WE SEE THE FUTURE DIFFERENTLY. INNOVATION AS STANDARD TOLEDO ENGINEERING / TECOGLAS / ZEDTEC / KTG ENGINEERING / KTG SYSTEMS / EAE TECH ® www.teco.com The TECO Group works with its customers to innovate and modernise their glassmaking processes. Furnaces, forehearths and glass plant equipment, all designed with sustainability in mind.








Editor: Nadine Bloxsome nadinebloxsome@quartzltd.com
Tel: +44 (0) 1737 855115
Assistant Editor: Zahra Awan Tel: +44 (0) 1737 855038 zahraawan@quartltd.com
Production Editor: Annie Baker
Production: Carol Baird
Sales Manager/Advertisement
production: Esme Horn esmehorn@quartzltd.com
Tel: +44 (0) 1737 855136
www.furnaces-international.com






Subscriptions: Jack Homewood subscriptions@quartzltd.com
Managing Director: Tony Crinion
Published by: Quartz Business Media Ltd, Quartz House, 20 Clarendon Road, Redhill, Surrey RH1 1QX, UK. Tel: +44 (0)1737 855000. Email: furnaces@quartzltd.com www.furnaces-international.com




1 Furnaces International June 2024
Furnaces International is published quarterly and distributed worldwide digitally © Quartz Business Media Ltd, 2024
CONTENTS C 8 12 32 25
Front cover: GRANCO CLARK




Welcome to the June issue of Furnaces International magazine!
In this edition, we shine a spotlight on greener furnace technologies, exploring innovative approaches to reduce environmental impact while enhancing efficiency and performance. From sustainable energy sources to emissions reduction strategies, we uncover the pivotal role of furnace technology in driving sustainability across sectors.
Additionally, we venture into the realm of thermal processing for space and additive manufacturing, uncovering the unique challenges and opportunities presented by these dynamic fields. From heat treatment in zero-gravity environments to the integration of advanced materials in additive manufacturing processes, we explore the frontier of furnace technology in space exploration and advanced manufacturing.
We are also delighted to feature The Advanced Forming Research Centre (AFRC) as a world-leading metals research centre with a specific focus on metal forming and forging. Through collaborative research and innovative solutions, AFRC is spearheading advancements in metal processing, forging new pathways for industry growth.
Nadine Bloxsome, Editor, Furnaces International, nadinebloxsome@quartzltd.com


GLOBAL FURNACES 5 Global Furnaces News 8 Future with Future Forge 12 Thermal processing for space and additive manufacturing GREENER FURNACES 15 Greener Furnaces News 20 Lazar CCBF technology - greener, cleaner, and stronger 25 Hydrogen: Strategic development and expansion LIFE OF A FURNACE 28 Life of a Furnace News 32 Best Practices in Rotary Kiln Maintenance 36 RATH: Lightweight refractory lining for tunnel kiln cars
2 Furnaces International June 2024 www.furnaces-international.com CONTENTS AND C OMMENT SUPPORTERS OF FURNACES INTERNATIONAL




✓SINGLE CHAMBER / MULTI CHAMBER FURNACES
✓SCRAP DECOATING SYSTEMS
✓TILTING ROTARY MELTING FURNACES
✓SCRAP CHARGING MACHINES
✓LAUNDER SYSTEMS
✓CASTING / HOLDING FURNACES
✓HOMOGENIZING OVENS
✓COOLERS
✓SOW PRE-HEATERS
✓REPAIR & ALTERATIONS














































ST. LOUIS, MISSOURI, USA 800 325 7075 | www.gillespiepowers.com | 314 423 9460
The SORG Group unites industry-leading forces, each distinguished by experience, reliability, and innovation. Combined, we provide a seamless hot end process, from batch and cullet handling to melting technologies and furnace design, to furnace construction and complete lifecycle services.

FURNACE ADVANCING AS ONE IN BATCH, FURNACE AND SERVICE










SERVICE
sorggroup.com
sks.net BATCH
eme.de sorg.de
ArcelorMittal Brasil orders twin-ladle furnace station from Danieli
ArcelorMittal Brasil has chosen Danieli Centro Met technology and equipment for a twin-ladle furnace station to be installed at the Tubarão integrated steel plant in Serra, Espirito Santo state, where 7+ Mt/yr of high-quality, flat carbon steel products are produced.
The new twin-ladle furnace station will be placed in the melt-shop bay between converters and continuous casting machines to complete the refining area, remove sulphur contents and make quality adjustments to the steel bath, to produce USIBOR steel for automotive applications.
Characterized by ladle pass-through design, upside-down design electrode lifting/turning system, and Q-Reg, the new installation will increase melt shop capability, says Danieli, to produce low-sulphur grades for the automotive industry.
Danieli’s new fume-treatment plant, water-treatment plant and compressed-air plant will serve the twin-ladle

furnace.
A new material handling system, a semi-gantry crane dedicated to ladle furnace station maintenance, and a laboratory for slag analysis also are part of the total order.
Danieli Automation process and electric controls featuring Q-Reg® advanced electrode regulation system for improved arc control and optimal performance, and AC transformer will handle the new secondary metallurgy station.
Kanthal to expand production in Japan with SEK 100m investment
Industrial heating solutions provider Kanthal has announced plans to expand its production capacity in Sakura, Japan, with an investment of approximately SEK 100 million.
The aim is to capture mid- and long-term market growth in Asia.
At the Kanthal production site in Sakura, Japan, the company manufactures products for electrification of industrial heating processes.
The total investment will reach approximately SEK 100 million between 2024 and 2025 and includes the development of a new facility near the current premises in

Sakura, as well as new equipment and a new layout. The expansion is expected to be fully operational in the end of 2025, increasing the current production capacity by
approximately 60% and enabling additional job opportunities.
“We see this investment as necessary to meet our customers’ current and future needs. We expect a rapidly growing demand for our heating solutions, both for our traditional products but also for our high temperature process gas heaters, as they enable industries to make the green technology shift. The investment will ensure that we can capture the demand in Asia,” said Simon Lile, VP and president of business unit heating systems at Kanthal.
NEWS GLOBAL FURNACE 5 Furnaces International June 2024
www.furnaces-international.com
SGD Pharma invests €20M to build furnace and upgrade facility in China
SGD Pharma has invested more than €20 million to upgrade its Zhanjiang plant in China. The refurbishment involves a complete rebuild of its furnace and comprehensive improvement of the plant’s facilities.
Using the most advanced design and technologies, this new furnace allows the Zhanjiang plant to increase capacity, improve energy performance and minimise energy consumption, reducing the Group’s carbon footprint in line with its environmental commitments and long-term decarbonisation roadmap. SGD Pharma’s objective is to reduce CO2 emissions from 2020 by 35% in 2030 and by 65% in 2040.
Alongside the furnace rebuild,
production lines and inspection equipment at the plant have been upgraded to improve glass quality and production flexibility. The plant now offers feeder coloration and a range of coloured glass options to meet specific requirements, mainly for luxury beauty products.
Chunyan Zheng, Deputy General Manager at SGD Pharma Zhanjiang plant, said: “This significant investment allows us to improve the operational excellence of Zhanjiang plant making sure that we manufacture the best in quality to serve our customers worldwide. We are delighted with the improvements to our plant and are excited about the new features that we can now provide our customers, for example feeder coloration.”

Frédéric Barbier, General Manager of SGD Pharma BU APAC, adds: “SGD Pharma has been working with the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) on the reduction of CO 2 emissions and has developed a 1.5°C decarbonisation pathway and target validation.
Zhanjiang plant is a critical part of this ambitious decarbonisation plan. It is fantastic to see our new furnace working in a way that helps us to not only increase productivity but also minimise environmental impact. This €20 million renovation project illustrates our sustained investment strategy, and ongoing commitment towards a more sustainable future.”





NEWS GLOBAL FURNACE 6 Furnaces International June 2024 www.furnaces-international.com





GLASS SERVICE Tying Technology Together Help the planet existing chnology educe CO2 with: l Boost l More boost l Electric forehearth l Superboost l Hybrid ur naces ble future from Glass Service and FIC The World,s Number One in Fur nace Technology FIC (UK) Limited Long Rock Industrial Estate, Penzance, Cornwall TR20 8HX, United Kingdom www.fic-uk.com +44 (0) 1736 366 962

Future Forge Future Forge
Future with
Alastair Conway* and David Easton spoke with Furnaces International in an exclusive interview on the development of FutureForge.
1Who/ what is the Advanced Forming Research Centre?
The Advanced Forming Research Centre (AFRC) is a world-leading metals research centre with a specific focus on metal forming and forging. We help businesses of all sizes to look at productivity improvements, testing and trialling new technologies and ideas before turning them into a commercial reality. Among our members and partners are some of the world’s leading manufacturing firms operating in a range of sectors. The success of the AFRC led to the development of the wider National Manufacturing Institute Scotland (NMIS), which is operated by the University of Strathclyde and now comprises five R&D centres and is part of the High Value Manufacturing Catapult (HVMC).
*head of operations, forging and incremental technologies team lead at the University of Strathclyde’s Advanced Forming Research Centre, part of the National Manufacturing Institute Scotland
GLOBAL FURNACES 8
Furnaces International June 2024 www.furnaces-international.com
2
When did plans for FutureForge begin?
The idea for FutureForge was first discussed around 2016, with the core project kicking off the following year and we officially opened the facility in March 2024.

