MEDVETDENT.

Topical affairs in Medicine, Veterinary and Dentistry
Editors
Theme: The Future
Jess Mountain What is there to look forward to?
Tasnuba Lamia
Freya Barton
STAHS MAGAZINE Issue 1 | May 2023
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to the Magazine: A letter from the editors
2. The Future of Psychology in Healthcare - Izzy Skaliotis
3. The Future of Breast Cancer Treatments and Diagnostics – Nethaya Bulathsinhala
4. The Mechanism of β- Lactam antibiotics, Resistance and Future Advancements – Tasnuba Lamia
5. ‘Under Pressure’: The Future of Hypertension Treatment – Tishe Afolayan
6. What Technological Advancements Could Change the Future of Veterinary Medicine? – Lily Patino
7. The Future of Brain Computer Interfaces (BCIs) - Nicole Dodge
8. The Future of Therapy – Gina Walter
9. Could Medium Chain Triglycerides (MCT) provide a possible treatment for Alzheimer’s? – Habisha Vigneswaran
Introduction to the Magazine: A letter from the Editors
26/04/2023
Dear readers,
We hope that you are pleased to see the first-ever magazine post from the Medicine, Veterinary and Dentistry (MedVetDent) Society at STAHS! Every half-term, you will be reading a wonderful menagerie and assortment of articles written and published by STAHS’ very own cohort of talented, aspiring Medics, Vets and Dentists.
This magazine sets out to provide a pathway for aspiring medics and STEM students alike to stay in the loop about current affairs. Regardless, it is welcome for any interested readers as we will be covering a variety of themes such as ethics, global issues, political issues and much more. We welcome anybody interested from Years 10-13 to write opinionated and informed pieces of their choosing. We hope that we can provide a platform for students to delve deeper into their interests and hone their skills as researchers and publishers.
Furthermore, we would like to take a moment to thank all our applicants who have submitted their articles for publication in our first issue. The hopeful future success of this magazine will be due to the collective convergence of all your input and efforts that have made this publication possible, and we thus really appreciate your hard work and contribution to this magazine.
So, sit back, relax and happy reading!
Your editors and founders,
Psychology has played an increasingly important role in healthcare over the past few decades. The field of psychology has advanced significantly since its early days, and its applications have become more diversified, impacting healthcare in ways that were previously unimaginable. The future of psychology in healthcare is bright, and its potential is limitless.
“Neither the mindless nor the brainless can be tolerated in medicine.” Lean Eisenberg, one of the leading figures in psychiatry, emphasizes
The Future of Psychology in Healthcare
 Izzy Skaliotis
Izzy Skaliotis
the importance of integrating the biomedical and psychosocial sciences in a way that helps us to understand how the brain and the mind work. Clinical psychology plays a vital part here and allows psychologists to better understand and treat their patients. One of the most significant contributions of psychology to healthcare is the development of evidencebased treatments for mental health disorders.
Freya Barton, Jess Mountain and Tasnuba Lamia
Evidence-based treatments are those that have been rigorously tested in clinical trials and found to be effective in treating specific mental health conditions. Examples of evidence-based treatments include cognitivebehavioural therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, and mindfulness-based interventions. The development of these treatments has revolutionized mental healthcare and has allowed clinicians to provide targeted and effective treatments to individuals suffering from mental health disorders. For example, research carried out by the University of Bristol found that when people who suffer from depression were given CBT, as well as the usual care they received such as antidepressants, it significantly reduced depression symptoms and improved quality of life in the long term (46 months on average) for patients where their depression had not responded to medication. These benefits continued to be found, on average, 40 months after they had finished therapy. Over the long term, 43% of patients had seen improvements, and they reported at least a 50% decrease in their depressive symptoms, compared to the 27% of people who continued with their usual care alone. Furthermore, the study found that this type of ‘high intensity’ CBT was also a cost-effective treatment from the health service’s perspective. This evidence suggests that there are clear benefits to investing in ‘high intensity’ CBT, both in terms of improved patient outcomes and cost savings for the health service.
Another area where psychology has had a significant impact on healthcare is in the prevention of chronic diseases. Psychological interventions have been shown to be effective in helping individuals make healthy lifestyle choices, such as quitting smoking, reducing
alcohol consumption, and adopting a healthy diet and exercise routine. Psychological interventions have also been shown to be effective in helping individuals manage chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease. In 2016, many studies on psychological intervention for substance-based addictions were reviewed and the results of each study were compared. These studies collectively indicate that even when receiving a lowintensity psychological intervention, compared to the controls receiving no psychological intervention, the people receiving treatment show some positive changes. More importantly, it should be noted that research designs are essential to establish that a given psychological intervention does work. In other words, while a given psychological intervention may seem logical and effective, its universal clinical usage would only arrive after it has been proven to be effective through vigorous research. This leaves many opportunities for psychologists to carry out and apply research to develop this area of psychology. In the future, psychology is expected to play an even greater role in healthcare. With the emergence of new technologies such as telemedicine, online therapy, and virtual reality, it is expected that psychological interventions will become more accessible and personalized. Telemedicine in particular has the potential to revolutionize mental healthcare by providing remote access to mental health services to individuals who may not have access to such services in their local areas.
