









catchment Evidence Review Bampton – Bampton Stream (839) Exploring flood risk potential at the micro catchment scale
Micro
This document is an output from the Devon and Cornwall Soils Alliance, delivered by Westcountry Rivers Trust.

2
Executive Summary
Flood risk is a major issue for numerous communities across the South West and with the expected future impacts of climate change, as well as compounding factors such as population growth and development, it is a problem that is becoming all the more urgent. A number of projects are currently underway to understand the causes of flooding and investigate potential solutions. This includes the Upstream Thinking - Rapid Response Catchments project and Devon and CornwallSoils Alliance (more info on page 6).
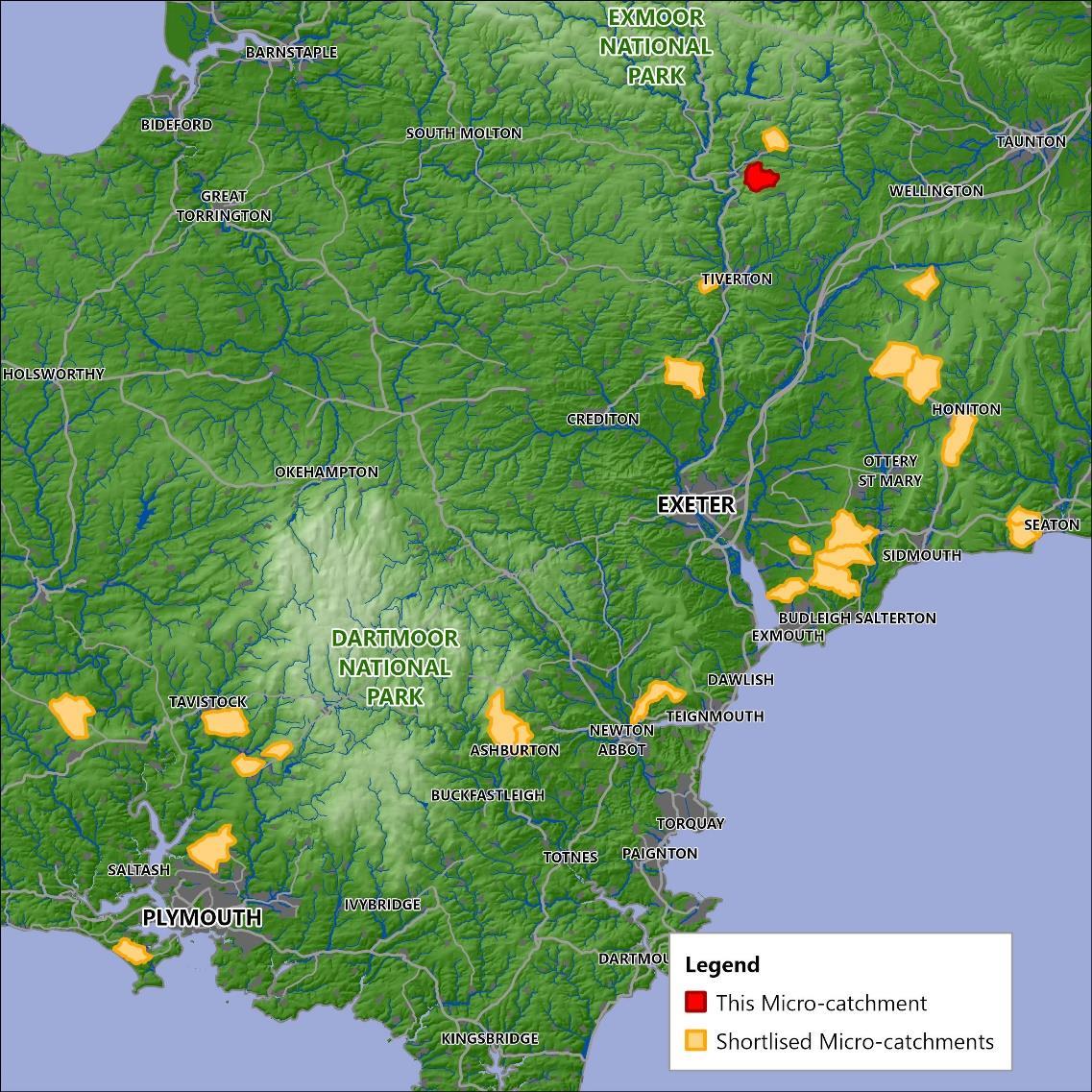
A mapping exercise was carried out to identify all the micro-catchments (5km2 or 10km2)above flood-risk properties in Devon and Cornwall. The idea being that Natural Flood Management (NFM) measures and engagement with the local community weremost likely to be effective at this scale. These micro-catchments were then prioritised according to several factors. The catchment described in this report, the Bampton Stream, is one of those prioritised micro-catchments.
The micro-catchment for the Bampton Stream is 466.3ha and highlights 15 properties potentially at riskfrom fluvial and surface water flooding. There are multiple possible contributing causes of this, including the topography, land use, and scarcity of habitats such as woodland. The catchment is failing Water FrameworkDirective (WFD) regulations on chemical status and is within a Drinking Water Safeguard Zone at riskof contamination by pesticides.
A rapid walkover survey wascarried out by an experienced surveyor from the Westcountry RiversTrust (WRT) to further inform potential issues and opportunities for flood riskmitigation. During the walkover, the micro-catchment displayed localised flood risk. There is opportunity to effect localised flood improvement, and the ability to mitigate part of a larger flood risk downstream (less localised) should not be discounted, especially as Bampton is very close. The walkover, also presented many opportunities to deliver or contribute towards WFD (Water Framework Directive) ecological improvement whilstbenefiting wider flood riskand drought resilience at the same time.
Implementation of Natural Flood Management (NFM) measures may have the potential to mitigate some of the flood risk and simultaneously make progress towards reaching “good” WFD status for the wider Lower Batherm catchment that would ultimately benefit the local community. The NFM opportunities identified in this report include riparianwoodland planting and other habitat creation or enhancement surrounding existing habitats across the catchment to slow surface water flow into watercourses and enhance habitat networks. In addition, there are opportunities for floodplain reconnection and runoff attenuation at multiple locations. Co-benefits need to be considered when designing these NFM measures, and this presents a major opportunity for community engagement to facilitate their delivery if desired.
3
4 Contents Overview How this Document Works 5 Introduction 6 Micro-catchment Prioritisation 7 Why this Catchment? 8 Thematic Chapters Micro-catchment Overview 9 Priority Areas and Drivers 12 Existing Natural Assets and their Condition 22 Issues 30 Opportunities 34 Appendicesand Data Sources 49
Overview
How this Document Works
This documentisa study for causesof flooding,priorityconsiderations,and opportunitiesforNFMin the micro-catchmentforthe Bampton Stream,covering a rural area eastof Bampton.
The study is builton multiple layersof mapped environmentalinformationand the results of the walkoversurvey. This informationhasbeenused to explore the current state of the catchmentand its environment, and then map areasfor further investigationand actionsto make improvements. This micro-catchment scaleassessmentwillbe usedto guide efforts incommunityengagement andNFM.
The study has 5 key chapters,based on the current status of the micro-catchmentand whatopportunitiesthere mightbe.
1. Micro-catchmentOverview
2. PriorityAreasand Drivers
• Flooding
• WaterQuality
• WaterQuantity
• Designated Sites
• Tourism and Recreation
3. Existing Natural Assetsand Their Condition
• Habitats
• Soils
• Crops
4. Issues
• Abstraction,Discharges,Pollution,and Runoff
• HydrologicalConnectivity
• Issues identified during Walkovers
5. Opportunities
• Existing Opportunities
• OpportunitiesIdentified during Walkovers
It isnot possible to map all aspectsof the status of the micro-catchmentwithexisting datasets,and the true state of the catchmentmay not be fully reflected inthe datasetsforvariousreasons including the age of the data,the resolution, and the level of local knowledge takeninto consideration when the data has beencollected and mapped.
Assessing the qualityand conditionof natural assetsin particularischallenging due to the level of detail required.Nonetheless,the availabledata has beenreviewed and the bestdata currently availablehasbeenused. A full set of referencescan be found on pages52-55.
5
Introduction
Flooding isa problem thatis experienced widelyacrossDevonand Cornwall,witha large portionof caseslinked to rivers(fluvial flooding as opposed to surface wateror sea).Riverwaterqualityisalso a key issue in the region,withall 381assessed rivers failing to achieve “good” statusin 2019.One importantreasonfor waterqualityfailure islinked to soil erosion.Soil erosioncan also contribute to increased fluvial flood riskdue to reduced channel capacitiesand blockages.Therefore,waterqualityand floodriskdriversare often interlinked and the solutionsto alleviate these pressures are often multifunctional.Two projectscurrentlyunderwayare aiming to tackle these issues by working withlocal communitiesto deliver small-scale,land-basedmeasures(“nature-basedsolutions”).These projectsare Devonand Cornwall SoilsAlliance (DCSA) and Upstream Thinking Rapid Response Catchments(UST-RRC).
Afteritwas found that over 40%of soilsacrossDevonand Cornwall are degraded,the collaborativeprojectof the DCSA waslaunched inJune 2019. This aimsto build the capacityand capabilityinsoilsadvice forthe projectpartnersacrossthe 2 counties to work towards restoring degraded soils. One significantbenefitof improving soil healthisgreatersurface waterinfiltrationinto the ground before itreachesand overwhelmswatercourses, thereby reducing flood riskand preventing potential pollutantsfrom entering the water.Thisalso has the potential to make considerable Water FrameworkDirective (WFD) improvementsto waterquality.
AcrossDevonand Cornwall there are hundreds of Rapid Response Catchmentsthat are characterised byquicklydraining catchmentareasunder 10km2 (and under 5km2) , where during high rainfall eventssurface flowsand overland run off overwhelm small communities(1-50propertiesin flood zone 1).Flood eventshave increased inthese types of catchmentdue to degraded soilsthatno longerhave the infiltrationcapacity,simplified drainage patternsand more variable and extreme weatherpatternsassociated witha changing climate.UST-RRCwill focusonworking withsmall communitiesinthese rapid response catchments to help them develop and delivertheirown climate resilience plansbyrestoring some of the hydrological functionalitywithinthe landscape.
The DCSA isworking in partnership with the UST-RRCprojectacrossDevonto develop 24preparatoryinvestigationsonprioritisedmicrocatchmentsto identifylikelyareasfornature-based solutionsand NFM (Natural Flood Management) interventionswhere land ownership showsa willingnessand waterqualitycanbe improved.Communityengagementwill be criticalwhenimplementing NFMasmeasures need to be numerous and spread out across the catchmentto provide the greatestbenefits.If propertyowners and landownerscan work togetherand share perspectives, then measures canbe designed thatare agreeable to all stakeholdersinvolved.Thisalso helpsto fostera sense of community stewardship overtheir catchmentand NFM measuresthat would enhance theirlongevityand resilience.
6
Overview
Overview
Methodology
There may be opportunitieseverywhere forNFM measures and other nature-based solutionsatlow cost that also bring additional benefits to human health,biodiversity,and the aestheticsof the landscape. However,the scattered and fragmented locationsof propertiesat flood riskand the limited accessible fundsrequiresidentifying only the largestclustersof flood riskpropertieswiththe smallestupstream micro-catchmentsto deliverthe mostimpactwiththe resources available.
The processof identifying priorityareasforopportunitiesto deliver improved waterqualityand quantityforclimate change resilience wasundertaken in four steps.
1. The South Westareasof Devonand Cornwall were modelled using GIS (Geographic InformationSystems) to identifywhere opportunityareaswere located.
2. The modelled opportunityareaswere ground-truthed in theory using desk-based studies
3. The top prioritised opportunityareaswhere ground-truthed physicallyusing rapid walkoversurveys
4. Internal evidence reviews,external evidence reviews,and 2pagers summary documentswill be writtenfor24 trial investigationareas where physical interventionscan take place.
For more informationonthe first 3steps please see the appendix.
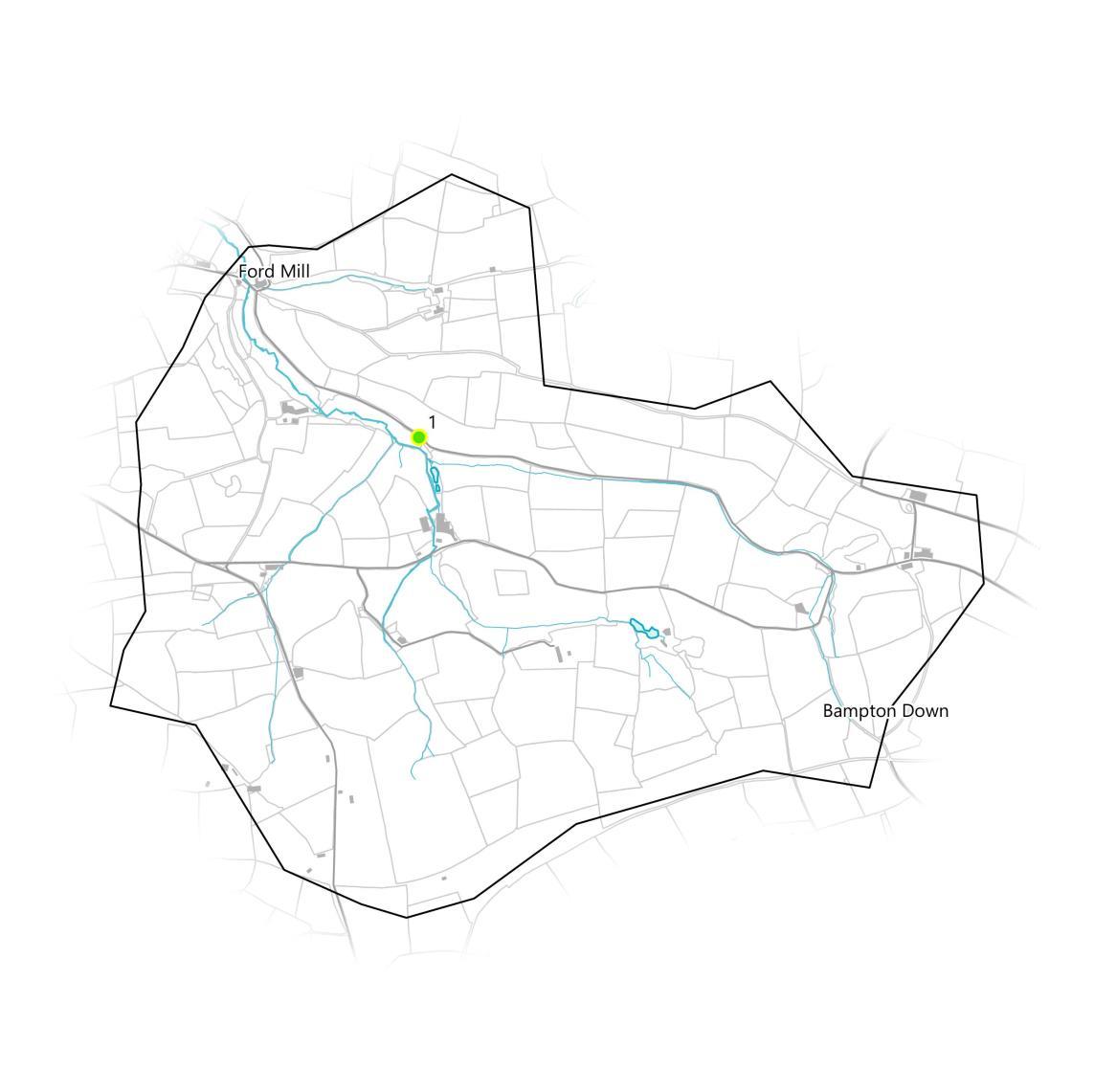
The final 24micro-catchments,including the BamptonStream whichis shown in red.
7
Overview
Why this Catchment?
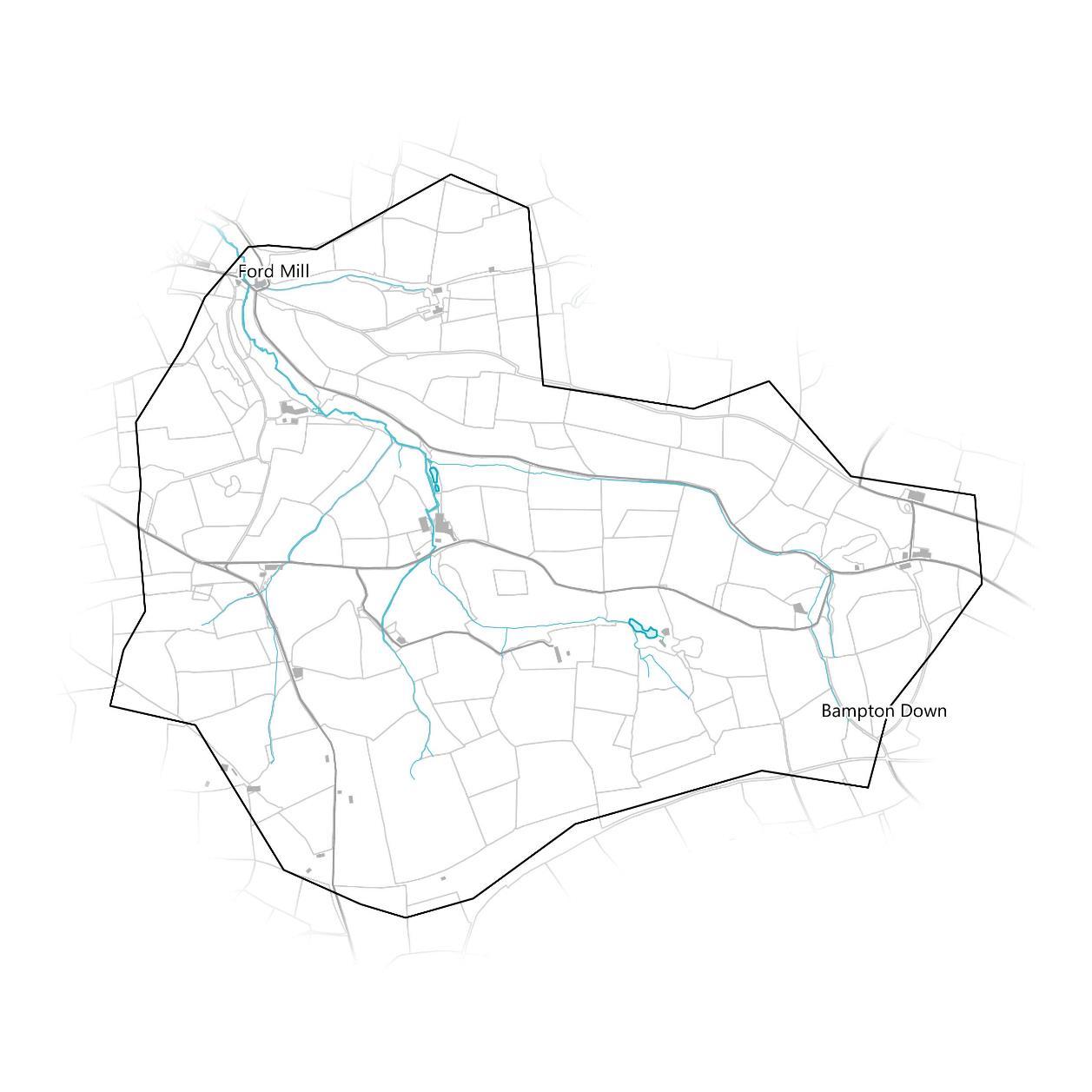
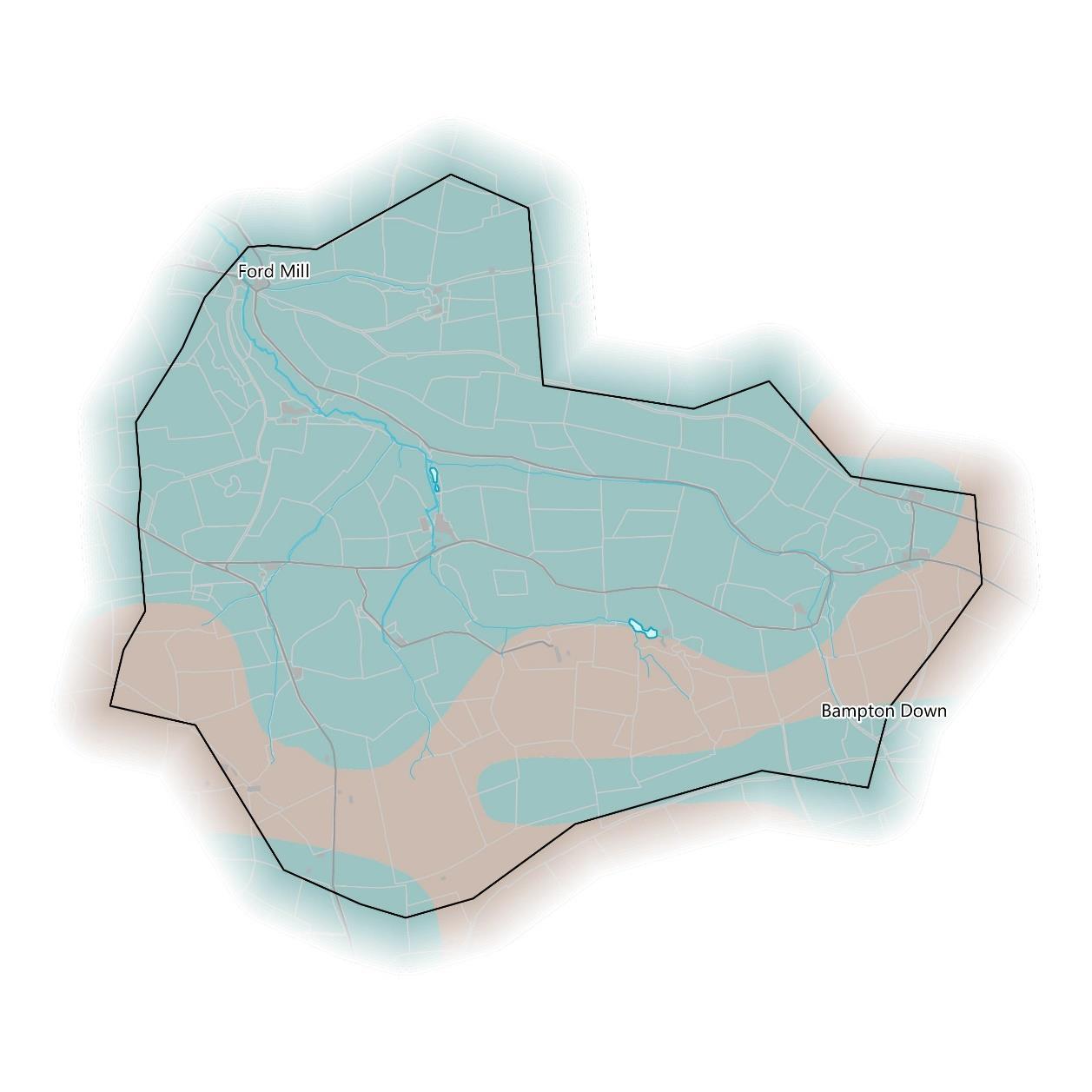
Themicro-catchment was selectedin theGISmodelling step becauseit contains alarge numberof properties at FordMill and elsewhere in thecatchment that arepotentially at flood risk.
The map below showswhichbuildingsoverlap withthe EA’s modelled “Flood Zone 2” area,specificallyareasatriskof flooding from rivers,as identified during the micro-catchmentmapping process.
There are 5 buildingspotentiallyatriskout of 76 in the catchment, approximately6.58%of them.
The catchment’ssize of 4.66km2 givesanarea of 0.93km2 perbuilding atrisk.
The waterframeworkdirective (WFD)statusinthe widerLower Batherm catchmentisModerate.


