
3 minute read
Navigation and 3D Inference System
For now, focus on the background. The default background color is beige. You will probably want to adjust the background color to white. This will make the edges and faces easier to see. Double-click on the background color swatch. A color menu will appear. Adjust the value to make the background white.
Checking the Sky or Ground tab will add a faded simulated sky or ground to the model environment. For now, keep both options unchecked (Fig. 2-22).
Advertisement
Navigation and 3D Inference System
SketchUp is a two-dimensional interface allowing for movement in a three-dimensional environment. Without a reference system, it would be difficult to orient your projects. SketchUp’s inference system helps you find your position in 3D space and ensure precision. The inference system is comprised of drawing axes, point inferences, and linear inferences.
Fig. 2-22: The Background setting for Sky and Ground is turned on in a SketchUp model.
Navigation
You need to understand how to move around the SketchUp environment. The basics are:
Middle Mouse Button (MMB) The middle mouse button allows you to zoom in and out. holding the Middle Mouse Button Holding the middle mouse button and moving the mouse will cause SketchUp to orbit. holding Shift+Middle Mouse Button Hold the Shift+middle mouse button (Shift+MMB) will cause a little hand to appear as the mouse pointer, allowing you to pan around the model.
SketchUp requires geometry to be present to easily move in 3D space. If you try to zoom in on an “empty” space, the Zoom function may be slow or unresponsive. If you zoom in and out when the cursor is aligned over any geometry, the Zoom function will respond. The same is true for orbiting; make sure the cursor is aligned over geometry and then orbit. This will cause SketchUp to orbit around the geometry the cursor is referencing.
Inference System
SketchUp utilizes specific visual cues to help you find your relative position within the model environment. This is called the inference system and is comprised of the following:
Drawing on Axes The drawing axes are composed of three lines: red, green, and blue. These lines represent directions in 3D space: green and red represent horizontal space. The blue axis represents the vertical dimension (Fig. 2-23).
Point Inference
Point inference helps connect and attach geometry in 3D space. The Point Inference system appears as little colored boxes on edges and faces. Because you can identify the connection points, the inference system allows you to connect lines and surfaces with accuracy and precision. Geometry can be “snapped” to identified connection points (Fig. 2-24).
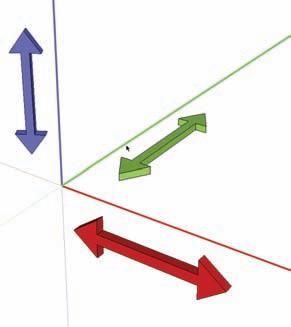
Fig. 2-24: Drawing axes. Fig. 2-24: The point inference system.

Example: Draw a simple 2D line with the Line tool. Next, hover the Line tool at either end of the drawn line. A little green box appears at the endpoints. Move the Line tool over the drawn line and find some of the other colored points listed in Table 2-1. Do the same thing with a single face.
Linear Inferences
When drawing lines, or moving or copying objects, SketchUp will indicate the direction of movement by displaying a dashed-colored line that is green, red, or blue; each line represents a drawing axis. This is SketchUp’s way of indicating the axis on which the geometry is being drawn, moved, or copied (Fig. 2-25 through Fig. 2-28).
Table 2-1: Inference Box Colors Inference Color Endpoint Green Midpoint Cyan Intersection Red “x” On Edge Red Center (of Circle) Green On Face Blue

Fig. 2-25: The Line tool drawing on an axis indicated by linear inference.










