet slightly different criteria for antimicrobial effectiveness testing. The four categories are summarized in the table below:
1. Injections, other parenterals, otic products, and sterile ophthalmic products made with aqueous bases or vehicles.
2. Topically used products made with aqueous bases or vehicles, nonsterile nasal products, and emulsions.
3. Oral products excluding antacids made with aqueous bases or vehicles.
4. Antacids made with an aqueous base.
The four categories indicated above have unique requirements for the antimicrobials to be considered effective as shown in table 1.
Products with a water activity (aw) of ≥0.6 are susceptible to microbial contamination and require preservative efficacy testing under USP <51>. This threshold is established because most bacteria, yeasts, and molds can grow at this level of water activity, making preservatives necessary to inhibit microbial growth.
To ensure compliance with USP <51> standards, manufacturers must utilize water activity meters to accurately measure and control water activity in their products. This process is crucial to help manufacturers meet regulatory requirements and maintain the integrity and safety of their products throughout their shelf life.
Compliance with regulatory standards like USP <51> is not just a legal requirement; it is essential for safeguarding consumer health
and maintaining brand reputation. The antimicrobial effectiveness and challenge tests provide a scientific basis for using preservatives, ensuring that products remain safe for use over their intended shelf life.
Manufacturers must carefully select preservatives based on the product’s formulation, intended use, and storage conditions. Additionally, ongoing stability testing is essential to verify that the preservative system remains effective throughout the product’s shelf life.
In conclusion, the USP <51> Antimicrobial Effectiveness Test and related challenge tests are vital tools in the pharmaceutical industry. These tests ensure that non-sterile aqueous pharmaceutical products are protected against microbial contamination, thereby safeguarding consumer health and maintaining product efficacy and integrity. As pharmaceutical products often have prolonged shelf lives and are exposed to various potential contaminants, rigorous antimicrobial effectiveness testing is crucial. Adhering to USP <51> standards helps pharmaceutical companies meet regulatory requirements and maintain high-quality standards, ultimately contributing to the trust and safety of healthcare products. By focusing on these aspects, pharmaceutical companies can ensure that their products remain safe, effective, and reliable throughout their intended use.





Author info
กองบรรณาธิการนิตยสารอินโนแล็บ INNOLAB team innolab@media-matter.com
367 พ.ศ. 2567 ฉบับที่ 383 พ.ศ. 2560 (ฉบับที่ 401) พ.ศ. 2562 และฉบับที่ 410 พ.ศ. 2562
เนื้อห � ที่บังคับใช้ในประก � ศฉบับนี้
มีก � รแก้และเพิ่มเติมจ � กกฎหม � ยเดิม
หล � ยจุด บทคว � มนี้จะนำ�เสนอบ � งจุด
ที่น่�สนใจ ห�กต้องก�รเอกส�รฉบับเต็ม
ส�ม�รถด�วน์โหลดได้จ�กเว็บไซต์ของกอง อ�ห�ร สำ�นักง�นคณะกรรมก�รอ�ห�รและ
ย� (food.fda.moph.go.th/food-law/ food-labeling)
นิยามเพิ่มเติม
“สี” หม�ยถึง สีต�มประก�ศกระทรวง
ส�ธ�รณสุขว่�ด้วยวัตถุเจือปนอ�ห�ร “วันหมดอ�ยุ” และ “ควรบริโภคก่อน”
เพิ่มเติมข้อคว�ม “และหลังจ�กวันที่ระบุไว้
นั้น อ�ห�รนั้นว�งจำ�หน่�ยไม่ได้
การบังคับใช้ หลักเกณฑ์ของประก�ศนี้จะบังคับใช้
กับผลิตภัณฑ์อ�ห�รที่บรรจุไว้ในภ�ชนะ
หรือผู้แบ่งบรรจุหรือผู้ปรุงหรือผู้จำ�หน่�ย อ�ห�ร - อ�ห�รที่ไม่ได้จำ�หน่�ยโดยตรงต่อ
The criteria for labeling food products in packaging in Thailand have been updated according to the Ministry of Public Health’s Notification (No. 450) B.E. 2567, issued by virtue of the Food Act B.E. 2522, Re: Labeling of Prepackaged Foods. This notification, effective from July 19, 2024, replaces previous notifications, including Notification No. 367 B.E. 2567, No. 383 B.E. 2560, No. 401 B.E. 2562, and No. 410 B.E. 2562.
This new notification includes several revisions and additions to the previous regulations. This article highlights some key points. For the full document, you can download it from the Food Division, Food and Drug Administration’s website (food.fda.moph.go.th/food-law/ food-labeling).
- “Color” refers to colors defined under the Ministry of Public Health’s notification regarding food additives.
- For “Expiration Date” and “Best Before Date,” an additional note is added: “And after the specified date, the food cannot be sold.”
The criteria in this notification apply to food products packaged in containers that are wrapped or sealed to prevent the food from spilling out and are ready for sale, distribution, or exchange for commercial purposes. If a food item is covered by a specific Ministry of Public Health notification regarding labeling, it must comply with both that notification and this one. Information required on packaged food labels depended on selling purposes:
- Food sold directly to consumers, or to repackers, processors, or food sellers.
- Food not sold directly to consumers, repackers, processors, or food sellers, with a label stating “For food processing use only” or similar wording.
- Packaged food produced for export.
- The specific name of the food, common name, or regular name used, such as roasted peanuts, chicken massaman curry, or yakisoba.
- A name indicating the type or category of the food, such as skimmed milk powder, beverages, yogurt, palm oil, or drinking water.
- If a trade name is used, the food type or category must be indicated alongside, e.g., AA (drinking water).
- If the food name might mislead consumers about the food’s specific characteristics or origin, an additional descriptor must be included, such as the substance used, production method, appearance, plant or animal part, or origin, e.g., tuna in brine, dried bananas, or Japanese steamed egg.
- The food name must not be false or misleading, and it must not claim any false properties of the food. The label must not include text, names, pictures, or symbols suggesting the presence of ingredients that are not actually included.
If allergens are used or there is a possibility of allergen contamination during production:
1. Display “Allergen Information: Contains ….” in a clear, visible, and easily readable position, such as “Allergen Information: Contains wheat flour, milk powder.”
2. If contamination is possible, display “Allergen Information: May contain ….” in a similar clear position or display a text with similar meaning.
Types of Allergens/Hypersensitivity Substances
1. Gluten-containing cereals, including wheat, rye, barley, oats, spelt, or their hybrids, and products made from these grains.
2. Shellfish such as crab, shrimp, lobster, etc., and their products.
3. Eggs and egg products.
4. Fish and fish products.
5. Peanuts and peanut products.
6. Soybeans and soybean products.
7. Milk and milk products, including lactose.
8. Tree nuts and nut products, such as almonds, walnuts, pecans, etc.
9. Sulfites in quantities of 10 mg/ kg or more.
10. Additional allergens from previous notifications include shellfish, squid, and products from shellfish and squid.
Foods that contain allergens or hypersensitivity substances as key ingredients and have food names that clearly specify the allergen or hypersensitivity-causing substance, such as “pasteurized cow’s milk” or “roasted peanuts.”, the mandatory labeling is exempted.
The label must indicate the presence of food additives when used, or when they are present in the raw materials used in the production of the food, if they are present in amounts that achieve the intended purpose of using the additive.
- Name of the functional category of food additives along with the specific name or the name of the category of food additives along
with the number according to the International Numbering System (INS) for Food Additives.
- Name of the functional category of colors, preservatives, sweeteners, and flavor enhancers: For other functional categories, the statement “Food Additive” should be displayed along with the “INS Number” or the “Specific Name.”
- “Color” followed by the specific name or INS number: The type of color, whether natural or synthetic, may also be specified, depending on the case.
- “Preservative” followed by the specific name or INS number.
- For substances functioning as flavor enhancers and sweeteners: The functional category must be followed by the specific name.
- For food additives that are not “preservatives,” “flavor enhancers,” “sweeteners,” or “colors”: The statement “Food Additive” may be displayed instead of the name of the functional category of food additives.
1. Claims about foods that are prohibited by Ministry of Public Health notifications.
2. Claims about food additives not permitted under the relevant notifications.
3. Claims about substances not naturally present in that food or not formed during its production process.
- Foods that naturally do not contain a certain substance: For example, it is prohibited to use statements like “Cholesterol-free water” since water naturally does not contain cholesterol.
- Foods that do not contain a certain substance due to the production process: For example, it is prohibited to use statements like “Trans-fat free syrup” since the production process for syrup does not create trans-fats.
- Substances that are prohibited for use in food according to the Ministry of Public Health: For example, it is prohibited to use statements like “Borax-free fish balls” since borax is already prohibited in food.
- Statements that do not cause consumer misunderstanding about
the product: For example, it is prohibited to use the name “Dory fish” for “Vietnamese striped catfish” (Pangasius hypophthalmus) as it may mislead consumers into thinking it is “Dory” or “John Dory” (Zenopsis conchifera), which is a deep-sea fish.
- Foods sold directly by the producer to consumers, such as street vendors or through e-commerce.
- Fresh foods that have not undergone any processing.
- Fresh foods that have been peeled, cut, or otherwise processed to reduce size, and are not intended for consumer sale. Food may or may not be refrigerated and is packaged in a container that allows the condition of the fresh food to be visible.
- Packaged foods produced and sold for service within restaurants, hotels, schools, hospitals, and similar institutions, including food delivery services. If exempted packaged foods receive a food registration number, they must comply with this notification.

