Teacher Manual
Grade 5




1. Puzzle

Note: Use the following points to prepare for the session beforehand. Avoid reading the points in the class.
In the Previous Grade…
● Conji helped Mel recover her memory.
● There was a change in all the robots and machines due to an anomaly in Avora’s timeline.
● Mel and Conji’s arrival in Nexus caused an interchange in the meaning of binary digits.
● With Conji by Mel’s side, the duo once again become a ray of hope for Avora to fix the timeline.
● Conji recalls how he and Mel overcame all the challenges thrown by Lord Ero.
● Mel disguises herself as a dragon to prank Conji.
● To make up for the prank, Mel agrees to teach Conji about computers.
● Eva joins them on their journey of learning about computers.
The content covered in this chapter is aligned with the following CSTA Standards
● 1B-CS–01 Computing Systems
This chapter is divided into the following classroom sessions
1. Difference and Analytical Engines
2. Generations of Computers I
3. Generations of Computers II
In this session, students will learn about –
● Computers
● Analytical Engine
● Difference Engine
Keywords
● Storage: A process by which digital data is stored in a storage device by a computer
● Calculator: A small electronic device used for doing mathematical calculations

Brief the story of the previous grade
Read or invite the students to read the story aloud
Discuss computers, analytical engine and difference engine
Fill Up – Q1, 2 Find the Truth – Q1, Q2 Answer in Short - Q1
Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Recap the story covered in the previous grade.
● Read or Invite two students to read the story aloud from Page 2 to 4 up to Mel’s words “You know….., right?”
● Say: Let’s learn about computers, the first computer ever made: The Analytical Engine; and a device with storage capacity: The Difference Engine.
CS Concepts Explain
Computer
Analytical Engine
Difference Engine
As given in Panel 1 on Page 5
As given in Panel 3 on Page 5
As given in Panel 1 on Page 6
● Present the scenario: Consider your father has asked you to help him in calculating monthly expenses.
● Discuss:
■ Which device will you use to perform calculations?
Possible Responses: Calculator; Computer; Analytical Engine.
■ Which device lets you store the answer to your calculations?
Possible Responses: Computer; Difference Engine; Storage device.
■ What challenges do you think you would face if the computers we see today were as big as the first generation computers?
Possible Responses: They would need huge spaces to store them; they would be expensive; they would be immovable.
■ Why do you think the machine to solve maths problems was called a Difference Engine?
Possible Responses: They could do calculations; they could find the difference between two numbers.
● lf time allows, discuss all four questions, or discuss the first two.
● Conduct Fill Up section at page 13:
■ Say: Avorians are at war against hostile powers. Let’s help Mel and Conji fill in the blanks to prepare themselves.
■ Read Q1 and 2 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● Conduct Find the Truth on Page 13:
■ Say: Let’s practise more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q1 and 2 aloud, one by one. After each sentence, ask if it is true or false.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Write answers in your books.
● Conduct Answer in Short on Page 14:
■ Say: Let’s test our learnings to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q1 aloud.
■ Invite some students to share responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Write answers in your books.
Note
● If time permits, discuss the section Answer in Short - Q2 or, assign it as the homework.
● Conclude: Today, we learned about the first computers ever made: Analytical Engines and Difference Engines.
● Ask the following probing questions:
● When do you think you would need computers to perform calculations?
Possible Responses: to solve math problems; to add or subtract large numbers; to do 10-digit multiplication
● What do you think the Analytical Engine could do?
Possible Responses: Solve math problems; Add; Subtract; Multiply; Divide
● Assign Q2 from Answer in Short as homework.
In this session, students will learn about –

● Generations of computers
● Details of the first four generations of computers
Keywords
● Generation of computers: Indicates the change in the technology of computers that were in use
● GUI: Graphical User Interface is a way to communicate with a computer using interactive icons
Revise the story of the previous session
Recall the concepts of Analytical engine and Difference engine
Discuss the first four generations of computer
Inform that we are in the fifth generation of computers
● Recap the story covered in the previous session.
● Instruct: Let’s recall the concepts learned so far.
● Invite some students to recall and share the concepts aligned with the chapter story.
● Say: Currently, we are in the fifth generation of computers. Let’s learn about the first four generations of computers.
Hint about the current generation of computers
As given in Panel 2 on Page 6
As given in Panel 2 on Page 50
First four generations of computers
As given in Panel 2 on Page 6, Page 7, and Page 8
● Present the scenario: Consider you are building a computer.
● Discuss:
■ If you are in the 1940s, which areas will your computer be used in?
Possible Responses: Military; Industries; Scientists.
■ Why can only these areas use your computer?
Possible Responses: The computers are expensive; Use a lot of electricity; Very advanced computers of their time.
■ You build a PC. Which generation does it NOT belong to?
Possible Responses: First-generation computers, Second-generation computers, Thirdgeneration computers, Fifth-generation computers.
■ What are the features of the PC you have made?
Possible Responses: generates less heat; is faster; has a mouse; has GUI; can be used by anyone.
● If time allows, discuss all four questions, or discuss the first two.
● Conduct Fill Up on Page 13:
■ Read Q3 and 5 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● Conduct Find the Truth on Page 13:
■ Say: Let’s practice more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q3 and 4 aloud, one by one. After each sentence, ask if it is true or false.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Write answers in your books.
● Conduct Tick the Correct Answer on Page 14:
■ Say: Let’s test our learnings to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q4 and 5 aloud.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
Note
● If time permits, discuss the section Answer in Short - Q3 or, assign it as the homework.
● Conclude: Today, we learned about the first four generations of computers. We also learned about the generation of computers we are in.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ Why could people not build small and fast computers in the 1950s?
Possible responses: they did not have the knowledge; technology was not advanced enough; there was no need.
■ Name computers you see in your daily life.
Possible Responses: smartwatch; phone; laptop; calculator.
● Assign the following as homework:
■ Answer in Short – Q3
■ DIY – Fun time Q1 – 3
Objectives
In this session, students will learn about –

● Fifth-generation computers
● Supercomputers
Keywords
● Artificial Intelligence: The ability of computers to perform tasks which previously required human intelligence
● Weather forecasting: Prediction of weather conditions in a certain place
Revise the story of the previous session
Read the story aloud/ask the students to read the story aloud
● Recap the story covered in the previous session.
● Say: There is a new character in this chapter.
● Introduce Eva to the students.

● Instruct: Let’s learn how the story moves ahead. We will read from page 9.
● Say: Let’s learn about the fifth generation of computers, and the most powerful computers: the supercomputers.
CS Concepts Explain
Fifth Generation of Computers As given from Panel 1 on Page 9
Supercomputers
From web as given in Panel 2 on Page 50
As given from Panel 1 on Page 10
● Present the scenario: Consider you want to plan a trip to the mountains. And, before you plan, you first want to check the weather conditions in the area.
● Discuss:
■ Which type of computer can you use for weather forecasting?
Possible Responses: Supercomputers; very powerful computers
■ Which generation computer cannot be used here?
Possible Responses: First-generation computers; Second-generation computers; Thirdgeneration computers; Fourth-generation computers; Fifth-generation computers
■ Name the generation if the device you used is your phone to check the weather in the mountains.
Possible Responses: Fifth-generation computers; Fourth-generation computers; Current generation of computers
■ Why do you think we need fifth-generation computers in this situation?
Possible Responses: to save time; to make the computers less expensive; to make the computers widely available; to save space; to make the computers available for everybody
● If time allows, discuss all four questions, or discuss the first two.
min
● Conduct Fill-Up on Page 13:
■ Read Q4 aloud.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answer in your books.
● Conduct Find the Truth on Page 13:
■ Say: Let’s practice more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q5 aloud. Ask if it is true or false.
■ Invite some students to share responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answer in your books.
● Conduct Tick the Correct Answer on Page 14:
■ Say: Let’s test our learnings to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q1, 2, and 3 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● If time permits, discuss the section Answer in Short - Q4, 5 or, assign it as the homework.
● Conclude: Today, we learned about the fifth generation of computers and supercomputers.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ List some features of Fifth-generation computers.
Possible responses: faster; easier; cheaper to use; take less space; widely available; based on AI
■ Name computers you see in your daily life.
Possible Responses: Smartwatch; Phone; Laptop; Calculator.
● Assign the following as homework:
■ Answer in Short - Q4, and 5
■ Match Me
■ DIY – Fun time Q4 - 5
Note: Use the following points to prepare for the session beforehand. Avoid reading the points in the class.
● On a bright sunny day in Avora, Conji was flying on his magical broom.
● He recalled how he and Mel had overcome the challenges thrown by Lord Ero.
● Mel disguised herself as a dragon to prank Conji in the air.
● Mel agreed to compensate for the prank by teaching Conji about computers.
● Eva joined them on their journey of learning about computers.
● After their lesson, all of them headed towards the cafeteria to have lunch.
● Mel and Conji continue their discussion about Avora’s creation.
● They recall how the combination of magic and technology led to Avora’s birth.
● They recall Ms. Idea’s explanation of a spell that was given to the first wizard to save Avora from Lord Ero.
● Mel teaches Conji about Internet services as they study ancient Avora.
● The kids started looking for the special spell over the internet.
● Elder Wizard and Elder Robot hint at where they could find the spell.
The content covered in this chapter is aligned with the following CSTA Standard
● 1B-NI-04 – Networks and the Internet
1. Introduction to Internet
2. Internet Services
3. Basic Internet Terms
In this session, students will learn about –
● The Internet – introduction
● Internet Service providers

● Types of Internet connection
Keywords
● GBPS: Stands for GigaBits Per Second, Gbps is a method of measuring how much data is being transmitted per second
● Satellite: Refers to a machine that is launched into space and moves around Earth or another body in space
● Server: Main computer that accepts and responds to requests made over a network
Action Plan
● Recap the story covered in the previous chapter.
● Instruct: Let’s learn how the story moves ahead. We will read page 18.
● Read the story aloud OR invite two students to read the characters’ dialogue aloud.
● Say: Let me introduce what the Internet is.
CS Concepts Explain ISP
Types of ISP
As given in Panel 3 on Page 19
As given from Panel 4 on Page 19 to Panel 1 on Page 20
● Present the scenario: Consider your school wants to have an Internet connection.
● Discuss:
■ What elements will you require?
Possible Responses: computer; mouse; ISP; DSL; a computer lab; telephone line; satellite; fibre optics
■ Which type of connection would give your school the fastest internet speed?
Possible Responses: Fibre; DSL
■ What can you use the internet for at your school?
Possible Responses: Search for images; learn different concepts; watch videos; watch educational movies
■ Name some Internet service providers you are familiar with.
Possible Responses: Jio; Vodafone; Airtel; BSNL
● Conduct Fill Up on Page 27:
■ Say: Conji wants to add some pictures of their adventures from the safe. Let’s help Conji open the safe by filling in the blanks.
■ Read Q1, 3, 4, and 5 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● Conduct Find the Truth on Page 27:
■ Say: Let’s practise some more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q5 aloud. After the sentence, ask if it is true or false.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answer in your books.
● Conduct Answer in short on Page 29:
■ Say: Help Mel and Conji prepare for the final examinations by answering the question below.
■ Read Q1 aloud.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answer in your books.
● If time permits, discuss the section Tick the Correct Answer – Q2. Or, assign it as homework.
● Conclude: Today, we learned about the Internet, ISPs, and Types of Internet connections.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ What do you think will happen if the internet goes off for one entire day?
Possible Responses: we will be disconnected from the internet; we will not be able to access the internet; offices will be closed
■ For what purposes do you think you would need an Internet connection at your home?
Possible Responses: to get help with homework; to watch movies online; to read books; for parent’s office work; to shop online
● Assign the following as homework:
■ Tick the Correct Answer – Q2
■ DIY activity – Part B (Abbreviations) – Q1, 2, and 3.
In this session, students will learn about –
● WWW
● IP address
● Creating an Email account
● IP Address: Stands for Internet protocol address; a unique address that identifies a device on the internet or a local network
● WWW: Stands for World Wide Web. It is a collection of different websites you can access through the internet

● Email: Electronic mail; a way to send and receive messages over the internet
Recall and connect the story from the previous session
Discuss the key concepts covered –
WWW IP Email
Creating an Email account
Fill Up – Q2
Tick the Correct Answer – Q4 Answer in short – Q2
Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Recap the story and concepts covered in the previous session.
● Instruct: Let’s learn how the story moves ahead. We will learn more about the internet today.
● Say: Let me introduce you to WWW – World Wide Web.
WWW
IP Address
As given in Panel 2 on Page 20
As given in Panel 3 on Page 20
Email As given in Panel 1 on Page 21
Creating an Email account As given from Panel 2 on Page 21 to Panel 1 on Page 23
● Present the scenario: Consider you want to know about some good picnic spots near your town.
● Discuss:
■ How will you search for picnic spots using your smartphone?
Possible Responses: Internet; WWW; the web
■ What search words will you type?
Possible Responses: Picnic Spots near me; Picnic Spots in my city; Holiday spots; Nearby Mountains
■ After deciding on the picnic spot, what other information about it can you search for online?
Possible Responses: Water availability; Sports availability; Sanitation; Prime spot
■ Name the address of your computer.
Possible Responses: IP address; unique address; address of the computer
● Conduct Fill Up section on Page 27:
■ Say: Conji wants to add some pictures of their adventures from the safe. Let’s help Conji open the safe by filling in the blanks.
■ Read Q2 aloud.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answer in your books.
● Conduct Tick the correct answer on Page 28:
■ Say: Let’s practise more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q4 aloud. After the sentence, ask if it is true or false.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answer in your books.
● Conduct Answer in short on Page 29:
■ Say: Help Mel and Conji prepare for the final examinations by answering the question below.
■ Read Q2 aloud.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Write the final answer on the board so that students can note it down.
Note
● If time permits, discuss the section Find the truth – Q2, 3. Or, assign it as homework.
● Conclude: Today, we learned about WWW, IP address, Email, and email account creation using gmail.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ For what purposes do you use your email?
Possible Responses: Send messages, documents, image files; seek information about something
■ Suppose you wish to send messages to the tourism department of your town. Which internet service would you use?
Possible Responses: Email, Gmail; Outlook mail; Twitter
● Assign the following as homework:
■ Find the truth – Q2, 3
■ DIY activity – Part B (Abbreviations) – Q4, 5
Objectives
In this session, students will learn about –
● Social Media
● Social networking sites
■ Image-sharing sites
■ Video-hosting platforms

