Smart City Under The Challenges Of Climate Change









Research Background
Methodology
ContemporaryConcern:ClimateChange
Smart City:in Definition
Smart CityFramework
DISCUSSION
Six-Characteristics of Smart City
InRespond to Climate Change
Smart Governance:Policies and Commitment
Smart People:Engagement ofDifferent Actors
Smart Environment: Efficient Useof Energyand Water, Cities’ Emission
Smart Mobility:Transportation
Smart Living:Housing and Pleasant Living
Smart Economy:As an Outcome of ClimateActions












95% - 100% of increasing global temperature caused by human activity.
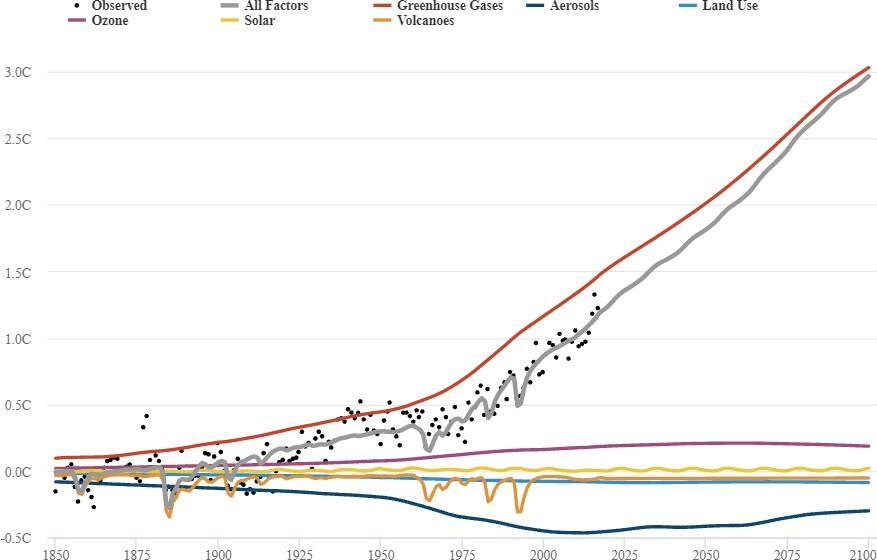
IPCC stated in the 2014 fift assessment report, summary for policymakers that it is “extremely likely that more than half of the observed increase in global average surface temperature” from 1951 to 2010 was caused by human activity
Source: CarbonBrief(2018) using Highcharts

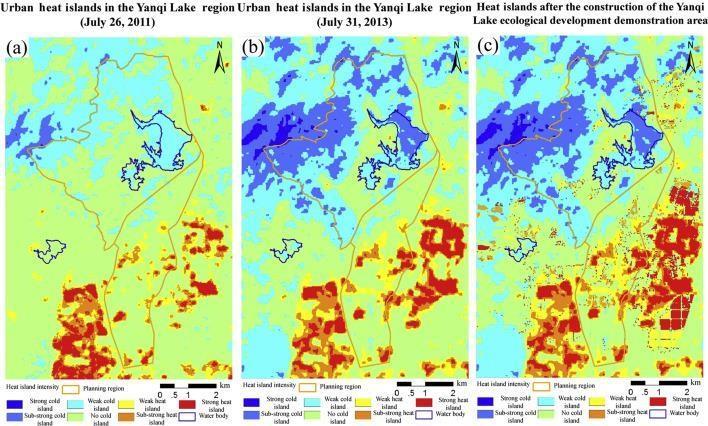
70% of cities are already dealing with the effects of climatechange, andnearlyallareat risk. Over90% of all urbanareas that are coastal, putting most cities on Earth at risk of flooding from risingsealevelsandpowerfulstorms. The increased focus on cities over the past decade, coupled with the challenges that climate change will certainly bring about, has encouraged a large push by all scales of governments to generate activities, innovations, and transformative changes to help cities address theimpacts ofclimatechange.






As the center of commerce, culture and innovation, and the birthplace for some of humankind’s greatest ideas, there lies opportunities for bringing new and innovative ways of monitoring, understanding,analyzing,planning,andmanagingcities
For instance, technological shift enabled city to perform real-time decision making on realtime data. And that is, more or less, explains the concept of asmart city.

