ConQuest

CONSULTING AND STRATEGY CLUB
IIM SHILLONG







ConQuest, the Consulting & Strategy Club of IIM Shillong, was founded in 2008 with a vision of delivering sustainable solutions to society by acting as a forum between the industry and students passionate about strategy and consulting. It strives to equip the students with domain knowledge and skills by facilitating consulting assignments, expert talks, online newsletters, and competitions.
In this edition of the Sectoral Analysis, we cover the ed-tech sector in India which has witnessed significant growth in recent years, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. As schools and universities were forced to shut down physical classrooms, online learning platforms emerged as a viable alternative. This led to a surge in demand for ed tech products and services, creating opportunities for both established players and new entrants in the market.










The Indian ed-tech sector is characterized by diverse players, from global giants such as Coursera and Udemy to homegrown startups like Byju's and Vedantu. These companies offer a variety of products and services, including online courses, live tutoring, test preparation materials, and learning management systems.











While the sector has seen tremendous growth, it has faced challenges, particularly regarding access and affordability. There are concerns that online education may exacerbate existing inequalities as access to digital infrastructure remains uneven across the country. Additionally, there is a need for innovative models that can make ed tech products and services more affordable and accessible to students from lower-income backgrounds. Another significant trend in the Indian ed tech sector is the increasing adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies. These technologies are being used to personalize learning experiences, provide real-time feedback, and create adaptive assessments. AI and ML can also help ed tech companies analyze student data to identify learning gaps and develop targeted interventions.
Despite these challenges, the ed-tech sector in India has immense potential to transform the country's education landscape. The right policies and investments can help bridge the gap in access to quality education and prepare the workforce for the demands of a rapidly changing economy. As such, it is a space to watch in the coming years.
AANCHAL CHOWDHURY ADITI PATHAK ANIKET SINGH ARPITA NAINA ISHAN SINHA KARNIKA PAGARIA SAHIL MEHTA SAMREEN REHMANI SHIVAM ARORA SHUBHAM SHARMA DEEPALI SINGH BAGHEL PARIDHI JAIN PRATIK RATHI SHRUTI GUPTA VIVEK BANSAL YUGADHYA MATHURIA

Radios introduced to the classroom.
Overhead projectors begin to be used.
Videotapes are introduced.
The photocopier is developed.
Handheld calculators enter classrooms.
The Scantron is developed.
Smart boards are introduced in schools.

Laptops are made available.
The iPhone is introduced.
The public gets access to the Internet.
iPads are used in schools.
The Edtech sector refers to the use of technology to facilitate and enhance teaching and learning processes. It includes the development and implementation of software, hardware, and platforms that can be used to deliver educational content, provide assessment and feedback, and support collaboration and communication among students and educators.

Edtech, short for education technology, refers to the use of software and hardware to enhance teaching and learning.
The Edtech sector has seen significant growth and adoption in recent years, as technological advancements have made it easier to create and deliver high-quality educational content online. This has led to the emergence of a wide range of Edtech solutions, from online learning platforms and educational apps to virtual and augmented reality tools and AI-powered adaptive learning systems.
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted the ed-tech sector, accelerating the adoption of technology in education and increasing the demand for online learning solutions.
As schools and universities were forced to shut down physical classrooms, online learning platforms emerged as a viable alternative. This led to a surge in demand for ed tech products and services, creating opportunities for both established players and new entrants in the market.With schools and universities closing down due to the pandemic, many educational institutions quickly shifted to online learning to ensure students could continue their studies remotely. This sudden shift to remote learning resulted in a surge in demand for ed-tech tools and platforms that could support virtual classrooms, online assessments, and other educational activities.
Edtech companies responded to this demand by rapidly developing and launching new products and services to meet the needs of teachers and students. Online learning platforms, video conferencing tools, and collaboration software were among the most popular products during the pandemic.
The pandemic has also highlighted the need for more personalized and adaptive learning experiences and the importance of digital literacy skills for educators and students. As a result, ed-tech companies have focused on developing more sophisticated and engaging digital content, including virtual and augmented reality experiences, on supporting remote and blended learning environments.
Overall, the pandemic has accelerated the growth and adoption of ed-tech solutions, and it is expected to have a lasting impact on the way that education is delivered and experienced in the future.
Traditional schooling's one-size-fits-all concept has long been criticized by educators, parents, and students. As a result, the whole education sector banded together to streamline ideas and solutions in order to construct a better path forward - a digital path forward. Here are success stories of some of the pioneers in the EdTeach industry worldwide which are changing the way people learn.