■ Community blogs
■ Instant messengers
Keywords
● Social Media: A community where we can connect with people across the world using an internet connection
Recall and connect the story and concepts from the previous session
Discuss the key concepts to be covered –
Social media
Social networking sites
Find the truth – Q1, 4 Tick the correct answer –Q1, 3, and 5 Answer in short – Q3, 4, 5
Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Recap the story and concepts covered in the previous session.
● Instruct: Let’s learn how the story moves ahead. We will learn more about social media today.
● Say: Let me tell you about social media, and various social networking websites.
CS Concepts Explain
Social Media
Social Networking Websites
As given in Panel 2 on Page 23
As given from Panel 2 on Page 23 to Panel 1 on Page 24
● Present the scenario: Let’s say you want to blog about your picnic experience.
● Discuss:
■ Where can you share your experience on the internet?
Possible Responses: Social media; social networking sites; Instagram; Facebook
■ Where can you blog about your picnic?
Possible Responses: Facebook; Discord; Tumblr; Medium
■ Where can you upload videos related to your picnic?
Possible Responses: YouTube; Vimeo; Instagram
■ Which app would you use to send instant messages to your friends and family about the picnic?
Possible Responses: WhatsApp; Messenger; Instagram
● Conduct Find the truth on Page 27:
14 min
■ Say: Conji wants to get pictures of their second adventure. Let’s help him by filling in the blanks.
■ Read Q1, and 4 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answer in your books.
● Conduct Tick the correct answer on Page 27:
■ Say: Let’s practise some more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q1, 3, 5 aloud. After the sentence of each question, ask the students about their answers.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answer in your books.
● Conduct Answer in short on Page 27:
■ Say: Help Mel and Conji prepare for the final examinations by answering the questions below.
■ Read Q3, 4, and 5 aloud.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Write the final answer on the board so that students can note them down.
● If time permits, discuss the section Match Me – Q1, 4 Or, assign it as homework.
min
● Conclude: Today, we learned about social media and various social networking sites.
● Ask the following probing question:
■ Which social media networking sites do members of your family use?
Possible Responses: Youtube; Prime Video; Netflix; Disney Hotstar; Zee5; LinkedIn; SonyLIV
■ Which platform would you use to watch your favourite movie?
Possible Responses: Youtube; Prime Video; Vimeo; Netflix; Disney Hotstar; Zee5
● Assign the following as homework:
■ Find the truth – Q1 and 4
■ DIY activity – Part A
Note: Use the following points to prepare for the session beforehand. Avoid reading the points in the class.
● Mel and Conji recalled how the combination of magic and technology led to Avora’s birth.
● They recalled Ms. Idea’s explanation of a spell that was given to the first wizard to save Avora from Lord Ero.
● Mel taught Conji about Internet services as they studied ancient Avora.
● Elder Wizard and Elder Robot gave them a hint to look for the spell over the internet.
● Mel and Conji try the spell that shielded Avora in the past.
● The spell fails.
● Elder Wizard and Elder Robot tell them about the First Elder Wizard.
● Mel and Conji learn about cyber security.
● They decide to visit the Idea Centre and ask Ms. Idea for clarifications.
The content covered in this chapter is aligned with the following CSTA Standard
● 1B-NI–05 Computing Systems
This chapter is divided into the following classroom sessions
1. Cyber Security, Hacker, Cyber Attack, Cyber Security Software, Malware
2. Types of Malware, Cyber Security Breaches and its Types
3. Data Loss Prevention Software and Ethical Hacking
In this session, students will learn about –
● Cyber Security
● Hacker
● Cyber Attack
● Cyber Security Software

● Malware
● Cyber Security: A process of protecting the personal data stored on our computers
● Hacker: A person who breaks into computers without permission
● Cyber Attack: An act of breaking into computers without permission
● Malware: Software designed to damage the computer system by getting access to personal information
Read or Invite students to read the story aloud and CS concepts covered in the previous chapter
Discuss cyber security, hacker, cyber attack, cyber security software, malware
Action Plan
● Recap the story covered in the previous chapter.
Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Read or Invite two students to read the story aloud from Page 32 to Panel 1 of Page 34 up to Elder Robot’s words, “Well then, disturb you.”
● Say: Let me explain what Cyber Security is all about.
● Present the scenario: Consider you wish to protect your home from thieves.
● Discuss:
■ What security systems should you use?
Possible Responses: install CCTV cameras; lock our homes; install burglar alarms; keep our important documents safe
■ Which activity in the cyber world is this scenario similar to?
Possible Responses: Cyber security; installing security software; password protection
■ Suppose you want to give a laptop to your family member who lives a distance from your house. How would you transport it safely?
Possible Responses: wrap the laptop in a cloth and deliver it; take a car to deliver it; do not tell many people about your plan; insure your laptop to prevent loss in case of theft
■ What do you think can happen if hackers get your personal information?
Possible Responses: Cyber bullying; identity theft; money loss; security loss
● If time allows, discuss all four questions, or discuss the first two.
● Conduct Fill Up on Page 44:
■ Say: Conji is stuck in a cage in the Avora jungle. Let’s help Conji fill in the blanks to open the cage.
■ Read Q2, 3, 4 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● Conduct Find the Truth on Page 44:
■ Say: Let’s practise some more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q1, 2 aloud, one by one. After each sentence, ask if it is true or false.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● Conclude: Today, we learned about Computer Security and Cyber Attacks.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ Why do you think you should not provide your personal information on a public platform?
Possible Responses: to prevent cyber stalking; to protect yourself and your family from cyberattacks; to prevent any financial loss
■ Why do you think cyber security is important?
Possible Responses: to protect our personal information; to shield our systems; to prevent hacking
● Assign the following as homework:
■ Brain Teasers: Answer in Short – Q1
In this session, students will learn about –
● Types of Malware
● Cyber Security Breaches
● Types of Security Breaches
Keywords
● Cyber Security Breaches: Events that provide hackers unauthorised access to our computer data, applications, networks, or devices
Revise the story and CS concepts covered in the previous session
Discuss the types of malware, cyber security breaches, types of security breaches

Fill Up – Q1, 5 Find the truth – Q3, 4 Answer in Short – Q2, 4, 5
Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Recap the story covered in the previous chapter.
● Read or Invite two students to read the story aloud on Panel 2 of Page 36 up to Conji’s words “Malware…the internet.”
● Say: Let me explain the types of Malware, Security Breach, and types of Security Breaches
CS Concepts Page Number
Types of Malware
Cyber Security Breach
Types of Security Breaches
As given from Panel 3 on Page 36 to Panel 1 on Page 38
As given in Panel 2 on Page 38
As given from Panel 3 on Page 38 to Panel 2 on Page 39
● Present the scenario: Consider you have a computer system
● Discuss:
■ You get an email containing a link which seems to be from a known source, what should you do?
Possible Responses: Open the link right away; check if it is actually from a known source; do not open it; do not provide personal information
■ Suppose you click on a link from an unknown source and it asks for your bank account information, what should you do?
Possible Responses: we should not provide any personal information; immediately close the link; safeguard your information by installing relevant software
■ Suppose you are creating a profile on a social media website, what information do you think you can give?
Possible Responses: Name; city; state; country
■ Which information should you not put in a public profile?
Possible Responses: Phone number; email account details; bank account information; complete address; OTP
● If time allows, discuss all four questions, or discuss the first two.
● Conduct Fill Up on Page 44:
■ Say: Conji is stuck in a cage in the Avora jungle. Let’s help Conji fill in the blanks to open the cage.
■ Read Q1, 5 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● Conduct Find the Truth on Page 44:
■ Say: Let’s practise some more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q3, 4 aloud, one by one. After each sentence, ask if it is true or false.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● Conduct Answer in Short on Page 46:
■ Say: Let’s help Conji face the last test by answering these questions.
■ Read Q2, 4, 5 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Write the final answers on the board so that students can take notes.
● If time permits, discuss the section Tick the Correct Answer – Q3 or, assign it as homework.
● Conclude: Today, we learned about types of Malware, Security Breach and its types.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ What devices do you think can be infected in a network?
Possible Responses: personal devices; USB drives; visited websites; laptops
■ What are the different types of malware that you can be exposed to?
Possible Responses: Virus; Worms; Spyware; Trojan
● Assign the following as homework:
■ Brain Teasers: Tick the Correct Answer – Q3
■ Brain Teasers: Match Me
■ DIY: Odd One Out – Q1, 3, 4
In this session, students will learn about –
● Data Loss Prevention Software

● Ethical Hacking
Keywords
● Data Loss Prevention Software: Prevents a cyber attack by detecting the possible cyber threats
● Ethical Hacking: A process of spotting any weaknesses in an application, system or organisation’s software so that the weaknesses can be removed and security can be increased
Read or Invite students to read the story aloud and CS concepts covered in the previous session
Discuss data loss prevention software, and ethical hacking
Find the Truth – Q5 Tick the Correct Answer – Q1, 2, 4, 5 Answer in Short – Q3
Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Recap the story covered in the previous chapter.
● Read or Invite two students to read the story aloud on Panel 1 of Page 40 up to Conji’s words, “So……… a cyberattack.”
● Say: Let me explain how we can prevent cyber attacks.
CS Concepts Page Number
Data Loss Prevention Softwares
Ethical Hacking
As given from Panel 1 of Page 40 to Panel 2 on Page 41
As given in Panel 4 on Page 41
● Present the scenario: Consider your mom uses a number of apps on her phone.
● Discuss:
■ How can you make sure that your mom’s personal information is safe in a network?
Possible Responses: Use VPNs; install data breach prevention softwares; use encrypted connection
■ Which Antivirus softwares can you use to spot and destroy a virus in case of virus attack?
Possible Responses: McAfee; Norton; Quick Heal; Kaspersky
■ How do you think the makers of the app would detect any weak points in the app’s network?
Possible Responses: Lawfully hacking; ethical hacking; legally breaking into the network and fixing the weak points
■ What do you think has happened if there is unauthorised access to one of the app’s data?
Possible Responses: it is hacked; data breach; identity theft
Note
● If time allows, discuss all four questions, or discuss the first two.
● Conduct Find the Truth on Page 44:
■ Say: Let’s practise some more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q5 sentence aloud. Ask if it is true or false.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● Conduct Tick the Correct Answer on Page 45:
■ Say: Let’s practise more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q1, 2, 4, 5 aloud, one by one. After the sentence, ask if it is true or false.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answer in your books.
● Conduct Answer in Short on Page 46:
■ Say: Let’s help Conji face the last test by answering the following questions.
■ Read Q3 aloud.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Write the final answers on the board so that students can take notes.
● If time permits, discuss the section Odd One Out from DIY – Q2 or, assign it as homework.
● Conclude: Today, we learned about Data Loss Prevention Software and Ethical Hacking.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ What will you do to prevent data loss from your computer?
Possible Responses: install data loss prevention software; install firewalls; Anti-spyware; Antivirus; VPN
■ Where do you think ethical hacking can be used?
Possible Responses: Banks; defence; intelligence agencies; government websites
● Assign the following from DIY as homework:
■ Search and Be Safe – Q1, 2
■ Answer in Short – Q1, 5
■ Odd One Out – Q2
Note: Use the following points to prepare for the session beforehand. Avoid reading the points in the class.
● Mel and Conji tried the spell that shielded Avora in the past, but it failed.
● Elder Wizard and Elder Robot told them about the First Elder Wizard who used the ancient spell to shield Avora.
● Mel and Conji learned about cyber security.
● They decided to visit the Idea Centre and ask Ms. Idea for clarification.
● Mel and Conji meet Ms Idea. and the muses in the Idea Centre.
● They seek answers from Ms. Idea about the spell.
● The muses try to calm the kids down and show them a slideshow.
● Mel and Conji learn about Google Slides.
The content covered in this chapter is aligned with the following CSTA Standard
● 1B-DA–06 Data Analysis
This chapter is divided into the following classroom and lab sessions
1. GIFs in Google Slides I
2. GIFs in Google Slides II
3. Adding Music and Videos in Slides I
4. Adding Music and Videos in Slides II
In this session, students will learn about –
● Adding GIFs on Google Slides
● Resizing a GIF
● Adding a GIF online
● Uploading a file to Google Drive
● GIF: Stands for Graphic Interchange Format and is a series of images or soundless video that loops continuously and doesn’t require anyone to press Play
Revise the story and CS concepts covered in the previous chapter
Read or Invite students to read the story of the chapter
Discuss what GIFs are, how to add GIFs, how to resize GIFs, and how to upload a file on Drive
Warm-Up
● Recap the story covered in the previous chapter.
● Recap the stor y covered in the previous chapter
● Recap the stor y covered in the previous chapter
● Say: There arenew characters in this chapter
● Say: There are new characters in this chapter.
● Say: There arenew characters in this chapter
● Introduce Ms. Idea and the muses to the students.
● Introduce Ms Idea and the muses to the students
● Introduce Ms Idea and the muses to the students


● Instruct: Let's learn how the stor y moves ahead We will read from Page 50 to Panel 2 on Page 56 up to to our slides in the text
● Instruct: Let’s learn how the story moves ahead. We will read from Page 50 to Panel 2 on Page 56 up to “to our slides” in the text.
● Instruct: Let's learn how the stor y moves ahead We will read from Page 50 to Panel 2 on Page 56 up to “to our slides” in the text
● Read the stor y aloud OR invite 4 students to read the characters’ dialogue ●
● Read the stor y aloud OR invite 4 students to read the characters dialogue ●
● Read the story aloud OR invite 4 students to read the characters’ dialogue.