There has been a sharp increase in the number of people in Japan suffering with the rare but dangerous bacterial condition, streptococcal toxic shock syndrome (STSS). According to reports, cases of this potentially fatal group A streptococcus illness have more than tripled in Tokyo compared with this time last year.
In 2023, a record number of cases of a potentially fatal “flesh-eating disease”, the STSS, were reported in Japan. The number of patients diagnosed with STSS had decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic, but confirmed cases surged to 941 last year, topping the previous record of 894 set in 2019, according to the National Institute of Infectious Diseases (NIID). An estimated 30% of STSS cases end in death because symptoms can suddenly worsen.
The bacterium is called flesh-eating because it causes necrosis of a band of tissue that surrounds the muscles of patients. STSS can be caused not only by group A streptococcus but also by the group G strain. In some cases, an infection can turn deadly, especially among adults over 30. Most patients who come down with STSS are senior citizens. According to the NIID, the group A strain leads to more fatalities among those under 50. Sixty-five patients under 50 were diagnosed with STSS between July and December 2023. About one-third of them, or 21, died.
While experts are not entirely certain why cases have risen so sharply to record levels, many believe it could be due to people being less vigilant about protecting themselves from infection after COVID measures were dropped. Many countries, including the UK, have seen a similar increase in illnesses caused by group A streptococcus in the post-lockdown period – highlighting the continued burden that these bacteria have on public health.
Group A streptococcus is a betahemolytic Gram-positive called Streptococcus pyogenes. Between 5% and 20% of healthy adults have these bacteria living inside them without any symptoms. But even when they don’t cause illness. S. pyogenes is responsible for a wide range of infections that are mostly common and fairly mild. If the bacteria enter the bloodstream an infection can become severe and lifethreatening and is called an invasive group A streptococcus (iGAS). Infection of group A streptococcus may spread through direct contact with mucus or sores on the skin. Group A streptococcus infections can cause over 500,000 deaths per year. Despite the emergence of antibiotics as a treatment for group A streptococcus, cases of iGAS are an increasing problem, particularly on the continent of Africa. There are many other species of Streptococcus, including group B streptococcus S. agalactiae, and S. pneumoniae, which cause other types of infections. Several virulence factors contribute to the pathogenesis of group A streptococcus, such as M protein, hemolysins, and extracellular enzymes.
Group A streptococcus can still be
spread to other people unknowingly through touch, coughs and sneezes. Group A streptococcus is commonly spread through close contact with an infected person. This means that people who spend time in crowded places – such as schools or dormitories – may be at greater risk of catching these bacteria. Even people who aren’t ill can be colonized by them, as they are well adapted to grow in healthy human hosts.
But group A streptococcus can shift from being symptom-free and harmless into the source of numerous diseases. Infection may be triggered by larger numbers of the bacteria, mutation to a more aggressive strain, or perhaps some reduction in host defenses. Most often, this will cause localized, short-lived infections – such as strep throat, tonsillitis or impetigo on the skin.
However, group A streptococcus can also ambush patients a few weeks after these milder infections, causing severe, lifelong complications –including rheumatic heart fever or inflammation of the kidneys. These complications are more common in certain populations, such as those who are homeless or living in poverty, or people with drug and alcohol use problems.
Group A streptococcus can also cause more severe illnesses, including scarlet fever, sinusitis, pneumonia, cellulitis, bone and blood infections. In rare cases, group A streptococcus can spread from cuts and wounds deep into soft tissues and muscle, leading to necrotizing fasciitis. And streptococci can in some situations release immune-activating toxins that activate the immune cells in tissues, triggering STSS.
The initial symptoms of STSS are sore throat, fever, diarrhea, vomiting and lethargy. Some patients have died within dozens of hours due to multiple organ failure or breathing problems. The bacterium often enters the bloodstream and spinal fluid where bacteria cannot normally be detected. That leads to a sudden decrease in functioning of many organs.
Low blood pressure follows, leading to cold hands and feet, a rapid heart rate and breathing too. Without the blood pressure they need to function, organs then begin to fail, usually 24 to 48 hours after the symptoms emerged. STSS has a high mortality rate – ranging from 5% in younger patients who have been admitted quickly to intensive care, to up to 70% in the elderly.
STSS is more common in people who have a poor immune system–including the elderly, people taking
Why Group A: The Lancefield Classification
steroid medications, people recovering from a recent illness (particularly chickenpox), those with type 2 diabetes, and people with drug and alcohol problems. The elderly are a large and growing component of Japan’s population, which may explain why cases of STSS are particularly high there.
The rise in STSS cases is probably also a consequence of fewer COVID restrictions in this post-lockdown period. Public health measures such as mask wearing, washing and disinfecting hands and social distancing all helped to reduce the spread of group A streptococcus.
Although the infection process is still not known, the bacterium has been known to infect patients through wounds on the hands and feet. Normal measures to prevent infectious diseases, such as washing hands and keeping a wound clean, should be taken. Immediate medical treatment should be started if the symptoms seem different from normal. It is suggested to visit a medical institution if a wound begins to swell or becomes painful, and if other symptoms of infection, such as a fever, appear.
Treatment for suspected STSS should be delivered as rapidly as possible. Patients will require oxygen,
intravenous fluids and even cardiac support, alongside antibiotics and intravenous immune antibodies to deactivate Group A streptococcus toxins. Even if referral and treatment is given quickly, it may still take patients many weeks to recover from the physical effects. Fortunately, group A streptococcus remain responsive to penicillin, although resistance has been identified in some strains. This means that group A streptococcus – and STSS – remain treatable. Researchers are also working on developing a protective vaccine against group A streptococcus. If successful, this would not only protect against milder illnesses caused by streptococci, but also against rheumatic fever and perhaps the more acute severe illnesses such as STSS.
Group A streptococcus is estimated to contribute to more than half a million deaths globally each year. While relatively few of these are the consequence of STSS, this number highlights a need to better monitor group A streptococcus, their evolution and the diseases they cause. Protecting yourself against Group A streptococcus remains relatively simple. Many of the practices we followed during the height of the pandemic – such as wearing masks, washing hands and avoiding crowds – can help us avoid group A streptococcus too.
Lancefield grouping, created by Rebecca Lancefield, was historically used to organize the various members of the family Streptococcaceae, which includes the genera Lactococcus and Streptococcus, but now is largely superfluous due to explosive growth in the number of streptococcal species identified since the 1970s. It is a serological method for classifying streptococci into one of 20 groups (designated by a letter) based on the presence of polysaccharide and teichoic acid antigens in the bacterial cell wall. The technique is now performed using commercial latex agglutination test kits, which allow rapid detection of clinically important streptococcal groups. Some streptococci, for example S. pneumoniae, have not been assigned to a group because their antigen extracts fail to react with group antisera.
The classification assigns a letter code to each serotype. There are 20 described serotypes assigned the letters A to V (excluding E, I and J). Many - but not all - species of streptococcus are beta-hemolytic. Though there are many groups of streptococci, the principal organisms that are known to cause human disease to belong to group A (S. pyogenes), group B (S. agalactiae), group C/G (S. dysgalactiae), both members of group D (S. gallolyticus and S. infantarius), and two alpha-hemolytic groups that lack the Lancefield carbohydrate antigen: S. pneumoniae and Viridans streptococci.

