The Urban Miner



To recycle the natural, artificial, and built environment.
Designing an educational campus that encompasses the recycling process.






Part 1: Research and Analysis
Waste Production in the United States
Thesis Statement
The Recycling Process
Site Selection and Analysis
Precedent Analysis
Part 2: Design
Site Overview Site Approach
Table of Contents
Recycling Center The Tour
Part 2: Design
Site Overview








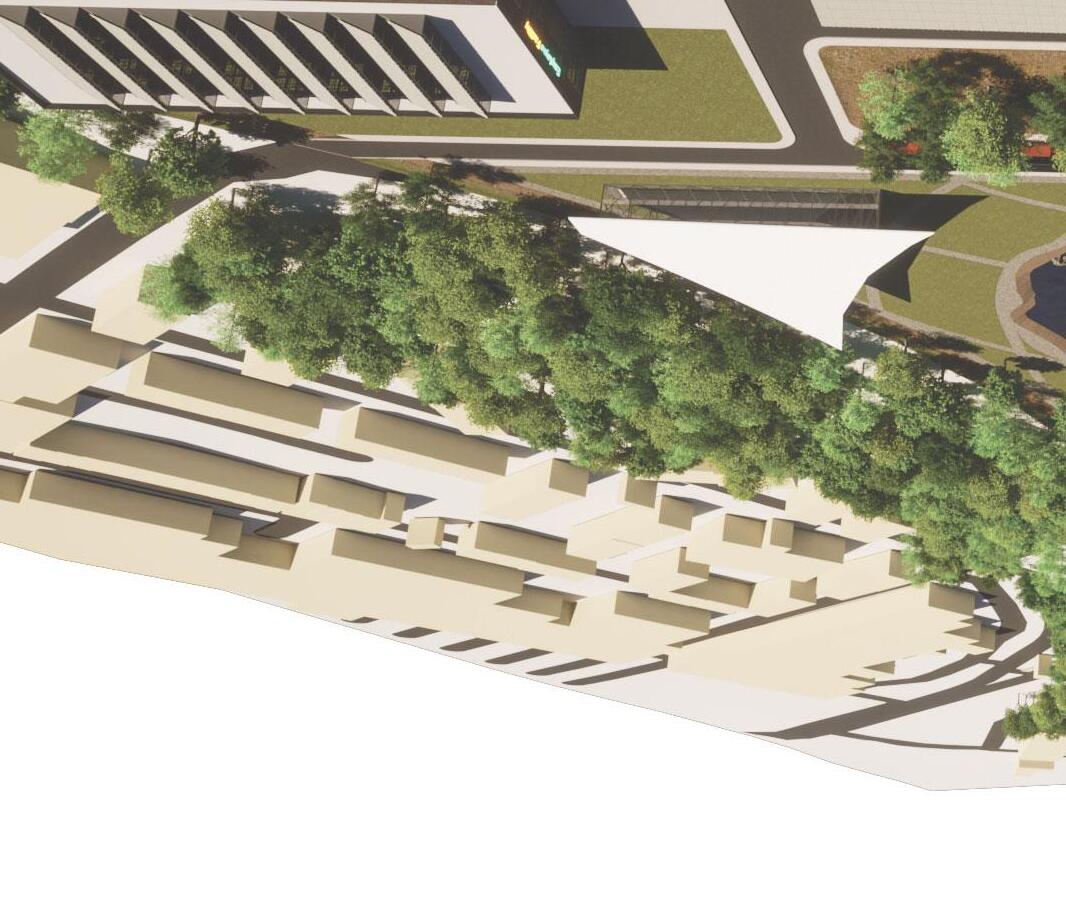


 Birds Eye: North
Birds Eye: West
Birds Eye: North
Birds Eye: West


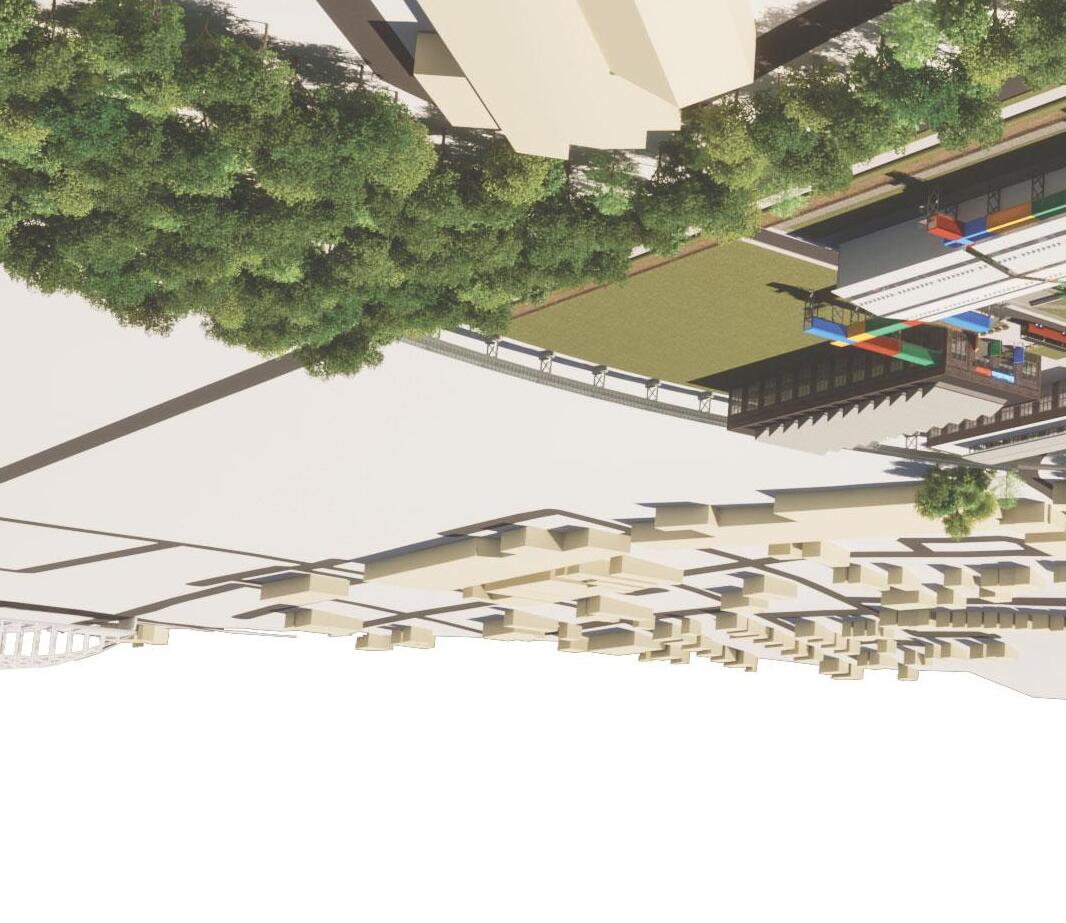








 Birds Eye: East
Birds Eye: South
Birds Eye: East
Birds Eye: South
Site Approach







Site Plan
Educational Center
The Educational Center is a 28,000ft2 facility for providing information on recycling, the history of recycling, and the recycling process. Inside the building are exhibits spaces, laboratories, and classrooms. The exhibit spaces will take you through the history of recycling and the it’s state today. The laboratories can be utilized by those who are looking for an answer to the waste problem. Local universities will have access to these spaces and will be able to host classes here.
Fabrication + Refurbishment
The Fabrication +Refurbishment Shop will be another location for recycling. Within the shop, people will be able to drop-off materials, furniture, electronics, and oddities that wouldn’t be recycled at a normal facility. Within the shop, people can work on whatever they brought in, or create something entirely new in the open work areas. The shop will also host classes for those who would like to learn more about refurbishment.
Employee Center
The Employee Center is a 21,000ft2 facility for the employees and their training. Within the facility, the employees have access to common rooms, locker rooms and kitchen areas. There will also be spaces within the facility to train on smaller scale recycling equipment and to learn about deconstruction processes.

Multi-Purpose Hall
Located to the southwest of the site, the Multi-Purpose Hall functions as an openfloor event space. The building is 8,000ft2 and can be set up to accommodate a number of event types and occasions, whether it is a National Recycling Congress Event or a community meeting space.
Campus Commons
A breathe of greenery to the campus. Once a brownfield, the Campus Commons are brought back to life with the help of mycelium and the brownfield remediation process. In the center of the commons is a 55,000 ft2 bioretention pond built to combat the potential flooding the site might face. Surrounding the BR Pond are a number of trails for locals and visitors to utilize at their convenience.