3Why build FutureForge?
The catalyst for the facility was the desire to provide a platform for high integrity forging, which allows companies to utilise advanced technology and demonstrate new possibilities at the right scale. The AFRC already had the capability to complete smaller scale forging research but, to carry this on to the scale that industry needs, we needed to build a dedicated new space.
Forging is a traditional manufacturing process dating back thousands of years and is still vital to nationally important industries such as aerospace, defence, marine and energy. However, it remains a bit of a ‘dark art’ with limited use of technology and a reliance on talented individuals, many of whom are now approaching retirement age.
The multi-million-pound investment, supported by the Aerospace Technology Institute (ATI), the HVM Catapult and Scottish Enterprise, means we now have an industry-scale platform unlike any other that we know of in Europe and even America. There was a gap that we chose to fill, to help the forging industry modernise, embrace net-zero, unlock energy savings, accelerate productivity and ultimately transform the industry for future generations.
5
Do you see FutureForge as a turning point for manufacturing in the UK?
FutureForge is a really strong addition to what we are currently doing to support the future of UK manufacturing. Transforming the industry is a big challenge that no organisation will be able to solve single-handedly, but we are already starting to see signs of a rebound. Particularly in forging, where well-established companies are attracting new investment and winning new contracts, there are reasons to be optimistic.
With access to a facility like FutureForge, companies that are strategically important to the UK can get the support they may need to go through a modernisation and digitisation process. At the moment, technology adoption is still fairly low compared to other sectors and, while there is a desire to change that, not all businesses have the knowledge or expertise to do so. FutureForge can support their digital journey.
7
Focusing on technology, what are the features of FutureForge?
FutureForge comprises a tri-modal 2,000 tonne press offering open die, closed die, and iso-thermal forging capabilities, instantaneous data analytics through a state-of-the-art control room, and a custom-built smart robotics manipulator.
It also has two furnaces: one powered by electricity and the other by gas which make it unique and will be key for a net zero transition. Both furnaces have a working volume of 2.7 (W) x 1.5 (H) x 4 (L) m3 and capability to work in the range of 400-1250ºC.
The route for manufacturing many critical components may have been signed off decades ago, before sustainability was
4 Why Scotland?
The AFRC has a team of around 100 engineers and researchers with decades of experience and expertise in materials science, forging and forming, working with a range of global partners and our team connects into the capabilities of the wider NMIS group. We already had a significant capability here, and the next natural step was for us to expand the facility to offer even more support to the forging industry. Scotland has a deep-rooted history of manufacturing, a desire to future-proof the sector and a highly connected innovation ecosystem, and FutureForge undoubtedly fits in with that.
6
What industries is FutureForge most interested in?
We are primarily interested in high integrity, high value industries that are deemed critical to the UK, such as aerospace, energy, renewables, marine, and nuclear, but we are open to hearing from any potential partners who are keen to collaborate on research using the platform.
part of the conversation, so we need to be able to prove the safety and integrity of parts made with a furnace powered by renewable energy sources to help with that transition. We hope to be able to give our customers and, in turn, their customers the confidence to invest in new all-electric factories themselves, by offering the ability to do trials here first.
GLOBAL FURNACES 9 Furnaces International June 2024 www.furnaces-international.com
8
Focusing on Industry 4.0, what technology have/ will you implement?
Advanced industry 4.0 capabilities will enable companies from overseas to connect in real-time with the AFRC remotely and benefit from the skills and expertise of its people, along with the ground-breaking R&D equipment, no matter where they are based. FutureForge incorporates up to 2,000 channels of data – which is far more than any industrial press should need – but by collecting as much information as possible we can develop a roadmap for how the data can be best used in reality. We are also working on digital twins and simulation tools from microstructural to component level, and speaking to the manufacturers of the furnaces and forging press regularly to gather additional inputs and fill any gaps needed to create digital passports for various parts.
10
Do you have any R&D projects that you are/ will/ plan on working on that you could tell us about?
Due to the nature of the work, we treat each project confidentially. However, we can say that we have projects involving all three modes of the press looking at different types of forging with different materials. We have a couple of projects looking at the furnaces in isolation, using the test bed to measure and improve energy efficiency. We are also actively looking at AI modelling capabilities and how that can be integrated into the digital twin and modelling aspects of FutureForge and we’re speaking to different organisations who have the expertise to assist with that next step.

12
What would you like to see change in industry in the next 10 years, how can FutureForge assist with this?
It would be great to see every forging house adopting some of the digital technology over the next decade to boost their efficiency and competitiveness. Our role with FutureForge is to demonstrate the possibilities and show companies the value of investing in more modern processes. Some of the digitisation may be more off-theshelf, plug-and-play type of equipment, but other elements may be more complex. We want to help to derisk that and remove some of the barriers that may exist to progress across the entire sector.
9
How will FutureForge work with companies across the world?
The new facility has helped to put us on the map and establish our place at the heart of the niche global forging community. We are already working on FutureForge projects with partners from all over the world, one in Japan, one in France and one in the USA, for example. Although we are located in Scotland, our digital capability means we can conduct research here and share instant results worldwide.
Of course, we are also still working with the many UK-based and European members that have helped us to get to this point including the likes of Sheffield Forgemasters, Aubert & Duval and RollsRoyce.
11
How does FutureForge go beyond R&D? What are your visions for assisting the progression of industry in commercial practice?
While FutureForge primarily exists as a facility to support R&D, there is huge potential. Beyond modernising the sector’s current ways of working, it could unlock new opportunities for companies to take manufacturing in-house, strengthening UK supply chains and increasing our global competitiveness. It could also help with the development of new products and materials in a timely and intelligent manner, which could benefit everyone in the forging community. For instance, having industrial scale furnaces allows companies to fully de-risk future investments by running production scale trials and gaining valuable data on energy consumption, cost, and efficiency. There is also a potential impact on the next generation of forgers, and seeing how digitisation shapes their careers. It is a traditional industry where the craft has typically been passed down from one generation to the next, but there is an opportunity to change the perception of forging so that it is seen as more forward-thinking and data-driven, which may help to attract more young talented engineers into the sector.
To find out more, please visit: www.strath.ac.uk/research/advancedformingresearchcentre/accessourcapabilities/futureforge
GLOBAL FURNACES 10 Furnaces International June 2024 www.furnaces-international.com

































11 Furnaces International xx 2023 The Directory is the essential guide to steel manufacturers, producers, suppliers of plant equipment and services to the steel industry. It provides comprehensive listings, product information and key contact details. CONNECTING THE INTERNATIONAL STEEL INDUSTRY www.steeltimesint.com DIRECTORY 2023 Since 1866 BUYERSGUIDE.indd 18/09/2023 12:40:58 WWW.STEELTIMESINT.COM @SteelTimesInt Steel Times International Directory FOR MORE INFORMATION ON ADVERTISING OR HOW TO BE LISTED CONTACT: ESME HORN esmehorn@quartzltd.com +44 (0) 1737 855 136 FROM JUST £105 Excelsius Global Services GmbH Bgm.-Dr.-Nebel-Straße 14 D-97816 Lohr am Main Germany Tel.: +49 (0) 9352 6044-00 Fax: +49 (0) 9352 6044-19 Web: www.spie-excelsius.com #WE ARE SPIE SPIE EX CELSIUS
Thermal processing for space and additive manufacturing
By Noel Brady*


This article has been provided by Heat Treat Today
For more information, visit www.heattreattoday.com

The race to space is in full swing with public and private sector companies staking their claim in this new frontier. And breakthroughs in technology and materials offer the potential to propel humanity to unprecedented distances. Success hinges not only on the ability to discover novel solutions but also on the capacity to prepare those solutions for efficient, large-scale production.
Space Today: Making Life on Earth Better, Safer, and More Connected
According to NASA, 95% of space missions in the next decade will stay in low Earth orbit (LEO) and geostationary orbit (GEO). That means the first wave of commercial activity in space will be largely focused on making life on Earth better.
Several worldwide broadband satellites are already in orbit, offering more consistent, reliable internet signals around the globe. Defense campaigns are using advanced satellite machine learning to improve asteroid and missile detection, along with revolutionary laser technology that has made intersatellite communication possible for the first time — and the travel of information faster. And to help make life in space safe and successful, NASA is developing a scalable network of public GPS receivers for easy, short-range space navigation and tourism.
All this to say, parts are being developed for a wide range of applications, a huge portion of which are being additively manufactured.
Thermal Processing Standards Necessary for AM Adoption
However promising additive manufacturing is for space, the adoption of AM has still been limited due to the lack of standards for proprietary material and 3D printing applications. Many thermal processing experts are joining research institutions and OEMs in the drive to bring AM into mainstream manufacturing with new industry standards and production-ready solutions that help achieve ROI.
The R&D process for discovering these standards can be lengthy and expensive because it requires trial and error. A prototype or small run of parts must be manu- *Metallurgical Engineer, Paulo
GLOBAL FURNACES 12 Furnaces International June 2024 www.furnaces-international.com




on a regular schedule — with the potential to have multiple clients’ parts in the furnace at once. For example, a heat treater may have a standard titanium coach cycle they run once a day. See Table A for several coach cycles run at Paulo.
Coach cycles use recipes that were designed for cast parts and have been around since before additive was a viable form of manufacturing. While it’s true that cast parts and AM parts have similarities, such as their high porosity, it doesn’t mean that the recipes are optimal for preparing today’s parts for heavy space applications. That’s where custom cycles come into play.
Custom cycles are ideal for new or proprietary materials that don’t yet have recipes defined or that are not commonly heat treated enough to run on a regular schedule. The distinction between the two is important because not all heat treaters are equipped to run both types. While you may be able to find a coach recipe that gets you close to where you need to be, it certainly may not be optimal, especially for parts that will have a heavy life of service.
Heat treaters with flexibility of custom and coach cycles, along with full-cycle data reporting, offer a high level of control that is vital for helping the industry

