










The changing preferences for newer colors, patterns and textures is now taking a turn towards more functional features in fabrics. Seeing longer work hours and flexibility of work from home, youngsters are looking for soft, antimicrobial, odourcontrol, wrinkle-free and healthy clothes selections. One of the rising needs from citizens is increasing desire for natural fibers and fabrics.
Focusing on innovative textiles, modern fibers are being developed that are ecofriendly, light, resilient, mechanically flexible and easy to process. They are also blended to acquire properties such as sensory capabilities, electrical conductivity and data transmission. Using hydrophobic cotton, plant-based textiles and shape memory polymers materials are some of the suggestive trends for present day clothes. Some companies are in the process of using post-consumer waste to produce recycled textiles. The technology uses AI and robotics to convert used discarded garments into new clothing threads. Few companies are also carrying out research on printing technology that helps to gently remove the textile design without harming the material. This technology enables multiple decoloring and recoloring of old fabrics. Overall it optimizes the use of water resources and decreases release of number of chemicals in the environment.
In providing latest solutions, textile manufacturers are using microelectronics, biotechnology and nanomaterials to improve the interconnection between components.

Nanotechnology is used in apparels, as nano particles have high surface area to volume ratio, which gives increased affinity for fabric giving improved durability, breathability etc.
Some of the benefits are nano size titanium dioxide, zinc oxide, viscous and nano antimony dioxide, tin dioxide have been found to provide anti-static effect, as they are electrically conducting materials causing the effective decay of static charge.
Moreover nano materials are used as inorganic UV blockers as they have been found to be highly efficient in absorbing and scattering UV radiation.
In effect, smart clothes use a variety of IoT sensors to collect a person’s biometric and physical data for effective health monitoring. Moreover, durable sensors are being developed to withstand multiple wash cycles. This offers the desired technology advantage and also prevents harm to the environment. In conclusion, our clothes that provide attractive look and feel solutions will now become smarter, and take care of our health as well.
For suggestions or feedback write to editorial@worldofchemicals.com
Cover Image Source : freepik.com





The rise of e-commerce and access to new technologies has accelerated counterfeiting and other forms of illicit trade. That makes fighting counterfeit medical products an ever-more urgent priority for pharma companies both in terms of patient safety and brand reputation.
Yann
IschiDirector, New Channels and Partnerships, SICPA

Within the Volkswagen Group, we have a clear strategy for how we want to put battery-electric vehicles into series production across our brands and in many different market segments. However, a major qualification for success in the volume market is more powerful battery concepts. In Volkswagen Group R&D we are focusing on close cooperation, not only with industrial partners but also with the smart minds of the scientific community.
Dr Ulrich Eichhorn
Head, Group R&D, Volkswagen AG.
India is a very important market for polyurethanes and has a wonderful potential for growth. When leaders of the industry from all over the world get together under one roof, it leads to better production and faster growth of the industry
R C BhargavaFormer CEO and current Chairman, Maruti Suzuki.
Indian Solar Manufacturers Association (ISMA) members have expressed positive sentiments as manufacturing and Make in India initiative gathered momentum. The phenomenal growth opportunity of Renewal Energy is unparalleled in the world today, looking at current and future energy consumption in India over the next 2-3 decades. All stakeholders have immense opportunities especially those who make and develop products in India.
K N SubramaniamCEO, Moserbear Solar Ltd and Treasurer, Indian Solar Manufacturers Association (ISMA)
NEW DELHI, INDIA: Cairn Oil & Gas announced the production milestone in the development of its Mangala oilfield in the prolific Rajasthan block, in an onshore play in western India. The subsidiary of the Vedanta group said, it had past cumulative production of 500 million barrels from Mangala Oilfield.
Mangala oilfield was discovered in 2004 and put into production in 2009, has been the object of a huge polymer flood project for enhanced oil recovery. It is part of the complex of oilfields also including Bhagyam and Aishwarya, situated in the Barmer district of Rajasthan.
“We are happy to have achieved this milestone of producing 500 mmbbl of oil from our Mangala oilfield. This brings us closer to our target of doubling our production capacities in line with our chairman’s vision to contribute 50% to India’s domestic oil and gas production, and contribute towards the country’s energy Aatmanirbharta,” stated Cairn Oil & Gas deputy chief executive Prachur Sah.
Mangala is India’s private-sector oil and gas producer, with interests in 62 exploration and production blocks. It also contributes towards the socio-economic development. Cairn aims to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050 while pressing ahead future investments plan.

MUMBAI, INDIA: BASF broke ground on its new Polyurethane Application Development Laboratory in Mumbai, India.
The new lab will have equipment’s in 2,000 square meter space approximately and is expected to be fully operational in 2024. It will offer improved customer support services ranging from troubleshooting to customized formulations, line trials, and customer training sessions and will strengthen the bond between high-growth industries, including consumer appliances, footwear, furniture, and transportation.
This will help drive innovation with customers alongside the Creation Centre, at BASF’s Innovation Campus in Mumbai.
“As a part of the global innovation network, the lab will enable global and regional BASF teams to work closely with local customers in testing and formulation optimization,” said Andy Postlethwaite, senior vice president, performance materials Asia Pacific.
“The new lab reinforces our commitment to strengthening our product development capabilities and providing fast and advanced technical service for our customers,” said Krishnamohan Narayan, Managing Director, BASF India Limited and Head, BASF Group Companies in India.
MUMBAI, INDIA: Reliance New Energy Limited (RNEL) said it has signed an agreement to invest $12 million to acquire 20 percent stake in Caelux Corporation’s perovskite-based solar technology. The transaction will be completed by end of September.

The investment will accelerate product and technology development for Caelux, including its pilot line in the US and for expanding the commercial development of its technology.
Beside the Caelux transaction, Reliance will also set-up a global scale integrated photovoltaic Giga factory at Jamnagar, Gujarat. Through this investment and collaboration, Reliance will be able to produce more powerful and lower cost solar modules leveraging Caelux’s products.
“The investment in Caelux aligns with our strategy to create the most advanced green energy manufacturing ecosystem, backed by world class
talent, and built on the pillars of technological innovation achieved through strategic partnerships,” said Mukesh Ambani, chairman and managing director of Reliance Industries Limited.
“We believe Caelux’s proprietary perovskite based solar technology provides us with access to next leg of innovation in crystalline solar modules. We will work along with team at Caelux to accelerate its product development and commercialization of its technology,” added Ambani.
“Caelux’s ‘perovskite on glass’ architecture is the innovation the solar industry needs to significantly reduce costs and accelerate renewables penetration. As an early backer of Caelux, we have been impressed with their technical progress and are excited to continue working with them as they embark on their commercial journey with Reliance,” said Vinod Khosla, Khosla ventures.
NEW DELHI, INDIA: Taking the pledge of Carbon neutrality, UFlex signed an Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with CREDUCE – Carbon Credits Consultancy as their consulting partners to achieve ‘carbon neutrality’ and make India strides towards achieving the sustainability goals.
To reduce dependency on fossil fuels and shift the concentration towards plastic waste management and sustainable production process, UFlex and CREDUCE took a stand that will lead to positive environment impacts such as decreasing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
The scope would encompass an analysis on carbon footprint & neutrality, creating and formalizing carbon & plastic credit balances as a part of sustainable roadmap for the future.
“We were always committed to steer our group towards sustainable environmental practices, especially to achieve carbon neutrality in Scope 1 & Scope 2 emissions. We aspire to cut about 175,000 tonnes of
carbon emission equivalent by the end of year 2024, across the group,” asserts Jeevaraj Pillai, joint president of UFlex.
“Socio-Environmental sustainability has always been one of our core organizational values for quite some time now and we have articulated & imbibed the same in all walks of our functioning,” states Manas Kumar Sarkar, general manager– HR & sustainability at flexible packaging business of UFlex.
As a socially responsible corporation, UFlex has been leading the way in creating future-ready, technology-driven sustainable solutions towards a cleaner and greener tomorrow with CREDUCE technologies Limited.
“We would be able to strategize a path towards complete zero carbon footprint. These accruals of carbon credits would be clubbed with community development initiatives like smokeless cook-stoves & clean drinking potable water,” said Shailendra Singh Rao, director at CREDUCE.
AMSTERDAM, NETHERLANDS: AkzoNobel India said it has signed letters of intent with two India start-up challenge winners viz. HyperReality Technologies and Fluid AI.
Bengaluru-based HyperReality Technologies offers a collaboration platform for inspiration, visualization of a space in metaverse. Headquartered in Mumbai, Fluid AI offers multi-channel conversational immersive and interactive AI platform to guide consumers during their painting journey.
AkzoNobel said that winning the ‘Paint the Future’ award opened more doors for these start-ups. Having signed letters of intent to work together on sustainable business opportunities, the two winners now join AkzoNobel’s accelerator program.
“Over the next six months, the goal is clear – to work together with our winners and develop a digital value proposition,” said Oscar Wezenbeek, managing director of AkzoNobel decorative Paints in Southeast and South Asia and chair of AkzoNobel India.
“This startup challenge is about collaborating with equally passionate Indian startups to boost the magic of Dulux and paint the future of paint consumers’ digital experience,” said Rajiv Rajgopal, managing director of AkzoNobel India.
“From the depth of the expert sessions to the sheer amount of industry knowledge we’ve gained, this bootcamp has been a collaborative experience unlike any other,” said Sobin Thombra, CEO, HyperReality Technologies.
“We’re stoked about our win,” said the co-founders of Fluid AI, Abhinav Aggarwal and Raghav Aggarwal. “AkzoNobel’s astute understanding of our artificial intelligence solution is a gateway to bringing new consumer-centric disruptions in the paints sector.”
The India startup challenge is the third regional edition of Paint the Future. Run in partnership with NASSCOM Industry Partnership Program (NIPP), the challenge attracted 207 submissions from 33 cities across India.
the company’s ever expanding internal products pipeline to support its Large-Scale Manufacturing business model.
The facility will feature seven synthetic labs and 55 German-made fume hoods, allowing the company to undertake 110 reactions every day.
Each of the fume hoods has automation to regulate many experimentrelated parameters, allowing for the greatest levels of safety. The R&D centre also has a specialized quality control and assurance lab.