● Say: Let me explain GIFs to you.
If you are teaching without a projector
If you are teaching with a projector
Open Google Slides on your computer system
CS Concepts Explain Demonstrate
Adding a GIF As given in Panel 3 on Page 52
How to add GIFs from a computer. Resizing a GIF As given in Panel 1 on Page 54
Adding an Online GIF As given in Panel 3 on Page 54
Upload a file to drive As given in Panel 1 on Page 56
How to resize GIFs.
How to add online GIFs in slides.
How to upload a file to drive.
● Present the scenario: Consider you are creating a project on Languages of the World on Google Slides.
● Discuss:
■ How will you make your project interesting?
Possible Responses: We can add elements like - Text; Images; Shapes; Videos; GIFs; Music etc.
■ What steps will you follow to add the GIFs to the slides?
Possible Responses: Click Insert, select GIF, select “Upload from Computer”; upload from the web; Select from the web.
■ What are the options for saving your project for future use?
Possible Responses: Save on your computer; Save on Google Drive; Save on a hard disk; pendrive/flash drive etc.
■ Why do we use Google Slides?
Possible Responses: To create presentations for school; projects; product introductions; sales; explaining concepts; pictorial and interactive ways of presenting information.
● Conduct Fill Up on Page 61:
■ Say: Mel’s grandmother is trapped by the witches. Let’s help Mel rescue her by filling in the blanks.
■ Read Q1, 2, and 5 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● Conduct Tick the Correct Answer on Page 62:
■ Say: Let’s practise some more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q1, 4, and 5 aloud, one by one. After the sentence, ask which of the options is correct.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answer in your books.
Note
● If time permits, discuss Brain Teaser Find the Truth – Q 3, 4, and 5 else, assign it in the homework.
Chapter 4
• Getting Started with Google Slides
● Conclude: Today, we learned to add GIFs to Google Slides from the computer and from the web, resize GIFs, and upload files on Google Drive.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ For what purposes do you think you would need to insert a GIF in a slide?
Possible Responses: Digital Greeting Card; Project Work; Invitation; Memes
■ What can you do with a GIF in slides?
Possible Responses: Add a GIF (from the computer or from the Web); resize a GIF; Drag a GIF to a different location
● Assign the following as homework:
■ From Brain Teaser – Find the Truth – Q3, 4, and 5
■ From DIY Activity – Answer in Short

In this session, students will apply what they learned from the previous class to complete tasks on Google Slides.
● GIF: Stands for Graphic Interchange Format and it is a series of images or soundless video that loops continuously and doesn’t require anyone to press Play
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Say: Let’s revise what we have learned.
● Instruct: Go to the Panel and open Lab on Images in GIFs in Google Slides - II.
● Show slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slide in the panel.
● Discuss the following questions one by one to check students’ understanding:
■ When would you need to add GIFs while creating slides?
Possible Responses: To make digital greeting cards; project work; invitations.
■ If you wished to create a project in Google Slides, which topic would you choose?
Possible Responses: Invitation cards; Stories and comics for children; a recipe cookbook; Social media posts; Diplomas and certificates; A journal; An eBook.
■ Which elements would you add to your project?
Possible Responses: image; text; title; GIFs; videos; music.
Chapter 4
• Getting Started with Google Slides
■ Why do we need to resize an inserted GIF in Google Slides?
Possible Responses: To get rid of unwanted parts of a GIF; to customise the GIF; to reduce the size; to make the GIF bigger or smaller.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Address if students have any other doubts related to the concepts presented in the slides.
● Instruct: We know how to insert and resize a GIF on Google Slides.

● Now, let’s practise our learning. Click on the Practice button on the Assignment page to attempt the activity.
● Click on the Attempt button to open the activity page.
● Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
● Instruct: Click on Confirm button to submit your work when you are done with the activity.
● Instruct: Click on Confirm button to submit your work when you are done with the activity.
● Conclude: Today, we have learned how to add GIFs to Google Slides and upload files on Drive.
● Instruct: Practise the same activity at home.
● Assign the following as homework:
● Conclude: Today, we have learned how to add GIFs to Google Slides and upload files on Drive
■ Project: Make a project on one of the topics that you wanted to create a project on (Invitation cards/Stories and comics for children/a recipe book/Social media posts/ Diplomas and certificates/A journal/An eBook) using the tools you learnt today.
● Instruct: Practise the same activity at home.
● Assign the following as homework:
● The project is optional, kindly assign as per feasibility.
○ Project: Make a project on one of the topics that you wanted to create a project on (Invitation cards/Stories and comics for children/ a recipe book / Social media posts/Diplomas and cer tificates/A journal/ An eBook) using the tools you learnt today.

In this session, students will learn how to –
● Add music in Google Slides
● Add videos in Google Slides
Keywords
● YouTube: Is a video-sharing service where users can watch, like, share, comment and upload their own videos
● URL: Stands for Uniform Resource Locator and is the address of a given unique resource/page on the Web
Revise the story and CS concepts covered in the previous chapter
Read or Invite students to read the story of the chapter
Fill
Up
Q2, 3
2
● Recap the story covered in the previous session.
● Invite a few students to recall the CS concepts covered in the previous session.
● Say: Let me explain how we can add music and videos in Google Slides.
Scenarios
If you are teaching with a projector
Open Google Slides on your computer system
CS Concepts Explain Demonstrate
Add music to slides
As given in Panel 1 on Page 57
If you are teaching without a projector OR
Add video from YouTube As given in Panel 2 on Page 58
Add video using URL As given in Panel 3 on Page 58
Chapter 4
• Getting Started with Google Slides
How to add music to slides
How to add video from YouTube
How to add video using URL
● Present the scenario: Consider you are creating a project on Cultures of the World on Google Slides.
● Discuss:
■ What elements will you add to the project?
Possible Responses: Text; Images; Shapes; Videos; Music; GIFs; etc.
■ What steps will you follow to add the videos to the slides?
Possible Responses: Click on insert → select “Video” → select “YouTube”; Click on insert → select “Video” → select “Google Drive”; Click on insert → select video → paste the link in the URL bar.
■ What steps will you follow to add the music to the slides?
Possible Responses: Click on insert → select “Audio” → select “Google Drive”; Click on insert → select “Audio” → paste the link in the URL bar.
■ What sources will you use to collect data for your project?
Possible Responses: Internet; books; magazines; newspapers; encyclopedias.
● Conduct Fill Up on Page 61:
■ Say: Mel’s grandmother is trapped by the witches. Let’s help Mel rescue her by filling in the blanks.
■ Read Q3 and 4 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● Conduct Tick the Correct Answer on Page 62:
■ Say: Let’s practise some more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q2 and 3 aloud, one by one. After the sentence, ask which of the options is correct.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Tick the final answers in your books.
● Conduct Find the Truth on Page 63:
■ Say: Let’s practise some more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q1 and 2 aloud, one by one. After each sentence, ask if it is true or false.

■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● If time permits, discuss Brain Teaser Match Me or assign it as homework.
● Conclude: Today, we learned about adding music and videos to slides in Google Slides.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ Where do you think presentations can be used?
Possible Responses: demonstrations; introductions; lectures; presenting a new idea/ product etc.
■ How are presentations made more interactive?
Possible Responses: By adding charts; images; videos; music; animations; transitions etc.
● Assign the following Brain Teaser exercises as homework:
■ Match Me
■ Answer in Short
In this session, students will learn how to –
● Add music in Google Slides
● Add videos in Google Slides
● YouTube: Is a video-sharing service where users can watch, like, share, comment and upload their own videos.
● URL: Stands for Uniform Resource Locator and is the address of a given unique resource/page on the Web
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Say: Let’s revise what we have learned.
● Instruct: Go to the Panel and open Lab on Music & Videos in Slides – II.
● Show slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slide in the panel.
● Discuss the following questions one by one to check students’ understanding:
■ When would you need to add music to slides?
Possible Responses: To make the slides better; for fun; to explain better; for effect
Chapter 4 • Getting Started with Google Slides
■ When would you need to add videos to slides?
Possible Responses: To make the students learn concepts visually; to present a visual to the audience; it makes the presentation interactive; engaging
■ What options are available in the Insert tab?
Possible Responses: We can add Image; GIF; Video; Audio
■ Are you aware of other applications similar to Google Slides?
Possible Responses: Prezi; Canva; Microsoft Powerpoint; Pitch; GeniallyApple Keynote; Microsoft Powerpoint Online; Adobe Presenter.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Address if students have any other doubts related to the concepts presented in the slides.
● Instruct: We know how to add music and videos in Google Slides.
● Now, let’s practise our learning. Click on the Practice button on the Assignment page to attempt the activity.
● Click on the Attempt button to open the activity page.
● Make the students practice the activity till the concepts in the session are covered.
● Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
● Instruct: Click on Confirm button to submit your work when you are done with the activity.
● Instruct: Click on Confirm button to submit your work when you are done with the activity
● Conclude: Today, we have learned how to add music and videos in Google Slides.
● Conclude: Today, we have learned how to add music and videos in Google Slides
● Instruct: Practise the same activity at home.
● Instruct: Practise the same activity at home
● Assign the following as homework:
● Assign the following as homework:
○ Project: Make a project on Various Cultures’ Music and complete the tasks mentioned in the Lab Time activity on Page 66 in your book
■ Project: Make a project on Various Cultures’ Music and complete the tasks mentioned in the Lab Time activity on Page 66 in your book.
● The project is optional, kindly assign if feasible.

Note: Use the following points to prepare for the session beforehand. Avoid reading the points in the class.
● Mel and Conji met Ms. Idea and the muses at the Idea Centre.
● Mel and Conji had unravelled the mystery of the spell.
● They sought answers from Ms. Idea about the spell.
● The muses tried to calm the kids down and showed them a slideshow.
● Mel and Conji started learning about Google Slides.
● Mel and Conji are in Ms. Idea’s office with the muses.
● Ms. Idea tells the two about the spell and asks them to create a shield over Eva to save her from Lord Ero.
● Ms. Idea tells Mel and Conji when to cast the spell on Lord Ero.
● The two wish to leave for Avora but according to the protocol they have to finish the concepts on Google Slides first.
● Mel and Conji go back to Avora and save Eva but soon they realise the great risk.
The content covered in this chapter is aligned with the following CSTA Standard
● 1B-DA–06 Data & Analysis
This chapter is divided into the following classroom and lab sessions
1. Animations in Google Slides I
2. Animations in Google Slides II
3. Transitions in Google Slides I
4. Transitions in Google Slides II
In this session, students will learn about –

● Animations
● Types of animations in Google Slides
● How to apply animations
Keywords
● Animation: The process of giving the illusion of movement to drawings, models, or objects
Warm-Up Engage Build Sum-Up
Revise the story and CS concepts covered in the previous chapter
Read or Invite students to read the story of the chapter
Discuss animations, types of animations in Google Slides, and how to apply animations
Fill Up – Q1, 2, 3 Find the truth – Q1, 4, 5
Conclude the concepts Assign homework
Action Plan
● Recap the story covered in the previous chapter.
● Read or Invite two students to read the story aloud from Page 68 to Panel 1 of Page 70 up to the muse’s words, “Teach Conji now. ”
min
Scenarios
If you are teaching with a projector Open Google Slides on your computer system
CS Concepts Explain Demonstrate
What are animations As given in Panel 2 on Page 70
If you are teaching without a projector OR
Adding an animation As given in Panel 1 on Page 71
Fly in from Left As given in Panel 1 on Page 72
Fade in As given in Panel 2 on Page 72
Fly in from bottom As given in Panel 1 on Page 73
Show an illustration of animated images to students
How to add animations to an object in Google Slides.
Show the effect of using this animation.
Show the effect of using this animation.
Show the effect of using this animation.
● Present the scenario: Consider you have created a project on Google Slides. (You can refer to the one created in the previous chapter)
● Discuss:
■ What objects of your presentation would you like to animate?
Possible Responses: shapes; characters/images; text.
■ Why do you want to add animations?
Possible Responses: becomes appealing; interactive; interesting.
■ Suppose you want to add animations to a text box added on a slide. How will you do that?
Possible Responses: Select the text box → Click on insert → select “Animation” → select “Fade in” from the Animation Pane; Choose Fly from left; Fly-in from bottom.
■ How can you make your presentation interactive?
Possible Responses: add images; videos; GIFs; animations; transitions; music; text in different fonts and styles.
Note
If time allows, discuss all four questions, or discuss the first two.
● Conduct Fill Up on Page 79:
■ Say: Eva needs to write some notes. Let’s help Eva fill in the blanks to get the points.
■ Read Q1, 2, and 3 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● Conduct Find the Truth on Page 79:
■ Say: Let’s practise some more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q1, 4, and 5 aloud, one by one. After each sentence, ask if it is true or false.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Write the final answers in your books.
Note
If time permits, discuss Brain Teaser Answer in Short – Q1, 2, and 4 or assign them as homework.
● Conclude: Today, we learned about animations in Google Slides.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ Where have you seen the use of animations in your day-to-day life?
Possible Responses: animated movies; cartoons; animated motion pictures; reels; animated rhymes.
■ Which is your favourite animated movie/cartoon?
Possible Responses: Chota bheem; Motu Patlu; Shiva; Rudra; The Super Mario Bros.; Mummies; Demon Slayer: Kimetsu No Yaiba - To the Swordsmith Village (2023); The Boss Baby: Christmas Bonus; Brown and Friends.
● Assign the following Brain Teaser exercises as homework:
■ Answer in Short – Q1, 2, and 4
■ Answer in Detail – Q1, 3, and 4
In this session, students will apply what they learned from the previous class to complete tasks on Google Slides.
● Animation: The process of giving the illusion of movement to drawings, models, or objects
Present the slides on Animations in Slides – II on Tekie Platform
Discuss the topics covered in the slides Attempt the activity on the Assignment page Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Say: Let’s revise what we have learned.
● Instruct: Go to the Panel and open Lab on Animations in Slides – II.
● Show slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slide in the panel.
● Discuss the following questions one by one to check students’ understanding:
■ Why would you need to add animations while creating slides?
Possible Responses: To make it interesting; interactive; appealing.
■ If you wish to create an animated project in Google Slides, which topic would you choose?
Possible Responses: Air Pollution; Water Crisis; Festivals or Events; Children’s Day; Indian culture and heritage; about Yourself; My Aim In Life; Value of Time.
■ Which elements would you animate in your project?
Possible Responses: image; text; title; GIFs; videos; shapes; charts.

