INTRODUCTION
Focus on the basics:
Improve institutions and regulations:
› Health;
Poor institutions and high levels of corruption are likely to hinder private sector investment and development as these factors create uncertainty about public services delivery, efficiency and costs.
› Basic education; › Infrastructure. Research from the World Bank shows that statistically, for cities with low levels of industrialisation and productivity, good institutions, social infrastructure (such as education and health) and basic physical infrastructures are the key determinants for success.
Develop a coordinated and comprehensive growth strategy: Achieving competitiveness requires improvements on a range of very different aspects, and there is a risk that decisions are taken individually with little considerations for how they interact. Instead, decisions should be coordinated around overarching goals (e.g., transport strategy should reflect and respond to strategies relating to poverty, skills and employment) and they should also be comprehensive (e.g., sectoral strategies should examine and target every step of the supply chain, not just the sector itself).
Utilise existing resources and comparative advantages: Successful cities should make the most of the assets and resources they already have, rather than trying to attract new types of industries that are not necessarily adapted. There is not a silver-bullet policy to improve competitiveness.
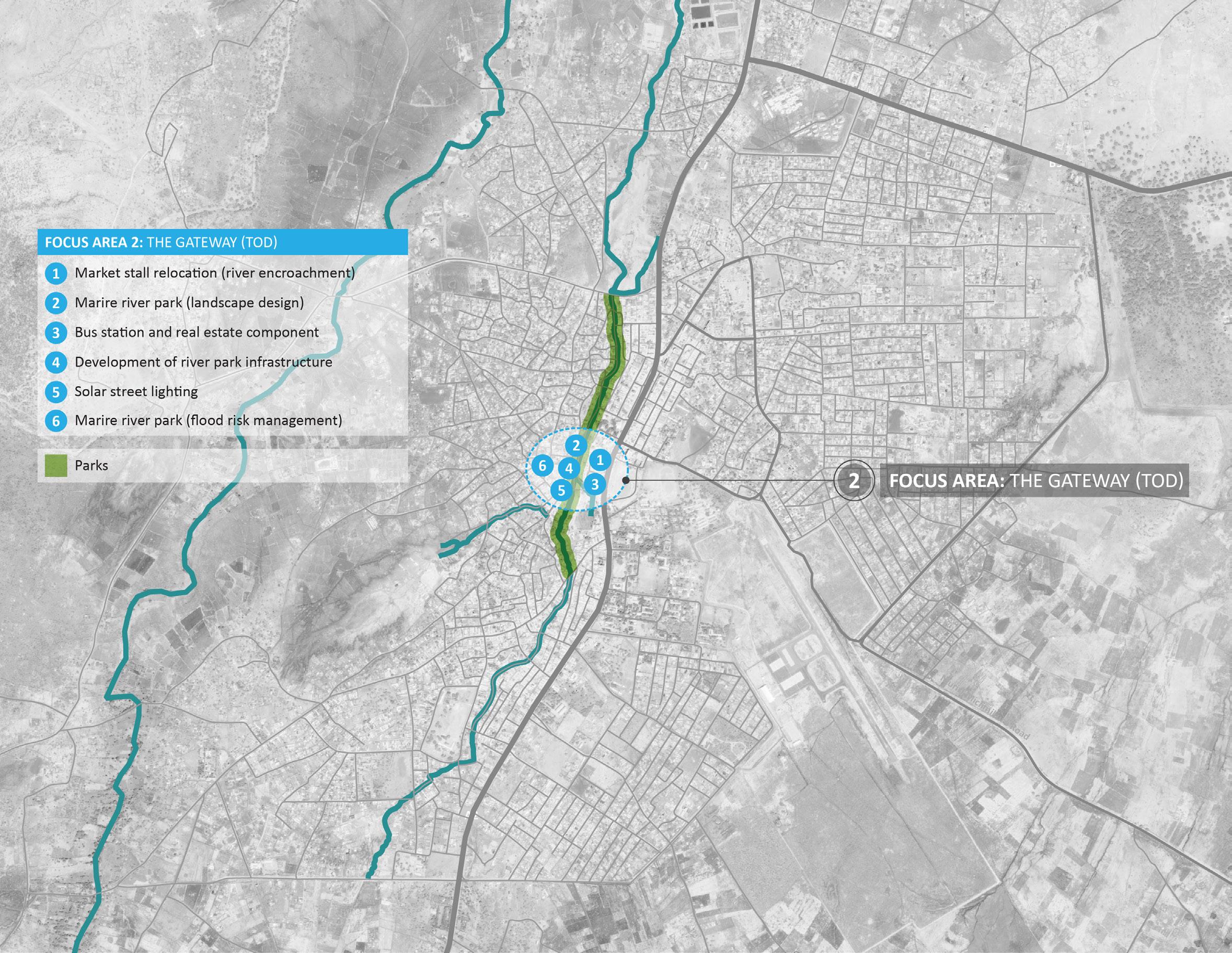
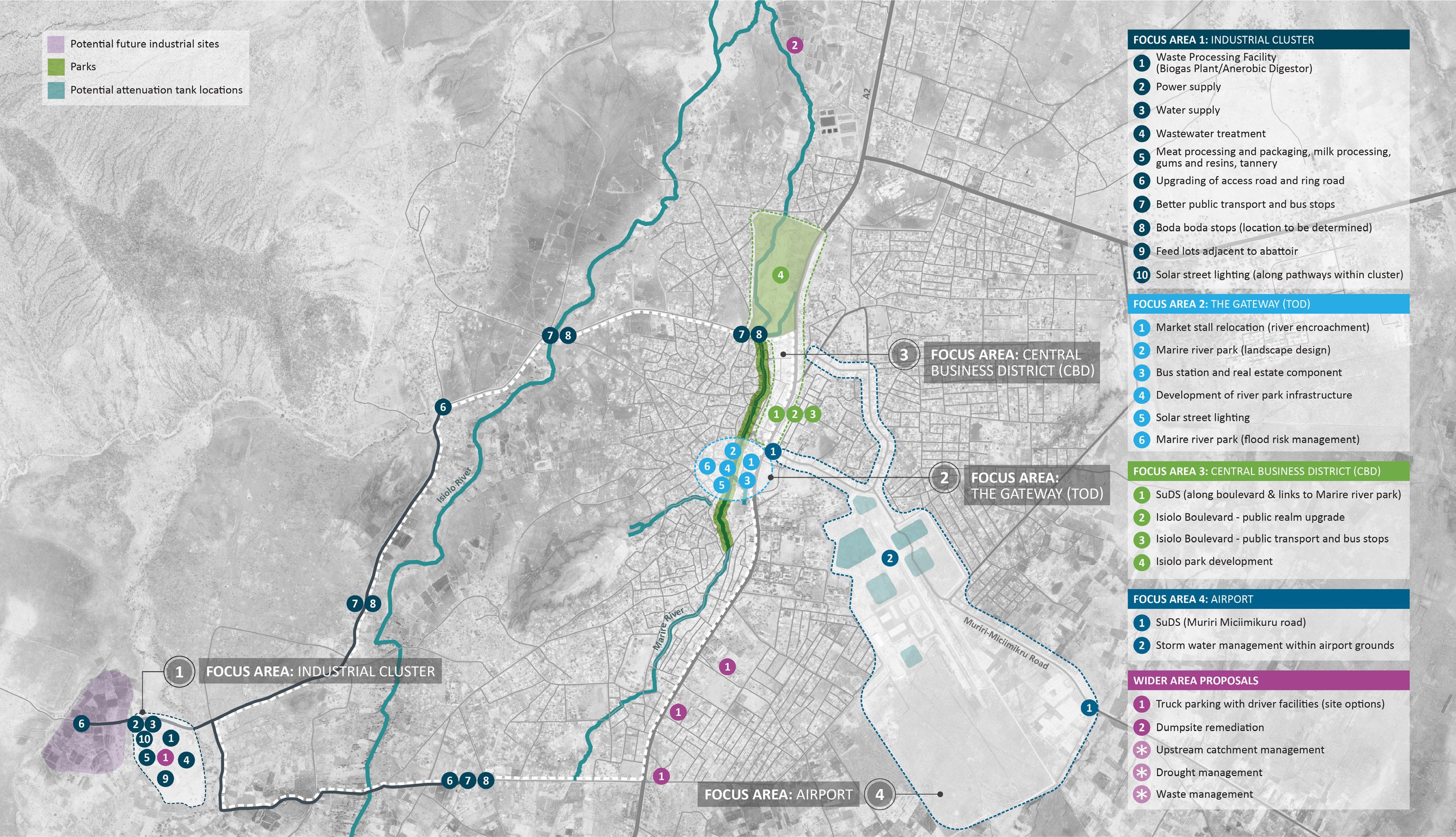
1.5. Structure of this report Following this introduction, the report is structured as follows: › Section 2 provides a summary of key findings from the Isiolo Diagnostics Report which forms the basis for the development of the Isiolo UEP. Summaries of the demographic and economic profiles and the infrastructure and environmental assessments are presented. The section details the key challenges and drivers for growth, identifying Isiolo’s key sectors; › Section 3 set outs the Urban Economic Development