Rails to Trails
Bordering the north edge of the site is a decommissioned railroad track. To bring back a connection between two areas and to encourage walkability around the site, the railroad will be converted to a walking trail. The new trail, along with trails around the site will create new activities to get outside for.

Educational Pathway
After visiting the Educational Center, the Educational Pathway will lead you on a tour of the recycling center and provide you with an opportunity to visualize what you have just learned about. Recycling 31 shipping containers, the pathway winds through the Recycling Center to give you a view of the whole process.
Recycling Center
The Recycling Center is a 43,000ft2 addition to the site that will handle the recycling for the town of McKees Rocks and the surrounding area. A facility of this size will be able to handle nearly 250 tons of waste/day. As that material moves through the recycling process and is sorted, it will be moved to the exterior storage yard, adjacent to the facility.
ByBlock Production Facility

Following the recycling and sorting process, plastic can be allocated to two areas, storage or reuse. The ByBlock Production Facility will use plastic to make a building material alternative to a concrete masonry unit. Using steam and pressure, this process will convert 22 pounds of plastic into a 16” x 8” x 8” CMU alternative. These blocks can then be used in the future construction of homes or shops in the area.
Eco-Tower

Rounding out the end of the tour and serving as a beacon for the site, stands the Eco-Tower. Sitting at the southern most part of the site and along the new main road, the tower is visible to the town and surrounding area. Along with it’s function as a wayfinder for the site, the tower will also harvest rainwater, collect solar energy with photovoltaic panels, and will be coated in titanium dioxide.

Recycling Process to Recycling Center
Original Diagram

Recycling Process to Recycling Center
Material is transported to the site by garbage trucks or pedestrians.
Truck is weighed for Material Weight
Material Is Unloaded
Excavator feeds material into Drumfeeder Conveyor Belt delivers the material to the first sorting station: By Hand
Tipping Floor
Educational Pathway
Electronics, Toys, and Hazarous Materials
Recycling Center
Automatic Sifting Glass is often crushed during the delivery and sorting process. Sifters separate glass from the rest.
Rubber Stars Spinning stars separate cardboard from the line.
Screen Sorting
Heavy material falls to a lower conveyer
Paper is sorted out by screens
Can Identification
Plastic Sorting
ByBlock
Tin Containers Continue through the Process
Cans are identified by a laser system and sorted Aluminum is magnetically drawn down.
Cleaning Plastics
Washing
Crushing PP, PET, PS, Acr
Chipping
Drying
Delivered after the Recycling Process
Load into Blocker
Steam and Pressure fuse plastics together to form the CMU Alternative
The recycling process is a compact and contained process. To better understand the process, I extracted the compact recycling process into a linear diagram for my colleagues, advisors, and myself. After working with the diagram, I realized that this was easy to understand and that a building could be developed from this linear form.
Reading from Left to Right: The BROWN box would become the Tipping Floor, handling material delivery to the Recycling Center. Continuing through the process, and the longest form, is the Recycling Center, outlined in GREEN.
Plastic has two routes to follow at the end of the recycling process. One of the routes is for the plastic to be washed, crushed, chipped, dried, and then baled and potentially used at a different material recovery facility. The alternative route is for the plastic to be used in the new ByBlock Production Facility. This facility can take in all types of plastic and use them to create a CMU alternative. Converting 22 pounds of plastic to 22 pounds of building material alternative. This building is outlined in YELLOW.
The bottom of the diagram shows the material sorted out during the process. This area will become the storage yard adjacent to the recycling center, outlined in GRAY.
To break up the linear form, the Educational Pathway will wind throughout the recycling center, in light GREEN.
Storage
GlassCardboardTinPaperAluminumPlasticByBlock
Floor Plan: Perspective
















































































Educational Center Tipping Floor Intercontinental Highway Floor Plan: Perspective Annotated Bioswales Flood Berm
Commons Rails - toTrails
Pathway
Campus
Educational































 Recycling Center
ByBlock Production Facility
Recycling Center
ByBlock Production Facility
YardByBlock
Eco-Tower
Storage
Storage Yard
McKee Street
Tin GlassPaperAluminumPlastic Cardboard
The Grove
Integration
The Pittsburgh and Lake Erie Railroad Company moved out of McKees Rocks in the earlier 1970’s; leaving a community without jobs and a large brownfield dividing two larger neighborhoods in their wake. This project aims to begin the development of the southernmost part of the site. Bringing both jobs and land back to McKees Rocks.
Equitable Communities






From the time P&LE owned and operated the site to long after they left, the site has lacked pedestrian friendly areas. The project will utilize the decommissioned railway for a Rails-to-Trails conversion. This new trail will connect communities by an elevated walkway. Additional trails and bike paths will be developed across the site.