Contact
Sujjarluck Phu-aiem (Sugar), Marketing Executive, Fi Asia l CPHI SEA l Propak Connect, Informa Markets sujjarluck.p@informa.com +66 (0) 2 036 0500 ext. 237
อุตสาหกรรมอาหารและเครื่องดื่มกำาลังเตรียมตัวสำาหรับการแสดงนวัตกรรมและการเติบโตอย่างยิ่งใหญ่ในงาน Food Ingredients (Fi) Asia Indonesia
กันยายน 2567 พบกับผู้จัดแสดงสินค้ากว่า
ภ�ยใตธีม “Evaluating the Future of the Food Value Chain Through Innovation and Sustainability” Food Ingredients (Fi) Asia Indonesia มุ่ง
เน้นก�รนำ�เสนอนวัตกรรมและก�รปฏบตที่
เป็นมิตรกับสิ่งแวดล้อมในภ�คอ�ห�รและ
เค รื่ อง ดื่ม ใน ป นี้ พบกับน วัตกรรมล �สุด
ในส่วนผสมอ�ห�รและกระบวนก�รผลิต จ�กแบรนด์ระดับโลกและเทคโนโลยที่ล� สมัยม�กม�ย
ไฮไลตทที่น่าจับตามอง
Bev Hub: พื้นที่จัดแสดงนวัตกรรม
ล�สุดจ�กอุตส�หกรรมเครื่องดื่ม หนึ่งในสิ่งที่ดึงดูดคว�มสนใจที่ Food
Ingredients (Fi) Asia Indonesia คือ
Bev Hub พื้นที่ก�รแสดงนวัตกรรมล�สุด
Halal Workshop และ Coaching Clinic
ฮ�ล�ล Food Ingredients (Fi) Asia
Indonesia จะม Halal Workshop และ
Coaching Clinic
Halal Industry
Empowerment Center (PPIH) และ
Innovation Tour
Snack Bar:
Sustainability Square: เรียนรู้การ
ป ฏ บ ติอ ย่าง ยั่ ง ยืนใน อุตสาหกรรม
อาหารและร่วมสนุกกับกิจกรรมประจาบูท
คว�มยั่งยืนจะเป็นจุดเน้นหลักในง�น
นี้ Sustainability Square ร่วมสัมผัส
ประสบก�รณ เช่น ศิลปะก�รทำ�เต�หู้ ที่
ผู้เข�ร่วมส�ม�รถเรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับก�รปฏบต
ที่ยั่ง ยืนในอุตส�หกรรมอ�ห�ร เกมและ
กิจกรรมที่สนุกสน�น จัดโดยพันธมิตรด�น
คว�มยั่งยืนของ Food Ingredient (Fi)
Asia เน้นคว�มสำ�คัญของโครงก�รที่เป็น
มิตรกับสิ่งแวดล้อม