■ What type of animation can you apply to objects in Google Slides?
Possible Responses: Fly-in from left; fly-in from bottom; fade-in.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Address if students have any other doubts related to the concepts presented in the slides.
● Instruct: We know how to add animations to objects on Google Slide.
● Now, let’s practise our learning. Click on the Practice button on the Assignment page to attempt the activity.
● Click on the Attempt button to open the activity page.
● Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
● Instruct: Click on the Confirm button to submit your work when you are done with the activity.
● Conclude: Today, we have learned how to add animations to objects in Google Slides.
● Instruct: Practise the same activity at home.
● Assign the following as homework:
■ Lab time
Note
The project is optional, kindly assign if feasible.
In this session, students will learn –

● What transitions are
● How to add transitions to Google Slides
● How to control the speed of transitions
Keywords
● Transition: The visual effect that occurs when you move from one slide to the next during a presentation
Revise the story and CS concepts covered in the previous chapter
Read or Invite students to read the story of the chapter
Discuss what are transitions, how to add transitions to Google Slides, and how to control the speed of transitions
● Recap the story covered in the previous session.
● Invite a few students to recall the CS concepts covered in the previous session.
● Read or Invite two students to read the story aloud from Panel 1 Page 74.
● Say: Let me explain transitions in Google Slides.
If you are teaching without a projector
Scenarios
If you are teaching with a projector Open Google Slides on your computer system
CS Concepts Explain Demonstrate
Add transitions
Adjust the speed of transitions
As given in Panel 1 on Page 74
As given in Panel 1 on Page 75
OR
How to add transitions to slides
How to control the speed of transitions
● Present the scenario: Consider you are creating a project on Heritage of India on Google Slides.
● Discuss:
■ How will you find information for your project?
Possible Responses: Books; encyclopaedias; internet; magazines; journals; newspapers.
■ What elements will you add to the project?
Possible Responses: Text; Images; Shapes; Videos; Music; GIFs; animations; transitions.
■ Why do you want to add transitions?
Possible Responses: for smooth and clear transitions; helps the audience to shift their attention from one idea to the other; makes it appealing; visually enhances the presentation.
■ How will you add transitions to a slide?
Possible Responses: Select the slide → Click on “Slide”→ select “Transition” → select the effect like “Fade in” from the Transition Pane; Choose effects like Dissolve; Fade; Flip; Cube.
● Conduct Fill Up on Page 79:
■ Say: Eva has to write a few notes. Let’s help her by filling in the blanks.
■ Read Q4 and 5 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● Conduct Find the Truth on Page 79:
■ Say: Let’s practise some more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q2 and 3 aloud, one by one. After each sentence, ask if it is true or false.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● Conduct Answer in Detail on Page 82:
■ Say: Let’s help Eva prepare a presentation on Google Slides by answering the questions in detail.
■ Read Q2 and 5 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Write the final answers on the board so that students can take notes.
If time permits, discuss Brain Teasers Match Me and Tick the Correct Answer else, assign it in the homework.
● Conclude: Today we learned about Transitions in Google Slides.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ Where do you think presentations can be used?
Possible Responses: demonstrations; introduction; lecture; present a new idea/product.
■ How are presentations made more interactive?
Possible Responses: By adding charts; images; videos; music; animations; transitions.
● Assign the following exercises as homework:
■ Brain Teasers: Tick the Correct Answer
■ Brain Teasers: Match Me
■ DIY
In this session, students will apply what they have learned from the previous class to complete tasks on Google Slides.
● Transition: The visual effect that occurs when you move from one slide to the next during a presentation
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Say: Let’s revise what we have learned.
● Instruct: Go to the Panel and open Lab on Transitions and Presentations Slides –II

● Show slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slide in the panel.
● Discuss the following questions one by one to check students’ understanding:
■ Which is the first transition that you would like to try?
Possible Responses: Dissolve; Fade; Cube; Flip; Gallery; Slide from left; Slide from right
■ Why do you think we call them Transitions?
Possible Responses: Transition means from one to the other; transitions from one slide to another; go from one idea to another
■ How do we add transitions to slides?
Possible Responses: Click on “Slide” menu → Select “Transitions” → Select a transition → Adjust the speed → Play and see the preview → Apply to current slide or all the slides
■ What options are available under the Slide menu?
Possible Responses: New slide; Duplicate Slide; Delete Slide; Transition; Skip slide; change background etc
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Address if students have any other doubts related to the concepts presented in the slides.
Build
● Instruct: We know how to add transitions in Google Slides.
15 min
● Now, let’s practise our learning. Click on the Practice button on the Assignment page to attempt the activity.
● Click on the Attempt button to open the activity page.
Make the students practice the activity up to the concepts covered in the session.
● Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
● Instruct: Click on the Confirm button to submit your work when you are done with the activity.
Sum-Up
● Conclude: Today, we have learned about Transitions in Google Slides.
● Instruct: Practise the same activity at home.
● Assign the following as homework:
5 min
■ Project: Make a project on your hobbies (things that you like to do) and add transitions to the slides.
The project is optional, kindly assign as if feasible.
Chapter 5
• Advanced Features of Google Slides
Note: Use the following points to prepare for the session beforehand. Avoid reading the points in the class.
● Mel and Conji were in Ms. Idea’s office with the muses.
● Ms. Idea told the two about the spell and asked them to create a shield over Eva to save Eva from Lord Ero.
● Ms. Idea told Mel and Conji when to cast the spell on Lord Ero.
● The two wished to leave for Avora but according to the protocol they had to finish the concepts on Google Slides first.
● Mel and Conji went back to Avora and saved Eva but soon they realised the great risk.
● Mel and Conji land in a strange place where they meet Joy.
● The duo recalls the incident that took place just before they landed there.
● Joy takes them around the new place which is the Ministry of Happiness.
● They start learning about Google Sheets.
● Mel and Conji wish to check the Happiness index of Avora.
The content covered in this chapter is aligned with the following CSTA Standard
● 1B-DA–06 Data & Analysis
This chapter is divided into the following classroom and lab sessions
1. Basics of Google Sheets I
2. Basics of Google Sheets II
3. Google Sheets Tools I
4. Google Sheets Tools II
In this session, students will learn about –

● What are Google Sheets and how to open them
● Uses of Google Sheets
● What is a cell and cell address
● Entering data in cells
● Google Sheets: Are made up of rows and columns and are used to store and analyse data
● Cell Address: A combination of the column letter and row number that identifies a cell

Revise the story and CS concepts covered in the previous chapter
Read or Invite students to read the story of the chapter
their uses; what cells are
how we name them
Action
Plan
● Recap the story covered in the previous chapter.
min
If you are teaching with a projector
Open Google Sheets on your computer system
CS Concepts Explain Demonstrate
What are Google Sheets and their uses
How to open Sheets As given in Panel 1 on Page 89
What is a cell
As given in Panels 3 and 5 on Page 88
If you are teaching without a projector OR
As given in Panel 2 on Page 89
Naming cell/Cell Address As given in Panel 1 on Page 90
Data types in cells As given in Panels 2 and 3 on Page 91, and Panel 1 on Page 92
Show what sheets look like.
How to open Google Sheets.
Show what a cell looks like.
Show how we name cells.
Show how we enter data in cells.
● Present the scenario: Consider your teacher asks you to help her store the marks of all the students in the class.
● Discuss:
■ What uses and benefits will you tell her to convince her to use Google Sheets?
Possible Responses: sheets are used to edit; analyse; organise data; we can perform mathematical calculations; we can collaborate and work on the same document simultaneously.
■ For what other purpose can you use Google Sheets?
Possible Responses: Keeping track of cricket scores; Maintaining records of pocket money.
■ What kind of data can be added in cells?
Possible Responses: Plain text or names and special characters (like _ * % $ @); numbers; currency; date; time; percentage; formulas.
■ How can you perform calculations in Sheets?
Possible Responses: use built-in formula like SUM and auto sum features; Add cell address like =(a1+a2… so on); AVERAGE(Cell1: cell_n).
● If time allows, discuss all four questions, or discuss the first two.
● Conduct Fill Up on Page 97:
8 min
■ Say: Let’s help Eva fill in the blanks and find some unusual creatures that she has seen.
■ Read all the questions aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● Conduct Tick the Correct Answer on Page 98:
■ Say: Let’s practise some more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q1, 2, and 3 aloud, one by one. After the sentence, ask which of the options is correct.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Mark the final answers in your books.
● If time permits, discuss Brain Teaser Answer in One Line – Q1, 2, and 3 or assign them as homework.
• Getting Started with Google Sheets
● Conclude: Today, we learned about the basics of Google Sheets.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ Who can use Google Sheets (people/occupations)?
Possible Responses: teachers; accountants; salespeople; analysts; businessmen; corporate workers.
■ Do you know any other platforms/software that do the same work as Google Sheets?
Possible Responses: Microsoft Excel; Libreoffice Calc; Smartsheets; Zoho sheets; Airtable.
● Assign the following Brain Teaser exercises as homework:
■ Answer in One Line – Q1, 2, and 3
■ Answer in Detail – Q2, 3, and 4

In this session, students will apply what they learned from the previous class to complete tasks on Google Slides.
● Google Sheets: Are made up of rows and columns and are used to store and analyse data
● Cell Address: A combination of the column letter and row number that identifies a cell
Present the slides on Intro to Google Sheets – II on
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Say: Let’s revise what we have learned.
● Instruct: Go to the Panel and open Lab on Intro to Google Sheets – II.
● Show slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slide in the panel.
● Discuss the following questions one by one to check students’ understanding:
■ What are the uses of Sheets?
Possible Responses: sheets are used to edit; analyse; organise data; we can perform mathematical calculations; we can collaborate and work on the same document simultaneously.
■ How do we open Sheets?
Possible Responses: From our Google Drive; type in the URL for sheets and press the new + button.
■ How and what kind of data can be added to cells?
Possible Responses: just type in the cells; add numbers; text; percentages; currency; date; formulas.
■ How do we name cells in Google Sheets? (ask the students to give the cell address of a few cells – give them random row and column numbers)
Possible Responses: column letter row number
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Address any other doubts students may have related to the concepts presented in the slides.
● Instruct: We know a few basics of Google Sheets.
● Now, let’s practise our learning. Click on the Practice button on the Assignment page to attempt the activity.
● Click on the Attempt button to open the activity page.
● Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
● Instruct: Click on the Confirm button to submit your work when you are done with the activity.

● Conclude: Today, we have learned a few basic concepts of Google Sheets.
● Instruct: Practise the same activity at home.
● Assign the following as homework:
■ Lab time on Page 101
● The project is optional. Kindly assign if feasible.
In this session, students will learn –
● What are header cells
● Hide/unhide options
● Spell check
● Find and replace tools
Keywords
● Header Cell: Is the cell containing the heading
● Spell check: A tool in the menu that checks for and suggests correct spelling
● Find and replace: A tool in the Edit menu that helps find and replace words
● Hide/unhide: Is a functionality in Google Sheets where we can hide and unhide worksheets
Revise the story and CS concepts covered in the previous chapter
Read or Invite students to read the story of the chapter
Discuss what header cells are, how we can hide and unhide sheets
Tick the Correct Answer – Q4, 5 Answer in One Line – Q 4, 5 Answer in Detail – Q1, 5
Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Recap the story covered in the previous session.
● Invite a few students to recall the CS concepts covered in the previous session.
● Say: Let me explain some features of Google Sheets. Scenarios
If you are teaching without a projector
If you are teaching with a projector
Open Google Sheets on your computer system
CS Concepts Explain Demonstrate
Header Cells
As given in Panel 2 on Page 92
Hide/unhide As given in Panel 2 on Page 93
Spell Check As given in Panel 3 on Page 93
Find and replace As given in Panel 1 and 2 on Page 94 and Panel 1 on Page 95
Find and replace all
Chapter 6
As given in Panel 1 and 2 on Page 94 and Panel 1 on Page 95
• Getting Started with Google Sheets
OR
What are header cells
Show how to hide/unhide worksheets
Show how to use spell check on Sheets
Show how to use find and replace
Show how to use find and replace all
● Present the scenario: Consider you have a lot of data in a workbook that contains multiple sheets.
● Discuss:
■ How will you find information about a person in the list/data?
Possible Responses: use find functionality; use filters.
■ You need to perform some calculations on the data. On what kind of data is it possible? What functions can be used?
Possible Responses: on numbers; SUM(); AVERAGE(); COUNT(); PRODUCT() .
■ There are multiple instances where the spelling of a student’s name is written incorrectly. Can you change it? How?