Millions of workers worldwide are not working at a desk. The industry is demanding. It is not uncommon for there to be insufficient time for introduction and training. Even if the training is available, linguistic difficulties stand in the way. All at the expense of worker happiness, productivity, and safety.
Germany-based how.fm is a firm formed in 2018 that targets a sector that has mostly been disregarded by technological innovation, focusing its efforts on blue-collar employees. Its products are geared for workers who do not sit at a desk all day, such as those in construction, manufacturing, and agriculture. Every day, the platform enables warehouse operators to onboard, upskill, and support their employees. According to the company, the off-the-job training it provides has reduced attrition by 5% throughout its client base. The company also says that the on-the-job training it provides has decreased ramp time by 15%, enhanced production quality by 30%, and resulted in 50% fewer interruptions.
Unacademy was founded in 2010 by Gaurav Munjal, a former Google employee. The company started as a YouTube channel where Munjal would upload videos of his lectures on various topics.

Online learning platforms were not widely used in India at the time. Unacademy, on the other hand, saw the opportunity and opted to take a chance on revamping the nation's learning method. The platform was developed with the goal of providing affordable and high-quality education to all Indians.
Unacademy is now India's largest learning platform, bringing together top educators for millions of students in need of improved educational quality. The Unacademy program is available not only to 10+2 students, but also to college aspirants who are preparing for competitive exams such as CAT, GATE, UPSC, and others. The learning platform is actually transforming the way people study in India, with over 35,000 hours of educational content. The platform makes quality education available to everyone, regardless of location or economic status. This is an uplifting story of how a group of dedicated people is transforming the face of education in India.

Effective educational experiences should not only be measurable, but also experienced and applied, and the themes should be relevant to the difficulties people will face on the job in workplaces and industries undergoing enormous upheaval and change in the coming years. Esme Learning is addressing this head-on by providing people with experiences and resources to learn how to work in the new future of work. Esme, based in Boston, presently collaborates with some of the world's most prestigious universities, including MIT, Sad Business School, the University of Oxford, and Imperial College Business School.
Esme Learning, founded in 2019 by digital learning pioneers, is revolutionizing remote learning via the use of AI-enabled tools and years of peer-reviewed cognitive and neuroscience research to provide an immersive and highly practical collaborative learning experience. Executives gain technical skills & learn business best practices from specialists in a wide range of frontier sectors.

upGrad was founded in 2015 by Ronnie Screwvala, Mayank Kumar, and Phalgun Kompalli with a view to “to impact the lives of working professionals by helping them upskill while they work.” The issue was that there was a significant gap between what was taught in business schools and the actual challenges encountered by entrepreneurs. As a result, the founders decided to create upGrad to solve this problem.

The goal is for every entrepreneur in India who wants to earn an MBA or specialized training in d to be able to do so without leaving their employment. Each of the programmes offered by upGrad is in conjunction with a world-class university, such as IIT Madras, Duke CE, Deakin University, Liverpool John Moores University, and others.
According to Deloitte's evaluation of upGrad results, 5 out of 6 learners experience favourable professional progress. After completing their MBA programmes, upGrad students receive an average income increase of 52%.

“There are one billion school students in the world and the vast majority are studying the same way their ancestors were 150 years ago.”
Simon Hay and Joe Mathewson, co-founders of Firefly, created the education technology solution out of their "own frustrations" regarding offline learning while completing their GCSEs, and they continue to receive full grades for international scale-up success.

