



Volume: 113. Issue.9. September 2024





Volume: 113. Issue.9. September 2024

Illegal Mining Gangs Devastate Amazon Rainforest in pursuit of green energy minerals
The Amazon rainforest, often referred to as the “lungs of the Earth,” is under siege from illegal mining operations targeting precious minerals essential for green energy technologies. 07 Creating a Zero-Harm Workplace: The 3C’s Approach to Safety 28 The Irritating Fallacy of the Gold-Silver Ratio
Iron ore mining continues to play a crucial role in the global economy, supporting the steel industry and other industrial sectors. Nevertheless, the industry encounters a multitude of obstacles, ranging from political conflicts and environmental scrutiny to technological disruptions.
The Twin Pillars of Modern Mining Management: Sustainability & Technology


INSIGHTS FROM INDUSTRY PROFESSIONALS A Discussion on Leadership, Work-Life Balance, & Environmental Responsibility
As the 2024 U.S. election approaches, we take a look at how automation, AI, and the decline of coal are reshaping the industry, impacting job security, and influencing voter sentiments in key battleground states. 14
06 U.S. Defense Department Boosts Electra Battery Materials Corp. with $20 Million Grant
08 Copper production soars in 2024
08 Global Market Faces Record Surplus Amid Faltering Demand
10 Australian Mining Industry Struggles with Talent Shortage
12 U.S.-Philippines Nuclear Tech Pact Makes Strategic Progress

16 FiberConnect 2024: Unveiling the Booming US Fibre Optic Market
20 Amendment to nickel low-carbon briquette premium
21 Lithium prices: Where is the highest risk of curtailment?
30 Lucara Diamond Corp at the Karowe Mine
32 Botswana Unearths SecondLargest Diamond
The Future of Mining Jobs in the U.S.: A Critical Issue for the 2024 Election
39 New Tech to Battle Corrosion: Game-Changer for Mining Equipment Maintenance
40 Power Quality Challenges in Electrification of Steel Production
41 De Grey Mining Secures $150 Million NAIF Loan
44 China Tightens Export Controls on Antimony
46 Statistics
Skillings Mining Review of CFX Network LLC, publishes comprehensive information on global mining, iron ore markets and critical industry issues via Skillings Mining Review Monthly Magazine and weekly. SMR Americas, Global Skillings and Skilling Equipment Gear newsletters.

Skillings Mining Review (ISSN 0037-6329) is published monthly, 12 issues per year by CFX Network, 350 W. Venice Ave. #1184 Venice, Florida 34284. Phone: (888) 444 7854 x 4. Printed in the USA.
Payments & Billing: 350 W. Venice Ave. #1184, Venice, FL 34284. Periodicals Postage Paid at: Venice, Florida and additional mail offices.
Postmaster: Send address changes to:
SKILLINGS MINING
Digital Monthly Magazine 12 issues
Paywall-free website experience
Digital archive back to 1912
Skillings video stories and podcasts
Subscriber-only newsletter
Rich multimedia contentData, Photographs and Visuals
Access paperless reading across multiple platforms. Portable, carry with you, anytime, anywhere
UNITED STATES
$72 Monthly in US Funds
$109 Monthly in US (Funds 1st Class Mail)
OUTSIDE OF THE U.S.A.
$250 US Monthly for 7-21 day delivery
$335 US Monthly for Air Mail Service All funds are monthly
Skillings mining review, 350 W. Venice Ave. #1184, Venice, Florida 34284.
Phone: (888) 444 7854 x 4.
Fax: (888) 261-6014.
Email: Advertising@skillings.net.
PUBLISHER CHARLES PITTS chas.pitts@skillings.net
EDITOR-IN-CHIEF JOHN EDWARD john.edward@skillings.net
CONTRIBUTING EDITORS ROB RAMOS AALIYAH ZOLETA MARIE GABRIELLE
MEDIA PRODUCTION STANISLAV PAVLISHIN media.team@ cfxnetwork.com
MANAGING EDITOR SAKSHI SINGLA sakshi.singla@skillings.net
CREATIVE DIRECTOR MO SHINE mo.shine@skillings.net
DIRECTOR OF SALES & MARKETING CHRISTINE MARIE advertising@skillings.net
MEDIA ADMINISTRATOR SALINI KRISHNAN salini.krishnan@ cfxnetwork.com
PROFILES IN MINING mining.profiles@skillings.net
GENERAL CONTACT INFORMATION info@cfxnetwork.com
CUSTOMER SERVICE/ SUBSCRIPTION QUESTIONS: For renewals, address changes, e-mail preferences and subscription account status contact Circulation and Subscriptions: subscriptions@Skillings.net. Editorial matter may be reproduced only by stating the name of this publication, date of the issue in which material appears, and the byline, if the article carries one.
Vedanta Ltd has reported a significant increase in its first-quarter profits, driven by higher aluminium and zinc prices.
The company’s consolidated net profit surged by 37% year-on-year (YoY) to H3,606 crore, surpassing market expectations.
Vedanta’s revenue from operations rose by 6% YoY to H35,239 crore, compared to H33,342 crore in the same quarter last year. The company’s Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization (EBITDA) saw an impressive 47% YoY increase, reaching H10,275 crore, with margins standing at 34%.
Arun Misra, Executive Director of Vedanta, attributed the robust performance to improved margins and substantial cost reductions across all operations.
“We have delivered a strong start to the year, with exceptional EBITDA and PAT improvement on the back of improved margins, and robust cost reduction across all operations,” Misra stated.
Vedanta’s aluminium unit, the largest producer of the metal in India, reported a 14% increase in pre-tax profit, amounting to H135.15 billion. The company achieved its highest-ever alumina production at the Lanjigarh refinery, producing 539
kilotonnes (kt), a 36% YoY increase. Additionally, cast metal production of aluminium rose by 3% YoY to 596 kt, while the cost of production decreased by 11% YoY.
In the zinc segment, domestic mined production reached a record 263 kt, up 2% YoY, with refined metal production also hitting a new high at 262 kt, a 1% YoY increase. However, the mined metal production of Zinc International fell by 45% YoY due to lower milled tonnes and zinc grades, although the overall cost of production decreased by 4% quarter-on-quarter.

Apple Inc cuts jobs in its digital services division, indicating a shift in focus towards AI and emerging technologies.
Apple Inc. has recently reduced its digital services workforce by approximately 100 employees. The layoffs, affecting teams within Apple’s bookstore services and other digital areas, are part of the company's broader strategy to refocus on emerging technologies like artificial intelligence.
This decision, overseen by Senior Vice President Eddy Cue, highlights Apple’s effort to streamline operations and align resources with its evolving technology goals. Unlike other tech giants, Apple has traditionally avoided significant job cuts, making this move particularly noteworthy. The cuts suggest a shift towards enhancing services and concentrating on high-growth areas, such as AI, in preparation for the upcoming iPhone 16, which is expected to feature advanced AI capabilities.
The layoffs reflect a broader trend in the tech sector where companies are adjusting their workforces in response to economic pressures and shifting market demands. Apple’s proactive approach underscores its commitment to innovation and strategic resource allocation. As Apple prepares for upcoming product launches, these changes signal a key shift in its strategy to maintain leadership in the competitive tech landscape.
The U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) has committed $20 million to Electra Battery Materials Corp. to establish North America’s first battery-grade cobalt refinery.
The U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) has committed $20 million to Electra Battery Materials Corp., a Toronto-based firm poised to establish North America’s first battery-grade cobalt refinery. This substantial funding injection aims to catalyze the construction of a facility near Cobalt, Ontario, a project that could reshape the region’s role in the battery supply chain.
Electra Battery Materials is on a mission to revive a dormant refinery in Cobalt, a move that could significantly impact the battery industry. However, the company has faced challenges securing the remaining $60 million necessary to complete the project’s machinery and equipment. CEO Trent Mell has expressed optimism that the DoD’s endorsement will not only validate the project but also attract additional investments.
THE PLANNED COBALT REFINERY IS EXPECTED TO PRODUCE 6,500 TONNES OF BATTERYGRADE COBALT ANNUALLY, SUFFICIENT FOR ONE MILLION ELECTRIC VEHICLES.
With a target to bring the refinery online by 2026, Electra’s endeavor highlights a growing focus on the midstream segment of the battery supply chain. This sector, which transforms raw materials into finished products for electric vehicles and energy storage, is gaining momentum alongside upstream mining and downstream manufacturing.
The $20 million grant from the U.S. DoD is part of a broader initiative under the Defense Production Act and funded through the Additional Ukraine Supplemental Appropriations Act. This investment underscores a strategic shift towards bolstering national security through energy independence, extending beyond traditional climate and economic arguments.
Ensuring workplace safety is essential for both employee well-being and organizational success. Achieving a zero-harm environment is not just an aspirational goal but a necessary one, requiring a structured approach based on the 3C’s: Compliance, Competence, and Commitment. Each of these components is crucial for maintaining a secure and effective work environment.
Compliance with safety regulations is the foundational step toward a safer workplace. Organizations must adhere to industry-specific laws, such as the Mine Health and Safety Act (MHSA) for
mining and the Occupational Health and Safety Act (OHSA) for general industries.
Competence includes equipping employees with the necessary skills to perform tasks safely and adapt to industry changes. Competence involves more than technical expertise; it requires the ability to assess risks and make informed decisions.
Continuous development through regular training, coaching, and certifications helps reduce workplace accidents and promotes a proactive approach to risk management.
Commitment is the cornerstone of an effective safety culture. It reflects a steadfast dedication to prioritizing employee well-being and creating an environment where safety is a core value. A strong commitment to safety means managing risks proactively and ensuring employees feel valued and protected. Leaders play a crucial role by modeling safety behaviors, empowering employees to report hazards, and fostering open communication. This commitment helps create a culture where employees can report risks and near-misses without fear of retribution, ensuring a safer workplace for everyone.