Possible Responses: Yes we can change it; Use the find and replace functionality; we can find the instances and change manually.
■ You want to name sheets so that they are clear to your teacher. What will you do?
Possible Responses: Rename sheets to show the classes the teacher takes; rename sheets according to the subjects the teacher teaches.
● Conduct Tick the Correct Answer on Page 98:
■ Say: Help Mel find the Roboman’s family by choosing the correct option.
■ Read Q4 and 5 aloud, one by one. After the sentence, ask which of the options is correct.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Tick the final answers in your books.
● Conduct the Answer in One Line on Page 99:
■ Say: Let’s answer the questions in one line.
■ Read Q4 and 5 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Write the final answers on the board so that students can take notes.
● Conduct Answer in Detail on Page 99:
■ Say: Let’s help Eva answer the questions in detail.
■ Read Q1 and 5 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Write the final answers on the board so that students can take notes.
● If time permits, discuss Brain Teasers Match Me or assign it as homework.
● Conclude: Today we learned about some tools in Google Sheets.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ What is the benefit of sheets?
Possible Responses: we can collaborate with multiple people; we can give access to selected people; we can add data in tabular form; helps us perform calculations on data; analysing is easier.
■ What tools/functionality are you aware of with Google Sheets?
Possible Responses: We can add charts; edit information to present well; data visualisation.
● Assign the following exercises as homework:
■ Brain Teasers: Match Me
■ DIY
In this session, students will apply what they have learned from the previous class to complete tasks on Google Sheets.
● Header Cell: Is the cell containing the heading
● Spell check: A tool in the menu that checks for and suggests correct spelling of words
● Find and replace: A tool in the Edit menu that helps find and replace words
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Say: Let’s revise what we have learned.
● Instruct: Go to the Panel and open Lab on Google Sheets Tools – II.
● Show slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slide in the panel.
● Discuss the following questions one by one to check students’ understanding:
■ Name a few tools that we can use in Google Sheets?
Possible Responses: Spell check; Find and replace; autocomplete; arithmetic functions.
■ Name a few mathematical functions and how we can use them?
Possible Responses: SUM(); AVERAGE(); COUNT(); PRODUCT(); we start typing in the cell which should contain the answer/result; each function begins with an = (equal to) sign.
■ How can we add and rename sheets?
Possible Responses: Click on + → Click on the small triangle just beside the sheet tab → Select an option to duplicate/rename the sheet; double-click on the sheet and rename it.
■ In what case can we use the find and replace functionality?
Possible Responses: to find words/names in a sheet; to replace data; to find data; to look for particular information.
• Getting Started with Google Sheets
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Address any other doubts students may have related to the concepts presented in the slides.
15 min
● Instruct: We know a few features that we can use in Google Sheets.
● Now, let’s practise what we have learned. Click on the Practice button on the Assignment page to attempt the activity.
● Click on the Attempt button to open the activity page.
● Make the students practise the activity up to the concepts covered in the session.
● Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
● Instruct: Click on the Confirm button to submit your work when you are done with the activity.

Sum-Up
● Conclude: Today, we have learned about Tools in Google Sheets.
● Instruct: Practise the same activity at home.
● Assign the following as homework:
■ Activity II on Page 95.
■ Case Study on Page 100.
The case study is optional, kindly assign if feasible.
5 min
Note: Use the following points to prepare for the session beforehand. Avoid reading the points in the class.
● Mel and Conji landed in a strange place where they met Joy.
● The duo recalled the incident that took place just before they landed there.
● Joy took them around the new place which is the Ministry of Happiness.
● They started learning about Google Sheets.
● Mel and Conji wished to check the Happiness Index of Avora.
● Mel and Conji meet Mr. Fate.
● Mr. Fate is just about to tell the kids about the Happiness Index when he is called to Mr. Times’ office for an urgent meeting.
● Meanwhile, the kids learn more about Google Sheets with Joy.
● Mr. Time informs Mr. Fate about the change in the Happiness Index of Avora due to the kids’ entry into the Ministry of Happiness.
● Mr. Fate is worried about how he will break this news to the kids.
The content covered in this chapter is aligned with the following CSTA Standard
● 1B-DA–06 Data Analysis
This chapter is divided into the following classroom and lab sessions
1. Text Formatting in Sheets I
2. Text Formatting in Sheets II
3. Cells in Sheets I
4. Cells in Sheets II
In this session, students will learn about –
● What is formatting
● How to change font size
● How to change font style
● How to change font colour
● Formatting a cell: Changing the appearance of a cell
● Font: The design of letters or numbers in a cell

Revise the story and CS concepts covered in the previous chapter
Read or Invite students to read the story of the chapter
Discuss formatting, font, how to change the font size, font style, and font colour of the text in cells
Fill Up
Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Recap the story covered in the previous chapter.
● Say: There are new characters in this chapter.
● Introduce Mr. Fate and Mr. Time to the students.

● Instruct: Let’s learn how the story moves ahead. We will read from Page 104 to Panel 1 on Page 107 up to “Let’s start with changing the font size.” in the text.
● Read the story aloud OR invite 4 students to read the characters’ dialogue.

● Say: Let me explain formatting to you.
If you are teaching without a projector
If you are teaching with a projector
Open Google Sheets on your computer system
CS Concepts Explain Demonstrate
formatting
As given in Panel 6 on Page 106
OR
Explain what formatting is. font As given in Panel 1 on Page 107
What is a font?
How to change the font size? changing the font style As given in Panel 2 on Page 107
changing the font size As given in Panel 1 on Page 107
How to change the font style? changing the font colour As given in Panel 1 on Page 108
How to change the font colour?
● Present the scenario: Consider you have created a data sheet in Google Sheets.
● Discuss:
■ How will you make your data look interesting?
Possible Responses: We can format text; change font size; font colour; font style
■ How can you change the font size of text?
Possible Responses: Select the text → change the font size in the toolbar; Ctrl + Shift + . ; Ctrl + Shift +, .
■ Name a few font styles that we can use in Sheets.
Possible Responses: Arial; Comic Sans; Georgia; Robota; Verdana; Muli; Impact.
■ How can we add new colours for use in Sheets?
Possible Responses: In the toolbar we click on the A (Font color) option → From the drop-down click on the + symbol in the Custom color option → select any colour from the palette.
10 min
● Conduct Fill Up on Page 115:
■ Say: Let’s fill in the blanks.
■ Read Q1 and 2 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● Conduct Tick the Correct Answer on Page 116:
■ Say: Let’s practise some more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q2 aloud, one by one. After the sentence, ask which of the options is correct.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Mark the final answer in your books.
● Conduct Find the Truth on Page 117:
■ Say: Let’s practise some more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q1 and 2 aloud, one by one. After each sentence, ask if it is true or false.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
Note
● If time permits, discuss DIY Find the Truth – Q3 or assign it as homework.
● Conclude: Today, we learned about formatting in Google Sheets.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ Why do we need formatting?
Possible Responses: To make the data look presentable; to make it easier to understand; to modify content for clarity.
■ Why do we use Google Sheets?
Possible Responses: to add data in a tabular form; to store data in one location; to store data once and then access it anytime using the internet; we can collaborate and work simultaneously on the sheets; we can give access to people we want to share the data with and hence providing data security.
● Assign the following DIY Activity as homework:

■ Find the Truth – Q3
■ Fill Up
In this session, students will apply what they learned from the previous class to complete tasks on Google Sheets.
● Formatting a cell: Changing the appearance of a cell
● Font: The design of letters or numbers in a cell
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Say: Let’s revise what we have learned.
● Instruct: Go to the Panel and open Lab on Formatting in Sheets - II.
● Show slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slide in the panel.
● Discuss the following questions one by one to check students’ understanding:
■ What is formatting?
Possible Responses: changing font styles; font colour; font style; making changes to the text appearance
■ How can you change the font style of text?
Possible Responses: Select the text → change the font style from the toolbar
■ Name a few font styles that we can use in Sheets.
Possible Responses: Arial; Comic Sans; Georgia; Robota; Verdana; Muli; Impact
■ How can we make the text larger in Sheets?
Possible Responses: In the toolbar we click on the Font size option → From the drop-down click on 14 or a larger number → The font size of the selected text will become large.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Address any other doubts students may have related to the concepts presented in the slides.
● Instruct: We know how to perform formatting in Google Sheets.
● Now, let’s practise our learning. Click on the Practice button on the Assignment page to attempt the activity.
● Click on the Attempt button to open the activity page.
● Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
● Instruct: Click on the Confirm button to submit your work when you are done with the activity.
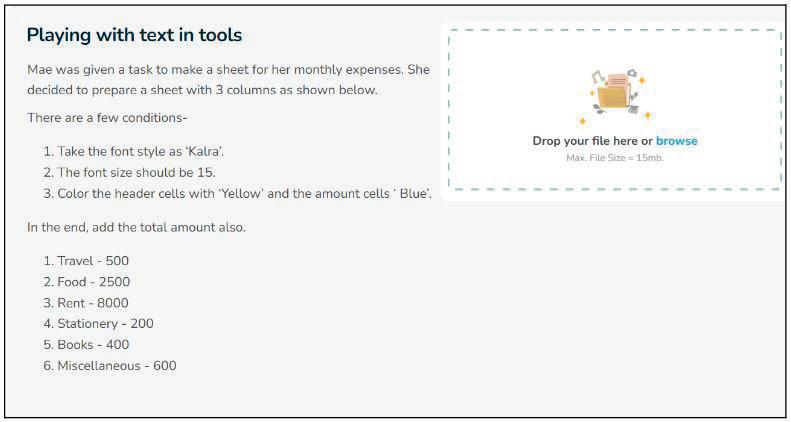
5 min
● Conclude: Today, we have learned how to format text in Google Sheets.
● Instruct: Practise the same activity at home.
● Assign the following as homework:
■ Project: Make a sheet of a list of books that you wish to read. Write the details/description of each book, its price, author’s name and so on. Format the text, applying the knowledge that you learnt today.
● The project is optional, kindly assign if feasible.

In this session, students will learn how to –
● Add a border to a cell
● Add colour to a cell
● Insert a new cell
● Insert a new column or row
● Add numbers and perform calculations in a cell
Keywords
● Fill Color: A tool that helps colour the entire cell
● Formula bar: A bar at the top where the formula in a cell appears
Revise the story and CS concepts covered in the previous chapter
Read or Invite students to read the story of the chapter
Discuss how to add border, colour, insert a cell, add numbers in a cell, and perform calculations
Fill Up – Q3, 4, and 5 Tick the Correct Answer – Q1, 3, 4, and 5
Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Recap the story covered in the previous session.
● Invite a few students to recall the CS concepts covered in the previous session.
● Introduce the students to Mr. Time.
● Say: Let me explain how we can work with cells in Google Sheets.
If you are teaching with a projector Open Google Slides on your computer system
CS Concepts Explain Demonstrate
Add a border
Add colour
Insert a cell
Inserting rows and columns
Adding numbers and performing calculations
If you are teaching without a projector OR
As given in Panel 1 on Page 109
As given in Panel 2 on Page 109
As given in Panel 2 on Page 110
As given in Panel 1 on Page 111
As given in Panel 1 on Page 112
How to add a border to a cell?
How to add colour to a cell?
How to insert a cell?
How to insert rows and columns?
How to add numbers and perform calculations?
● Present the scenario: Consider you have created a project on collecting data about different genres of books.
● Discuss:
■ What can be the different column headings of your project?
Possible Responses: Book name; Author Name; Edition; Published by; Published in the year; Series; price; Description.
■ What kind of data can be stored in cells?
Possible Responses: Plain text; numbers; formulae; percentages; dates.
■ How can you format the sheet that you created?
Possible Responses: Change the font size; colour; style; cell border.

■ On what kind of data can calculations be performed?
Possible Responses: numbers; dates; percentages
● Conduct Fill Up on Page 115:
■ Say: Let’s fill in the blanks.
■ Read Q3, 4, and 5 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● Conduct Tick the Correct Answer on Page 116:
■ Say: Let’s practise some more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q1, 3, 4, and 5 aloud, one by one. After the sentence, ask which of the options is correct.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Tick the final answers in your books.
● If time permits, discuss DIY Find the Truth – Q5 or assign it as homework.
● Conclude: Today, we learned about adding colour and a border to a cell, inserting a new cell, row, or column, adding numbers, and formulae in Google Sheets.

● Ask the following probing questions:
■ Name a few types of borders that we have in Sheets.
Possible Responses: Accept the descriptions of any of the options shown in the image below.
■ How can we make Sheets more interactive?
Possible Responses: By adding charts; images; formatting.
● Assign the following Brain Teaser exercise as homework:
■ Match Me
In this session, students will apply what they learned from the previous class to complete tasks on Google Sheets.
● Fill Color: A tool that helps colour the entire cell
● Formula bar: A bar at the top where the formula in a cell appears
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Say: Let’s revise what we have learned.
● Instruct: Go to the Panel and open Lab on Cells in Sheets – II.
● Show slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slide in the panel.
● Discuss the following questions one by one to check students’ understanding:
■ When would you need to insert a new cell?
Possible Responses: when we need to add more data; when change is required; if we want to modify content.
■ How can you perform calculations in Sheets?
Possible Responses: use a formula; begin the formula with = and write the calculations e.g. (=C1+C2); Use built-in formulae like SUM; AVERAGE etc.
■ How can we insert a cell in Sheets?
Possible Responses: Use the Insert Menu; Right-click and insert the cell using any of the two options
→ Insert cells and Shift right; insert cells and shift down.
■ Are you aware of other applications similar to Google Sheets?
Possible Responses: Microsoft Excel; LibreOffice Calc; Aritable; Zoho Sheets; Smartsheets.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Address any other doubts students may have related to the concepts presented in the slides.
15 min
● Instruct: We know how to perform functions in cells in Google Sheets.
● Now, let’s practise our learning. Click on the Practice button on the Assignment page to attempt the activity.
● Click on the Attempt button to open the activity page.
● Make the students practise the activity until the concepts in the session are covered.
● Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
● Instruct: Click on the Confirm button to submit your work when you are done with the activity.