The food and beverage industry is gearing up for a grand showcase of innovation and growth at Fi Asia Indonesia 2024, which promises to be larger than ever before. Set to take place at the Jakarta International Expo from 4-6 September 2024, this year’s event is expected to attract over 700 branded suppliers from 38 countries and more than 22,800 attendees, surpassing pre-COVID levels.
Under the theme “Evaluating the Future of the Food Value Chain Through Innovation and Sustainability”
Fi Asia Indonesia aims to highlight pioneering advancements and ecofriendly practices in the food and beverage sector. The exhibition will feature a vast array of global brands and groundbreaking technologies, with exhibitors showcasing the latest innovations in food ingredients and processing.
Highlights to Watch For Bev Hub: Trendy Beverages in the Spotlight
One of the standout attractions at Fi Asia Indonesia 2024 is the Bev Hub, dedicated to showcasing the latest trends in beverages from Indonesia and Southeast Asia. This hub will feature innovative drink concepts, new flavors, and sustainable packaging solutions, offering a glimpse into the future of the beverage industry.
Innovation Zone: Pioneering Ingredients
The Innovation Zone will spotlight new ingredients and their applications in food production. From novel functional ingredients to sustainable and clean label solutions, this zone provides attendees with insights into the latest developments driving the food industry forward.
With the growing importance of halal products, Fi Asia Indonesia 2024 will feature a Halal Workshop and a Halal Coaching Clinic. The Halal Workshop will offer valuable information on the halal certification process and market opportunities, while the Halal Coaching Clinic, organized by the Halal Industry Empowerment Center (PPIH) and the Ministry of Industry, will provide detailed guidance on obtaining halal certification.
The Innovation Tour offers a guided, one-hour exploration of the exhibition hall, focusing on trending themes in the Indonesian F&B industry such as:
- Sugar reduction and sugar replacement
- Functional food concepts for holistic health
- Healthy snacks
Square: Engaging and Educational Sustainability will be a core focus at the event. The Sustainability Square will feature interactive experiences like the Art of Making Tempe, where attendees can learn about traditional and sustainable food practices. Fun games and activities organized by sustainability partners will highlight the importance of eco-friendly initiatives.
The Snack Bar will showcase a variety of snack products, reflecting the rich diversity and flavors of Indonesia’s snack market. This area will provide attendees with the chance to sample innovative snack offerings and discover new trends in the snack industry.
Fi Asia Indonesia 2024 will feature seven international pavilions, each representing a different country’s unique contributions to the food and beverage industry. The pavilions
will include China, India, Japan, USA, Malaysia and Thailand. These pavilions offer a unique opportunity to explore global trends, discover new products, and connect with international suppliers.
A series of international conferences and seminars will also take place, bringing together industry leaders, experts, and innovators to share insights and discuss the latest trends and challenges. Topics will range from market trends and regulatory updates to scientific advancements and sustainable practices.
Fi Asia Indonesia is set to be a monumental event, surpassing the scale and scope of pre-COVID editions. This year’s exhibition promises to be an unmissable gathering for the food and beverage industry. Don’t miss out on this opportunity. Preregister today to secure your place at Fi Asia Indonesia 2024. Visit www. fiasia.com and click “Attend” or email fiasia@informa.com for more information.








Chaivarong Sanyaluxruechai
Assistant

เอเชีย 2024” (Vitafoods Asia 2024) จัดยิ่งใหญ่รับกระแสความนิยม
(Nutraceuticals) มาแรงทั่วโลก
ผู้จัดงานเตรียมขนทัพสุดยอดนวัตกรรมเสริมอาหารและสารสกัด
ส่วนผสมสำาหรับผลิตภัณฑ์เสริมอาหาร และผลิตภัณฑ์เพื่อสุขภาพอันดับหนึ่งในภูมิภาคเอเชีย เผยตลาดสารสกัด
และผลิตภัณฑ์เสริมอาหารของประเทศไทยมีโอกาสโตก้าวกระโดดแตะ
(ประเทศไทย) เปิดเผย
ว่� อุตส�หกรรมเสริมอ�ห�รและส�รสกัด
กำ�ลังเติบโตอย่�งม�กในตล�ดเอเชีย โดย ประเทศไทยเป็นหนึ่งในตล�ดที่ใหญ่ที่สุดใน
ภูมิภ�คเอเชียแปซิฟิก อ้�งอิงร�ยง�นจ�ก
Euromonitor International ตล�ดส�รสกัด
และผลิตภัณฑ์เสริมอ�ห�ร (Nutraceuticals)
ของประเทศไทยมีมูลค่� 190 พันล้�นบ�ท
ในปี 2565 และค�ดว่�จะเติบโตเป็น 239
พันล้�นบ�ท ในปี 2569
“Vitafoods Asia 2024,” leading nutraceutical event for Asia, is set to bring new excitement to the nutraceutical industry which is expanding rapidly worldwide thanks to the healthcare trend. Informa Markets (Thailand), the organizer of the event, promises to bring exciting innovations, technology, ingredients and health products to showcase at the event. Vitafoods Asia 2024, scheduled for 18-20 September 2027 at Hall 1-3, Queen Sirikit National Convention Center, Bangkok, Thailand, is hoped to also support the rapidly growing Thai nutraceutical market which has a strong potential to reach 230 billion baht value by 2026. The event is expected to welcome over 10,000 participants this year.
Ms. Rungphech Chitanuwat, Regional Portfolio Director – ASEAN, Informa Markets said that Asian nutraceutical market is expanding significantly. Thailand is a major market with 190 million baht value in 2022 and forecasted to expand to 239 billion baht in 2026 as reported by Euromonitor International.
The strong trend is driven by continuous launches of innovative products and the strong health trend momentum. Thailand is a major market that attracts attention from both existing market players and new entrants.
Vitafoods Asia 2024 is an exhibition designed to meet diverse needs and interests of people in industry and health-conscious consumers. Euromonitor reported that more than half of Southeast Asian consumers believe that in the next five years they will have better health in the next and the Climate Change will have more impact of their lives.
Healthy foods will, therefore, play a key role in maintaining good health in the future.
Vitafoods Asia 2024 is an annual event aimed to grow the network of people in nutraceutical industry. The event will serve as a platform to promote learning and long-term cooperation among people in the industry. It, at the same time, provides an opportunity for businesses to find high quality ingredients and products, meet directly with manufacturers, innovators and technical experts, and exchange knowledge and experience with suppliers.
This year, more than 600 brands from 70 countries will participate in the event. Each products and solutions will be organized in different zones, including ingredients and raw materials, contract manufacturer and private label, branded finished products, food supplements, vitamins, natural ingredients, herbal extract, nutritional products, packaging and

