
























































































































































































































































In South Africa, your options when leaving school are limited, and more so for some than others.
Our universities can only accommodate about 10% of all graduating grade 12s, which means out of more than 700,000 full-time grade 12s writing exams this year, only approximately 70,000 will be able to go to university. Apart from the limited places available in our universities, there are also other challenges: the affordability factor, matric exemption, living conditions, no desire to study further, not prepared academically, and family commitment.
School leavers also have the option to go to TVET Colleges or various private educational institutions, yet they may face exactly the same challenges as going to university i.e. affordability, family commitments, etc.
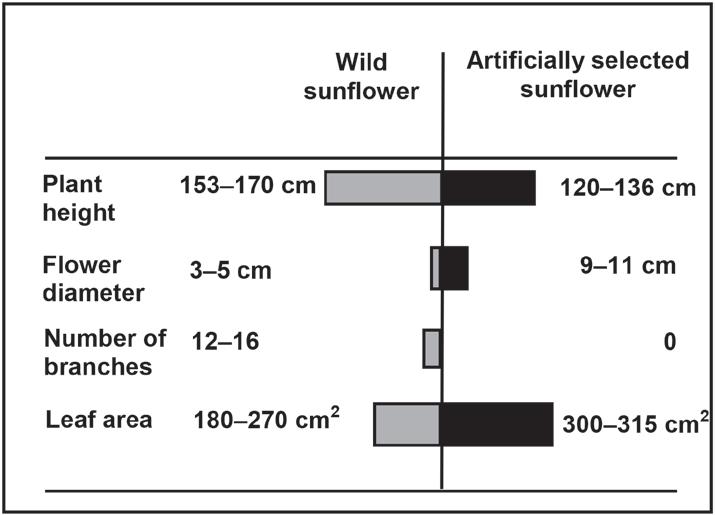
The next challenge the student faces if they are lucky enough to attend university is that between 50 to 60% of first year students will drop out (Source: https://bit.ly/3Sg5rcS), scary indeed. The
Minister of Higher Education points out that of 100 students who complete grades 1 to 12, only six will manage to complete their
We face another challenge: that of finding a job after leaving university or without going to university at all and instead looking for a job after leaving school. There aren’t many of them. With over 8-million unemployed people, South Africa has one of the highest unemployment rates in the world. In addition, we have a staggering youth unemployment rate of 71.9%, and President Cyril Ramaphosa states, “No society can thrive or grow when the vast majority of its young people are
What are your alternatives? School leavers who cannot find a job or study should explore entrepreneurship, where they can create their own jobs by creating their own businesses if they cannot find a job or study.
Being an entrepreneur and starting your own business is

What has the first six months at college been like for you? They have been challenging. I had to adapt to being a student, mother, partner, daughter and worker at the same time. It was not an easy transition, however, I managed to work out a schedule for myself that allowed me to set time apart for my studies while fulfilling my other responsibilities as well.

I like the fact that classes are online, and that I can log in from any location and continue my studies instead of having to physically rush to classes. This still gives me a chance to work. It is very flexible
Where do you see yourself in three In three years I’ll be done with my studies. I am hopeful that I will then be in Training and Development within a company for a permanent and









What is the best advice you have been given this year? This has been a challenging year, even more so, an emotionally challenging one. After my mom passed away, I was given very
What advice would you give to a student writing Matric? It is important to stay focused on the end goal. However, when





surprisingly affordable, and it does not take years of studying to achieve success or at least an income. In many cases, one can start a business in three months with effective entrepreneurial training, and work online from anywhere in the world. Working internationally can also bring foreign currency into the country.
A second advantage of becoming an entrepreneur is that if you are planning on taking a gap year, you can still study for an hour a day to start your own business, earn money, and still take that gap year, which is highly recommended anyway regardless of whether you intend to continue your studies.

In studying entrepreneurship, one gets a glimpse into 50+ areas of business, such as marketing, design, social media, etc., and this gives the student access to other possible careers.
Choose your path carefully when leaving school.
things become overwhelming, it is okay to take a break, in fact a break is important. Work smart, not hard, it will benefit your mental health.
What makes you happy and focused as a student?
I have a very relaxed and comfortable study environment. When doing my assignments and studying I play my favourite music. It allows me to focus on the task at hand as it clears and calms my mind. Being able to tell everyone who supported me in the past that their efforts did not go to waste is what keeps me motivated and happy as a student. I take learning and improving as my way to show them that I appreciate what they’ve done for me.
What makes you laugh a lot?

I’m sure every mother would say “my child”. My son is my true joy, he is a funny little character. He always finds ways to crack me up. He always has something funny to say. If not that, then he has a funny dance move to show me. Sometimes he is not even aware that he is making me laugh, but trust me when I tell you, he’s always up to something funny.
What do you worry about?
I worry about running out of time to fulfil all my duties. I sometimes feel like there aren’t enough hours in a day to complete what I need to do. Juggling my studies, family responsibilities and work does become challenging. Though I try to strictly stick to my schedule there are times when I do fall behind, but I manage to catch up. What worries me most is what if it all gets too much and I am not able to catch up in time.
Who is your best role model?
My mom was my role model. She always pushed me out of my comfort zone. She always believed in me. She also matriculated and immediately after, she started working. Later in her life she then went to study and got her NQ7 at Wits University for a new manager’s programme. She would tell me that it was never too late to start. Those were her encouraging words.
The official papers in this supplement have been published with the endorsement of the Department of Basic Education. For more Matric Questions and Memoranda go to https://www.education.gov.za/














1.1.6 Which ONE of the following will lead to a decrease in water quality?








A. Eutrophication
B. Use of aquifers
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A to D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1
Which of the following are hormones that directly stimulate the development of the endometrium?
A. FSH and LH.
B. Progesterone and oestrogen.
C. FSH and progesterone.
D. LH and oestrogen.
1.1.2
A function of the iris of the eye is to …
A. refract light to form a clear image.

B. control the amount of light that enters the eye.
C. convert the light stimuli into impulses.
D. prevent reflection of light within the eye.
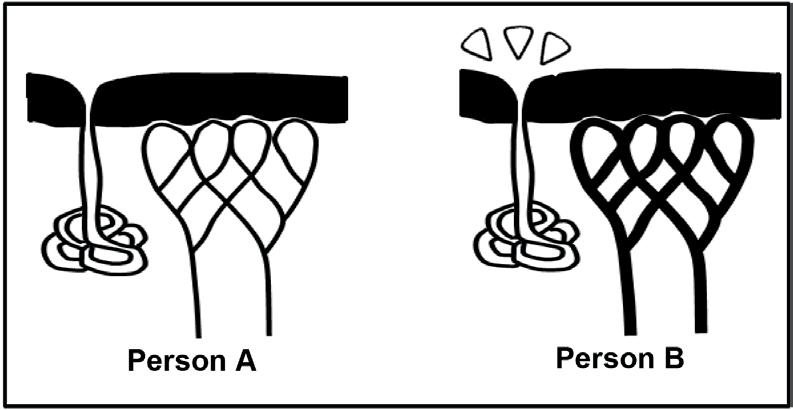
1.1.3 Diagram A and diagram B below represent the same part of the same human eye under different conditions.
1.1.7
C. Maintaining wetlands
D. Drought
A chemical used in laboratories prevents spindle fibres from forming in cells undergoing meiosis. As a result meiosis cannot start on the completion of interphase.
In an investigation, this chemical was added to cells in the anthers of the flowers of rice plants. Each cell in the anther has 24 chromosomes.
What is the expected number of chromosomes in each cell at the end of the investigation?
A. 12 replicated chromosomes
B. 24 replicated chromosomes
C. 24 unreplicated chromosomes
D. 48 unreplicated chromosomes
1.1.8
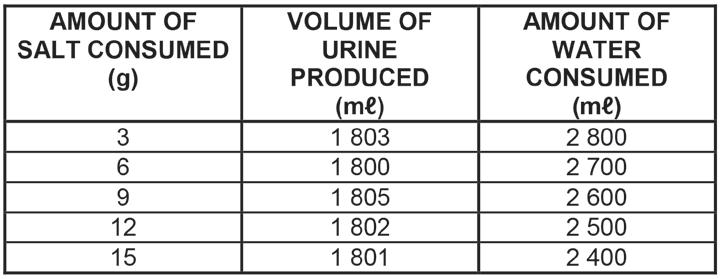
A scientist designed an investigation to test the following:
Eating more salt will decrease urine production and increase water consumption.
The table below shows the results of the investigation.
same human eye under different conditions.
Which diagram, with a corresponding reason, represents a person looking at an object 10 metres away?

A. Diagram A because the suspensory ligaments are taut/tight and the lens is less convex.
B. Diagram A because the lens is more convex and the suspensory ligaments are slack.
C. Diagram B because the lens is more convex and the suspensory ligaments are slack.
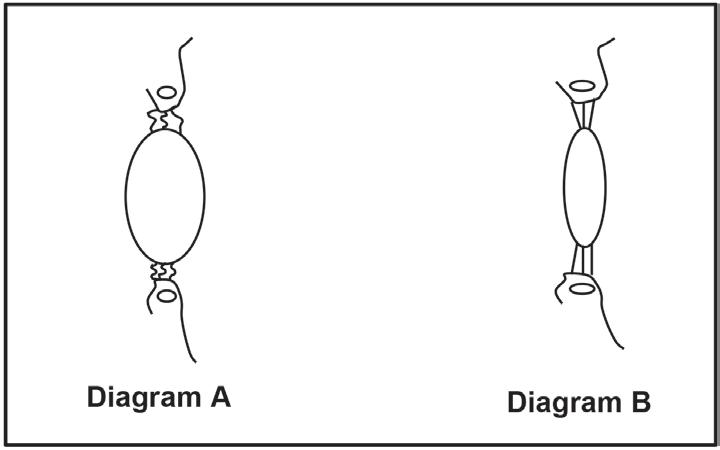
D. Diagram B because the suspensory ligaments are taut/tight and the lens is less convex.
1.1.4 Which of the following are plant growth hormones?
A. Prolactin and abscisic acid.
B. Abscisic acid and glucagon.
C. Gibberellins and abscisic acid.
D. ADH and gibberellins.
1.1.9

A possible conclusion from the results above is that eating more salt …
A. decreases urine production and increases the amount of water consumed.

B. increases urine production and decreases the amount of water consumed.


C. has little effect on urine production and decreases the amount of water consumed.
D. has little effect on urine production and increases the amount of water consumed.


An advantage of internal fertilisation is that …


A. sperm and ova are protected within the female's body.
B. there is better parental care.
C. more gametes will be produced.
D. the foetus receives food directly from the mother.
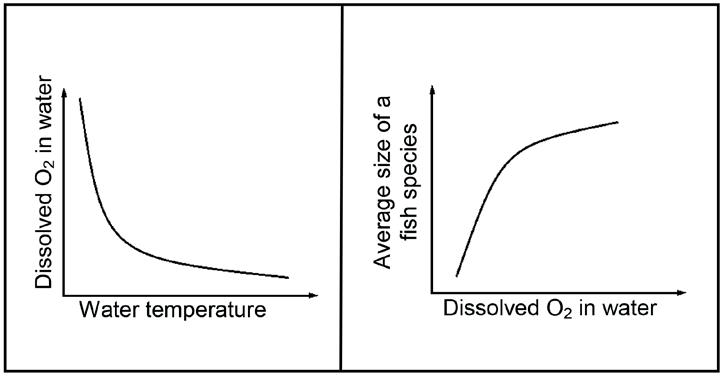
1.1.10 The graphs below represent the results of an investigation to determine if there is a possible relationship between temperature and the dissolved oxygen content of water and fish size.
1.4 The diagram below represents a sequence of events that may take
the human
Which ONE of the following is a possible interpretation based on information from both graphs?
A. There will be no relationship between water temperature and fish size.
B. As the temperature of the water increases, the amount of dissolved oxygen will increase.
C. The average size of the fish will decrease as the temperature of the water increases.
D. The amount of dissolved oxygen in the water will not influence fish size.
(10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Give the correct biological term for EACH of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.10) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.2.1 The type of egg produced by reptiles that has extra-embryonic membranes
1.2.2 The type of development in birds where the hatchlings' eyes are open and their bodies are covered with down feathers
1.2.3 The part of the brain that receives impulses from the maculae
1.2.4 The dark pigmented layer of the eye
1.2.5 The structure that connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain
1.2.6 The part of the brain that controls body temperature
1.2.7 The gas in the blood which, when increased, causes an increase in the breathing rate

1.2.8 Plant growth responses to external stimuli
1.2.9 A substance containing plant hormones used to kill unwanted plants
1.2.10 The illegal hunting and killing of animals (10)
1.3 Indicate whether each of the descriptions in COLUMN I apply to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A AND B or NONE
1.4.1 Identify the process taking place at I in the diagram above. (1)
1.4.2 State the type of cell division that takes place at II in the diagram above. (1)
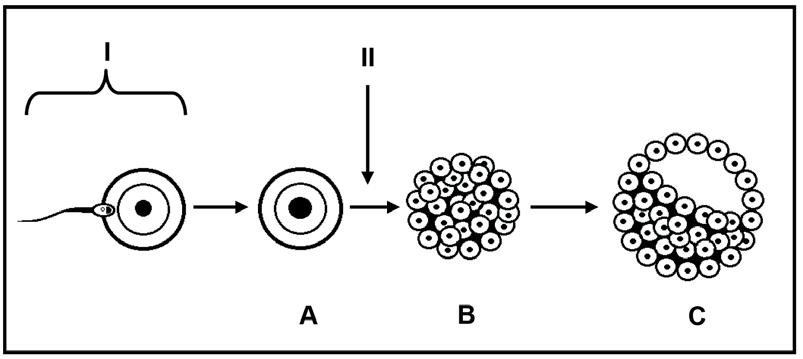
1.4.3 Name TWO functional extra-embryonic

that
produced by structure C (2)