Firefly, a London-based EdTech firm formed in 2000 by two 15-year-old students, is driven by the global social impact it achieves rather than meeting preset financial targets.
The platform provides a fully interactive experience for teachers, students, and parents, allowing them to assign homework, track student progress, send feedback, and share learning resources.
The Indian edtech industry has been growing rapidly in recent years, driven by innovation in technology and the rising demand for education. The industry has been attracting significant investments and is expected to continue to grow in the future. In this analysis, we will examine the Indian edtech industry using Porter's Five Forces framework, which assesses the competitive forces in an industry and helps to understand the industry's attractiveness.
The threat of new entrants in the Indian edtech industry is relatively low. The industry requires significant investments in technology and infrastructure, which can be a barrier for new entrants. Additionally, the industry is highly regulated, and new entrants would need to comply with various regulations and standards. Furthermore, the industry is highly competitive, and new entrants would need to establish a strong brand and reputation in order to attract customers.
The bargaining power of suppliers in the Indian edtech industry is relatively low. The industry relies on a wide range of suppliers, including technology providers, content providers, and service providers. However, the industry is highly competitive, and suppliers would need to offer competitive prices and high-quality products in order to attract customers.

Additionally, the industry is constantly evolving,andsupplierswouldneedtokeepup with the latest trends in order to remain competitive.
The bargaining power of buyers in the Indian edtech industry is relatively high. The industry serves a large and diverse market, and buyers have many options to choose from. Additionally,buyersarebecomingincreasingly savvy and are demanding high-quality products and services at competitive prices. Furthermore, buyers are becoming more sophisticated and are demanding more personalized and customized products and services.
Thethreatofsubstituteproductsorservicesin the Indian edtech industry is relatively high. The industry faces competition from traditional educational institutions, such as schools and universities, as well as from other forms of education, such as books and selfstudy materials. Additionally, the industry faces competition from other forms of technology, such as mobile apps and online platforms, which can provide similar services at lower costs. As a result, edtech companies would need to offer high-quality products and services at competitive prices in order to remaincompetitive.
The intensity of competitive rivalry in the Indian edtech industry is relatively high. The industry is highly competitive, and companies are vying for market share and customers. Additionally, the industry is constantly evolving, and companies are constantly trying to stay ahead of the curve by introducing new products and services.
Furthermore, the industry is attracting significant investments, and companies are using these funds to expand and grow their businesses. As a result, companies would need to be innovative and agile in order to remain competitive.
A PESTLE analysis is a framework that examines the political, economic, sociocultural, technological, legal and environmental factors that may affect a company'sabilitytoenteranewmarket.Here is a comprehensive PESTLE analysis of the IndianEdtechindustry.
India has a large and growing population, which creates a large potential market for Edtech companies. The Indian government has launched several initiatives to promote the growth of the edtech industry in the country. For example, the government has launched the National Education Policy 2020, which aims to encourage the use of technology in education
and make it more accessible to students. The Indian government has been investing in digital infrastructure such as the National Optical Fiber Network, to provide internet connectivity to remote and rural areas. and promoting the use of technology in education, which can provide opportunities for Edtech companies. However, there are also regulations and policies that Edtech companies must navigate, such as data privacy laws and content censorship regulations.
India has a large and growing middle class, which can provide a significant market for Edtech products and services.
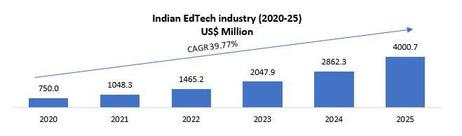
The Indian economy has been growing at a steady rate, which can provide a conducive environment for the growth of the Edtech industry.The market size of the edtech industry in India was estimated to be around $1.96 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of around 22% from 2021 to 2026. The increasing popularity of online education is also likely to attract more investment into the sector, which will further drive its growth.