related equipment.
Also, part of the event is the innovation zone featuring business know-how seminars such as trend and potential in the food supplement markets in Asia and Australia, registration of herbal products, labeling of food supplements for the elderly, marketing strategies for food supplements, food supplements for pets, research update on Pre-Pro-Postbiotics, Collagen Peptides, Ashwagandha and mushroom extracts, etc.
Other highlights at Vitafoods Asia 2024 can be found in the New Products & New Ingredients Zone, the Tasting Bar and the Vitafoods Asia 5K Run.
Visitors will also find more interesting products from government sector and leading universities in the Academic to Commercial Zone, Lift Elements activities, Innovation Health Hub which presents new trend, and the Sustainability Square. The two talk stages are set to share

experience and insights from people in the industry.
Vitafoods Asia 2024 also contributes to the Thai food supplements industry, creating added value to agricultural products, growing new business opportunities, and enabling Thai food supplement business to grow in the international market. It also encourages businesses, general public and students to participate in the Vitafoods Asia Nutraceutical Awards 2024, held under “Local Ingredients to Global Nutraceuticals” theme. Winners will receive quality certification and opportunity to further develop and commercialize their products as well as to have their products showcased in the Vitafoods Asia 2024.
Target group of the event are producers, distributors, advisors, retailers, researchers, scientists, academics, importers, wholesalers and trade associations related to nutraceuticals, foods, food supplements, medicine, health foods, drinks, personal care products. The event expects to attract more than 10,000 participants.
“Informa Markets has a strong commitment to supporting Thai businesses and increasing their access to new business opportunities. We hope to help Thailand becoming the
nutraceutical manufacturing hub and market in Asia,” said Rungphech. Dr. Kittiwut Kasemwong, Leader of Nano Agricultural Chemistry and Processing Research Team, National Science and Technology Development Agency (NSTDA), noted that NSTDA focuses on adding value and upgrading Thailand’s food and health-related product market with emphasis on natural ingredients. The agency has promoted the use of herbal extract and microbes to develop health-promoting products, which also has potential to reduce production costs, dependence on imported products and technology. At the same time, local operators’ capability is promoted. All these are NSDTA’s effort to drive industry’s growth.
Dr. Natthapasut Phattirasinsiri, Director of Biotech Industry Club, the Federation of Thai Industries (FTI), said that Thailand has an advantage on medical and health technology, especially biomedical science. The country’s large biodiversity has contributed to national competitiveness and is a key factor promoting researches on health and medical products, functional foods, herbs, biopharmaceutical products, and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). This is key to support the

development of Thailand’s medical and health products, which also helps reduce imports. More importantly, this will support Thailand development as a knowledge economy with strong income generation potential.
Mr. Nakah Tawichawat, Director of Dietary Supplement Industry Club, the Federation of Thai Industries (FTI) said Thailand’s food supplements and herbs has high growth potential driven by the increasing ageing population. The food supplement market currently accounts for over 30% of the beauty, cosmetics and food supplement market.
Vitafoods Asia 2024 will open new opportunities for businesses and drive growth of the Thai nutraceutical industry. The general public and those interested in food ingredients and health foods are invited to participate in the event scheduled for 18-20 September 2024, from 10:00-18:00 hrs., at Hall 1-3, Queen Sirikit National Convention Center. For more information and registration, click www.vitafoodsasia. com.


Chaivarong Sanyaluxruechai
Assistant Marketing Manager, informa markets Chaivarong.S@informa.com
โดยปีนี้ผนึก 2 ง�นใหญ่ระดับน�น�ช�ติ
“Medlab Asia และ Asia Health 2024” ง�นแสดงเทคโนโลยีและนวัตกรรม อุตส�หกรรมห้องปฏิบัติก�รท�งก�รแพทย์ และเครื่องมือแพทย์ของอ�เซียน ร่วมกันจัด
ง�นภ�ยใต้ธีม ‘International Healthcare Week’ สร้�งแรงกระเพื่อมลูกใหญ่ให้กับ อุตส�หกรรมย�และสุขภ�พในไทย
ปีนี้ “ซีพีเอชไอ เซ�ท์อีส เอเชีย 2024 (CPHI South East Asia 2024)” ม�ใน
ลูกเล่นที่สดใหม่
แม้ง�น “CPHI South East Asia
ทำ�ให้ง�นในปีนี้เป็นประสบก�รณ์ที่คุ้มค่� และเป็นพื้นที่ของผู้ผลิตย�ชั้นนำ�ของไทย ได้แสดงศักยภ�พ
ย�และผู้ประกอบก�รในประเทศไทยให้ก�ร
ตอบรับเข้�ร่วมจัดแสดงสินค้�และนวัตกรรม
ภ�ยในง�น นำ�โดย บริษัท บ�งกอกแล็ป
แอนด์ คอสเมติค จำ�กัด (มห�ชน) บริษัท
ที.แมน ฟ�ร์ม�ซูติคอล จำ�กัด (มห�ชน)
บริษัท โอลิค (ประเทศไทย) จำ�กัด บริษัท
เกร๊ทเตอร์ฟ�ร์ม่� จำ�กัด บริษัท ชุมชน
เภสัชกรรม จำ�กัด (มห�ชน) ฯลฯ ทุกพื้นที่เต็มฮอลล์แสดงสินค้� 1-3 ของ
ศูนย์ก�รประชุมแห่งช�ติสิริกิติ์ กว่� 15,000
ต � ร � งเมตรยังอัดแน่นไปด้วยผลิตภัณฑ์
เทคโนโลยี โซลูชันล้ำ�สมัย และบริก � ร
ต่�งๆ จ�กบรรด�ผู้ผลิตและซัพพล�ยเออร์ย�ชั้นนำ�จ�กน�น�ช�ติ กิจกรรมสัมมน�ให้
คว�มรู้ รวมถึงโอก�สในก�รสร้�งเครือข่�ย
ท�งธุรกิจที่เปิดให้องค์กรต่�งๆ ที่เข้�ร่วม ง�นได้ห�โอก�สในก�รประส�นคว�มร่วม มือเป็นพันธมิตรท�งธุรกิจในอน�คตด้�นโซนไฮไลต์ของง�นปีนี้ต้องยกให้ Main Conference ซึ่งเป็นพื้นที่ติดต�มทุก