copper production soars in 2024
AN ANALYSIS OF THE ICSG’S AUGUST 2024 bulletin, that paints a picture of recovery and expansion in the global Copper market.
The global copper market is experiencing a significant shift, with the surplus of refined copper quadrupling in the first half of 2024 compared to the same period last year.
The ICSG’s August 2024 bulletin paints a picture of recovery and expansion. Global mine production increased by 3.1% in the first six months of the year, rebounding from earlier constraints, particularly in Chile, Indonesia, and the United States. This recovery has been further bolstered by new production from the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), which saw an 8.5% increase in output.
Chile, the world’s largest copper producer, posted a 2.4% growth in mine output during this period. However, it remains 4.5% below the average production levels seen over the past five years, reflecting the lingering effects of earlier disruptions. Meanwhile, Indonesia’s output surged by 33%, recovering from severe operational constraints caused by extreme weather events at the Grasberg and Batu Hijau mines in early 2023. The U.S. also saw a 10% increase, driven by a recovery from reduced production in the first half of 2023.
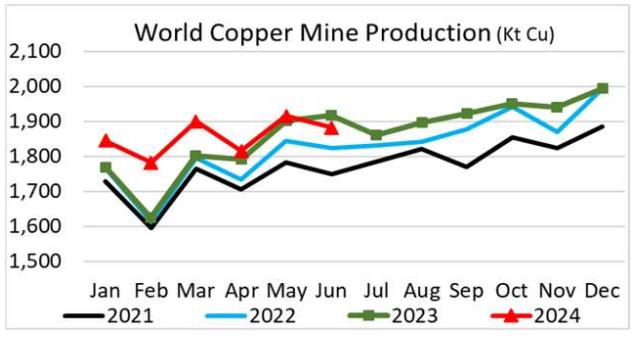
Credit: ICSG
Refined copper production also saw a significant uptick, rising by 6.2% in the first half of 2024. This growth was driven largely by expansions in China and the DRC, which together account for more than half of the world’s refined copper output.
Chinese refined production increased by approximately 7%, thanks to the start-up of new smelters and refineries. In the DRC, refined production grew by 12%,
fueled by the ramp-up of new electrowinning plants.
Other major markets, including Japan and the U.S., also contributed to the global increase. Japan’s refined copper production rose by 3.7%, while the U.S. saw a substantial 15% jump, largely due to the resumption of operations at the Kennecott smelter following a maintenance shutdown in May 2023.
On the demand side, the ICSG’s preliminary data reveals a more nuanced picture. Global apparent refined copper usage grew by 3.3% in the first half of the year, but this growth was uneven across regions. China, the world’s largest copper consumer, saw a 3.5% increase in apparent demand, despite a sharp 74% rise in its refined copper exports. Excluding China, global copper usage grew by around 3%, with weaker demand in the European Union, Japan, and the U.S. being offset by stronger growth in other Asian markets.

As the global energy transition accelerates, Australia’s mining industry finds itself at a crossroads. Rich in resources but facing an acute shortage of STEM talent, the sector’s future hinges on cultivating a new generation of skilled workers.
Suzy Urbaniak, a geologist and former school teacher, has dedicated two decades to addressing this challenge through the CoRE Learning Foundation, an initiative aimed at reshaping Earth science education.
At the recent World Mining Congress in Brisbane, Urbaniak emphasized that Australia’s resource-rich landscape could significantly contribute to global energy demands. However, she cautioned that the industry’s potential remains untapped without a strong pipeline of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) professionals.
“The natural gift of resources can’t be realized without a robust STEM talent pipeline,” Urbaniak asserted, underlining the necessity of engaging young students early in their education. Her vision is clear: more primary and secondary students must be made aware of the crucial role the resources sector plays in the global economy, as well as the diverse career opportunities it offers.
Urbaniak’s CoRE Foundation seeks to bridge this gap by transforming the way Earth science is taught in schools. The foundation’s flagship program, Gamifying Earth Science, aligns educational content with the digitalized future of the mining industry. This innovative approach has already reached over 20 schools and engaged more than 4,000 students through immersive field trips. In addition, about 70 schools nationwide have adopted CoRE’s game-based learning modules, exposing a broader audience to the sector.
CoRE’s impact will be prominently featured at the upcoming International Mining and Resources Conference (IMARC) in Sydney. Urbaniak and her team will demonstrate their

methods to an international audience of over 120 companies and 9,000 delegates. With nearly 400 students set to participate in hands-on activities, including a gamified booth experience and career speed-dating sessions with industry professionals, the event promises to spotlight the urgent need for educational innovation.
Urbaniak believes that building trust and fostering relationships are key to attracting future talent. “Nothing happens without a relationship. You need to have trust, and to remember that anything that comes out of your mouth, even if it’s one statement, is something that can be absorbed and maybe reflected on later,” she noted.
Her approach is rooted in a deep understanding of both the industry’s needs and the educational strategies required to meet them. “We need the industry to sustain our lives,” Urbaniak remarked, “but we must do so in a way that is sustainable, with strong environmental and social governance.”
The broader economic implications are clear. As Australia navigates the challenges of the energy transition, the success of initiatives like CoRE will play a critical role in ensuring that the mining industry remains both competitive and sustainable. The IMARC event, set for October 29–31 at ICC Sydney, will offer a vital platform for discussing these challenges and exploring the future of mining education.


is particularly significant, given the current geopolitical landscape in Southeast Asia.

The U.S.-Philippines partnership reached a significant milestone when their Civil Nuclear Cooperation Agreement officially entered into force. This landmark agreement formalized the framework for transferring advanced nuclear technology and materials from the U.S. to the Philippines, aimed at peaceful energy generation.
This development not only advances the Philippines’ goal of energy diversification but also strengthens U.S. influence in Southeast Asia amid rising tensions with China. The agreement allows for the deployment of cutting-edge small modular reactors (SMRs), a crucial step toward enhancing the Philippines’ energy security. SMRs, known for their efficiency and safety, are expected to play a pivotal role in reducing the country’s dependence on imported fossil fuels. The timing of this agreement is particularly significant, given the current geopolitical
landscape in Southeast Asia. As China continues to assert its dominance in the South China Sea, the U.S. is leveraging this nuclear pact to reinforce its alliances in the region. The Philippines, facing increased pressure from Beijing, sees this cooperation as a way to assert its sovereignty and align more closely with the U.S.
The nuclear agreement is just one facet of the growing U.S.-Philippines partnership. The two nations are also
working to expand collaboration in the critical minerals sector, particularly in the extraction and processing of nickel and cobalt. These minerals are essential for the production of batteries and other technologies key to the global clean energy transition.
However, environmental and social concerns surrounding mining practices in the Philippines need to be addressed to ensure that this partnership is sustainable and benefits local communities.
Industry experts have mixed views on the implications of this nuclear agreement. Some see it as a crucial step for the Philippines in achieving energy security and reducing greenhouse gas
emissions. “This agreement is a win for the Philippines, providing access to advanced technology that can meet growing energy demands sustainably,” says Dr. Maria Santos, an energy policy analyst.
The U.S.-Philippines Civil Nuclear Cooperation Agreement marks a defining moment in the two nations’ relationship, with farreaching implications for energy security and regional stability.
Conversely, others warn of potential regional destabilization. “The introduction of nuclear technology in Southeast Asia could escalate tensions, particularly with China, and could lead to an arms race,” cautions Robert Jacobs, a senior fellow at the Asia-Pacific Security Institute.
The U.S.-Philippines Civil Nuclear Cooperation Agreement marks a defining moment in the two nations’ relationship, with far-reaching implications for energy security and regional stability. As the Philippines embarks on its nuclear journey, the success of this partnership will hinge on careful management of both the strategic and environmental challenges that lie ahead.

THE AMAZON RAINFOREST, OFTEN REFERRED TO AS THE “lungs of the Earth,” is under siege from illegal mining operations targeting precious minerals essential for green energy technologies.
The Amazon rainforest, often referred to as the “lungs of the Earth,” is under siege from illegal mining operations targeting precious minerals essential for green energy technologies. These operations are not only devastating the environment but also threatening indigenous communities and fueling criminal enterprises.
The Rise of Illegal Mining in the Amazon Rainforest
Illegal mining in the Amazon has surged in recent years, driven by the global
demand for minerals like cassiterite, a key component in producing tin used in electronics and renewable energy technologies. According to a recent investigation by The Guardian, these mining activities are wreaking havoc on the Yanomami Indigenous Territory in Brazil, leading to deforestation, river pollution, and severe health impacts on local communities.
These illegal mining operations are not isolated incidents but are part of a
broader network of criminal activities. A comprehensive investigation by a team of 37 journalists across 11 countries, known as the Amazon Underworld project, has mapped out the presence of armed groups and illicit economies in the Amazon.
The project revealed that rivers in southern Venezuela, for instance, are used as trafficking routes for mining supplies, further entrenching the power of these criminal networks.
The Yanomami people, one of the most isolated indigenous groups in the Amazon, are facing an existential threat. The influx of miners has brought diseases, violence, and environmental degradation. Reports indicate that mercury in gold extraction has contaminated rivers, leading to poisoning and long-term health issues among the Yanomami.
The Brazilian government has been criticized for its inadequate response to these illegal activities, with enforcement agencies like IBAMA (Brazilian Institute of Environment and Renewable Natural Resources) struggling to combat the well-armed and organized mining gangs.


The environmental toll of illegal mining is catastrophic. Mining barges, often called dragas, dredge river beds, causing severe sedimentation and altering river courses. Mercury in gold extraction contaminates water sources, affecting aquatic life and the communities that rely on these rivers for sustenance. The deforestation and habitat destruction caused by mining operations also contribute to the loss of biodiversity in one of the world’s most vital ecosystems.
The minerals extracted from the Amazon are crucial for the global transition to green energy. However, their extraction’s environmental and human costs raise significant ethical and sustainability concerns. The international community must address the demand for these minerals by ensuring that their extraction does not come at the Amazon’s and its inhabitants’ expense.
CRU’s Wire & Cable Analysts recently took the opportunity to attend Fiber Connect 2024 – the largest fibre optics conference in North America connecting both domestic and international players operating within the region.