The Indian population is diverse and multicultural, which can provide opportunities for Edtech companies to develop content and services that cater to different segments of the population. Despite the growth of the edtech industry in India, there is still a significant digital divide between urban and rural areas.
This presents a challenge for edtech companies in terms of reaching out to students in rural areas who may not have access to the necessary technology or internet connectivity. Edtech companies must also navigate through the cultural and linguistic barriers There are still traditional views on education in India that prioritize face-to-face interaction with teachers. Edtech companies will need to work on overcoming these perceptions and convincing students and parents of the benefits of technology-based education.
Technological:
The growth of the edtech industry is largely driven by the increasing penetration of the internet and mobile devices. With a large number of students having access to smartphones and internet connectivity, edtech companies are able to reach a wider audience. The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a significant increase in the usage of video conferencing and collaboration tools in the Indian edtech space. Edtech companies are using these tools to provide live online classes and facilitate collaboration between students and teachers. Virtual and augmented reality technologies are also being used by edtech companies in India to provide immersive learning experiences for students.
Legal:
India has data privacy laws and content censorship regulations that Edtech companies must comply with. The legal environment of
the Indian edtech space is regulated by a combination of domestic laws and international treaties. The key laws that impact the edtech industry in India include: The Information Technology Act (2000), Copyright Act (1957), The Patents Act (1970), The TradeRelated Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Agreement, Personal Data Protection Bill (2019). The legal and regulatory frameworks in place for the protection of intellectual property can provide opportunities for Edtech companies. Companies operating in the edtech space need to be aware of these laws and comply with them to avoid legal difficulties.


Environmental:
The Indian edtech space has been growing rapidly in recent years, but it also faces various environmental challenges. . The fast-paced growth of edtech also results in a high amount of electronic waste, which can be harmful to environment if not disposed of properly.As more and more personal and sensitive information is shared and stored online, the risk of data breaches and cyber attacks increases.
The EdTech sector in India has seen rapid growth in recent years, with the increasing penetration of technology and internet connectivity, and a growing awareness of the importance of education. The following are someoftherevenuemodelscommonlyusedin theIndianEdTechsector:
1.Subscription-basedmodel:Thismodelisone of the most popular revenue models in the EdTech industry. In this model, customers pay a recurring fee to access the education servicesofferedbythecompany.Forexample, BYJU'S, one of India's largest EdTech companies,offersasubscription-basedservice that provides students with access to online video tutorials, practice tests, and other learningmaterials.
2.Advertising-based model: In this model, EdTechcompaniesgeneraterevenuebyselling advertising space on their platforms. For example, Embibe, an AI-based EdTech platform, provides free study material to students and generates revenue by selling advertising space to educational institutions, publishers,andotherbusinesses.
3.Commission-based model: This model involves EdTech companies partnering with educational institutions to provide their students with online courses, and earning a commission for every student who enrolls in these courses. For example, Coursera, a global EdTech company, has partnered with leading Indian universities to offer online courses, and earns a commission for every student who enrollsinthesecourses.
4.Freemium model: In this model, EdTech companies offer a basic version of their platform for free, and charge customers for access to premium features or services. For example, Unacademy, an Indian EdTech company, offers free online classes, but chargesafeeforaccesstoitspaidcourses,live classes,andotherpremiumservices.
5.Micro-transactions model: In this model, EdTech companies earn revenue by charging customers for individual services, such as access to a particular course or exam preparation material. For example, Toppr, an Indian EdTech company, charges students for accesstoitsonlinecourses,practicetests,and otherexampreparationmaterial..
6.Enterprise model: In this model, edtech companies offer their services to corporate clients and institutions, charging them for accesstotheirplatformandotherservices.For example, Talentsoft provides an LMS platform to corporate clients and charges them for accesstotheirplatformandservices.
These are some of the revenue models commonly used in the Indian EdTech sector. The specific revenue model adopted by a company will depend on its target market, the type of services offered, and the company's overallbusinessstrategy.