1.4.4 Identify the stage of development indicated by: a. A (1) b. B (1) c. C (1)






1.4.5 Name the part of the female reproductive system where the events in the diagram above usually take place. (1)
1.4.6 Give the chromosome number of the cell at A if this cell is going to develop into a child with Down syndrome. (1) (9)
1.5 The diagram below shows the hormones involved in the homeostatic control of metabolism in the human body. X is a gland found around the larynx in the neck.
1.5.1 Identify EACH of the following:





The gland that secretes hormone A (1) b. Hormone B (1)
1.5.2 Name the mechanism in the diagram that regulates the level of hormone B (1)
1.5.3 Half of gland X was surgically removed in a person.
TWO possible effects that this would have on the secretion of the hormones referred to in the diagram above. (2)

QUESTION 2
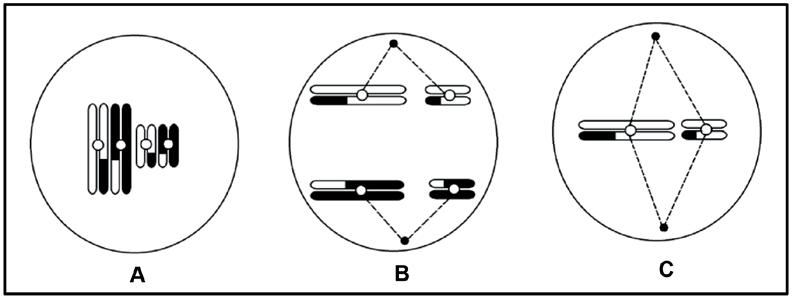
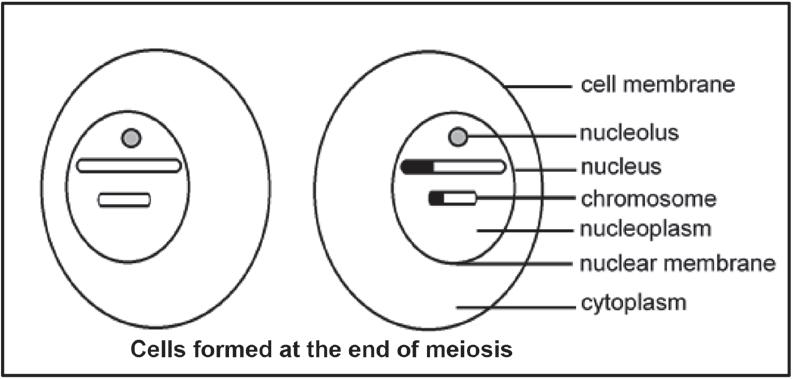
2.1 The diagrams below represent various phases of meiosis.
2.1.1 Identify the phase of meiosis in diagram:
a. A (1)
b. B (1)



2.1.2 Draw a labelled diagram to show the cells that will be formed at the end of meiosis from the cell in diagram C. (5) (7)
2.2 Read the extract below about a medical condition in male babies called cryptorchidism.

Cryptorchidism occurs in new-borns when one or both of the testes do not descend into the scrotal sac at birth, but remains inside the abdominal cavity.
Cryptorchidism occurs in approximately 3–5% of full-term male infants while approximately one-third of premature male babies are born with this condition.
If the testes do not descend naturally by the age of one, treatment is needed. Treatment may involve administering testosterone, but the most common treatment is surgery.
If cryptorchidism is not resolved, it may lead to infertility when both the testes do not descend and an increased risk of testicular cancer by the age of 30 to 40 years.
2.2.1 State ONE function of testosterone not mentioned in the extract above. (1)
2.2.2 According to the extract, state TWO ways in which cryptorchidism is treated. (2)
2.2.3 What percentage of premature male babies are born with cryptorchidism? (1)



2.2.4 From the extract, give ONE reason, other than infertility, why cryptorchidism needs to be treated if the condition is not resolved naturally. (1)

2.2.5 Explain why undescended testes may lead to infertility in young males. (2) (7)
2.3 Some women take longer to fall pregnant compared to others. A woman with a normal, fertile male partner, who takes longer than 12 months to fall pregnant, is said to be subfertile.
An investigation was conducted to determine the effect of BMI (body mass index) and smoking on subfertility.


A total of 2 587 women between the ages of 20 and 30 participated in the investigation. All of the women were at least 20 weeks pregnant, had planned to fall pregnant and conceived naturally.
The following information was obtained from each woman:

• Height and mass
• Time taken to fall pregnant (in months)
• Smoking habits
Of the total number of women who participated, 1 510 were subfertile.
2.3.1 Give ONE reason why the women were asked for their height and mass. (1)
2.3.2 Determine how many of the participants were subfertile smokers with a BMI ≥30. Show ALL calculations. (3)
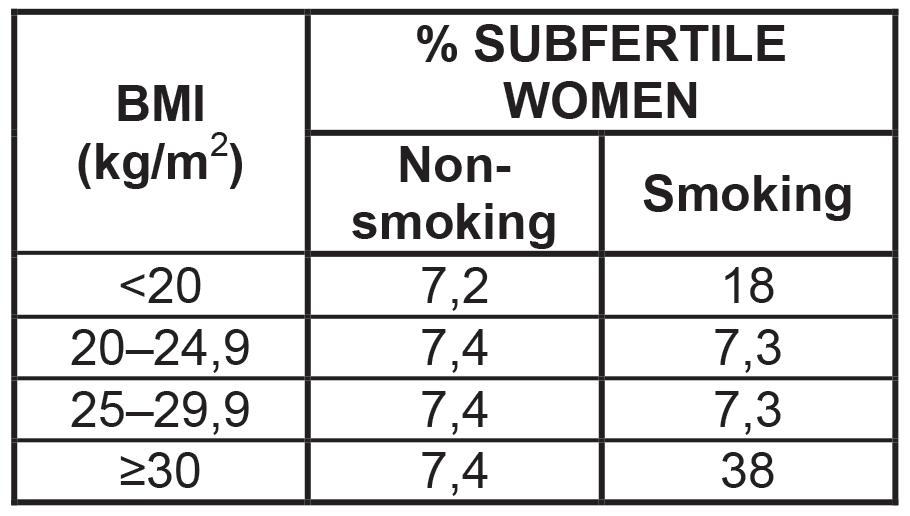
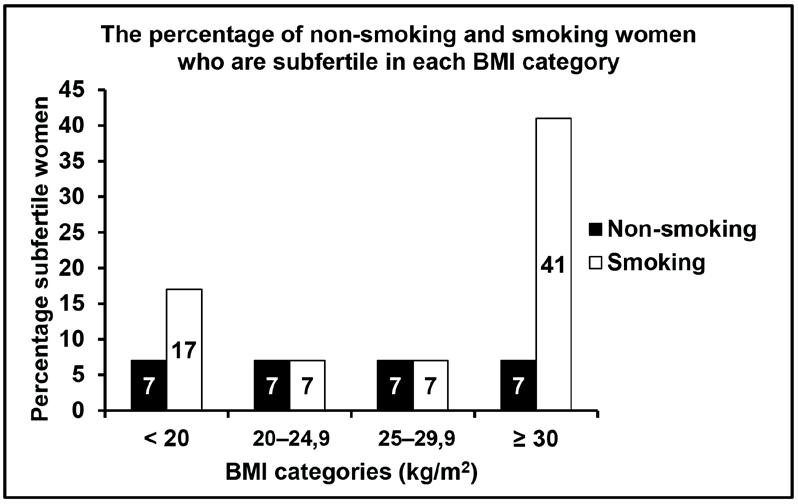
2.3.3 Suggest why only women with planned pregnancies were included in the investigation. (2)
2.3.4 State ONE factor that was kept constant in this investigation. (1)
2.3.5 Based on the information in the above graph, what advice should be given to women who want to increase their chances of falling pregnant? (2)
2.3.6 The investigation was carried out in another country and the results below were obtained.
Explain why the results of the original investigation can be considered to be reliable.
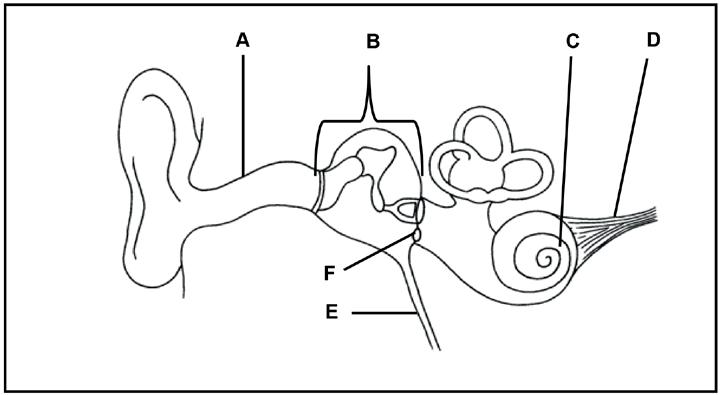
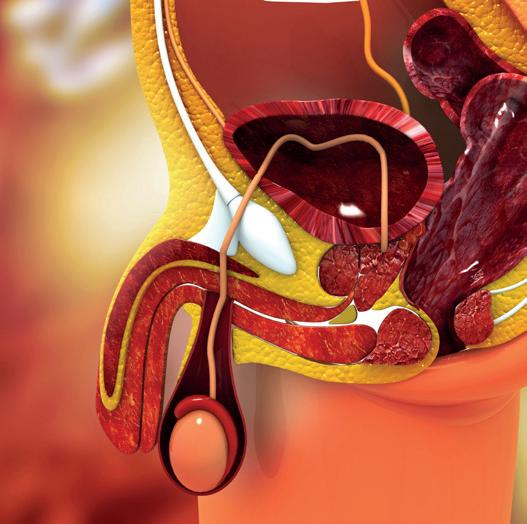
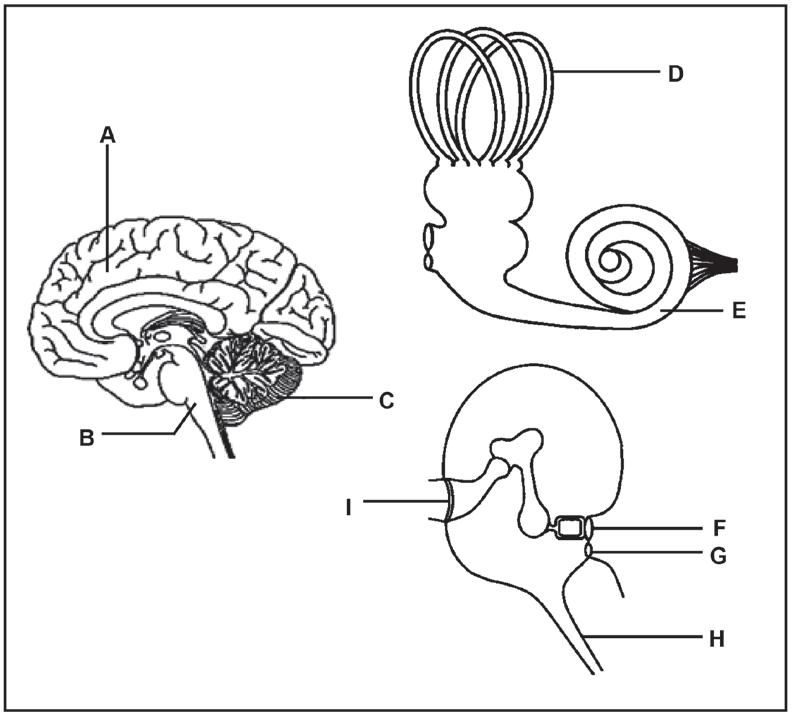
2.4 Study the diagram below.
2.4.1 Give ONE function of part:







2.4.2 Write down only the LETTER of the part where sound is transmitted in the form of:


A pressure wave in a liquid (1)
An electrical impulse (1)
2.4.3 Explain the effect if the receptors in region C are damaged. (3)

2.4.4 Describe how the parts of the middle ear, including the membranes, assist with amplifying sounds. (3)
2.4.5 Describe the role of the semi-circular canals in maintaining balance.