INDIA:
The centre will assist to meet the rising demand in the CRAMS business (Contract research and manufacturing services) areas and will support efforts to increase the efficiency of existing products.
Aether Industries’ newest R&D centre will also enable innovation for
The DCS (Distributed control system) automation system is also included in the pilot plant, allowing the company to test goods at various scales, ranging from a few grams to several kilos to several MTs, employing various technologies such as continuous reactions and highpressure reactions.
The firm has committed roughly INR 330 million to remodel and triple the capacity of the R&D centre to assist the company’s development into new markets through new and creative products and processes for international projects.
TOKYO, JAPAN: Toray Industries announced that it has opened Toray India Water Research Center at the IIT Madras Research Park (IITMRP), in Chennai.
The center will step up R&D into applications for its water-treatment membrane technology to help India meet surging treatment demand in the years ahead and overcome water shortages.
IITM has been ranked first in the Indian government’s National Institutional Ranking Framework for the past four years and has a solid record in water treatment.
The new facility in India will collaborate with the Toray Singapore Water Research Center to support research and development that grows the company’s water treatment business in Southern and South Asia. The Singapore site was inaugurated in August 2009.
About 600 million people experience extreme water stress. This problem will likely worsen as the population grows and the economy develops, with water demand exceedingly twice the available supply by 2030. An urgent need to resolve shortages has propelled efforts around nation to improve the water supply infrastructure and reuse wastewater, stated the company.


FLORIDA, US/ LUTON, UK: Hertz and bp announced the signing of a memorandum of understanding (MoU) for the development for US network of Electric Vehicle charging stations which will be powered by bp pulse (bp’s global electrification and charging solution brand).
bp pulse will build and manage a network for fast-charging hubs to serve Hertz customers, including taxi and ride sharing drivers, as well as the public.
The agreement also involves the management of Hertz’s charging infrastructure by bp pulse and the customization of its Omega software to ensure Hertz’s growing fleet of electric rental cars to recharge quickly and efficiently.
Omega helps fleet operations by automating charging when the energy value is low, whereas offering real-time visibility to electric vehicles, chargers, power usage and lower emission and more.
“Hertz is accelerating the adoption of electrification by investing in the largest rental fleet of electric vehicles in North America and expanding the availability of charging stations. We are excited to partner with bp
pulse to create a national charging infrastructure for the Hertz EV fleet,” stated Stephen Scherr, Hertz ceo.
On the other hand, Hertz has invested in thousands of charging stations across its locations, and its partnership with bp will enhance and enable its US Charging footprint. Hertz’s objective is to make it’s one-quarter of fleet to be electric by the end of 2024.
“Working together to deliver charging facilities and design solutions, we believe we can take the EV driving experience to the next level for US customers,” commented Bernard Looney, bp chief executive.
“This is a landmark moment. It shows the power of bringing together bp’s digital and operational capabilities with a partner like Hertz. Together with its industry-leading electrification ambitions, we can change the future of electric rental cars,” stated Vic Shao, founder of Amply Power and president of bp pulse’s fleet division in the United States.
bp plus is expanding its global network of high-speed charging for card, light commercial vehicles, and trucks, with a global target of more than 100,000 chargers by 2030.

PARIS, FRANCE: TotalEnergies and SARIA said they have agreed to develop and produce sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) at the Grandpuits refinery in France. TotalEnergies is transforming it’s Grandpuits refinery into a zero-crude platform by 2024.
The agreement is a major step towards converting feedstock supply (used cooking oils and animal fats) to sustainable aviation fuel and the conversion will enable SAF production capacity to reach 210,000 tons per year, 25 percent higher than foreseen in the initial project announced in 2020.
TotalEnergies will take 50 percent of SARIA’s production capacity, that will supply animal methyl ester (AFME) and used cooking oils to Grandpuits refinery. On the other hand, SARIA will take an
equivalent share in the biofuel business, which will remain operated by TotalEnergies.
“I am delighted to conclude this strategic partnership with SARIA, which reinforces the conversion of the Grandpuits refinery into a zerocrude platform oriented towards SAF. This is a major milestone in our ambition to become one of the leaders in sustainable aviation fuels,” said Bernard Pinatel, president of refining & chemicals at TotalEnergies.
“SAF is the most efficient solution to immediately reduce CO2 emissions from air travel, and its development is fully in line with the Company’s Climate ambition to get to net zero by 2050, together with society,” added Pinatel.
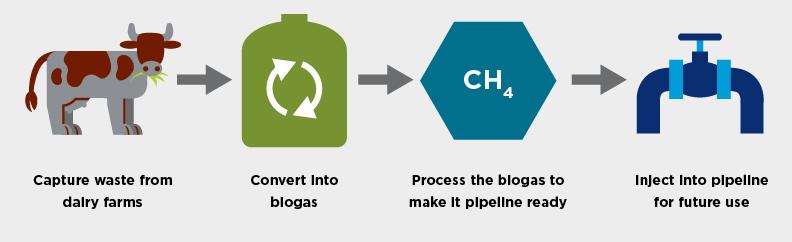
SAN RAMON/VISALIA, US: Finding inspiration in nature is one way Chevron is working to provide an alternative source of power through dairy farms.
Chevron Inc, subsidiary of Chevron Corporation, and California Bioenergy LLC (CalBio) announced a partnership to produce and market diary biomethane as a renewable natural gas (RNG) transporting fuel in California.
The JV is one of the ways to help and protect the environment, provide a renewable energy source, and comply with low-carbon fuel regulations.
The partnership with CalBioGas Hilmar has secured initial funding from Chevron to begin developing infrastructure for biomethane projects in the state’s Merced County.
Manure produces methane as it decomposes and contributes to excess nutrients in waterways.
CalBio’s technology and operational experience will help dairy farmers to build anaerobic digesters and methane capture to convert biomethane to RNG.
Chevron will provide funding to seven digesters and one central upgrading facility across a cluster of diary farms in Merced County.
“This project brings together support from many groups, including seven California Dairy farmers, who are national leaders in milk and cheese production; Chevron, one of California’s largest energy companies; and grant funding from the California Department of Food and Agriculture.
The strong support from these partners will help California with its emission reduction targets,” said Neil Black, president of CalBio.
The diary project will be designed to send biogas to a processing facility where it will be upgraded to renewable natural gas and sent to a local utility via pipeline.
“The investment underscores our commitment to produce 40,000 MMBTU/D of RNG by 2030 and grow the lower carbon businesses that we believe will be a bigger part of the future,” said Andy Walz, president of Americas Fuels & Lubricants for Chevron.
LyondellBasell and Genox Recycling jointly announced they have signed Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to establish a joint venture (JV) to build a plastics recycling plant in Zhaoqing, Guangdong Province in 2023.
The plastic recycling plant will use mechanical recycling technology to recycle post-consumer plastic waste and produce new polymers sold under the LyondellBasell CirculenRecover product portfolio.
The Joint venture aims to reduce the increasing number of plastic wastes, support the growing demand of circular and sustainable solutions, and promote high-quality development of local recycling, the company stated.
“Advancing a circular economy that enables plastic waste to be transformed into more sustainable solutions for our customers is important to us, and we are pleased to collaborate with Genox Recycling to make this happen,” said Limin Fu, vice president of LyondellBasell China Polyolefins.
“This new joint venture will help develop the local plastics recycling infrastructure in China and is an important milestone for LyondellBasell to contribute to its goal to produce and market two million metric tons of recycled and renewable-based polymers annually by 2030,” added Fu.
“Genox Recycling believes that innovation and collaboration are necessary ways to achieve carbon neutrality,” said Jingfa Jiang, chairman of Genox Recycling.
LEVERKUSEN, GERMANY: Covestro opened a new production facility for the manufacture of aniline at Antwerp, Belgium.
Adding up aniline capacity, the company will strengthen its European production network for methylene-di-phenylene isocyanate (MDI).
Covestro will invest €300 million ($291 million) to build the aniline plant, which is scheduled to be operational, depending on the volatile economic situation in early 2025.
At the beginning of the year, Covestro awarded Maire Tecnimont an engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) contract for the project.
Aniline is key material for MDI, used to make rigid polyurethane foam. Due to the global trend towards sustainability and climate neutrality, the global MDI market is expected to grow by around 6 percent per year in the medium term.
Covestro says, given the current high electricity and gas prices, especially in Europe, demand for efficient insulation is likely to continue increasing.
“With the expansion of our aniline production, we are addressing the further increase in demand from our customers for energy-efficient solutions for the insulation of buildings and refrigeration appliances,” said Klaus Schafer, chief technology officer at Covestro.
“The capacity expansion of aniline will ensure the sustainable and efficient supply of our MDI network in Europe,” said Georg Wagner, Covestro Antwerp site manager.
The new plant will use technologies that improve energy efficiency. will help to significantly increase the energy efficiency of production in Antwerp.
With the commissioning of the new plant, the share of steam generated from process heat at Antwerp site will double to 40 percent of local demand, and the use of fossil fuels will decline.
The potential savings correspond to up to 27,000 tons of CO2 emissions and craving its path to reach climate-neutral by 2035.
GERMANY: The increasing demand of two Evonik’s coating additive product led the company to increase the capacity for their architectural paints- TEGO Phobe hydrophobing agents and TEGO Viscoplus polyurethane thickeners and will be made available from October.