5 min
● Conclude: Today, we have learned some formatting in Google Sheets.
● Instruct: Practise the same activity at home.
● Assign the following as homework:
■ Project: Make a project on creating a sheet of data with your favourite songs. Add details like release year/date, singer, album/film, etc. Perform various types of cell formatting that you have learnt in this session.
● The project is optional. Kindly assign if feasible.
1. Analytical Engine is a machine that could solve math problems. It was created by English mathematician Charles Babbage.
2. Difference engine is a device created by Charles Babbage that could read numbers and print mathematical tables. It also had storage.
3. GUI stands for Graphical User Interface. It allows us to interact with computers using icons instead of just text.
4. First Generation computers were very expensive, used a lot of electricity and produced a huge amount of heat. Whereas Fifth generation computers are less expensive, compact, use less electricity and are faster than first generation computers.
5. Supercomputers are extremely powerful and fast computers. They are mostly used for engineering and scientific work that needs high speed calculations like weather forecasting.
Brain Teasers
E Answer in Short
1. The internet is a network of computers working independently and can share information with each other. Airtel, Jio, Vodafone are some ISPs.
2. Email or electronic mail is a way to send and receive messages across the internet. Gmail is the most common email.

3. Instant Messenger apps are used to send text messages online. These messages can be transmitted to more than one recipients. One of the most commonly used instant messaging app is WhatsApp.
4. Social Networking Sites help us connect with friends, family, and brands. Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn are some examples of social networking sites.
5. Video Hosting Platforms help creators display their content and share it with an audience that enjoys their content. Examples include YouTube and Vimeo.
A
B Abbreviations
Name Answer
1. Internet Service Providers
2. Digital Subscriber Line
3. World Wide Web
4. Internet Protocol
5. Electronic Mail
Brain Teasers Section Section Name Answer
A Fill Up
B Find the Truth
C Tick the Correct Answer
1. Virus
2. Hacker
3. Cyberattack
4. Cyber Security
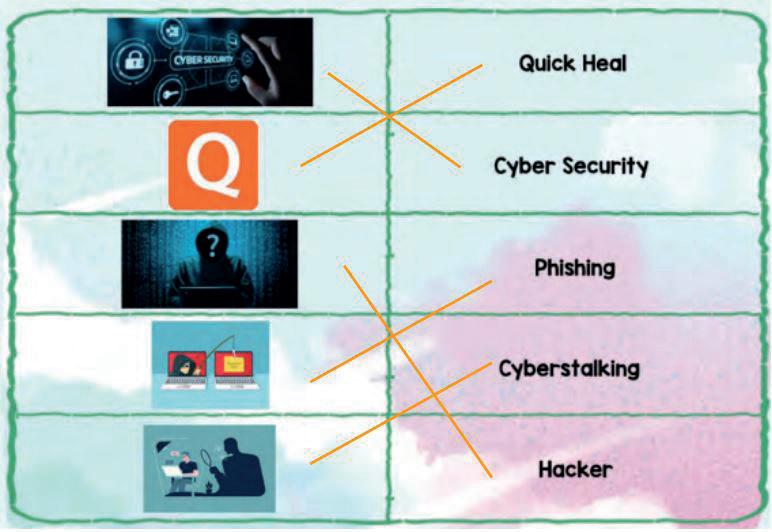
5. Trojan
1. b. Ethical hacking 2. a. Firewalls
3. d. All of the above 4. d. All of the above
5. a. Anti-spyware
D Match Me
E Answer in Short
1. A cyberattack happens when a hacker gets access to your digital personal data (like – bank account details, identity documents etc.) without your permission.
2. A trojan program appears like a regular link or website, but it is actually an infected software that spreads throughout your device.
3. Phishing, Identity Theft, Cyberstalking.
4. Phishing is when you get an email that appears to come from a known website. It gives a link that might interest you. When you click on it, hackers get access to your system.
5. Antivirus spots and destroys a virus. Examples are Norton, McAfee, Quick Heal and Kaspersky.
DIY
Section Section Name Answer
A Odd One Out
1. Security Breach
4. Bacteria
B Answer in Short
1. VPN (Virtual Private Network) is an encrypted connection on the internet between a device and the network. It hides your online activity, ensures the safe delivery of private information and protects you from unauthorised access to your data.
2. A worm can spread to other systems and devices. A worm will not harm or affect other programs. Instead, it will affect the sites that you visit most often.
3. Hackers and cybercriminals use spyware to monitor your activities. Spyware can give hackers access to your usernames, passwords and personal data by logging inputs throughout the day.
4. A cyber security breach is an event that ends up providing a hacker with unauthorised access to your computer data, applications, networks or devices.
5. Ethical hacking is the process of spotting any weaknesses in an application, system or organisation’s software. Ethical hackers accomplish this by breaking into the systems legally and locating any security flaws.

1. Videos can be added from YouTube using the URL link of the videos. To do that, click on the Insert menu and select Video. From the pop-up, select the YouTube tab and paste the URL in the search bar.
2. Open your Google Drive. Click on the + (New) option in the left pane of your Google Drive window. Select the File Upload option. From the pop-up menu, browse and select the file you wish to upload.
3. To add GIFs, click on the Insert menu. Select “Image”, choose Upload from Computer, then choose a GIF. We can also add online GIFs using the Search the web option.
4. Videos can be added from YouTube using the URL link of the videos. To do that, click on the Insert menu and select Video. From the pop-up, select the YouTube tab and paste the URL in the search bar.
5. To add music to your slide, you need to add it to your Drive. Then, click on the Insert menu. Click on “Audio”. Choose an audio file from your Drive.
Answer in Short
1. A slide is a single page of a presentation. A slide show is an exposition of a series of slides or images on an electronic device or in a projection screen.
2. GIF stands for Graphics Interchange Format. GIF files also allow images or frames to be combined, creating basic animations.
3. Google Drive is used to store files using the internet. Many users find it convenient to put files on Google Drive because they can access it anywhere anytime using the internet on any device.
4. Google Slides is an online presentation app that lets you create and format presentations and work with other people.
E Answer in Short
1. Animation is the process of giving the illusion of movement to drawings, models, or objects.
2. The three types of animations used in Google Slides are Fly-in from left, Fade-in, and Fly-in from bottom.
3. Transition is the visual effect that occurs when you move from one slide to the next during a presentation
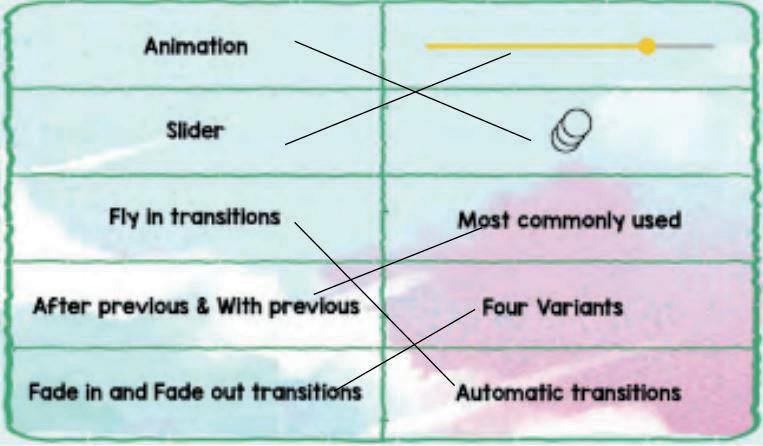
4. Using the On click option shows the animation effect on the object when a mouse is clicked.

5. We can set the speed of transitions in Google Slides using the slider.
F Answer in Detail
1. Animations in Google Slides can be added using the Insert menu. Select the object that you want to animate, then click on Insert. From the drop-down select “Animation”. Choose the type of animation.
2. To add transitions to a slide, click on the Slide Menu. From the drop-down select Transition. Choose the options to add transitions to your slide.
3. Fade-in animation means when an object transitions from completely transparent to completely opaque. It appears gradually on the slide.
4. When animating objects we can reveal each object one by one with left clicks of the mouse. With automatic settings we can set the timer and the object appears after that certain amount of time.
5. Click on option is used to decide when the animation will be visible. It can be either on mouse click, after or with the previous animation. The slider, on the other hand, is used to adjust the speed of animations and transitions. DIY
A Find the Odd One
Section Name Answer
1. On click – The rest of the options are types of animations
2. Fade out – The rest of the options determine when the animation will be visible.
B Who am I?
1. Slide Menu
2. Slider
3. Fade in 4. On click
5. From from bottom
A Fill Up
1. rows and columns
2. Letters and numbers
3. cells
4. Plain text
5. formula bar.
B Match Me
C Tick the Correct Answer
D Answer in One Line
1. D 2. A 3. A 4. C 5. A
1. Google Sheets helps us store data.
2. Google Sheets is used to edit, organise and analyse data.
3. In the C1 cell we will write the formula = C2+C3+C4 and press enter.
4. A cell that contains a heading is called a header cell.
5. We can hide/unhide data using the small arrow button shown just beside the column letter once we select the entire row.
E Answer in Detail
1. Click on the “Edit” menu, then choose the “Find and replace” option from the drop-down list. Write the word you wish to find in the dialogue box that appears. You can also type a word in the Replace box to replace the word in the document.
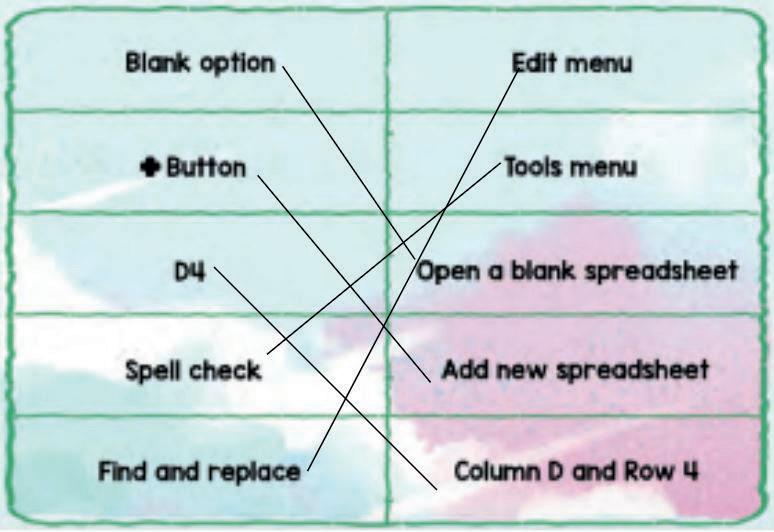
2. Double click on the cell where you want your formula to appear, then type “=” without quotes followed by the formula. Press Enter to save the formula or click on another cell. The results will appear in the cell while the formula appears in the formula bar.
Example-
=SUM(C1+C2+C3) or =AVERAGE(C1:C10)
3. Data can be stored as plain text, numbers, currency, dates, and percentages.
4. Open your Google Drive using your Gmail user id and password. Click on the +(New) symbol. Then select Google Sheets from the drop-down menu that appears.
5. The cells are formed by the intersection of rows and columns. The rows are identified using numbers and the columns are marked by letters. A cell name is a combination of numbers and letters. It is formed by Column Letter+Row Number. For example, if we want to write the cell address of the 3rd row in Column C we will name the cell C3.



The content covered in this chapter is aligned with the following CSTA Standard
● 1B-AP–09 Variables
● 1B-AP–10 Control
This chapter is divided into the following lab sessions
1. Print Statement
2. Operations
3. Variables
4. Comparison Operators
5. Logical Operators
6. Conditions
In this session, students will learn about –
● Programming
● Basic blocks in Blockly – Print, number, text
Keywords
● Programming: A set of instructions given to the computer to perform a particular task
● Coding: A term for computer programming
● Programming Language: A language which can be used to give instructions to the computer
● Block-based Coding: Instructions are given to the computer using programming blocks
Discuss the word “coding” with students

Show the video “Meet Koi and Newt” in the panel
● Say: Today, the session topic is “Print Statement”. What does the word “coding” mean?
● Invite 1 or 2 responses from the students, but don’t give the correct answer yet.
● Say: Let’s watch a video together and come up with a definition of “coding” afterwards.
● Show the video “Meet Koi and Newt” in the panel.
● Explain the following concepts from the coding booklet -
● Show slides one by one and discuss the blocks shown on the slide in the panel.
● Discuss the Quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Ask the students to complete the Assignment
● Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
● Present the scenario: (Conduct this activity only if time permits)
Let’s assume that I (the teacher) am a computer. Consider you want me to give you a pencil. What should your instructions be? The instructions should be in English for now.
■ To conduct this activity smoothly, consider picking one student at a time.
■ Whenever the students give you an instruction, think if it is a clear instruction or not. If not, come up with a counter-question.
■ Let the students think. Do not give away the answer. Here are some possible responses
■ Students: Please, give me a pencil.
■ Teacher: But I (the computer) don’t know where the pencil is.
■ Students: On the table, there is a pencil box. Look inside the pencil box. Locate a pencil and pick up the pencil.
■ Teacher: With what should I pick up the pencil?
■ Students: With your hand
■ Teacher: Yes, but I have two hands. Which one should I use?
■ Students: Use your right hand to pick up the pencil from the pencil box on your table.
■ Teacher: *picks up the chalk and stands still*
■ Students: Now, give it to me.
(Teacher keeps this conversation going until students come up with a clear set of sequential instructions.)
When the students come up with a clear set of instructions, ask them to draw conclusions from this activity.
Here are the conclusions:
1. A computer needs clear instructions to complete a task.
2. The instructions should be in the proper order.
3. The instructions should be given in a language that the computer understands.
4. When you write instructions for the computer, you are coding/programming.
2 min
● Conclude: Today, we learned about coding. We were introduced to block-based coding named Blockly.
● Ask the following probing questions: (Conduct the activities only if the time permits)
■ When you are giving instructions to the computer, is it important to write the instruction in a certain order?
Explanation: Yes. If the instructions are not in order, the computer will not be able to perform a task properly. Let’s say we want to add two numbers and print the result. If we give the print command first and the addition command after that, the program will not work.
■ Do you think the computer would understand my instructions if I give instructions in Spanish?
Explanation: No. The computer only understands computer languages. Spanish is a human language which the computer doesn’t understand.
In this session, students will learn about –
● Operators
● Maths blocks
Keywords
● Math Block: All the operator blocks available under Math Block in Blockly
Revise the concepts from the previous coding class
Show the video “The Zombie Game”
Discuss operators and maths blocks
Attempt the activities related to maths with Blockly
Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Revise the concepts learned in the previous class.
● Show the video, “The Zombie Game” on the panel.
● Discuss the concepts shown in the video
● Say: We can perform various mathematical functions using blocks under the Math Block in Blockly.