Finally, psychology is expected to play a significant role in the integration of mental and physical healthcare. Mental and physical health are inextricably linked and addressing one without addressing the other can lead to minimal end results. By integrating mental
and physical healthcare, clinicians can provide more comprehensive care to individuals, which improves overall health outcomes and also reduces healthcare costs. The Mental Health Foundation states that physical health problems can increase the risk of developing mental health problems significantly, and the same goes for the other way around. Almost one in three people who have a long-term physical health condition also have a mental health problem, usually anxiety or depression. The effect of poor mental health on physical health problems is thought to cost the NHS at least £8 billion a year. Exercise and a good diet are recommended to keep you physically well, and there are reasons behind this. Firstly, aerobic exercises such as jogging, swimming, cycling, walking, and dancing have been proven by research to reduce anxiety and depression symptoms. Secondly, studies
In conclusion, the future of psychology in healthcare is promising. The field of psychology has already made significant contributions to mental and physical healthcare, and the continued development of new technologies and treatment modalities is
comparing "traditional" diets, such as the Mediterranean diet and the traditional Japanese diet, to a typical "Western" diet, have shown that “traditional diets” tend to reduce depression risk by 25% to 35% compared to typical “Western” diets. According to scientists, this difference can be explained by the fact that these traditional diets tend to be rich in vegetables, fruits, fish and seafood, and contain smaller amounts of lean meats and dairy. In addition, they also avoid processed and refined foods and sugars, which are very commonly found in “Western” diets. What’s more, many of these unprocessed foods are fermented, which act as natural probiotics. In conclusion, it is evident that diet and exercise have a positive effect on mental health. It is therefore important to consider the potential impacts of diet and exercise on mental health and to make healthy choices.
expected to expand the impact of psychology even further. As healthcare continues to evolve, psychology will undoubtedly continue to play an important role in improving the health and well-being of individuals around the world.
Citations
Article read: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3410123/ Read on 07/05/2023
Article read: https://www.psych.ox.ac.uk/news/study-finds-cbt-offers-long-term-benefits-forpeople-with-depression read on 07/05/2023 Article read: https://www.kingsfund.org.uk/projects/time-think-differently/trends-disease-and-disabilitymental-physical-health read on 15/05/2023
Article read: https://www.mentalhealth.org.uk/explore-mental-health/a-z-topics/physical-healthand-mental-
health#:~:text=Physical%20health%20problems%20significantly%20increase,most%20often%20de pression%20or%20anxiety read on 15/05/2023
Article read: https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/nutritional-psychiatry-your-brain-on-food201511168626 read on 15/05/2023
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers in the world, amassing to 7.8 million women diagnosed with it in the past 5 years. In 2020, there were 2.3 million women diagnosed with breast cancer and 685 000 deaths globally. Being in the bracket of one of the most common and detrimental diseases in the world, breast cancer poses to be the largest threat to women’s health. Over the years, considerable progress has been made in understanding the complexities of breast cancer and improving the techniques of diagnosis and innovative treatments with new technologies. The battle against breast cancer is still ongoing. However, the future holds immense potential for further advancements. There is currently evidence of advancements in research, technology and personalized medicine which is gradually transforming the process of breast cancer prevention and diagnosis. In this article, I explore the new developments that have been made, the role of precision medicine, the potential of immunotherapy and the importance of patient empowerment in shaping a brighter future for
The Future of Breast Cancer Treatment and Diagnostics
 Nethaya Bulathsinhala
Nethaya Bulathsinhala
breast cancer.
The anatomy of the breast is such that there’s glandular tissue with lobules and ducts within it. Breast cancer arises in the epithelium (lining cells) of the ducts or the lobules in the glandular tissue of the breast. Cancerous growth only occurs in the duct or the lobule, so it causes no symptoms and has minimal potential to spread (metastasis). Over time these stage 0 cancers progress and invade the surrounding breast tissue and spread to the lymph nodes or other organs in the body. The treatment for breast cancer can be highly effective if it is identified early before widespread metastasis. Treatment usually consists of a combination of surgical removal, radiation therapy and medication including hormonal therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted biological therapy in some cases. These processes help to treat microscopic cancer that has spread from the breast tumor through the blood.
One of the most promising aspects of the
treatment of breast cancer is precision medicine. By understanding the unique molecular characteristics of each tumor and the genetic makeup of the patient, healthcare professionals can tailor treatments specifically to complement the patient at hand. This approach of personalization maximizes patient satisfaction and the efficiency of treatment while minimizing the side effects that can arise. Genomic Profiling, which is a sub-part of Precision Medicine, involves identifying the specific genetic alterations driving the growth of any tumor through DNA sequencing. Researchers can uncover genetic biomarkers that predict responses to various treatments. This then allows clinicians to select targeted therapies that attack cancer cells with enhanced accuracy. In the future, Genomic Profiling is said to be more accessible, making personalized treatment strategies a standard method of care for breast cancer patients.
As well as this, early detection plays a crucial role in breast cancer management, as it allows for effective treatments and improved outcomes.
As in most industries in the 21st century, AI has made its mark in the world of treatment for cancers. The integration of Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms allows for improved breast cancer screening as it can analyze vast amounts of mammographic data. There is more detail in subtle patterns and abnormalities that may be missed by human radiologists and this technology shows exciting potential for improving early detection rates and reducing false biopsies. For example, mammography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and molecular breast imaging (MBI), improve accuracy in diagnosis and reduce false diagnoses, but when paired with AI prove even further efficiency in scanning. There have also been multiple breakthroughs in imaging
techniques, such as digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) which offers higher sensitivity and improved accuracy in detecting breast tumors. According to the Mayo Clinic, “Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) is a technique that allows health care professionals to view multiple images of the breast rather than the typical single image obtained with the conventional mammogram. Conventional mammograms provide doctors with a single 2D image to evaluate the breast.” This description shows that DBT is an improved and more detailed method for doctors to assess breast images, and to see multiple images of a patient.
Immunotherapy has emerged as a revolutionary cancer treatment, by harnessing the body’s immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells. Traditionally, breast cancer has been considered less immunogenic (able to produce an immune response), however recent research has shown that a subset of breast cancer has immunotherapeutic potential. Scientists are exploring immunotherapeutic approaches such as immune checkpoint inhibitors that can enhance the body’s immune response against breast cancer. Idealistically, a combination of therapies, such as chemotherapy or targeted therapies and immunotherapeutic approaches is recommended to boost treatment outcomes. Other examples of innovative treatment approaches are oncolytic viruses, nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems and gene therapies which overcome treatment resistance.
A more complex treatment that promises to be an efficient method of treatment for breast cancer, is liquid biopsies, which involve analyzing circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), from a patient’s blood sample. It is a noninvasive method for monitoring disease
progression and detecting any resistance to treatment as well as posing as a blueprint for further treatment decisions. Liquid biopsies identify genetic mutations and monitor the response to treatment, allowing doctors and healthcare professionals to make real-time adjustments to treatment plans. In the future, liquid biopsies may replace invasive tissue biopsies, due to their real-time monitoring ability and the advantage of early detection of treatment resistance or the recurrence of disease.