“The capacity increase is our response to the increased demand for additives for architectural paints. The additional capacity in Europe will not only increase European, but also global supply security,” said Nadia
Lenhardt, head of the decorative coatings market segment in EMEA. Hydrophobing agents are primarily used to give facade paints a water repellent finish. Emulsions based on silicone resins such as TEGO® Phobe 1659 are characterized by a particularly efficient reduction in water absorption.
Polysiloxanes such as TEGO® Phobe 1409 produce a very good waterbeading effect. On the other hand, TEGO Viscoplus products are liquid and contain no organic solvents.
BRUSSELS, BELGIUM/ PERTH, AUSTRALIA: Solvay and Hastings Technology Metals (HAS) has signed a non-binary Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) for the supply of Mixed Rare Earth Carbonate (MREC).
Under the agreement, the supply of an initial 2,500 tonnes of Mixed Rare Earth Carbonate (MREC) will be sent from Hastings’ Yangibana rare earth project in Western Australia to Solvay’s plant in La Rochelle, France.
The Yangibana Project is a significant Australian Rare Earths Project, containing substantial Neodymium and Praseodymium resources.
On the other hand, the La Rochelle plant manufactures around 4000 tons of rare earth-based formulation products each year for the automotive pollution control, polishing and electronics markets.
Solvay recently announced that its plans to expand and upgrade the La Rochelle plant to produce separated rare earth oxides for the permanent magnets market.
“This is a very significant agreement for Hastings. We are delighted that Solvay has chosen to work with Hastings as it re-enters the rare earth oxides separation business at a time when long term demand for NdPr oxides is experiencing strong growth,” said Charles Lew, Hastings Executive Chairman.
“After announcing our plan to make La Rochelle a rare earths hub in Europe, we’re excited to take this next step,” said Solvay CEO Ilham Kadri.
“We want to help Europe power its new economy with more autonomous and sustainable solutions for electric mobility, clean energy generation and sensitive electronics applications,” added Kadri.
next five years, including cathodes, sulphates, carbonates, and oxides of various metals extracted from spent batteries and other sources.
Both the companies same aim to share energy transition and understand to meet the growing demand of Li-ion batteries and support the advancement of circular economy by supplying raw materials back into the battery supply chain.

As part of its mission to expand its recycling footprint, Lohum will procure spent batteries and recycle them at its plant.
“At Lohum, we recognize that Lithium Carbonate extraction through recycling consumes significantly fewer resources than conventional mining. Our partnership with Glencore underpins our global commitment to expanding the availability of existing battery resources through recycling,” state Rajat Verma, founder & CEO of Lohum.
“This major development will directly boost India’s battery industry and energy security, leading to large scale value creation in employment, domestic ecosystem growth, and import savings on LIB raw materials,” added Verma.
DELHI, INDIA: Lohum join hands with Glencore for a strategic partnership to advance circularity in the Li-ion battery supply chain.
The $200 million association between Lohum and Glencore is aligned with the government’s vision of scaling up the Electric Vehicle’s sector.
Under the alliance, Lohum will supply Glencore with 10,000 Metric Ton (MT) of specialty chemicals for the battery supply chain for the
An expanding focus on Li-ion battery recycling is inevitable to meet the raw material demand for the Electric Vehicle adoption.
“Our focus on a greener future is aligned and supports Glencore’s ambition to reach net-zero carbon emissions by 2050. Part of our approach is to seamlessly combine primary as well as recycled feed streams to provide the critical metals needed for the transition to a low carbon future,” commented Jyothish George, co-head of marketing zinc and copper (Metal), from Glencore.

NORWAY: Equinor announced that Al Cook, executive vice president for Exploration and Production International has signed, effective October.
Cook will continue in his current position in Equinor till 1st April 2023, stated the company.
“I would like to thank AI for his contribution to focusing and optimizing our international oil and gas business, and I congratulate him on his new appointment,” said Anders Opedal, president, and CEO of Equinor.

“I am grateful for the opportunity I have had to contribute in shaping and delivering Equinor’s strategy of becoming a broad energy company. And I am particularly proud of the performance improvements we have delivered together. After years of commuting between Norway and the UK,” said Cook.
Al Cook held the position of executive vice president for Global Strategy & Business Development from 2018 until January 2021. Prior to that, Cook was a senior vice president in Development & Production International overseeing operations.
GERMANY: The Management Board of Covestro has extended the contract of board of management member Klaus Schafer by six months until the end of June 2023, effective October.

Shafen has been a member of the board of management of Covestro AG since 2015 and as a chief technology officer (CTO), he is responsible for production and technology as well as all chemical production sites of the company.
Jointly, Schafer and the supervisory board have agreed to extend his contract for the period from January 1, 2023, to June 30, 2023, to ensure personnel stability for Covestro to the upcoming change in market policy.
“We are very pleased that we were able to convince Klaus Schafer to remain on the Covestro board of management beyond his planned tenure. The current geopolitical challenges pose major issues even for a company as resilient as Covestro,” said Richard Pott, chairman, supervisory board, Covestro AG.
“In my more than thirty years of professional life, this industry has never faced greater challenges. For me, continuing to support Covestro in this situation, even against my original plans, is a matter of course,” said Schafer.
GERMANY: Brenntag SE said it is represented in the newly elected presidium of the VCI (German Chemical Industry Association) by Brenntag CEO Christian Kohlpaintner. The general meeting voted on September 29 to elect him as a member of the trade association’s governing body.
“As a representative of Brenntag SE, I look forward to bringing the perspective of chemical distribution to the work of the association and to representing the interests of our industry together with my colleagues on the Executive Committee in these challenging times,” said Kohlpaintner.
“The VCI remains well positioned as a leading business association and an effective industrial policy actor in Berlin and Brussels. As the strong voice of the industry, we will continue to show politicians solutions and demand action. Everything is at stake for us now: the future of our industrial location and sustainable transformation. I am pleased that Christian Kohlpaintner is actively supporting us on our way,” said VCI general manager Wolfgang Grosse Entrup.
chemical giant SABIC and recently stepped down from the board of Swiss specialty chemicals producer Clariant.
During his 17-year tenure at Ineos, the British-born executive was instrumental in the integration of Styrolution, formerly a joint venture between Ineos and BASF, along with the consolidation of the PetroIneos JV.
“We are very happy that Calum has accepted the designated CEO role in this strategic investment and are convinced that his highly relevant experience at both INEOS and Synthomer will be invaluable during the integration and subsequent growth of the engineering materials business. We look forward to working with him and the future executive management team on this exciting venture,” said Ronald Ayles, managing partner at Advent.
“LANXESS and Advent will support Calum during the integration phase as the joint venture establishes itself as a strong global player in this highly attractive market, following merger clearances,” stated Matthias Zachert, CEO of LANXESS.


The new company is expected to have sales of around Euro 3 billion and to be one of the leading suppliers to the attractive and growing automotive, electronics, electrical and consumer goods segments, with a particular focus on environmentally friendly and sustainable products, stated Lanxess.
MacLean has extensive global experience as CEO of companies in the petrochemicals, polymers, and specialty chemicals fields, most recently as head of Synthomer.
He is currently a non-executive board director of Saudi Arabian
“I am truly excited by the challenge and opportunity to lead the merger of equals of two highly successful and complementary businesses with rich heritages from DSM and LANXESS. The combination will create a truly global engineering materials business and an exciting future for both employee teams and customers going forward,” said Calum MacLean, the CEO-designate of the joint venture.