Change


The Recycling Center is sized to accommodate future growth in material. Using the recycled material to produce Byblocks may be used in the future development of the site. In the event of climate refugees, Byblock can be used to create housing or in the development of the northern half of the site. Furthering the development of the site and the connectivity of the town to the site.


Discovery
Discovery will be possible throughout the site. From the Educational Center’s exhibits and labs, to the Educational Pathway and the walk through the Recycling Center. Visitors, students, and the community can learn about the recycling process and the benefits it possesses. Stepping out to the commons will provide you with opportunities to learn about natural remediation and the native flora of PA.
Economy


Through Adaptive Reuse, Urban Mining, and Natural remediation, the project will aim to bring the site back to lie. Adaptively reusing three existing buildings on site. Mining materials from buildings labeled for demolition. Bringing life back to the site through natural remediation.


Resources










The material selection for this project primarily stems from recycling the built environment. The Recycling Center will reuse the corrugated steel and structure from an old steel house adjacent to the site. Using this material, the project will be able to house the nearly 60,000ft2 Recycling Center and the Byblock Production Facility. 31 shipping containers are reused and altered to create the Educational Pathway.
Energy










































Photovoltaic Panels will be situated on the rooftops of each building, as well as providing shade for the parking lot on the west edge of the site. Altogether, the solar panel array has the potential to produce 1,200 mega-watt hours of electricity per year.












Wellbeing




The site has long been a brownfield dividing the town. Along with the development of the site, another goal of the project has been to give space back to the community. This comes in the form of the Campus Commons. Providing a public space for the community to use, something the town currently lacks.
Water






The project will utilize rainwater harvesting throughout the site. Harvested rainwater will be used in the Byblock Production Facility as steam to bind the plastics together. This can also be used throughout the buildings in the restrooms and for watering the vegetation situated throughout the courtyard. The site has the potential to catch 2.4 million gallons of water per year.
Ecosystems


Along with remediating the site naturally, the project aims to bring native flora back to the site. Natural remediation through mycelium has proven effect in remediating sites quickly, as well as bring native flora back to life. A small grove to the south will be expanded and brought back onto the site. The bioswales will also use native vegetation as a means to mitigate flooding hazards.

A Tour of the Campus







 1. Along Intercontinental Highway
1. Along Intercontinental Highway






 2. Entrance to the Campus
2. Entrance to the Campus






 3. Entrance to the Educational Center
3. Entrance to the Educational Center







4. Entrance
to the Exhibits





 5. The Laboratories
5. The Laboratories







6. In the Exhibits






 7. From the Gantry Crane
7. From the Gantry Crane







8. On the Mezzanine

 9. The Educational Pathway
9. The Educational Pathway






 10. The Tipping Floor
10. The Tipping Floor







Start of the Process
11. The Recycling Center The






12. The Recycling Center
of the Process
End






13.
The Eco-Tower
A Walk Through the Park


Panoramas
Scan the QR Code below to access Panoramas from around the site.




To navigate, move around with your finger or tap the at the top of your screen to enable VR. Use the to switch positions in the panorama.
Icon Locations
McKees Rocks Recycling Campus
Educational Center
Eco-Tower
McKR Recycling Center







You
Thank
Jack Holcomb
Fall 2022 CUArch: Technology and Media in Architecture and Interiors





















 Birds Eye: North
Birds Eye: West
Birds Eye: North
Birds Eye: West











 Birds Eye: East
Birds Eye: South
Birds Eye: East
Birds Eye: South






































































































































 1. Along Intercontinental Highway
1. Along Intercontinental Highway






 2. Entrance to the Campus
2. Entrance to the Campus






 3. Entrance to the Educational Center
3. Entrance to the Educational Center












 5. The Laboratories
5. The Laboratories













 7. From the Gantry Crane
7. From the Gantry Crane








 9. The Educational Pathway
9. The Educational Pathway






 10. The Tipping Floor
10. The Tipping Floor
