The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the education industry, forcing many schools and universities to shift to onlinelearning.Thishasresultedinadramatic increase in demand for educational technology as a means of delivering remote education.
As schools and universities were forced to close their doors due to the pandemic, online learning became the only option for many students. This has led to a surge in the adoption of virtual learning platforms and other ed tech tools, such as video conferencingsoftware,onlinecoursecontent, anddigitalassessmenttools.
The shift to online learning has also highlighted the need for better technology infrastructure, including high-speed internet access and reliable devices. This has resulted in increased investment in ed tech, both by educational institutions and private companies.

.
ThereisanincreasingfocusonSTEM(science, technology,engineering,andmath)education and skills development, both in traditional educational institutions and in the workforce. This is driven by a number of factors, including the increasing demand for workers with STEM skills, the growing importance of technology and innovation in the global economy, and the need for solutions to complex problems such as climate change andpublichealth.
Inrecentyears,therehasbeenaconcerted
efforttoencouragemorestudents,especially underrepresented groups, to pursue STEM fields. This has led to the development of a rangeofeducationalprograms,initiatives,and resources designed to improve STEM educationandpromoteSTEMcareers. Educational technology has played a key role in this effort, with the development of digital learning resources and tools that support STEM education, such as interactive simulations, online labs, and coding platforms. These technologies help to make STEM education more engaging and accessible, providing students with the opportunity to experiment and explore in a safeandcontrolledenvironment.
The technological advancements in areas such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and data analytics are transforming the ed tech industry. These technologies are enabling the creation of more effective and personalized learning experiences that cater to individual learner needs. For instance, AI-powered learning platforms can adapt to the learner's pace, style, and preferences, delivering a tailored learning experience. Additionally, the use of ML algorithms can help identify knowledge gaps and provide recommendations to learners on what content they should focus on to improve their understanding. Such advancements in technology are driving growth in the ed tech industry and are expectedtocontinuetodosointhefuture.
Content development is a crucial cost driver in the ed tech industry. To offer high-quality learningexperiences,edtechcompaniesneed toinvestindevelopingengaging,relevant,and informative educational content that caters totheneedsoftheirtargetaudience.Content development costs can include expenses related to hiring subject matter experts, instructional designers, graphic designers, and writers. In addition to direct expenses, there are also indirect costs associated with content development, such as project management, quality assurance, and postproduction editing. These costs can add up quickly, making content development a significantcostdriverforedtechcompanies.
Infrastructure and hosting costs are a major cost driver in the ed tech industry. As education moves more online and remote, there is an increased demand for reliable and scalableinfrastructuretosupportthedelivery of educational content and services. This includes the cost of servers, bandwidth, storage, and other hardware and software needed to run and maintain online platforms and services. In addition to the costs of maintaining hardware, there are also ongoing costs associated with software and security updates, backups, disaster recovery, and other operational expenses. These costs can be particularly challenging for startups and smaller ed tech companies, as they may not have the financial resources to invest in the infrastructure needed to compete with larger playersinthemarket.Asaresult,many
ed tech companies turn to cloud-based infrastructure providers like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform to reduce their costs and focus on theircorebusinessactivities.

Creating and updating technology platforms and software requires specialized skills and resources, including developers, designers, project managers, and quality assurance professionals. In addition to initial developmentcosts,ongoingmaintenanceand updates are needed to ensure the platform remainssecureandfunctional,whichcanbea significant expense over the product's life cycle. To minimize these costs, ed tech companies may use open-source software, work with offshore development teams, or partnerwiththird-partytechnologyvendors.
Customersupportandservicecostsintheed tech industry can be significant, as users may require assistance with technical issues, billing inquiries, and other concerns. Providing timely and effective customer service is essential for maintaining customer satisfaction and retention, but can require a dedicated support team and infrastructure. This may include hiring and training staff, implementing customer service software, and providing multiple channels for support, such as email, phone, or chat. Customer input should also need to be monitored and analysedtoimprovesupportservices.

The policy envisions the integration of technology in education to enhance access, quality,andequityineducation.Itencourages the development of digital infrastructure, online education platforms, and digital content creation. The NEP also emphasizes the need to promote digital literacy among students, teachers, and educational institutions. The policy seeks to create a flexible and innovative education system that prepares learners for the challenges of the 21stcentury.