Styrolution has announced the introduction of a comprehensive range of sustainable solutions for its specialty ABS product group Novodur®/ Novodur® High Heat addressing applications in a range of industries including automotive, electronics and household. The individual grades come with a significant product carbon footprint (PCF) saving of up to -71 percent as compared to the respective non-ECO product reference.
Like its non-ECO counterpart, the new Novodur ECO MR P2HAT is a general purpose ABS grade providing high flowability, good stiffness and high gloss. The material is available with a 30 percent, 50 percent or 70 percent post-consumer mechanically recycled content (PCR). The product comes in various colours or in black and offers a PCF saving of up to 57 percent. A product for self-colouring is available as well.
Novodur ECO MR P2H-AT is currently under evaluation by various customers to become a material of choice for various household appliances.
With Novodur ECO P2MC B50 and Novodur ECO HD M203
FC B50, INEOS Styrolution offers two grades with 50 percent contribution of bio-attributed content. Both grades are available in various colours and as an NR (natural) option. PCF savings are up to -71 percent.
Novodur ECO P2MC B50 has been designed specifically for electroplating making it a material of choice for various sanitary and automotive appliances. Novodur ECO HD M203 FC B50 is an attractive offering also suitable for the medical industry.
The Novodur High Heat (HH) family of products includes all ABS products modified to allow thermally stressed components to meet stringent stability requirements. Today, three sustainable grades are introduced in this product group: Novodur ECO HH106 MR30, Novodur ECO H605 MR30 and Novodur ECO H801 MR40. PCF saving is up to -28 percent and the recycled content is 30 percent and 40 percent, respectively.
The products, available in black, are targeting the automotive industry, but may be of interest in other industries as well.
“This announcement for sustainable ABS specialty solutions follows our earlier announcements on sustainable ASA, SAN, SMMA and SBC products. – It will not be the last such announcement. We will continue on our journey to deliver sustainable options for all our product groups,” said Dr. Eike Jahnke, vice president specialties EMEA.


launched four new LNP™ ELCRES™ FST copolymer resins that comply with the European railway standard EN45545 R6-HL 2 for train seating. Designers can benefit from these new material solutions, which not only meet the new regulatory requirements but also provide expanded opportunities to create sleek seating designs.
Compared to thermosets and aluminum, the new ELCRES resins offer lighter weight and efficient processing without requiring secondary operations. To achieve a seamless aesthetic look in an all-inone seat unit or a design with a separate back shell without painting, SABIC offers precision color matching for its extrusion grade (LNP ELCRES FST2732E resin) and injection molding grade (LNP ELCRES FST2432 resin). For customers that require more-sustainable solutions, SABIC supplies bio-based version of each grade.
“Since the EN45545 standard came into effect, the rail industry has faced challenges in obtaining compliant thermoplastic materials – and SABIC has been proactive in providing solutions,” noted Brian Rice, senior manager, global product management, LNP/NORYL, specialties, SABIC. “With our new LNP ELCRES FST products, we not only met customers’ high expectations for compliance, performance, aesthetics and manufacturability, but we also addressed their sustainability goals with bio-based versions. With multiple grades to choose from, manufacturers can once again leverage the advantages of thermoplastics in their seating applications.”
Meeting customer requirements for compliance with stringent EN4 5545 standard
LNP ELCRES FST copolymers address demands from customers like Monte Meao, a Portuguese rail seating provider, for high-performance thermoplastics that help address the stringent requirements of the harmonized European rail fire protection standard, EN45545.

“We needed an injection molding material that complies with the safety requirements set forth in the EN45545 standard for railway seating and offers long-term durability for our customers. SABIC’s LNP ELCRES FST2432 copolymer provided a good combination of physical properties and a flexible processing window,” said Fernando Cerqueira, CEO of Monte Meao.
SABIC’s bio-based versions of both the extrusion and injection molding grades were developed to expand the sustainability benefits of the LNP ELCRES FST materials beyond paint elimination
and weight reduction. LNP ELCRES FST2732EB (extrusion) and LNP ELCRES FST2432B (injection molding) products incorporate 55 percent renewable feedstocks from crude tall oil and other waste products.
Both are potential drop-in solutions that deliver the same high performance and regulatory compliance as the fossil-based grades. An Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) carbon dioxide (CO2) equivalent analysis showed these bio-based products reduced carbon emissions by 33 percent vs. their fossil-based counterparts.
Custom color and chemical resistance enhance
The new LNP ELCRES FST copolymers offer molded-in color options from a broad palette, including custom colors, to help enable OEMs and railway operators to brand their seats as part of the interior Molded-in color eliminates the need for secondary painting, thereby reducing cost and CO2 footprint.
To maintain the attractive appearance of rail seating over its lifetime, the SABIC materials provide excellent chemical resistance that simplifies graffiti removal, and a good balance of stiffness and impact resistance to improve durability and extend useful life. Also, the increased stiffness of the LNP ELCRES FST grades compared to standard PC allows the same part to be manufactured using less material, for potential cost savings.
“Our new LNP ELCRES FST copolymers are the result of a major technological breakthrough that helps ensure compliance with stringent fire protection requirements of the European railway standard,” commented Luc Govaerts, director, formulation & application, specialties, SABIC.
“By bringing together a proprietary copolymer material and an enhanced additive package, our team delivered the outstanding flame-smoketoxicity performance that customers are seeking. We took this major development effort one step further by formulating drop-in, bio-based versions of both grades to offer the industry new options for increasing the sustainability of rail seating.”
SABIC’s Specialties business will feature the new LNP ELCRES FST materials. Parts to be displayed will include the back of an R6 train seat (injection molded) and a portion of an R6 seat (extruded and thermoformed).
The company will also be featuring a new pelletfed additive manufacturing (PFAM) grade that is well-suited for rail seating and other large parts in Germany.
Evonik aims to make the recycling of lithium simpler, more costeffective, and more environmentally friendly. This metal is essential for the batteries used to drive millions of electric vehicles. At present, however, up to 95 percent is not recycled after use.
Evonik’s researchers have therefore adopted a new approach, focusing highly efficient recycling of lithium using an electrochemical process with a ceramic membrane. The technology is currently being tested on a pilot scale. It is highly efficient and generates high-purity lithium hydroxide that is suitable for the manufacture of new batteries.
Following proof of concept in the lab, the technology now needs to be driven forward—and Evonik is working on that at its sites in Hanau and Marl in Germany. Its specialists are confident that the ceramic membrane process will be market-ready in three to five years.

“In a few years, many lithium-ion batteries will be coming to the end of their service life. As a result, there will be a sharp rise in the volume of spent batteries that can be used to recycle lithium. Moreover,
new production facilities are being set up in Europe for large-scale production of batteries for electric vehicles. That will generate production waste containing lithium,” said Elisabeth Gorman, lithium recycling expert at Evonik.
“A third factor is legislation: The EU, in particular, is pressing for valuable raw materials to be re-used in the production cycle. That is already realistic for cobalt and nickel, but the recycling rate for lithium is less than 5 percent at present,” added Gorman.
Gorman is responsible for market development of lithium recycling at Creavis, Evonik’s strategic innovation unit and business incubator, and is familiar with the legal situation: In the EU, it is stipulated that in four years’ time at least 35 percent of the lithium from spent batteries will have to be recovered. From 2030, the percentage has to be increased to 70 percent. China and the US also have government regulations on the recovery of lithium.
The processes currently used to recover metals from spent batteries are based on smelting (pyrometallurgical process), leaching (hydrometallurgical process), or a combination of the two. These processes have proven effective for the recovery of cobalt and nickel.
Conventional reprocessing of lithium is also based on hydrometallurgic processes. However, the processes are cost-intensive, require large quantities of energy and water, and involve many interim steps and additional chemicals. There are therefore good reasons to look for better alternatives.
Evonik has taken up this challenge. Experts at this specialty chemicals company are working on the development of a ceramic membrane with selectivity for lithium ions, which forms the heart of an electrochemical process. The aim is selective and efficient recovery of lithium salts from spent batteries—while minimizing the use of energy and chemicals.