factured, then heat treated, and tested for the desired properties. If a test part’s yield strength is not where it should be, for example, then the heat treating recipe is adjusted, perhaps by lowering the temperature and increasing the pressure, and can be tested again on a new batch of parts.
Coach vs. Custom Cycles
In heat treating, there are two different types of cycles, and it’s important to know the difference when you’re working with any commercial heat treater. Coach cycles tend to be more economical because these are shared cycles — existing recipes that are in high demand and run
progress and scale for production. This is also a big reason why some in-house heat treating operations may choose to outsource some of their work: first collaborating with experienced commercial heat treaters to prove the specification for a new part with custom cycles before scaling for production.
Common Cycle Adjustments for AM
There are five primary parameters that can be adjusted in the heat treating of AM parts to achieve the desired results: temperature, pressure, time, cooling rate, and heating rate. For AM parts, adjustments to the temperature and pressure are a go-to for achieving parts with higher
yield strength. For example, running a cycle 50°F cooler, but at 5 ksi higher pressure may yield better results.
There may also be certain heating ramp rates and intermediate holds before parts get to the max temperature, to allow for consistent heating and enhance the material properties. The same goes for the cooling process: controlling the rate at which a part cools with specific holding times and intermediate quenches.
Hot Isostatic Pressing, Space, and Additive Manufacturing
Hot isostatic pressing (HIP) combines high temperature and pressure to improve a part’s mechanical properties and performance at extreme temperatures. The sealed HIP vessel provides uniform pressure to bring parts to 100% theoretical density with minimal distortion. The high level of control and uniformity has made HIP the gold standard for AM parts for space.
Similar to cast parts, 3D-printed materials tend to have porous microstructures that can compromise part performance. HIP is the only process that’s able to eliminate these pores without compromising the complex geometries and nearnet dimensions that are achieved in the printing process.
Benefits of HIP for space parts:
� Better fatigue resistance
� Greater resistance to impact, wear, and abrasion
� Improved ductility
For this process, Paulo’s Cleveland division is equipped with a Quintus QIH-122 HIP vessel, which is specially modified with additional thermocouples for more precise temperature control and greater data collection. A higher level of accuracy allows us to iterate with confidence and find an efficient path to production-ready development.
One primary benefit of the Quintus QIH-122 HIP is the ability to have faster cooling at a controlled rate, which allows you to heat treat and solution treat in one furnace. This cooling rate allows great efficiency that cannot be seen with other HIP vessels on the market.
It is critical that heat treaters adapt to meet the needs of this fast-evolving industry. Many commercial heat treaters do not yet have the level of data or dynamic cycle offerings necessary and will only run HIP coach cycles with set parameters.
GLOBAL
13 Furnaces International June 2024 www.furnaces-international.com
FURNACES
Table A. Example of Coach Cycles for Space Alloys.
In other words, many are not equipped to economically iterate and adapt heat treating recipes for new parts. Without custom cycles, controlled cooling, and a higher level of data, it is impossible to push the boundaries of what’s possible.
Space Parts Requiring Thermal Processing
The future of space travel requires parts that can not only perform under high levels of mechanical pressure and extreme temperatures but are also durable enough for long-range and repeat missions. Heat treatment is a critical step in preparing rocket engine components, among others, for commission. Other space components commonly heat treat treated are:
� Volutes
� Turbine manifolds
� Bearing housings
� Fuel inlets


� Housings, support housings
� Bearing supports
� Turbo components
Since the inception of NASA’s Space Shuttle Program, Paulo has treated integral components for launch and propulsion, along with many parts currently in orbit on the International Space Station.
Materials Used in Space Parts
New materials and applications are being explored every day. Proprietary alloy blends bring unique properties and promising potential in the push for stronger, faster, longer-lasting parts. But with unique properties comes the need for unique heat treating processes. Several high-performance superalloys used for space include:
� Inconel 718, 625
� Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V)
� Hastelloy C22
� Haynes 214, 282
� GRCop Copper
Inconel 718, a championed space alloy, was originally used as a premier casting material before being adopted for AM. This nickel-based material features an extremely high tensile and yield strength that makes it ideal for components taking on a high mechanical load in extreme environments ranging from combustive to cryogenic — making this a natural material to adopt for space in the early days of 3D printing.
Because casting and 3D printing both result in similar porous microstructures, the heat treating process used for Inconel castings could also be adapted. Finding new opportunities within existing alloys like this is a highly efficient way to gain material advantage in today’s race to space. �
To learn more about adapting alloys and heat treating processes for AM parts, Visit: https://www.paulo. com/resources/thermal-processing-for-space-additive-manufacturing-the-essential-guide/?utm_campaign=heat-treat-today-publication-2024&utm_medium=vanity&utm_source=heat-teat-today&utm_content=heat-treat-today-2024-vanity-spaceguide












Combining the advantages of Oxy-Fuel and Air-Fuel Combustion
Reducing Fuel Consumption up to 60%
Reducing Oxygen Consumption up to 40%
Reducing CO2 emissions up to 60%
• Lowest NO x thanks to flameless operation
• Lowest Dross thanks to flame operation
• Reduces Exhaust Volumes
• Increased Melting Rate
• Low Maintenance




GLOBAL FURNACES 14 Furnaces International June 2024 www.furnaces-international.com
“Your Journey to CO2 neutrality starts here” contact@hotwork.ag | www.hotwork.ag | CO2 Reduction
Melting
IPCU (Integrated Pressure Control Unit) hotwork_half page.indd 1 07/06/2024 14:23
OptiFlame
Technology
Putting hydrogen to the test with HRASTNIK1860

Sorg have been working with Hrastnik1860 to test the use of hydrogen for glass production on an industrial scale.
SORG has already tested various burner types. Our newly developed SDB underport burner has been operated with 100% H2 in the GWI Hy-Glass project, while another test with a natural gas/H2 and LPG/H2 mixture is about to start.
During December 2023, the oxyfuel-powered glass production plant of Hrastnik1860 was
switched from gas to hydrogen. Individual burner pairs were gradually switched, with the hydrogen content in the gas increased and the oxygen adapted to the lower oxygen demand. A second test switched the melting furnace burners directly from 100% natural gas to 100% hydrogen.
This trial shows that a furnace can be switched to hydrogen by adapting the heating system to the different physical properties of gas and hydrogen.
SSAB continues transformation with fossilfree mini-mill in Sweden
SSAB’s Board of Directors have taken the decision to proceed with the next step in SSABs transition, building a state-of-theart fossil-free mini-mill in Luleå, Sweden. When completed SSAB will close the current blast furnace-based production system. This will reduce Sweden’s CO2 emissions with 7% in addition to the 3% from the Oxelösund mill conversion.
The new Luleå mill will have a capacity of 2.5 mton/year and consist of two electric arc furnaces, advanced secondary metallurgy, a direct strip rolling mill to produce SSABs specialty products, and a cold rolling complex to serve the mobility segment with a broader offering of premium products. The new mill will be supplied with a mix of fossil free sponge iron from the Hybrit demonstration plant in Gällivare and recycled scrap.
“The transformation of Luleå is a major step on our journey to fossil-free steel production. We will remove 7% of Sweden’s carbon dioxide emissions, strengthen our competitive position and safeguard jobs with the most cost-effective and sustainable strip production in Europe,” says SSAB’s President and CEO Martin Lindqvist.
The total mini-mill investment is estimated to EUR 4.5 billion including contingencies. By investing in new technologies,
SSAB is avoiding investments otherwise required in existing plant and equipment of EUR 2 billion during the next 10 years. The plan is to fund the investment with own cash flows and within SSAB’s financial targets.
The investment will result in significant value creation. Compared to the current system the yearly EBITDA improvement is estimated to be more than SEK 5 billion/ year at current commodity forecasts. The new mini-mill will have a better cost position with lower fixed costs, higher efficiency, shorter lead times and eliminated CO2 costs. The mill design includes a production increase of 0.5 mton/year, a mix improvement with 1 mton/year increase of special and premium steel grades.
Startup of the new mill is planned at the end of 2028 with full capacity one year later. Environmental permits are expected at the end of 2024. The investment is an important step in SSAB’s strategy to establish a leading position in emission free special and premium steels. To date SSAB has entered 55 partnerships with leading customers for our fossil free and zero steels.
SSAB took a decision 2023 to transform the steel mill in Oxelösund to fossil-free production and the project is

proceeding according to plan. The reasons to proceed with Luleå as a second step is driven by financial considerations, as well as the fact that the Raahe mill has more advanced equipment in better condition. As a third step a transformation for Raahe, Finland, is planned. The timing for the project will depend on SSAB’s financing and execution capacity, as well as the learnings from the Luleå project.
“Together with our partner LKAB we are making a commitment to eliminate the CO2 emissions from our value chain and establish the new benchmark technology for a fossil-free future. In the process we are also safeguarding Nordic industrial competitiveness for decades to come, and supporting the thousands of customers that rely on quality steel from our value chain,” concludes Martin Lindqvist.
NEWS GREENER FURNACE 15 Furnaces International June 2024 www.furnaces-international.com
ABB and Captimise to set a path for decarbonisation in the cement industry

