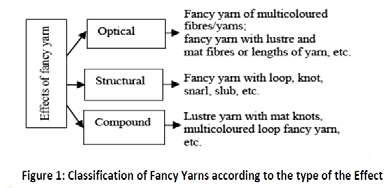
TECHNICAL TE X TILE
47
Application of Micro-ElectroMechanical Systems(MEMS) in textile industry MS. Sakshi Taori
Introduction: In today’s world, micro-scale and nanoscale devices are extensively used in various optic, electric, semiconductors, mechanical, chemical, pharmaceutical applications. At the heart of this technology are the Micro-electric and mechanical (MEMS) sensors. MEMS can be defined as a miniaturized system with characteristic sizes ranging from 100nm to 1mm containing a combination of electric and mechanical components. The MEMS fabrication technology involves a micro-machining process that selectively etches away parts present in the silicon wafer and adds new layers of electrical and mechanical components. That creates a major difference between the traditional IC manufacturing that only fabricates electric components like conductors and insulators versus MEMS which provide a combination of electric and other mechanical elements such as Gears, Cantilever, beams, diaphragms, etc. These micromachines can be used as both sensors and actuators along with a combined application as transducers depending on the specific requirements. Nowadays, advanced research is happening in the field of smart sensors that are systems reacting passively or actively to a given stimulus. Coming to the working principle of a MEMS sensor, it is based on the change in physical energy of any movable structure like a cantilever, gear, or membrane due to the application of an external force. This deflection in energy is measured using an optimal electric or optical technique and is finally used to back-calculate the applied external force. The different domains of physical energy can be categorized as Mechanical (Length, area, volume, torque, pressure), Chemical (Concentration,
MR. Yash Trivedi
enzyme selectivity, spectroscopy, composition), Thermal (Temperature, entropy, heat flow), Electric (Voltage, resistance, inductance, capacitance, polarization, piezoresistive effect, dipole moment, etc.), Magnetic (permeability, flux density, field intensity,magnetic moment,) and Radiant (Intensity, Wavelength, Refractive index, transmittance). Types and Application of MEMS: Due to their high sensitivity, accuracy, reproducibility (manufacturing at scale), reliability, and reduction in costs, MEMS are used in various applications. 1) MEMS Accelerometers – These are micro-devices used to measure force and acceleration. Two broad categories are piezoresistive and capacitive. Variable Capacitive (VC) sensors are low range, highly sensitive devices whereas piezoresistive (PR) sensors are higher range, low sensitivity devices. They are widely used in smartphones to switch tabs or pocket-mode operations, gravity sensors, digital compass, GPS Tracking. 2) MEMS Gyroscopes – These are micro-devices that measure angular/ rotational motion (Revolution per second RPS) or displacement of an object. Physically they can be assumed as spinning wheel/disc/beam mounted on an axle that is free for rotation and contains an oscillating component to detect acceleration. They are widely used to ensure safety in vehicle stability, image stabilization, airbag systems, automatic roll-over prevention, car navigation, and also photography and industrial robotics. 3) MEMS Pressure Sensors – Based on the type of measurements and pressure
requirements, these micro-devices are further classified into Absolute pressure sensor, Vacuum pressure sensor, Sealed pressure sensor, Gauge pressure sensor, Differential pressure sensor. These sensors are used to calculate the external pressure and have a huge demand in defense, medical, aerospace, industrial, automotive, beverage applications. For e.g. The MEMS pressure sensor can be used to measure the fluid pressure in humans in case of a brain hemorrhage. Due to their small size, they easily get inserted into the human body compared to macro-devices. 4) MEMS Magnetic field sensors – Magnetic MEMS are used to detect and measure the electromagnetic interactions between magnetic materials and active or passive sources of the magnetic field. The change in magnetic force causes a change in voltage frequency. These sensors are extensively used in linear angle, linear speed, and position measurements in the industrial, consumer, and automotive industries. Some other types include: 5) MEMS gas sensors – Micro-devices used to detect different types of gases and their concentration. 6) Bio MEMS- Micro-scale sensors used for biological and biomedical applications that may or may not have direct electric or mechanical functions. Examples include implantable microelectrodes used to send and detect nervous signals for enhanced disease identification and monitoring clinical parameters, microtools like microneedles, tiny forceps that are used for surgeries, drug delivery, vaccination, etc. Need for sensors in the Textile Industry: The field of textile is not just limited
J U LY 2 0 2 1