The smart cities concept developed by Giffinger and Gudrun (2010) covers a wide range of the most important aspects in cities’ development: smart economy, smart people, smart governance, smart mobility, smart environment and smartliving.
With the use of ICT on every important aspects in cities’, smart city expected to directing cities to be more sustainable.
In that matters, climate change supposedly has a place in developing smart city, considering it is a part what ‘sustainable’ aims for.

Nevertheless, There are some critics toward the implementation of smart city. Whether the policy and governance of smart city will become too technocratic, narrowlyminded on technology, and also regard to other aspects of social and environmental sustainability.



















Of Smart City UnderThe Challenges Of Climate Change


Climate change has induced a wide array of adverse effects, including sea level rise, floods,

droughts, extreme weather events, and coastal erosion. In the future, hundreds of millions of people

living in urban areas will be affected by different impactsof climate change (IPCC, 2014,2001).






Helping decision makers and communities understand the potential opportunities associated with integrated solutions for climate change will encourage urgent and deliberate strides towards adapting cities to the dynamic climate reality.







Huang-Lachmann, J.T. (2019) stated that, there’s a rising trend within the publications on the topic of climate adaptation benefits and smart cities within the last 10 years. This suggests that both of these research area are becoming increasingly important. Thus, the understanding of the smart cities approach within the literature on climate change adaptationis afieldworthy of increased attention andresearch.




There is a lack of consensus on the definition and conceptualization of smart cities. Smart cities are conceptualized differently based on the field of research, as well as the purpose of building a given smart city.






As a consequence, there still is a lack of conceptual clarity around the smart city concept, or inconsistent understanding of what it means. (what it means to be “smart” within local context).





a city in which ICT is merged with traditional infrastructures, coordinated and integrated using new digital technologies(Batty et al., 2012). a city that works with the community to implement ICT that ultimately improvesthe quality of life for the community (Deakin and Al Waer, 2011).


ICT is not a sufficient criteria for enhancing city functions. In fact, a singular focus on technology and disregarding other key elements such as social, economic, and human capital or sustainability can paint an incomplete picture of smart cities.






a city that “infuses information into its physical infrastructure to improve conveniences, facilitate mobility, add efficiencies, conserve energy, improve the quality of air and water, identify problems and fix them quickly, recover rapidly from disasters, collect data to make better decisions, deploy resources effectively, and share data to enable collaboration across entitiesand domains” (Nam dan Pardo, 2011).

al.,
With many of the daunting climate change challenges cities currently face are being experienced across sectors and interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary strategies are often required to solve them. The development of operational tools to support cities is crucial and, therefore, so is studying thecommonalities and characteristics ofsmart cities andresilience(Papaetal., 2015).
Furthermore, the smart city framework developed by Giffinger and Gudrun(2010)will beused to examinethe practices andbenefitsof smartcity inthe fieldof climatechange adaptation.
MOBILITY
ENVIRONMENT
PEOPLE
The six characteristics of smart cities developed by Giffinger and Gudrun (2010) are useful to examine the smart city applications in cities, while the factors of the six characteristics (Giffinger and Gudrun, 2010) create a detailed and clearly defined framework which could be used to define boundariesof smart cities.

not
It is found that six-characteristics of smart city are not working in linear, instead they are dependonothers.
SMART MOBILIT Y SMART ENVIRONMENT
Smart people and smart governance are acting as the foundation together with smart environment dimension. Together, they build the base layer for further development
SMART ECONOM Y of other smart city dimensions and climate change adaptation.
SMART LIVING
It is found that six-characteristics of smart city are not working in linear, instead they are dependonothers.
SMART MOBILIT Y
Smart people and smart governance are acting asthe foundation together with smart environment dimension.
Together, they build the base layer for further development
SMART ECONOM Y of other smart city dimensions and climate change adaptation.
SMART LIVING
It is found that six-characteristics of smart city are not working in linear, instead they are dependonothers.
GOVERNAN CE
Y
ENVIRONMENT
PEOPLE
Smart mobility and smart living consists of hardware and software around people who are living in the smart environment.







When city commites to such networking involved other region or country, it helps to pursue their climate goals. Governance and policies affairs in dimension of smart governance often cover only the operational and innovation matters of public service. It’s often missed the opportunity to implement monitoring andevaluation systeminregards of climatechangeactions.


Therefore, there is sometimes a disconnect between the governance of smart cities and the governance for climate change mitigationandadaptation.