Despite the promising developments and improved methods that have been introduced, there are several challenges that need to be addressed for the future of breast cancer research, treatment, and care. The largest factor is the lack of equitable access to these treatments across diverse populations and economies. Socioeconomic factors, racial disparities and geographic barriers can limit access to state-of-the-art therapies such as
these new developments. There are however concerns with the use of AI including the ethical issues surrounding data privacy, consent and whether health professionals are equipped with enough knowledge on the responsible use of AI algorithms.
Citations
Although these challenges exist, the future of breast cancer treatment is clearly promising and improving as doctors and healthcare professionals around the world are working with patients to fight against breast cancer every day. Organizations and charitable groups continue to fund and support research into breast cancer, to improve survivorship and save millions of women who are impacted worldwide.
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/breastcancer#:~:text=Reducing%20global%20breast%20cancer%20mortality,under%2070%20years%20of%20age
https://www.michiganmedicine.org/health-lab/when-are-we-going-cure-cancer-bright-future-breastcancer-research
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5481194/
https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/precision-medicine-breast-cancer/about/pac20385240#:~:text=Precision%20medicine%20for%20breast%20cancer%20is%20an%20approach%20to%20 diagnosis,collected%20for%20analysis%2C%20often%20genetic.
https://www.breastcancer.org/screening-testing/molecular-profiling#:~:text=Advertisement,Broad%20molecular%20profiling%20tests%20look%20at%20all%20the%20genes%20in,next%2Dgeneration %20sequencing
https://www.mdanderson.org/cancerwise/does-immunotherapy-treat-breast-cancer.h00159385101.html#:~:text=Can%20immunotherapy%20treat%20breast%20cancer,most%20common%20type %20of%20immunotherapy.
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/ebiom/article/PIIS2352-3964(23)000634/fulltext#:~:text=Artificial%20intelligence%20(AI)%20has%20been,faced%20by%20breast%20screening%2 0programs.
https://www.cancer.net/blog/2022-11/liquid-biopsies-cancer-what-know-and-whatexpect#:~:text=A%20liquid%20biopsy%20is%20a,the%20tumor%20into%20the%20bloodstream. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9097801/
β-Lactam antibiotics are a widely used group of antibiotics that work by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. They are one of the most effective and widely used antibiotics in clinical practice to treat bacterial infection. These antibiotics possess several beneficial qualities ranging from their broad spectrum of activity, low toxicity, effectiveness, and safety profile. Despite their success, there is a growing concern regarding the emergence of bacterial resistance to β-Lactams. This article aims to provide insight into the chemical mechanism of β-Lactam antibiotics, resistance to the drug and future advancements in this area.
The Bio-Chemical Mechanism of β-Lactam Antibiotics
The Mechanism of β- Lactam antibiotics, Resistance and Future Advancements
 Tasnuba Lamia
Tasnuba Lamia
β-Lactam antibiotics are characterized by their β-lactam ring structure essential for their activity. This fundamental structure is present in several classes of antibiotics including carbapenems, penicillin and cephalosporins. The ring is a four-membered lactam (cyclic amide) composed of three carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom all covalently bonded (functional group -CONH-). The carbon atom highlighted in Figure 1 is covalently bound to a sulphur, hydrogen and nitrogen atom and is sp3 hybridised. This has an ideal bond angle of 109.5 degrees (tetrahedral). Despite this, the molecular geometry of this part of the lactam is actually closer to about 90 degrees. This results in angle straining and reduced amide resonance of the molecule, subsequently giving the molecule a high
 Figure 1: Lactam structure of penicillin. The red circle highlights the sp3 hybridisation of the carbon atom. (Wikepedia)
Figure 1: Lactam structure of penicillin. The red circle highlights the sp3 hybridisation of the carbon atom. (Wikepedia)
reactivity, easy hydrolysis and immense effectiveness in triggering bacterial lysis.
Most bacteria are encased in a cell wall, mainly composed of the polysaccharide peptidoglycan. The cell wall is essential to prevent the cell from bursting when osmotic pressure is present and maintains the shape of the cell. The repeating monomers in peptidoglycan alternate between NAcetylmuramic acid and N-acetyl glucosamine which are cross-linked by amino acid chains. The enzyme Transpeptidase, also referred to as penicillin-binding proteins (PBP), is present in most bacteria and catalyses the cross-linking between peptidoglycan molecules. In gram-negative bacteria, synthesis of the peptidoglycan occurs in the bacterial cytoplasm and then moves to a cell wall acceptor in the periplasm.
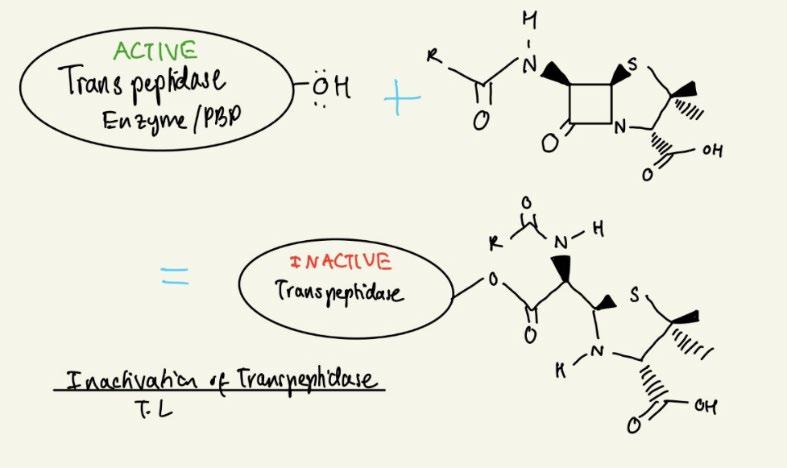
An active PBP enzyme has an OH group attached to it. This acts as a nucleophile (electron-pair donor) and attacks the carbonyl carbon on the β-Lactam ring acting as an electrophile (electron-pair acceptor). In the βLactam ring, these electrons are then ‘kicked off’ the oxygen atom. The reformation of the carbonyl group kicks these electrons onto the nitrogen atom (nucleophilic acyl substitution). This product consist of the transpeptidase enzyme attached to the β-Lactam antibiotic. The OH group that was responsible for the activation of the Transpeptidase enzyme is no longer present, disabling the enzyme and subsequently enabling bacterial lysis (death). By inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, these bacterial cells now burst from a high osmotic pressure compared to their surrounding environment. The PBP enzyme complex also stimulates the release of automatic lysins which digest any remaining cell wall.