If property ownersare willing to workwithland owners and vice versa, then small-scale NFMmeasuresupstream in the catchmenthave the potential to benefita large numberof propertiesand improve water quality.

8
Micro-catchment Overview


Topography

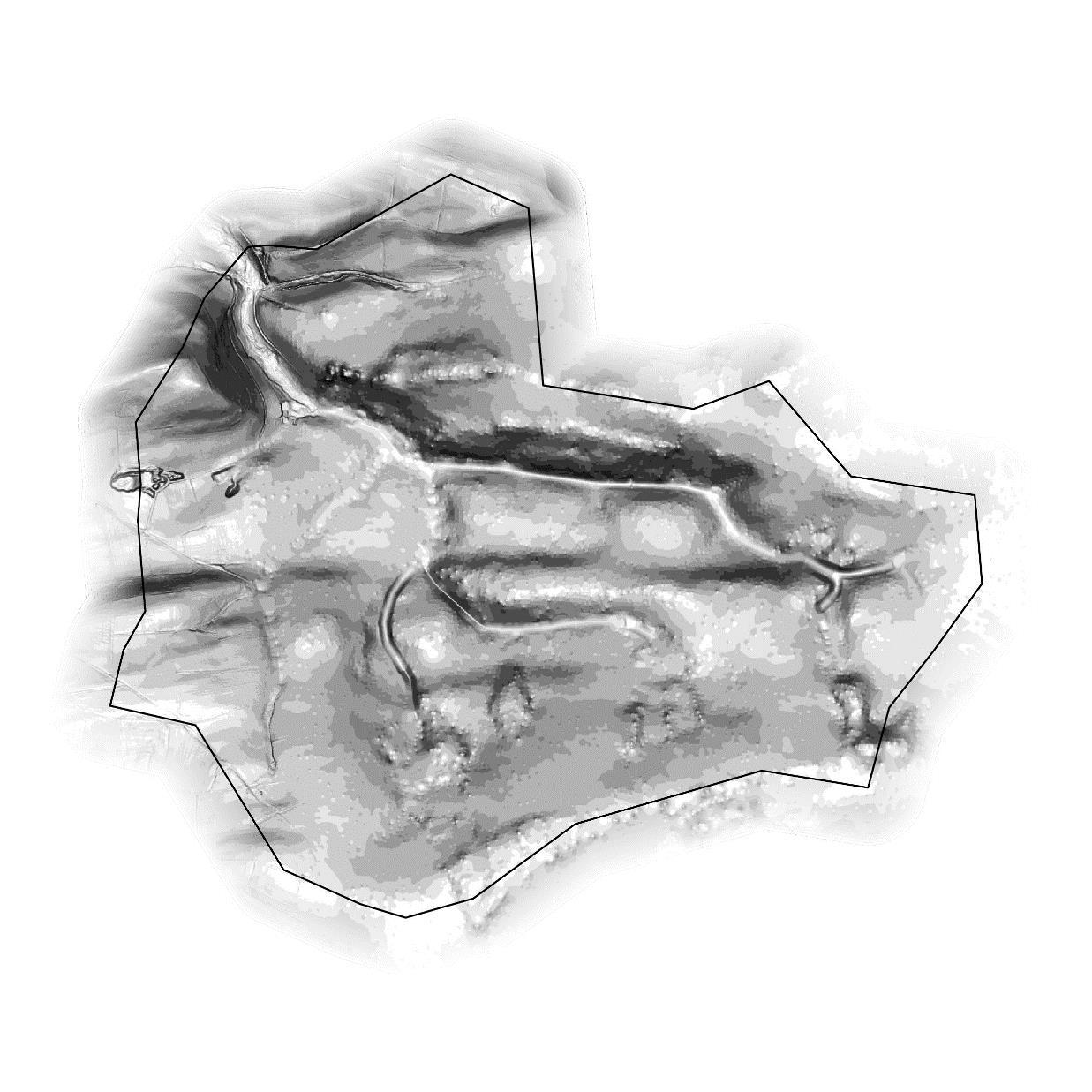
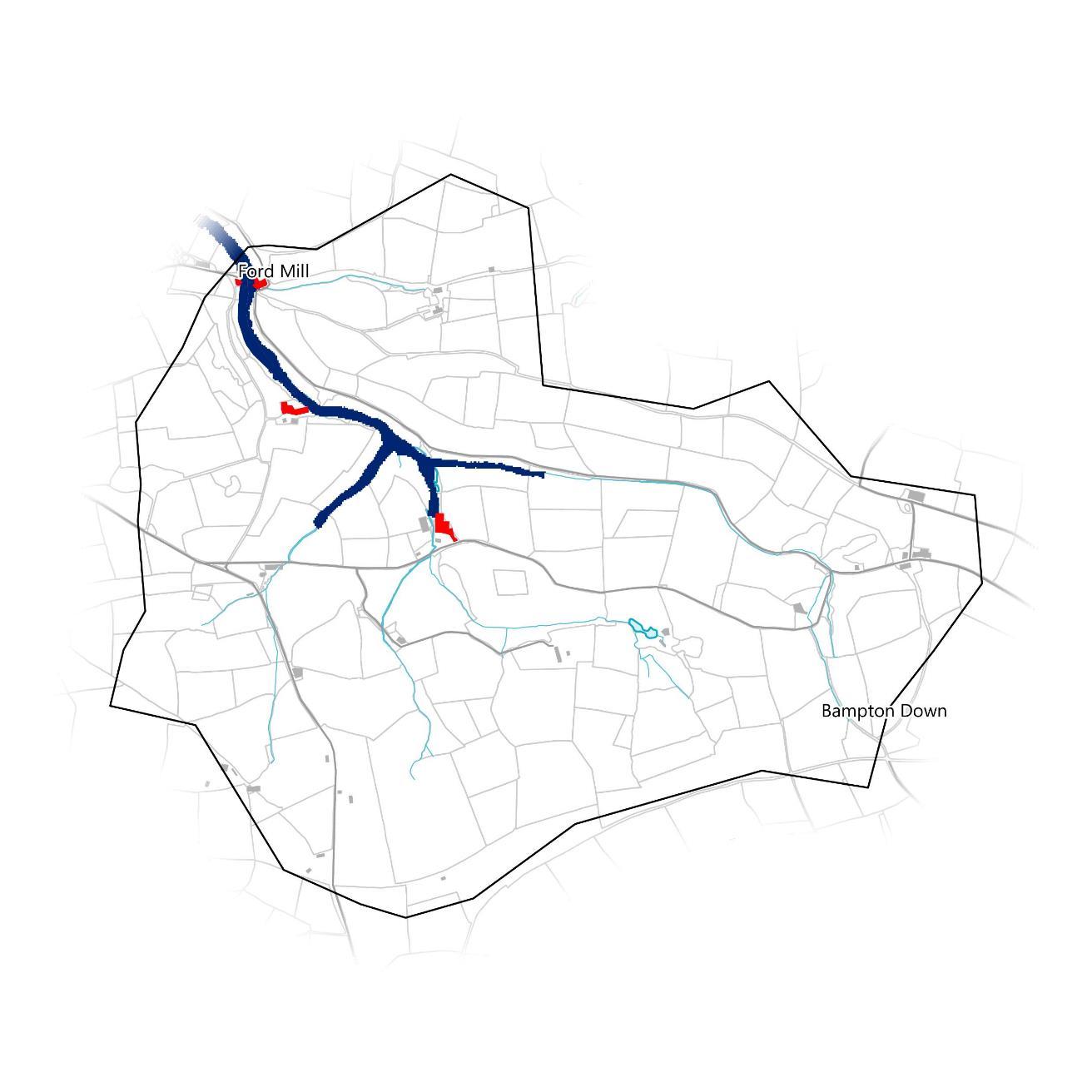
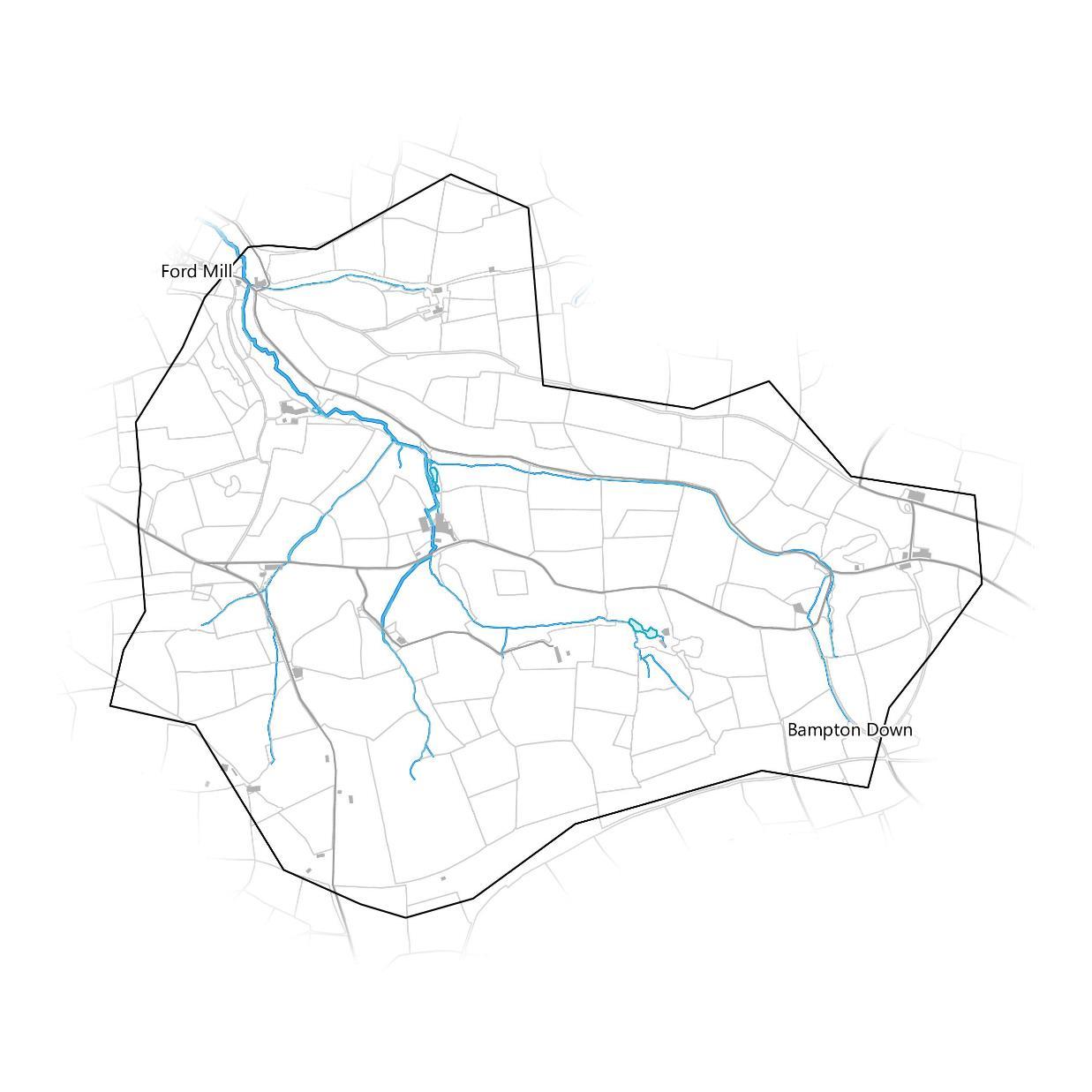
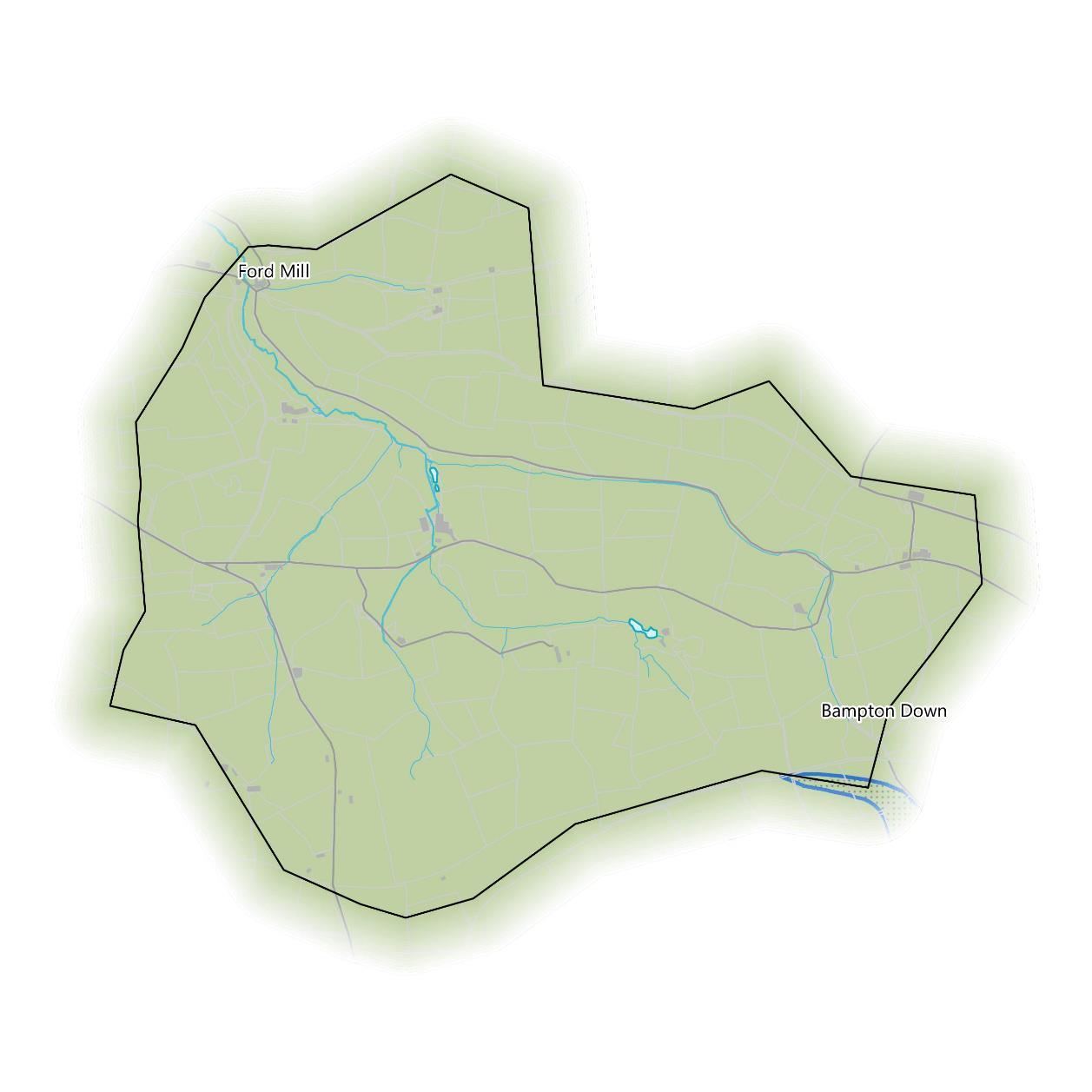
The micro-catchment covers the rural area between Ford Mill and Bampton Down. The micro-catchment forms the watershed for an unnamed watercourse that this report will refer to as the Bampton Stream and its tributaries, that flows northwest through Ford Mill. The total river length present in the catchment is approximately 9.7km. Overall, the micro-catchment falls within the Bampton County Parish and is administered by Bampton Town Council,
The map on the right shows the steepness of slopes. The catchment exhibits a long valley fed into by several smaller valleys that the Bampton Stream and its tributaries run along the bottom of. The main valley and the catchment outlet in the northwest are particularly steep-sided.
9
Micro-catchment Overview
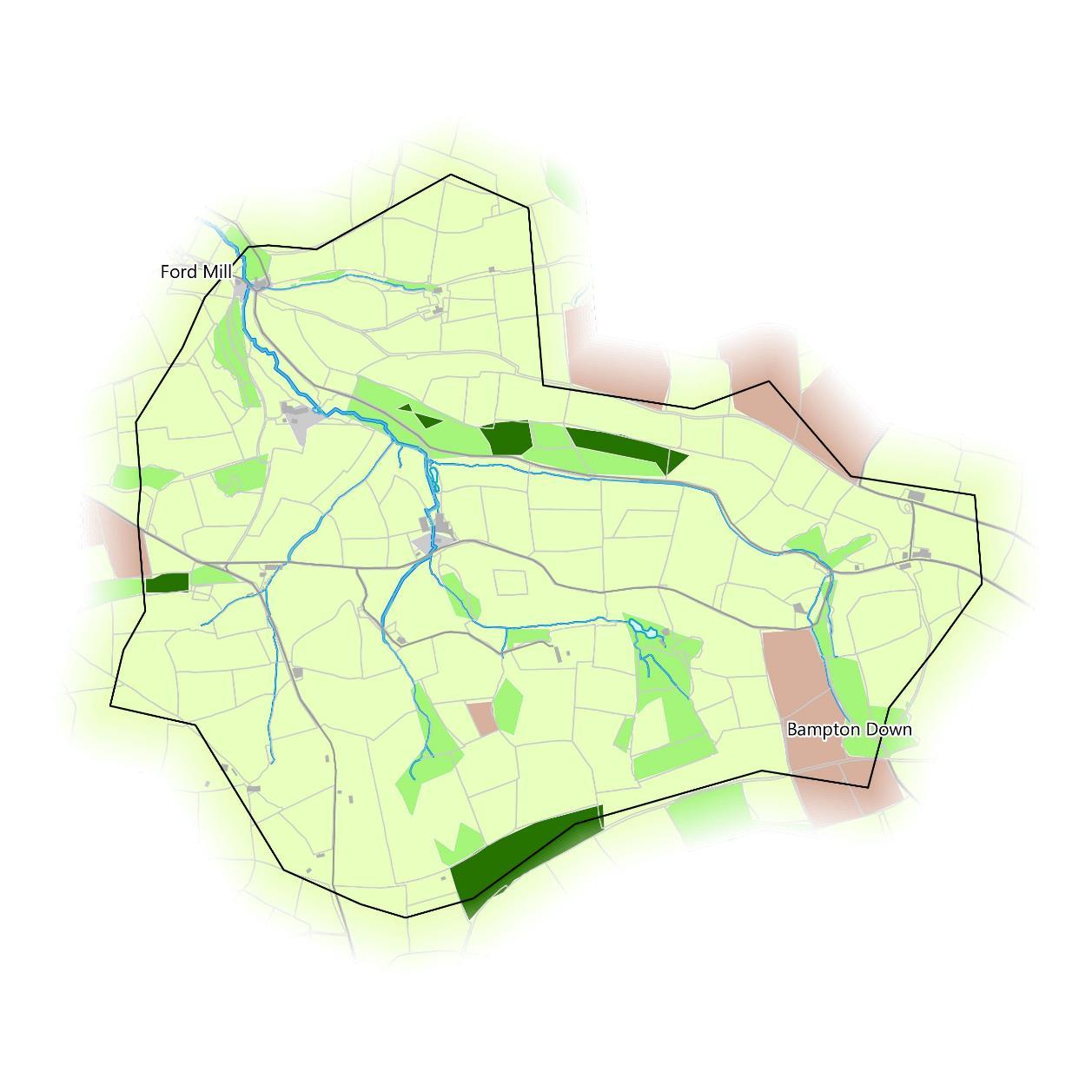
Land Cover