In line with CRU’s Optical Fibre Cables (OFC) Market Outlook and OFC Monitor, major themes continue to dominate the narrative in the US market, including the timeline and implementation of the Broadband Equity, Access and Deployment (BEAD) Program, fibre cable deployments, capacity expansions and constraints, rapid evolution in end-use markets (e.g. datacentres) and many more.
Over $1 billion has been allocated for digital equity, with $840 million directed towards state-level initiatives. However, workforce development remains a significant challenge.
The BEAD program aims to bridge the digital divide by providing substantial funding to improve broadband access
across the US. Based on data from CRU’s OFC service, as of now, 32 eligible entities have completed all ten phases of the program, while 25 are on the verge of completion. The program’s success is underpinned by the Spectrum & National Security Act, which has been deliberated in the Senate as of April 2024 and still is.
NTIA Chief Alan Davidson announced a proposed document allowing states to use alternative technologies for BEAD projects, including unlicensed spectrum fixed wireless services and cable solutions. This development acknowledges the financial and practical limitations of deploying fibre to every unserved area, especially in very rural locations.
However, high-tier ISPs remain optimistic about the timely arrival of BEAD funds in the near future; while some middle to low-tier players have lost faith in the program’s timeline and are focusing on utilising private funding to expand their networks.
Over $1 billion has been allocated for digital equity, with $840 million directed towards state-level initiatives. However, workforce development

remains a significant challenge. The broader industry highlights 78,000 jobs in broadband infrastructure needed for projects in the US, but workforce capacity issues continue to hinder the progress.
Apart from BEAD, there was a significant update regarding the potential revival of the Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP). The ACP has been at a halt since June 2024 as additional funding legislation failed to pass. Since then, the Senate Commerce Committee has recently advanced an amendment to fund the ACP with $7 billion, attached to the Plan for Broadband Act. This move aims to streamline federal broadband programs and extend ACP funding.

Eric Lia of Verizon highlighted the significant challenges in rural broadband expansion during his keynote speech. Approximately 8.8 million people in the US remain underserved, primarily due to the high costs associated with deployments of optical cable for longhaul and last-mile connectivity. Exist-

ing infrastructure and the high cost of longer cable lengths are major barriers to the expansion.
Additionally, securing central office real estate and navigating varying state regulations complicate deployment efforts, adding to the overall challenge.

Dr. Duncan, Earl of Qubitek, emphasised the transformative potential of quantum computing in enhancing network efficiency and security. The integration of AI with this technology promises massive capabilities, but also demands substantial power. Quantum computing offers improved energy efficiency compared to traditional methods. Moreover, quantum technologies can significantly bolster communication security, which is crucial for the transmission of sensitive data.
The conference underscored the evolving trends in FTTH installations, particularly the shift towards more efficient and future-proof solutions. While pre-connectorised cables offer faster installation and consistent quality, fusion splicing is favoured for its cost-effectiveness and future-proofing capabilities.
In addition, companies like Corning, AFL, and STL have pushed for the increased use of high-density fibre blown & drop cables, using bend-insensitive single-mode fibres such as G657A2 with reduced diameters down from 200 microns to as low as 190 microns.
These developments have been met with increased attention towards using microducts, as the aforementioned cabling solutions are suitable for many applications and needs from backbone networks to FTTx. However, in the US market, there


are current capacity issues with installers, resulting in high inventory levels due to limited movement. Additionally, participants at the convention highlighted the critical need for more middle-mile fibre assets in the US, as vendors and installers share the importance of redundancy and competitive options for providers. There is an emphasis on maintaining middle-mile infrastructure as short as possible to reduce latency and ensure high transmission speeds.
On the product side, companies have innovated extensively in fibre broadband access platforms. Currently, XGS-PON technology is widely deployed, providing up to 10 Gbps capacity (though practically closer to 8.5 Gbps). Some companies are moving towards 25G PON, offering true 25 Gbps speeds, and even 50G PON, which is in lab testing but not yet field-ready.
On the deployment side, companies like OFS are at the forefront of pushing the limits for installations, offering a comprehensive core product portfolio tailored for both multiple dwelling units (MDUs) and single-family units (SFUs).
The fibre optic and telecommunications industries face significant workforce and environmental challenges, particularly in the deployment of new infrastructure. With over 60% of the current workforce nearing retirement, there is a critical need for new technicians and field trades.
Additionally, varying state requirements for environmental permits slow down project approvals and increase costs. These challenges necessitate a coordinated effort to develop a skilled workforce and streamline regulatory processes to support the industry’s growth.

This decision follows a one-month consultation period which ended on Thursday August 29.
Significant shifts in market structure, including the closure of some nickel operations, have led to a reduction in the overall pool of liquidity available for briquettes broadly, but particularly low-carbon briquettes.
Interest in price transparency in low-carbon nickel still persists, however, and Fastmarkets remains committed to maintaining its price coverage of this market. In order to provide further transparency and increase the pool of liquidity available, Fastmarkets has amended the specifications of the assessment to include all shapes of Class 1 nickel which are deliverable or tradable via an exchange.
This amendment means that going forward the premium will also capture liquidity for uncut and cut cathode, pellets and rounds.
To provide feedback on this price or if you would like to provide price information by becoming a data submitter to this price, please contact Callum Perry and James McKeigue by email at: pricing@fastmarkets.com. Please add the subject heading “FAO: Callum Perry/ James McKeigue re: nickel low-carbon metal premium.” The first publication of the new price will be Monday September 2, 2024. To see all Fastmarkets pricing methodology and specification documents, go to https://www.fastmarkets.com/methodology.
Akobo Minerals, a prominent gold exploration and mining company based in Scandinavia with operations in Ethiopia, has provided an operational update from its Segele mining activities, reporting that the company has reached several critical milestones.
Daily ore production has commenced at the Segele mine. Since intersecting the ore body in the second tunnel two weeks ago, Akobo Minerals has been consistently producing and stockpiling ore. Currently, the company is in the early phases of ore extraction, advancing toward areas expected to contain high-grade material. Early results are promising, with substantial visible gold observed.
The processing plant at Segele has successfully been commissioned and is currently in the ramp-up phase. Although commissioning typically takes several months, Akobo Minerals has expedited the process, achieving significant progress within a short timeframe.

Feedback from experts and consultants indicates that the plant is in excellent condition.
The focus is now on fine-tuning the processes to maximize gold recovery and minimize losses. The first batch of very low-grade ore has been successfully processed through the entire plant, from crushing to smelting. While the gold yield was low, as anticipated, this marks a significant milestone, demonstrating the plant’s operational efficiency.
Looking ahead to September, Akobo Minerals expects to continue and expand ore production from the mine and run the processing plant in batches to secure maximum gold recovery. The gold will then be further processed at our partner MKS PAMP’s refinery in Switzerland and then sold in the gold spot market.
Current spodumene concentrate market prices pose a significant challenge for several pegmatite producers, with almost 25% of production falling into negative cash margins according to our new Lithium Asset Service database.
Operators are curtailing production and seeking to reduce costs, but this is also causing projects to rethink strategies. Lithium supply has changed notably since the 2018 market boom, with almost double the amount of operational assets, and several new mining jurisdictions emerging – but are they safe of curtailment? CRU’s asset analysis shows that Zimbabwe’s new operations are comfortably situated in the middle
of the pegmatite cost curve, while Chinese lepidolite assets are responsible for some of the highest production costs in the industry.
In addition to the high operating costs, lepidolite producers face environmental legislation constraints that will increase the risk of curtailment in China. The lithium carbonate price has reached its lowest point since August 2021, after an

83% decline from the peak in late 2022. The magnitude and rate of change in the lithium carbonate price is driving rapid downward adjustments to the margins among lithium producers.
At a forecasted average spot concentrate price of $1,120 /dmt in 2024, one tenth of the lithium pegmatite supply will be cash-margin-negative in 2024, according to our asset database.


by Charles Pitts
IRON ORE MINING CONTINUES TO PLAY A CRUCIAL ROLE IN the global economy, supporting the steel industry and other industrial sectors. Nevertheless, the industry encounters a multitude of obstacles, ranging from political conflicts and environmental scrutiny to technological disruptions. Successfully navigating these dynamics demands a deep comprehension of market trends, a steadfast dedication to sustainability, and a readiness to embrace innovation.
Over the past few years, the iron ore market has been quite volatile, mainly because of geopolitical tensions, supply disruptions, and changing demand from major economies, with China being a significant player. This comprehensive analysis delves into the current status of global iron ore mining, shedding light on major participants, market patterns, technological progress, and forthcoming obstacles.
Iron ore is primarily extracted from regions with abundant deposits, such as Australia, Brazil, China, and India. These countries collectively contribute to more than 80% of the world's iron ore production. Australia and Brazil account for over 50% of global iron ore exports. The seaborne iron ore trade plays a vital role, as China emerges as the leading importer, acquiring almost two-thirds of the worldwide supply to support its steelmaking sector.
The global iron ore market is valued at approximately $299 billion in 2024, with production concentrated in a few key regions, notably Australia, Brazil, and China. Despite a modest increase in global production over the past five years, the industry has experienced significant revenue growth, driven by elevated iron ore