The Mechanism of Resistance
Despite their success, the use of β- Lactam antibiotics is increasingly being limited by the emergence of bacterial resistance. Resistance to beta-lactams can occur through two main routes:
Route 1: Transformation
When a bacterium acquires a mutation to its gene during cell replication, this gene can result in advantageous resistance to antibiotics. When a bacterium with this gene dies, naked DNA (DNA not associated with histone proteins) is released into the surrounding environment. If another bacterium is nearby, it can uptake the naked DNA containing the resistant gene. The resistance gene can then be transferred from the naked DNA to the chromosome of the host bacteria (homologous transformation). Once the bacterium develops enough of this resistance gene, it can express an altered PBP which can still cross-link the bacterial cell wall but has a reduced affinity for the βLactam ring.
Route 2: Production of β- Lactamases
Β- Lactamases are enzymes that can inactivate the antibiotic before it can exert its effect on the bacteria. The gene coding for these enzymes may be in the host DNA or
bacterial plasmids. Bacteria can pass these resistant plasmids to each other by forming a small channel when close together (conjugation). In gram-positive bacteria, if this plasmid is transcribed and translated, the bacteria will produce these enzymes which hydrolyse and destroy the β- lactam ring.
Future Advancements in β-Lactam Antibiotics
To tackle resistance, developing future advancements can increase the efficacy of βLactam antibiotics. This includes modifying existing β-lactam antibiotics, the development of β-lactamase inhibitors and the discovery of new ones.
β-Lactamase inhibitors are compounds that combine with β-Lactam antibiotics and prevent the production of β-lactamase. Several inhibitors have been developed including sulbactam, clavulanic acid and tazobactam.
However, the use of β-Lactamase inhibitors has also led to emerging resistance. Some bacteria have evolved and produce new βLactamases that destroy these inhibitors reducing the effectiveness of this strategy. To address this issue, new β-Lactamase inhibitors with varying chemical structures are being developed such as avibactam.
Another strategy for overcoming resistance is the modification of existing β-Lactam antibiotics. This can involve the addition of chemical groups to the antibiotic molecule to increase its stability and enhance its activity. An example to showcase this is the
Citations available on request
modification of penicillin G to create amoxicillin which has improved activity against Gram-negative bacteria.
Another modification strategy is the development of prodrugs. These are inactive compounds that activate once in the body, enhancing the kinetics of the antibiotic and its half-life. An example of a β-Lactam prodrug is Fosfomycin, which is switched to active Fosfomycin tromethamine in the body.
The discovery of novel β-Lactam antibiotics involves the identification of new compounds with β-Lactam activity or modifying existing compounds to generate new derivatives with better activity. This could expand the variety of β-Lactam activity and help target resistance mechanisms. Some of these antibiotics could instead target the plasma membrane or other essential metabolic processes of the bacterium.
β-Lactam antibiotics are a vital group of antibiotics that have been used for decades to treat bacterial infections. Despite this, the emergence of bacterial resistance to βLactams is growing and thus new strategies and required to maintain their efficiency. The development of new β-Lactamase inhibitors, modification of existing β-Lactam antibiotics and the discovery of novel β-Lactam antibiotics are all promising approaches to target resistance. The field of antibiotic research is continually evolving, and exploration of new approaches is vital to maintain their effectiveness.
What is Hypertension and why is it important?
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, occurs when the pressure in the blood vessels is unusually high[1]. This high pressure exerts strain on the walls of the heart and arteries which, if untreated, can result in a myriad of other cardiovascular diseases such as a stroke or heart attack for example.
Blood pressure is measured using 2 numbers: systolic and diastolic. The systolic pressure (higher number) measures the blood pressure in your arteries when your heart beats and the diastolic pressure (lower number) measures the blood pressure in your arteries between heartbeats (during rest). [2] Both are measured in mmHg (millimetres of mercury). Healthy blood pressure may vary slightly from patient to patient, however, ideal readings vary from 90/60mmHg to 120/80mmHg. The
‘Under Pressure’: The Future of Hypertension Treatment
Tishe Afolayan
risk of hypertension increases when blood pressure falls between 121/81mmHg and 139/89mmHg.[3] Hypertension, often referred to as “the silent killer”, is extremely important as it usually shows no apparent symptoms which is why 1 in 4 adults have the condition without knowing. [4] As a result, the NHS advises that healthy adults over 40 years old should have their blood pressure checked at least once every 5 years. The NHS offers free health check-up appointments for adults aged 40 to 74 in England to spot early signs of conditions such as stroke, kidney diseases and heart diseases (including hypertension). [5] In the UK, blood pressure testing is available in local GP practices, some pharmacies and workplaces and at an NHS health check appointment. [6] It is estimated that over 14 million adults in the UK are diagnosed with hypertension and of this, 5 million are still undiagnosed due to lack of
awareness and many continue to remain unaware until more complex health challenges arise such as a heart attack. [7]
What are the Treatments that are currently available?
Whether a patient has mild or severe hypertension, doctors advise implementing healthier lifestyle changes such as reducing salt intake to less than 6g a day, losing weight and increasing exercise. The earlier these changes are made, the lower the likelihood of having to be prescribed medications.  The current treatments available can be used in isolation or more commonly combined with other medications and may need to be taken for the entirety of a person’s life. Many of the drugs available do produce side effects such as dizziness, headaches and tiredness, however, this should not prevent a person from continuing to take their medication unless a doctor may advise changing medications. It is crucial to administer the correct dosages as directed to allow the medication to work optimally, although the patient may not feel any changes.