The starting point is the black mass. This is the term used by experts to refer to what remains of spent lithium-ion batteries when the plastic parts have been removed and the rest has been ground to powder.
The black mass contains a mixture of lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese. Processing of this black mass results in lithium leachate. Evonik’s research team processes this leachate electrochemically with the aid of a ceramic membrane with selectivity for lithium ions. Selectivity means that the membrane only allows positively charged lithium cations to pass from the side with the leachate and the positively charged anode to the other side, where there is a negatively charged cathode. Here, the lithium ions are combined with hydroxide to form battery-grade lithium hydroxide with almost 100 percent purity.
Demand for lithium is set to rise as a result of the ongoing shift from combustion engines to electric vehicles. Experts predict that in the long term recycling will contribute around 25 percent of the lithium salts required.
At the same time, this could limit damage to the landscape and greatly reduce dependency on suppliers. Gorman is confident that in a few years Evonik’s newly developed membrane will facilitate efficient recycling of lithium—and be recognized for its sustainability.
 BY G S PATNAIK
BY G S PATNAIK
Flexible packaging is a means of packaging products through the use of non-rigid materials, which allows for more economical and customizable options. It is a relatively new method in the packaging market and has grown popular due to its high efficiency and costeffective nature.
This packaging method uses a variety of flexible materials, including oils, plastic and paper to create pouches, bags and other pliable product containers. Flexible packages are particularly useful in industries that require versatile packaging such as the food and beverage, personal care and pharmaceutical industries.
Flexible packaging comes in a variety of materials, shapes, and sizes, and is typically produced in either formed or unformed configurations. Formed products are pre-shaped with the option of filling and sealing yourself in-house, while unformed products typically come on a roll that is sent to co-packers for forming and filling. The materials used in flexible packaging are easy to manipulate and combine into innovative and customizable styles, such as: Sample pouches, Printed Pouches, Sachets, Printed Roll Stock, Stock Bags etc.
Not only does flexible packaging use less material than its rigid counterparts, leading to a lower overall packaging cost, it also creates
less waste. It is said that flexible packaging formats create 50 percent less waste than rigid ones, while also reducing greenhouse gas emissions and BTU consumption.
Flexible packaging is one of the fastest growing segments of the packaging industry, it adds value and marketability to food and nonfood products alike – combining the best qualities of plastic, film, paper and aluminium foil to deliver a broad range of protective properties while employing a minimum of material.
The industry continues to advance at an unprecedented rate. Innovation and advancements in technology have led to the development of lighter weight packaging that enhance flexible packaging’s shelf appeal, strength, product protection, and the ability to be sealed. There are numerous examples of innovation in flexible packaging.
Each one starts from an idea: meat should stay fresher longer, shipping costs should be lower and medicines should be safer for the consumer. With its versatility, custom qualities, efficiency in conserving resources, and sustainability, there’s no better time to consider switching to flexible packaging.
Flexible Packaging entails a package or container of flexible or easily yielding materials that when filled or closed can be readily changed in shape. They are used for consumer and institutional products and in industrial applications to protect, market and distribute a vast variety of products.
As Rigid packaging is made from denser and thicker materials while flexible packaging is mostly made from plastic, film, foil, and paper which makes them less heavy than the rigid packaging. Rigid packaging provides better protection against the heat and other barriers when compared to the other one.
Flexible packaging is a means of packaging products through the use of non-rigid materials, which allow for more economical and customizable options. This packaging method uses a variety of flexible materials, including foil, plastic, and paper, to create pouches, bags, and other pliable product containers.
Flexible packaging can be composed of film, plastic, paper, or foil, to name a few materials.
• Polyolefin (POF) ...
• Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE) ...
• Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) ...
• Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET, PETE) ...
• Polypropylene (PP) ...
• Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC, Vinyl)
Sample Pouches: Sample pouches are small packets composed of film and/or foil that get heat-sealed. They are typically pre-formed for easy in-house filling and sealing.
Printed Pouches: Printed pouches are sample pouches on which the product and brand information is printed for marketing purposes.
Sachets: Sachets are flat packets made of layered packaging material. They are frequently used for single-use pharmaceutical and personal care products. These are great for trade shows where you want to distribute samples.
Printed Roll Stock: Printed roll stock consists of unformed pouch material with product information pre-printed on it. These rolls get sent to a co-packer to get formed, filled, and sealed.
Stock Bags: Stock bags are simple, blank formed bags or pouches. These can be used as blank bags/pouches or you can adhere a label to these in order to promote your brand.
The basic manufacturing process for flexible packaging includes:
1. rotogravure printing. 2. adhesive lamination. 3. flexographic printing. 4. extrusion lamination or coating, and. 5. finishing.
The global flexible packaging market was valued at $182.3 billion in 2020, and is projected to reach $325.6 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 6.2 percent from 2021 to 2030.
Owing to the rising focus on sustainability, traditional rigid packaging solutions are being substituted by innovative and more sustainable flexible packaging. The growing market demand for customer-friendly packages and heightened product protection is expected to boost flexible packaging as a viable and cost-effective substitute.

E-commerce, digital printing, and sustainability are driving market development and growth. Customers are increasingly becoming more eager to pay extra for certain product attributes boosted by flexible packaging. For instance, according to the Flexible Packaging Association, more than 60 percent of consumers in North America are keen to pay more for tangible and functional packaging benefits, such as product protection, shipping friendly, and supply chain efficacy, among others.
Flexible packaging is mainly used for food, which contributes to more than 60 percent of the total market, according to the Flexible Packaging Association. Also brand owners are taking on films, pouches and bags as a go-to packaging solution, acknowledgments in part to extensive acceptance by American consumers1.

The e-commerce retail packaging sector has grown to 65 million monthly unique visitors, accumulating an annual increase of 55 percent. India’s e-commerce revenue is predicted to be the highest rate in the world, growing at an annual rate of 51 percent and increasing to $120 bn in 2020 from $30 bn in 2016, according to an ASSOCHAMForrester report2.
Beauty products manufacturers are also investing in eco-friendly packaging approaches to make more sustainable usage of plastics in the personal care industry.
India is Expected to Witness Significant Growth in the Asia-Pacific Region. The packaging is the fifth largest sector in the Indian economy and is one of the highest growth sectors in the country. According to the Packaging Industry Association of India (PIAI), the sector is growing at 22 -25 percent per annum.
With the rising population, increasing income levels, urbanization, changing lifestyles, increasing internet penetration, and growing economy, the demand for packaging has been growing. According to the World Bank, approximately a third of the total population in the country lives in cities.
In recent years, India has witnessed sustainable packaging growth owing to the increase of packaged food consumption and awareness, and demand for quality products. Consumer awareness surrounding packaged food, specifically packaged food deliveries, has heightened.
The packaging industry in the country is moving towards flexible packaging owing to its multi-fold energy and environmental benefits. Flexible packaging uses the best characteristics of plastic, paper, and aluminium foil, without compromising on the product’s freshness, barrier protection, durability, printability, and ease of use.
Looking into the demand for environmental protection, it has become a concern for all to stop using plastic / foils for packaging. Plastic is not degradable and affecting the environment and health of flora and fauna. Toxic chemicals leach out of plastic and are found in the blood and tissue of nearly all of us. Exposure to them is linked to cancers, birth defects, impaired immunity, endocrine disruption and other ailments.
The biodegradable and recyclable materials used in eco-friendly packaging can take a variety of different forms: Bioplastics, or plantbased plastics. Recycled paper and plastics. Post-consumer products, such as recycled bulk bags.
There are various eco-friendly food packaging options that are better for the planet and health of living beings.
• Paper & Board packaging which are bio-degradable

• Glass containers. Glass has a multitude of uses and benefits for daily life
• Stainless steel
• Bamboo
• Rice husk
• Wood Dust
• Gelatine films
As the variety of foods containing grease is abundant, the types of oilresistant materials used in food packaging has diversified in recent years. Environmental protection and safety issues continue to be important, and as a result, scholars have paid increasing attention to paper packaging materials. Oil and grease resistant paper is one of them, which imparts barrier properties for oil and grease.
The oil and grease resistance of paper after surface sizing with aqueous dispersions composed of film forming polymers, their mixtures with fluorinated polymer or fluorinated polymer and silver nanoparticles were compared. The oil and grease resistance of paper was regulated by changing the composition and intake of aqueous dispersions and paper grade, and it was evaluated by the content of fine surface pores, contact angle, oil absorptiveness, grease resistance, oil repellence on the inclined surface and oil penetration time.
The aqueous dispersions were applied on one side or on both sides of paper surface in the size press. The film forming polymer has created a physical barrier against oil and grease, while combination with the fluorinated polymer developed a physical and chemical barrier.
The papers sized with aqueous dispersions containing a mixture of film forming and fluorinated polymer with the addition of silver nanoparticles, achieved high oil and grease resistance even with lower consumption of the fluorinated polymer, and also achieved an antimicrobial surface. The more porous paper has achieved the required oil and grease resistance at higher polymers intake. Compounds such as PE, EVOH, and palm wax are often compounded with cellulose to reduce the porosity and wettability of paper materials and thereby improve their oil resistance. However, these composite papers lose some of their biodegradability and recyclability. Consequently, coating derived from biomass polymers have great research potential in food packaging applications3
The rapid surge in e-commerce sales has led to an increase in package waste. These brands are incorporating sustainable packaging into their fulfilment processes.
E-commerce sales jumped a whopping 49 percent in April in response to COVID-19, and since then, online retailers have been scrambling to keep up with the increased demand in shipments. In addition to using more boxes or bags, there is also more in-thebox protection used to make sure the package contents make it safely to its destination. If the materials are not properly disposed of, this additional packaging may lead to a rise in consumer waste.
In spite of all this increased consumption, online shoppers still care about the environmental impact of their purchases. In a recent survey, 83 percent of consumers said they considered the environment at the checkout screen, including the excessive waste it might be generating, and the increase in their carbon footprint. In that same study, 78 percent of respondents said that companies could be doing more to mitigate packaging waste.
More and more brands are becoming conscious about their impact on the environment. Eco-friendly products in the fashion, personal care, and other sectors have been popular for years. But now those same values are being extended to their packaging and fulfilment strategies, and mainstream companies are joining them.
With the uncertainty of in-person retail is amplified by COVID-19, deliveries and the unboxing experiences are becoming one of the primary ways for brands to build a relationship with
their consumers. And part of that relationship is about honouring the sanctity of the environment.
In recent years, India has seen sustainable packaging growth due to the increase of packaged food consumption and awareness, and demand for quality products. Consumer awareness surrounding packaged food, specifically packaged food deliveries, has heightened.
Earlier this year, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) announced new packaging regulations to replace the former 2011 provisions. The new regulations comprise of a migration limit of 60mg/kg or 10mg/dm2 and migration limits for specific contaminates in plastic packaging materials. Looking into threat to environment and negligible possibilities of recyclability, Recycled plastics and newspaper used for food packaging have also been banned. New labelling regulations were also revised.
In terms of India’s beverage packaging, materials such as glass and rigid plastics account for 70 percent of the total packaging market. PET is the material most used to package water, accounting for around 55 percent of India’s packaged water sector.
Projected to reach a CAGR of 4.17 percent to $142.2 bn by 2023, it is predicted that the nation will see continued demand for PET bottles, along with a new demand for liquid packaging cartons due to their longer shelf life and ease in transportation.
Author: G S Patnaik is General Manager (QA & TS) at J K Paper Ltd.
During 1990s and the years that followed, office spaces were getting rapidly computerised internationally. In this backdrop, the demand of Writing & Printing (W&P) papers was expected to be adversely affected. But during this one and half decades, the consumption continued to grow across geographies. Ironically, the demand for copying papers outgrew any other type of paper or paperboards during these years, which should have been the immediate victim of workplace computerisation.