ItisaflagshipprogramlaunchedbytheIndian government to promote the adoption of digital technologies and infrastructure in the country. The program aims to empower citizens by providing them with access to digital services and information, including education..Itencouragesthedevelopmentof digital infrastructure, including high-speed internet connectivity, and supports the creation of digital content and services. The program also focuses on promoting digital literacy and digital skills development to enhancethecapacityofcitizenstoparticipate inthedigitaleconomy.
The Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) is an initiative launched by the Indian government to promote innovation and entrepreneurship in various sectors, including education. AIM supports the creation of startups and provides them with funding, mentoring, and networking opportunities. The program aims to promote a culture of innovation and encourage the development of solutions to address pressing societal challenges, includingthoserelatedtoeducation.
SWAYAM (Study Webs of Active-Learning for Young Aspiring Minds) is an online learning platform launched by the Indian government. The platform provides access to free courses and resources from some of the best universitiesandinstitutionsinIndia.Itaimsto promote online education and bridge the digital divide by making high-quality education accessible to all. The platform offersawiderangeofcourses,includingthose relatedtoschooleducation,highereducation, vocational education, and teacher training. The courses are designed to be interactive, engaging,andself-paced,enablinglearnersto acquire knowledge and skills at their own pace.
FDI policy aims to promote growth and innovation in the ed tech sector while safeguarding the interests of Indian stakeholders.
Startup India initiative was launched in 2016 by the Indian government to promote and support startups in the country. The initiative includes various measures such as tax exemptions, funding support, and simplification of regulations to encourage entrepreneurship and innovation in India. The edtechindustryhasalsobenefittedfromthis initiative, with several startups receiving funding and support from the government. Thegovernment'sfocusonpromotingedtech startupsisaimedataddressingthechallenges in the education sector and improving access toqualityeducationforall. .

The Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policy regulates the amount of foreign investment allowed in the ed tech sector in India. As per the current policy, up to 100% FDI is allowed in the ed tech sector, subject to certain conditions.Forinstance,foreigninvestmentis not permitted in companies that offer franchisee-based models or those that operate in the pre-primary and primary education sectors. The policy also requires that ed tech companies comply with certain reportingandcompliancerequirements.The

The Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (DISHA) is a government program launched in 2015 to promote digital literacy and digital empowerment among citizens in India. The program aims to provide training to around 60 million Indians in the use of digital technologies, such as computers, mobile devices, and the internet. The program includes several measures to deliver digital education and training, such as e-learning platforms, mobile apps, and online tutorials. DISHA also provides financial support to citizens for purchasing digital devices and availing internet services. The program has been particularly beneficial for people from ruralandmarginalizedcommunities,whohave limited access to digital technologies. DISHA is part of the government's larger vision of creating a digitally empowered society and leveraging technology to drive socioeconomicdevelopmentinthecountry.

In a number of educational institutions, education and technology are not yet woven together particularly successfully. The overall opposition of administrators and teachers has slowed the introduction of technology in educational institutions. Despite the fact that the education business must continuously seek out new ways to expand and improve, it may be good to determine whether newly created concepts and technology assist the industry in advancing and becoming more relevant.
To successfully provide solutions in the education technology space, EdTech enterprises joining or stabilising in the educational sector must first understand the market and its challenges. The major function of education technology should be to demonstrate the actual value of its service or product, including the issues it can help solve, the aid it can provide, and the opportunities it may generate. Only then will we witness a greateruptakeofEdTech!
learning applications. They aid businesses in achieving improved efficiency and productivity.
High bandwidth is frequently required for EdTech systems since video buffering and robust analytics are frequently required. For an EdTech product to function, high-speed Internet and a dependable gadget are required; yet, India has not yet fully commoditized this pair for its vast population. Slowly, EdTech businesses would build applications that address these challenges, and the technology surrounding connectivity would improve, giving EdTech a further competitiveedge.
.
Anysectorthatwantstoprosperandsurvive needs resources that keep up with internationaltrends,futurerequirements,and up-and-coming technological breakthroughs. Early EdTech was plagued by various obstacles, including a lack of technical expertise and the inability to compete with other enterprises. However, times are changing, and EdTech businesses are investing in high-quality resources and systemsforthedevelopmentofnoveldigital
There are growing worries regarding the privacy and security of data as more educational information is being saved and shared online. These concerns include the potential for data breaches as well as inappropriateuseofstudentinformation.