The range of hypertension drugs primarily used includes ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), calcium channel blockers, diuretics and beta blockers. Many of these medications work very similarly by either widening blood vessels or helping them to relax to reduce the strain caused by abnormally high blood pressure, thereby making it easier to pump blood around the body. Age and ethnicity play vital roles in the treatment plans that patients are prescribed, as people of African or Caribbean descent will usually be offered a calcium channel blocker, for example. [8]
Jointly led trials by CinCor Pharma, USA and Queen Mary University of London (QMUL) researchers have revealed that a new drug –Baxdrostat – could prove to successfully be used as a treatment for patients who are resistant to currently available high blood pressure medications. This comes as a result of Phase II trials that involved 248 patients who were given daily doses of Baxdrostat at varying amounts or placebo. These patients were all taking at least 3 hypertension medications and the Baxdrostat doses were taken in addition to their usual treatments. The trial lasted 12 weeks and it was seen that the group of patients who were given the highest dosage of Baxdrostat had a 20-point fall in blood pressure and an 11-point fall in the group given the placebo treatment. [9]
So why has this drug proved to be effective?
Aldosterone is a hormone that regulates the salt content in the body. Baxdrostat works by preventing the production of this hormone. It increases blood pressure and causes the body to retain salt. Patients who are resistant to current high blood pressure medications have slightly raised levels of aldosterone production and Baxdrostat has thus far provided a noticeable fall in blood pressure for these patients. Professor of Endocrine Hypertension and co-senior of the study Professor Morris Brown at QMUL has said “The results of this first-of-its-kind drug are exciting although more testing is required before we can draw any comparisons with any existing medications. But Baxdrostat could potentially offer hope to many people who do not respond to traditional hypertension treatment.” [10]
Can Baxdrostat really work?
Baxdrostat – The Future of Hypertension Treatment?
Although more research and testing are needed before solid comparisons can be made, I have hope that Baxdrostat can continue to prove successful in treating patients with severe hypertension that is resistant to current medications. Scientists are under pressure to find new, cutting-edge
ways of treating and managing disease and if this medication were to pass the next trial phases, over 500,000 lives in the UK could be saved as well as changing the future of treatments for cardiovascular diseases as a whole.
Citations
• [1] https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/high-blood-pressure-hypertension/treatment/
• [2] https://www.cdc.gov/bloodpressure/about.htm
• [3] https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/high-blood-pressure-hypertension/
• [4] https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/high-blood-pressure-hypertension/treatment/
• [5] https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/high-blood-pressure-hypertension/diagnosis/
• [6]
• [7] https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/heart-matters-magazine/medical/highblood-pressure-latest-news
• [8] https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/high-blood-pressure-hypertension/treatment/
• [9] https://www.qmul.ac.uk/media/news/2022/smd/new-drug-can-successfully-treatpatients-typically-resistant-to-high-blood-pressure-treatment.html
• [10] https://www.qmul.ac.uk/media/news/2022/smd/new-drug-can-successfully-treatpatients-typically-resistant-to-high-blood-pressure-treatment.html
In recent years, the field of veterinary medicine has experienced remarkable technological advancements, which have completely transformed the way we care for our beloved animals. It has enabled vets to make faster diagnoses, and more accurate prognoses, and ultimately save more animals' lives. Whilst it’s difficult to predict the future, it’s almost certain that technology will continue to develop and will therefore have a huge impact on how veterinary medicine evolves in the future.
In the last 10 years, there have been significant changes with respect to diagnosis, treatment and care within veterinary medicine which advanced technology has played a massive role in. MRI, ultrasound scans, and CT are imaging technologies that have mostly been used in human medicine but are now commonly used for treating animals. These imaging technologies provide detailed visualizations of internal structures, enabling accurate diagnosis and treatment planning which additionally helps minimise invasive
What Technological Advancements could change the Future of Veterinary Medicine?
 Lily Patino
Lily Patino
procedures and reduced patient discomfort and recovery time.
In addition, laparoscopic surgery is a procedure that allows access to the abdominal or thoracic cavity without having to make large incisions. It is also known as ‘keyhole’ surgery due to several 0.5-1cm incisions that are made so ports, a light source and a small camera can be inserted. Laparoscopic surgery has been adopted from human medicine and adapted to the animal kingdom. The main advantage of laparoscopic surgery is that it minimises invasive procedures which in return reduces patient discomfort and recovery time.
Laparoscopic surgery on horse abdomen
The most recent technology in veterinary medicine is the use of robots. Robots have the potential to make veterinary care more efficient and effective. Meanwhile, there is research going on to develop RIBA, a nursing assistant that can lift up and set down animals. RIBA can overcome the back problems and exhaustion vets, nurses, and technicians face on a daily basis and additionally can provide more security and safety when transporting the animals. With robots potentially being able to carry out this time-consuming task, it allows the vets to spend more time on patients. Clinical workers spend a lot of work and time cleaning and disinfecting hospital areas which can be very time-consuming especially due to the fact that there has been an increase in antibiotic-resistant bacteria. This has meant that there has been research into sanitation and disinfection robots that use UV disinfection methodologies to destroy microorganisms.
In human medicine, robotic surgery has been a recent and successful advancement. The first general laparoscopic surgery was performed by the Da Vinci robot in 2000 and robotic surgery has been used around Europe since then. The robot's main role is to increase visibility, precision and flexibility leading to a more successful surgical outcome as its flexibility means that smaller incisions can be made contributing to less hospitalisation time and therefore quicker recovery.
I have had first-hand experience seeing this in practice as I was lucky enough to watch 3 surgeries carried out by my uncle who was the first surgeon to use the Versius surgical robot for life-saving cancer treatment.