The way the land is used has significant impacts on flood management. Land use has been mapped here using the Centre for Ecology and Hydrology’s (CEH) Land Cover Map 2019. This is a model derived from satellite imagery at 25m resolution.
The land use here is primarily improved grassland, accounting for 77% of the catchment. Patches of broadleaved and coniferous woodland are spread throughout the catchment, accounting for another 17%. There are a few fields of arable and horticultural land in the northeast and southeast at Bampton Down that cover another 5%.
It should be noted that this land cover map model is not a perfect representation of land use as it simplifies UK land cover into very broad classes.
10
Micro-catchment Overview
Land Cover
Land use observed during the catchment walkover mostly matched the land use mapped here using the Centre for Ecology and Hydrology’s (CEH) Land Cover Map 2019.
The catchment is dominated by pasture with a few pockets of wooded land.
This catchment is very steep sided, and this was noticeable on a lot of the pastured slopes where ‘mini-terracing’ was occurring through natural slumping of the slope displaying small lines across the slope.
The catchment appeared to be mainly farming for beef and sheep production.
There are a number of disused quarries in and around the catchment and Bampton.

11
Upper catchment looking west down the main Bampton Stream channel.
Priority Areas and Drivers
Flooding hasthe potential to negativelyaffectpeople and communities. Byconsidering boththe vulnerabilityof communitiesand the opportunitiesforland managementinterventions,actionscanbe targeted to have a positive impactoncommunitiesmostatrisk.
Flooding isone of a number of natural hazardswhichcan cause harm to people,the environmentand the economy.The primarydriverfor targeting thiscatchment isflooding.However,there are otherpriorityareasand driverswhich will be affected byNFMand candetermine the mostappropriate type of NFM forthe catchment. These are mapped inthe following pages.

12
Priority Areas and Drivers
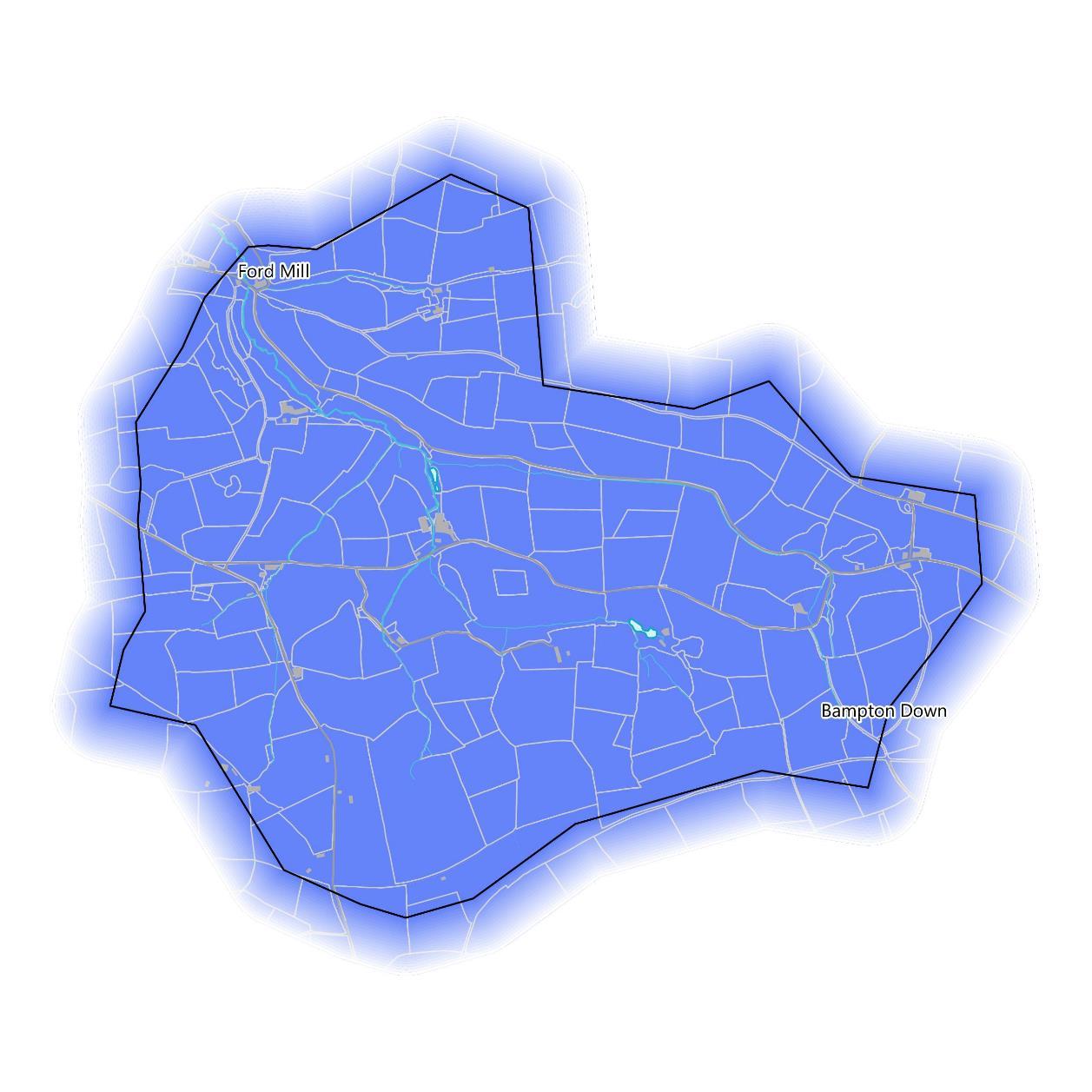
Flooding
The Neighbourhood Flood Vulnerability Index (NFVI) characterises vulnerability as communities likely to experience losses in wellbeing during flood events. This is based on their susceptibility, preparedness, responsiveness, and ability to recover, all without significant support from emergency services.
All of the buildings in the catchment are classed as “Relatively Low” in the NFVI, meaning that they are slightly less vulnerable to losses in wellbeing from a flood event than the UK average.
13
Priority Areas and Drivers
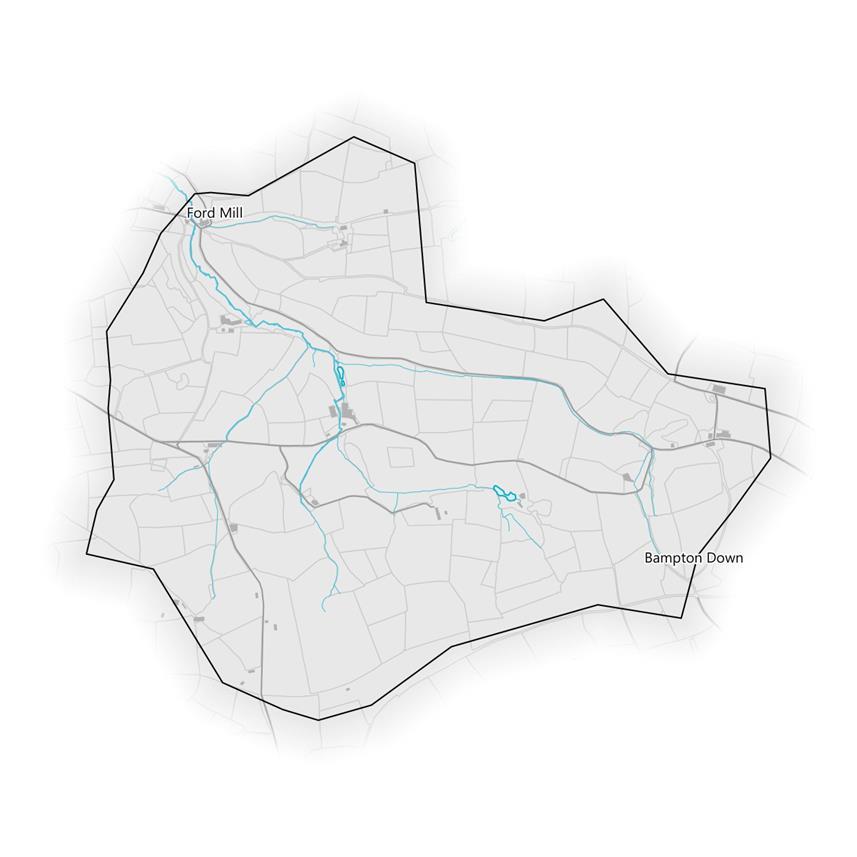
Flooding
The Social Flood Risk Index (SFRI) is a geographic measure of flood disadvantage. It identifies communities who are both exposed to flood risk by living on a flood plain and who are more vulnerable to the effects of flooding, due to factors such as health, preparedness and the availability of community support. Higher numbers of people living in a flood plain coinciding with high social vulnerability result in higher index values. The map highlights neighbourhoods identified as at riskof fluvial flooding higher than the national average. Please note that this is based on flood risk from rivers and the sea, so coastal areas may not be affected by changes in land management upstream.
At present, all areas in the catchment are classed as “Exposed” in the SFRI for river and coastal flooding, though the NFVI remains below the UK mean. This doesn’t increase in future projected scenarios of 2 and 4 degree temperature increases by the 2050s.