● Explain the following concepts from the coding booklet -
CS Concepts
Operator Block
Even/Odd Block
Positive/Negative Block
Prime Numbers
As given on Page 2
As given on Page 4
As given on Page 4
As given on Page 5
● Ask the students to open the Maths with Blockly section.
● Discuss the Quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Ask the students to complete the Assignment
● Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
Note
● If time permits, discuss the Worksheet Solving - Operations activity and complete it in class. Otherwise, assign it as homework.
● Conclude: Today, we have learned Operations. Additionally, we have learned about the various mathematical operators present in the math operator block.
● Assign the following as homework -
■ Complete the Worksheet Solving – Operations at home.
In this session, students will learn about –
● Variables
● Data Types
Keywords
● Variable: A memory location to store a value in a computer
● Data Types: Types of data a variable can hold
Revise the concepts from the previous coding class
Show the video “Horror Movie” in the panel
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Discuss the homework from the previous session.
● Play the video “Horror Movies” on the panel. Let the student watch the complete video.
● Explain the following concepts from the coding booklet -

CS Concepts Explain
Introduction to Variables
Naming a Variable
Updating Values of a Variable
Data Types
As given on Page 5
As given on Page 6
As given on Page 9
As given on Page 11
min
● Discuss the Quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Ask the students to complete the Assignment
● Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
● If time permits, discuss the activities mentioned under the homework section and complete it in class. Otherwise, assign it as homework.
2 min
Sum-Up
● Conclude: Today, we have learned about variables.
● Assign the following as homework –
1. Create a variable named num1 and store the value 5 in it. Create another variable named num2 and store the value 26 in it. Add both numbers using an operator block and print it.
2. Assign the Q2 from Practice Questions (Page 23, Coding booklet)
In this session, students will learn about –
● Comparison Operators
Keywords
● Comparison Operators: Compare two values of the same data type, i.e., either numbers or strings
Revise the learnings from the previous class
Show the video “Super Speed: Fastest Car Mission” in the panel
Discuss comparison operators like - equal, not equal, greater than, less than, etc.
Attempt the activities related to comparison operators
Conclude the concepts
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Revise the Variables learned in the previous class.
● Play the video “Super Speed: Fastest Car Mission” in the panel. Let the student watch the complete video.
● Explain the following concepts from the coding bookletCS Concepts
Equal (=)

Not Equal (≠)
Less than (<)
Less than or equal to (<=)
Greater than (>)
As given on Page 12
As given on Page 12
As given on Page 12
As given on Page 12
As given on Page 12
Greater than or equal to (>=) As given on Page 13
● Show slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slide in the panel.
● Discuss the Quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Ask the students to complete the Coding Assignment.
● Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
● If time permits, discuss the activities mentioned under the homework section and complete it in class. Otherwise, assign it as homework.
Sum-Up 2 min
● Conclude: Today, we have learned about Comparison Operators.
● Assign the following as homework –
■ Create a variable named num1 and store the value 25 in it. Create another variable named num2 and store the value 30 in it. Create a variable result and store the num1 * num2 Check if the result is greater than 500 or not.
In this session, students will learn about –
● Logical Operators
Keywords
● Logical Operators: Used to compare two or more conditions, which are formed using the comparison operator
Revise the learnings from the previous class
Show the video “Logical Operators” in the panel
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Revise the Comparison Operators learned in the previous class.
● Play the video “Logical Operators” on the panel. Let the student watch the complete video.
● Explain the following concepts from the coding booklet -

CS Concepts Explain
AND Operator
OR Operator
NOT Operator
As given on Page 14
As given on Page 15
As given on Page 17
● Show slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slide in the panel.
● Discuss the Quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Ask the students to complete the Assignment or give it as homework.
● Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
● Conclude: Today, we have learned about Logical Operators.
● Assign the following as homework –
■ Practise the truth tables at home.
In this session, students will learn about –
● Conditions
● Conditions: Used to make decisions
Revise
Show
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Revise the Logical Operators learned in the previous class.
● Play the video “Conditions” in the panel. Let the students watch the complete video.
● Explain the following concepts from the coding booklet -

If-else Statement
If-do Block
Else-if Block
As given on Page 17
As given on Page 18
As given on Page 19
● Show slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slide on the panel.
● Discuss the Quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Ask the students to complete the Assignment or give it as homework.
● Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
Note
● If time permits, discuss the Q1 from Practice Questions (Page 23, Coding booklet) and complete it in class. Otherwise, assign it as homework.
● Conclude: Today, we have learned about Conditions.
● Assign the following as homework -
1. Assign the Q1 from Practice Questions (Page 23, Coding booklet)
The content covered in this chapter is aligned with the following CSTA Standard
● 1B-AP-10 Control
● 1B-AP-13 Program Development
This chapter is divided into the following lab sessions
1. Loops I
2. Loops II
3. Loops III
4. Timer Clock Project
In this session, students will learn about –
● Loops and iteration
● Types of loops
● Repeat block
● Loop: A set of instructions carried out repeatedly until a particular condition is met
● Iteration: Each block of code in a loop
● Repeat Block: Allows you to repeat a code for a specified number of times
Recall the concepts covered in the previous coding chapter
Play the video given in the panel to introduce the concepts to be covered in this session
Conduct Conclude the session Assign the homework 7 min 5 min 15 min 3 min
given
● Say: Today, the topic is “Loops”. What does the word “loop” mean?

● Say: Let’s watch a video together and come up with a definition of “loop” afterwards.
● Instruct: Go to the Tekie panel and open the lab on loops.
● Play the video given on the panel for the same topic.
7 min Warm-Up 5
Engage
● Discuss the quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Conduct example 2 to print numbers from 1 to 5 given in the Coding Booklet on Page 27:
■ Explain the activity to the students.
■ Instruct: Click on the Practice button on the Assignment page to attempt the activity.
■ Instruct: Click on the Attempt button to open the activity page.
■ Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
■ Assist the students if any of them are struggling.
■ Instruct: Click on Yes button to submit the activity.
● If time permits, conduct the additional activity given in the Coding Booklet on page 26 Example 1.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ If you had to write a program that plays your favourite song on repeat 10 times, what is the shortest way to code it?
Possible Responses: Use loop repeat 10 times; Use repeat block (10)
■ What does the number 10 stand for in the question I asked above?
Possible Responses: number of times the loop/code/command repeats
● Assign the following project as homework:
■ Example 3 given in the Coding Booklet on page 27.
Note
● The project is optional. Assign it if feasible.
In this session, students will learn about –

● Repeat while block
● Repeat until block
● Repeat While: Repeats a single block or multiple blocks in a loop while a condition is true
● Repeat Until: Repeats a single block or multiple blocks in a loop until a condition that you set is met
Recall the concepts covered in the previous coding session
Play the video given in the panel to introduce the concepts to be covered in this session
Discuss repeat while and repeat until blocks
Conduct the activity given in the panel in the Coding Booklet
Conclude the session Assign the homework
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Revise the concepts learned in the previous class.
● Show the video, “Repeat While and Repeat Until” in the panel.
● Ask the students to attempt the quiz questions from the panel and discuss the answers.
● Conduct Example 1 part a and b given in the Coding Booklet from Page 29 and Page 30:
■ Explain the activity to the students.
■ Instruct: Click on the Practice button on the Assignment page to attempt the activity.
■ Instruct: Click on the Attempt button to open the activity page.
■ Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
■ Assist the students if any of them are struggling.
■ Instruct: Click on the Yes button to submit the activity.
Note
● If time permits, conduct the additional activity given in the Coding Booklet on Page 30 (Example 2).
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ What is a repeat while block?
Possible Responses: Repeat while block iterates through one or more blocks in a loop while a condition is met.
■ What is a repeat until block?
Possible Responses: Repeat while block iterates through one or more blocks in a loop until a condition is met.
● Assign the following project as homework:
■ Example 1 given in the Coding Booklet on Page 28.
Note
● The project is optional. Assign it if feasible.
In this session, students will learn how to use a “break-out” block.
● Loop Termination: Ending a loop and moving to the next block
Recall the concepts covered in the previous coding session
Play the video given in the panel to introduce the concepts to be covered in this session
Discuss the “breakout” block Conduct the activity given in the panel in the coding booklet

Conclude the session Assign the homework
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Revise the concepts learned in the previous class.
● Show the video, “Break-Out Block” on the panel.
● Discuss the quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Conduct Solved Example 1.1 as practice given in the Coding Booklet on Page 32.
■ Explain the activity to the students.
■ Instruct: Click on the Practice button on the Assignment page to attempt the activity.
■ Instruct: Click on the Attempt button to open the activity page.
■ Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
■ Assist the students if any of them are struggling.
■ Instruct: Click on Yes button to submit the activity.
Note
● If time permits, conduct the additional activity given in the Coding Booklet on Page 33 (Solved Example 1.3).
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ What block do we use to terminate a loop?
Possible Responses: Break-out block
■ What happens once you terminate a loop?
Possible Responses: It executes codes outside the loop body
● Assign the following project as homework:
■ Solved Example 1.2 given in the Coding Booklet on Page 32.
Note
● The project is optional. Assign it if feasible.
In this session, students will apply the knowledge of loop blocks learnt in this chapter.
● Loop: A set of instructions carried out repeatedly until a particular condition is met
● Repeat Block: Allows you to repeat a code a specified number of times
● Repeat While: Repeats a single block or multiple blocks in a loop while a condition is true
● Repeat Until: Repeats a single block or multiple blocks in a loop until a condition that you set is met
● Loop Termination: Ending a loop and moving to the next block
Recall the concepts covered in the previous coding session
Play the video given in the panel to introduce the concepts to be covered in this session

Discuss the steps explained in the video
Conduct the activity given in the panel from the Coding Booklet
Conclude the session Assign the homework
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Revise the concepts learned in the previous class.
● Show the video, “Timer Clock Project” in the panel.
● Discuss the quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Conduct Timer Clock Project as practice given in the Coding Booklet on Page 33.
■ Explain the activity to the students.
■ Instruct: Click on the Practice button on the Assignment page to attempt the activity.
■ Instruct: Click on the Attempt button to open the activity page.
■ Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
■ Assist the students if any of them are struggling.
■ Instruct: Click on the Yes button to submit the activity.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ How many types of loop blocks did we use in this activity?
Possible Responses: 2; 3
■ Does using a loop block make the code easier to understand?
Possible Responses: Yes; No
Explanation: A loop allows us to reduce the number of times we need to type a code. If a problem requires multiple executions of the same code, it saves us space and clearly mentions the number of iterations we have executed.
● Ask the students to revise and practise the concepts learnt in this chapter.
The content covered in this chapter is aligned with the following CSTA Standard
● 1B-AP-10 Control
● 1B-AP-11 Modularity
This chapter is divided into the following lab sessions
1. Introduction to Functions
2. Functions with Inputs
3. Practice
In this session, student will learn about –
● What is a function
● Advantages of a function
● Declaration and definition of a function
● Function: Is a sequence of commands that can be reused together later in a program
● Declaration: Is giving the function a name
Recall the concepts covered in the previous coding chapter
Play the video given in the panel to introduce the concepts to be covered in this session
Discuss the meaning of functions, their advantages, how to declare and define a function
● Say: Today, the session topic is “Functions”. What does the word “function” mean?