Finally, these predictions came true in 2008 and thereafter. The financial crisis triggered a sustained contraction in demand for W&P grades. While this contraction was most severe in mechanical and
semichemical grades, the woodfree varieties were also significantly affected. However, this contraction was confined to developed economies only while the rest of the world continued to witness demand growth.
As digitization made rapid inroads into our life and work, over last one decade, the demand growth has been decelerating gradually in practically all geographies including India. Perhaps, like sub-prime crisis of 2008, another trigger was needed to push the W&P grades from deceleration to demand contraction; that trigger could well be the pandemic of 2020.
Our generation and the ones preceding it were mostly comfortable with reading from a sheet of paper. But the younger generations are at home reading or interacting with a screen even for long hours. This fundamental change in the way people consume printed content is guiding the fate of writing & printing papers. The pandemic and its repercussions have boosted this trend in multiple ways:
1. Work from home culture is here to stay, at least in part
2. On line education will take away another slice of W&P demand
3. Publishing industry is rapidly driving shift towards digital books. It reduces production and distribution cost as well as the turn-around time
4. eCommerce has killed a big part of commercial printing eg, POP material, leaflets etc
While energy and food prices are at high level, globally most of the manufactured commodity prices have begun to soften and this includes paper. Sometime in 2023, the dust will settle on global supply chain disruption. Prevailing demand supply contradictions in pulp, waste paper and paper will ebb and extent of damage to demand by the pandemic will become clearer.
When such a scenario unfolds, the industry will be forced to make quick and drastic changes to its business to remain relevant or even survive. As always, the survival kit will not be a silver bullet but will have to be a multi-pronged strategy:

1. New products and new markets
2. Calibrated sales & marketing initiatives
1. New Product and new markets: This is existing default reaction of most mills in times of difficult market conditions. Here it is pertinent to note that new products are not created by change of recipe or materials or significant intervention in manufacturing in upstream stage of the process. Downstream interventions like same product offered to new segment or markets thru different SKU or formats in new brands can be equally or more effective.
For manufacturers of printing papers, test-liner, kraft-liner, fluting, absorbent kraft are good examples of upstream intervention. But for upstream strategy to succeed, it is important that chosen products have large and growing markets to accommodate new players. Absorbent kraft may be of limited value from this perspective. On the other hand, relatively bigger and wider deckle machines needed to be competitive in containerboard market. It is important to note that success in new business will require more than the ability to manufacture a product with given specs.
The best case for downstream intervention is segments like flexible packaging and food service packaging. Like in any other segment, product and price are just basic qualifier for success. We will discuss some of these factors in the following parts.
2. Calibrated Sales & Marketing Initiatives: A product backed by a well calibrated sales and marketing initiatives ensures that the product enjoys faster acceptance, gains higher share and remains stable during periods of market downturns. Depending upon customer spread and market dynamics, suitable marketing initiatives, sales strategy and channel mix is required to get optimal results.
Business development is often said to be the “product management” function for B2B domain. This critical tool is waiting to be exploited by W&P industry in multiple segments like flexible packaging, containerboard, e-commerce shipping,
app-based food delivery services etc. Unfortunately, the industry has no experience or talent and will be best advised to acquire resources from other industries like packaging to succeed in business development endeavours.
Food delivery and single use disposables are largely unorganized and fragmented segments. Therefore, focussed development of the sales channel will be an essential element for gaining lead share in the market.
3. Building Supply Chain Competencies: This is perhaps the least acknowledged and the most potent of all tools for gaining competitive edge. This activity requires running several small initiatives to align outbound supply chain of one’s business to that of inbound supply chain priorities of one’s customers.
Some examples:
- Supply lead time is amongst most important requirement not just for paper but across industries and W&P industry is badly out of sync on this. There is an urgent need to bring down lead time to 1-2 weeks for some important segments
- Special sizes; never before opportunity today exists to accommodate larger number of special sizes. Wider machine deckle, better trim optimization software and market side opportunity for special size aggregation can enable the industry to access more markets and generate value
- Customer supply chain compatible product formats eg, flexible mix of reels, ream and skid packaging.
- Paper may be sold in weight but is used in area and length. Ability to supply in specific length and exact number of sheets are relevant in the age of digital printing.
The interests of the industry will be served best if it shifts away from investment led value creation to a knowledge and innovation led value creation model. The options and choices discussed above can be smartly deployed to generate superior value for the business and raise invisible barriers for the competition. Being pro-active and prepared is the best way to ride over the looming crisis.

Attention on ocean-friendly Personal Care is intensifying beyond packaging to the formulations, as consumers increasingly demand biodegradable cosmetic ingredients, and regulatory initiatives to ban microplastics in rinse-off products take shape.
Opacifiers are among the cosmetic additives impacted by these shifts. Used to impart a creamy white appearance and rich visual viscosity that many consumers find luxurious and caring for shampoos, conditioners, and liquid hand/body washes, formulators’ needs for alternatives to the most traditionallyused opacifiers for surfactant-based rinse-offs - styrene/ acrylates copolymer – are accelerating. These conventional water
dispersible solutions are non-biodegradable and considered as microplastics under an EU/EEA legislative proposal, meaning they will be banned in rinse-off formulations if restrictions take effect as expected in 2022.
To widen choice for the industry, Clariant has recently extended its natural ingredients portfolio with a 95 percent renewable carbon index (RCI), readily biodegradable, microplastic-free opacifier to support Personal Care formulators in minimizing the impact of rinse-off hair and body products on marine and river life.
“Because rinse-off formulation ingredients will usually end up in waterways and oceans, providing readily biodegradable solutions to this cosmetics sector is an important focus of our product development,” commented Hermann Bach, head, Strategic Marketing and Innovation, Clariant BU Industrial & Consumer Specialties. “The percentage of biodegradability in a final formulation depends on its proportion of readily biodegradable ingredients, therefore we are pleased to now offer a drop-in natural-derived option to support the sector in addressing this evolving priority without compromising on visual appeal.”
New Plantasens® OP 95 (INCI: Sodium Methyl Cocoyl Taurate (and) Glycol Distearate) offers a range of attributes that create an easy-to-use solution for opacifying a wide range of hair and body care applications and for supporting eco-conscious consumer behavior. In addition to its microplastic-free profile, it is sulfatefree, non-irritant, and non-hazardous to aquatic life. The product is based on coconut oil and palm (kernel) oil and can be purchased as a Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO) certified grade. The feedstock comes from Malaysia, Indonesia or the Philippines.
The following assessments highlight the new ingredient’s ability to answer formulators’ needs on multiple fronts from performance to sustainability.

Samples in the visual test of Figure 1 show particularly effective opacifying performance from Plantasens OP 95 even at low concentrations. Comparisons to a sulfate-free benchmark are shown at 0.2 percent active and at 0.6 percent active. Unlike the sulfate-free benchmark product, the same level of creamy whiteness is achieved with Clariant’s new ingredient at both concentrations.
over a 12 week period at room temperature. A standard formulation composition already used in the past with pearlizers was selected as the basis for the evaluation (Figure 2). To replicate current opacifier options for formulators, Plantasens OP 95 was compared to respective market benchmark products: two sulfate-free blends (one anionic / one amphoteric); a sulfate-based blend; and a styrene/ acrylate copolymer. The results over time can be seen in the Figure 2 graph.

Stable opacity is an important consideration in order to ensure the high visual expectations of Personal Care consumers are reached. The new Plantasens OP 95 biodegradable opacifier is able to sustain a high whiteness over time for microplastic-free formulations with only minimal loss in opacifying effect, achieving performance comparable to sulfate-based and acrylate-based opacifiers.
Transmission over time was determined by evaluating shower gel formulations containing different opacifiers at 1 wt. percent active,
Soft caring shower cream formulation & transmission over long time at 22ºC (room temperature)
More detailed testing was performed on the same formulations at 12 weeks at various temperatures: 5 degrees Celsius; 22 degrees Celsius; 40 degrees Celsius. In Figure 3, we observe that there is a constant opacifying effect at 5 and 22 degrees for sulfate-free solutions. Sulfate-free solutions lose slightly in their opacifying effect after 12 weeks at 40 degrees, however the difference is not visible to the eye.