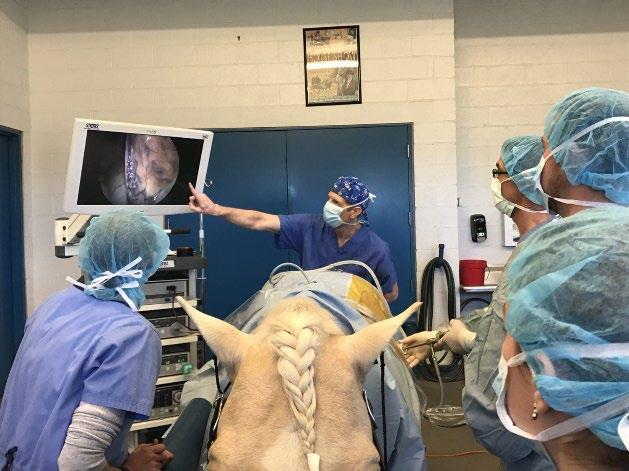
“Upper GI is an extremely busy department and adopting Versius signifies a new era for the speciality as many more patients will receive minimal access surgery and be treated with this high-quality technology.” It is estimated that over the next few years, the use of robots in human surgery will triple and so I strongly believe that we will see this type of surgery in veterinary medicine become more mainstream. The benefits that robots bring are precision and accuracy which are just as important in animals as in humans. On a slightly smaller scale, there have been many other inventions which help to prevent health issues and also provide better care for our pets.
Telemedicine is ‘the use of electronic communication and information technologies to provide clinical healthcare remotely.’ More recently since COVID, telemedicine has become more commonly used because people are recognising its benefits. It provides more efficient appointments and reduces waiting times which enables vets to see more patients. However, telemedicine isn’t always appropriate for every concern.
The use of digital dental X-rays and advancements in dental instruments has driven improvements in oral health in animals. Electronic devices that capture vital statistics such as temperature, heart rate, respiration
rate, pH levels etc are being increasingly used. These devices identify the problem at an early stage meaning quicker and more accurate treatment.
3D printing is now common use in everyday life, but this type of technology can be used by vets to get exact information on the insides of the animal prior to operating, by creating near–real bone models from computergenerated scans. For animals that need prosthetics, this 3D technology is used to custom design meaning a more successful outcome.
In an uncertain world, the one certainty is that technology will continue to evolve and will always have a huge impact on how we do things. We can see that in the last 20 years, veterinary medicine has already changed so
Citations
much due to technology and even in the past 3 years COVID has made the industry think differently and were almost forced to use technology in order to continue to practice safely. We now realise that these enforced changes actually bring real benefits to everyone.
However, animals and their welfare are hugely important, and I truly believe that there is no replacement for human interaction, emotional support and personal care, so whatever technological advancements occur in veterinary medicine, they will have to work hand in hand with the professionals and not instead of.
• Digital Technology and the Future of Veterinary Medicine (vetstoria.com)
• The robot era: Which could be their role in veterinary medicine? | The Vet Futurist
• Keyhole Surgery | Veterinary Laparoscopy | Vets4Pets
• Technological advancements in veterinary medicine (vetport.com)
• Learn About The Newest Advances in Veterinary Technology (carrington.edu)
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are hardware and software communications systems that permit cerebral activity alone to control computers or external devices. The immediate goal of BCI research is to provide communications capabilities to severely disabled people who are paralyzed by neurological neuromuscular disorders such as Multiple sclerosis, brain stem stroke or spinal cord injury. BCI creates a new non-muscular channel for relaying a person’s intentions to external devices such as computers, speech synthesizers, assistive appliances and neural prostheses. For example, researchers are developing BCIs that allow people with paralysis to spell words on a computer screen or regain control of their limbs. In addition, researchers are developing BCI-controlled robotic limbs that can provide users with a sense of touch.
Generally, BCIs connect to the brain in two different ways, either through implanted or wearable devices.
Implanted BCIs
The Future of Brain Computer Interfaces (BCIs)

Implanted BCIs are often surgically attached directly to brain tissue. These may be more appropriate for users with severe neuromuscular disorders or physical injuries.
Nicole Dodge
For example, a person with paralysis could use an implanted BCI that is attached to specific neurons to regain precise control of a limb. Implanted BCIs measure signals directly from the brain, reducing interference from other tissue. However, they pose surgical risks such as infection and rejection. Some implanted BCIs reduce risk by placing electrodes on the surface of the brain, a method called electrocorticography (ECoG).
Wearable BCIs
Wearable BCIs often require a cap containing conductors that measure brain activity detectable on the scalp. Most wearable BCIs use electroencephalography (EEG)to measure the brain's electrical activity. There is also an emerging method of functional near-infrared
spectroscopy (fNIRS) which shines near-infrared light through the skull to measure blood flow, which can indicate information such as the user’s intention.
Fewer than 40 people worldwide have implanted BCIs, all experimental. Even though using brain data is still theoretical, the global BCI market is expected to reach £5.34B by 2030 due to its recent advancements. For example, in April 2021, a device that uses a wireless EEG headset helped stroke patients regain arm and hand control. Not only have there been medical applications, but the military (the national aeronautics and space administration) has also used BCIs to help detect when pilots and traffic controllers are more likely to make mistakes.
The development of BCI technology was initially focused on helping paralyzed people control assistive devices using their thoughts. However, researchers are developing BCIs which can be used as a neurofeedback training tool to improve cognitive performance. For example, your BCI could detect that your attention level is too low compared with the importance of a given task and trigger an alert. It could also adapt the lighting in your house based on how stressed you are or prevent you from using your company car if drowsiness is detected.
cyberattacks because hackers could use malware to intercept brain signal data. Because each person generates unique brain signals and there is extreme difficulty in measuring signals, wearable BCIs range from hundreds to thousands of pounds which may result in unequal access. Researchers have also suggested that the translation of brain signals to a speech by a BCI could cause harm if it is not accurate (inaccurate translation might indicate consent that the person did not intend to give). Therefore, there are also societal and ethical implications.
Currently, BCI technology has advanced but they are still experimental. There are prospects that advancements in technology will lead to smaller, more portable, and non-invasive BCI devices, enhancing user comfort and accessibility. Ethical considerations surrounding BCIs also need to be addressed, leading to the development of robust neuroethical frameworks and guidelines.