● Invite 1 or 2 responses from the students, but don’t give the correct answer yet.
● Say: Let’s watch a video together and come up with the meaning of “function” afterwards.
● Instruct: Go to the Panel and open the Lab on Introduction to Functions
● Play the video given on the panel for the same topic.
● Discuss the Quiz questions given on the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
min
● Conduct Example 1 “Sum of two numbers” given on Page 37:
■ Explain the activity to the students.
■ Instruct: Click on the Practice button on the Assignment page to attempt the activity.
■ Instruct: Click on the Attempt button to open the activity page.
■ Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
■ Assist the students if any of them are struggling.
■ Instruct: Click on the Yes button to submit the activity.
● If time permits, conduct the additional activity given in the panel titled “Difference of two numbers”.
min
● Conclude: Today, we learned functions and how to create them.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ What are the possible problems that can occur if we don’t use functions while coding?
Possible Responses: Code will become lengthy with repetitions; Hard to manage large chunks of code at once; Difficult to identify bugs
Explanation: Functions breaks allow for separation between codes and help identify bugs easily
■ What is the difference between defining and declaring the function?
Possible Responses: Definition – gives a name to the code to identify it; Declaration – to add instructions inside the body of the function
● Assign the following project as homework:
■ Create a Print function given in the Coding Booklet on Page 37.
● The project is optional. Assign it if feasible.
In this session, students will learn about –
● Calling a function
● Types of functions
● Functions with inputs
● Function: Is a sequence of commands that can be reused together later in a program

● Calling a Function: Is telling the computer to run the created function
Recall the concepts covered in the previous coding session
Play the video given in the panel to introduce the concepts to be covered in this session
Discuss how to call a function, types of functions (in terms of accepting inputs), functions with inputs
Conduct the activity given in the panel from the Coding Booklet
Conclude the session Assign the homework
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Revise the concepts learned in the previous class.
● Show the video, “Functions II” in the panel.
● Discuss the Quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Conduct Example 2 given on Page 42:
■ Explain the activity to the students.
■ Instruct: Click on the Practice button on the Assignment page to attempt the activity.
■ Instruct: Click on the Attempt button to open the activity page.
■ Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
■ Assist the students if any of them are struggling.
■ Instruct: Click on the Yes button to submit the activity.
Note
● If time permits, conduct the additional activity given in the Coding Booklet on Page 46 (Practice Questions 1).
3 min
● Conclude: Today, we learned about how to call functions and functions with inputs.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ Why do we define a function?
Possible Responses: To name and identify it; To call it and use it later
■ What are the two types of functions we have discussed?
Possible Responses: Functions with inputs; Functions without inputs
● Assign the following project as homework:
■ Example 2 given in the Coding Booklet on Page 43
Note
● The project is optional. Assign it if feasible.
In this session, students will practise some activities based on their knowledge of functions.
● Function: Is a sequence of commands that can be reused together later in a program

Recall the concepts covered in the previous coding session
Play the video given in the panel to introduce the concepts to be covered in this session
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Revise the concepts learned in the previous class.
● Show the video, “Recap” in the panel.
● Discuss the Quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Conduct Solved Examples with Functions 3 as practice given in the Coding Booklet on Page 45:
■ Explain the activity to the students.
■ Instruct: Click on the Practice button on the Assignment page to attempt the activity.
■ Instruct: Click on the Attempt button to open the activity page.
■ Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
■ Assist the students if any of them are struggling.
■ Instruct: Click on the Yes button to submit the activity.
● If time permits, conduct the additional activity given in the Coding Booklet on Page 46 (Practice Questions 2).
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ How have functions benefited you while practising the activities today?
Possible Responses: Can be reused; Breaks the large problem into small chunks; Easy to find bugs
■ What kind of input would you give for a function defined as “multiply”?
Possible Responses: Numerals; Numbers
● Assign the following project as homework:
■ Solved Examples with Functions 2 on Page 45
Note
● The project is optional. Assign it if feasible.
The content covered in this chapter is aligned with the following CSTA Standards
● 1B-AP-09 -Variables
● 1B-AP-10 Control
This chapter is divided into the following lab sessions
1. Strings
2. More on Strings
In this session, students will learn about –
● Introduction to Strings
● Length of a String
● Empty String
● User Input
● Variables: Are containers that store values
● Strings: Are values that are put inside single (‘ ’) or double quotes (“ “) and they can be numbers, letters, special characters, or a combination of these
● Length of a String: Is the number of characters in a string
● Empty String: Is a string that does not hold any value
● Input: Is the information given to the computer by the user
Recall the concepts covered in the previous coding session
Play the video given in the panel to introduce the concepts to be covered in this session
Discuss variables, values they can store, strings, string length, empty strings, and taking user input using the prompt block
Length of Vocab! [Students can use their vocab skills and find the length of any word]

Action Plan
● Instruct: Go to the Panel and open the Lab on Strings.
Conclude the session Assign the homework
● Discuss the Quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Conduct Length of Vocab! activity given in the Panel:
■ Say: Today, we are going to work on strings entered by the user and find their length.
■ Instruct: Click on the Assignment section.
■ Instruct: Click on the Go to Practice button to attempt the activity.
■ Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
■ Instruct: Click on the Yes button to submit the activity.
● If time permits, conduct the additional activity given in the panel: Empty or Full [Students will check whether the information entered by the user has some length or it’s empty.]
● Conclude: Today, we have learned how a user can enter information in a prompt block to work on it.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ Is your house address a string?
Possible Responses: Yes; No
■ Can you find the length of a string without counting spaces?
Possible Responses: Yes; No [No, because space is also a character.]
● Assign the following project as homework:
■ Create a program to find the length of the information entered by the user.
● The project is optional. Assign it if feasible.
In this session, students will learn about –

● Combining Strings
● Substrings
● Combining Strings: Is bringing together multiple blocks of strings or variables in one string
● Substring: Is part of a string
Recall the concepts covered in the previous coding session
Play the video given in the panel to introduce the concepts to be covered in this session
Discuss combining strings and getting a substring from a string
Perform the activity given on the panel – Let’s Join Together
Conclude the session Assign the homework
● Instruct: Go to the Panel and open the Lab on More on Strings.
● Play the video given in the panel.
● Discuss the Quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Conduct Let’s Join Together activity given in the Panel:
■ Say: Students! Today we will learn how to join strings together with the help of an activity.
■ Instruct: Click on the Assignment section.
■ Instruct: Click on the Go to Practice button to attempt the activity.
■ Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
■ Instruct: Click on the Yes button to submit the activity.
Note
● If time permits, conduct the additional activity – Solve Examples 1 to 3 given on Pages 51 to 53 in their Coding Book.
● Conclude: Today, we learned about joining and taking out part of a string through different activities.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ Can we use the substring function to display more words from the word given?
Possible Responses: Yes; No.
[Yes]
■ Can we use combining and substring methods without getting input from the user?
Possible Responses: Yes; No
[Yes, we can enter strings in the text block to do it.]
● Assign the following project as homework:
■ Do the Practice Questions given on Page 53 in your Coding Book.
Note
● The project is optional. Assign it if feasible.
The content covered in this chapter is aligned with the following CSTA Standard
● 1B-AP-09 Variables
This chapter is divided into the following lab sessions
1. Introduction to Lists
2. Sublists and Adding Items
3. Iterating through a List
In this session, students will learn about –

● What is a list
● How to create lists
● List blocks
● Getting and removing items from lists
● Lists: An ordered collection of items
Recall the concepts covered in the previous coding chapter
Play the video given in the panel to introduce the concepts to be covered in this session
Getting
an Item – Example
● Invite 1 or 2 responses from the students, but don’t give the correct answer yet.
● Say: Let’s watch a video together and come up with the meaning of “lists” afterwards.
● Instruct: Go to the Panel and open the Lab on Lists.
● Play the video given in the panel for the same topic.
Action Plan 7 min Warm-Up 5 min Engage
● Discuss the Quiz questions given in the Panel.
min
● Conduct Get and Remove Example given in the Coding Booklet on Page 60:
■ Explain the activity to the students.
■ Instruct: Click on the Practice button on the Assignment page to attempt the activity.
■ Instruct: Click on the Attempt button to open the activity page.
■ Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
■ Assist the students if any of them are struggling.
■ Instruct: Click on the Yes button to submit the activity.
● If time permits, conduct the additional activity given in the Coding Booklet on Page 67 (Practice Questions 3).
3 min
● Conclude: Today, we learned about creating lists, how to get and remove items and some lists blocks.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ Give one example of lists that you see used in daily life.
Possible Responses: Grocery list; Ingredients of a recipe; Attendance sheet in a class
■ What is the one advantage of a list that you have observed?
Possible Responses: Organised; helps one to remember; Can add new items easily
● Assign the following project as homework:
■ Create a list of “Animals” and add 5 of your favourite animals in it. Find the first animal on the list. Also find the last animal and remove it from the list.
● The project is optional. Assign it if feasible.
In this session, students will learn about –
● What is a sublist
● How to get a sublist from a list
● How to add items to a list
● List: A collection of data stored together in one place
● Sublist: Is a part of a larger list

Recall the concepts covered in the previous coding session
Play the video given in the panel to introduce the concepts to be covered in this session
Discuss the meaning of sublist, how to get it from a list, and adding items to a list
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Revise the concepts learned in the previous class.
● Show the video, “Sublist and Adding items” in the panel.
● Discuss the Quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Conduct Practice Question 1 given in the Coding Booklet on Page 67:
■ Explain the activity to the students.
■ Instruct: Click on the Practice button on the Assignment page to attempt the activity.
■ Instruct: Click on the Attempt button to open the activity page.
■ Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
■ Assist the students if any of them are struggling.
■ Instruct: Click on the Yes button to submit the activity.
Note
● If time permits, conduct the Example given in the Coding Booklet on Page 63
● Conclude: Today, we learned about sublists and adding items to a list.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ What is a sublist?
Possible Responses: Part of a bigger list; A small part of a list
■ Do you think it is possible to add items in the middle of the list?
Possible Responses: Yes; No; Don’t know; Maybe
Explanation: Yes it is possible to add items anywhere in the list using the “insert at” block
● Assign the following project as homework:
■ Create a list of subjects you study at school. Extract the sublist from the 3rd position to 5th position. Print the list as well as the sublist.
Note
● The project is optional. Assign it if feasible.
In this session, students will learn about –
● Iterating through a list
● List: A collection of data stored together in one place
● Sublist: A part of the larger list

● Iteration: Is a repetition of a sequence of code
Recall the concepts covered in the previous coding session
Play the video given in the panel to introduce the concepts to be covered in this session
Discuss how to iterate through a list
Iterating through a List – Example 3
Conclude the session Assign the homework
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Revise the concepts learned in the previous class.
● Show the video, “Iterating through a list” in the panel.
● Discuss the Quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Conduct Example 3 given in the Coding Booklet on Page 66:
■ Explain the activity to the students.
■ Instruct: Click on the Practice button on the Assignment page to attempt the activity.
■ Instruct: Click on the Attempt button to open the activity page.
■ Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
■ Assist the students if any of them are struggling.
■ Instruct: Click on the Yes button to submit the activity.
● If time permits, conduct the additional activity Example 4 given in the Coding Booklet on Page 66.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ Which block operates on every item in the list?
Possible Responses: For-each
■ How does iterating through lists help us?
Possible Responses: Reduces the number of times we need to write the same code
● Assign the following project as homework:
■ Practice Questions 2 given in the Coding Booklet on Page 67
● The project is optional. Assign it if feasible.
The content covered in this chapter is aligned with the CSTA Standard
● 1B-AP-10 Control
This chapter is divided into the following lab sessions
In this session, students will learn through –
● Puzzles
● Puzzle: A game that tests a person’s knowledge or skills
● Trait: A differentiating quality
Recall the concepts covered in the previous coding session Play the video given in the panel to introduce the concepts to be covered in this session
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Revise the topics learned in the previous class.
● Instruct: Open the topic Puzzles on Page 69.
● Discuss the various puzzles given in the book.
● Conduct the Puzzle given on Page 69:
■ Say: Today we will solve puzzles in Blockly.
■ Instruct: Open the link on your computer and choose the first option (Puzzle).

■ Guide and help students to complete the activity.
■ Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
■ Instruct: Click on Check Answers to check the answer and move forward.
● If time permits, conduct the additional activity given in the panel.
Sum-Up
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ Name some traits of snails and ducks.
Possible Responses: Shell; Slime; Beak; Feathers
■ How many legs does a bee have?
Possible Responses: Six; Five; Four
In this session, students will learn through –
● Mazes
● Maze: A puzzle in which you have to find a path
Recall the concepts covered in the previous coding session
Play the video given in the panel to introduce the concepts to be covered in this session

● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Revise the topics learned in the previous class.
● Instruct: Open the topic Maze on Page 71.
● Discuss the various Mazes given in the book.
● Conduct the Maze given on Page 71:
■ Say: Today we will solve Mazes from 1 to 5 in Blockly.
■ Instruct: Open the link on your computer and choose the second option (Maze).
■ Guide and help students to complete the activity.
■ Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
■ Instruct: Click on Run Program to check the answer and move forward.
Note
● If time permits, conduct the additional activity given in the panel.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ Which script do we use for the maze?
Possible Responses: Javascript; Python; Blockly
■ Which button do we click after completing the code?
Possible Responses: OK; Next
● Assign the following project as homework:
■ Practice Questions (stages 6 to 10) on Page 79
Note
● The project is optional. Assign it if feasible.
Turtle
In this session, students will learn about –

● Turtle
● Turtle: An on-screen pen to draw on the screen
Discuss Turtle Attempt the activities related to Turtle 3.
Recall the concepts covered in the previous coding session
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Revise the topics learned in the previous class.
Conclude the session
● Instruct: Open the topic Turtle on Page 79.
● Discuss various activities given in the book.
● Conduct the Turtle given on Page 79:
■ Say: Today we will solve the Turtle activity in Blockly.
■ Instruct: Open the link on your computer and choose the fourth option (Turtle).
■ Guide and help students to complete the activity.
■ Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
■ Instruct: Click on Run Program to check the answer and move forward.
Note
● If time permits, conduct the additional activity given in the panel.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ How many steps can we move forward using turtles?
Possible Responses: 100; 50; 150; 20
■ Can a Turtle move backwards?
Possible Responses: Yes; No; Maybe
● Assign the following project as homework:
■ Practice Questions (stages 6 and 7) on Page 88
Note
● The project is optional. Assign it if feasible.
This Teacher Manual has been designed to implement Tekie, the storytelling-based Coding and Computer Science program. The manual consists of lesson plans within each chapter that teachers transact within classrooms and computer labs. Each lesson is based on a research-based ‘WEBS’ framework that simplifies pedagogical practices for teachers and enables them to deliver effectively.

• Sharp Lesson Planning: Each lesson plan focuses on specific sub-learning outcomes within a chapter and are designed for delivery within the stipulated class or lab time.
• Real-life and Application-based Questions: Additional questions that link Computer Science to real-life contexts and assist teachers to develop learners’ conceptual understanding and application skills.
• Support and Detailed Solutions: In-depth solutions for in-class and post-class activities to reinforce learning.
Uolo partners with K12 schools to bring technology-based learning programs. We believe pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 8,000 schools with more than 3 million learners across India, South East Asia, and the Middle East.
hello@uolo.com