prices. As of May 2024, the price of iron ore was around $118.88 per dry metric ton, having peaked at $214.43 in the previous years
The decline in demand from China: The Chinese economy's recent slowdown and the government's emphasis on reducing carbon emissions have had a significant impact on the demand for steel, which in turn has directly affected the prices of iron ore. During the first half of 2024, China experienced a decline in steel production, resulting in an excess of iron ore and causing a significant decrease in global prices compared to the previous year.
Supply disruptions caused by extreme weather events, such as cyclones in Australia and heavy rains in Brazil, have occasionally disrupted supply chains, leading to fluctuations in prices. In addition, the trade industry journalist must navigate through logistical challenges such as port congestion and shipping delays, which further complicate the task of maintaining a stable supply.
The mining landscape is being reshaped by growing concerns about sustainability and ESG issues. Companies that prioritize sustainable practices are gaining favor among investors. BHP has made a significant commitment to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, while Rio
Tinto is actively investing in renewable energy projects. Stricter environmental regulations are also impacting mining firms, especially in terms of tailings management and land rehabilitation.
Technological advancements have revolutionized various sectors, bringing about significant changes and improvements. These advancements have had a profound impact on industries, enabling them to streamline processes, increase efficiency, and drive innovation. From automation and artificial intelligence to cloud computing and data analytics, technology has become an integral part of modern businesses
The iron ore mining sector is adopting cutting-edge technologies to improve operational efficiency and minimize its ecological footprint. The mining industry is undergoing a revolutionary transformation with the advent of automation, artificial intelligence, and advanced data analytics.
Leading mining companies such as Rio Tinto and BHP are implementing cutting-edge technology to enhance safety measures and streamline operational expenses.
Ore sorting technology has made significant advancements, allowing miners to efficiently separate valuable ore from waste rock right at the extraction point. This not only helps in conserving energy but also minimizes waste, contributing to a more sustainable mining process.
a significant impact on the smooth functioning of the global supply chain. There is a growing trend where countries with abundant iron ore resources are taking more control over their mineral wealth. The imposition of royalties on mining exports in Brazil and export duties in India highlights a concerning rise in resource nationalism, which has the potential to impact global supply dynamics.
The implementation of more stringent environmental regulations is expected to result in higher operational expenses for companies involved in iron ore mining. Companies face the challenge of navigating intricate regulatory landscapes, especially when it comes to emissions, water usage, and land rehabilitation.
Navigating the complex landscape of developing new iron ore mines requires addressing a range of challenges, including exploration, community relations, financing, and regulatory compliance. Businesses that are able to tackle these obstacles by utilizing technological advancements, adopting sustainable methods, and forming strategic alliances will have a competitive advantage in meeting the growing need for iron ore.
Companies are making significant investments in technologies that aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with iron ore processing. These initiatives include hydrogen-based steelmaking technologies and carbon capture solutions.
There are significant obstacles on the horizon.
The iron ore market is significantly impacted by geopolitical tensions, including trade disputes between China and Australia. Imposing limitations on Chinese investments in Australian mines and implementing export tariffs can have
The future of global iron ore mining will be influenced by changing demand patterns, advancements in technology, and an increased emphasis on sustainability. Although there may be a temporary decrease in demand from China, the ongoing urbanization and industrialization in developing economies across Asia and Africa are projected to support long-term demand.
In addition, the growing demand for environmentally-friendly steel making technologies offers iron ore miners a chance to support global decarbonization efforts.
As the industry adjusts to these changes, mining companies that embrace sustainable practices, technological innovation, and strategic resource management will have a competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving market.
Navigating the complex landscape of developing new iron ore mines requires addressing a range of challenges, including exploration, community relations, financing, and regulatory compliance.
Businesses that are able to tackle these obstacles by utilizing technological advancements, adopting sustainable methods, and forming strategic alliances will have a competitive advantage in meeting the growing need for iron ore. This
demand is fueled by the expansion of global infrastructure and the ongoing industrialization of developing nations.
Geological Uncertainty: Discovering economically viable iron ore deposits necessitates thorough exploration and drilling efforts. Geological complexities, like variations in ore grade and the depth of deposits, introduce a level of uncertainty to resource estimation, which in turn increases the risk associated with the initial phases of mine development.
The exploration phase can be quite costly, as it requires the use of expensive technologies such as geophysical surveys and core drilling. Securing funding for these initial stages can be quite challenging, particularly during periods of fluctuating commodity prices.
Challenging Approval Processes: Acquiring the required permits and approvals can be a time-consuming endeavor, often spanning several years. This is due to the rigorous adherence to environmental regulations, land use policies, and the need for extensive community consultations. This process can cause significant delays in project timelines and increase costs.
Mines are required to conduct thorough assessments to evaluate the potential environmental impacts of their operations. Addressing the effects on water resources, biodiversity, and land degradation can often involve expensive and time-consuming research.
Managing mine tailings, which are the waste left after ore processing, poses significant environmental and safety concerns. Stricter regulations on tailings storage facilities have


been implemented following recent disasters, such as the Brumadinho dam collapse in Brazil. As a result, operational costs have increased.
Community Opposition: New mining projects are often met with opposition from local communities, environmental groups, and indigenous populations. These groups express concerns about the potential environmental degradation, displacement, and loss of livelihoods that may result from such projects. Securing community support through engagement, benefits sharing, and compensation programs is crucial yet poses a significant challenge.
In regions with indigenous populations, securing land access and agreements is a matter of utmost importance and sensitivity. Disregarding the rights of indigenous communities can result in legal disputes and cause significant setbacks to projects.
Challenging Terrain: Iron ore deposits are frequently found in remote or hard-to-reach regions that lack essential infrastructure such as roads, railways, and ports. Building

Australia is at the forefront of the global market, with its top mining companies being the largest iron ore producers. These companies, namely BHP, Rio Tinto, and Fortescue Metals Group, are reaping the benefits of vast and high-grade deposits in the Pilbara region.
According to the latest data, Australia's iron ore production has seen a significant 4% increase compared to the previous year. This growth can be attributed to the exceptional
performance of Rio Tinto's operations, which have achieved record outputs.
Brazil is home to Vale S.A. (NYSE:VALE), the leading global iron ore miner in terms of volume. Despite encountering obstacles like environmental scrutiny and tailings dam failures, Vale has successfully recovered, expanding its Northern System operations and investing in dry processing technology to enhance safety and efficiency.
this infrastructure necessitates substantial funding and cooperation with both governmental and private entities.
Infrastructure development, such as mine facilities, processing plants, and transportation networks, accounts for a significant portion of the total project costs. Obtaining funding for such extensive investments can pose challenges, particularly for emerging mining companies.
Iron ore prices are well-known for their unpredictable fluctuations, which can be attributed to factors such as global demand, supply disruptions, and geopolitical tensions. The volatility in prices can significantly affect the economic viability of a new mine, leading to investor caution.
The increasing expenses associated with labor, energy, and equipment have been consistently eating into profit
China heavily relies on imports for iron ore due to the lower-grade quality of its own reserves.
Chinese mining companies are making significant investments in projects abroad to ensure a steady supply of resources. This is evident from the increased ownership stakes of state-backed firms in mining ventures across Africa and South America.
India is quickly establishing itself as a major contender in the iron ore market, as both state-owned NMDC Ltd and private miners are ramping up their production capabilities. Nevertheless, India faces obstacles in achieving its export goals due to domestic regulatory hurdles and export duties.
margins. The financial challenges of mine development are further compounded by inflationary pressures and a growing demand for skilled labor.
The depletion of easily accessible high-grade iron ore deposits has led miners to turn their attention to lower-grade ores, which present more challenges and higher costs in the processing stage. It is crucial to develop more efficient beneficiation technologies in order to economically extract iron from lower-grade sources.
Embracing innovation and automation can lead to improved efficiency, although it does require a significant initial investment. Specialized skills and capital are essential in meeting the demands of integrating autonomous vehicles, AI-driven processing, and remote operations centers.
In light of the global push to reduce carbon emissions, mining companies are under mounting pressure to decarbonize their operations. Implementing these measures necessitates the adoption of renewable energy sources, the electrification of equipment, and the implementation of carbon capture technologies, all of which contribute to increased operational complexity.
Water use and management is a crucial aspect in mining operations, especially in arid regions where competition for water resources can be a pressing concern. Given the current challenges surrounding water scarcity, contamination risks, and regulatory pressures, it is crucial to explore and implement innovative water management solutions.
Countries with abundant iron ore resources may adopt policies that prioritize local beneficiation, impose export restrictions, or raise taxes and royalties. These actions have the potential to weaken the economic viability of projects and generate legal ambiguities.
Geopolitical tensions, like the ones between major iron ore exporters and importers, have the potential to disrupt trade flows and impact market access. Global supply chains can be significantly affected by trade disputes, resulting in the implementation of tariffs, quotas, or even complete export bans.
Efficient transport of iron ore from mine to market is crucial, but ports, rail, and shipping facilities can pose challenges, particularly during periods of high demand. Supply chain disruptions can have a major impact on delivery schedules and costs. Examples of these disruptions include labor strikes or equipment failures.
Challenges in the Global Supply Chain: The iron ore industry faces various challenges due to its reliance on intricate global supply chains that are susceptible to disruptions. These disruptions can arise from factors such as shipping delays, logistical mismanagement, and shifts in international regulations.
China's policy volatility, encompassing economic growth strategies, regulatory interventions, and long-term strategic goals, plays a pivotal role in shaping the global iron ore market. These policies not only affect immediate demand
and pricing but also have broader implications for global supply chains and market stability.
Zero COVID Policy and Economic Growth: China's stringent zero COVID policy and its slowing economic growth led to fluctuations in iron ore demand even today.
Lockdowns and restrictions dampened economic activity, reducing steel production and, consequently, iron ore demand. However, the Chinese government has also introduced stimulus measures aimed at boosting infrastructure construction, which could increase demand for iron ore.
Dependency on Imports: Despite being a major producer, China imports around 80% of its iron ore, primarily from Australia and Brazil. This heavy reliance on imports makes the market sensitive to Chinese policies affecting import volumes and domestic production goals.
Quarterly Pricing Mechanism: The shift from annual benchmark pricing to a quarterly pricing mechanism has made iron ore prices more sensitive to China's economic indicators, particularly GDP growth. The spot market, primarily developed in China, reacts quickly to changes in demand, leading to increased price volatility.
Regulatory Interventions: The Chinese government has occasionally intervened in the market to stabilize prices. Measures such as cracking down on price gouging and excessive speculation have been implemented to manage market dynamics. These interventions can lead to sudden shifts in market sentiment and pricing.
Increasing Self-sufficiency: China aims to reduce its dependency on imported iron ore by boosting domestic production and utilizing more scrap steel. This strategic shift, outlined in the 2021-25 Raw Material Development Plan, could alter global supply dynamics and affect long-term pricing.
Environmental Goals: China's push towards decarbonization, including plans to increase electric arc furnace capacity, could reduce the demand for traditional iron ore in favor of scrap steel, impacting global demand patterns.
The gold-silver ratio has long been a hallmark of market analysis, particularly among those who cling to the notion that the interplay between gold and silver prices provides insight into broader economic trends.
a guidepost for investment decisions, with some analysts claiming that it provides clues about inflation, deflation, or even impending market crashes. Other analysts watch the ratio and trade the underlying commodities, on a bet the ratio will ‘return to normal’.
In today’s financial landscape, the gold-silver ratio is increasingly being seen as a relic of the past—an obsolete metric clung to by those who fail to recognize the complexities of modern markets. In many ways, the persistence of belief in the gold-silver ratio mirrors the themes explored in Isaac Asimov’s award-winning Foundation series, where outdated systems of belief and control eventually crumble in the face of technological and intellectual progress.
The gold-silver ratio, in its most basic form, is a simple calculation of how many ounces of silver it takes to buy one ounce of gold. This ratio has fluctuated but has often hovered around 15:1 to 20:1 due to both metals’ role as money in ancient economies.
Today, the ratio is far more volatile, sometimes exceeding 80:1 or even 100:1, reflecting the increasingly divergent push/pulls for these metals. The chart above for the past 100 years shows that volatility and no ‘normal’.
As the chart shows, to the modern investor the current relevance of the gold-silver ratio is dubious at best. While gold continues to hold its place as a traditional store of value, silver’s role has shifted significantly.
Silver is not only an investment commodity and used in jewelry, it is also an industrial metal, heavily used in solar panels, electronics, and medical devices. The idea that these two metals should be linked in any meaningful way, based on a centuries-old ratio, is akin to believing that the economic principles governing the Roman Empire still apply in the modern, technology-driven world.
The Foundation series offers an illuminating allegory for why clinging to outdated economic theories, like the gold-silver ratio, is futile.
In the series, Hari Seldon creates the science of psychohistory, which allows him to predict the future of entire civilizations through the laws of mathematics
and probability. His predictions are precise, but they are based on the assumption that human behavior, over time, is largely predictable as long as the humans do not know their behaviour is being predicted.
As the series unfolds, unforeseen variables begin to disrupt the deterministic nature of his equations, throwing his predictions into question. Once the humans learn their behaviour is being predicted, they change their behaviour, making their behaviour unpredictable.
Just as the Foundation evolves beyond Seldon’s predictions, modern financial analysis must evolve beyond simplistic ratios like gold-silver. Today, investors rely on more nuanced metrics, including macroeconomic indicators, inflation forecasts, interest rate trends, sector-specific supply-demand dynamics, and government interventions. For instance, silver’s growing demand in green technologies like solar panels and electric vehicles introduces complexities that the traditional ratio cannot capture.
Similarly, gold’s role as a hedge against economic instability has become more multifaceted, shaped by everything from global central bank policies to digital assets like cryptocurrencies. The gold-silver ratio, in this context, is a relic. It offers a snapshot of a bygone era when both metals played similar roles in economies.
GLENCORE PLC, THE GLOBAL MINING and commodities trading giant, has been ordered to pay $150 million by Swiss prosecutors for failing to prevent bribery in its acquisition of mining assets in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC).
The Swiss Attorney-General’s Office stated that Glencore’s “failure to take all necessary and reasonable organizational measures” warranted a fine of 2 million Swiss francs (approximately $2.4 million) and an additional $150 million in compensation. The investigation revealed that the company did not implement adequate anti-bribery controls during its asset acquisitions in the DRC.
Kalidas Madhavpeddi, Chairman of Glencore, expressed relief at the conclusion of the inquiry, noting that the company is pleased to have settled these investigations related to incidents that occurred over a decade ago. He emphasized that this resolution addresses the last of the previously disclosed government investigations into Glencore’s historical misconduct.
This penalty is part of a broader pattern of legal challenges for Glencore. Just last week, the UK’s Serious Fraud Office (SFO) charged Alex Beard, Glencore’s former head of oil trading, with bribery offenses related to the company’s operations in
West Africa. Beard, who retired in 2019, is accused of conspiring to make corrupt payments to officials in Nigeria and Cameroon between 2007 and 2014. He is one of five former Glencore employees facing charges in this investigation, which has been ongoing since 2019.
The SFO’s Director, Nick Ephgrave, highlighted the significance of these charges, stating that bribery undermines financial markets and causes lasting harm to communities. The accused are scheduled to appear at Westminster Magistrates’ Court on September 10.
In 2022, Glencore admitted to corruption and market manipulation charges in both the US and UK. The company acknowledged engaging in bribery to secure contracts in multiple countries, including Brazil and South Sudan.
As part of the settlements, Glencore allocated up to $1.5 billion to resolve these investigations. The company also paid more than £280 million in the UK after an SFO inquiry found that it had paid $29 million in bribes to gain preferential access to oil in Africa.
In response to these legal challenges, Glencore has stated its commitment to ethical conduct and has implemented significant measures to enhance its compliance programs. A company spokesperson reiterated that the alleged conduct is unacceptable and that Glencore is dedicated to acting responsibly across all aspects of its business. This latest development underscores the ongoing scrutiny and legal repercussions facing Glencore.