Teachers need training and ongoing support to effectively integrate technology into their lesson plans. This can include both technical training (e.g. how to use specific software or hardware)aswellaspedagogicaltraining(e.g. how to design effective lessons that incorporate technology). Without sufficient training and support, teachers may be hesitanttouseed-techormaynotbeusingit toitsfullpotential.
One of the primary benefits of ed-tech is the ability to provide students with personalised learning experiences.The integration of data analytics inside adaptive learning platforms allows for the creation of individualised learning routes that are catered to the specific capabilities and limitations of each student. This can help boost student engagement,motivation,andachievement.

Adaptive learning is a technology-driven approach to education that uses data and analytics to personalize the learning experienceforindividualstudents.Thegoalof adaptive learning is to provide students with an education that is tailored to their unique needs, learning styles, and abilities. It uses a varietyoftoolsandtechniquestogatherdata about each student, such as their performance on assignments and assessments, the time they spend on tasks, and their interactions with educational content. This data is then analyzed using machine learning algorithms to identify patterns and predict how each student is likelytoperforminthefuture.
Based on this analysis, adaptive learning systems can then adjust the learning experience to better suit each student's needs. For example, if a student is struggling with a particular concept, the system may provide additional resources, such as videos or practice questions, to help the student masterthematerial.Alternatively,ifastudent is excelling in a particular area, the system may provide more challenging material to keepthestudentengagedandmotivated.
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are technologies that have the potential to revolutionizeeducation.VRtechnologycreates a completely immersive digital environment that simulates a real-world experience. AR, on the other hand, overlays digital content onto the real world, enhancing the user's experience. Both technologies can be used to provide unique educational experiences that aredifficulttoreplicateinthephysicalworld. In education, VR and AR can be used to enhance learning experiences by providing students with immersive and interactive educational content. For example, students can explore a virtual world to learn about history or geography, or they can dissect a virtual frog in a biology class. In a similar way, AR can be used to create interactive and engaging learning experiences, such as overlaying digital content on a physical object to help students understand complex concepts.
Moreover, VR and AR can be used to provide distancelearnerswithaccesstoimmersiveand interactive learning experiences that simulate real-world environments. Students who are unable to attend a physical classroom can still participate in an interactive classroom through VRorARtechnologies.

In India, the education technology (Ed-tech) sector has been growing rapidly in recent years. Here are some of the emerging trends inedtechinIndia:
Online learning platforms: The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of online learning platforms in India. There has been a surge in the use of platforms such as Byju's, Unacademy, and Vedantu, which offer online classes and interactive learning experiencestostudents.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning: Ed-tech companies are using AI and ML to personalize the learning experience for students. These technologies are being used to analyze student data and provide real-time feedback and recommendations to teachers andstudents.
Virtual and augmented reality: Virtual and augmented reality are becoming increasingly popular in the ed-tech sector in India. These technologies are used to create immersive and interactive learning experiences for students, makingeducationmoreengagingandeffective.
Gamification of learning: Ed-tech companies are using game-based learning techniques to make education more fun and engaging for students. This trend is particularly popular among younger students and is an effective waytopromotelearningandretention.
Use of blockchain technology: Blockchain technology is being used in the ed tech sector to create secure and decentralized platforms for storing and sharing student data. This can help to improve the transparency and security of student records, while also making it easier for students to share their educational records withpotentialemployersandorganizations.
Integration with cloud technology: Cloud technologyisbeingincreasinglyintegratedinto ed tech solutions in India. This allows for greater scalability and accessibility, as well as improved collaboration and data sharing betweenteachersandstudents.