QUESTION
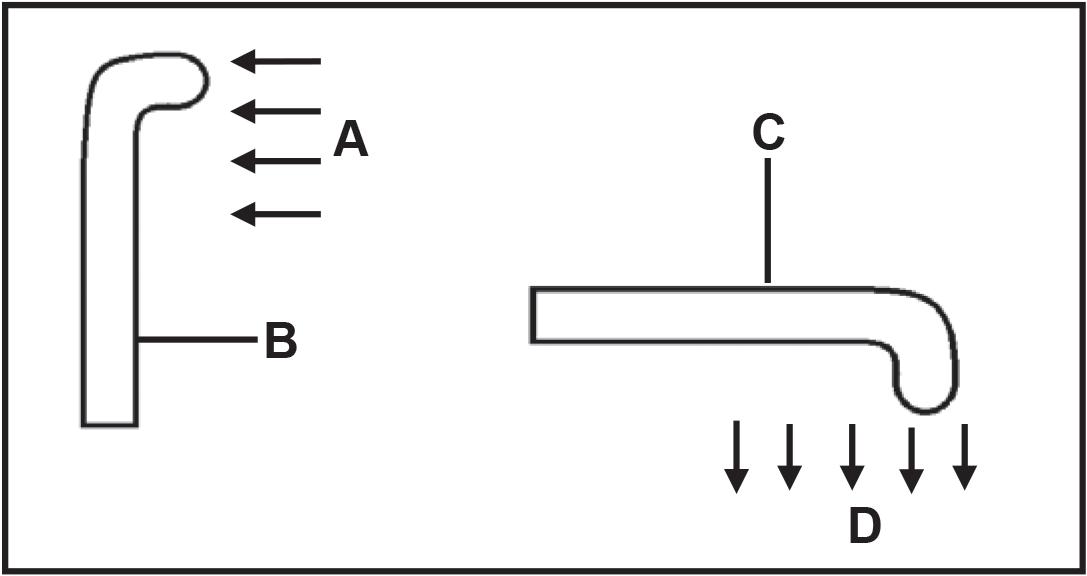
3.1 The diagrams below represent the growth responses of two different plant organs to external stimuli.
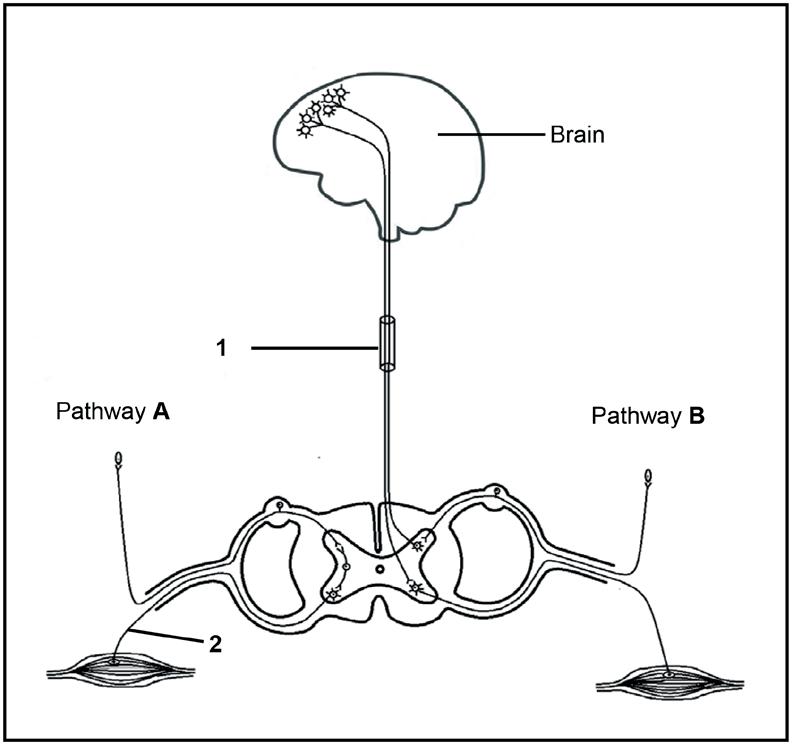
3.2.1 Which pathway, A or B, represents a reflex arc? (1)
3.2.2 Give a visible reason in the diagram for your answer to QUESTION 3.2.1. (1)
3.2.3 Describe the importance of a reflex action in the human body.(3)
3.2.4 Identify the part of the nervous system represented by 1. (1)
3.2.5 Explain ONE way in which the myelin sheath is important in the functioning of neurons. (2)
3.2.6 Describe how the person would be affected if the axon of neuron 2 was cut. (2)
3.2.7 Describe pathway B (6) (16)
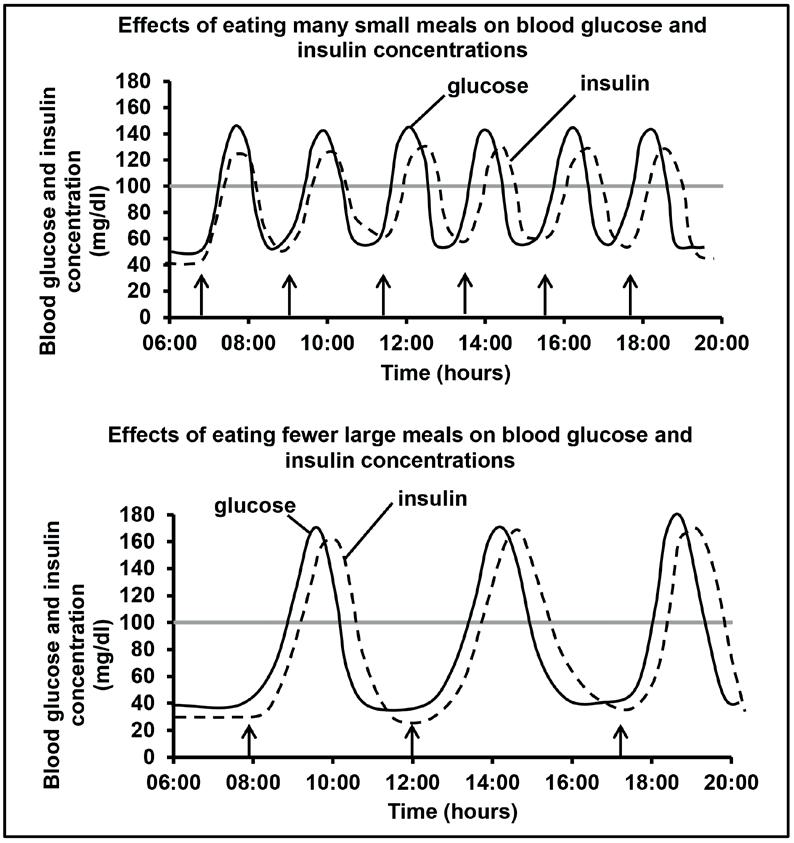
3.3 The graphs below show the effects of eating many small meals and eating fewer large meals on blood glucose and insulin concentrations in a normal person.
The arrows on the graphs below indicate when meals were eaten. The normal blood glucose concentration is 100 mg/dl.
3.1.1 Name the group of plant hormones that is responsible for the growth responses observed in the diagrams. (1)
3.1.2 Name the external stimulus at:





A (1)
D (1)

3.1.3 Give ONE observable reason why plant organ B is a stem. (1)
Explain the growth response observed in plant organ C. (3)
3.2 The diagram below represents two possible pathways, A and B, which a nerve impulse may follow in the human body.
3.3.1 State what happens to the blood glucose concentration immediately after a meal is eaten. (1)

3.3.2 Use the information in the graphs. Tabulate TWO ways in which eating fewer large meals and eating many small meals affect the blood insulin levels differently. (5)

3.3.3 Explain why eating many small meals per day is better for a diabetic person than eating fewer large meals a day. (4) (10)
































































2.1




















2.4.2
2.4.3
b.

ONE only)
c. Releases pressure from the inner ear√ (1) (Mark first ONE only)
(1)
D√ (1)
• The receptors cannot convert the stimuli into impulses√
• No impulses/fewer impulses are transmitted to the cerebrum√
and the person does not hear anything√/hearing
2.4.4
2.4.5
(3)
• The sound vibrations are transmitted from the large tympanic membrane√
• to the smaller oval window√
• through the ossicles√
• which are arranged from largest to smallest√

• This concentrates the vibrations√, amplifying them Any (3)
• A change in speed/direction of movement√
• stimulates the cristae√
• The stimulus is converted to an impulse√
• The impulse is transmitted to the cerebellum√
• via the auditory nerve√
• The cerebellum sends impulses to the muscles√ to restore balance Any (4)

3.1.4
• Auxins accumulated on the lower side√of the root
• The high concentration of auxins on the lower side of the root inhibits growth√
• The lower concentration of auxins on the upper side stimulates growth√
• causing uneven growth√/the root to bend downwards/positive geotropism
(3)
3.2 3.2.1 A√ (1)
3.2.2 The impulse does not travel to the brain√/goes directly from receptor to effector via the spinal cord (1)
3.2.3
• Allows the person to respond rapidly√
• and without thinking√/involuntarily
• to a stimulus√
• to prevent damage to the body√*
1* compulsory + any other 2 (3)
3.2.4 Nerve√/spinal cord (1)
3.2.5 • It acts as an insulator√
• and therefore, speeds up the nerve impulse√/prevents a short circuit (2)
3.2.6


3.2.7
• The person would be able to feel the stimulus√
• but would be unable to react√
• because the impulse would not be transmitted to the effector√
Any (2)
• The receptor receives the stimulus√
• and converts it into an impulse√
• which is transported by a sensory neuron√via the spinal cord
• to the brain√*/cerebrum

• The brain/cerebrum interprets the impulse√*
• The brain/cerebrum sends an impulse to a motor neuron√
• which conducts the impulse to the effector√
• to bring about a response√
2* compulsory + any other 4 (6) (16)
3.3 3.3.1 The level increases√ (1) 3.3.2 T√
Fewer larger meals More smaller meals
1. Maximum blood insulin concentration is higher√/ between 160-180 mg/dl
2. Minimum blood insulin concentration is lower√/ between 20-30 mg/dl
3. Blood insulin concentration rises and falls three times a day√/ less often

4. Large changes in insulin concentration√/between 140-160 mg/dl
QUESTION 3

3.1 3.1.1 Auxins√

3.3.3
5. Insulin concentration drops below minimum glucose concentration√
1. Maximum blood insulin concentration is lower√/ between 120-140 mg/dl
2. Minimum blood insulin concentration is higher√/40 mg/dl
Blood insulin concentration rises and falls six times a day√/more often


4. Small changes in insulin concentration√/between 80-100 mg/dl

Insulin concentration varies above and below minimum glucose concentration√


(Mark first TWO only) 1 for table + Any 2 x 2 (5)
• A diabetic may not produce sufficient insulin√
• When eating many smaller meals, less glucose√enters the blood
• less insulin√is needed
• to return blood glucose to normal√
in less
of organic waste in landfills√/rice paddies


• and the increased number of livestock√
• the concentration of methane/CH4 in the atmosphere has increased√
• This has caused the enhanced greenhouse effect√
• More heat is trapped in the atmosphere√
Impact of global warming on weather patterns (W)
• Higher temperatures√occur
• Heat waves occur√
• The distribution of rainfall changes√
• leading to increased rainfall in some areas√
• while other areas will have
(8)
• Storms are more severe√/frequent Any (3)
How changes in weather patterns affect food security (F)
• Food security decreases√*
Changes in rainfall patterns cause:
• Desertification√
• increased flooding√
• and wildfires√
• which increases soil erosion√resulting in:

» fewer crops to be planted√
» lower crop yields√
» less food for livestock√
• Higher environmental temperatures negatively affect livestock√/crops









• These factors further decrease food availability√
• Food becomes more expensive√
1*compulsory + Any other 5 (6) Content: (17) Synthesis: (3) (20)

Relevance Logical sequence Comprehensive



All information provided is relevant to the question
All the information provided is relevant to:


• The causes of rapid global warming
• The impact of global warming on weather patterns
• How changing weather patterns affect food security
There is no irrelevant information)
Ideas arranged in a logical/ cause-effect sequence
All the information regarding:
• The causes of rapid global warming
• The impact of global warming on weather patterns
• How changing weather patterns affect food security
arranged in a logical manner.
Answered all aspects required by the essay in sufficient detail

At least the following points should be included:
• The causes of rapid global warming (H) (5/8)
• The impact of global warming on weather patterns (W) (2/3)
• How changing weather patterns affect food security (F) (4/6)










1.1.3
Cornea.
Iris.
Choroid.
Lens.
to an
a result of
of the

structure in the




Yolk
Chorion.
Amnion.
Allantois.
1.1.4

1.1.5 Which structures secrete progesterone during pregnancy?

A. Adrenal gland and corpus luteum.
B. Corpus luteum and placenta.
C. Thyroid gland and Graafian follicle.
D. Pituitary gland and Graafian follicle.
1.1.6 Which ONE of the following shows the correct sequence of an impulse from the receptor in a simple reflex arc?

A. Sensory neuron through the dorsal root → motor neuron through the ventral root → effector
B. Motor neuron through the dorsal root → sensory neuron through the ventral root → effector
C. Sensory neuron through the dorsal root → effector → motor neuron through the ventral root
D. Effector → interneuron through the dorsal root → motor neuron through the ventral root.
1.1.7 Which ONE of the following would be a disadvantage when a biological method is used to control alien plant invasion?
A. Able to control alien plants without the use of harmful chemicals.
B. Some part of the alien plant may be left to regrow when mechanically removed.
C. The species introduced might be alien in the area and outcompete the indigenous species.
D. Chemicals might affect the indigenous plants in the area.
1.1.8 Which ONE of the following is a consequence of the destruction of wetlands?

A. Increased biodiversity.
B. Decreased water availability.
C. Decreased global warming.
D. Increased water quality.

1.1.9 Nocturnal animals have the ability to see clearly in the dark. They have …
A. bigger eyes.
B. more rods in the retina.


C. more cones in the retina.
D. no blind spot.
1.1.10 Which ONE of the following is CORRECT regarding the homeostatic control of glucose in the human body?

of the following
with regard to astigmatism?