INVESTOR I BUSINESS OWNER I GENERAL MANAGER I CHIEF OPERATIONS OFFICER, NICHOLASVILLE, KENTUCKY, UNITED STATES

“It’s been the central pillar of my career to have discipline and commitment to achieve goals and objectives. Leadership and company framing significantly influence our career impressions. As we progress, we need to transition from technical expertise to effective leadership, allowing our teams to grow. Integrating work and personal life is vital for a fulfilling lifestyle.”
SLR CONSULTING (CANADA) / FORMERLY ROSCOE POSTLE ASSOCIATES (RPA), GREATER TORONTO AREA, CANADA

“Soft skills are key to effective leadership. My MBA expanded my career opportunities by equipping me with people skills. Accountability and commitment are vital for success in today’s ever-changing market. Motivation and succession planning play significant roles in business. Work-life balance is crucial for maintaining motivation, and setting clear goals and being transparent are important. We should also act with integrity and avoid “greenwashing.”
A
In the dynamic and challenging world of mining, experience and innovation are key to navigating the complexities of the industry. Today, we have the privilege of speaking with two esteemed professionals who have made significant contributions to the field: The panel consisted of Ramon Romero, a seasoned mining professional emphasizing the significance of discipline and worklife integration and Eduardo Zamanillo, who highlighted the role of soft skills and accountability in effective leadership With decades of combined expertise, Ramon Romero & Eduardo Zamanillo share their career insights, the importance of leadership, and their visions for the future of mining. This interview delves into their professional journeys, highlighting the critical role of technology, the necessity of continuous learning, and the steps needed to enhance the industry's sustainability and public perception.
It's clear that discipline, leadership skills, and commitment are crucial for success in the mining industry. Goal setting, worklife balance, and advocating for oneself are significant factors in career growth. Additionally, we should foster positive work cultures, act with integrity, and be aware of the industry's impact on the environment and economy.
How do you approach the challenge of maintaining worklife balance in a demanding industry like mining? Any practical tips or strategies?
Ramon Romero: It’s important to delegate and empower your team, allowing them to take ownership of their responsibilities. This way, you can avoid being overly involved in every aspect and have more time for personal life. Additionally, leveraging technology to work efficiently can help create space for other activities.
Eduardo Zamanillo: Absolutely. Mining companies should prioritize transparency and authenticity when it comes to their environmental practices. It’s crucial to implement sustainable mining techniques and invest in technologies that minimize the industry’s environmental footprint. Additionally, companies should engage in responsible reclamation and rehabilitation of mining sites to ensure long-term environmental sustainability. Collaborating with environmental experts and regulatory bodies can also help maintain accountability.
Question is for Eduardo. You mentioned the significance of avoiding “greenwashing” in the industry. Could you elaborate on what actions you believe mining companies should take to ensure they have a positive environmental impact?
Eduardo Zamanillo: Absolutely. Mining companies should prioritize transparency and authenticity when it comes to their environmental practices. It’s crucial to implement sustainable mining techniques and invest in technologies that minimize the industry’s environmental footprint.
Additionally, companies should engage in responsible reclamation and rehabilitation of mining sites to ensure long-term environmental sustainability. Collaborating with environmental experts and regulatory bodies can also help maintain accountability.