ABB and Captimise are extending their collaboration to drive the adoption of cost-effective carbon capture, utilisation and storage (CCUS) technologies in the cement industry. Under a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), the two companies will develop screening, feasibility and Front-End Engineering and Design studies. The initiative will support cement producers in identifying suitable and cost-efficient carbon capture technologies covering their full carbon chain, from capture, liquefaction and buffer storage to transport, permanent storage and utilisation.
The initiative will combine ABB’s leading automation, electrification, instrumentation and digitalisation technologies, and its extensive
expertise in cement operations worldwide, with Captimise’s knowhow on cost-effective carbon capture technologies and its experience in CCUS projects across the US and Europe.
“Our ongoing relationship with ABB has materialised on a number of projects across different industries, and we look forward to exploring further opportunities for cement customers,” said Mattias Jones, CEO of Captimise. “We draw on a track-record of more than 25 live case studies with CO₂ emitters across Europe and the US and know we’ll be able to support operations of all sizes in cement through combined CCUS, automation and electrification technologies.”
“Reducing the carbon emissions from cement manufacturing is a major challenge and a top priority for this industry,” said Max Tschurtschenthaler, Global Business Unit Manager, Cement, ABB Process Industries. “We are on a mission to make it more cost-effective. By combining our worldclass automation, electrification and digital technologies with the know-how of partners like Captimise, we can further support the cement industry in achieving their climate and net zero targets.”
ABB and Captimise will also work together on promotional activities that bring their comprehensive study offering and services to potential customers in Europe.
www.furnaces-international.com NEWS GREENER FURNACES 16 Furnaces International June 2024
















www.schubert-salzer.com


Furnaces International June 2024 www.furnaces-international.com
the new generation of Schubert
Salzer pneumatic control valves
IO-Link
Discover
&
with
positioner and IIoT module and learn about the future of valve technology.
our experience to increase
success!
Benefit from
your
Salzer - Your Partner
the processing
OTTO JUNKER GMBH - GERMANY | ) +49 2473 601 0 | * SALES@OTTO-JUNKER.COM JUNKER INC - NORTH AMERICA | ) +1 630 231 377-0 | * INFO@JUNKERINC.COM WWW.OTTO-JUNKER.COM A CENTURY OF INNOVATION GREEN FURNACE TECHNOLOGY FOR MELTING, ROLLING AND EXTRUSION PLANTS DUOMELT INDUCTION FURNACE BILLET HEATING WITH IGBT-TECHNOLOGY STRIP FLOTATION FURNACE Starbar® and Moly-D® elements are made in the U.S.A. with a focus on providing the highest quality heating elements and service to the global market. 60 years of service and reliability I Squared R Element Co., Inc. Phone: +1 (716) 542-5511 Email: sales@isquaredrelement.com www.isquaredrelement.com Industrial Heating Quarter Page 1 11/30/2021 2:43:23 PM
Schubert &
in
industries!

PRINT + DIGITAL SUBSCRIPTION


6 print copies and a printed copy of the Aluminium International Today Directory
Digital copy of the magazine delivered to your inbox every month
Access to our digital archive of past issues, webinars and podcasts
Weekly Aluminium International Today newsletter



PLUS access to all digital issues of Furnaces International The leading journal for the global aluminium industry. Each issue contains a digest of global news, events, interviews, company and country profiles and regular regional economic briefings. Contact us today

DIGITAL ONLY SUBSCRIPTION
With a digital subscription you will receive all the benefits of the Print + Digital option, excluding print copies! Choose your subscription package...

subscriptions@quartzltd.com to take advantage of our special subscription packages. WWW.ALUMINIUMTODAY.COM
Betting on a transformation resulting in environmentally friendly heat and power

SFW ENERGIA Group in Poland, part of STEAG, acquired by REMONDIS.
The year 2023 began for REMONIDS in Poland with the acquisition of 100% of the shares in SFW Energia Sp. z o.o., based in Gliwice, which manages networks across the country. SFW Energia including its subsidiaries, such as in Mielec and Zduńska Wola, operates some production facilities, has its own certified testing laboratory and also, through its subsidiary Logistyka Paliwa i Energia, independently faces the challenges of supplying units with fuel.
With its planned investments in the district heating sector in Poland, REMONDIS wants to strengthen its cooperation with public and private customers. The company intends to make a strong commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and is therefore betting on a transformation resulting in the production of environmentally friendly heat and power. All for the fastest achievement of the key objectives of a closed loop economy.
In Public Private Partnerships, REMONDIS is the proven and reliable

partner, and the joint venture companies operating for many years in, among others, Poznań, Szczecin, Sosnowiec, Tarnowskie Góry, Krosno, Świdnik, Gliwice prove it. It means many years of working with local governments and faithfulness to our mission, which is to work for future generations, to educate residents in positive water, recycling and service behaviour and to act to improve the quality of the natural environment.
Now is the time to set new standards in next sectors of activity. Climate change and its progressive degradation require REMONDIS to pay even more attention to the issue of planetary pollution. The one most experts point to is related to the emission of greenhouse gases, and consequently global warming. Some of these emissions are due to old and inefficient heat sources. REMONDIS wants to fight for cleaner air, lower harmful emissions as well as the production of green heat supplied and electricity.
“For us, this is an important step in the development of REMONDIS in Poland. For many years, we have been investing
in technologies that contribute to decarbonisation – reducing carbon emissions and replacing fossil fuels with alternative energy sources. In this regard, we are increasingly bold in our focus on photovoltaics and we are a leader among water, recycling and services companies in the category of low-emission vehicles, whose fleet is gradually increasing year on year with us. We are aware that the acquisition of the SFW Energia Group is another opportunity to provide low-carbon heat and energy to many residents and industrial clients of the cities where our plants are located, but also a mission of sorts, especially in these times of galloping energy and fuel prices. I believe that with this transaction, our customers will live in a much cleaner environment, because the energy transition is one of the biggest challenges facing the world. We know what society’s expectations are in this regard and we want to be the driving force of change for the benefit of future generations of Poles,” says Marek Gębski PhD – Member of the Management Board of REMONIDS Sp. z o.o.
19 Furnaces International June 2024 www.furnaces-international.com NEWS GREENER FURNACE
Lazar CCBF technologygreener, cleaner, and stronger Lazar CCBF technologygreener, cleaner, and stronger

Rick Lazarou stood in an anode pit of a ring carbon baking furnace, assessing flue-wall deformations. As he looked around the steep walls, he considered how the primary reason for degradation was the continuous thermal cycling, and he wondered, “Why not create a furnace that keeps temperature at steady state?”
Lazarou imagined a vertical pit with green anodes inserted at the top and baked anodes continuously exiting the bottom, like a giant vertical pizza oven - and with that, the Lazar Continuous Carbon Baking Furnace (Lazar CCBF) was conceived.
Over time, Lazarou has brought together industry leaders and global research and development teams to take this concept from a sketch in New Zealand to bench-scale modeling in Australia; a pilot proof-of-concept project in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania USA; a full-
scale prototype plant in Hawesville, Kentucky USA, and its forthcoming iteration - a next-generation prototype plant for commercialization to be constructed in China in a joint venture between Axaeon Enterprises AG and Sunstone Development Co., Ltd. By addressing the shortcomings of traditional ring furnaces, the Lazar CCBF stands as a direct replacement that offers high-quality, environmentally superior, economical baking.
The Evolution of the Lazar CCBF Technology
The Lazar CCBF comprises vertical refractory columns with specific zones for preheating, baking, and cooling. Green carbon anodes surrounded by packing coke are continually fed through the top of the furnace. As the anodes move down through the furnace, aided by gravity, the Lazar CCBF maintains furnace components at an equilibrium temperature while only the anodes and packing coke experience temperature variations necessary for baking and cooling. This iso-thermal profile eliminates thermal cycling and the resulting damage. (See Figure 1 - The Lazar CCBF vertical column) Pre-feasibility studies in Melbourne, Australia and Frankfurt, Germany as well as initial design reviews through mathematical modeling by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) led to a pilot project in collaboration with ANH Refractories in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania in the early 2000s. This proof-of-concept operation yielded several interesting observations and conclusions, most notably, there was no slumping of the anodes and no damage to the refractory walls.
20 Furnaces International June 2024 www.furnaces-international.com