However, there are limitations and concerns with BCIs. Some researchers have recognized possible legal and security implications such as
Citations available on request
To conclude, brain-computer interfaces have emerged as a transformative technology, bridging the gap between the human brain and computers, revolutionizing fields such as healthcare and communication. As technology continues to advance, overcoming challenges and refining the accuracy, safety, and ethical aspects of BCIs will be crucial. The future of BCIs will allow the opportunity for individuals to harness the power of their minds and reshape the way we interact with technology.
In this generation, mental health is currently a heated issue. Or is it just more talked about? There is currently a heated debate due to the rise of social media, the recent global pandemic (COVID), climate change and other external events. These events can be seen to cause a lot of distress, anxiety, and depression for individuals, so mental health is progressively getting worse as time goes by. But surely mental health issues were always present in the past generations and were just not talked about enough? Perhaps these issues were less open for discussion and less information on mental health was available. Many questions arise in the present day on whether anxiety-enhancing events will continue to worsen, and what are the right methods to tackle this. In this article, I aim to explore answers to these questions.
Therapy is a treatment intended to relieve or heal a disorder. There are many types such as cognitive behavioral therapy, art therapy, drug therapy treatment, narrative therapy,

The Future of Therapy
Gina Walter
exposure therapy, person-centered therapy and so on. These highlight the many options that are available, but there could always be more as therapeutic methods continue to develop into the future to help cover all areas of mental health. It is also vital to ensure that this aid is available and accessible to everyone. There are nearly 300 mental disorders listed in the DSM-5 (handbook published by the American Psychiatric Association). To deal with every one of these, therapy needs to be very versatile. People are hugely different. The common phrase that “everyone is unique” may be cliche, but it is true! There are 8 billion people on this planet and every single one of these humans has a different genetic makeup - think about just how many combinations there must be. It varies how everyone reacts to therapy, whether it’s a medication or a talk-based therapy. To find what is best for everyone clinicians and scientists are currently researching to help.
Their aim for the future is to get to ‘precision medicine’, which aims to consider the difference between people’s genomes and their way of life. Raul Urrutia, who is a professor of surgery, and Warren P. Knowles, a professor of Genomics, say that this is so we can “diagnose with precision, predict with precision and cure with precision”. This emphasis on precision, including in the name of medicine, shows just how important it is that we look deeper into helping everyone's personal needs.
COVID-19 was a significant event that affected a lot of people’s mental health, stuck indoors without social interaction. There was a massive increase in the use of technology as everything had to be done online whether it was school or jobs. This encouraged ‘online therapy’, for some. However, a Zoom call with a stranger on the other side of the call may not seem personal for some, and the trustworthy environment that is development in a face-to-face scene may not be adequately established. Despite this, there are some benefits to this type of therapy that could lead to a more broad, useful, and efficient future in the involvement of technology in therapy.
Some of these benefits include:
- Convenience:
Someone who is suffering from a mental illness can struggle to get to real-life face-toface therapy due to having a lack of motivation or being unable to leave their house. This can prevent them from receiving the help they need and may force them to resort to other methods as drug therapy. As one of the NHS core values is non maleficence, healthcare should strive to limit as much harm to patients as possible. This should include avoiding therapeutical drugs until necessary. Therefore, online therapy is
an easier technique to get face-to-face therapy as you just must log on online from the comfort of your own home.
- Simple but effective:
This form of therapy can have an amazing effect in helping people’s lives. Apps are going to continue to develop, aiming to help prevent illness such as working on memory skills with simple games and providing a 24/7 constant support system. As technology continues to get more efficient and complex, more and more opportunities will be produced including working on more serious disorders, for example, schizophrenia.
On the other hand, technology can be seen as a negative. Some could argue the dangers of social media and see it as one of the main contributors to mental health implications in this generation. So, why would we encourage young people to increase their screen time even further? To deal with this issue we could see with each person what is more relevant to them. For example, if we have a young teenager struggling with confidence stemming from social media then in-person therapy would be more encouraged compared to an older person who rarely uses technology and won’t experience negative effects from using online therapy.The future of our planet also provides a lot of anxiety and depression for young people. Climate change is extremely scary for some, and I am sure you have seen in the news all the protests that recently have occurred. As global warming continues to worsen, this could be mirrored in people’s mental health.
It is surprisingly hard to find out more about therapy in the future – It seems that there will be a lot of advancements due to new technologies. We seem to have so much therapy already, and research are trying to
find new strategies to improve mental illness every day. It is undeniable that there is more we can do for mental illness, but I don’t think everyone is quite sure yet of how mental health will change in a decade. There could be another common cause of mental health issues that develops in the future, and we will have to adapt our therapy for any foreseen causes. Regardless of whether it is global
warming or another pandemic, the contributions to mental health and therapy are continually evolving.
Citations available on request
What is MCT?
MCT (medium chain triglycerides) is a form of a saturated fatty acid. It is known to have about 12 carbon atoms in its chain structure and it can digest materials easily and has a thermogenic effect when sent to the liver hence why it is generally good for patients who have difficulty metabolising different forms of fats in their diet. Some of these malabsorption problems include digestive disorders such as gallbladder infections and Chron’s disease.
Could MCT (Medium Chain Triglycerides) provide possible treatment for Alzheimer’s?
beta-hydroxybutyrate,which,inthefasting stateprovidebetter,moreefficientenergyfor thebrain,increasingfocusand concentration.” MCT helps athletic endurance because of their ability to convert fats into ketones. Athletes can use the MCT and
Habisha Vigneswaran
What are the benefits of MCT oil?
Some benefits of MCT oil are that it promotes weight loss, boosts your energy, provides athletic endurance, promotes gut health and helps with heart health. Dr Pedre states that “intheliver, MCTsareconvertedtointo ketoneslike
improve their muscle function and mitochondrial metabolism. The oil also supports digestion and nutrient absorption. Additionally, the MCT oil balance can help the bacteria living in your gut as it helps the digestive system and the expenditure. It can kill many pathogenic viruses and bacteria including Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Neisseria and many more.