Many cities have plans for climate change adaptation and mitigation, but they are rarely driven by the smart city agenda, and vice versa. The separation of these two major policy areas could result in inefficient implementation and missed opportunities for meaningful growth.

The previous studies have shown pratices of smart governance and smart people in climate change adaptation. First, there is participation of public in decision-making (Turhan, 2016; Hay and Mimura, 2006; Rajmis et al., 2009), where communities actively involved in planning and developingstrategy of adaptation.

Second, raising awareness and bolster lifelong learning (Cartwight et al, 2013). Where public gaining more information and have been trained to composing adaption strategy, therefore its empower them to develop more in a long run.

And the last, bridging people and governance (Gauthier et al., 2015). This is where planner stands in between to advocate or facilitate communities to become actively involved. It’s also an opportunity to do a cross-sectoral communication (Cartwright et al., 2013).

As this increasing the relation between communities and governance, this could become an opportunity for the vulnerable populations. Considering that, vulnerable populations are not only more likely to face severe impacts from climate change and related disasters, but they are also often left out the decision-making processesforclimateaction.


Based on facts that already stated before, cities has consume almost 70% of global energy consumption and responsible for the global emission causing climate change (especially when the recources is based on coal, fossil, oil,andother non-renewable source).
In dimension of smart environment, smart city aims to increasing the use of more renewable energy. Parks (2019) found that smart grids could help boost the integration of renewable energy sources,aswell asimprove efficiency.


When city is in hand of ICT, water use and conservation can surely be improved, including the reduction of leaks and tracking of broken pipes. The system monitoring technology can aid urban water managementefforts whichwill further climate changeadaptationindrought-proneregions.
Implementation of ICT such as mapping and forecasting would help goverments to accurately assess the state of their finitie water resources, so they can meet curret demand and make plans to meet future growth in demand.

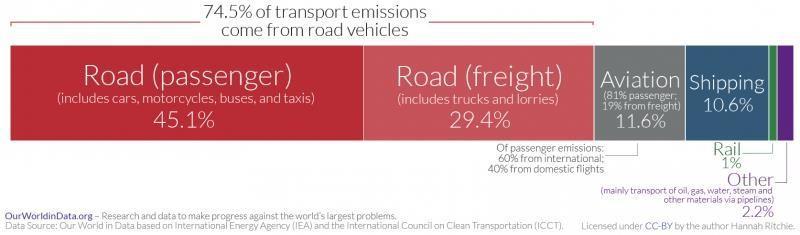
Cities (mostly in developing countries) often relying on cars and motorcycle caused by inadequate public transportation. Private transport is one of the world’s biggest sources of greenhouse gases, with emissions rising everyyear.
Data on increases or decreases in pollution due to traffic changes is analyzed for the causes of the pollution and used to plan accordingly, thus city could establishing priorities for initiatives to reduce emissions. Correct and current data is the basis forsmart decisions.
In China, similar technology has been employed to monitor air pollution levels in real-time and relay that information to citizens(Tamboetal., 2016).

During flooding from heavy rain, there are possible benefits in terms of water control, flood sensing, diversion of traffic, emergency services and even evacuation. With challenges of sea level rise, merged of ICT and infrastructure on smart citiy enabled cities to increase data acquisition and sharing information as a form of building resilience to change as it encourages preparedness. But when it comes to overcomesuchirreversible event,therearelimits.

Cities required to be ‘smart’ as means taking decision based on what data, projection, and information about future climate impact said. Long-term temporal scale is a crucial element in climate adaptation analysis, therefore cities shallnot stop on‘expectingwhatfuture may hold’step, buttakingarealactionas well.

In terms of climate change adaptation, both smart mobility and smart living focus on sustainable and innovative system. For smart mobility, city may apply congestion fee and tax-on emission policy. Whilst city provides adequate public transport, the policy applied encourage people to use public transport instead of private vehicle. As car and motorcycle contribute to cut its emissionin largenumber.

In the housing quality factor, ICT enabled ones to stimulate the micro-climate to design and build a future climate-proof architecture. Such investments related to housing could also pay back in cost savings from energy,water and production of urbangardening.
It may seems the practice is handed over to individuals or housing developer. More than that, cities could applied smart livng on community housing and slums area. The smart living application in adaptation could improve social aspects: by using green measures and information tools, slums are being upgraded and the perceptionof the lessprivilegedgroups is also evaluatedandincorporated insmartliving inadaptation.