14
Priority Areas and Drivers
Flooding
When considering flooding, it is necessary to investigate records of previous flood events and combine this with modelled scenarios of what could happen, particularly in the face of the uncertainty of climate change affecting weather patterns.
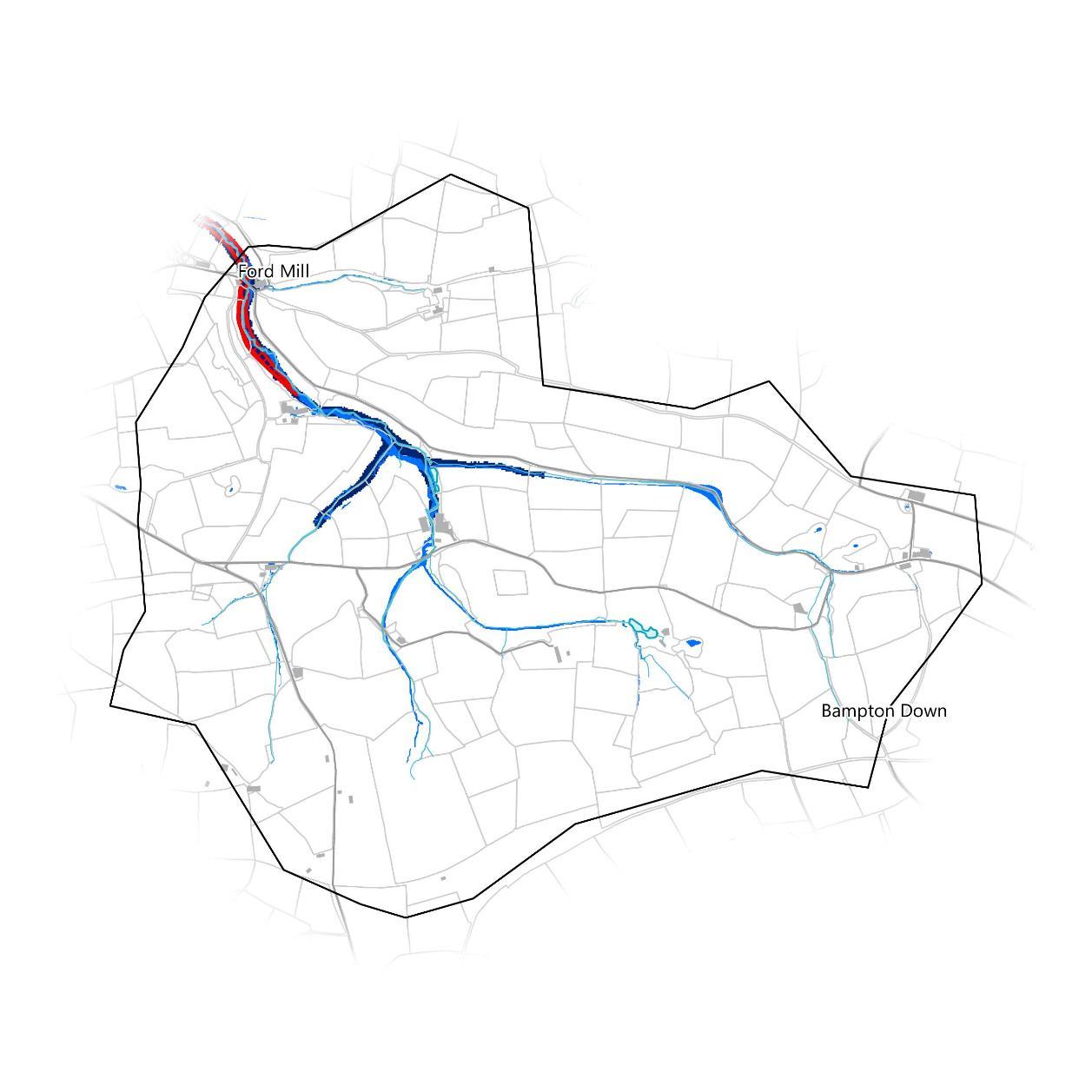
The Bampton Stream has previously flooded in September 1969 where channel capacity was exceeded with no raised defences. There is currently one building falling within the recorded flood outline. There are currently no flood defences in the catchment.
The EA’s modelled fluvial Flood Zone 2 dataset show areas predicted to flood from rivers in a storm event so severe it is likely to occur only once every 1000 years. There are 5 properties within Flood Zone 2 in the Bampton Stream catchment. This is also known as a 0.1% Annual Exceedance Probability. Flood Zone 2 was used to identify buildings potentially at flood risk as shown previously on page 8. Here, this occurs from Ford Mill to the confluence of the tributaries and extends further up three of them by approximately 400m.
The EA’s Risk of Flooding from Surface Water (RoFSW) dataset shows the extent of flooding caused by rainwater flowing across the ground towards the nearest water course in a 1 in 1000 year storm event. There are 13 properties at Risk of Flooding from Surface Water in the Bampton Stream catchment. This overlaps frequently with Flood Zone 2, but also shows depressions in the ground where surface water will accumulate. It is the only modelled riskof flooding on the tributaries beyond the extend of Flood Zone 2. There is a large area of modelled surface water flooding around the road in the northeast of the catchment.
15
Priority Areas and Drivers
Flooding
Flood risk seems to match the modelled risk. However some risk could be considered lower than modelled where the buildings in the catchment considered at risk may have managed pathways around the infrastructure.
Where a couple of properties are identified as at risk but appear to have their own resilience, this may alter the overall risk identified and therefore reduce priority of the catchment.
Bampton Town Council, who are immediately downstream in the main River Batherm, have an active flood response plan and an appointed flood warden.


Flood Resilience Meetings are held for the local community which may include immediate upstream neighbours who could be at risk. The last meeting like this was held in the Riverside Centre, 30/01/2020.
Any benefit to flooding in this Bampton Stream catchment would be highly likely to help resilience and flood avoidance in Bampton itself.
16
Priority Areas and Drivers
Water Quality
Clean and plentiful water is vital for a huge variety of our activities, and for supporting healthy ecosystems. Good water quality supports an efficient water supply, healthy natural habitats and cultural ecosystem services. A plentiful water supply is important for drinking water and household use, irrigation, industrial use and for maintaining habitats. Water quality is a key underpinning for the Water Framework Directive.
There are no Water Framework Directive monitoring sites, priority wetlands, or aquatic habitats in the catchment. It also does not fall within a Nitrate Vulnerable Zone (NVZ).
However, the catchment falls within a wider Drinking Water Safeguard Zone for Surface Water, identified as being at riskof failing the drinking water protection objectives due to contamination by pesticides.
It is also important to note that there is a historic landfill site on the catchment’s western boundary called “Higher Kiln Quarry & Tip”. The last input was made in June 1992.

For more information on water quality go to slide 26.

17
Priority Areas and Drivers

Water Quantity and Drought Risk
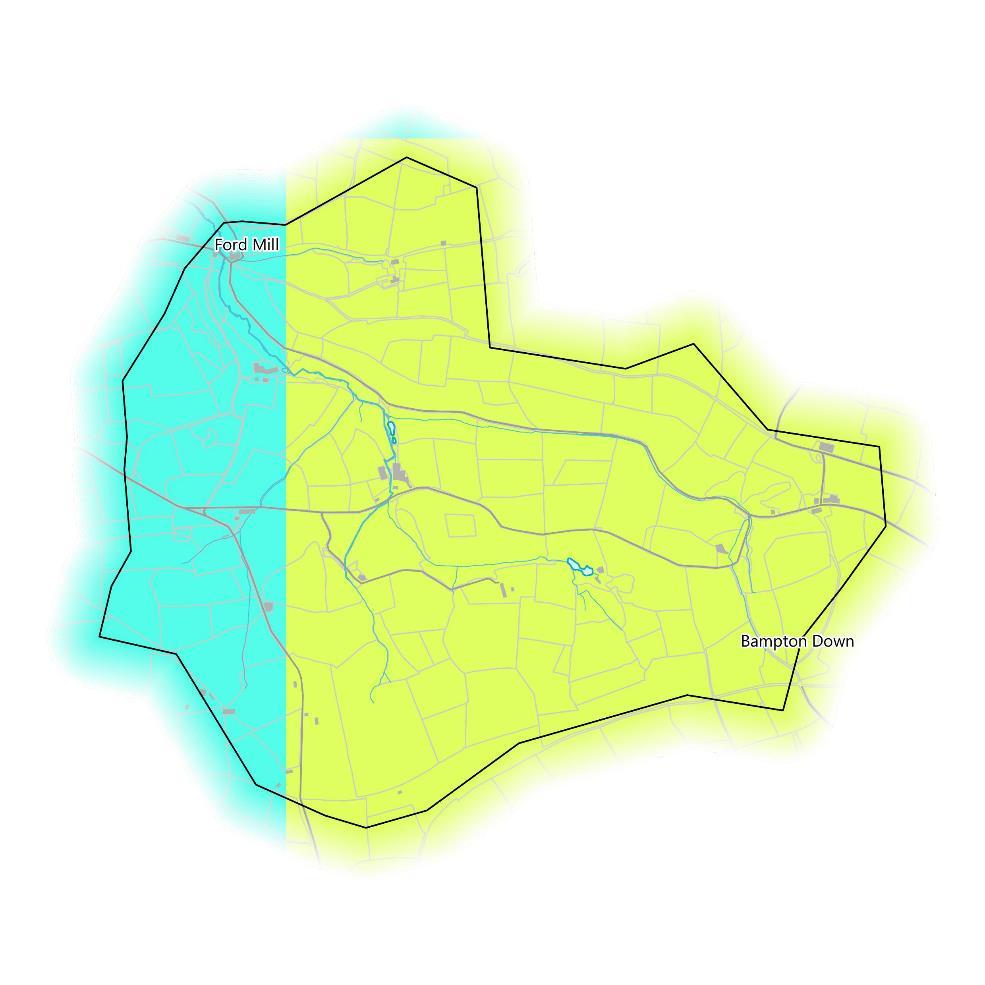
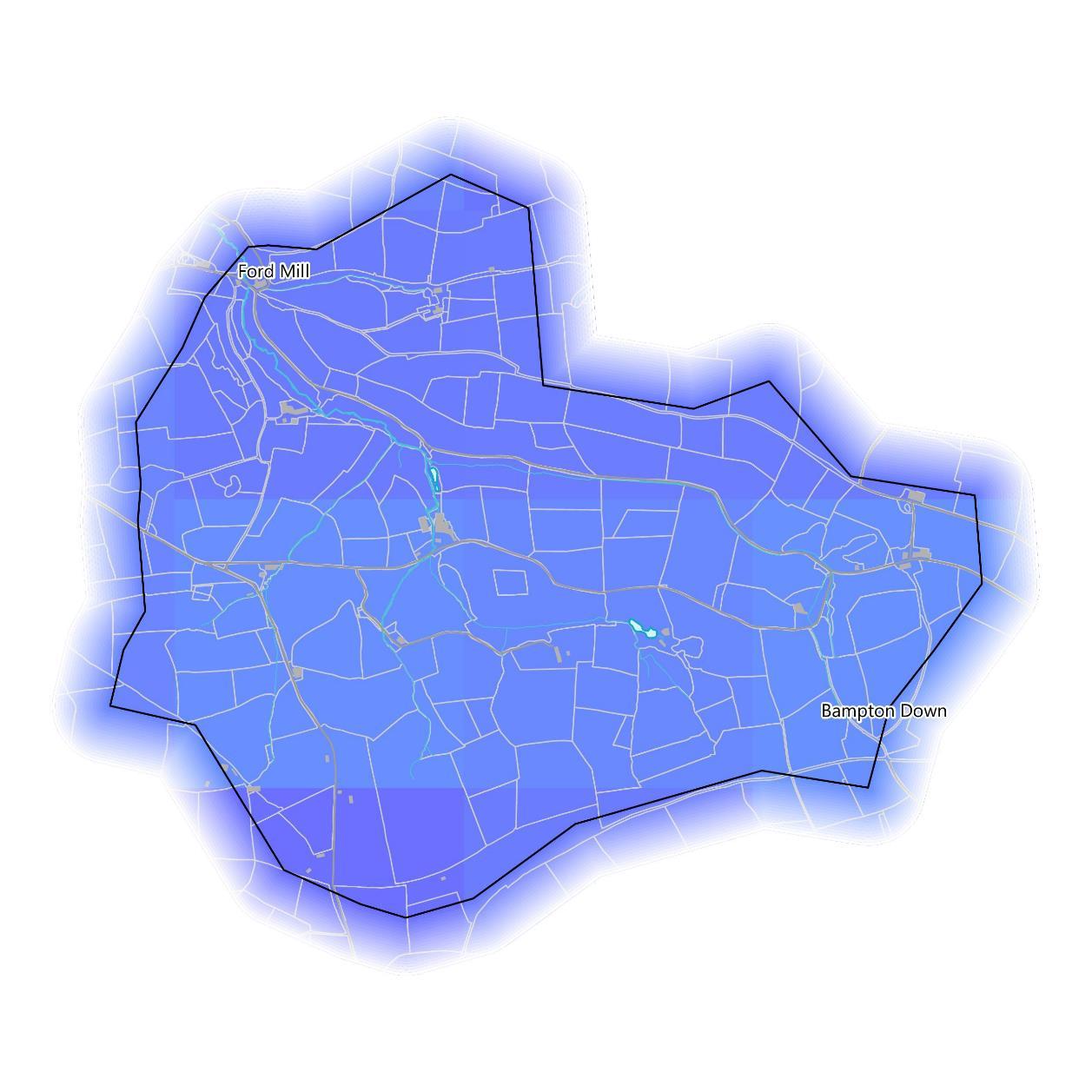
The amount of water available for abstraction is an indicator of how much drinking water is available for people. The catchment sits within an area where restricted water is currently available for licensed water abstraction (left map).
In the context of NFM, it is also necessary to consider water availability for plants and wildlife. Drought can cause vegetation to die back, leaving bare soil exposed and more vulnerable to erosion and runoff when it eventually rains. The Vegetation Health Index (VHI) uses satellite data to combine temperature and vegetation condition to characterise vegetation health. Areas are scored between 0 and 1 with lower values indicating low drought risk to plant health and higher values indicating higher risk. Mostof the catchment is scored relatively high at 0.607 on the VHI (right map), indicating higher riskto plant life from drought stress than the UK average. The west of the catchment scores significantly lower at 0.374, indicating less risk to plant life than the UK average.

18
Priority Areas and Drivers
Designated Sites
Designated habitat sites, from small local nature reserves all the way up to large national parks, need to be protected for the wealth of benefits they provide to people and the environment, including already providing some degree of NFM. A site being designated can be an indicator of habitat health.
However, there are no designations in the catchment.
19
Priority Areas and Drivers
Air Quality
Clean air is important for people’s health and for healthy ecosystems. Air quality is the term used to describe the levels of pollution in the air. When air quality is poor, pollutants in the air may be hazardous to people, particularly those with lung or heart conditions. In the past, the main air pollution problem was smoke and sulphur dioxide from fossil fuels such as coal. Now, the major threat to clean air is from traffic emissions. Petrol and diesel motor vehicles emit a variety of pollutants, principally carbon monoxide (CO), oxides of nitrogen (NOx), volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and particulate matter (PMx).
A growing body of researchsuggested that smaller particles, in particular PM less than 2.5μm in diameter (PM2.5), is a metric for air pollution which is closely associated with the adverse health effects of poor air quality. Therefore, this section will use data relating to PM2.5 where relevant.

Improvements to the soil and surrounding environment have the potential to also deliver improvements to air quality through natural filtering processes.
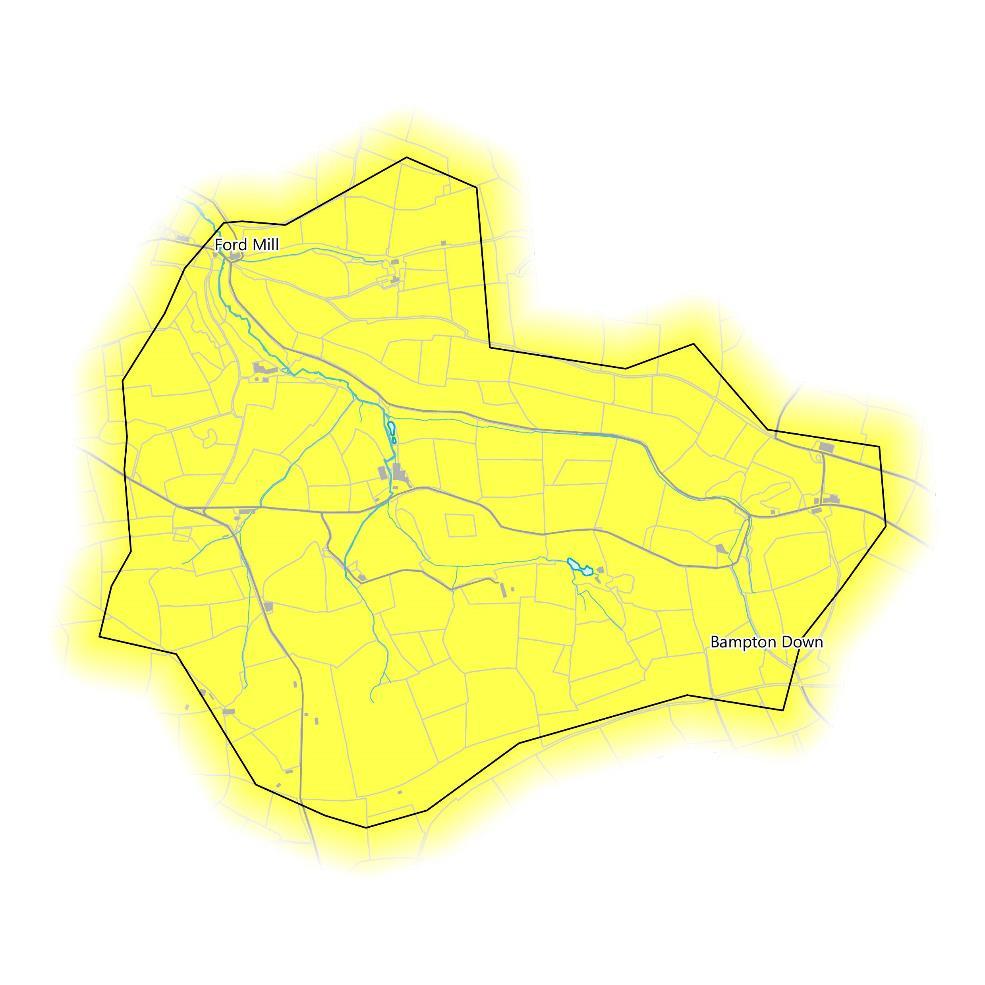
The catchment has low concentrations of background PM2.5 throughout with the highest recorded at 6.40PM2.5. in the eastat Bampton Down, and the lowest recorded at 6.13PM2.5 in the south
20
Priority Areas and Drivers

Tourism and Recreation
Areas and features important for tourism and recreation may also be at flood risk and it is necessary to protect them for a healthy society and environment.
The catchment doesn’t contain any greenspaces but it does contain numerous Public Rights of Way (PRoW)
A PRoW runs east from Ford Mill at the northwestern corner of the catchment to the northeast corner. Another PRoW runs along the southern edge of the catchment, mainly out of the watershed. Two more PRoW paths run through the agricultural land in the west of the catchment.

21
Existing Natural Assets and their Condition
Biodiversity,the varietyof life of earth,is valuable initsown right. Italso supports recreation,food,flood protection and climateregulation. This sectionwill predominantlyexplore whathabitatsand othernatural assetsare presentin the catchmentthat will already be contributing to NFM and could be improved withfurther NFM measures.Water, soilsand crops are natural assets in themselvesand will also be investigated.

22
Existing Natural Assets and their Condition

Habitats and their Condition
The natural assets mapped below are habitats which have the potential to support thriving plants and wildlife. Thriving vegetation is very valuable for NFM as it roughens the ground, thereby slowing down surface water flow, meaning water courses are less likely to be overwhelmed in a storm. In addition, plant roots provide structural support for the soil and prevent surface water washing soil into water courses.
Where the assets are present the landscape is likely to be contributing to the provision of habitats, biodiversity and even NFM. Where assets are absent there may be a lack of habitats which contribute to or support thriving plants and wildlife. Assets may still be present however in the form of crops and soils which are mapped in the following pages.
Multiple patches of broadleaved woodland are scattered in the catchment, and many of these are deciduous woodland priority habitats. Coniferous woodlands are also present in the north and south.

There are two areas of purple moor grass and rush pasture in the southeast and northwest. The latter has a thin strip of good quality semi-improved grassland on its south side.