A. Light cannot pass through the cornea.
B. Light cannot pass through the lens.
C. Refraction of light rays by the cornea is uneven.
D. The lens cannot become more rounded.
1.2.3 A condition of the cell where there is only one set of chromosomes
1.2.4 The response of a part of a plant to a light stimulus
1.2.5 A hormone that stimulates ovulation in humans
1.2.6 The part of the brain that connects the left and right hemispheres
1.2.7 The blood vessel that transports deoxygenated blood from the foetus towards the placenta
1.2.8 A small device that is inserted in the ear to drain fluids caused by a middle-ear infection
1.2.9 The branch of the autonomic nervous system that restores an increased heart rate back to normal
1.2.10 A structure in the eye that absorbs light to prevent internal reflection (10 x 1) (10)


1.3 Indicate whether each of the descriptions in COLUMN I apply to A ONLY B ONLY BOTH A AND B or NONE of the items in COLUMN II. Write A only, B only, both A and B or none next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.3) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 The functional connection between two consecutive neurons
1.3.2 The young develops and is nourished in an amniotic egg that is retained in the mother’s body
1.3.3 A reproductive strategy in vertebrates where internal fertilisation occurs
A: Receptor B: Synapse
A: Ovipary B: Vivipary
A: Altricial development B: Precocial development (3 x 2) (6)
1.4 The diagrams below show structures formed during human reproduction.
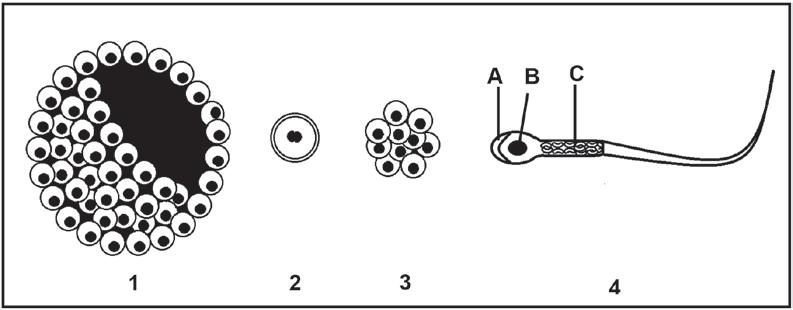
1.4.1 Identify part A (1)
1.4.2 Name the organelle found in large numbers in part C. (1)

1.4.3
NUMBER (
The diagrams below show different neurons.

Give only the NUMBERS (1 2 3 or 4) of TWO neurons that:
Transport impulses from the receptor to the central nervous system

Will have a faster transmission of impulses (2)
Are damaged if a person can feel the stimulus but is unable to react
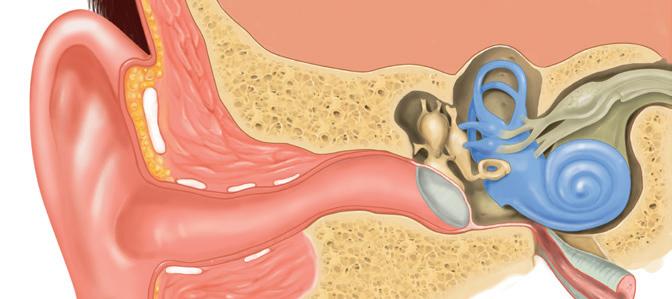
The diagrams below show different parts of the brain and the ear.
2.1.1 Identify part:











the LETTER
the type of

Give the LETTER and NAME of the part of the ear that absorbs excess pressure waves from the inner ear. (2)


Name the receptors found at part E (1)
Explain why damage to part B can lead to instant death. (2)
Describe how part C responds to impulses received from part D (3)
2.1.6 In older people, part F of the ear may harden. Explain how this condition may lead to hearing loss. (4)
The diagrams below show the results obtained.


Thyrotoxicosis is a medical condition caused by high levels of thyroxin in the blood. There was a sudden increase in the number of reported cases of this condition in one city. They suspected that this was due to people eating ground beef (minced meat) from a local butcher. The butcher added the thyroid glands of cattle when he produced the ground beef. Some people who ate this ground beef showed symptoms of increased heart rate, excessive sweating and weight loss.
Doctors conducted an investigation to determine if the ground beef caused the thyrotoxicosis. The normal thyroxin levels of 5 volunteers were measured. They were then given cooked ground beef from the butchery to eat. Their thyroxin concentration was measured every 4 hours on day 1 and then once a day for the next 23 days. The average thyroxin levels was calculated and recorded.
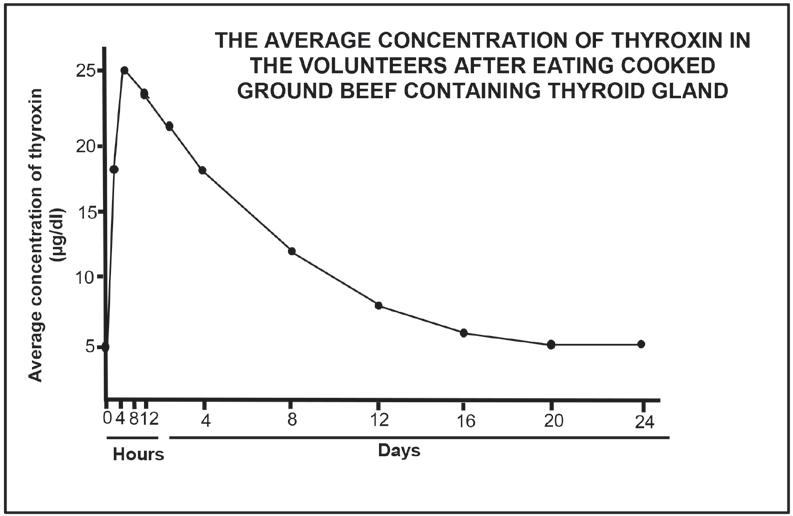
The results are shown in the graph below.
2.3.1 Give the average normal thyroxin concentration (μg/dl) in the blood of the volunteers. (1)
2.3.2 Calculate the percentage increase of the average thyroxin concentration in the first 8 hours after eating the ground beef. Show ALL working. (3)
2.3.3 Explain why thyrotoxicosis causes weight loss. (3)

2.3.4 Explain the expected concentration of TSH in the blood 8 hours after eating the ground beef. (4) (11)
2.4 An investigation was done to determine the effect of a plant hormone on plant growth:
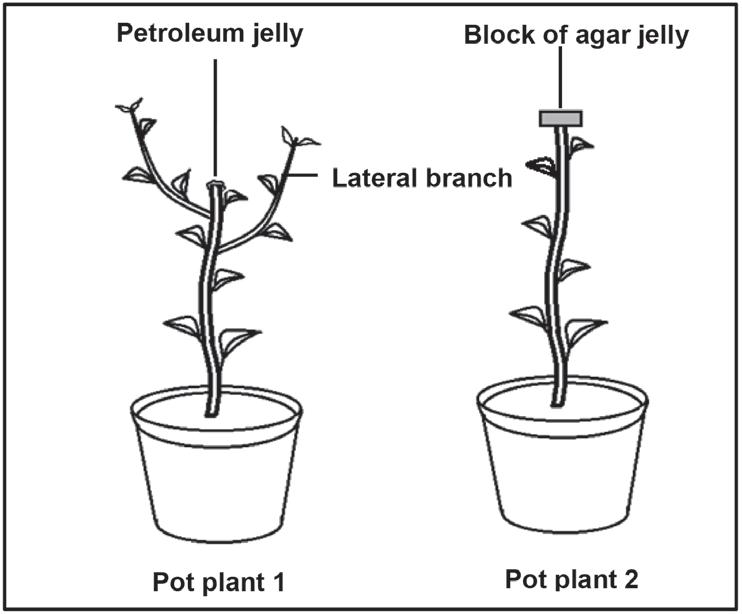
The procedure was as follows:
• Two pot plants (1 and 2) of the same species and age were used.
• The apical buds of both plants were cut at the same length along the stem.
• The cut surface of plant 1 was sealed with petroleum jelly





• The cut apical bud of pot plant 2 was placed on a block of agar jelly for 2 hours.
• The block of agar jelly was then placed on the cut surface of plant 2
• The plants were exposed to the same environmental conditions for 2 weeks.
• The growth of both plants was observed at the end of this period.
2.4.1 State why the apical bud was placed on a block of agar jelly for 2 hours. (2)
2.4.2 Describe the results obtained for plant 1 (2)

2.4.3 Explain how fruit farmers can use the knowledge from the results in QUESTION 2.4.2 to their benefit. (2)
2.4.4 Explain why the stem in pot plant 2 grew upwards. (3) (9) [40]
QUESTION 3

3.1 The diagrams below represent two phases of meiosis.
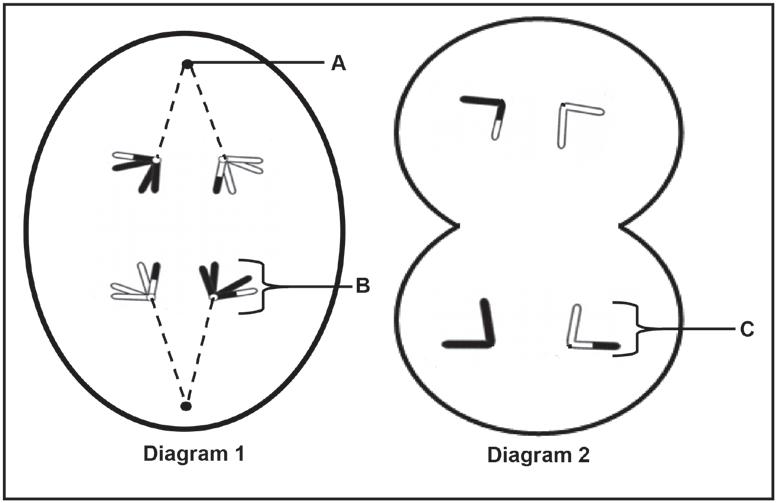
3.1.1 Identify part A (1)


3.1.2 Identify the phase represented by diagram 1. (1)

3.1.3 Describe the events that took place in the phase before the one represented in diagram 2 (2)
3.1.4 Name the process that causes the chromosomes to have a combination of genes as shown in the diagrams. (1)
3.1.5 Give ONE reason why the process named in QUESTION 3.1.4 is important. (1)

3.1.6 If this was a human cell, how many chromosomes would be present in the cell during the phase represented in diagram 1? (1)
3.1.7 Structure B and structure C are both chromosomes. Explain why they are structurally different. (3)
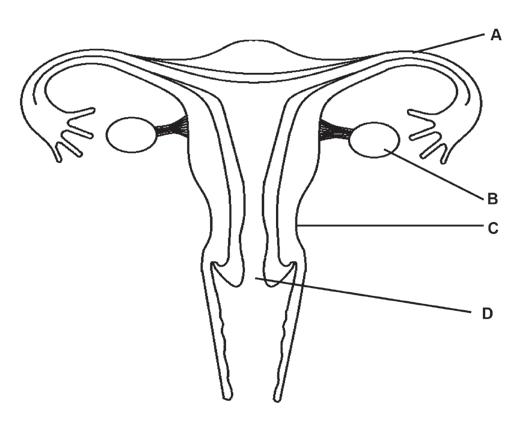
3.2 The structure below represents a part of the female reproductive system.

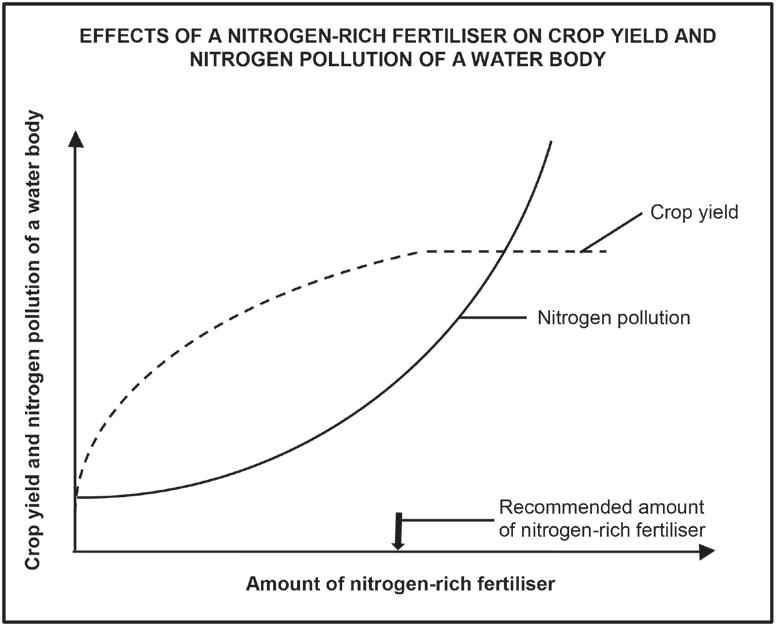
3.4 The graph below shows the influence of a nitrogen-rich fertiliser on crop yield and nitrogen pollution of a nearby water body.
3.2.1 Identify part D (1)
3.2.2 State ONE function of part A (1)

3.2.3 Describe the process of oogenesis as it occurs in part B. (4)
3.2.4 State ONE way in which structure C is suited for its function during pregnancy. (1)


3.2.5 A person undergoes a surgical operation to remove part B on both sides.
Explain why this person will not menstruate. (3) (10)
3.3 Male hormone contraceptive (birth control) pills have been in development for over 50 years. The pills contain a substance called TU, which inhibits the secretion of testosterone. There is, however, no product available on the market yet, mainly due to many side effects associated with the product.
An investigation was done to determine how TU affects male fertility.
The procedure was as follows:
• 308 healthy, male volunteers were selected.
• A sperm count for each volunteer was done initially.
• Each volunteer was given 500 mg of TU monthly over a period of 12 months.
• During the period of the investigation, the volunteers were asked to wear loose-fitting trousers and underwear made of the same light fabric.
• A sperm count was done weekly over a period of 24 months.
• The average sperm count was calculated per volunteer.
NOTE: Sperm count refers to the total number of healthy sperm per ml of semen and is an indication of male fertility.