The new opacifier has been assessed on a number of key parameters relevant to ease of use for formulators. It supports low formulation complexity by providing a liquid drop-in solution for formulators who want to work with cold processes. Thanks to its strongly shear thinning behavior, it rapidly finds the necessary viscosity level to be efficiently dispersed in the formulation, delivering a homogenous appearance to the final product.
Its ability to maintain viscosity level of the formulation has been demonstrated by addition of the product to various commercial formulations (Ghul, Axe, Garnier). The viscosity level changed only by +/- 10 percent and remained stable over 3 months of storage at room temperature and 40°C.
The drop-in opacifying performance attributes can be seen in practice in the following videos on Clariant.com
To demonstrate the relevance and suitability of the new opacifier for hitting rinse-off product performance and sustainability attributes, the development team evaluated and compared renewable carbon content, readily biodegradable and microplastic-free profiles of the
assessed opacifiers versus key performance parameters. Figure 4 provides an overview.
Addressing trends & sustainability claims
Appearance is a key driver for consumer choices in Personal Care. For rinse-off formulations, Plantasens OP 95 achieves a high level of opaque creamy whiteness to meet consumer perceptions regarding luxury, mildness, and care. At the same time, it is readily biodegradable, microplastic-free, and sulfate-free which makes it a viable alternative for enabling shifts towards more aquatic-friendly hair and body care applications. The new opacifier can aid product manufacturers in addressing trends and extending new sustainability claims to their rinse-off formulations, while formulators can also benefit from its ease of use.


Xenia® Materials has introduced the XECARB® ST, a new family of supertough carbon fiber composites custom-engineered to close a performance gap in the market and provide superior impact strength performance.
“There is a growing demand for lightweight composites in various new markets, such as sustainable mobility and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), where we have identified a need for higher impact resistance than previously offered by carbon fiber reinforced composites,” said Cristian Zanchetta, technical manager for R&D at Xenia® Materials.
“Our new XECARB® ST family meets these challenges while at the same time opening new opportunities for innovative applications in existing market segments, such as sports equipment, appliances, supercars and even additive manufacturing.”
XECARB® ST builds on the proven mechanical strengths of Xenia®’s successful XECARB® range, but shows significantly higher notched impact resistance, low temperature ductility and tensile elongation at break. With slightly lower density, the new carbon fiber composite technology offers these unmatched advantages together with further lightweighting possibilities.
Major customers seeking to improve the impact and cold impact performance of carbon fiber composite applications are already
evaluating the added potential for weight reductions, lower material and energy consumption, associated cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
XECARB® ST thermoplastic composites are based on selected polyamide matrix materials – PA66, PA6, PA11, PA12, PA6.10, PA6.12 and PA4.10 – addressing different mechanical, thermal and physical requirements. Standard carbon fiber content is 30 percent (CF30).
The PA6-based composites are also available as CF20, CF25, CF35 and CF40 grades. In addition, the portfolio includes two highmodulus materials for enhanced flexural strength, and provides a wide engineering window for further customization depending on specific application needs.
“Beyond winter and mountain sports equipment from boots and running shoes to bikes, these new high-impact carbon fiber composites will help us reach into other markets and further expand our customer base in Europe, APAC and North America,” said Enrico Mancinetti, sales manager. “Driving this growth, Xenia® Materials will also increase its European sales force with a strong focus on qualified local customer support and service.”


The mobility and automotive industries are in a time of rapid transformation. The industry is pushing not only for a more sustainable future for vehicles, but also for one that is safer, more connected and, of course, still profitable. With well over half a billion dollars of announced global investment into production of electric vehicles (EV) and EV batteries, OEMs and their Tier networks are moving at an accelerated pace to design, validate, and produce low and zero emission vehicles, while simultaneously transforming vehicles into some of the most electronically advanced devices in our daily lives.
The first half of 2022 saw light vehicle production and sales in key markets around the world, including China, Europe and the US, roughly flat compared to the same time frame last year, due to continued supply chain challenges, ongoing pandemic impacts, chronic labor shortages, and the conflict in Ukraine. The transition to electric vehicles, however, continues to accelerate with penetration in China up over 10 percent compared to last year, with EV sales representing almost a quarter of new vehicles purchased in 2022.
This fundamental change in powertrain technology continues to present substantial opportunities for materials science companies, like Dow, as we rapidly innovate to meet the needs of battery assembly and safety, new noise and vibration profiles, vehicle autonomy, and occupant experience.
In terms of things to come, we’re hyper-focused on enabling and partnering with our customers to succeed in delivering low-carbon mobility. This means developing new materials that will help our customers meet, and often exceed, new performance requirements and increasingly stringent sustainability regulations from world governments and expectations from their citizens. It requires enabling new levels of circularity to reduce waste and catalyze innovation.
It means engineering materials that increase the efficiency and consistency of vehicle production, while delivering the more comfortable, more satisfying, and safer cars that consumers desire. This is what gets our MobilityScience™ team excited and what is pushing us to accelerate continuing materials science innovation for OEMs and Tiers.
We see several megatrends that are impacting the mobility industry: electrification, enhanced safety like battery fire protection, connectivity and autonomy, and circularity and sustainability. Dow MobilityScience™ was created to provide OEMs and tiers with simplified and straightforward access to Dow’s full breadth of solutions and capabilities and address these megatrends.
Sustainability is one of the top priorities for our customers. Innovations in materials science present a huge opportunity for them to enable new levels of recyclability and circularity across the entire vehicle lifecycle. Collaborating with customers early in the design phase enables our MobilityScience™ team to recommend and create tailored, validated solutions that unlock efficiencies from design to end-of-life, using the least materials possible while delivering the highest performance.
The other megatrend I’d note is connectivity. The boundaries between industries are blurring, with vehicles becoming a computer on wheels. We see some of the most famous consumer electronics and software brands partnering with, or (potentially) becoming Mobility OEMs. The transistor count per vehicle continues to increase, and combined with governmental investment in the chip industry, opportunities exist across the value chain in many geographies for Dow materials in this segment.
Potential for mobility, auto industry materials manufacturers in Asia Pacific and India.
China in particular is leading the way in electric vehicles (EV) through their generous investments. For example, CATL, despite its small beginnings, has now grown into the world’s largest EV battery producer, having formed partnerships with several global OEMs and is investing across the globe. Rising incomes across APAC, combined with governmental incentives and mandates to go electric, drive expectations of tremendous growth in the region over the coming decade.
In India, we see materials developed for EV batteries and passenger vehicles being applied to two- and three-wheelers. These smaller vehicles have distinct materials needs but also benefit from innovations in lithium-ion battery technologies developed for larger vehicles. This segment represents additional growth opportunities for Dow as their vehicle electrification rate accelerates.