In 2011, Lazarou engaged the services of the Center for Innovation through Visualization and Simulation (CIVS) research center at Purdue University Calumet to assist in the design of a prototype furnace. The CIVS conducted thermo-kinetic studies showing that the Lazar CCBF solved the furnace degradation problem while improving the quality of baked anodes. In this study, Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) was used to evaluate the design by creating a 3D model to simulate the continuous movement of anodes through the Lazar CCBF. Parametric studies based on a variety of operating conditions produced additional data used to further optimize the Lazar CCBF design prior to the construction of the Hawesville, Kentucky prototype plant.
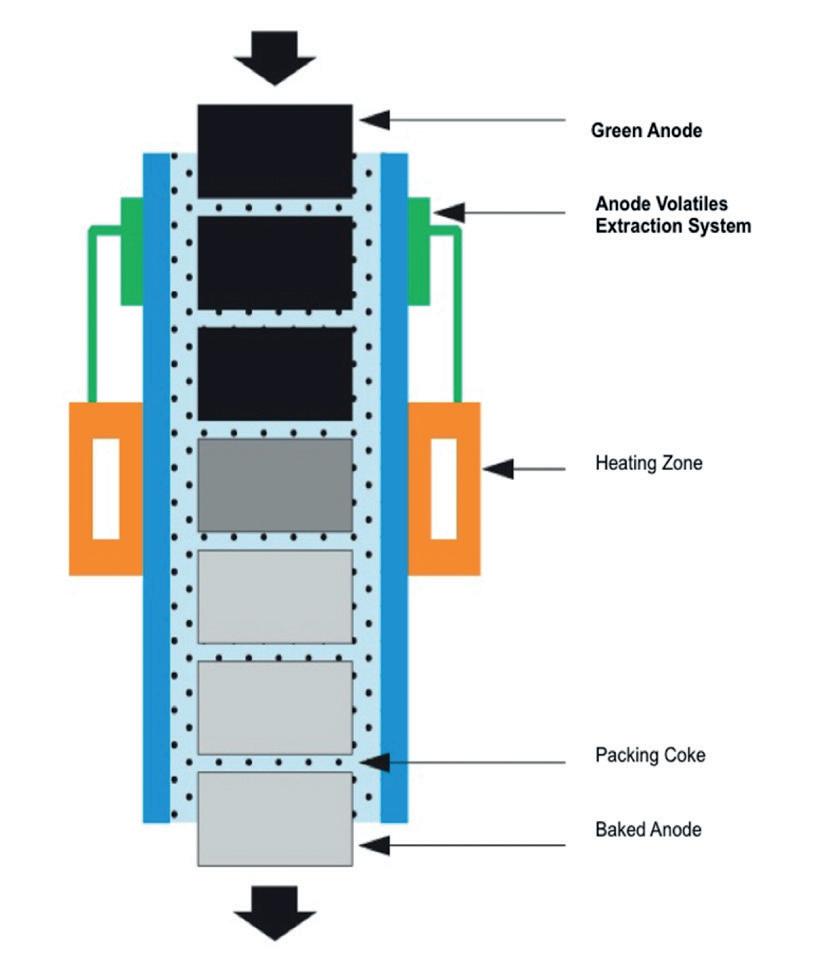
The main purpose of the Kentucky plant was to conduct additional R&D in a full-scale demonstration facility. The successful operation of the full-scale Lazar CCBF was celebrated in 2014. The Kentucky operation provided valuable data to further improve the design of the next-generation Lazar CCBF to be built in China.
Advantages of the Lazar CCBF Process
Primary industries face continuous pressure to reduce their carbon footprint and overall environmental impact. The Lazar CCBF technology achieves both goals while producing a higher quality carbon anode at a lower cost. Specifically, the benefits are:
Lower OPEX
Lazar CCBF operational costs are estimated to be up to 75% less than a ringtype furnace, due to:
� Significantly lower labor costs per baked anode on account of the Lazar CCBF’s automated process.
� Considerable reductions in refractory maintenance costs associated with the thermal degradation of flue walls experienced in traditional ring furnaces.
� Decreased burner fuel usage since thermal cycling is eliminated and volatile materials are used as a fuel source.
� Less packing coke.
� The Lazar CCBF process makes immediate delivery of baked anodes to potlines possible, greatly reducing or eliminating anode storage costs. Fur-

GREENER FURNACE 21 Furnaces International June 2024 www.furnaces-international.com
Figure 1.
The Lazar CCBF vertical column
Figure 3.
Cost comparisons between Lazar CCBF and traditional ring type furnace
thermore, the process makes it possible to deliver hot anodes to the potlines; eliminating unnecessary steps of cooling an anode and placing it in a hot reduction cell (which can shock cold anodes and increase the reject rates).
Increased Furnace Longevity
Extensive modeling indicates that the life expectancy of a Lazar CCBF refractory structure will be many times longer than that of ring-pit furnaces. This is attributed to:
� Refractories aren’t exposed to damaging thermal cycling.
� Complete extraction and destruction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from within refractory baking pits. The Lazar CCBF technology pulls PAHs out of the baking pits through the packing coke, and then diverts them into the furnace’s combustion system to fuel the baking process. This provides an additional advantage - combusted PAHs provide most of the calorific value required in baking anodes; thus, greatly reducing a burner’s fossil fuel requirements.
Lower Capital Expenditure
When compared to a conventional ringtype furnace, the estimated CAPEX of a Lazar CCBF furnace is expected to be between 30-45% lower due to:
� Fewer refractory bricks are needed to construct a Lazar CCBF.
� Baking furnace concrete tubs and supports are unnecessary.
� Reduced need for specialized equipment.
• Automated packing coke movement means multi-purpose cranes are not needed.
• Effective burning of volatiles minimizes the necessity for pollution control equipment.
• Lower retooling costs - the Lazar CCBF accommodates anodes of varied dimensions without needing structural modifications.
(See Figure 3: Cost comparisons between Lazar CCBF and traditional ring type furnace)
Safer Work Environment
The Lazar CCBF process enables a safer work environment.
� Plant air quality tests confirm that concentrations of pitch volatiles and other toxic gases were eliminated or vastly below the US OSHA permissible expo-
sure limits.
� Iso-thermal conditions eliminate the need for harmful ceramic fibers (used in traditional furnaces to protect furnace refractory structures from thermal-cycling degradation).
Process Flexibility
The Lazar CCBF process boasts variable anode movement rate. This variability allows a plant to:
� Regulate the total bake time
� Easily adjust the production rate to supply a pot room’s need of anodes
� Alter the thermal profile experienced by an anode without changing the flue wall design.
Footprint and Modularity
� The total footprint of a Lazar CCBF for a 250ktpa smelter is approximately 30% of the footprint needed for a comparable ring type furnace.
� Smelting plants can opt to phasein Lazar CCBF modules to maintain production requirements, while phasing out the equivalent production capacity from existing ring type furnaces until full conversion to the new technology is achieved – without interruptions to production.
� Plants can increase capacity by adding additional Lazar CCBF sections
� If necessary, Lazar CCBF sections can be split into smaller units for placement in different parts of a plant to accommodate space limitations
The next carbon baking transformation
When the Hall-Héroult smelting process
revolutionized aluminium production in the 19th Century (and the use of the Søderberg process in the early 20th Century), mass production of aluminium was finally possible and aluminium became so entrenched in our daily lives that it’s now impossible to imagine a world without it. The next carbon baking revolution might already be underway as primary industries search for technologies that will enable the crucial shift to more sustainable green manufacturing. While other technologies are in the exploration stage, the joint venture between Axaeon Enterprises AG, and Sunstone Development Co., Ltd to commercialize the Lazar CCBF makes it possible to deliver a sustainable green option now. �
References
1. Lazarou, R. (2024, April 10). History of the Lazar CCBF (S. Colbert, Interviewer).
2. Neill, D. (2015). The anode baking revolution. Aluminium International Today, 27(3). Retrieved from https://issuu. com/quartzmetals/docs/ait__july_august_2015
3. Walla, N., Dubec, S. J., & Lazarou, R. (2016). Lazar Continuous Carbon Baking - The Future is Now. Journal of Siberian Federal University. Engineering & Technologies, 9(5), 693–702. https://doi.org/10.17516/1999494x-2016-9-5-693-702
4. Zhou, Y., Wu, B., & Zhou, Chenn. Q. (2012). CFD thermal modeling of the anode baking furnace. Hong Kong: 2nd Asian-US-European Thermophysics Conference Thermal Science for Sustainable World.

GREENER FURNACE 22 Furnaces International June 2024 www.furnaces-international.com



sales@properzi.it For further info: Our Engineering Department now includes Fumes Treatment Systems upon request





















CONNECTING THE INTERNATIONAL GLASS INDUSTRY
Magazine
Glass International o ers readers the latest developments from the hollow, container, flat, and speciality glassmaking industry and is the o cial media partner for the global Glassman events.
Directory
The Glass International Directory is the essential guide for glass manufacturers and suppliers of glassmaking equipment worldwide. It provides comprehensive company listings, product information and key contact details, including an alphabetical listing of glass manufacturers and producers and suppliers of plant equipment and services. Now an online resource as well as being printed annually, be ensured that you are always up to date with the latest in glassmaking technology and industry contacts.
Website
Packed with the latest information on the glass manufacturing industry and continually updated with news. glass-international.com articles and interviews with leading industry gures.
Newsletter
A round-up of the top news stories is sent to more than 16,000 industry professionals each week as a free e-news bulletin. www.glass-international.com/e-newsletter
Online Events
Glass International hosts regular

BUSINESS MEDIA LTD PUBLISHED BY FIND OUT MORE AT GLASS-INTERNATIONAL.COM Join the Glass International Group