3.3.1 Identify the dependent variable in the investigation. (1)

3.3.2 State how the dependent variable in QUESTION 3.3.1 was measured. (1)
3.3.3 Name TWO other factors that should be considered when selecting volunteers. (2)





3.3.4 Explain how TU reduces fertility. (2)
3.3.5 Explain why wearing tight-fitting trousers will decrease male fertility. (2)
3.3.6 Suggest ONE reason for doing the sperm count for an additional 12 months after stopping the TU treatment. (1)
3.3.7 The contraceptive options that are currently available for men are limited to condoms and vasectomy. Vasectomy involves the cutting and tying of both the vas deferens. Explain how a vasectomy prevents pregnancy. (2) (11)
3.4.1 Name the process whereby excess nutrients accumulate in a water body. (1)



3.4.2 Explain why it will not economically benefit the farmer to use more than the recommended amount of fertiliser. (3)
3.4.3 Suggest ONE reason why farmers are advised to apply fertilisers to the soil during the dry season of the year. (1)
3.4.4 Explain the effect that an increase in nitrogen pollution will have on the number of bacteria in the water. (4) (9) [40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
Describe how the human body maintains the temperature and carbon dioxide concentration in the blood when they rise above normal limits. Also, describe the importance of carbon dioxide in regulating atmospheric temperature, and why increasing levels of carbon dioxide leads to global warming.
Content: (17) Synthesis: (3) [20]

NOTE: NO marks will be awarded for answers in the form of flow charts, tables or diagrams.
TOTAL SECTION C: 20 GRAND TOTAL: 150



1. If more information than marks allocated is given
Stop marking when maximum marks is reached and put a wavy line and 'max' in the right-hand margin.



2. If, for example, three reasons are required and five are given Mark the first three irrespective of whether all or some are correct/ incorrect.
3. If whole process is given when only a part of it is required
Read all and credit the relevant part.
4. If comparisons are asked for, but descriptions are given
Accept if the differences/similarities are clear.
5. If tabulation is required, but paragraphs are given
Candidates will lose marks for not tabulating.
6. If diagrams are given with annotations when descriptions are required Candidates will lose marks.
7. If flow charts are given instead of descriptions
Candidates will lose marks.
8. If sequence is muddled and links do not make sense
Where sequence and links are correct, credit. Where sequence and links are incorrect, do not credit. If sequence and links become correct again, resume credit.



9. Non-recognised abbreviations
Accept if first defined in answer. If not defined, do not credit the unrecognised abbreviation, but credit the rest of the answer if correct.
10. Wrong numbering
If answer fits into the correct sequence of questions, but the wrong number is given, it is acceptable.
11. If language used changes the intended meaning

Do not accept.
12. Spelling errors

If recognisable, accept the answer, provided it does not mean something else in Life Sciences or if it is out of context.
13. If common names are given in terminology


Accept, provided it was accepted at the national memo discussion meeting.
14. If only the letter is asked for, but only the name is given (and vice versa)
Do not credit.
15. If units are not given in measurements

Candidates will lose marks. Marking guidelines will allocate marks for units separately.
16. Be sensitive to the sense of an answer, which may be stated in a different way.

17. Caption
All illustrations (diagrams, graphs, tables, etc.) must have a caption.
18. Code-switching of official languages (terms and concepts)

A single word or two that appear(s) in any official language other than the learner's assessment language used to the greatest extent in his/her answers should be credited, if it is correct. A marker that is proficient in the relevant official language should be consulted. This is applicable to all official languages.

19. Changes to the marking guidelines

No changes must be made to the marking guidelines. The provincial internal moderator must be consulted, who in turn will consult with the national internal moderator (and the Umalusi moderators where necessary).
20. Official marking guidelines
Only marking guidelines bearing the signatures of the national internal moderator and the Umalusi moderators and distributed by the National Department of Basic Education via the provinces must be used.
1.3.2
(1)
1√ (1)
B
1.5.1
(2)
Mitosis√ (1)
• Shorter trees√
Auxins√in the block of agar
downwards√ into the stem
causing (cell) elongation√/growth resulting in upward growth of the stem (3) (9) [40]

3.1 3.1.1 Centriole√/centrosome (1)
3.1.2 Anaphase I√ (1)
3.1.3
• The spindle fibres contract√

• The centromeres split√
• Each chromatid is pulled to the opposite poles√ Any (2)
3.1.4 Crossing over√ (1)

3.1.5 It leads to (genetic) variation√ (1) (Mark first ONE only)



3.1.6 46√/23 pairs (1)

3.1.7
• Light rays are refracted
• so that a clear image
2.3.1
√μg/dl
– 5)
400√%
– 5)

} √ x 100
} √ x 100
380√%
a range between:


and 25 for the
380% and 400% for the
• Structure B consists of two DNA molecules√/contains a double thread/is made up of two chromatids
• because of DNA replication√
• Structure C consists of one DNA molecule√/ contains a single thread/chromatid


• because it is unreplicated√/as a result of the splitting of the chromosome during anaphase 2 Any (3) (10)
3.2 3.2.1 Cervix√ (1)




3.2.2
• The site of fertilisation√

• The site of zygote division√
• The transfer of the ovum/embryo to the uterus√ Any (1) (Mark first ONE only)
3.2.3
• Diploid cells in the ovary undergo mitosis√
• to form numerous follicles√
• Under the influence of FSH√
• one cell undergoes meiosis√
• to form a (haploid) ovum√ Any (4)
3.2.4
• It is a hollow organ√
• It has a muscular wall√
• It has a blood-rich lining√/endometrium Any (1) (Mark first ONE only)
3.2.5
• No follicle will develop√
• No oestrogen produced√
• and no progesterone produced√
• Therefore, the endometrium will not develop√* to be shed during menstruation Compulsory mark√*1 + Any 2 (3) (10)

3.3
3.3.4
3.3.5
•
•
•
•
•
•
3.3.7

•
3.4
3.4.2
•
Eutrophication√ (1)
• The crop yield reaches a maximum at the recommended amount√

• Using more fertilizer will cost more√ without increasing crop yield
• Therefore the profit will be less√ (3)
• The blood vessels in the skin dilate√/vasodilation takes place
• More blood flows to the surface of the skin√/sweat glands so that
• (More) heat is lost from the body√
• More sweat is produced√ and


• (More) heat is lost when sweat evaporates√
• The temperature of the body returns to normal√ Any (7)
When the carbon dioxide levels rise above normal (C):
• Receptor cells in the (carotid) artery in the neck/aorta are stimulated√
• to send impulses to the medulla oblongata√
• The medulla oblongata sends an impulse to the breathing muscles√
• to contract more actively√
• and increase the rate/depth of breathing√
• An impulse is also sent to the heart√
• to beat faster√
• More carbon dioxide is taken to the lungs√/exhaled
• The carbon dioxide levels return to normal√ Any (5)
Importance of carbon dioxide in regulating atmospheric temperature and its influence on global warming (A):
• Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas√

• It traps heat/ prevents it from escaping from the atmosphere√
• This is called the greenhouse effect√ which
• keeps the earth warm to make life on earth possible√
• An increase in carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere causes an enhanced greenhouse effect√
• More heat is trapped in the atmosphere√
• causing an increase in the average global temperature√ Any (5) Content (17) Synthesis (3) (20)
3.4.3
3.4.4
• Less fertiliser will be lost due to run-off√/leaching (Mark first ONE only) (1)
• Algal bloom√ occurs
• A layer of algae will form on the water, blocking out sunlight√
• The (water) plants die because they are unable to photosynthesise√
• Animals that feed on the plants will also die√
• Decomposition√ of the dead plants and animals
• cause an increase in the number of bacteria√* Compulsory mark√*1 + Any 3 (4) (9) [40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION
QUESTION
When temperature rises above normal (T):
• Receptors are stimulated√
• and send impulses to the hypothalamus√
• The hypothalamus sends impulses to the blood vessels in the skin√
• and to the sweat glands√

Relevance Logical sequence Comprehensive



All information provided is relevant to the question
All the information provided is relevant to:

• Homeostatic control of temperature when it rises above normal
• Homeostatic control of CO2
• Importance of CO2 in regulating atmosphere temperature and its influence on global warming
There
information
Ideas arranged in a logical/ cause-effect sequence
The sequence of the events in the:
• Homeostatic control of temperature
• Homeostatic control of CO2
• Importance of CO2 in regulating atmosphere temperature and its influence on global warming


Answered all aspects required by the essay in sufficient detail
The following must be included:
• Homeostatic control of temperature (T: 5/7)
• Homeostatic control of CO2 (C: 3/5)
• Importance of CO2 in regulating atmospheric temperature and its influence on global warming (A: 3/5)
in a

sequence
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
TOTAL:

1.1.1


the scientific
Homo erectus.
Homo habilis.
Australopithecus africanus.
D. Australopithecus afarensis.
1.1.2 Which ONE of the following is a structural feature of a bipedal organism?






A. Long, narrow pelvis.
B. Short, wide pelvis.
C. C-shaped vertebral column.
D. Longer arms.
1.1.3 A mother has blood group B and a father has blood group O They have three biological children and an adopted child. The blood groups of all the children are represented in the table below.
Nobuhle
William
Milly
Which child is

A. Nobuhle
William
Milly
Patrick
QUESTIONS 1.1.4 AND 1.1.5 ARE BASED ON THE TIMELINE BELOW SHOWING THE POSSIBLE EVOLUTION OF SOME HOMINIDS.
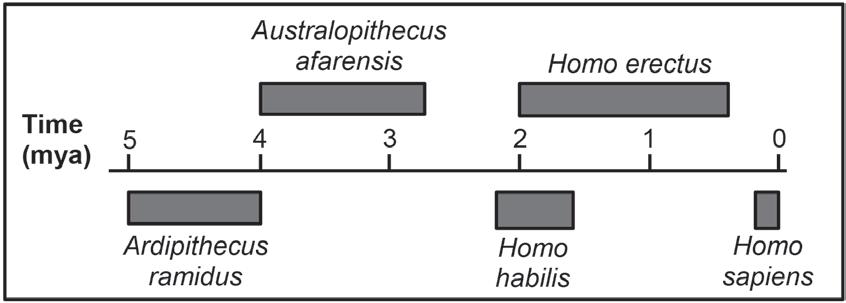
1.1.4 Which species inhabited the Earth for the longest period of time?
A. Australopithecus afarensis.
B. Homo erectus.
C. Homo habilis.
D. Homo sapiens.
1.1.5 How many years ago did the genus Homo first appear?



A. 2,2 mya.
B. 2,0 mya.
C. 1,6 mya.
D. 0,2 mya.
1.1.6 The list below describes some evolutionary events.
i. Each population undergoes natural selection differently and independently.
ii. There is no gene flow between the two populations.
iii. A population becomes separated.

iv. A geographical barrier forms.


v. The two populations become different phenotypically and genotypically.
Which ONE of the following combinations gives the CORRECT sequence of these events?
A. (v)
B. (iv)
(iv)
(ii)
1.1.7 The diagram below shows the fertility of the offspring produced

and
three populations of mice,

, interbreed.
Which ONE of the following statements is CORRECT?


A. All three populations are of the same species.
B. Populations X and Z are of the same species, but populations
and
C. Populations
and
different species.
and Z are different species, but populations
are of the same species.
D. Populations
and
are different species, but populations
and Z are of the same species.
QUESTIONS 1.1.8 AND 1.1.9 ARE BASED ON THE INFORMATION BELOW.
In a certain species of rabbits, body colour is controlled by two alleles where black (B) is dominant to white (b). Ear shape is controlled by a second gene. The allele for wide ears (E) is dominant to the allele for narrow ears (e).
1.1.8 What is the possible genotype for a black rabbit with narrow ears?
A. BbEe.
B. bbee.
C. BBEe.
D. Bbee.
1.1.9 What is the possible genotype of gametes produced by a white rabbit with narrow ears?

A. bbee.
B. be. C. BE, Be, bE and be.
D. bE and be. (9 x 2) (18)

1.2 Give the correct biological term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.9) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.2.1 The bonds between nitrogenous bases in a DNA molecule.
1.2.2 All the genes that make up an organism.
1.2.3 The type of evidence for human evolution that includes tool-making.
1.2.4 The process whereby new species are formed.
1.2.5 An inherited disorder where blood fails to clot properly.
1.2.6 The opening in the base of the skull through which the spinal cord passes.
1.2.7 Two or more alternative forms of a gene at the same locus.
1.2.8 The type of variation in a population with no intermediate phenotypes.