South East Asia 2025”

Winding down successfully, CPHI South East Asia 2024, the region’s leading pharmaceutical products and technology exhibition and conference held in Thailand from 10-12 July 2024, has ignited a big inspiration for the entire industry.
The event was organized in parallel with the Medlab Asia and Asia Health 2024, ASEAN’s two leading exhibitions and conferences on medical lab and equipment, under “International Healthcare Week” theme. The event took place at the Queen Sirikit National Convention Center (QSNCC).
CHPI South East Asia 2024 excited the industry with many interesting activities while maintaining its DNA as the key mechanism in promoting Thailand’s pharmaceutical security and the development of the entire industry. The end game is to support the country’s aim to become the largest and fastest growing medical hub in ASEAN.
Ms. Rungphech Chitanuwat, Regional Portfolio Director – ASEAN, Informa markets and Country General Manager – Philippines, disclosed, “There is a huge opportunity for Thai pharmaceutical producers in the export market. Thailand currently depends mainly on imported pharmaceutical
products. CPHI South East Asia 2024, therefore, focused on empowering local manufacturers and creating new opportunities for them. It is the only major event that brought together everyone in the industry, from reliable manufacturers to highquality products and manufacturing solutions and innovations.”
The exhibition and conference drew as many as 300 companies from 54 countries worldwide, welcomed 7,500 participants, and conducted over 3,272 business matches. The event also hosted more than 62 interesting conference topics.
The vibrant atmosphere and excitement at the CPHI South East Asia 2024 remained fresh in the participants’ memory. Each zone was creatively designed to enhance the highlights and each zone was named after major cities like Shanghai, Tokyo, Delhi, Milan and Bangkok. The organizer also arranged some colorful activities, such as Thai massage to treat office syndrome, herbal inhaler making workshop, and demonstration of the hermitstyle physical training (Rishi dat ton) to entertain participants and at the same time celebrated Thailand’s soft power.
Every single activity was carefully selected and prepared in order to give visitors and exhibitors a memorable experience. Meanwhile, full opportunity

was given to local pharmaceutical manufacturers to demonstrate their potential. This year, there are Thai manufacturers and business operators joined the event as exhibitors. Some of the exhibitors are Bangkok Lab and Cosmetics Public Company Limited, T.Man Pharmaceutical Public Company Limited, Olic (Thailand) Company Limited, Greater Pharma Company Limited and Community Pharmacy Public Company Limited.
Hall 1-3 of the QSNCC covering over 15,000 square meters were filled impressive technology, creative solutions and services from international pharmaceutical manufacturers and suppliers. Seminars and business networking sessions have fully provided the participants and exhibitors to exchange information, knowledge and updates and to build and strengthen relationship with other companies that will lead to future partnership.
Highlight is the main conference that enables participants to get the latest updates of the industry and learning more about local and international pharmaceutical industry growth trend. Such information is crucial to help local business upgrade and become international players in the future. The conference was held in Tokyo Room, Delhi Room and Milan Room.
Pharma Markets Hub is the area where participants found updated information necessary for companies

that are looking for opportunity to enter into other ASEAN countries. Through interesting seminars, the participants had full opportunity to explored borderless opportunity, establish, and grow their partnership network with industry experts.
The Innovation Stage provided a space for industry experts to take turn sharing their latest knowledge and in-depth information about pharmaceutical product packaging.
Pharma Quest is a challenging quiz competition where participants had the opportunity to show off their talents and knowledge about pharmacy. This has become one of the most attractive and enjoyable activities as it drew experts from different corner in Thailand to compete for the 120,000 baht prizes.
CPHI South East Asia 2024 is of course a big success for Thailand as the host country and for the organizer like Informa Markets. Under the leadership of Rungphech Chitanuwat, Informa Markets successfully brought the event, which had been held in Indonesia, to Thailand and organized the event in Thailand for 6 consecutive years. The success in Thailand has prompted Informa Markets to bring this successful model of CPHI South East Asia 2025 to be held again next year in Malaysia.


ProPak Asia 2024 surpassed expectations with over 68,218 attendees. Business deals at the event exceeded 5 billion baht