Ramon Romero: My final thought is that the mining industry has immense potential to make a positive impact on the environment, economy, and individuals’ lives. By embracing leadership, discipline, and work-life integration, we can create fulfilling careers while contributing to sustainable practices and inspiring future generations.
Eduardo Zamanillo: The mining industry must prioritize accountability and authenticity in its environmental practices. By avoiding “greenwashing” and investing in sustainable technologies, we can work towards a more responsible and environmentally conscious future. Let’s remember that small actions can have significant impacts.
Eduardo Zamanillo emphasizes the significance of soft skills in his career, considering them key to effective leadership. He credits his MBA for expanding his career opportunities by equipping him with a toolkit of people skills. Ed stresses the importance of accountability and commitment in achieving success, while also acknowledging the evolving nature of goals in today’s rapidly changing market. He highlights the importance of motivation and succession planning in businesses.
Ed believes that work-life balance is crucial for maintaining motivation and suggests setting clear goals and being transparent with oneself. He also encourages companies to avoid “greenwashing” and to act with integrity.
Ramon Romero, considers discipline as a crucial factor in achieving goals and objectives in his career. He believes that commitment can be fostered through discipline, which ultimately leads to success. According to Ramon, the effectiveness of leadership and the overall framing of a company influence the fluctuating nature of career impressions. He acknowledges the importance of relationships and influencing others, emphasizing the need for a transition from technical expertise to leadership when leading larger teams. Ramon believes in integrating work and personal life to create a fulfilling lifestyle.
largest diamond, a 2,492-carat gem discovered by Lucara Diamond Corp at the Karowe Mine. This monumental find, detected using advanced X-ray technology, underscores Botswana’s pivotal role in the global diamond industry.
In a dazzling find that reaffirms Botswana’s position as a global diamond hub, Lucara Diamond Corp announced the unearthing of a 2,492-carat gemstone at its Karowe Diamond Mine. This monumental discovery, heralded as the second-largest diamond ever found, underscores the evolving intersection of technology and natural resources in the diamond industry.
Botswana’s President Mokgweetsi Masisi was among the first to witness the breathtaking size of the gemstone, proudly holding the stone in his office in Gaborone. The diamond, weighing 498.4 grams, is likely the largest found since the 3,106-carat Cullinan diamond was unearthed in South Africa in 1905. The historical significance of this discovery cannot be overstated, positioning Botswana once again in the global spotlight for its contributions to the diamond industry.
Lucara Diamond Corp, a Canadian mining company, announced the find on Thursday, describing the stone as “one of the largest rough diamonds ever unearthed.”
What makes this discovery even more remarkable is the technology that made it possible. Lucara’s “Mega Diamond Recovery X-Ray Transmission” system, installed in 2017, played a critical role in detecting and recovering the massive stone. This cutting-edge technology is
designed to identify large diamonds within the rock before mining, a crucial advancement that prevents the common industry pitfall of inadvertently damaging or breaking large stones during extraction.
Lucara President William Lamb expressed the company’s elation over the discovery, stating,
“This find not only showcases the remarkable potential of our Karowe Mine, but also upholds our strategic investment in cutting-edge [X-Ray Transmission] technology.” The ability to recover such a significant stone intact, he added, “demonstrates the effectiveness of our approach to diamond recovery and our commitment to maximizing value for our shareholders and stakeholders.”
The implications of this technology are profound. As Tobias Kormind, managing director of 77 Diamonds, Europe’s largest online diamond jeweler, noted, “Given this new technology, we will likely see more where this came from” in the future. This sentiment is echoed throughout the industry, where there is growing optimism about the potential for future discoveries.
Botswana’s President Mokgweetsi Masisi was among the first to witness the breathtaking size of the gemstone, proudly holding the stone in his office in Gaborone.
The diamond mining industry is the backbone of Botswana’s economy, contributing over half of the country’s total export value. This latest discovery not only enhances Botswana’s reputation as a leading diamond producer but also highlights the socio-economic benefits that the industry delivers to the nation.
U.S. Critical Materials Corp. has entered into a groundbreaking strategic alliance with VerAI Discoveries Inc., an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered mineral discovery company, marking a significant step forward in environmentally responsible mineral exploration.
The collaboration aims to leverage VerAI’s advanced AI Targeting Platform technology to enhance the exploration capabilities of U.S. Critical Materials at its Sheep Creek rare earth properties in Montana. This partnership not only underscores the commitment to sustainable exploration but also positions both companies at the forefront of next-generation mineral discovery.
The alliance between U.S. Critical Materials and VerAI Discoveries focuses on utilizing AI to identify mineral deposits more accurately and efficiently, particularly in challenging terrains.
VerAI’s technology uses advanced algorithms to analyze geological data, increasing the likelihood of discovering rare earth elements (REE) while minimizing surface disturbances. This approach is particularly crucial in environmentally sensitive areas such as the Bitterroot Valley, where both companies are dedicated to protecting the natural landscape.
Jim Hedrick, President of U.S. Critical Materials and a former rare earth analyst with the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), highlighted the significance of the alliance: “Our focus on environmentally responsible exploration is greatly enhanced by the utilization of advanced artificial intelligence technology, which allows us to more precisely focus on potential target areas and thereby minimize surface disturbance.”
The Sheep Creek Area of Interest (AOI) in Montana is recognized for its rich geological potential, with independent geophysical surveys and validation from the Idaho National Laboratory confirming the presence of rare earth elements.
U.S. Critical Materials’ recent exploration results have been promising, with Total Rare Earth Elements (TREE) readings reaching up to 20.1% and combined neodymium-praseodymium concentrations of up to 3.3%. Additionally, gallium levels were reported at 348 parts per million (ppm), significantly above the

profitable production threshold of 50 ppm. These findings underscore the high-grade potential of the Sheep Creek properties and the strategic importance of this alliance in unlocking further critical mineral resources.
The application of AI technology by VerAI Discoveries is a game-changer for U.S. Critical Materials’ exploration efforts. By utilizing AI-driven exploration techniques, the partnership aims to generate and prioritize drill targets in covered terrains, thus significantly reducing the environmental footprint typically associated with traditional exploration methods.
Yair Frastai, CEO of VerAI Discoveries, expressed enthusiasm about the partnership: “We are thrilled to partner with U.S. Critical Materials, experts in REE exploration, to discover the much-needed rare earth elements in the U.S. At Sheep Creek, we have the opportunity and potential to make an important impact on the supply of critical minerals discovered in the U.S.” Frastai’s statement highlights the strategic importance of this collaboration in bolstering domestic rare earth element supply, which is vital for national security and technological innovation.
The mining industry is undergoing a transformative phase as it integrates advanced technologies to enhance efficiency, safety, and sustainability. This evolution is driven by the need to address complex challenges such as environmental concerns, operational efficiency, and global economic volatility. The industry's shift towards digitalization and innovative management practices is setting the stage for a more resilient and competitive future.

THE MINING INDUSTRY IS ON THE brink of a significant transformation, fueled by the adoption of cuttingedge technologies aimed at improving efficiency, safety, and sustainability. As it navigates environmental challenges, rising operational costs, and economic uncertainty, the sector is embracing digitalization and innovative approaches to build a more adaptable and competitive future.
Automation and Robotics: Automation technologies are revolutionizing mining operations, particularly in harsh and remote environments. Companies like LKAB in Northern Europe are deploying autonomous drills and trucks, minimizing human exposure to extreme conditions and enhancing operational safety and efficiency.
Sustainability and ESG Compliance: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors are becoming increasingly important for mining companies. The focus on achieving a net-positive impact across ESG factors is crucial for maintaining a license to operate and accessing capital. Companies are adopting sustainable technologies and processes to minimize environmental impact and improve their ESG performance.
Economic Volatility and Investment Strategies: The mining industry is navigating economic uncertainty due to geopolitical tensions and fluctuating commodity prices. Despite these chal-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI is becoming integral across the mining value chain, optimizing processes from mineral extraction to customer delivery. It enables predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and data-driven decision-making, leading to increased efficiency and reduced costs. BHP, for instance, leverages AI for predictive maintenance and energy optimization, contributing to safer and more efficient operations.
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT technologies facilitate real-time data integration and monitoring, providing a comprehensive view of mining operations. This integration allows for better decision-making and operational agility. Companies like Rio Tinto and Vale utilize IoT sensors to predict equipment failures and monitor safety hazards, significantly reducing downtime and accident rates.
Blockchain and Supply Chain Transparency: Blockchain technology is enhancing transparency and traceability in the mining supply chain. De Beers, for example, uses blockchain to track diamonds from mine to market, ensuring ethical sourcing and authenticity.
lenges, there is optimism for growth, particularly in regions like Western Australia, where investments in energy transition are strong. Mining leaders are strategically investing in technology to maximize existing resources and future-proof their operations.
Digital Talent and Workforce Development: As technology becomes more embedded in mining operations, there is a growing need for digital talent. Companies are focusing on workforce training and augmentation using AI and virtual reality to enhance skills and safety without exposing workers to hazards.
Cybersecurity and Risk Management: With the increasing digitalization of mining operations, cybersecurity has
become a critical concern. Protecting data and ensuring secure communications are vital for maintaining operational integrity and protecting intellectual property.
AI is revolutionizing decision-making processes in the mining industry by providing data-driven insights and enhancing operational efficiency across the entire value chain. By leveraging AI technologies, mining companies can make more informed, efficient, and sustainable decisions, leading to improved operational performance, enhanced safety, and reduced environmental impact.
AI systems analyze vast amounts of data from various sources, including on-site sensors and monitoring systems, to identify patterns and make informed decisions. This enables:
Predictive analytics: AI predicts potential equipment failures and maintenance needs, preventing costly downtimes and extending machinery lifespan.
Real-time monitoring: AI-powered systems provide up-todate information on operations, allowing for quick adjustments and optimizations.
AI enhances operational planning and efficiency through: Simulation and optimization: AI can simulate mining operations under various scenarios to identify the most efficient approaches, optimizing extraction processes and reducing waste.
Resource management: Machine learning models analyze historical and real-time data to predict mineral quality and quantity, enabling precise planning and extraction strategies.
AI plays a crucial role in improving safety in mining operations:
Risk prediction: AI-powered systems analyze data from sensors to predict and mitigate risks such as cave-ins, explosions, and toxic gas leaks.
Autonomous operations: AI enables the use of autonomous vehicles and drones in hazardous areas, reducing human exposure to dangerous conditions.
AI supports more sustainable mining practices by:
Energy optimization: AI algorithms manage and optimize energy consumption, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and operational costs.
Environmental impact monitoring: AI-equipped drones survey mining sites to assess land degradation, water pollution, and vegetation loss, allowing for timely corrective actions.
AI enhances the precision of exploration and extraction processes:
Deposit identification: Advanced algorithms analyze geological data to accurately predict the location of mineral deposits, reducing unnecessary drilling and excavation.