1.2.9 Chromosomes involved in sex determination. (9 x 1)(9)
1.3 Indicate whether each of the statements in COLUMN I applies




1.3.1
1.4
The diagram below shows the structure of a chromosome.
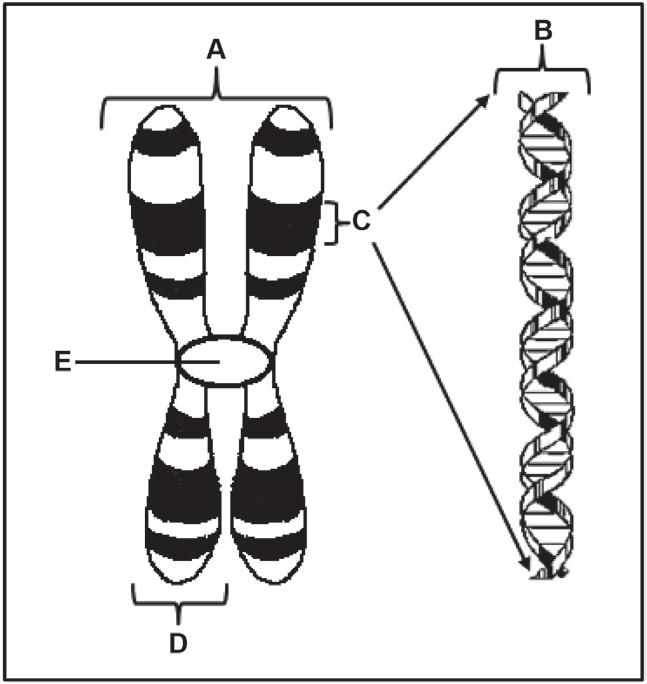
1.4.1 Identify parts D and E (2) 1.4.2 How many pairs of chromosomes are found in a normal human somatic cell? (1)
1.4.3 Give only the LETTER of the part that:


a. Attaches to the spindle fibres during cell division. (1)
b. Represents a gene. (1) 1.4.4 Name:



a. TWO organelles in an animal cell where DNA is found. (1)
b. The natural shape of a DNA molecule. (1)
c. The process whereby DNA makes an identical copy of itself (2) (9)

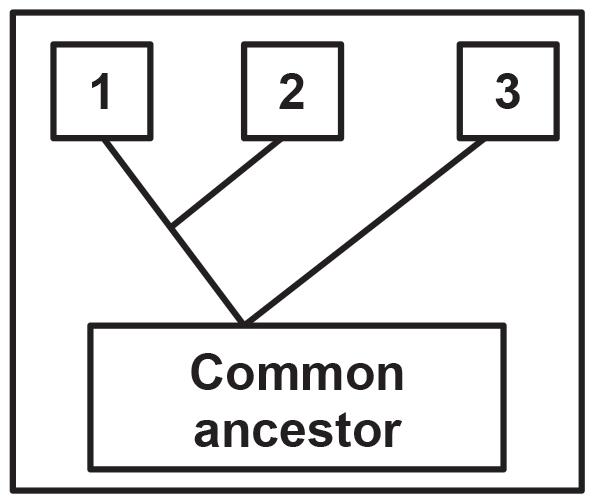
the extract below.
Trilobites are an extinct group of marine arthropods. Many of their fossils have been discovered. They had a tough exoskeleton and they are thought to be closely related to three other phyla of extinct arthropods, namely helmetids, tegopeltids and naraoids.
The tegopeltids and helmetids are the two most closely related phyla and are more closely related to trilobites than to naraoids.
Study the diagram below, which illustrates the possible evolutionary
among the four
represented by the letters M, N, O


P
1.5.1 Name the type of diagram illustrated. (1)
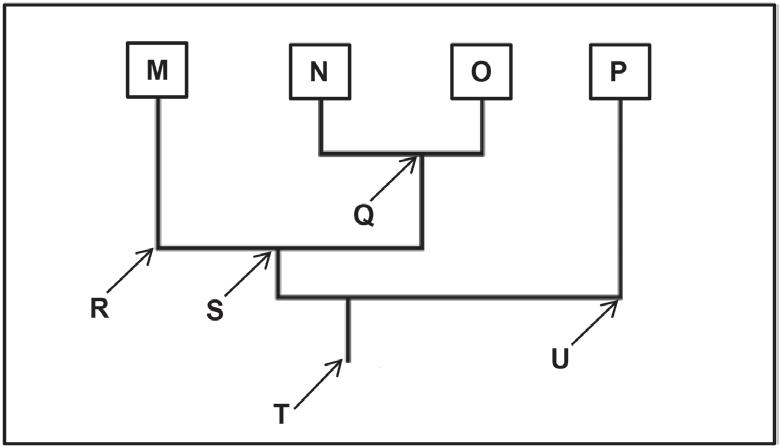
1.5.2
1.5.3 Give
1.5.4
2.1 The diagrams below represent the distribution
2.1.1 Explain why the gametes represented by diagrams C and D do not have any chromosomes. (3)
2.1.2 If gamete A is involved in fertilisation, describe how this may result in Down syndrome. (3)


2.1.3 Due to the process of crossing over, the chromosomes in diagrams A and B appear different to each other.
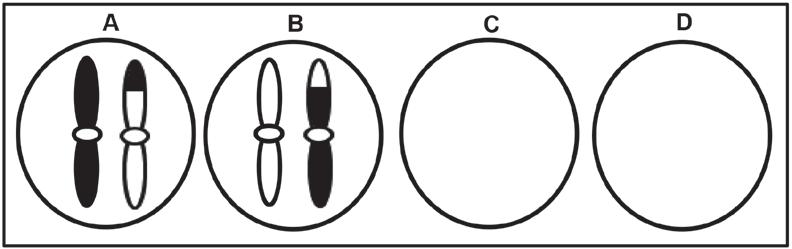

a. Identify the phase of meiosis during which crossing over occurs. (1)
b. Describe the events during crossing over. (3)
Explain the significance of crossing over in natural selection.
2.2 Severe combined immune deficiency syndrome (SCID) is a disorder affecting the immune system. It is caused by a sex-linked recessive allele (Xd).
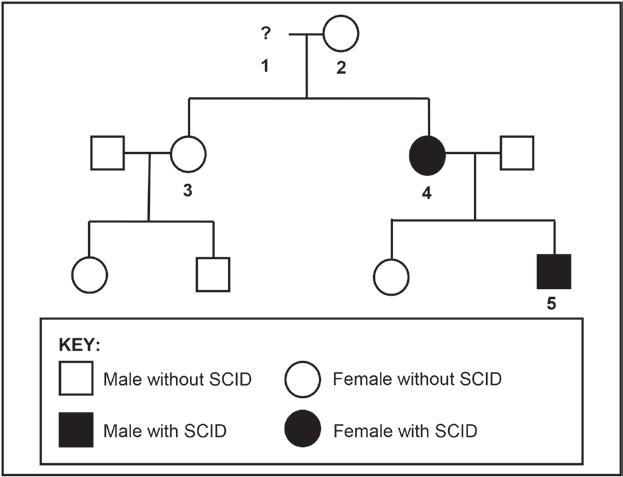
The diagram below shows the inheritance of the disorder in a family. It is not known if individual 1 has the disorder or not.
2.2.1 Give the:









a. Phenotype of individual 2 (1)
Phenotype of individual 1 (1)
c. Genotype of individual 3 (2)
2.2.2 Explain how individual 5 inherited the disorder. (2) (6)

2.3 Read the extract below.
The first cloned animal in Africa, a calf named Futhi, was born in North West in South Africa on 19 April 2003. No fertilisation was involved in the production of Futhi. She was produced from a single cell taken from the ear of a donor cow named LMJC 865. The donor cow had a high average milk yield of 78 litres a day. Cloning allows for the production of organisms with desired characteristics.
Some people argue that cloning reduces genetic variation in the offspring, with no further genetic improvement. Cloning is an expensive procedure and may not be economical for commercial agriculture.

2.3.1 According to the extract, state ONE: a. Advantage of cloning (1) b. Disadvantage of cloning (1)

2.3.2 State why the donor cell was taken from LMJC 865 and not from any other cow. (1)
2.3.3 State why an ear cell was used and not an ovum. (2)
2.3.4 Briefly describe the process of cloning (4) (9)



2.4 Flower colour (purple or white) in a particular plant species is controlled by two alleles, D and d

Four crosses were carried out to determine which
is dominant. Forty (40) offspring were produced in each cross. The phenotypes of the parents and offspring in each cross were recorded. The results are shown in the table below.
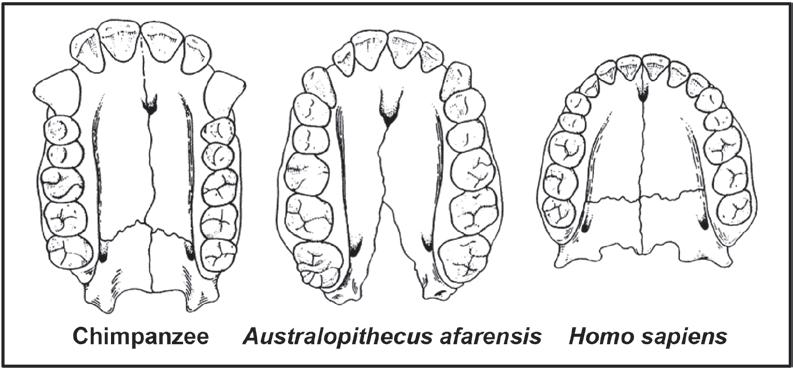
3.1 The diagrams below show the upper jaws of some fossils. These diagrams are drawn to scale.
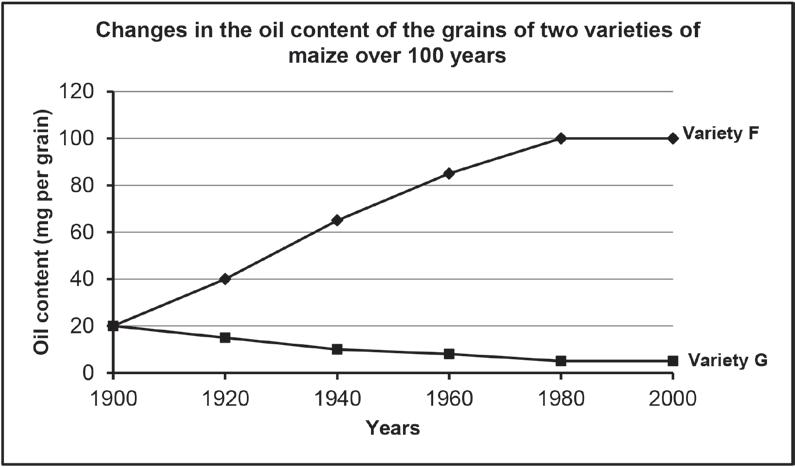
3.3 Artificial selection programmes have produced two varieties of maize. The one has grains with a high oil content (Variety F) and the other has grains with a low oil content (Variety G)
The graph below shows the changes in the oil content of the grains of the two varieties over 100 years of artificial selection.
3.1.1 Describe ONE visible difference between the jaw of a chimpanzee and that of Homo sapiens which show trends in human evolution. (2)
3.1.2 Based on the differences in dentition, what conclusion can be made about the change in diet from Australopithecus afarensis to Homo sapiens? (2)
3.1.3 Australopithecus may be described as a transitional species between the chimpanzee and Homo sapiens
a. Define a transitional species. (1)
b. Use ONE visible feature of the jaw to explain why A. afarensis may be described as a transitional species. (2) (7)
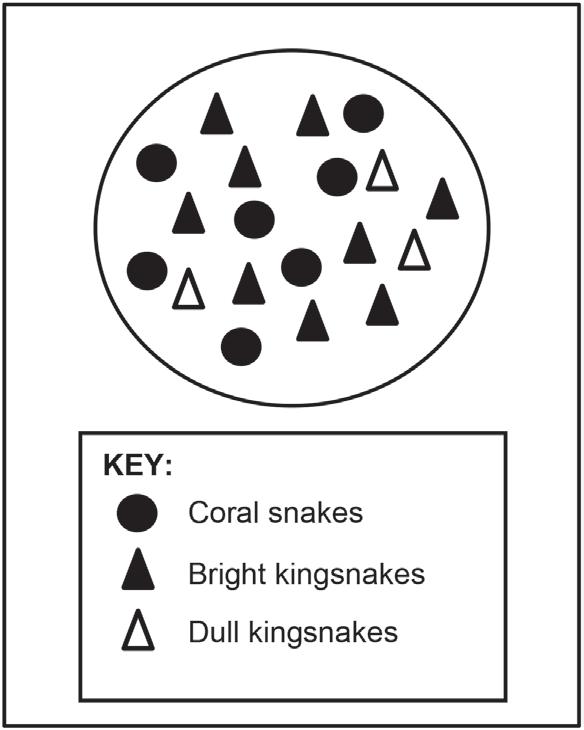
3.2 There are two variations in the colour of kingsnakes. Some have a bright colourful pattern and others have a dull pattern. Kingsnakes are non-poisonous to their predators.
Coral snakes also have a bright colour pattern, but are poisonous to their predators. This is a defence mechanism as predators avoid them.
Scientists observed that where kingsnakes shared the same habitat with coral snakes, there were more kingsnakes that had bright colourful patterns.
The diagram below represents the distribution of the snakes.
3.3.1 In which year did the two maize varieties have the same oil content? (1)
3.3.2 Calculate the percentage increase in the oil content of Variety F over the 100-year period. Show ALL working. (3)
3.3.3 Tabulate TWO differences between natural selection and artificial selection. (5) (9)
3.4 Weeds are problematic to farmers because they invade farm fields and outcompete crop plants for space. This reduces the crop yield.
Farmers spray their fields with chemicals, known as herbicides, to kill the weeds. Some weeds, however, have evolved to be resistant to herbicides.
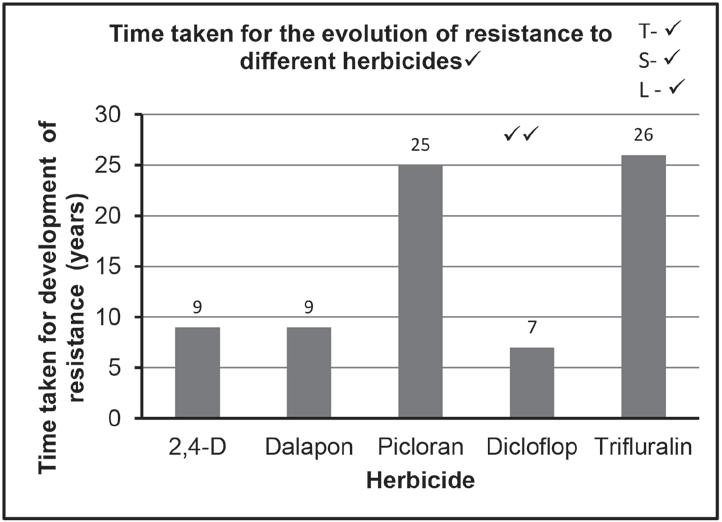
Scientists investigated the time it took for a species of weed to develop resistance to five types of herbicides. The results are shown in the table below.
Dalapon
3.2.1 Explain how the bright colour pattern of coral snakes influences their survival. (3)
3.2.2 Use Darwin's theory of evolution through natural selection to explain why there are more brightly coloured kingsnakes in this habitat. (6) (9)
3.4.1 Refer to the passage above and state how weeds act to reduce crop yield.
3.4.2 Identify the:














Independent variable
Dependent variable.
Name the herbicide:
which the weeds developed resistance the fastest. (1)
That remained effective for the longest period of time. (1)
3.4.4 The scientists used the same weed species when investigating resistance to the different herbicides.
Describe how the scientists would have determined the resistance of the weeds to the herbicides.
Explain how the use of the same weed species improved the validity of the investigation.
1.4.2
C√/B
b.
(DNA)
1.5 1.5.1 Phylogenetic
An exoskeleton√ (1)

(1)
Trilobites
Naraoids
SECTION B
2
2.1.1
Due to non-disjunction√/ Non-separation of a chromosome pair
during Anaphase I√
• Two chromosomes moved to the one pole√ and





• none moved to the other pole√ Any (3) 2.1.2 • Gamete A will have 24 chromosomes√/an extra chromosome
• and when it fertilises a normal ovum√/gamete with 23 chromosomes
• the zygote will have 3 chromosomes at position 21√/ 47 chromosomes (3)
2.1.3 a. Prophase I√ (1)
b. • Adjacent chromatids of homologous chromosomes cross√ • at a point called the chiasma√
• There is an exchange of DNA segments√/genetic material (3)

c. • Crossing over introduces genetic variation√ in gametes
• Genetic variation may result in favourable characteristics√
• that ensure a better chance of survival√
• when environmental conditions change√ OR

• Crossing over introduces genetic variation√ in gametes
• Genetic variation may result in unfavourable







• characteristics√
• that reduce the chance of survival√
• when environmental conditions change√ Any (3) (13)




2.2 2.2.1 a. Female without SCID√ (1)

b. Male with SCID√ (1) c. XDXd√√ (2)
2.2.2
2.3 2.3.1
• He inherited the recessive allele√ /Xd
• from the mother√/individual 4 (2) (6)
a. It allows for the production of organisms with desired characteristics√/ high average milk yield (1) (Mark first ONE only)
b. • It reduces genetic variation√ in offspring

• It results in no further genetic improvement√
• It is expensive√
• It may not be economical for commercial agriculture√ (Mark first ONE only) Any (1)

2.3.2 LMJC 865 had a high average milk-production yield√/ produced 78 litres per day/ had the desired characteristic (1)


2.3.3
2.3.4


• A diploid cell√/ a cell with all the genetic information is needed
• An ovum is a haploid cell√/ only contains half of the genetic information (2)
• The nucleus of an ovum is removed√ and replaced with
• the nucleus of a somatic donor cell√/ diploid donor cell
• The zygote is stimulated√
• for mitosis√ to occur
• The embryo is then placed into the uterus of an adult female√
• Plants may be cloned by vegetative reproduction√/asexual reproduction /tissue culture/grafting
• A plant with the desired characteristics is selected√
• A vegetative part of the “parent” plant structure is removed√/(examples) and
• placed inside a growth medium√/(examples)







• and allowed to grow√
2.4 2.4.1
2.4.2
•
•
sapiens
•
•
4 (4) (9)
√ (1)
When purple-flowering plants and white-flowering
3.2 3.2.1
and small/no spaces in Homo sapiens
the teeth in the chimpanzee
canines/teeth in the chimpanzee
in Homo sapiens
first ONE only)
and small
1 x 2 (2)
The diet changed from eating raw food√ in Australopithecus
• to a diet of cooked food√ in Homo sapiens (2) 3.1.3 a. A transitional species shows intermediate characteristics between two genera/species√
OR
It has characteristics common to both the ancestor species and the species that follows√ (1)
b. The jaw is smaller than that of the chimpanzee but larger than that of Homo sapiens√√
OR
The canines/ teeth are smaller than those of the chimpanzee but larger than those of Homo sapiens√√
OR
The jaw/palate shape is more rounded than that of the chimpanzee but less rounded than that of Homo sapiens√√ Any 1 x 2 (2) (Mark first ONE only) (7)
• The bright colour pattern is associated with being poisonous√
• thus reducing predation√ and
• improving the chances of survival√ (3)

3.2.2
• There is variation in the colour of kingsnakes√
• Some are bright in colour√/resemble the coral snakes and
• the others are dull in colour√
• Those with dull colours are killed√ by predators
• Those with bright colours are not eaten√
Type: Bar graph drawn (T) 1


Title of graph 1
Correct:
• Scale for Y-axis and (S)
• Width and interval of bars on X-axis

Correct:
• Label for X-axis and












• Label and unit for Y-axis (L) 1
Plotting of bars
1- 1 to 4 bars plotted correctly
All 5 bars plotted correctly (6)
TOTAL
QUESTION 4
Structure (S)
• RNA is single stranded√
• and is made up of nucleotides√which comprise:
• ribose√ sugar
• phosphate√group
• nitrogenous bases√ which are
• adenine, uracil, guanine and cytosine√/ (A, U, G and C)
• The phosphate group is attached to the ribose sugar√
• and the nitrogenous base is attached to the ribose sugar√
• Bases on RNA are arranged in triplets√
• as codons on mRNA√
• and anticodons on tRNA√
• RNA has a clover-leaf√/hairpin structure
B:
• tRNA has a place of attachment for an amino acid√ Any (9)
Involvement in protein synthesis (P)

• mRNA√ forms
• during transcription√/by copying the coded message from DNA

• and moves out of the nucleus√
• and attaches to the ribosome√
• During translation√
• the anticodon matches the codon√
• tRNA√
• brings the required amino acid√ to the ribosome
• Amino acids become attached by peptide bonds√
• to form the required protein√ Any (8) Content: (17)

Synthesis: (3) (20)

B. mitosis and random fertilisation.
C. random mating and random fertilisation.




D. mitosis and meiosis.
1.1.3 African apes and humans are similar. Both have …





A. small jaws and well-developed brow ridges.
B. opposable thumbs and bare fingertips.

C. gaps between their teeth and eyes in front.


D. an upright posture and a cranial ridge.
1.1.4 The diagram below shows Tiktaalik roseae, a fish that may be the ancestor of the first organisms to live on land.
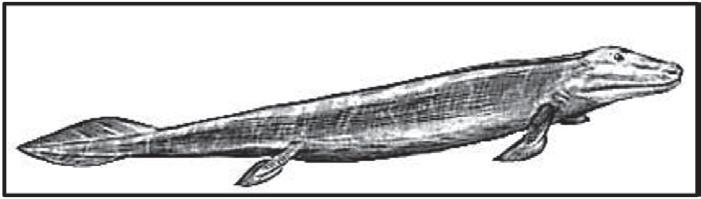
According to Lamarck, this species of fish may have evolved the ability to 'walk' on land by …
A. undergoing natural genetic mutations which caused the fins to develop into legs.

B. the process of natural selection.
C. passing on the acquired characteristic of fins to their offspring

D. stretching its fins and using them for 'walking'.
1.1.5 The diagram below shows some of the processes, molecules and structures that are involved in protein synthesis in a cell.

1.1.6

Lee
Louis
Tim White
1.1.8
1.1.10
A group of students observed that the long-term use of antibiotics results in the decreased control of bacterial infections. From this observation the students stated that:
Antibiotic resistance in bacteria is caused by the long-term use of antibiotics.


This statement is a/an … A. theory. B. aim. C. hypothesis. D. conclusion. (10 x 2) (20)










1.2 Give the correct biological term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question number (1.2.1 to 1.2.7) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.2.1 Similar structures in different organisms indicating descent with modification
1.2.2 Large, pointed teeth in African apes that are used for tearing food
1.2.3 The part of the skull that houses the brain
1.2.4 The non-sex chromosomes in humans
1.2.5 The network of genetic material found in the nucleus during interphase

1.2.6 The number, shape and arrangement of all the chromosomes in the nucleus of a somatic cell

1.2.7 Having a protruding jaw (7 x 1) (7)
1.3 Indicate whether each of the statements in COLUMN I apply to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A AND B or NONE of the items in COLUMN II. Write A only B only both A and B, or none next to the question number (1.3.1 to 1.3.3) in the ANSWER BOOK.
COLUMN I COLUMN II
1.3.1 Long and narrow pelvis
1.3.2 The point of attachment of two overlapping chromatids
1.3.3 Variation in human height
A: African apes B: Humans
A: Locus B: Chiasma
A: Continuous B: Discontinuous (3 x 2) (6)

1.4 The diagram below represents ALL the chromosomes in a cell that is undergoing normal cell division.

1.4.1
Name the:

a. Type of cell division that is occurring in the cell in the diagram (1)
b. Phase of cell division during which the chromosomes behave as shown in the diagram (1)
1.5
1.4.2 Where in the human female
would the type of cell division

in QUESTION
1.4.3 Give the LETTER
take place? (1)
NAME of the structure
to the spindle fibres. (2)
1.4.4 How many
1.6.2 Give the LETTER
found in each
at the end of this cell division? (1) (6)
the characteristics
The table
the
Fur
The Punnett

the

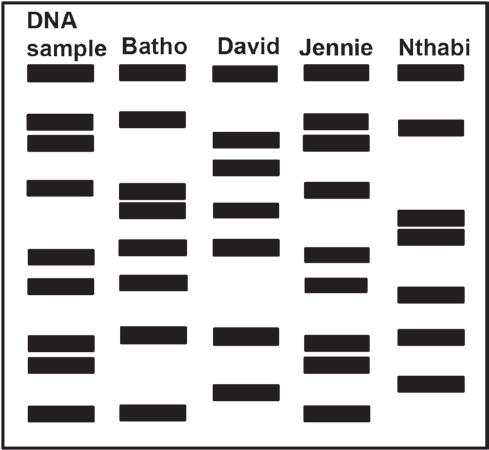
2.1 Detectives were investigating a crime scene and found blood on a broken window. They suspected that the blood was that of the criminal. To identify the criminal, they analysed a DNA sample from the blood and compared it to that of four suspects.
The diagram below was produced:
1.5.1 Name the:











a. Dominant phenotype for fur colour (1)
Recessive phenotype for fur texture (1)
1.5.2 Give the:
a. Genotype of offspring
(1)
b. Phenotype of the female parent (2)
Genotype of the male parent (1)
1.5.3 State the phenotype that ALL the offspring of this genetic cross have in common. (1) (7)
1.6 Scientists compare the number of differences in the amino acid sequence to see how closely related species are. Fewer differences in the amino acid sequence mean the species are more closely related.
Cytochrome C is a protein that occurs in many species. The amino acid sequence of this protein differs between species.
The table below shows the number of differences in the amino acid sequences of three species, A B and C
SPECIES
SPECIES
1.6.1 What type of evidence for evolution is being used in this table?
2.1.1 Name the technique that was used to identify the criminal. (1)
2.1.2 Who is the possible criminal? (1)
2.1.3 Explain your answer to QUESTION 2.1.2. (2)
2.1.4 State ONE other use of the technique identified in QUESTION 2.1.1. (1)
2.2 A farmer decided to have his best meat-producing bull cloned.
The following steps were used in the process:
• A muscle cell was taken from the bull and the nucleus was removed.
• An ovum was taken from a cow and the nucleus was removed and discarded.
• The nucleus from the muscle cell was placed in the empty ovum.
• The ovum was given an electric shock to stimulate normal cell division to produce an embryo.
• The embryo was placed in the uterus of a surrogate cow where it developed into the clone.
2.2.1 What is cloning? (1)
2.2.2 Explain why the nucleus of a muscle cell was used and not the nucleus of a sperm cell. (2)
2.2.3 Explain why the nucleus of the ovum was removed. (2)
2.2.4 State ONE benefit of cloning. (1)
2.3 A man with blood group AB and a woman who is heterozygous
blood group B plan to have children.
2.3.1 How many alleles control the inheritance of blood groups? (1)
2.3.2 Describe the type of dominance that occurs in the inheritance of blood group B in the woman. (3)
2.3.3 Use a genetic cross to show all the possible genotypes and phenotypes of their children. (6)
2.4 Sickle cell disease is caused by a recessive allele and first appeared in humans as a result of a gene mutation.
The table below shows the number of children born with sickle cell disease in some regions in a particular year.
Democratic Republic of Congo
United States of America
Nigeria
United
2.4.1 What is a gene mutation? (2)