Hydrogen: Strategic development and expansion
In recent years, the global energy landscape has witnessed a significant shift towards sustainability and decarbonisation. As nations strive to reduce their carbon footprint and combat climate change, hydrogen has emerged as a promising solution for clean energy. With its potential to power various sectors including transportation, industry, and heating, the hydrogen market is experiencing strategic developments and global expansion at an unprecedented pace.
The Rising Significance of Hydrogen Hydrogen, often dubbed as the “fuel of the future,” holds immense potential as a clean energy carrier. Unlike fossil fuels, hydrogen emits no greenhouse gases or pollutants when used in fuel cells or combustion processes, making it an attractive option for achieving carbon neutrality. Moreover, hydrogen can be produced from diverse renewable sources such as wind, solar, and biomass, further enhancing its appeal as a sustainable energy solution.
Strategic Developments Driving Market Growth
Several factors contribute to the rapid growth and development of the hydrogen market:
� Government Initiatives and Policies: Governments worldwide are implementing ambitious strategies and policies to promote hydrogen adoption. Initiatives such as hydrogen roadmaps, subsidies, and tax incentives incentivise investment in hydrogen infrastructure and technology development.
� Technological Advancements: Breakthroughs in hydrogen production, storage, and transportation technologies are driving down costs and improving efficiency. Innovations in electrolysis, hydrogen fuel cells, and hydrogen storage solutions are making hydrogen more competitive with traditional energy sources.
� Industry Collaboration and Part-
nerships: Collaboration between governments, industry players, and research institutions is fostering innovation and accelerating the deployment of hydrogen technologies. Strategic partnerships enable knowledge sharing, resource pooling, and scale-up of hydrogen projects, further catalysing market growth.
� Investment Influx: The hydrogen market is attracting significant investments from both public and private sectors. Venture capital funding, government grants, and corporate investments are fueling research, development, and commercialisation of hydrogen technologies across the value chain.
Global Expansion and Market Opportunities
The global hydrogen market is expanding rapidly, driven by growing demand across various sectors:
� Transportation: Hydrogen-powered vehicles, including cars, buses, trucks, and trains, offer zero-emission mobility solutions. Governments are incentivising the adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles through subsidies, infrastructure development, and regulatory measures as per report published by Persistence Market Research. As automakers invest in hydrogen technology and expand their product offerings, the transportation sector presents significant market opportunities for hydrogen.
� Industry: Industries such as steel manufacturing, chemicals, and refineries
STUDY: GREENER FURNACE 25 Furnaces International June 2024 www.furnaces-international.com
are exploring hydrogen as a clean alternative to fossil fuels for process heating and power generation. Hydrogen can replace coal and natural gas in industrial processes, reducing carbon emissions and enhancing sustainability. As companies seek to decarbonise their operations and comply with stringent environmental regulations, the industrial sector represents a key market for hydrogen applications.
� Energy Storage: Hydrogen can play a crucial role in energy storage and grid balancing, particularly in conjunction with renewable energy sources. Excess renewable energy can be used to produce hydrogen through electrolysis, which can then be stored and converted back to electricity when needed. As the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix continues to rise, the demand for hydrogen-based energy storage solutions is expected to grow, creating opportunities for market expansion.
� Power Generation: Hydrogen fuel cells offer a clean and reliable alternative to traditional power generation technologies. Fuel cell systems can be deployed for stationary power generation in remote areas, off-grid applications, and backup power systems. With advancements in fuel cell efficiency and durability, hydrogen-based power generation is becoming increasingly competitive with conventional fossil fuel-based generation methods.
Challenges and Outlook
Despite the promising growth prospects, the hydrogen market faces several challenges that need to be addressed:
� Cost Competitiveness: While the cost of hydrogen production has declined in recent years, it still remains higher than fossil fuels in many regions. Achieving cost parity with conventional fuels is crucial for widespread adoption of hydrogen across various sectors.
� Infrastructure Development: The widespread deployment of hydrogen infrastructure, including production facilities, refueling stations, and distribution networks, requires substantial investments and regulatory support. Infrastructure development efforts need to be coordinated to ensure seamless integration and accessibility of hydrogen across regions.
� Scaling Up Renewable Hydrogen Production: Scaling up the production of renewable hydrogen to meet growing demand poses technical and logistical
challenges. Electrolysis technologies need to be further optimised and deployed at scale to enable large-scale production of renewable hydrogen cost-effectively.
� Policy and Regulatory Frameworks: Harmonised policies and regulatory frameworks are essential to create a conducive environment for hydrogen investment and deployment. Governments need to provide long-term policy certainty, regulatory incentives, and market mechanisms to drive hydrogen market growth.
Despite these challenges, the outlook for the hydrogen market remains highly optimistic. With increasing awareness of the need for clean energy solutions and concerted efforts to mitigate climate change, hydrogen is poised to play a pivotal role in the global energy transition. Strategic developments, technological advancements, and market expansion efforts are laying the foundation for a hydrogen-powered future, driving sustainable growth and environmental stewardship in the years to come.
Investment and Innovation
Investment in hydrogen-related projects and research is on the rise, indicating growing confidence in the market’s potential. Governments, multinational corporations, and startups are allocating significant resources to develop innovative solutions and scale up hydrogen infrastructure.
� Government Support: Many governments are prioritising hydrogen in their energy agendas, allocating funds for research, development, and deployment. For example, the European Union’s Hydrogen Strategy aims to install 40 gigawatts of electrolysers for hydrogen production by 2030, fostering a vibrant hydrogen ecosystem.
� Corporate Initiatives: Leading multinational corporations across various industries are incorporating hydrogen into their sustainability strategies. Companies are investing in hydrogen technologies, forming partnerships, and setting ambitious targets to reduce carbon emissions. For instance, major automakers are ramping up production of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, signaling a shift towards zero-emission transportation.
� Startup Innovation: The startup ecosystem is buzzing with innovation in hydrogen technology, with numerous companies developing novel solutions to
address key challenges. From advanced electrolysis techniques to hydrogen storage innovations, startups are driving technological advancements and disrupting traditional energy paradigms.
International Collaboration
International collaboration is essential to unlock the full potential of the hydrogen economy and address global energy challenges. Cooperation among countries enables knowledge sharing, technology transfer, and resource mobilisation, accelerating the transition to a hydrogen-based energy system.
� International Partnerships: Countries are forging partnerships and alliances to promote hydrogen cooperation at the regional and global levels. Initiatives such as the Hydrogen Council, an international coalition of leading companies, are facilitating collaboration among stakeholders to advance the hydrogen agenda.
� Knowledge Exchange: International forums, conferences, and collaborative research projects serve as platforms for knowledge exchange and capacity building. Countries with advanced hydrogen infrastructure and expertise share best practices, lessons learned, and technical know-how with emerging hydrogen markets, fostering innovation and collaboration.
� Trade and Investment: International trade in hydrogen and hydrogen-related technologies is expanding, driven by increasing demand and market liberalisation. Countries with abundant renewable resources are leveraging their competitive advantage to become exporters of renewable hydrogen, creating new economic opportunities and strengthening energy security.
Conclusion
The hydrogen market is at a critical juncture, poised for exponential growth and transformation. Strategic developments, technological innovations, and global expansion efforts are laying the groundwork for a hydrogen-powered future, where clean energy drives sustainable development and mitigates climate change. As governments, industry stakeholders, and investors continue to prioritise hydrogen, the momentum towards a hydrogen economy is expected to accelerate, unlocking new opportunities and creating a more resilient and sustainable energy system for future generations. �
STUDY: GREENER FURNACE 26 Furnaces International June 2024 www.furnaces-international.com

IN-FURNACE THERMAL GLASS SURVEYS
GAIN INSIGHTS INTO THE THERMAL PROCESSES IN A GLASS MELT TANK WITH ACCURATE REAL-TIME TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENTS.

A unique service for the thermal optimisation of furnaces,the In-Furnace Thermal Glass Survey produces real-time and recorded images for analysis, supplementing traditional refractory inspections.
A SURVEY HELPS TO:

Improve productivity with optimised pull rates
Increase thermal and combustion efficiency
Lower fuel costs
Protect the refractory from damage
Extend campaign life

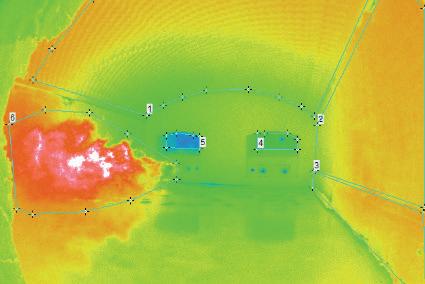


Optimise flame pattern to reduce energy consumption
Ensure emissions compliance






MARKET-LEADING TECHNOLOGY


Optimised for measuring high temperatures between 1000 to 1800°C (1832 to 3272°F), the NIR-B Glass thermal imager creates detailed and live highresolution images from within the furnace. Dedicated image processing software ensures accurate data analysis. The Lancom 4 portable multi-gas analyser measures up to eight flue gases for the optimisation of combustion and emissions processes.

LEARN MORE: WWW.AMETEK-LAND.COM | LAND.ENQUIRY@AMETEK.COM
NIR-B Glass


Bricking Solutions introduces BrickCheck
probe can also feature an optional protective coating for measurements on brick up to 212 degrees Fahrenheit (100 degrees Celsius). The handheld instrument measures and displays the thickness of refractory brick and concrete for industrial ovens, kilns and furnaces as well as unreinforced refractory concrete. It can be used on cement, dolomite, magnesite or fireclay bricks and measure a range up to 11.8 inches (300 millimeters).

Bricking Solutions has introduced BrickCheck. BrickCheck measures the thickness of refractory lining inside industrial furnaces, ovens and kilns quickly and easily in a nondestructive way after calibration.
The readings can be used to ensure smooth operation of a vessel and help plan future maintenance in any facility that uses refractory, including cement, pulp and paper, lime and metal processing facilities. BrickCheck replaces the popular, discontinued Linometer system in the Bricking Solutions line.
“Customers need to minimise the risk of refractory failure. The ability to monitor the thickness of the refractory in their vessels gives them the knowledge they need to identify wear trends before kiln failure,” said Jeff Mirisola, Bricking Solutions vice president of global sales and service.
“Using BrickCheck allows operations to plan for maintenance and downtime, limiting the impact on productivity and profitability. It’s easy to use and doesn’t damage the brick layers as much as drill core methods.”
BrickCheck includes a control unit, measuring probe, connecting cable, anti-dust cover, carrying case, plastic case and instruction manual. Three AA (LR05) batteries power the unit for up to 150 hours. The
The device uses electromagnetic measuring through the eddy currents principle to determine brick thickness. The magnetic probe is placed against the brick, and the 4-digit display shows the measurement in centimeters. The probe is accurate within 0.1 of an inch (5 millimeters). The probe and telescoping extension arm give operators a full range of motion, allowing them to measure the full circumference of the vessel without bending, stretching or stooping.
The operator calibrates BrickCheck by drilling a single trial hole. This virtually eliminates the extensive, repeated damage to the shell that the drill core method can cause where up to 200 holes may be required. The BrickCheck process is also 10 times faster.
Operators can transfer data from the device via USB or Bluetooth connection, making transfers easy for operators. BrickCheck works like a USB mass storage device and stores as much as 1 million individual readings and 9,801 separate measurement series as CSV files that can be read in programs like Microsoft Excel. This information can be analysed to see what the normal wear rate is for the vessel as well as how it varies over time, giving operators the information needed to notice hotspots or abnormal brick wear.
28 Furnaces International June 2024 www.furnaces-international.com
NEWS LIFE OF A FURNACE
Breakthrough technology for steelmakers
Nippon Steel Stainless Steel Corporation and Sojitz Group met with our induction team at Fives headquarters in Paris for a detailed design review of the transverse flux induction heating system.
CELES EcoTransFlux™ is an induction heating technology with very high heating rates at extremely high temperatures, and a compact footprint.
It also has a minimal environmental footprint, making it beneficial for steelmakers to improve their carbon, stainless or electrical steel production.
A transverse flux induction heater with very high heating rates at very high temperatures designed for the specific requirements of high-strength carbon, stainless or silicon steel grades. Because