Adaptive extraction: AI assesses changing geological conditions in real-time and adjusts extraction techniques accordingly, maximizing yield and minimizing waste.
AI enables more comprehensive decision-making by incorporating multiple factors:
Holistic approach: AI-powered multi-objective optimization tools can integrate economic, environmental, and social factors into decision-making processes.
Stakeholder considerations: Interactive multi-objective optimization (iMOO) approaches allow for the incorporation of diverse societal needs and stakeholder preferences in decision-making.
AI plays a crucial role in predicting geological changes in mining operations, enhancing safety, efficiency, and resource management.
By leveraging AI in these ways, mining companies can make more informed decisions about exploration, extraction, and safety measures.
Pattern recognition: AI identifies subtle patterns in geological data that might be overlooked by human geologists.
Historical data integration: Machine learning models incorporate centuries of core sample data to find resources that were previously missed.
AI systems can integrate various data sources, including seismic data, satellite imagery, core samples, and historical mining data, to create comprehensive models of the geological landscape. Machine learning algorithms analyze these complex datasets to identify patterns and correlations that would be challenging for humans to detect, allowing for more precise predictions of geological formations and potential changes. AI algorithms can process and analyze vast amounts of geological data much faster and more accurately than traditional methods.
AI-powered systems use real-time data from various sensors to predict geological changes:
Seismic activity prediction: AI analyzes data from seismic sensors to forecast earthquakes and rock bursts, allowing for timely evacuations.
Environmental condition monitoring: Sensors detect changes in environmental conditions, with AI interpreting this data to predict potential hazards.
Machine learning algorithms, particularly those based on neural networks, are used to predict the location of mineral deposits by analyzing patterns in geological data. These models can identify subtle anomalies that may indicate the presence of valuable minerals, thus improving exploration efficiency and reducing the cost and time involved in traditional exploration methods.
AI-powered sensors and IoT devices deployed in mines provide real-time data on conditions such as ground stability, rock stress, and seismic activity. AI models process this data to detect early signs of geological changes, such as potential rock falls or shifts in mine walls, enabling preventive actions to ensure safety and minimize disruptions.
AI models simulate geological processes like erosion, sedimentation, and tectonic shifts, helping to predict how these factors may affect mining operations over time. By modeling these dynamic processes, AI helps mining companies better understand the risks associated with geological changes and adapt their mining strategies accordingly.
AI enhances the accuracy of resource estimation, which is crucial for mining operations: Precise mineral reserve estimates: AI algorithms examine geological data patterns and historical mining data to provide more accurate estimates of mineral reserves.
Quality and quantity prediction: Machine learning models analyze historical and real-time data to predict the quality and quantity of minerals in specific areas.
AI enhances geological mapping by analyzing geophysical survey data more accurately. Machine learning models can create detailed 3D maps of the subsurface, highlighting potential fault lines, rock types, and other critical features that inform safer and more efficient mining operations.
AI significantly improves the exploration process: Potential site identification: AI-driven geospatial analysis tools analyze satellite and drone imagery to identify promising areas for mineral deposits.
Risk reduction: By rapidly identifying potential mining sites, AI reduces the risk of exploratory failures and saves valuable time and resources.
AI helps optimize drilling paths and extraction methods by predicting the most productive areas and minimizing the impact on surrounding geological structures. Predictive analytics guide decision-making to avoid drilling in unstable areas, reducing the risk of triggering unwanted geological changes.
AI helps in adjusting extraction methods based on changing geological conditions:
Real-time adjustments: AI assesses changing geological conditions in real-time and can adjust extraction techniques accordingly to maximize yield and minimize waste.
AI predicts how mining activities might alter local geology and hydrology, helping companies mitigate negative environmental impacts. Predictive models assess the potential for land subsidence, groundwater contamination, and other environmental changes, allowing mining companies to plan for sustainable operations.
approaches, we take a look at how automation, AI, and the decline of coal are reshaping the industry, impacting job security, and influencing voter sentiments in key battleground states.

As the 2024 U.S. election approaches, the future of mining jobs is emerging as a pivotal issue that could sway voters in key battleground states. With the rise of automation and artificial intelligence (AI), coupled with the decline of traditional coal mining, the industry faces a complex and uncertain future. This evolving landscape is not just about jobs; it’s about the economic stability of communities that have long relied on mining.
Donald Trump and Kamala Harris are acutely aware of the stakes, and their positions on mining jobs, particularly in swing states like Pennsylvania and West Virginia that are heavily reliant on the industry, could significantly influence voter turnout and sway the election results.
Automation and AI are transforming the mining industry, promising increased efficiency and safety. However, these advancements come with the cost of significant job cuts. According to industry reports, AI-driven automation could reduce the need for human labor in various mining operations, from exploration to extraction. A recent article on ChannelLife highlights the growing concern that these technological advancements may lead to a significant reduction in mining jobs .
This shift has already begun to manifest. For example, Whitehaven Coal announced the cutting of 192 jobs at mines recently acquired from BHP. The move is
part of a broader trend where companies are increasingly relying on technology to streamline operations, leading to workforce reductions . While automation may enhance productivity, the human cost is undeniable, particularly in regions where mining is a major employer.
The decline of coal mining in the U.S. has been a source of tension in recent years, exacerbated by environmental regulations and the shift towards cleaner energy sources. This downturn has had a profound impact on coal-dependent communities, where job losses have led to economic instability and outmigration. The Trump administration made coal mining jobs a focal point of its economic agenda, promising to bring back jobs to the sector. However, the reality has been far more complex.
While automation and the decline of coal present challenges, there are also opportunities in the mining sector, particularly in the extraction of critical minerals like copper. The demand for these minerals is expected to rise as the world transitions to renewable energy and electric vehicles. A copper mine in Michigan’s Upper Peninsula, for instance, could bring much-needed jobs to the area. However, as MLive reports, not everyone is in favor of the mine, with concerns about environmental impact and local opposition presenting hurdles .
analysis are advancing mining equipment maintenance and corrosion monitoring in mining to boost safety and efficiency
The mining industry faces challenges in mining equipment maintenance, as corrosion monitoring in mining becomes essential to maintain structural integrity and operational efficiency. Recent research published in Applied Sciences has highlighted the urgent need for advanced monitoring and maintenance strategies to combat these risks. The study leverages spectral and wavelet analysis to enhance the detection of corrosion’s subtle yet damaging effects on mining equipment, particularly focusing on the rotary arm of an ERc 1400-30/7 bucket excavator. This article delves into the findings, implications, and potential shift in maintenance practices within the industry.
Corrosion impacts the mining industry, where harsh environmental conditions accelerate the degradation of metal structures, emphasizing the need for effective corrosion monitoring in mining.
Traditional methods of assessing structural health often miss early signs of material fatigue and decay. This not only affects safety but also results in substan-
tial economic losses due to unexpected equipment failures and increased maintenance costs.
The study conducted by researchers Radu S.M., Vîlceanu F., and colleagues addresses these challenges by introducing advanced analytical techniques—specifically spectral and wavelet analysis—that provide a more detailed understanding of how corrosion impacts mining equipment maintenance. Early detection of corrosion-related issues could be key to extending the lifespan of critical machinery and improving overall operational safety.
The research focused on the rotary arm of an ERc 1400-30/7 bucket excavator, subjecting it to a series of corrosion tests crucial for mining equipment maintenance.
The first step involved preparing the surface with abrasive discs to enhance the accuracy of ultrasonic measurements, which were used to assess the metal’s thickness at various points. This non-destructive approach ensured that the testing process did not compromise the equipment’s integrity.
Read More here: https://skillings.net/ new-tech-to-battle-corrosion-gamechanger-for-mining-equipment-maintenance/

Discover the challenges and solutions in electrifying steel production through Electric Arc Furnaces (EAFs), including power quality issues like harmonics and flicker, and explore advanced mitigation techniques crucial for the Green Steel initiative.
The Green Steel initiative represents a critical shift in the steel industry, aimed at reducing carbon emissions by transitioning from fossil fuel-based production to electrical energy-based processes. A cornerstone of this transformation is the adoption of Electric Arc Furnaces (EAFs), which are pivotal in decarbonizing the steel production process. However, integrating EAFs into existing grids introduces significant power quality challenges that must be addressed to ensure system stability and efficiency.
An Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) uses electricity to generate an intense arc between electrodes, typically made of carbon or graphite. This arc generates extreme heat, which melts and refines scrap metal, primarily steel. The process involves placing or dropping metal into the furnace, often via a crane or conveyor belt system equipped with monitoring and control capabilities. The molten steel is then extracted for various industrial applications.
emissions and energy loss by submerging the arc within the charge material. Despite their benefits in reducing carbon emissions, EAFs present power quality challenges such as low power factor, harmonics, and power-line flicker. EAFs typically operate at a low power factor (0.15 to 0.85), causing inefficiencies and increased environmental impact, though advanced technologies can raise this to 0.93-0.95 to meet regulatory requirements.
Maintaining power quality is critical to the success of the Green Steel initiative. EAFs and their associated equipment are specialized, and any failure in this system can lead to significant production losses, affecting other related processes like Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) production, Refining (RH/VD), and Continuous Casting.
EAFs are classified into different types based on their design and technological advancements:
Conventional Electric Arc Furnaces (EAFs) use either alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC) for operation, with AC EAFs being more common but generating significant disturbances due to arcing, impacting power quality. Advanced multicell technology furnaces like the Q-One AC Furnace (Danieli) and AURA DC Furnace (SMS) offer improvements by reducing power quality issues and enhancing energy efficiency. Submerged arc furnaces also help mitigate
Harmonics, generated by nonlinear loads like EAFs, can cause overheating, vibrations, and noise, necessitating advanced control systems to minimize disturbances. Power-line flicker, caused by rapid voltage fluctuations, is more pronounced in AC EAFs and affects lighting conditions, making mitigation crucial for maintaining power quality and regulatory compliance.
Maintaining power quality is critical to the success of the Green Steel initiative. EAFs and their associated equipment are specialized, and any failure in this system can lead to significant production losses, affecting other related processes like Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) production, Refining (RH/VD), and Continuous Casting.
Electrical pollution, if not kept within specified limits, can degrade system performance, reduce efficiency, increase failure rates, and lead to higher maintenance costs. Furthermore, strict regulatory compliance is essential, as failure to meet power quality standards at the point of common coupling can result in substantial fines.
Pilbara, WA – De Grey Mining Ltd has solidified its financial backing for the Hemi gold project in Western Australia’s Pilbara region with a pivotal $150 million loan from the Federal Government’s Northern Australia Infrastructure Facility (NAIF).
This loan forms a crucial component of the company’s $1 billion senior debt facility, signaling a significant step forward for one of Australia’s most promising gold projects.
The NAIF loan is not merely a financial boost; it represents a strong vote of confidence from the Australian government in the Hemi gold project. The $1 billion debt package, which includes the NAIF loan, is nearly complete, with term sheets already approved by commercial banks for the remaining amount. Additionally, a $130 million cost overrun facility is included in the funding package, ensuring the project stays on track even in the face of potential financial challenges.
Glenn Jardine, De Grey’s managing director, acknowledged the critical role played by government officials in securing the loan.
“We appreciate the strong support for the development of Hemi shown by NAIF and would like to acknowledge the important role played by the Minister for Resources and Northern Australia, Hon. Madeleine King MP, and the Special Envoy for Northern Australia, Luke Gosling OAM,” Jardine stated.