23
Existing Natural Assets and their Condition
Water Framework Directive
It is important to determine the current condition of water quality. Poor water quality can be detrimental to people, wildlife, and may cause other negative effects during a flood event. Good water quality should always be protected. A key set of evidence used to assess the water quality in a catchment is the Water Framework Directive (WFD). The status of a waterbody is measured using a series of parameters and is recorded on the scale: high; good; moderate; poor; bad (with moderate and worse being regarded as a failure).
There are no assessed WFD river waterbodies present. However, the microcatchment sits within and on the edge of the larger Lower Batherm river waterbody catchment, accounting for 26% of it’s area.

The Lower Batherm is overall classed as Moderate meaning it is failing WFD regulations. It is currently failing on both ecological and chemical status. In 2019, 100% of waterbodies in the UK failed on chemical status after the EA included monitoring “mercury and its compounds” and “Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE)” into its water quality monitoring methodology.

24
Existing Natural Assets and their Condition
Water Framework Directive
The Lower Batherm was assessed as Good or High for most ecological classification elements but was classed as Moderate for Fish, Phosphate, Macrophytes and Phytobenthos. Its overall ecological status is therefore Moderate and is consequently failing WFD regulations on ecological grounds.
It is failing for Fish due to poor livestock, nutrient, and soil management, as well as continuous sewage discharge by South West Water (SWW) and barriers creating ecological discontinuity.
The waterbody is classed as Good for most chemical classification items, except for the previously mentioned Mercury and its compounds and PBDEs where it is classed as Failing. In addition, it is also failing for Benzo(gh-i)perylene. The Lower Batherm’s overall chemical status is consequently failing and is therefore failing WFD regulations on chemical grounds as well as ecological.
The reasons for not achieving good status for Benzo(g-h-i)perylene are currently under investigation.
The are over 60 metrics that the EA can use to monitor waterbody catchment statuses. For more information and a breakdown of this catchment’s status go to link.

Waterbody: Lower Batherm
Waterbody ID: GB108045015070
Ecological Status
Macrophytesand Phytobenthos
Benzo(g-h-i)perylene
Mercuryand Its Compounds
Chemical Status
Polybrominateddiphenyl ethers (PBDE)
25
Fish Phosphate
Existing Natural Assets and their Condition
Crops

Crops can be a natural assetin themselves, providing the food we eat and storing carbon. Some crops however, could be considered natural liabilities. One such crop is maize which is planted in wide rows, leaving bare soil exposed and without structural supportfrom roots. Furthermore, it is often harvested in late-Autumn when the weather becomes wetter, meaning little to no vegetation can regrow to protect it over Winter. This leaves the soil much more susceptible to being carried away by surface water runoff. Despite this, maize can be successfully managed to grow and harvest while minimising runoff.
The Crop Map of England (CROME) dataset is derived from satellite data and generalised to hexagons. It identifies the buildings as non-vegetated with the majority of the catchment classed as grassland, and various scattered clusters of trees. Some maize is grown on the western and northern boundaries in isolated fields. Several fields of barley and oats are being grown in the southeast at Bampton Down.
26
Existing Natural Assets and their Condition
Soils
The nature of the soil can determine how much surface water infiltrates into the ground, as well as what plants will growand where. Understanding soils is vital to providing effective NFM and improving water quality. The aim with water quality improvements is to keep the soil on the land and improve groundwater infiltration and recharge, therefore allowing a slower and more naturally filtered water route to the river.
Degraded soil structure, where the soil profile is compacted at shallow depths or capped at the surface and impermeable can lead to excessive unnatural run-off of surface water instead of percolation and infiltration. More than 60% of soils in Devon and Cornwall are naturally well-drained and should rarely become saturated. The Farming Rules for Water (FRFW) were introduced at the start of 2018 as legislation to help protect surface water quality. The regulations are designed to help manage cultivated agricultural land well, without over-management, nutrient run-off, or waste affecting surface water.
The diagram above shows good soil structure on the left and compacted soil structure on the right. In compacted soil, little surface water can infiltrate into the soil subsoil due to surface capping or compacted layers, while vegetation can be deprived of oxygen due to compression of pores that normally transport air and water (sourced from SEPA NFM Handbook).

27
Existing Natural Assets and their Condition
Soils
The NATMAP soils dataset from Cranfield University shows that the catchment is primarily composed of the soil series Neath, with a non-linear band of the soil series Hallsworth 2 running horizontally across the south.
At the time of the walkover survey, soil health in the catchment was considered good in some places and possibly adequate or poor in others depending on historic land use and how well the soil is actively managed in recent times. Further investigation would be needed to conclusively determine the soil status, and this is recommended as it is beneficial for the productivity of the land as well as the natural functioning benefits that can be derived.
Compaction wasn’t determined at the time of survey but could be considered when looking at soil health to help the overall productivity and function.

The above map was created using the NATMAPvector dataset from Cranfield University in March 2022
28
Existing Natural Assets and their Condition
Geology
Geological conditions impacts groundwater and soil type. When rocks are sufficiently permeable it can lead to groundwater flooding. If local flooding is caused be groundwater levels then it is unlikely that changes to land management and NFM will improve flood resilience.

The north of the catchment is primarily composed of chert, limestone, and mudstone. The south of the catchment is made of claystone and mudstone, a narrow horizontal band of which is also presentin the north. The Bampton Stream itself has underlying riverine clay and floodplain sands and gravel.
The walkover didn’t uncover any initial suspicion of groundwater flooding and the perception is that any flood risk would originate from surface flow.
29
Issues
Multiple issues have already been mentioned and mapped that could be contributing to flood risk and WFD failures. However, there are further potential issues that may be influential which will be explored in the following pages.

30
Issues

Pollution and Abstraction
Pollution incidences themselves will directly affect water quality, but consented discharges into watercourses and chemical runoff from roads exacerbated by rainwater may also be sources of pollution.
There are no recorded pollution incidences in the catchment, but there is one source of consented discharges present for agriculture south of Ford Mill. This is for treated effluent being discharged into a soakaway.
Licensed water abstraction points may serve as sources of risk to ground water quantity and availability. However, there are no water abstraction points present in this catchment.
31
Issues
Hydrological Connectivity

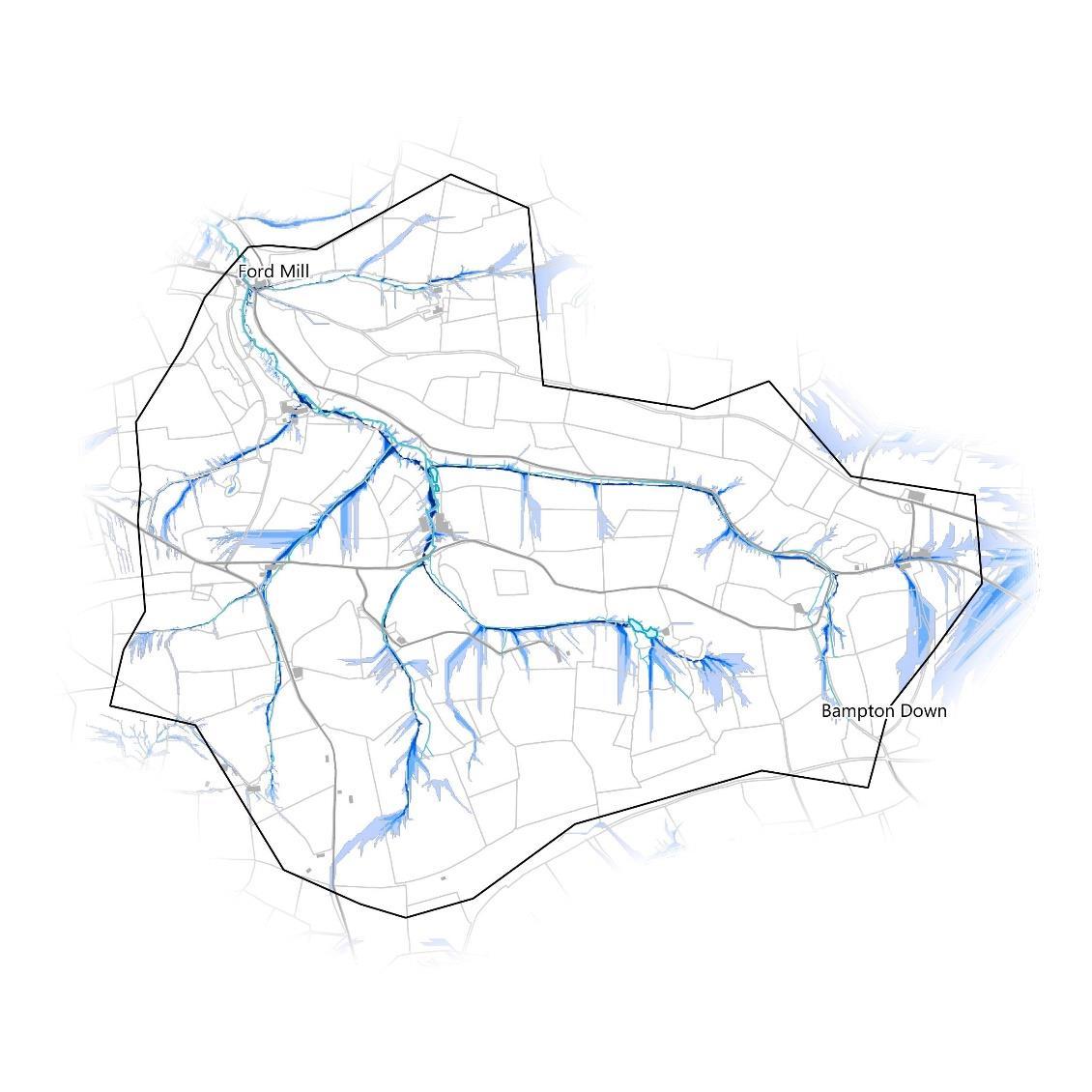
Surface flow pathways are the routes rainwater accumulates and follows when it lands to the nearest depression or watercourse. As it flows, surface water can pick up any number of chemicals, soil, and debris and carry them into the watercourse with it. This serves to demonstrate why community engagement and working with land owners is so important, as the effects of practices upstream in the catchment cascade down via these routes. Pathways have been modelled in 2 different ways here.
The first are modelled using topographic data and software called SCIMAP (left). Only the routes with above average wetness are shown. The flat topography of floodplains skews the modelling process and the pathways in these areas should be considered unreliable.
The second method uses SCALGO Live (right). Flow routes with at least 1km2 upstream area are shown. Areas that would be flooded if 15cm of rain were to fall during a storm event are also mapped. Flooded areas are coloured by their water volume from light to dark.
32
Issues
Issues Identified During Walkover Surveys
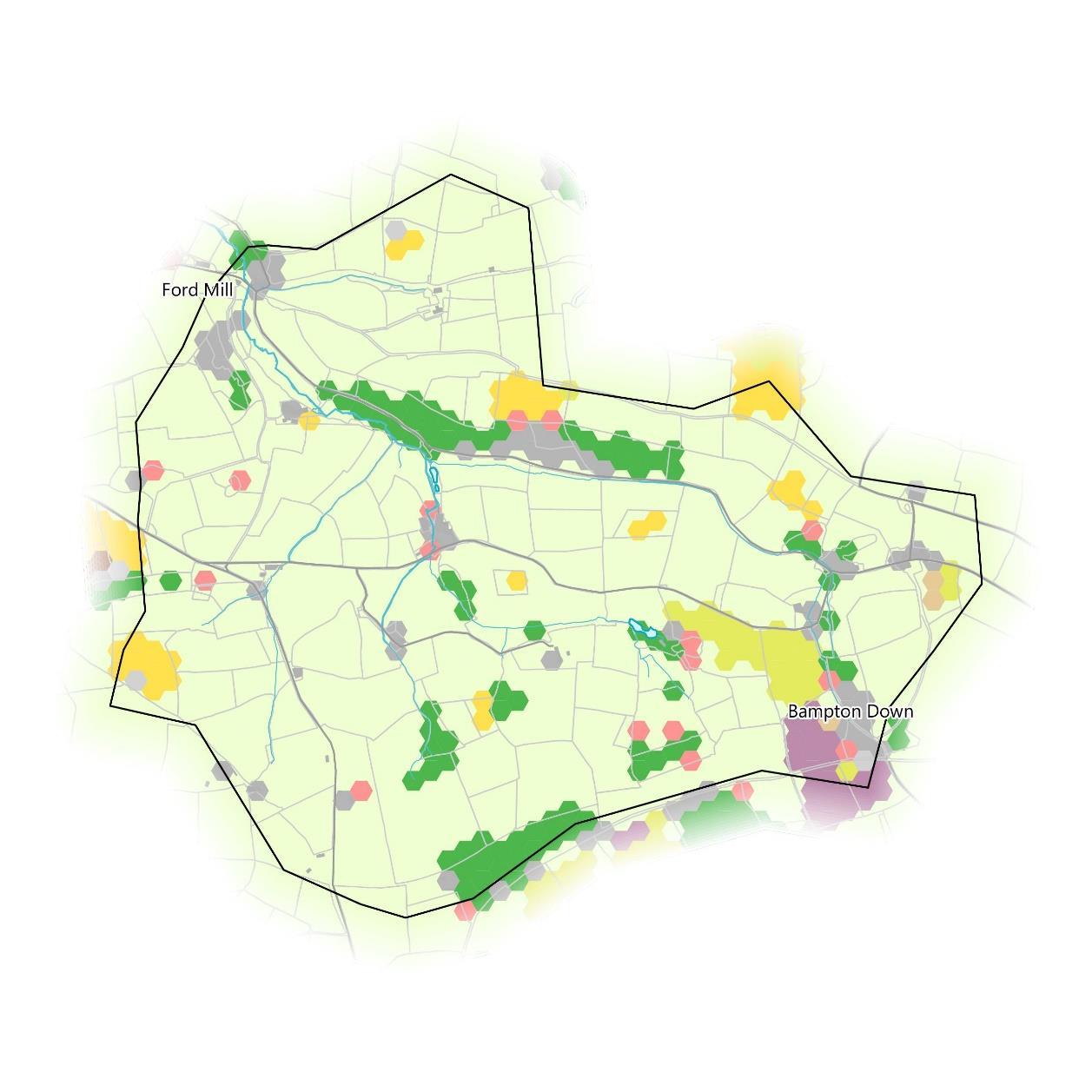
During the walkover surveys, experienced surveyors at WRT recorded points of interest and concern, as well as potential natural flood management opportunities. The results are mapped (right) but it should be noted that the map is by no means exhaustive.
Pathways exaggerating a rapid response of surface water flow in this catchment may be a solvable issue.
Some overland flow was visible over saturated ground and some run-off had obvious pathways such as roads and tracks that made progress to the river more rapid.
The saturation of the ground indicates the water table is full, but this may also indicate an impermeable layer of the soil whether it’s compaction or capping. It is recommended that this be investigated further to see if the ground has more potential for increased infiltration. Although minimal, there was some winter (wet weather) higher risk from exposed soil as the hillside field only had a sparce covering of grass in February.

If other crops are occasionally grown on such a slope with a late harvest then soil run-off with surface water can be a risk.

This map of issues was generated after one walkover survey, reflecting the situation at the time of survey. It is not exhaustive and doesn’t reflect all issues present in the catchment which will take much more effort to determine. A greater range of all the issues is present within the previous section. Any projects delivering in the catchment should undertake their own walkovers for confirmation and addition to the list.