it replaces a gas-fired furnace, you can achieve a significant reduction in NOx and CO2 emissions.
VERSATILE, COMPACT AND ECONOMICAL
High-flux induction heating solutions offer an alternative to conventional steel strip heating processes. CELES EcoTransFlux™, transverse flux induction heating technology is a proven alternative for very rapid heating at high temperatures:
� Heating capability: up to 1,200°C
� High heating rates: up to 400°C/ sec
� Heating of non-magnetic materials: stainless steel, Gen3 AHSS, etc.
� Thermal efficiency above 75% regardless of strip format
� Compact units for easier integration
� Minimised environmental impact
NextGen® System for improved furnace efficiency
The installation and commissioning of Tenova’s NextGen® will provide enhanced EAF efficiency, real-time monitoring, and control capabilities.
Dongkuk Steel Mill Co. Ltd. has recently contracted Tenova Goodfellow Inc., a subsidiary of Tenova, to improve its furnace efficiency. The scope of the contract involves the supply and installation of Tenova’s NextGen® System at Dongkuk’s Incheon Plant in Dong-gu, Incheon, Republic of Korea.
The NextGen® System, tailored for Dongkuk Steel’s 120-ton AC shaft furnace, incorporates advanced hardware and temperature sensors for off-gas measurement which include two sampling stations and a central cabinet.
Characterized by its hybrid laser/extractive off-gas analysis system, NextGen® offers numerous benefits. It provides faster analytical response times and a comprehensive spectrum of process analysis, covering CO, H2O, CO2, O2, and H2. This empowers oper-

ators with real-time monitoring and control capabilities, leading to minimized operational risks and optimized production efficiency. In addition, the system’s low mainte-
nance requirements contribute to cost savings in both hardware and installation.
“We are very proud to have been selected as a valued partner with Dongkuk Steel,” states Marcello Pozzi, Tenova Goodfellow Inc.’s CEO. “Tenova’s latest NextGen® System will incorporate our newest improvements for an automatic probe cleaning system, humidity detection upstream and COppm downstream measurements for improved asset protection.”
The installation and commissioning of the system is expected to be realized by end of 2024.

29 www.furnaces-international.com NEWS LIFE OF A FURNACE
HWI and Calderys extended portfolio of high temperature solutions
In February 2023, Calderys and HWI joined forces to create a single, high temperature solutions provider. Now, the two have become a unified Group, and are sharing technologies from one region to another to offer an expanded portfolio of world-class refractory products for high temperature industries around the globe.
A year ago, HWI and Calderys were united under single ownership, and so became the Calderys Group. The new Group immediately began an exciting program to share technologies, transferring a selection of Calderys solutions in the Americas to HWI - a member of Calderys, and bringing a selection of HWI products to EMEA and APAC, available through Calderys.
The first stages of this technology sharing program are already bearing fruit, as customers in EMEA and APAC have access to a number of carefully selected, high-value HWI refractory products, and customers in the Americas can benefit from Calderys’ tried-and-tested products, including steel casting fluxes.
“The past 12 months have been exciting, demanding, and very productive for our newly-formed Group,” says President and CEO, Michel Cornelissen. “The combination brought together two dynamic businesses with complimentary product ranges, and created the opportunity for technology sharing and cooperation for the benefit of the world’s high temperature manufacturing sectors. I am delighted that we are already seeing great results.”
HWI products in EMEA
By manufacturing a carefully selected range of HWI’s products in Europe, Calderys is able to provide EMEA customers with short lead times, small stock holdings at customer sites, and high levels of

local, technical support. Product evolution will also be undertaken locally, meaning products can be developed and fine-tuned to meet the specific needs of EMEA customers’ process developments, including, for example, ‘green steel’ applications.
Calderys will thus bring to the EMEA market a combined portfolio of refractory bricks and monolithics for various high temperature segments. These products will complement those the company already produces in the EMEA region, providing customers with an expanded and improved array of solutions for a wide range of applications, including steel, direct reduced iron (DRI), glass, copper, and petrochemical.
HWI products in APAC
Over the last few months, Calderys has already transferred dozens of HWI products for production to the Calderys Bekasi (Indonesia) site, with many more to be transferred during the first months of 2024.
The products to be manufactured locally are those in highest demand, as well as products complementary to the full Calderys portfolio, including dense castables and, due later in 2024, a combination of lightweight castables,
additional dense castable, wet mortars, and patching materials, for power generation, petrochemical, nickel production, cement, and glass.
Demand for HWI products in Indonesia is particularly high, but work is also ongoing to make available key HWI products around the APAC region, particularly products for the petrochemical sector.
Calderys solutions in the Americas
In the Americas, HWI customers now benefit from an overall broadened portfolio including Calderys’ monolithics and pre-shaped technologies, and the company’s proven steel casting fluxes, insulating fire bricks, tundish monolithics, and purging plugs. Some more work is expected in the coming months to transfer the production of additional Calderys items to HWI facilities.
Michel Cornelissen concludes:
“Throughout 2024, we will continue to add to, and update, our product portfolios, as HWI solutions are tested and made available in all geographic regions via Calderys´ global network, and Calderys products are made available in the Americas through HWI, now a member of Calderys”.
NEWS LIFE OF A FURNACE 30 Furnaces International June 2024 www.furnaces-international.com




Best Practices in Rotary Kiln Maintenance
By Craig Peppin*
*Customer Service Manager, FEECO International
Setting the Stage for Success

The following covers the most important aspects of rotary kiln maintenance.



Rotary kilns represent a significant capital investment, making extending their service life a top priority among plant managers. Further, unexpected kiln shutdowns have the potential to hold an entire operation at a standstill. For these reasons, proper maintenance is pivotal to minimising downtime and maintenance costs, while fostering process efficiency.
An effective maintenance program starts even before the equipment reaches the site, with design and fabrication techniques setting the stage for the kiln’s service life. Inferior materials of construction, low-quality fabrication techniques, and sub-par designs pave the way for frequent issues.
This means that finding an experienced original equipment manufacturer (OEM) is the first step in ensuring a long kiln service life. Look for providers with proven experience that can tailor the system’s design to the project’s unique challenges and objectives to avoid the pitfalls of a low-quality, one-size-fits-all solution.
Take a Preventative Approach to Maintenance
The second most effective way to avoid maintenance issues is to prevent them from the start with a preventative maintenance program. While this can vary depending on the operation, it generally incorporates several key facets:
LIFE OF A FURNACE 32
Furnaces International June 2024 www.furnaces-international.com
FEECO rotaty kiln
Properly Train Operators
Operators should be trained in rotary kiln operation and maintenance to prevent issues that can otherwise result from improper operation. As an example, leaving the burner running while the kiln is not in rotation can cause localised heating on the drum shell, resulting in shell warp or deflection. Personnel should be able to recognise what is “normal” for their kiln and where deviations from normality indicate potential issues.
Operators and maintenance personnel should also be trained in proper lubrication of the equipment, following OEM recommendations for both type and frequency.
Conduct Regular Inspections
Inspections are a critical line of defense in any preventative maintenance program. In addition to proper training, operators and maintenance personnel should have clear guidelines on how and when to inspect various kiln components. At a minimum, operators should regularly conduct inspections on the following, looking for visual or auditory abnormalities:
� Breeching seals
� Girth & pinion gears
� Chain & sprocket
� Tires and trunnions
� Thrust rollers
� Drum shell
� Drum internals
Ideally, operators will have predefined checklists detailing the components they need to check daily, weekly, monthly, and so forth.
Inspections should also include taking and documenting various measurements indicative of mechanical stability:
� Tire creep (floating tires only)
� Cold gap
� Drum float
� Tire & trunnion diameters
� Tire & trunnion hardness
� Root gap (gear & pinion drives only)
� Backlash (gear & pinion drives only)
� Shell temperature
OEM Inspections
In addition to on-site personnel regularly monitoring the kiln, it’s also a good idea to bring in the OEM to conduct an inspection annually (or more frequently in especially harsh operating conditions).
The OEM can provide a more in-depth

analysis of mechanical and structural components to give a full picture of kiln health and identify any potential issues to address. Any identified issues or worn components should be addressed as quickly as possible to avoid escalating damage and unexpected failures.
Common Kiln Maintenance Procedures
While a well-built kiln should experience minimal issues, normal wear and tear can present problems, particularly if the kiln is not regularly inspected and maintained. Common kiln issues are outlined here.
Misalignment
Misalignment is the most common issue rotary drums of all types encounter, kilns included; the dynamic loads and constant rotation of the unit can cause the drum to fall out of perfect alignment over time. Further, several mechanical issues have the potential to cause misalignment.
When misalignment occurs, it affects the entire unit, putting added stress on all mechanical and structural components, making it essential to resolve the
misalignment as quickly as possible.
Rotary kilns can be realigned through the traditional method of manual measurement and adjustment, or through the use of advanced laser tracking systems and software. The latter is recommended, as it reduces potential for human error and ensures a more precise alignment in faster time.
The rotary kiln will also require realignment after any major repairs, as these typically change base conditions. Uncorrected misalignment will eventually cause mechanical components to fail. Figure 1.
Improper Float
Float refers to the positioning of the drum between thrust rollers, which help to keep the drum from drifting longitudinally. Improper float is typically indicated by a tire riding too hard against the thrust roller. This ultimately causes damage to the thrust roller and tire. In extreme cases, the drum may eventually drift off its base. As such, improper float should be addressed quickly to circumvent further damage.