ประเทศไทย
คว�มสำ�เร็จของง�น ProPak Asia 2024
มหกรรมเทคโนโลยีก�รประมวลผลและบรรจุ
หล�ยประก�รของง�นในปีนี้ นิทรรศก�รนี้
เป็นก�รรวมตัวของบริษัทชั้นนำ�ระดับโลก ผู้
เชี่ยวช�ญในอุตส�หกรรม นักนวัตกรรม ผู้
ผลิตเทคโนโลยี และองค์กรทั้งภ�ครัฐและ
เอกชน โดยจัดแสดงแนวโน้มและทิศท�ง
ล่�สุดในอุตส�หกรรมอ�ห�รและเครื่องดื่ม
เกษตรกรรม ผลิตภัณฑ์ดูแลส่วนบุคคล
เครื่องสำ�อ�ง ย� ก�รผลิต สินค้�อุปโภค
บริโภค ก�รแปรรูป และอุตส�หกรรมบรรจุ
ภัณฑ์ สิ่งนี้ทำ�ให้ผู้เข้�ร่วมและผู้ประกอบ
ก�รได้รับข้อมูลเชิงลึกที่มีคุณค่�เพื่อเพิ่ม ประสิทธิภ�พก�รผลิตและธุรกิจของพวกเข� แนวโน้มสำ�คัญที่ขับเคลื่อนก�รเปลี่ยนแปลง
ในอุตส�หกรรม ได้แก่ ระบบโรงง�นอัจฉริยะ ก�รผลิตและเครื่องจักรอัตโนมัติ
ProPak Asia
ทุกปี ผู้แสดงสินค้�ต่�งเห็นพ้องต้องกันว่�ง�น ProPak Asia เป็นง�นสำ�คัญที่ต้องเข้�ร่วม
ดึงดูดผู้เข้�ร่วมง�นที่มีคุณภ�พจำ�นวนม�ก
นัก ลงทุน
เปิดโอก�สให้ผู้แสดงสินค้�ได้แสดงผลิตภัณฑ์ และเทคโนโลยีของตน ตลอดจนสร้�งเครือ ข่�ยและสร้�งคว�มร่วมมือกับพันธมิตรใน อุตส�หกรรมจ�กทั่วโลก ง�น ProPak Asia 2024 มีผู้แสดง สินค้�กว่� 2,000 ร�ยจ�ก 42 ประเทศ
INNOLAB team innolab@media-matter.com
ที่ปรึกษ�โครงก�รวิจัยด้�นอ�ห�ร ศูนย์
บริก�รวิช�ก�รแห่งจุฬ�ลงกรณ์มห�วิทย�ลัย ดร.สุพรรณี

Mr.Sanchai Numboonnam, General Manager of Informa Markets in Thailand, highlighted the success of ProPak Asia 2024, a regional exhibition of processing and packaging technology. He emphasized several noteworthy aspects of this year’s event. The exhibition brought together leading global companies, industry experts, innovators, technology manufacturers, and both public and private organisations. They showcased the latest trends and directions in the food and beverage, agriculture, personal care, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, FMCG, processing, and packaging industries. This provided attendees and entrepreneurs with valuable insights to enhance their production and business efficiency.
Key trends driving change in the industry include smart factory systems, automated production and machinery, robotics and AI, and new sustainable, eco-friendly innovations in machinery, raw materials, and packaging. These advancements enhance product safety standards, detect contaminants, utilize resources efficiently, control and reduce production and energy

costs, improve collaboration between machines and humans, and promote the use of biodegradable materials for production and packaging.
A survey of attendees from around the world revealed that ProPak Asia is regarded as a must-visit industrial trade show in the region every year. Exhibitors agree, noting that ProPak Asia is an essential event to participate in. It attracts a large number of quality attendees, including genuine industry entrepreneurs, investors, and enthusiasts. This provides exhibitors with the opportunity to showcase their products and technologies, and to network and build partnerships with industry peers from around the world.
ProPak Asia 2024 featured over 2,000 exhibitors from 42 countries worldwide. The event included 14 officially supported international pavilions from 12 countries, such as Australia, France, Switzerland, Italy, North America, Bavaria, China, Japan, Korea, Singapore, Malaysia, and Taiwan (ROC). In total, the event drew 68,218 attendees from 83 countries.
Asean Paper Bangkok

The trade and business negotiations at the event reached a value of 5 billion baht, marking an 11% increase from the previous year. ProPak Asia not only supports the growth and development of Thai entrepreneurs but also enhances Thailand’s position as a regional hub for the food and beverage, agriculture, personal care, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, FMCG, processing, and packaging industries. Additionally, it attracts investments and generates income for the country on a significant scale.
ProPak Asia 2025 is set to be held on June 11-14, 2025 at BITEC, Bangna. The event will feature extensive participation from global industry leaders, showcasing cutting-edge innovations and technologies. It will include valuable knowledge-sharing through conferences and seminars, alongside the debut of Asean Paper Bangkok, an exhibition dedicated to the pulp and paper industry in ASEAN, held concurrently with ProPak Asia 2025. This combined event aims to cover all aspects of the packaging industry. For more details and updates, please visit www.propakasia.com.

เหล่านี้จะจัดแสดงความก้าวหน้าล่าสุดในอุตสาหกรรมการดูแลสุขภาพ
เจมส์ ซี.เอฟ. หวง ประธ�นของ TAITRA
เป็นผู้กล่�วเปิดง�น เข�เน้นว่�ก�รผส�น
เทคโนโลยีเข้�กับก�รรักษ�พย�บ�ลจะช่วย
ปฏิวัติวงก�รดูแลสุขภ�พ รวมถึง AI จะกล�ย
เป็นพันธมิตรอันช�ญฉล�ดของเหล่�แพทย์ทั้ง
หล�ย และง�น Medical Taiwan ในปีนี้ก็
ทำ�ให้วิสัยทัศน์ดังกล่�วเป็นรูปเป็นร่�งขึ้นม�
พ�วิเลียนสุขภ�พดิจิทัลและโซนสต�ร์ตอัป M-Novator คับคั่งไปด้วยผู้จัดแสดงสินค้� ที่นำ�เสนอโซลูชันนวัตกรรมอย่�งก�รดูแล
ผู้สูงอ�ยุด้วย AI ระบบติดต�มสุขภ�พ
และก�รวินิจฉัยอัจฉริยะ ตัวอย่�งเช่น หู
ฟัง IoT สวมใส่ได้ของ Decentralized Biotechnology โคมไฟดูแลอัจฉริยะของ
H.P.B. Hi-Tech แพลตฟอร์มเทคโนโลยีก�ร
MtM+ Technology และ AI
พ�วิเลียนก�รแพทย์อัจฉริยะและพ�วิเลียน ก�รแพทย์ท�งไกลและอุปกรณ์ก�รแพทย์ อัจฉริยะจัดโดยสม�คมอุตส�หกรรมก�ร
รับก�รรับรองทั้งในไต้หวันและต่�งประเทศ รวมถึงส�ม�รถสำ�รวจและเจรจ�เปิดโอก�ส ท�งธุรกิจเกี่ยวกับโซลูชันนวัตกรรมเหล่�นี้
PAHSCO, BenQ Materials, Chang Gung Medical Technology, Advantech, Wellell
Joson-Care
Atelier-k
700 ร�ยได้ลงทะเบียนล่วงหน้�เพื่อเข้�ชม
ง�น Medical Taiwan แล้ว และภ�ยใน
ง�นยังมีก�รจัดกิจกรรมแลกเปลี่ยนระหว่�ง
ประเทศอีกหล�ยง�น ซึ่งรวมถึงโอก�สใน
ก�รจับคู่ธุรกิจแบบตัวต่อตัว เช่น ก�รจัดห�
เครื่องมือแพทย์อัจฉริยะของไต้หวันและ
Medical Taiwan 2024
Medical Taiwan

Medical Taiwan, the International Medical, Health & Care Expo organized by TAITRA, will take place at the Taipei Nangang Exhibition Center, Hall 2 on June 20-22. This year’s exhibition features three main themes: All-Age Healthcare, Smart Medical, and the Supply Chain Gallery. A total of 280 companies from 10 countries are participating, spread across five highlight pavilions: the Smart Medical Pavilion, Telemedicine and Smart Medical Devices Pavilion, Digital Health Pavilion, M-Novator Startup Zone, and the Japan Pavilion. These pavilions will showcase the latest advancements in the healthcare industry.