2.4.2 Which region had the highest number of children born with sickle cell disease in that year? (1)
2.4.3 What percentage of the worldwide total of children born with sickle cell disease came from the Democratic Republic of Congo? Show ALL calculations. (3)
2.4.4 Use the letters D and d to give the genotype of a person who: a. Suffers from sickle cell disease (1) b. Carries the allele but does not suffer from the disease (1) (8)
2.5 Goltz syndrome is a sex-linked genetic disorder. It is caused by a dominant allele XG
The diagram below shows the inheritance of Goltz syndrome in a family.
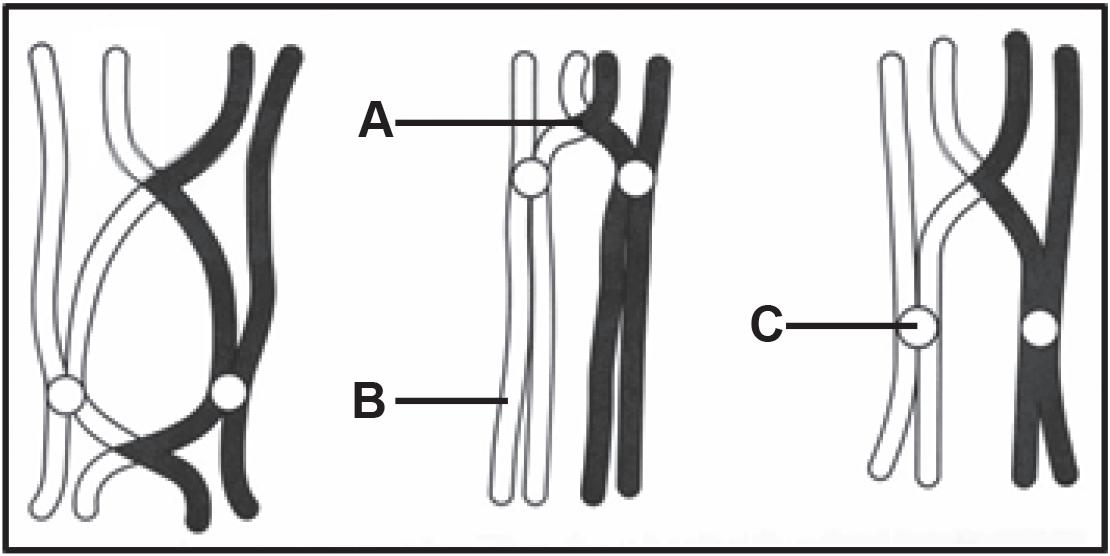
3.1 Describe the process of natural selection. (7)
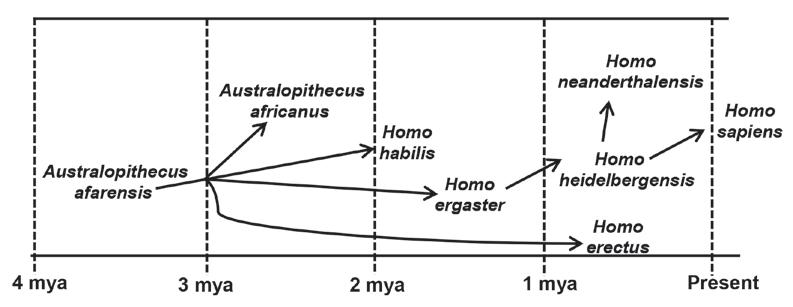
3.2 Fossil evidence for humans may be interpreted in different ways. One possible model of human evolution is shown below.
3.2.1 Name the family to which all of the represented organisms belong. (1)
3.2.2 Describe how cultural evidence is used to support the theory of human evolution. (2)
3.2.3 How long ago did the most recent common ancestor of H. erectus and H. heidelbergensis exist on earth? (1)
3.2.4 Explain a possible reason why H. ergaster was placed between A. afarensis and H. heidelbergensis on the model. (2)
3.2.5 Explain how the fossils of organisms that existed from 4 mya to present time are used to support the 'Out of Africa' hypothesis. (3) (9)
3.3 Male long-tailed widowbirds have extremely long tail feathers that they use in mating displays to attract females.
Scientists conducted an investigation to determine the relationship between the length of the male long-tailed widowbird's tail and its mating success.
The procedure was as follows:
• A total of 27 male long-tailed widowbirds was sampled and divided into 3 equal groups.
• The tail feathers of the birds in each group were treated in the following way:
» Group 1 – Cut short

» Group 2 – Made longer by adding artificial feathers



» Group 3 – Left unchanged
• The 3 groups of male long-tailed widowbirds, along with female long-tailed widowbirds, were released into an environment suitable for mating.
• Each time a pair mated successfully they produced a nest and all the nests were counted.
• The average number of nests produced by each group was calculated and used as an indication of mating success.
The results are shown in the table below.
2.5.1 Name the type of diagram shown. (1)


2.5.2 How many: a. Females are in this family (1) b. Males in the F1-generation have Goltz syndrome (1)
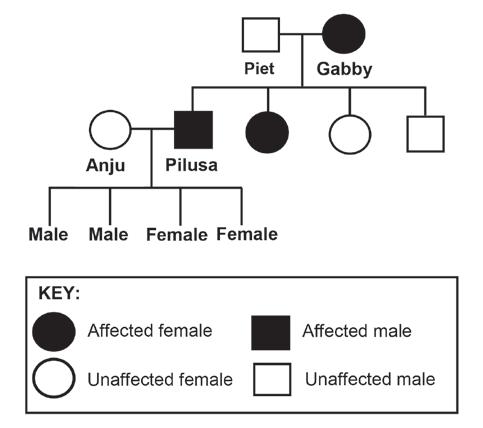
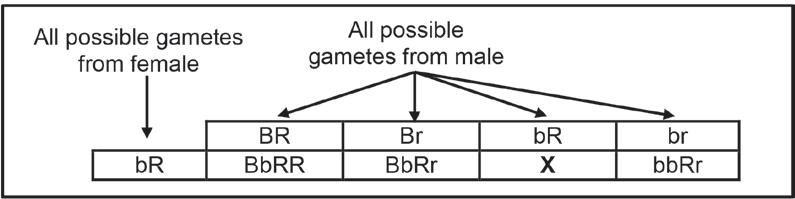
2.5.3 Give Gabby's genotype. (2)
2.5.4 Anju and Pilusa have four children. Give the phenotype of their sons. (2)
2.5.5 Explain your answer to QUESTION 2.5.4. (4) (11) [40]
Name the:

occurs in

3.3.2

Scientists

in



Madagascar is an island off the East
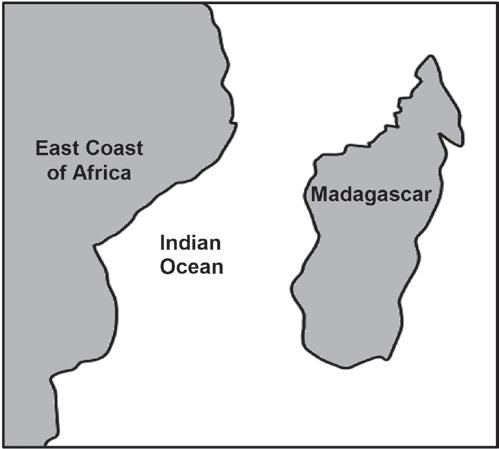
of






shown in the












Describe
3.4.1
TOTAL

NOTE:
Content: (17)









Synthesis: (3) (20)



2.1 2.1.1 DNA profiling√ (1)
2.1.2 Jennie√ (1)
2.1.3
2.1.4

• Jennie’s DNA profile√/ bands
• matches the DNA profile/ bands of the sample√from the crime scene (2)
Proof of paternity√
• Tracing missing persons√
• Identification of genetic disorders√
• Establishing family relations√
• Matching tissues for organ transplants√


• Identifying dead persons√ /animals Any (1) (Mark first ONE only) (5)
2.2 2.2.1 The production of (genetically) identical organisms√ (1)



2.2.2
2.2.3
2.2.4
• A muscle cell contains all the genetic material√ of the bull/ is diploid whereas

• a sperm cell has only half of the genetic material√/ is haploid (2)
• To remove the genetic material of the cow√
• so that only the genetic material from the (best meat producing) bull is present√ (2)
• To produce organisms with desired traits√ e.g. health; appearance; nutritious; yield; shelf-life; etc



• Conservation of threatened species√
• To create tissues/organs for transplant√ (Mark first ONE only) Any (1) (6)
2.3 2.3.1 3√/ Three (1)
2.3.2
2.3.3
• Complete dominance√
• The allele for blood group B/

• the allele for blood group
is dominant
is






and
(3)
3.2.4
3.2.5
• H. ergaster shows characteristics of both√ A. afarensis and H. heidelbergensis
• therefore it is a transitional√ species (2)
• The fossils of Australopithecus were ONLY found in Africa√
• The fossils of Homo habilis were ONLY found in Africa√
• The OLDEST fossils of Homo erectus were found in Africa√
• The OLDEST fossils of Homo sapiens were found in Africa√√
• This suggests that (the ancestors of) Homo sapiens originated in Africa √* *1 Compulsory + Any 2 (3) (9)
3.3 3.3.1 a. (Species-specific) courtship behaviour√ (1)
3.3.2
b. Length of the (male long-tailed widowbird's) tails√ (1)
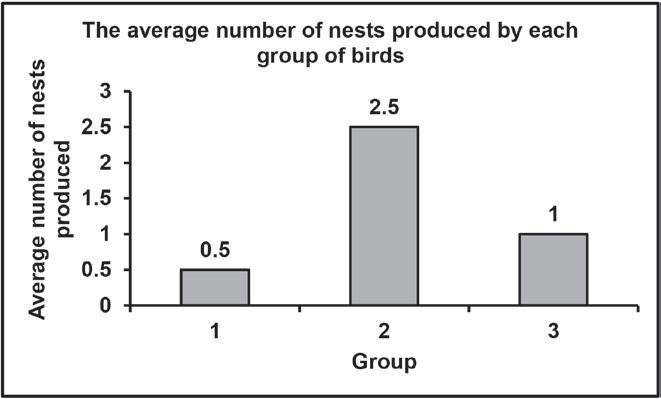
• A larger sample size√
• increases the reliability√ of the investigation (2) 3.3.3




• To serve as a control√
• so that it can be compared√with the other groups
• and show that the tail length is the only factor that affects the results√ /improves the validity of the investigation Any (2)
3.3.4 (6)

Guideline for assessing the graph






Correct type of graph (T) Bar graph drawn 1 Caption of graph (C) Both variables included 1 Axes labels (L) X- and Y-axis correctly labelled 1 Scale for X- and Y-axis(S) • Equal space between bars and width of bars for X-axis and
• Correct scale for Y-axis
1
Plotting of bars (P) 1 to 2 bars plotted correctly All 3 bars plotted correctly 1 2
3.3.5 The longer the (male long-tailed widowbird's) tail, the higher the mating success√√ OR
The shorter the (male long-tailed widowbird's) tail, the lower the mating success√√ (2) (14)
3.4 3.4.1
3.4.2
• There was once one large continent√ and



• the common ancestor existed throughout this continent√
• When Madagascar separated√
• the common ancestor was found in both√ regions (4)
• The common ancestor became separated into two groups by the ocean√*
• There was no gene flow between the two groups√
• Each group experienced different environmental conditions√
• and underwent natural selection independently√
• The individuals in each group
• genotypically and phenotypically
•
form the pottos
lemurs
• Eventually if the two groups are
4
Location (P)
• The DNA is located in the




• and mitochondria
•
Structure (S)
• DNA is a double-stranded√molecule that
• forms a helix√
• It is made up of nucleotides
• Each nucleotide has a deoxyribose sugar
• a phosphate group√ and



• a nitrogenous base√
• The bases are A, T, C and G√
again,
molecule




• which join to form complementary pairs√/ (A to T and C to G)



• held by hydrogen bonds√
DNA replication (D)
• The DNA (double helix) unwinds√ and
• unzips√/hydrogen bonds break
















• to form two separate strands√


• Both DNA strands serve as templates√
• to build a complementary DNA√/(A to T and C to G)
• using free (DNA) nucleotides√ from the nucleoplasm


• This results in two identical (DNA) molecules√
• Each molecule consists of one original strand and one new strand√ Any (6)

Significance of DNA replication for mitosis (M)
• The genetic material/DNA is doubled√
• so that each cell receives the same amount of DNA√

• to ensure that all the daughter cells are (genetically) identical√ Any (2)
Content: (17) Synthesis: (3) (20)






Generally All information provided is relevant to the question
In this essay in Q4
Ideas arranged in a logical/ cause-effect sequence
Only information relevant to:
• Location and structure of DNA
• Process of DNA replication
• Significance of DNA replication for mitosis
The description for each of:
• Location and structure of DNA
• Process of DNA replication
• Significance of DNA replication for mitosis
There is no irrelevant information Is logical and sequential
All aspects required by the essay have been sufficiently addressed
At least the following marks should be obtained for:

• Location of DNA (P:1/2)
• Structure of DNA (S:5/7)
• Process of DNA replication (D:4/6)
• Significance of DNA replication for mitosis (M:1/2)
Mark 1 1 1

TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150