LIFE OF
33 www.furnaces-international.com
A FURNACE
Figure 1. A FEECO Customer Service Engineer performs a laser alignment.
Figure 2. Tire grinding in progress.
Proper float is achieved through careful adjustment or skewing of trunnion bearings in order to influence the amount and direction of longitudinal thrust the drum experiences. While this process, referred to as “training,” is simple, it should only be conducted by a professional; the potential to cause significant damage to tires, trunnions, drive components, and more through seemingly insignificant adjustments is high.
Worn Tires & Trunnions
Wear on tires and trunnions can result from a number of different factors, with misalignment, fugitive material, improper lubrication, and more among them. As part of the kiln’s structural base, when tires or trunnions become worn, all mechanical components experience increased stress.
Wear such as spalling, pitting, timing marks, and the like can typically be remediated through grinding, in which the worn component(s) is strategically ground to remove wear. In cases of severe wear, however, the component will need to be replaced, underscoring the importance of trained operators conducting regular inspections. Figure 2.
Worn Breeching Seals
Breeching seals prevent air ingress into the system, which could otherwise alter processing conditions. These seals can become worn over time but are more likely to become damaged if the kiln has fallen out of alignment.
Wear may look different depending on the type of seal employed but is typically indicated by damaged or missing leaf plates (in leaf seals), visual or auditory abnormalities where the kiln meets the breechings, or unexplained process inefficiencies. Figure 3.
Worn or Damaged Refractory
In direct-fired kilns utilising a refractory lining, upholding the integrity of the refractory is critical to the longevity of the unit. Because refractory protects the drum shell, a damaged or thin spot can quickly allow heat to penetrate the refractory and damage the carbon steel shell. Damaged refractory may also become an issue if it breaks away and enters the product stream, contaminating product and potentially damaging other components.
A problem with refractory is typically

hard to spot until it’s too late, again, making regular inspections essential. Operators should routinely inspect kiln internals and quickly address any signs of trouble. Further, operators should regularly run a temp gun over the drum’s shell, looking for hot spots or spikes in temperature that could indicate a refractory issue.
While refractory issues can result from improper installation, they are most commonly a result of cycling, or the recurrent heating and cooling of the unit resulting from regular shutdowns. This constant thermal cycling of the refractory can cause stress, resulting in cracks that can escalate into major problems. Chemical incompatibility between the refractory and the material being processed is another common culprit in refractory failure.
Repair options differ depending on the type of refractory (castable or brick) in use. Figure 4
Not Sure Where to Start? Bring in an Expert!
Those unsure of where to start in addressing their kiln issues and developing a preventative maintenance program should work with their OEM or other qualified rotary kiln service provider.
In addition to setting out maintenance needs, having a good service provider on-hand can also be a life saver in the event of an issue, helping to significantly reduce downtime.
Similarly, work with a qualified provider to keep an inventory of spare parts, which can also help to manage costs and downtime in the event of an issue, or serve as a preventative replacement.
Concluding Remarks
As a capital expense and major component in industrial processes, maximising rotary kiln service life is a top priority. While equipment design is an essential factor in minimising future maintenance requirements, plant managers can keep their kiln in good working order through a solid preventative maintenance program. This should include properly training operators and maintenance personnel, regular inspections and bringing in the OEM for a yearly evaluation, and resolving any identified issues as quickly as possible. Work with a qualified kiln service provider to establish maintenance needs and address repairs and replacements. �

LIFE OF A FURNACE 34
Furnaces International June 2024
Figure 3. Replacement Leaf Seal
Figure 4. A FEECO Customer Service Engineer inspects rotary kiln refractory and internals.












CONNECTING THE INTERNATIONAL STEEL INDUSTRY
Magazine
Steel Times International is the key publication for the steel market, reporting on iron and steel making issues from all corners of the globe.
Directory
The Steel Times International Directory is the essential guide to steel manufacturers, producers, suppliers of plant equipment and services to the steel industry. Order your print or digital copy priced from £105 or subscribers.
Website
Packed with information on the steel industry and continually updated with news for steel professionals, www.steeltimesint.com features special articles and interviews with leading industry gures.
Newsletter
A round-up of the top news stories is sent to more than 7,000 industry professionals each week. You can register online to receive the weekly newsletter and keep up-to-date with the latest news from across the steel manufacturing industry. www.steeltimesint.com/e-newsletter
Online Events

Since 1866 BUSINESS MEDIA LTD PUBLISHED BY FIND OUT MORE AT STEELTIMESINT.COM Join the Steel Times International Group @SteelTimesInt
RATH: Lightweight refractory lining for tunnel kiln cars

Like many other industrial sectors that use high-temperature processes, the brick industry faces major challenges when it comes to energy and environmental issues: Among other things, energy must be saved and the CO2 footprint reduced. The optimal refractory lining for high-temperature furnaces is a key factor in this respect. “When it comes to saving energy, having the right refractory lining is crucial, especially for manufacturing processes in the brick industry. It’s been proven that the optimal refractory lining contributes significantly to energy savings. It’s a topic that RATH has been working on intensively for some time now,” says Alexander Jüttner, Head of Sales Ceramics & Special Furnaces, RATH Group.
Lightweight lining:
Savings of up to 70 % in its specific energy consumption
High-temperature furnaces are increasingly being lined with lightweight or ultra-lightweight refractory linings. This has a number of important advantages: In addition to much lower heat losses,
these linings offer greatly simplified repair procedures. As a result, downtimes are significantly reduced, and repair and maintenance work can be carried out more easily.
In addition, energy consumption is also significantly reduced. This is demonstrated by the lightweight lining of a tunnel kiln car that RATH has developed for a company in the European brick industry.
“With this newly designed tunnel kiln car, which absorbs very little process heat, we have been able to show that equipping it with lighter refractory materials can lead to savings of up to 70 % in its specific energy consumption, without changing the process parameters or the dimensions of the furnace”, explains Alexander Jüttner.
RATH offers many refractory lining options thanks to its comprehensive and versatile product range. Whether it’s dense bricks, concretes, insulating bricks or components made from high-temperature wool, RATH’s application engineers always develop a customised concept that brings the greatest benefits to the customer.

ECOREF®: Analysis in five steps
Reduce energy consumption by customising the refractory lining: That’s where RATH ECOREF® comesin. Using this analysis and concept approach, our engineering experts determine the best refractory lining for any given application – based on the corresponding technological, ecological and business objectives and depending on numerous distinct process and plant parameters. It takes five steps to determine the most suitable lining concept. This involves an extensive analysis of the system and operating parameters. What is particularly relevant is whether a system is operated periodically or continuously, how often the system is used and what its dimensions, operating temperature and temperature profile are. The operating process that is carried out with the system, which materials are heated and the atmosphere in which this takes place are also taken into account. The result of the analysis: concrete savings potentials, defined in kilowatt hours. “Energy savings are always due to an interaction of many factors. RATH ECOREF® can make a significant contribution to achieving a good overall result here,” summarises Alexander Jüttner.
The expert for refractory linings in the ceramics industry
For more than 130 years, RATH has been producing outstanding refractory linings for industrial high-temperature applications – including the ceramics industry. In this industry, too, RATH is not only a full-range supplier of refractory products, but has comprehensive engineering and consulting expertise and offers worldwide project management for industrial furnace projects. Whether chamber furnace, bogie hearth furnace, pusher plate furnace, roller furnace, tunnel or bell-type furnace – RATH covers the complete spectrum when it comes to ceramic furnace systems. �
www.rath-group.com/ceramics
STUDY: LIFE OF A FURNACE 36 Furnaces International June 2024 www.furnaces-international.com





GLASS SERVICE Are you looking to the future for CO2 reduction? Then look no further than FIC... Tying Technology Together The eventual solution is hybrid fur naces operating at up to 80% electricity BUT small steps increase electric boost to reduce the CO2 then superboost. GS and FIC are THE companies to supply CFD modelling of your flexible future fur naces. FIC ...the pathway to a cleaner future www.fic-uk.com +44 (0) 1736 366 962 The World,s Number One in Fur nace Technology FIC (UK) Limited Long Rock Industrial Estate, Penzance, Cornwall TR20 8HX, United Kingdom




Thru-process TUS
• No trailing thermocouples so quick, safe and effective




• Measure from up to 20 thermocouples with a single data logger
• Ideal for surveying semi-continuous, continuous or modular furnaces
• Live RF telemetry TUS data collection options

• Oil, salt and water quench thermal barrier options
Batch TUS
• Efficient real time TUS of static furnaces

• Robust compact external data logger design
• Easy to transport and set-up
• Thermocouple type and plug connection options for quick installation
• Cold junction compensation to give accurate data in changing environmental temperatures
Thermal View Survey Software

• Fully compliant with AMS2750G & CQI-9
• Full 0.1 °C / 0.1 °F resolution/readability
• Apply accurate data logger and thermocouple correction factors with ease


• Full control over real time data collection and TUS analysis
• Generate your complete TUS reports with efficiency and confidence


PhoenixTM GmbH Germany info@phoenixtm.de PhoenixTM Ltd UK sales@phoenixtm.com PhoenixTM LLC USA info@phoenixtm.com ... where experience counts ! The comprehensive Temperature Uniformity Survey range!
Full Process Monitoring - TUS & Temperature / Optical Profiling www.phoenixtm.com Visit us for more information: Make Your TUS Operations……Easy, Efficient & Fully Compliant