WSP Global, a leading engineering and professional services firm, has announced its acquisition of Power Engineers for $1.78 billion.
The intent is aimed at bolstering WSP Global’s capabilities in the power and energy sectors, particularly as the demand for sustainable energy solutions continues to rise globally. WSP Global’s decision to acquire Power Engineers aligns with its growth strategy to expand its expertise and market presence in the energy sector. Power Engineers, known for its engineering services in power delivery and renewable energy, will enhance WSP’s offerings and strengthen its position in the North American market. The acquisition is expected to close by the end of the year, subject to regulatory approvals and customary closing conditions.
The acquisition comes at a time when the energy sector is undergoing significant transformation, driven by the global push towards renewable energy and decarbonization. Companies in the engineering and infrastructure sectors are increasingly seeking to diversify their portfolios to include more sustainable and resilient energy solutions. By acquiring Power Engineers, WSP Global aims to capitalize on these trends and expand its service offerings to include more comprehensive energy solutions.
Industry analysts view this acquisition as a positive step for WSP Global, enhancing its competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market. The integration of Power Engineers’ expertise is expected to provide WSP with a broader range of services, from traditional power engineering to innovative renewable energy projects. This move is also anticipated to create new opportunities for growth and collaboration within the energy sector.
The global mining automation market, valued at US$ 3.65 billion in 2023, is projected to nearly double, reaching US$ 7.37 billion by 2032, according to a recent report by Astute Analytica. This surge, driven by a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 8.12% from 2024 to 2032, highlights the growing demand for advanced automation technologies in the mining industry.
The adoption of automation technologies such as autonomous haulage systems, remote-controlled equipment, and advanced robotics is revolutionizing the mining sector. As companies strive to enhance operational efficiency, improve safety standards, and reduce labor costs, automation offers a pathway to more precise and cost-effective mining operations.
Key drivers of market growth include:
Productivity Improvements: Automation helps streamline mining processes, reducing downtime and increasing productivity.
Worker Safety: Advanced robotics and remote-controlled machinery reduce human exposure to hazardous mining conditions.
Technological Advancements: The increasing availability of sophisticated automation technologies is making it easier for companies to adopt innovative solutions.
Sustainable Mining Practices: The industry’s shift towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly practices is further fueling automation adoption.
C29 Metals has successfully secured an additional tenement adjoining its Ulytau Uranium Project in Kazakhstan, significantly expanding the project’s footprint by approximately 213 square kilometers.
C29 Metals has successfully secured an additional tenement adjoining its Ulytau Uranium Project in Kazakhstan, significantly expanding the project’s footprint by approximately 213 square kilometers. This strategic acquisition is set to enhance the potential for substantial uranium discoveries in the region. The newly acquired southern tenement, identified by application number 1905EA, is located in the Almaty region of southern Kazakhstan, approximately 15 kilometers southwest of the historic Bota Burum mine. This region has been a prominent hub for uranium exploration since 1953, with the Bota Burum mine commencing operations in 1956 and continuing production until 1991. The mine’s total reserves are reported to be around 20,000 tonnes of uranium, equivalent to 44 million pounds.
C29 Metals believes that the new tenement shares a similar mineralized trend with the existing Ulytau project area, indicating significant potential for further uranium discoveries. Historical geological work in the area has already highlighted substantial uranium deposits, positioning the Ulytau project for notable development.
Shannon Green, Managing Director of C29 Metals, expressed his enthusiasm about the acquisition: “It is very exciting to have this highly prospective application granted in such a rapid time frame. This is further demonstration of the positive operating environment in Kazakhstan and the support the company is enjoying.”
In March 2024, C29 Metals signed a binding agreement to acquire complete ownership of the Ulytau Uranium Project. Following this agreement, the company announced plans to initiate ground geological works immediately through its established in-country network. The initial efforts will focus on field mapping, locating historic drill collars, and translating technical documents and data to create a new geological database.
Discover why investing in silicon mining stocks is a strategic choice. Explore the top companies driving the industry with market growth, innovation, and resilience.
The silicon mining industry is a vital component of the global economy, driving advancements in technology, renewable energy, and more. Investing in silicon mining companies provides an opportunity to capitalize on market growth, innovation, and diversified revenue streams. This article explores some of the leading silicon mining companies and why they are considered attractive investments.
1. FERROGLOBE (NASDAQ)
Ferroglobe is a leading producer of silicon metal with extensive global operations and integrated production processes. The company’s control over the entire production chain, from mining to high-purity silicon manufacturing, positions it as a key player in the market.
2. DOW INC. (NYSE)
Known for its diversified materials science business, Dow plays a significant role in silicon metal production. The company’s vast integration across various industries, including automotive, construction, and electronics, uniquely positions it to benefit from growing demand. Dow’s commitment to sustainability and innovation in advanced materials further enhances its appeal, especially for long-term investors.
Wacker Chemie AG specializes in silicon-based materials and holds a substantial share of the silicon metal market. Recognized for its advanced technology and continuous R&D, Wacker Chemie maintains a competitive edge. The company’s expansion into silicon wafers and solar applications signals significant growth potential, aligning with the global shift towards renewable energy.
(SHA:603260)
As a leading Chinese producer, Hoshine Silicon Industry Co., Ltd is known for its large-scale operations and focus on high-quality silicon metal. The company’s aggressive expansion and investments in
advanced production technologies have solidified its market position. Hoshine plays a crucial role in the supply chains for electric vehicles and renewable energy, making it a strategic investment for those focused on green technologies.
5.
Elkem ASA, based in Norway, is a major producer of silicon-based advanced materials catering to the solar, electronics, and automotive industries. The company’s diversification of its product offerings and commitment to reducing carbon emissions align well with global sustainability trends. Elkem’s strong balance sheet and focus on innovation make it a compelling investment for those interested in sustainable business practices.

China has recently intensified its control over global critical mineral supplies by imposing export restrictions on antimony, a metal essential for military applications, including ammunition.

part of a series of similar measures affecting other critical minerals, such as graphite, gallium, and germanium. These minerals are crucial for the production of semiconductors, batteries, and other high-tech applications. The restrictions are perceived as a strategic maneuver by China to leverage its control over these resources in the face of escalating trade tensions with the West.
This move is part of a broader strategy by Beijing to maintain its dominance in the critical minerals sector, which has become increasingly geopolitically significant as nations transition to clean energy technologies.
Antimony, used in various military and industrial applications, has seen a surge in prices this year, underscoring its strategic importance. China’s decision to restrict exports of this mineral is seen
as a response to Western efforts to reduce dependency on Chinese-controlled supply chains.
The West, particularly the United States and Europe, has been actively seeking to diversify sources of critical minerals, essential for technologies like electric vehicles and renewable energy systems, to mitigate the risks associated with China’s dominant position. China’s export controls on antimony are part of a series of similar measures affecting
other critical minerals, such as graphite, gallium, and germanium. These minerals are crucial for the production of semiconductors, batteries, and other high-tech applications. The restrictions are perceived as a strategic maneuver by China to leverage its control over these resources in the face of escalating trade tensions with the West.
The geopolitical implications of China’s actions are significant. Western countries, particularly the United States, have been implementing policies to counter China’s influence in the critical minerals market.
The U.S. Inflation Reduction Act, for instance, aims to boost domestic production and processing of critical minerals, thereby reducing reliance on Chinese imports. Similarly, legislative efforts in the U.S. Congress are focused on fostering alternative supply chains and encouraging international collaboration to secure critical mineral resources.
China’s strategic positioning in the critical minerals market is not merely a result of its geological resources but also a consequence of long-term investments in global mining operations and refining capabilities. This has allowed China to establish a near-monopoly in the processing of many essential minerals, thereby creating a chokepoint in global supply chains.



MINING INFO YOU DON’T HAVE TO DIG FOR...
SUBSCRIBE NOW!





World crude steel production for the 71 countries reporting to the World Steel Association (worldsteel) was 161.4 million tonnes (Mt) in June 2024, a 0.5% increase compared to June 2023.
Africa produced 1.6 Mt in June 2024, down 9.6% on June 2023. Asia and Oceania produced 120.6 Mt, up 0.3%. The EU (27) produced 11.1 Mt, up 5.1%. Europe, Other produced 3.8 Mt, up 2.1%. The Middle East produced 4.6 Mt, down 2.7%. North America produced 8.9 Mt, down 1.9%. Russia & other CIS + Ukraine produced 7.4 Mt, up 1.4%. South America produced 3.5 Mt, up 4.1%. The 71 countries included in this table accounted for approximately 98% of total world crude steel production in 2023.Regions and countries covered by the table: Africa, Asia and Oceania, European Union (27), Europe,other, Middle East, North America, Russia & other CIS + Ukraine, South America.
China produced 91.6 Mt in June 2024, up 0.2% on June 2023. India produced 12.3 Mt, up 6.0%. Japan produced 7.0 Mt, down 4.2%. The United States produced 6.7 Mt, down 1.5%. Russia is estimated
Table
to have produced 6.0 Mt, down 4.1%. South Korea produced 5.1 Mt, down 7.2%. Germany produced 3.2 Mt, down 8.9%. Türkiye produced 3.1 Mt, up 4.3%. Iran produced 2.6 Mt, down 8.5%. Brazil produced 2.9 Mt, up 11.8%.
Top 10 steel-producing countries
The 71 countries included in this table accounted for approximately 98% of total world crude steel production in 2023. Regions and countries covered by the table:Africa: Egypt, Libya, South Africa, Tunisia Asia and Oceania: Australia, China, India, Japan, Mongolia, New Zealand, Pakistan, South Korea, Taiwan (China), Thailand, Viet Nam,European Union (27),Europe, Other: Macedonia, Norway, Serbia, Türkiye, United Kingdom,Middle East: Iran, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates,North America: Canada, Cuba, El Salvador, Guatemala, Mexico, United States,Russia & other CIS + Ukraine: Belarus, Kazakhstan, Russia, Ukraine,South America: Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Paraguay, Peru, Uruguay, Venezuela
e – annual figure estimated using partial data or non-worldsteel resources. * The world total production figure in this table includes estimates of other countries that only report annually.
The World Steel Association (worldsteel) has published the 2024 edition of World Steel in Figures.
Edwin Basson, Director General, worldsteel, said, ‘Steel is everywhere in our lives, and for good reason. It has built the modern world and will be equally indispensable to the world as it moves
forward. World Steel in Figures provides a fascinating snapshot of the dynamics of today’s steel industry, including everything from production and production processes, to demand, trade, safety and more.’
The World Steel Association (worldsteel) is one of the largest and most dynamic
industry associations in the world, with members in every major steel-producing country.
worldsteel represents steel producers, national and regional steel industry associations, and steel research institutes. Members represent around 85% of global steel production.