33
Opportunities

34
Opportunities
Working With Natural Processes
There are many options to reduce flood and coastal erosion risk across the country which involve implementing measures that help to protect, restore and emulate the natural functions. These options are known as Working With Natural Processes (WWNP) or Natural Flood Management (NFM). These measures increase flood resilience by slowing the flow of water and disperse energy to keep the water at the top of the catchment or to improve groundwater infiltration and recharge, therefore allowing a slower and more naturally filtered water route to the river.
Where rapid surface water run-off has been noted there may be opportunities for WWNP to mitigate both water quality and to regulate flow. An example of some NFM interventions are given below. They are intended to slow water, store water, increase infiltration and intercept rainfall.
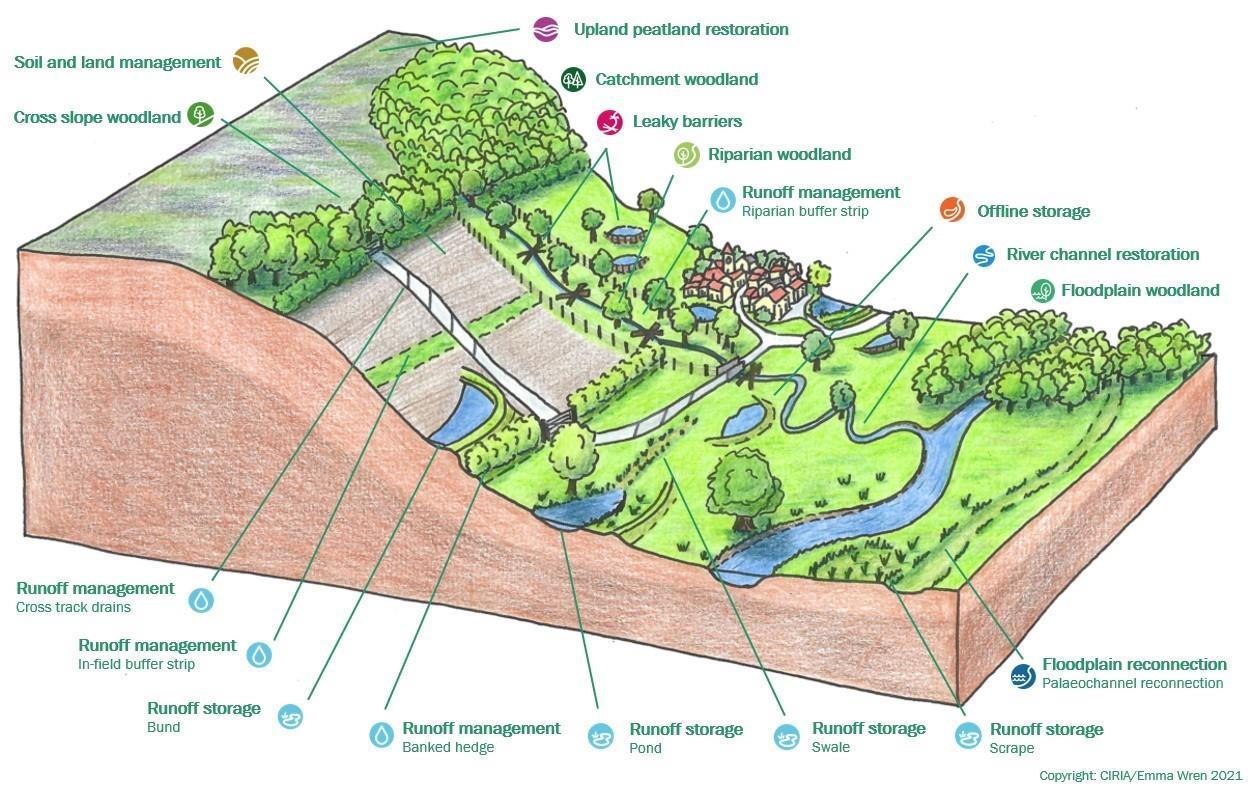
35
The illustration above shows various natural flood management techniques (sourced from CIRIA).
Opportunities
Working With Natural Processes
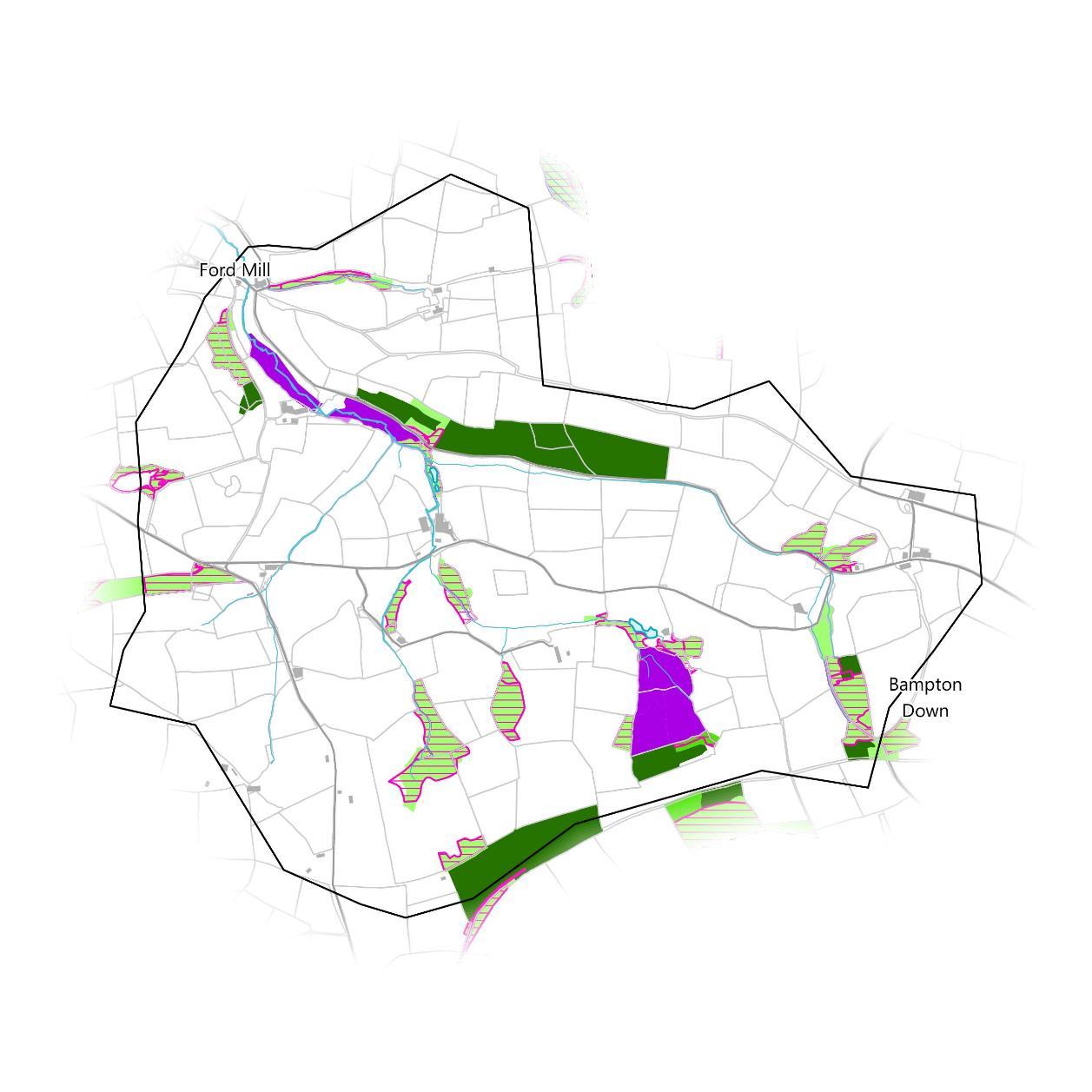
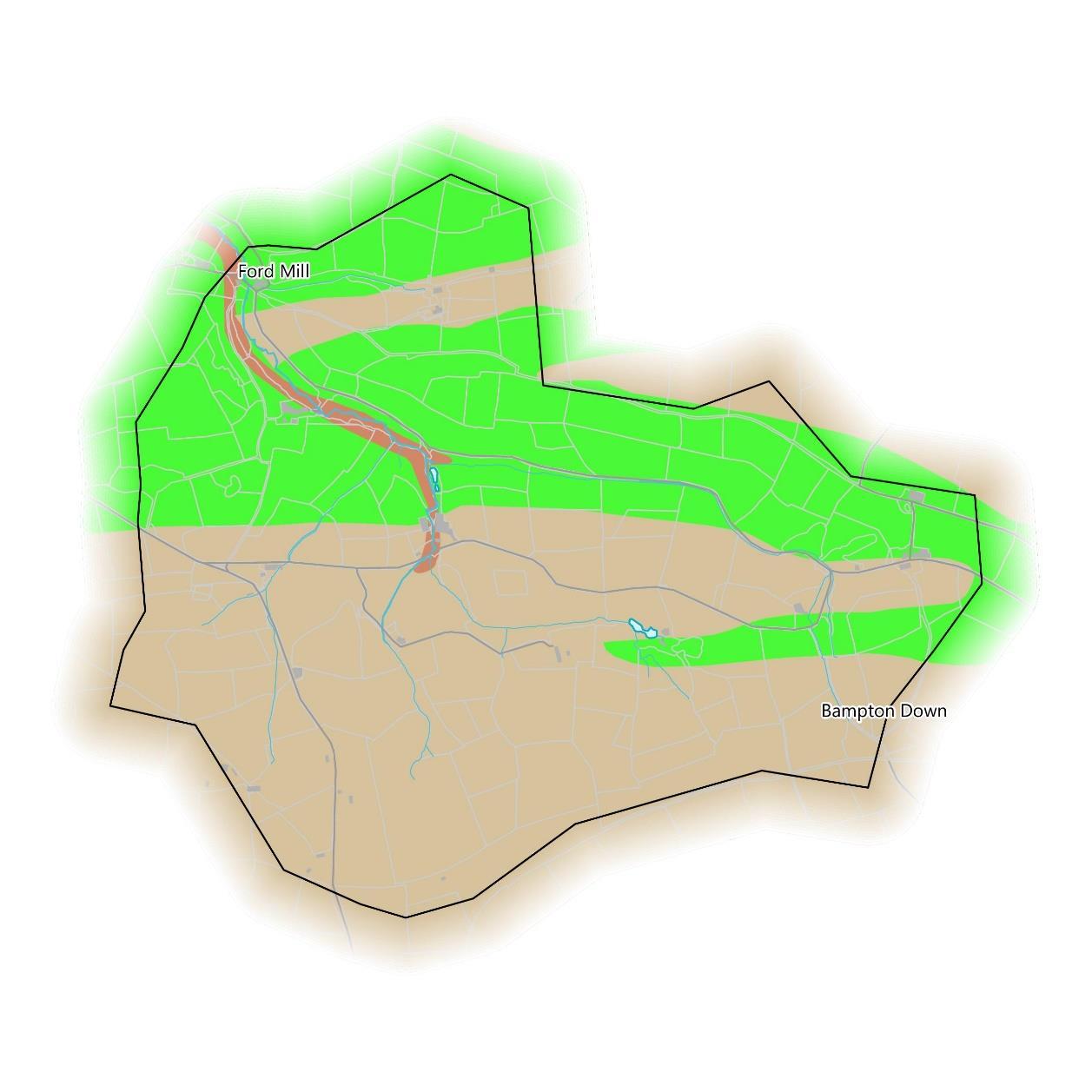
The Environment Agency have mapped potential opportunities for WWNP to reduce flood and coastal erosion risk across the country. These include opportunities for different types of woodland planting, floodplain reconnection features like restored riverside wetlands and meadows, and runoff attenuation features which aim to slow pathways of water across the land, like storage ponds or leaky barriers. Anumber of areas are also excluded from the woodland maps such as urban areas and existing woodland. These are mapped separately on page 39.
The greatest opportunity identified by these WWNP datasets for the catchment is riparian tree planting along the full length of the Bampton Stream and all of its tributaries. Much of this also overlaps with floodplain woodland planting opportunities.

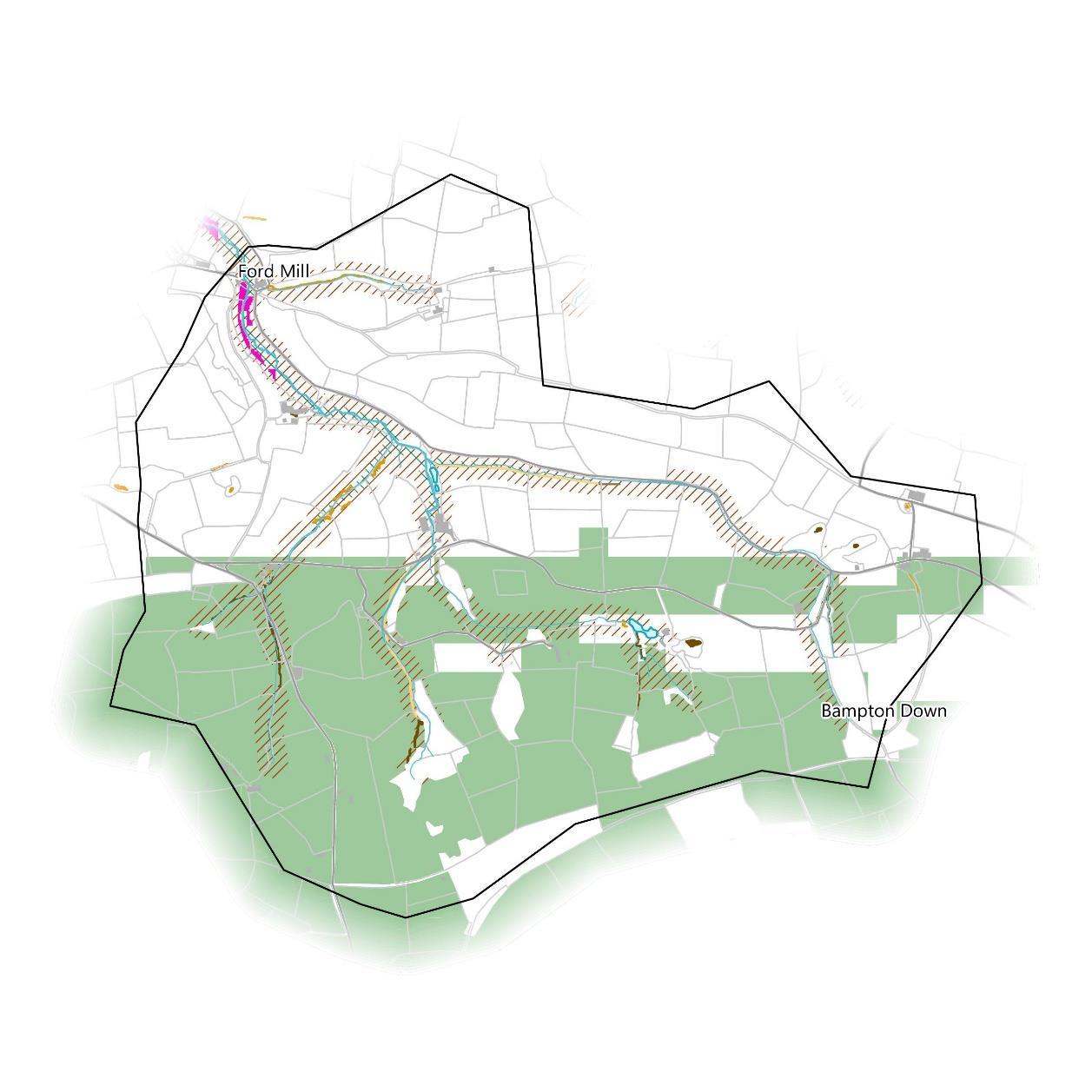
In addition, there are opportunities to construct smaller scale runoff attenuation features in many of the tributaries and the main roads that are strategically placed to slow the flow of surface water before it reaches the water course, allowing excess water to dissipate rather than flood during a storm event.
Furthermore, it may be possible to reconnect some small areas of floodplains downstream at Ford Mill.
The south of the catchment also overlaps an area identified as potentially contributing to reduced flood risk if woodland planting is undertaken at a large scale to increase surface roughness and slow down surface water flow.
36
Opportunities
Habitat Creation and River Restoration Projects
There may be current habitat creation and river restoration projects where opportunities exist to work together with organisations to provide simultaneous benefits to habitats, rivers, and flood resilience.
Natural England have also identified opportunities to expand on existing habitats to create habitat networks across the landscape.
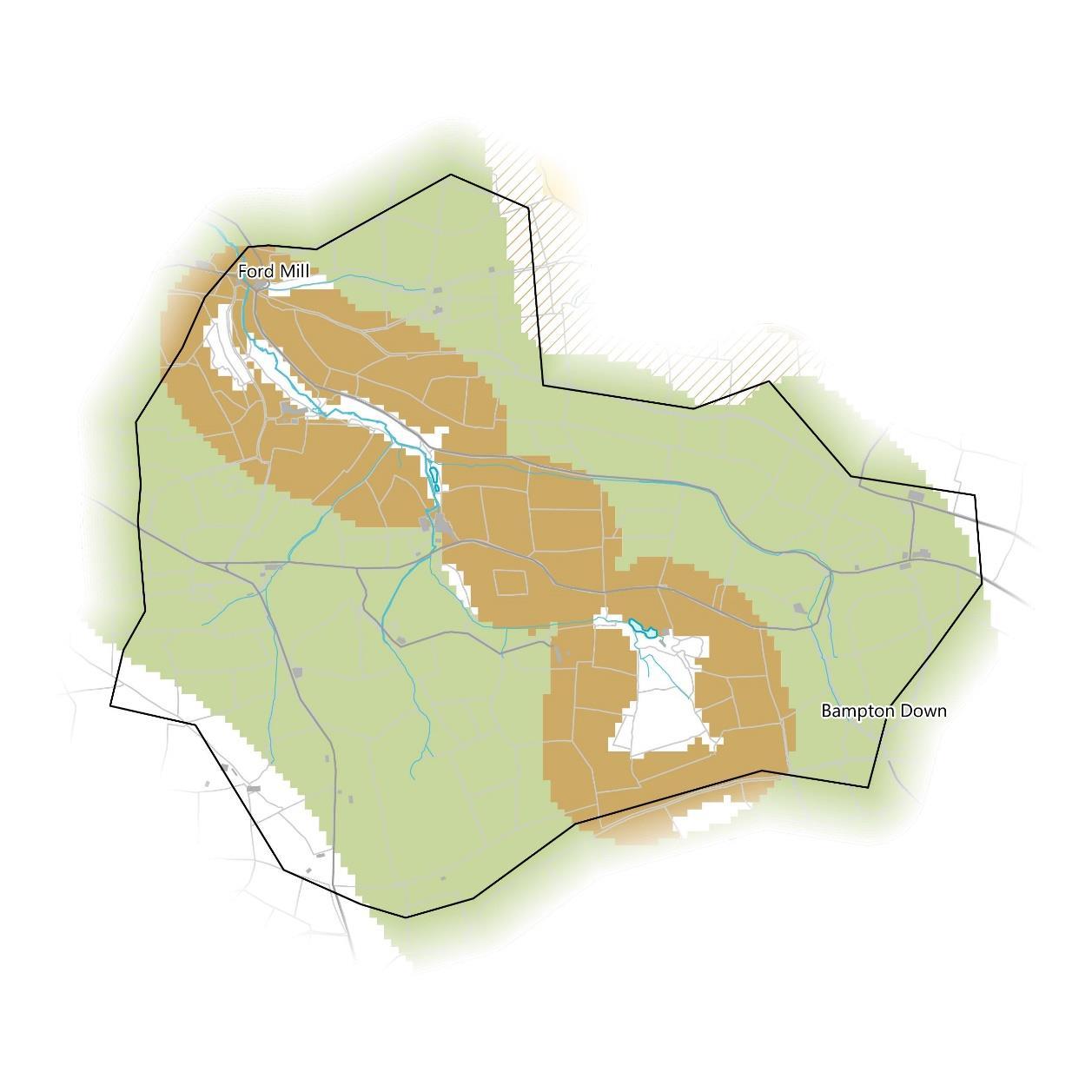
While there are no recorded habitat creation or river restoration projects in the catchment, there are significant opportunities for expanding habitat networks around existing priority habitats (see page 23).
Surrounding the purple moor grass and rush pastures and some of the patches of deciduous woodland along the Bampton Stream is Network Enhancement Zone 1, defined as “Land within close proximity to the existing habitat components that are more likely to be suitable for habitat re-creation for the particular habitat. These areas are primarily based on soils but in many cases has been refined by also using other data such as hydrology, altitude and proximity to the coast.”
Covering most of the restof the catchment is the Network Expansion Zone, defined as “Land within relatively close proximity to the Network Enhancement Zones that are more likely to be suitable for habitat creation for the particular habitat and identifying possible locations for connecting and linking up networks across a landscape.”