AMATA Corporation PCL, together with Hotel Nikko AMATA City Chonburi, and VNU Asia Pacific have announced a landmark collaboration aimed at advancing the fields of life sciences and healthcare in Thailand. The partnership, formalized today, seeks to bolster the country’s healthcare ecosystem and expand industry networks on both local and global fronts.
Central to this collaboration is the establishment of an international wellness& biotech cluster, including a world-class oncology center in the Thailand Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC) area. This initiative aligns closely with Thailand’s vision to become a leading medical hub in the region. Leveraging partnerships with renowned international entities, AMATA MEDITOWN aims to offer comprehensive, whole-value chain of manufacturing and treatment solutions, starting from the area of oncology, ranging from preventive approach to advanced diagnosis and treatment options, to increase an accessibility for the clinical trial.
In addition to the treatment part,
AMATA MEDITOWN is set to pioneer Thailand’s first physical biotech cluster. This innovative cluster will encompass a robust ecosystem designed to support biotechnology advancements, foster research and development, and attract global biotech investments to Thailand.
“We are excited to embark on this journey with VNU Asia Pacific,” said Ms. Lena Ng, Chief Business Officer at AMATA Corporation PCL. “This partnership marks a significant step towards enhancing Thailand’s position as a hub for cutting-edge healthcare solutions. As our facilities, Hotel Nikko AMATA City Chonburi, has an experience hosting many international events, together with VNU Asia Pacific, we look forward to leveraging Health & Innovation Asia as a platform to showcase our initiatives, forge new partnerships, and expand our global footprint in the healthcare sector.”
Health & Innovation Asia in co-location with Thailand LAB INTERNATIONAL, Bio Asia Pacific and FutureCHEM INTERNATIONAL, organized by VNU Asia Pacific, serves as an ideal venue for AMATA MEDITOWN to introduce its ambitious projects to a global audience. These events will provide a unique opportunity to connect with industry leaders, investors, and stakeholders interested in advancing healthcare
innovation.
“We are proud to collaborate with AMATA MEDITOWN on this transformative journey,” said Mr. Igor Jan Palka, Managing Director at VNU Asia Pacific. “Apart from Thailand LAB INTERNATIONAL & Bio Asia Pacific, Health & Innovation Asia is dedicated to fostering dialogue and partnerships that drive innovation in healthcare. We believe that together with AMATA MEDITOWN, we can contribute significantly to advancing healthcare solutions in Thailand and beyond.”
On the same day, Hotel Nikko Amata City Chonburi also inked the service contract with VNU to host the international bio and medical conference at Hotel Nikko Amata before the Health & Innovation Asia main event to create the publicity and insightful sharing session with global players and bio medical professionals.
Health & Innovation Asia attendees are encouraged to visit AMATA MEDITOWN’s booth to learn more about their pioneering initiatives in healthcare and biotechnology. For more information, visit www.thailandlab. com, www.bioasiapacific.com, www. health-innovation-asia.com
For more details of AMATA MEDITOWN, please visit https://www. amata.com and Hotel nikko AMATA City Chonburi, please visit https://hotelnikkoamatacitychonburi.com
- June 24, 2024






Fill out your detail or attach your business card
Subscription Date .................................................................................. Where did you find us? ................................................................................
Your name Your job title
Your e-mail Your mobile number .......................................................................................
Company name
Company address
Website Tel no. ........................................... Fax no. ..........................................
Name and address on receipt □ Same as above □ Other, please specify
Your industry (please select your interest by inputting ü)
□ Food/Beverage □ Supplements/Nutraceuticals □ Cosmetics □ Pharmaceuticals/Medicals
□ Environment □ Energy □ Other, please specify ................................................................................
Your business (please select your interest by inputting ü)
□ Manufacturer □ Distributor □ Certification body □ Laboratory service
□ Academics □ Government body □ Consultancy □ Other, please specify ..............................................
Your job function (please select your interest by inputting ü)
□ Management □ Purchasing □ Sales/Marketing □ QC/QA □ QMR/Document Control
□ R&D □ Chemist □ Microbiologist □ Production □ Consultant
□ Other, please specify ..............................................................................................
Your interest (please select your interest by inputting ü)
□ Ingredients □ Additives □ Chemicals □ Reagents □ Methods □ Techniques □ Instruments □ Equipment □ Tools □ Softwares
□ Lab Facilities □ Lab Design □ Laws/Regulations □ Standards □ Interview
□ Industry/Market trend □ Other, please specify ..............................................................................................
Your engagement (please rank the score 1-5, 5 = most engaged)
Enhancing work capability Seeking products & services Finding out industry movement
_ Joining INNOLAB’s activities, seminar and conferences _ Other, please specify .........................................................................................
Your preferred communication channel (please rank the score 1-5, 5 = most convenient) _ E-mail _ Post mail _ Fax _ Facebook, www.facebook.com/innolabmagazine
Other, please specify ..............................................................................................
Your interest seminar topic
Your suggestion
Your subscription
Domestic reader □ 1-year 900 THB Oversea reader □ 1-year 90 USD □ 2-year 1690

Scan for payment <<< 1-year 2-year >>> - Mobile/internet banking - Credit cards

Please remit payment to MEDIA MATTER Co., Ltd., savings account number 1082280729, Siam Commercial Bank Pcl. The swift code is SICOTHBK. Please send the pay-in slip via fax number +66 2878 1026 or innolab@media-matter.com