On the focus of climate change, economy
considered as an outcome of adaptation and mitigation.
As matter of climate economy, the benefits of climate actions are not always directly linked to cities’ making more money in short term. It could be improved of quality of living, satisfaction, job creation, and institutionaland adaptive capacity.




Ecosystemservices
Use of GIS for analysingheat,exposure and vulnerability
Ability to calculatethe averagevaluein monetaryunits of selectedservices providedbygreenspacesin urbanareas
Extreme weatherevents
Use of GIS-basedprobabilisticmodelto calculatefactorslike windand local topographicalfactors
Ability to calculatethe costeffectiveness of adaptationstrategisbasedonregional increasesin damage costsfor various climate changescenarios
Health
Use of meteorologicalmodelforhealth impact
Provideprojectionsofeconomicimpactof climate changeadaptationrelatedto human health
Infrastructure Regression model for calculating benefits of green infrastructure for climate change adaptation
Findngs provide implications that urban greening has the potential to save more money annually Adressing inequality toward access to infrastructure
Sea levelrise andcoastalsystem
Modellingthe returnwaterlevel correspondingtovariousreturnperiods
Use of diital elevationmodelfor topography
Watersupply,waterresources management,anddroughts
GIS-basedriskassessmentonflood damage
RealIn Optionsanalysis
Analysisof temporalpatternsof water demandsat differentgrowthstageswith local precipitationandtemperature
Identifyingadaptationoptionswhichare climate-proofcouldincreaseclimate robustnessandadditionalpaybackwith cobenefits
Ability to estimate the net benefits of climate adaptation measures for the futurescenario
Calculationof cost-saving,positive outcomeson the environmentandwater savingsforhouseholds

Cities has faced many challenges, such as, urban growth that caused climate change, and in turn would cause huge impact to cities life. In regards of techonological shifts, cities have opportunities to make use of it in every cities’ aspect. And then, there goes the concept of smart city.
Referring to smart city’s characteristics that cover all the important cities’ aspect, including, governance, people, economy, mobility, living, and environment, these framework may applied in climatechange actionscontext as means to mitigate and adapt to climate change.
The implementation required cross-sector to work together, thus cities' would gain the benefits of it. Benefits consist of investment payback from energy and water costs savings, as well as possible avoided damages and reduced risks.

Aeris. (2019).” How Smart Cities Combat Climate Change:IoT and Traffic Reduction”. Accessed on https://www.aeris.com/news/post/how-smart-cities-combat-climatechange-iot-and-traffic-reduction/
Huang-Lachmann,J.T. (2019).Systematic reviewof smart citiesand climate change adaptation. Sustainability Accounting, Management and Policy Journal.
IoTNews. (2020). “Smartcities will help fight climate change but more awareness isneeded”. Accessed on https://iottechnews.com/news/2021/aug/11/smart-cities-will-helpfight-climate-change-but-more-awareness-is-needed/
Kolokotsa, Dionysia. "Smart cooling systems for the urban environment. Using renewable technologies to face the urban climate change." Solar Energy154(2017):101-111.
Kumar, P. (2021).Climate Change and Cities:ChallengesAhead.Frontiersin Sustainable Cities,3, 5.
Lin, B. B.,Ossola, A., Alberti, M., Andersson, E.,Bai, X., Dobbs, C., ... & Tan, P. Y. (2021). Integrating solutions to adapt cities for climate change. The Lancet Planetary Health, 5(7), e479-e486.
Marić, I., Pucar, M., & Kovačević, B. (2016). Reducing the impact of climate change by applying information technologies and measures for improving energy efficiencyin urban planning. Energy and Buildings, 115,102-111.
Papa, R., Galderisi, A.,Majello, M. C. V., & Saretta, E. (2015). Smart and resilient cities. A systemic approach for developing cross-sectoral strategiesin the face of climate change.
TeMA- Journalof Land Use,Mobility and Environment,8(1), 19–49
Parks, D. (2019). Energy efficiency left behind? Policy assemblages in Sweden’s most climate-smart city. EuropeanPlanning Studies, 27(2),318–335.
Rathore,M. M., Ahmad, A., Paul, A., & Rho, S. (2016). Urban planning and building smart citiesbased on the internet of things using big data analytics. Computer networks, 101,