Some small areas on the northern boundary are classed as Network Enhancement Zone 2, “Land within close proximity to the existing habitat components that are unlikely to be suitable for habitat re-creation but where other types of habitat may be created or land management may be enhanced including delivery of suitable Green Infrastructure.”
37
Opportunities
Agri-environment Schemes

Agri-environment schemes are government initiatives that aim to financially compensate farmers for providing benefits to wildlife on their land. Areas under agri-environment scheme agreements may provide opportunities simultaneously for the landowner to meet the agreement’s objectives and deliver NFM to benefit the catchment community.
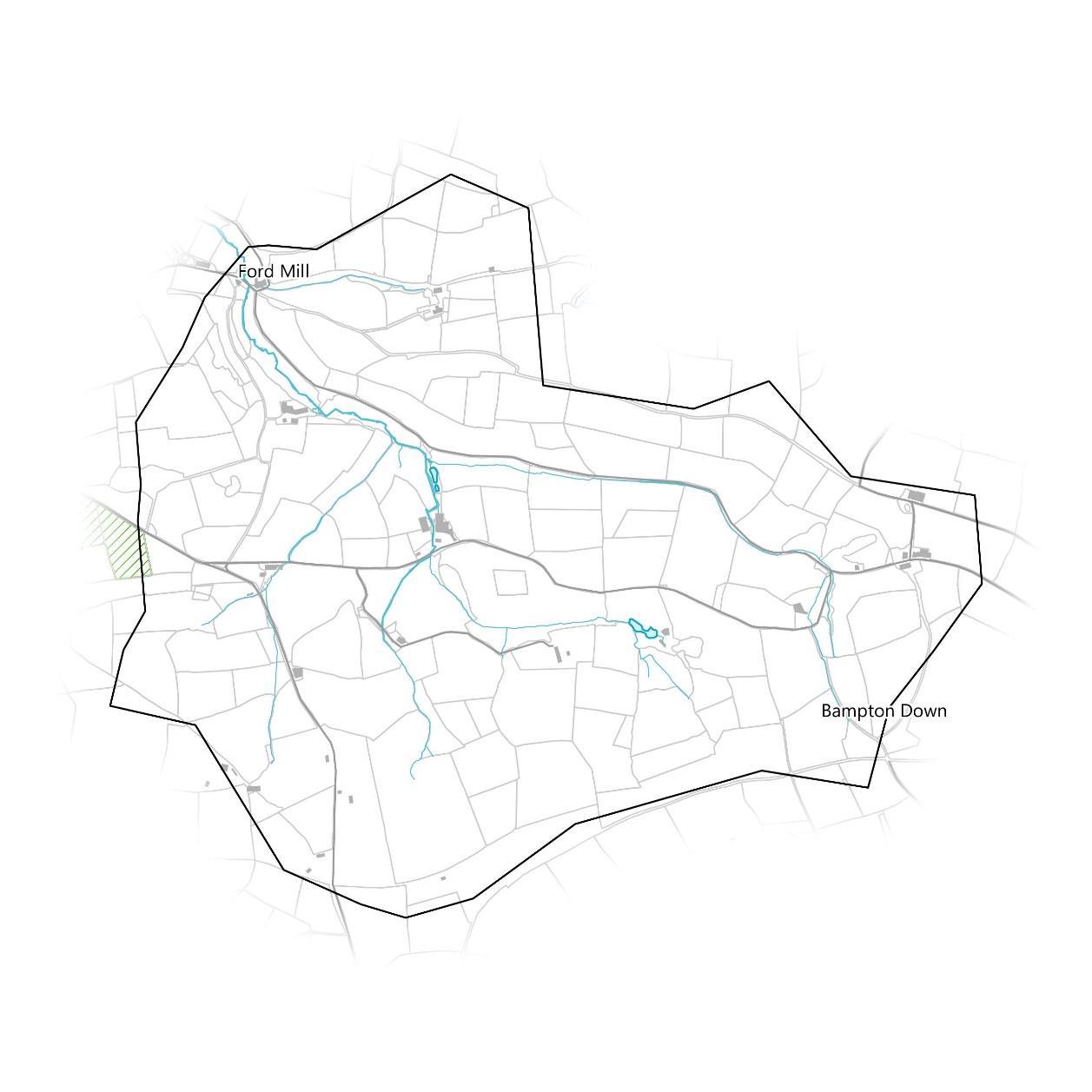
Nearly all of the land parcels in the catchment are not under any agrienvironment schemes, aside from one on the western boundary that is under an Organic Farming Scheme Agreement.
There may be opportunities for land owners in the catchment to enter into agri-environment schemes. Habitat creation around the stream and its tributaries in particular may be facilitated in the Habitat Enhancement and Expansion Zones as identified on page 37 if land owners were to enter into an agri-environment scheme.
38
Opportunities
Restrictive Areas
A further consideration for the targeting of NFM via soil improvement, habitat enhancements, restoration or creation is existing areas which may not be suitable for changes in land use or land management. This may be because they are already valuable sites for wildlife (e.g. designated wildlife sites), because the land use is difficult to change (e.g. urban land) or because the land is highly valuable for farming (high grade agricultural land). There may be further historic or natural heritage designations to consider.

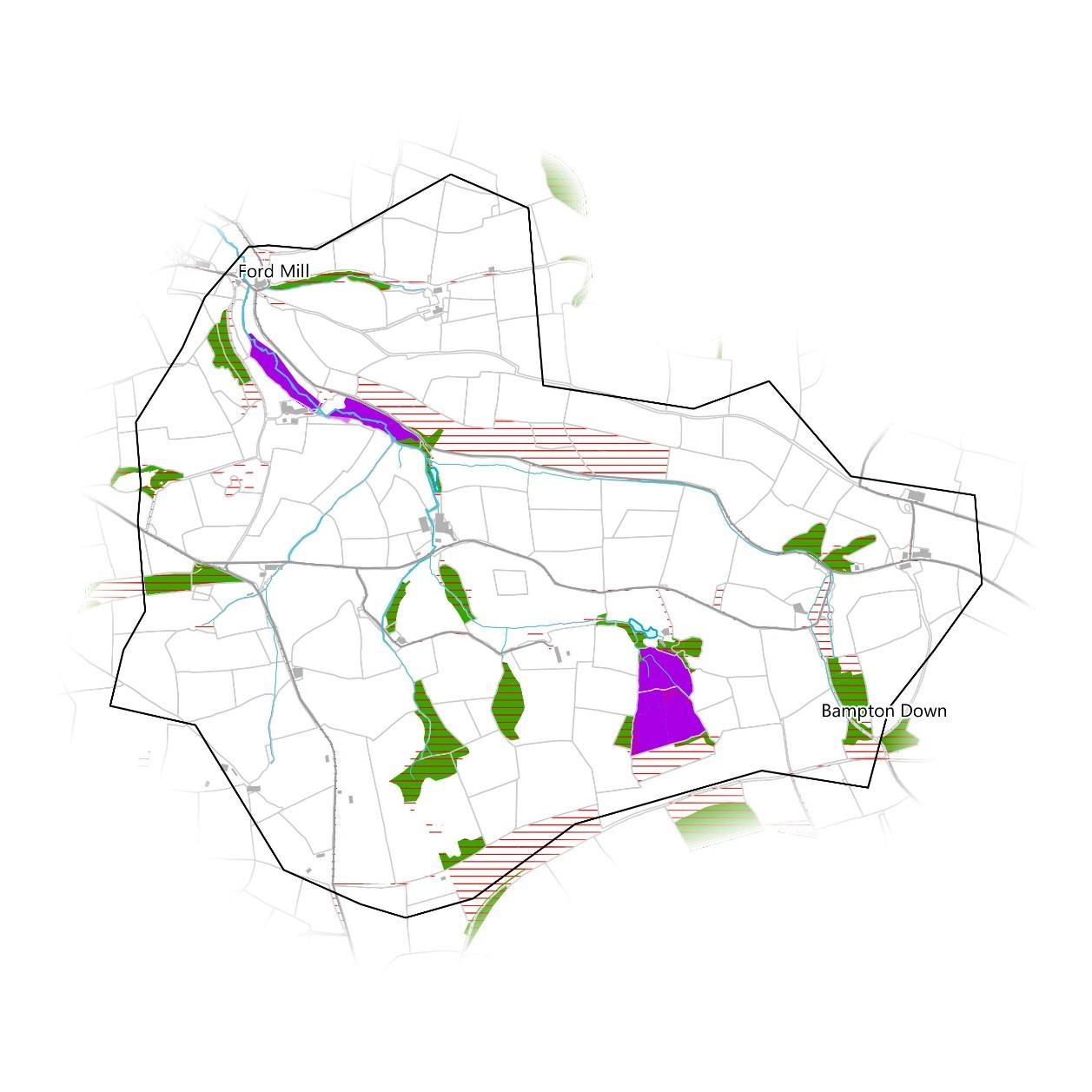
There are no designated sites or areas in the catchment that might provide administrative challenges. However, the deciduous woodland, purple moor grass, and good quality semi-improved grassland priority habitats may. There is still the opportunity to improve these habitats further though by getting more partner organisations involved in the process and even access additional sources of funding.
The WWNP woodland constraints dataset highlights any urban areas and existing woodlands (including woodlands not listed as priority habitats not shown here) where additional tree planting may be difficult. This excludes all of the woodlands and much of the farm building clusters. This does not mean urban tree planting is impossible, and would also provide another avenue to get the community involved the closer the planting is. The southwest area of the catchment on the other hand has few to no constraints.

The agricultural land grade is grade 3 and 4 across the catchment which is considered average and below average respectively, and there is therefore no high grade land present. There are also no scheduled monuments present.
39
Opportunities
Opportunities Identified During Walkover Surveys
During the walkover surveys, experienced surveyors at WRT identified opportunities for NFM measures and improvements to other key considerations mentioned. The results are mapped (right) but it should be noted that the map is by no means exhaustive.
Some opportunities were obvious enhancements of already-occurring features.
One sloping field was ponding behind the Devon bank and this could be increased in volume and shade to attenuate and promote groundwater recharge, as well as provide shade for stock.

From the mid-catchment to the downstream extent, the river has some floodplain with marginal wet vegetation.
There are numerous opportunities to enhance the floodplain with features such as ponds or scrapes; or to plant wet woodland trees or enhance rush or culm.

This would have to be by agreement with the landowner and integration into an existing or future business model for the holding.
This map of opportunities was generated after one walkover survey, reflecting the situation at the time of survey. It is not exhaustive and doesn’t reflect all opportunities present in the catchment which will take much more effort to determine. A greater range of all the opportunities is present within the following section. Engagement with landowners and stakeholders is required for a more comprehensive list of opportunities and ascertain if suggestions can be implemented in conjunction with current land use, future land use and business plans.
40
Opportunities
Soil Opportunities Identified During Walkover Surveys
There may be some opportunities to improve flood resilience and surface water quality in the Bampton Stream through changes to soil management.

It’s recommended that the soil is examined by a soil expert to see if compaction or capping is an issue that could be rectified for the benefit of the landowner as well as rainfall acceptance.
There may also be extra opportunity at the head of the catchment for wetland or culm restoration that wasn’t mapped.
41
NaturalFlood Management (NFM) or Working withNaturalProcesses (WWNP) Potential benefit in catchment Potential provider identified Locationof opportunity matches GISmaps Improve soil healthand rainfall acceptance potential ✓ N/A Sub-soil,aeration,ordecompaction ✓ N/A Contour ploughing or cross slope working N/A Change land use ✓ N/A Interspersed woodland or agroforestryforinfiltration ✓ N/A Peatland/wetland/culmrestoration ✓ ✓
Opportunities
Pathway Interruption Opportunities Identified During Walkover Surveys
There may be some opportunities to improve flood resilience and surface water quality in the Bampton Stream through water pathway interruption.
Promotion of cross-slope and contoured interruptions to arrest flows and promote infiltration to groundwater recharge is of great benefit for water and climate change adaptation. Reducing rapid surface water run-off and increasing attenuation and infiltration will provide better water quality and drought resilience at the same time as reducing flood risk throughout the catchment downstream.
Where sparce or lone trees exist, there may be opportunity to expand tree planting if agreed with the landowner.

42
NaturalFlood Management (NFM) or Working withNaturalProcesses (WWNP) Potential benefit in catchment Potential provider identified Locationof opportunity matches GISmaps Cross-slope planting of treesor hedges ✓ ✓ Gatewayrelocation N/A Cross-slope buffer(beetle bankor cross-drain) ✓ ✓ Timber/stone instream deflectors ✓ N/A
Opportunities
Attenuation Opportunities Identified During Walkover Surveys
There may be some opportunities to improve flood resilience and surface water quality in the Bampton Stream through water attenuation on non-floodplain wetland.
Larger fields used for stock could consider implementing features that would benefit both stock health and wellbeing, as well as environmental function and reduced run-off.
This could be done as a mosaic or as corridors with minimal intrusion into the current business model if desired.

43
NaturalFlood Management (NFM) or Working withNaturalProcesses (WWNP) Potential benefit in catchment Potential provider identified Locationof opportunity matches GISmaps Attenuationpond / farm pond / wildlife pond ✓ N/A Run-off scrape or swale / temporarypond ✓ N/A Run-off bunded storage oroff-line storage ✓ N/A Blind ditching indrainage ditches ✓ N/A Headwaterdrainage management ✓ N/A
Opportunities
Slow the Flow Opportunities Identified During Walkover Surveys
There may be some opportunities to improve flood resilience and surface water quality in the Bampton Stream through increasing channel and floodplain roughness to slow the flow.
The catchment is quite steep in places and interventions in the steepestareas will be of limited value, but the key to slowing the flow is likely to be multiple features working in sequence and synchronicity to hold back pockets of water in less steep areas.
Large woody debris and floodplain reconnection could be a good opportunity in the mid and lower catchment areas if it fits with the land managers’ business models.

44
NaturalFlood Management (NFM) or Working withNaturalProcesses (WWNP) Potential benefit in catchment Potential provider identified Locationof opportunity matches GISmaps Channel restoration,sinuosity N/A Large/coarse woodeddebris introduction ✓ N/A Floodplainreconnection (palaeochannelreconnection) ✓ N/A Riparianbufferstripsor woodland (sloped) ✓ ✓ Floodplainwoodland orwet woodland ✓ ✓ Peak flow leakybarriers N/A Bed renaturalisation– armour/ gravel augmentation ✓ N/A
Engagement

45
Engagement
Current Engagement
There are 17 landowners in the catchment. The 3 largest landowners own 54.77% of the catchment. WRT has engaged with farmers managing 65% of the total farm area under UST.
The parish council meets on the firstWednesday of every month at 7 pm in the LARCS building. The best contact is the parish clerk. The parish council has a flood response plan, link:
http://www.bamptontowncouncil.gov.uk/_UserFiles/Files/Bampton%20Floo d%20Response%20July%202021.pdf.

The flooding incident hotline is 0800 807060 and the flood incident duty officer can be contacted on 0800 678 1247.
The aims of the flood plan are to preserve life and the safety of people, minimise flood damage to property and enable the town to return to business as usual as quickly as possible.
There is a river watch scheme in place with a plan including flood warden and volunteers.
46
Engagement
Getting Involved
As well as the opportunities identified in the previous section, there may be opportunities for you to get involved as an individual.
WRT runs a Citizen Science Investigation (CSI) team of volunteers across the south west, whereby volunteers receive a testing kit and training to procure water samples from a watercourse. Westcountry CSI aims to engage people with their local environment, and produce water monitoring data that can identify pollution events quickly and target improvement work.
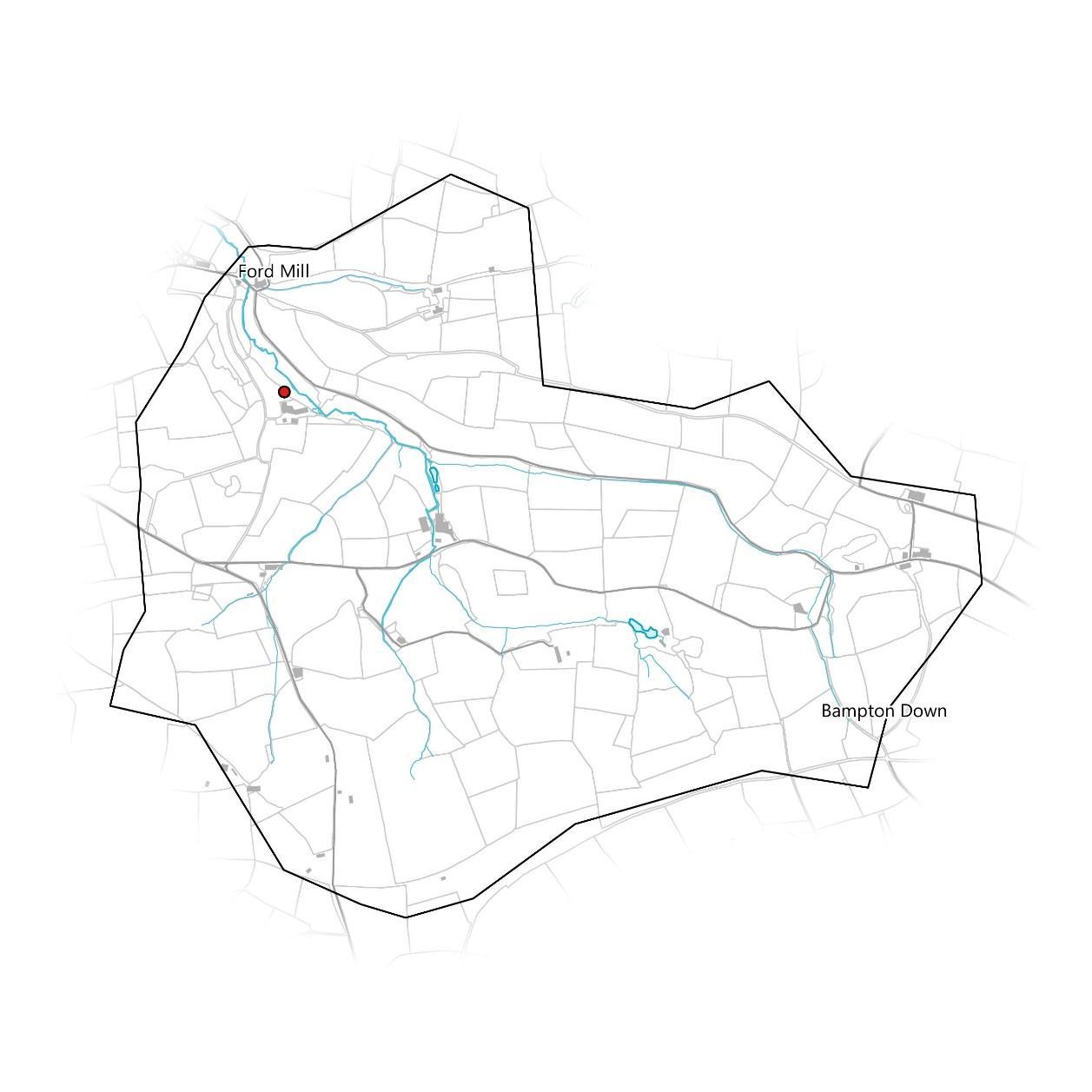
There are two active CSI sampling site and one free sampling site that could be taken up at Ford Mill at the catchment outlet. There may be the potential for more sampling sites along the main Bampton Stream and on any of the tributaries if there is suitable access to the water.