These emerging trends are helping to drive innovation and improve the quality of education in India. By leveraging technology, ed tech companies are creating new opportunities for students to learn and grow, and helping to address some of the key challengesfacingtheeducationsectorinIndia.

Ed-tech companies are using chatbots to provide students with 24/7 access to educational resources and support. Chatbots can also help to automate administrative tasks and provide real-time feedback to teachers and students. The most hot topic in the world of chatbots is between ChatGPT, a bot created by OpenAI, and Bard ai, the bot createdbyGoogleinresponsetoChatGPT.
ChatGPT: is a conversational language model developed by OpenAI, a leading artificial intelligence research laboratory based in San Francisco, California. OpenAI was founded in 2015 by Elon Musk, Sam Altman, Greg Brockman, Ilya Sutskever, and Wojciech Zaremba with the goal of advancing AI in a responsible and safe manner, and ensuring that AI's benefits are as widely and equitably distributedaspossible.

The GPT (Generative Pretrained Transformer) series of models, which ChatGPT is a part of, are based on the Transformer architecture, a deeplearningmodelforprocessingsequential data such as text. GPT-3, the third generation of the GPT series, was trained on a massive corpus of internet text, allowing it to generate human-likeresponsestovariousprompts.
The release of GPT-3 in 2020 caused a great deal of excitement in the AI research community, as it demonstrated the ability of AI to generate coherent and seemingly human-like text which paved the way to developconversationalmodelslikeChatGPT.
Bard: Google's AI chatbot, called "Bard", is a state-of-the-art conversational AI model developed by the Google Brain team. Bard was trained on a massive amount of data from the internet and is designed to converse in a human-like manner. The goal of Bard is to generate more human-like and diverse responses in conversations compared to other AImodelslikeOpenAI'sGPTseries.
Bard uses a combination of deep learning techniques, including neural machine translationandsequence-to-sequencemodels, to generate its responses. It has been trained on a diverse range of topics, including news, politics, sports, entertainment and technology, making it capable of having conversations on a widerangeofsubjects.
Bard has been praised for its ability to generate coherent and informative responses and has been shown to outperform other conversational AI on various benchmarks. The technologybehindBardhasthepotentialtobe applied to various areas, including customer service,virtualassistants,andchatbots.

TheEdTechmarketisworth$340billionandcouldreach$605billioninvalueby2027.
After 6 months, workers forget up to 90% of the material covered through traditional workplace training. That means huge opportunities for EdTech companies that can boost thosenumbers.
Many are unaware of how Byju’s, an Indian ed-tech giant, has partnered with a multinational tech company like Google to help offer more comprehensive learning solutions for schools in thecountry.
Over 70% of colleges expect to launch one or more online undergraduate programs in the nextthreeyears
Corporate EdTech’s market size could more than double over the next half-decade. While most of the EdTech market share belongs to North America, Europe and the Asia-Pacific regionshouldseefastergrowththisdecade.
The K-12 game-based learning market is expected to grow 20% per year through 2025. The industry is poised to add over $9 billion in market value in the first half of the 2020s. The US andCanadaareforecastedtomakeupoverone-thirdofthatgrowth.



Byju’s, an Indian EdTech startup built around a freemium tutoring app, is the world’s leading EdTechunicornwitha$21billionvaluation
Classroom engagement and instruction platforms like Kahoot! and Quizizz make up 23% of all edtech solutions used by K-12 schools. General solutions like Google’s suite of programs (Docs,Slides,Drives,etc.)makeupanother18%.
EdTech usage in schools has increased 99% since 2020. Prior to the pandemic, school districts averaged 703 EdTech solutions per month. Today, they use an average of 1403 EdTechsolutions.


MindkBusinessModel
INC42EmergingRevenueModels
Builtin-Edtech

Study.com
TheStartupLab
Oldenburg
Geomotiv
EdtechReview
MindK.com
TheBastion-EdtechRegulations
TimesofIndia-EmergingTrends
TheJournal-ValueChain