Plan, which is underlined by Isiolo’s economic vision. Each of the three key sectors is presented with a summary of its SWOT analysis and a Sector Action Plan. The identified Value Chain projects are then set out in detail. Section 3 outlines the Development Framework and supporting climate resilient infrastructure projects that have been identified for enabling urban and economic growth within Isiolo; › Section 4 presents a range of implementation considerations to support the next stages of the SUED Programme.
The report is supported by a series of appendices, in which: › Appendix A - Isiolo Diagnostic Report The purpose of the report is to assess the current position of the economy and state of infrastructure, alongside the regional, national and international context, before the consideration of emerging economic growth opportunities and infrastructure needs; › Appendix B - UEP Technical Briefing Paper Provides a Briefing Paper that captures the process followed from identification to assessment of growth opportunities for Isiolo and provides recommendations on those with the greatest potential to maximise benefits and be developed further. The contents of this report will form the backbone of the Isiolo UEP; › Appendix C - Isiolo Social Inclusion Study This study was a key part of the diagnostic process and engaged with special interest groups through interviews and focus group discussions. The study identified the groups that are excluded in socio-economic activities in Isiolo and explored how and why they are excluded. The Study made a series of recommendations for the SUED programme to ensure inclusion and to address the multiple barriers (communication, physical, attitudinal and organisational) that these groups face;
› Appendix D - Climate Vulnerability Assessment Has been undertaken to outline the climate vulnerability context for the selected infrastructure projects to be developed in Isiolo. The Climate Vulnerability Assessment will complement associated pre-feasibility and feasibility study assessments.
10