For more information about Westcountry CSI, including instructions on what’s involved and how to sign up, visit our website at wrt.org.uk/westcountry-csi
Another opportunity for you to get involved in is the Riverfly Partnership’s Anglers’ Riverfly Monitoring Initiative (ARMI). This recognises that anglers are very well placed to monitor river water quality and facilitates communication between them and their local Environment Agency contact.
There are no riverfly survey sites within the micro-catchment, but, as with CSI sites, it may be possible to start a new site if there is suitable access to the water and with communication with the Environment Agency.
For more information on ARMI, visit their website at riverflies.org/anglersriverfly-monitoring-initiative-armi
47
Summary and Next Steps
Multiple reasonsforthe possible causesand remediesforflooding inthe micro-catchmentforthe BamptonStream have beenmapped inthis study, as have otherfactorsthat are key to considerwhen making NFM decisions.
It islikelythat a combinationof causesare at playhere contributing to there being propertiesatsome flood risk,including the topographyand land use. Howeverthe flood risk maynot be as high as modelled incurrentcircumstances.That isnot to say that flood risk won’t rise in the future, and that interventions will help future-proof againstdroughtand waterqualityaswell asflooding,butinvestmentmay need to be justified further.
Benefitsarising from thiscatchmentmay also be realised ina largercumulative contextelsewhere downstream.
The catchmentdoesn’t appearto be asintensivelymanaged assome of the surrounding area,but itstill presents withnumerous opportunitiesto improve bothwaterresilience and qualityif desired.
There is a questionoverwhether interventions inthis catchment will provide significantbenefitasthe flood riskinthe immediate vicinitymaynot be as much as anticipated.Therefore,itisrecommended thatfurtherinvestigationbe made into the local impact,butalso into the widerimpactof Bamptonand if the catchmentarea could help alleviate the downstream problem.
The nextsteps could then be to engage and empowerthe community inthe catchment to discuss and worktowardsbuilding flood resilience through some of the opportunitiesmapped inthe previouspages.It isimperative thatpropertyownersand landownersshare perspectivesand work togetherto find solutionsagreeable to all sides.Mostopportunitieswill providesecondarybenefitstowardsimproving the catchment’sWFD ecologicalstatus.
48
Appendix

49
Methodology Details
Step 1: Micro-catchment Mapping Method
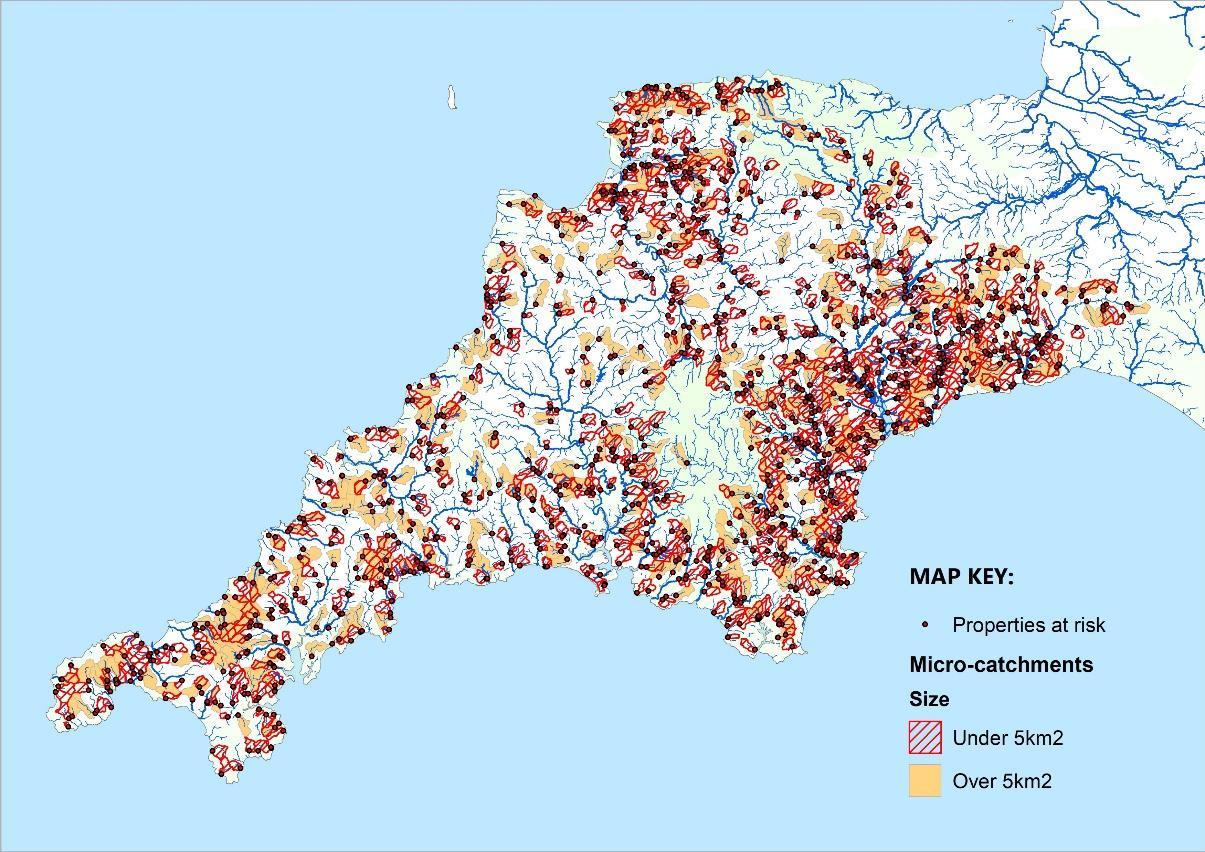
The processforidentifying the highest-impacting locationsof NFMmeasures acrossDevonand Cornwall involved several stepsin a Geographic InformationSystem (GIS).The first step was to identifywatercourseswithan upstream watershed less than 10km2 and less than 5km2 in size,then to identifypropertiesadjacentto these watercoursesthat overlapped withthe EnvironmentAgency’s (EA) fluvial “Flood Zone 2”dataset.Next,pour pointswere placed onthe watercoursesin front of the furthest downstream flood riskproperties.These pourpoints were thenused to delineate the upstream micro-catchmentboundaries.A total of 1270micro-catchmentswithpropertiespotentiallyatriskwere identified across the 2counties.
For every micro-catchmentidentified,itsarea wasdividedbythe number of flood risk propertieswithinitto calculate the area perproperty atrisk foreach micro-catchment.Those withthe lowestarea perpropertyindicated higherpotential forsmall-scaleNFMmeasuresto benefitthe greatest number of flood riskproperties.
Lastly,additional factors,suchas WFD classificationsand previousWRT engagementwithfarmers,were considered alongsidethe area perproperty atflood risk toprioritise a small numberof micro-catchmentsto targetcommunityengagementand NFM delivery.
Modelling assumptionsand constraints:
➢ Due to the large geographic extent(Devonand Cornwall)and the manual elementof the mapping (bothcausing the mapping processto be time-consuming),the resolution/accuracyof some datasetsmaybe compromised.
➢ The buildingsdataset(OS VectorMap Buildings) isnotasaccurate as OS MasterMap - some propertiesare amalgamatedinto a single polygon and very small buildingsare notshown. Therefore propertiesatriskof flooding maybe underestimated.
➢ Potential flood-riskisidentifiedbyselecting building polygonsthatintersectthe flood zones;no detailed local information (e.g.drainage or defences) ormodelling hasbeenused.
➢ The spatial resolutionof the topographydata iscoarse (50m).Thisisused to calculate the upstream catchmentarea foreach communityat-risk. Therefore,some errors mayoccur (additionsoromissions) whenidentifying micro-catchments.
➢ The mapping method involvesanelementof manual validation,whichhasthe potential to be subjective and/orpossible errors.
50
Methodology Details
Step 2: Theoretical Ground Truthing
Once catchmentswere modelled and the informationtabulated to show theoretical flood risk in conjunctionwithWFD failures, a systematic approach to ground-truthing was adopted.
Catchmentsthat were perceived to have elevated water quality and water quantity risks were discussed with local land management advisors and regulators to determine if the modelled risk was likely to be correct.
Upon a theoretical, or desk-based ground-truthing,the catchmentswere then surveyed using a rapid walkover survey to observe run-off pathways and confirm if useful managed interventions could be implemented to reduce flood risk locallyand improvewater quality in the process.
Step 3: Rapid Walkover Survey
A further modelling process using SCIMAP was undertaken to identify high risk run-off pathways of the specific micro-catchmentbeingsurveyed to assist the surveyor in locating issues within a <10km2 area.
Where possible, surveyors reacted to high rainfall predictions and went out to observe the catchmentwhen the conditions were right.
Walkover surveys were undertaken noting observations about surface water run-offand taking photographs of key areas and issues. All walkovers aimed to provide:
➢ Dry or Wet weather photos,
➢ Identify stakeholder PROVIDERS where NFM can be instigated,
➢ Identify stakeholder BENEFICIARIES by property and number people,
➢ Establish opportunities in each catchmentand feasibility of action.
Georeferenced photos were taken to provide a visualoverview of issues, opportunities, and as general reference notes.
Where issues and opportunities existed, further investigation was made or attempted to establish the realistic chances of further action. This was achieved by either speaking withthe localcommunityor contacting communitygroupsor key landowners.
All 1270 micro-catchments with properties potentially at risk were identified across the 2 counties.
51
References and further information
Reference
Resourcedescription
Link
CIRIA (Slide 43)
The Construction Industry Research and Information Association’s (CIRIA) Natural Flood Management Manual (C802) (PDF)
https://www.ciria.org/Books/Free_publications/C802F.aspx
FRFW (Slide 32)
Statutory guidance for Farming Rules for Water (FRFW) (Webpages)
https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/applying-thefarming-rules-for-water/applying-the-farming-rules-for-water
SEPA NFM Handbook (Slide 32)
Handbook describing various natural flood management interventions and case studies (PDF)
https://www.sepa.org.uk/media/163560/sepa-natural-floodmanagement-handbook1.pdf
52
Mapping Data Sources
Dataset Source
AttributionStatement
Agricultural Land Classification Natural England © Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crowncopyright anddatabase right2022.
Air Quality Management Areas UKAIR
© Crown copyright and database rights licensed under Defra's PublicSectorMapping Agreementwith Ordnance Survey(licence No. 100022861) and the Land andProperty Services Department(Northern Ireland) MOU206.
Ancient Woodland Natural England © Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crowncopyright anddatabase right2022.
AONB Natural England © Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crowncopyright anddatabase right2022.
Areas Benefitting fromFlood Defences EnvironmentAgency
© EnvironmentAgency copyrightand/or database right 2018. Allrights reserved.Some features of this mapare based on digital spatial data from the Centre for Ecology & Hydrology,© NERC (CEH) © Crowncopyright anddatabase rights 2018Ordnance Survey 100024198
Bathing Water Monitoring Locations EnvironmentAgency © EnvironmentAgency copyrightand/or database right 2015. All rights reserved.
Consented Discharges
Country Parks
Countryside StewardshipScheme Agreements
NaturalEngland © Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crowncopyright anddatabase right2022.
Natural England © Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crowncopyright anddatabase right2022.
Crop Map of England Rural Payments Agency
CRoW Access Land NaturalEngland
CRoW RegisteredCommonLand
© Rural Payments Agency
© Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crowncopyright anddatabase right2022.
NaturalEngland © Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crowncopyright anddatabase right2022.
DetailedRiver Network EnvironmentAgency © EnvironmentAgency Crown copyrightand databse right 2022.
Drinking Water Safeguard Zones (Ground Water)
Drinking Water Safeguard Zones (Surface Water)
EnvironmentAgency © EnvironmentAgency and/ordatabase rights. Derivedfrom BGSdigital data under licence from British Geological Surveycopyright NERC.
EnvironmentAgency © EnvironmentAgency copyrightand/or database right.All rights reserved. Derived fromBGS digitaldata underlicence fromBritish Geological Survey ©NERC. Derived fromCentre of Ecology andHydrology data ©CEH
Energy Crop Scheme Agreements NaturalEngland © Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crowncopyright anddatabase right2022.
Environmental Stewardship Scheme Agreements
Flood Defences
Flood Zone 2
Natural England © Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crowncopyright anddatabase right2022.
EnvironmentAgency © EnvironmentAgency copyrightand/or database right 2020. Allrights reserved.
EnvironmentAgency
© EnvironmentAgency copyrightand/or database right 2018. All rights reserved.Some features of this map are basedon digital spatial data from the Centre for Ecology & Hydrology,© NERC (CEH). © Crown copyrightand database rights 2018 Ordnance Survey 100024198
Greenspaces Ordnance Survey Contains OS data © Crown copyrightand database right 2022
HabitatNetworks
Hillshade
HistoricLandfill Sites
Natural England © Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crowncopyright anddatabase right2022.
EnvironmentAgency © EnvironmentAgency copyrightand/or database right 2018. All rights reserved.Contains information © Local Authorities
53
Mapping Data Sources
Dataset Source
AttributionStatement
Land Parcels Rural Payments Agency © Crown copyright and database rights 2020 OS
LCM2019 25m Parcels Centre for Ecology and Hydrology Morton, D., Marston, C. G, O’Neil, A. W., & Rowland, C. S. (2020). Land Cover Map 2019 (25m rasterised land parcels, GB) [Data set]. NERC Environmental Information Data Centre. https://doi.org/10.5285/F15289DA-6424-4A5E-BD92-48C4D9C830CC
LNR Natural England © Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crown copyright and database right 2022.
MCZ Natural England © Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crown copyright and database right 2022.
National Forest Inventory Forestry Commission Contains Forestry Commission information licensed under the Open Government Licence v3.0
National Trails
Natural England © Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crown copyright and database right 2022.
NATMAPvector Cranfield University Soil data © Cranfield University (NSRI) and for the Controller of HMSO 2019
Nitrate Vulnerable Zones 2021 Combined Environment Agency
© Environment Agency copyright and/or database right. Derived in part from geological mapping data provided by the British Geological Survey © NERC. Derived in part from data provided by the National Soils Research Institute © Cranfield University. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crown copyright and database rights 2016. Derived in part from data provided by the Department for theEnvironment, Farming and Rural Affairs © Crown 2016 copyright Defra. Derived in part from data provided by the Centre for Ecology and Hydrology © NERC. Derived in part from data provided by UK Water Companies.
National Parks Natural England © Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crown copyright and database right 2022.
Organic Farming Scheme Agreements Natural England © Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crown copyright and database right 2022.
OS Open Datasets Ordnance Survey Contains OS data © Crown copyright and database right 2022
Permitted Waste Sites Environment Agency © Environment Agency copyright and/or database right 2015. All rights reserved.
PM2.5 2020 UKAIR © UKAIR crown copyright
Pollution Incidents Environment Agency
Priority Habitat Creation and Restoration Projects Environment Agency © Environment Agency copyright and/or database right 2015. All rights reserved.
Priority Habitat Inventory Natural England © Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crown copyright and database right 2022.
Priority Habitats (Aquatic and Wetlands) Natural England © Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crown copyright and database right 2022.
Priority Roads for Catchment Management of Runoff Highways England
Priority Roads for Catchment Management of Surface Water Highways England
Public Rights of Way Ordnance Survey Contains OS data © Crown copyright and database right 2022
Ramsar Natural England © Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crown copyright and database right 2022.
Recorded Flood Outlines Environment Agency © Environment Agency copyright and/or database right 2018. All rights reserved.
River Restoration Projects The River Restoration Center
54
Mapping Data Sources
Dataset Source AttributionStatement
RoFSW Extent 1in 1000 EnvironmentAgency © EnvironmentAgency copyrightand/or database right 2015. All rights reserved.
RPA Land Parcels Rural Payments Agency © Crown copyright and database rights 2020OS
SACs Natural England © Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crowncopyright anddatabase right2022.
SCALGO Live
Scheduled Monuments HistoricEngland © HistoricEngland2022. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crowncopyright anddatabase right2022
SCIMAP Flow Pathways SCIMAP SCIMAP modelling system- SCIMAP was developed atDurham andLancasterUniversities as part of a NERCgrant
Slope TellusSW Ferraccioli,F.; Gerard,F.; Robinson, C.; Jordan,T.;Biszczuk,M.; Ireland, L.; Beasley,M.; Vidamour,A.; Barker, A.; Arnold, R.; Dinn, M.; Fox,A.; Howard, A. (2014). LiDAR based Digital Terrain Model (DTM) data for SouthWestEngland. NERC Environmental InformationData Centre. https://doi.org/10.5285/e2a742df-3772-481a-97d6-0de5133f4812
Source ProtectionZones EnvironmentAgency © EnvironmentAgency copyrightand/or database right 2016. All rights reserved.
SPAs Natural England
© Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crowncopyright anddatabase right2022.
SSSI Units Natural England © Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crowncopyright anddatabase right2022.
SSSIs Natural England © Natural England copyright. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crowncopyright anddatabase right2022.
Vegetation Health Index
Water Abstraction Licenses
Water Resource Availability and Abstraction Reliability Cycle 2
Centre for Ecology and Hydrology
© UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology
EnvironmentAgency
WFD Monitoring Sites EnvironmentAgency
© EnvironmentAgency copyrightand/or database right 2015. All rights reserved.
WFD River Waterbody Catchments EnvironmentAgency © EnvironmentAgency copyrightand/or database right 2015. All rights reserved.
WFD River Waterbody Status EnvironmentAgency
WIMS Locations EnvironmentAgency Uses Environment Agency waterquality data from the WaterQuality Archive (Beta)
WWNP Datasets EnvironmentAgency © EnvironmentAgency copyrightand/or database right 2015. All rights reserved.
55

























































