Coconut oil naturally consists of mediumchain triglycerides. It is known that coconut oil can be used as a treatment for Alzheimer's
disease. When a patient is diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease, neurones stop functioning and they lose connections with other neurones. Alzheimer's disease patients are unable to use glucose to gain energy in a normal manner which leads to the nerve cells with no energy, subsequently damaging the processes vital to neurones and their networks. This damages parts of the brain involving the entorhinal cortex and hippocampus which controls the memory segment. It also negatively affects the cerebral cortex which is responsible for higher-level processes of the human brain including language, memory, reasoning, thought and learning and so more. However, coconut oil is an alternative energy source which can be used for the brain due to the MCT present in the oil. Since MCT is a nutritional source of ketones, these ketones could be an alternative source of cerebral fuel.
Even though there are many benefits of MCT oil such as its possible positive impacts on Alzheimer’s disease, there is not enough scientific evidence to guarantee this theory. For example, Alzheimer’s.org.uksaysthat therewasaclinicaltrialintothepotential effectsofcoconutoilbeingconductedinthe USAhowever this trial had to come to a sudden end in 2017 as there were not enough people enrolled. Due to the lack of people, it was hard for researchers and scientists to understand and determine the benefits of MCT in coconut.
What are the negative effects of MCT?
The possible negative dose effects of MCT oil are that large amounts of the oil can cause minor abdominal pain, vomiting and nausea. It is also known that if you take MCT oil for a very long time it can build up unhealthy fats in your liver. Pregnant women are advised against taking MCT and also patients who have liver disease as they are at a particularly higher risk of developing unhealthy fats. A health online market website called planet paleo has stated that “oneofthecommonest sideeffectsoftakingtoomuchMCToilis loosebowels.Inotherwords , youmight experiencediarrhoea,alongwithstomach aches,crampingandflatulence’.
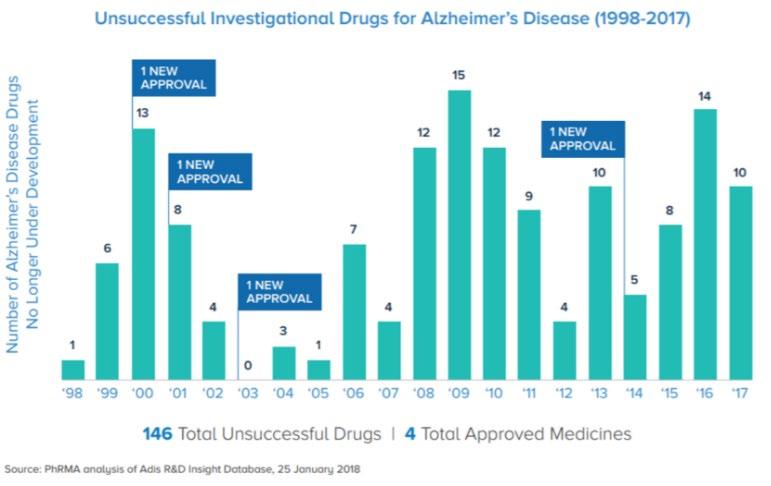
The image above shows the success rates of many drugs which have been used for Alzheimer’s disease. As you can see, there have only been 4 approved medicines and 146 unsuccessful drugs. Due to the lack of medicines for Alzheimer’s, I truly believe that MCT oil should be tested in the future and be promoted for future generations as there is a high chance for it to help prevent and potentially cure the disease.
Citations available on request
Why is MCT oil not prescribed as treatment currently?
Veterinary Schools in the UK
There are currently 11 vet schools in the UK, these are:
• Royal Veterinary College, London (RVC)
• University of Cambridge
• University of Liverpool
• The Royal (Dick) School of Veterinary Studies, University of Edinburgh
• University of Glasgow
• University of Bristol
• University of Nottingham
• University of Surrey
• Harper and Keele Veterinary School
• The Aberystwyth School of Veterinary Science (in collaboration with the RVC)
• University of Central Lancashire

To apply for Veterinary Science at any of these universities, work experience is recommended and for many it is a requirement. For example, the Royal Veterinary College require applicants to have a minimum of 70 hours in one or more veterinary practices and 70 hours in one or more non-clinical environments with live animals. A few examples of non-clinical work experience placements include farms, stables, animal shelters, lambing, kennels and catteries.
Work experience is a vital part of your vet school application, and it is definitely worth taking the time to check the websites of where you may interested in applying to ensure

A Guide to Applying for Dentistry
How can I make my application stand out? (Medify)

• Get a high UCAT score
• Perfect your personal statement
• Adopt a reflective and confident tone during your dental school interview
• Know what the admissions tutors are looking for by looking at your desired University websites
• Achieve the minimum entry requirements but aim to achieve even better!
The Different Types of Medical Courses

• Traditional Course - Taught in a classroom for the first few pre-clinical years. (Around 3 years). You have no patient contact for the preclinical years and develop your scientific understanding of Medicine first. Great if you want to build a strong medical foundation first but not so great if you are someone who prefers a handson, patients contact approach.
• Integrated courses - Combines classroom and clinical environments from the start. The teaching is either problem based, case based, or enquiry based.

• Intercalated courses - Intercalated courses allow you to take a year out to gain a BSc or BMSc in a related subject. Your course will be one year longer, but by the end of everything, you will end up with two degrees, one in medicine or dentistry, and another e.g BSc/ BMSc. Depending on the course, this could be optional or compulsory - but it is not offered by every Medical School.
Source: The Medic Portal
St Albans High School for Girls
Townsend Avenue, St Albans, Hertfordshire, AL1 3SJ
info@stahs.org.uk
stahs.org.uk





 Izzy Skaliotis
Izzy Skaliotis
 Nethaya Bulathsinhala
Nethaya Bulathsinhala
 Tasnuba Lamia
Tasnuba Lamia
 Figure 1: Lactam structure of penicillin. The red circle highlights the sp3 hybridisation of the carbon atom. (Wikepedia)
Figure 1: Lactam structure of penicillin. The red circle highlights the sp3 hybridisation of the carbon atom. (Wikepedia)


 Lily Patino
Lily Patino