Scope for materials innovation in the e-mobility segment.
We believe there are opportunities for sustainable innovation at every phase of the vehicle life cycle, whether we’re talking about electric, autonomous, or ICE vehicles. Our MobilityScience™ team is focused on engineering solutions for sustainable disassembly, exploring new adhesive/sealant/coating technologies to create parts that can be reused, repaired or recycled, and we’re committed to generating value from waste. Dow is also investing in lower-carbon material offerings.
Cutting-edge materials, like silicone and polyurethane sealants and thermally-conductive adhesives, are helping enable the next generation of e-mobility to achieve lighter weight, longer range, greater comfort, enhanced safety, and a lower carbon footprint. Major areas of opportunity for materials innovation for e-mobility specifically are in battery fire protection applications, lightweighting through the use of toughened plastics in place of metals, electrically conductive adhesives as part of an electromagnetic shielding package, crystal clear silicones for stylistic and adaptive beam lighting, and foams and coatings to reduce the road, wind, and other noise that we now hear in absence of the internal combustion engine.
The infrastructure necessary to support deployment of electric vehicles – passenger and things like long haul and last mile delivery vehicles; even tractors – is another area ripe for innovation. We need to deploy hundreds of thousands of charging stations across the globe, each requiring electronics and wire and cable solutions similar to those in an electric vehicle.
As fuel cells become more ubiquitous in applications where batteries aren’t sufficient, we’ll need infrastructure and renewable energy to generate, store, and distribute hydrogen. As autonomous vehicles are deployed, 5G cellular and wireless networks will grow and further develop. All these applications use highly engineered materials and are produced from many of the basic and specialty chemicals Dow manufactures.
Role of digital technology in growth of mobility, auto materials manufacturing.
Dow works with various software and hardware vendors and partners to utilize digital technology, automation, and artificial intelligence across our operations. In research and development, partnerships with several well-known and start-up companies help organize and mine data, and then apply machine learning and AI models to accelerate everything from the creation of a new efficiency enhancing catalysts to development of a highly engineered adhesive formulations.
We are also applying these technologies to improve plant reliability through, for example, prediction of failure of a process component, and optimization of our supply chain. These examples are not unique to the Mobility & Automotive market, but directly impact our ability to rapidly innovate during this disruptive transition, and to more reliably serve our customers.
Insight into Dow and Jaguar TCS Racing partnership.
Dow seeks partnership that share our vision for electrification and are aligned with our corporate sustainability values and objectives. We found this in the sport of Formula E and with the Jaguar TCS Racing team – carbon neutral from inception; accessible and
inclusive to the world’s most iconic city centers and their populations; it represents the legacy and future of innovation.
Now, as the Official Materials Science Partner of Jaguar TCS Racing, Dow brings its expertise in application development, 100 years of innovation in transportation, and its materials science innovation capabilities to the Formula E circuit. Dow became a partner of Jaguar TCS Racing in 2020 and became their Official Materials Science Partner in 2021.
Since then, our MobilityScience™ team and the Jaguar TCS Racing team have been partnering to identify solutions and innovate technologies that will help the Jaguar I-TYPE 5 electric racecar perform better, faster, and for longer.
Arguably the most powerful aspect of our collaboration with Jaguar TCS Racing is that it allows our engineers to use the track as a real-world test bed for the electric vehicle (EV) technologies that are shaping and enabling a low-carbon future for consumers on the road. The success of the partnership so far can be attributed to shared belief in the power of collaboration, a passion for creative problem-solving, and high-touch communication.
As we journey together into Season 9 of the ABB FIA Formula E World Championship and the introduction of the fastest, lightest, most powerful, and most efficient electric race car ever built, we’re excited to continue to help Jaguar TCS Racing identify the best solutions to further optimize efficiency and performance and highlight our commitment to low-carbon mobility.
R&D process, materials innovation for Dow and Jaguar TCS Racing.
Racing is one of the world’s most exciting and competitive sports. But it’s not just for the excitement of the sport that Dow decided to engage in Formula E. The partnership has opened an entirely new and creative way for us to put our materials science solutions to the test. For both road and race cars, materials can make a huge impact.
At the start of the partnership, our MobilityScience™ team sat down with engineers at Jaguar TCS Racing to identify the primary challenges they’re facing and determine where performance improvement opportunities exist. This initial conversation has evolved to often daily interactions between our teams in a constant loop of idea generation, design, testing, measurement, and feedback.
To date, we’ve been able to help Jaguar TCS Racing: improve thermal management, increasing overall vehicle efficiency; begin to explore improved illumination options for the garage environment, based on mouldable, optically clear silicones, that provide more light with less energy and are less prone to damage in the race environment; and adhesives solutions to ensure more effective assembly and component durability. We have also started working with the team on innovating solutions to combat EMI challenges throughout development of high output power electronics.
Materials segment strategies for improved safety, performance and sustainability.
As part of our effort to innovate for fast-moving automotive applications and to collaborate to ensure safety, performance, reliability, and sustainability for our customers in real-time, one major initiative is the creation of MobilityScience™ Studios – a series of workspaces that feature a world-class suite of testing capabilities and collaboration spaces. To date, we have launched two studios focused on acoustics and powertrains.
Incorporating recycling, bio-based concepts in mobility, automotive materials segment.
Dow is focused on finding new opportunities for increased sustainability at every phase of the vehicle lifecycle: design, production, use and end-of-life. Let me share some of the more impactful announcements.

Earlier this year, we announced the world’s first carbon neutral (scope 1 and 2) ethylene production facility, which will be located in Alberta, Canada. This multi-billion dollar investment will decarbonize 20 percent of Dow’s ethylene capacity, while growing our ability to meet global polyethylene demand.
We have also formed partnerships with several companies that will convert waste plastic into recycled feedstocks for the synthesis of virgin-like plastics and, further, source non-food competing, bio-derived feedstocks and other ‘waste’ streams that are co-fed to our crackers for the production of new ethylene and propylene derivatives (polyethylene and polyurethane, for example).
Several products are offered to the Mobility & Automotive
At the MobilityScience™ Studio at our headquarters location, Midland, MI, OEMs and Tiers not only have access to our vast portfolio of polyurethane foams, elastomers, resins, coatings materials, and specialty chemicals, but also have the opportunity to work in tandem with our team to develop solutions that meet their exact needs. At the Studio in Lake Jackson, TX, our capabilities are aimed at the development and commercialization of sealing, powertrain and fluid transfer system components such as weatherstrips, belts and hoses.
Focusing in on sustainability specifically, Dow has identified three focus areas where we believe we can make the biggest difference: low-carbon and more processable materials, circular solutions, and safer materials. Within those three areas, there are a wide variety of initiatives that have helped us positively impact the mobility industry. Examples include investment in the creation of a carbonneutral silicone and renewable energy sources to power our own plants and rigorous Life Cycle Assessments (LCAs) for our key products like NORDEL™ Ethylene Propylene Diene Terpolymer (EPDM).
We also participate in a variety of mobility ecosystems at the government and regulatory level as a part of our efforts to protect and advance mobility innovation for OEMs and tiers. A recent example is helping to bring the possibilities of adaptive beam lighting technology and mobile optical materials from Europe to advance driving safety in the North American marketplace.
segment, including bio-polyethylene, SPECFLEX™ C polyol for seating foam, and carbon neutral DOWSIL™ 844 sealant.
Opportunities for raw materials chemicals, polymers and silicones manufacturers. Electrification and automation of the transportation fleet, and supporting infrastructure, is a once-in-a-hundred-years opportunity. Along with that come many opportunities for materials. We need to continue to invent new materials that improve safety (prevent thermal runaway in batteries, for example) and manage heat, but there is also tremendous opportunity in the area of sustainability.
We should embrace the challenge of minimizing use of our limited natural resources in cost effective ways. We want to leave the planet in a better place for our children. We often say every challenge is an opportunity, and this time is no different. Dow’s chemists, chemical engineers, material scientists, and polymer chemists are well poised to tackle these challenges in economically sustainable ways.

Macro economy making a difference for industrial gases providers.
The world is witnessing several global macro-economic shifts which is affecting the potential business opportunities arising therefrom, especially in Electronics and Automobiles sector. Issues related to ocean freight; shipping schedules have had an impact on growth projects due to delay in deliveries of certain imported parts of plants. This also had an impact on certain imported gases in meeting timely deliveries to customers.
There is huge impact on project costs due to heavy increase in metal markets and shipping disruption. Most of metal items like steel, aluminium and copper price has gone up substantially, resulting cost impact on tanks, vessels, structural items, mechanical contracts, civil jobs etc.
At the same time due to shipping disruption, freight forwarding cost has gone up significantly, and also due to lack of vessels availability, most of the imported items are getting delayed due to which site construction is getting affected. However, to mitigate these risks,
Linde as an organization is taking various steps including developing alternate suppliers to reduce the impact and the delay in supply of goods.
Development in the industrial gases segment.
The industrial gases market is expected to grow at ~9 percent. The consolidation in steel segment is expected to boost gas demands with opportunity for liquid sales to enhance productivity (SAIL, Tata Steel, JSW, Vedanta). On the other hand, the Indian auto industry is expected to reach 19-21 Trillion INR by 2026. With BSVI implementation, demand of Argon and Specialty gases is expected to grow by 25 percent.
Healthcare too is poised for faster growth. Post Covid, the digitalization wave is expected to propel growth in electronics. Lastly, the growth expected in Specialty gases like Ammonia, Silane & Nitrous Oxide will mainly be from new & expansion of PV Solar projects. There is also an opportunity to sell Liquid Nitrogen & Onsite Nitrogen plants.

Potential for Indian industrial gases providers.
As per our company offerings, we will evaluate potential Clean Energy opportunities, such as hydrogen refuelling on a case-by-case basis, depending on various factors like our ability to undertake the opportunity in a safe manner, accessibility of cost efficient and reliable technology and other parameters. We also see a strong potential from electronic gases in the future.
Digital technology to support industrial gases segment in India.
During the pandemic & in currently tightening market due to inflationary pressure, focus is on healthy growth. Healthy growth means good revenue opportunities & reducing costs while maintaining customer experience.
Digitalization for good revenue options include analytical or web platform solutions for new customer onboarding work process, customer base assessment and customer price management. Digitalization solutions focusing on cost efficiencies include supply chain optimization solution, reduction of manual tasks using technologies such as RPA, KPIs dashboards. Customer experience enhancement is also another key area for digitalization.
Company’s R&D and innovation in industrial gases segment.
Innovating for customer is at the core of Linde India’s engagement with its customers. It has been actively migrating technologies developed by our Global R&D team for Iron & Steel, Glass, Food & Beverage, Manufacturing, Specialty Chemical and Pharmaceutical industries.
Our technologies have been deployed for achieving various objective of Decarbonisation, Reducing Energy consumption, Emission reduction and Productivity improvement, Cryo-freezing and Grinding technologies.
The company has been constantly, and aggressively pursuing application driven gas sales and will continue to focus on this area.
Strategies to improve sustainability for the company.
Sustainable activities are part of our overall operations and customers offerings. Some of the strategies that we follow to improve sustainability are – sourcing majority of Renewable Energy (RE) through offsite Solar, wind and hybrid projects with RE generators, purchasing green certificates and participation in Virtual PPAs and RE power sourcing at large onsites.
Our activities also include reducing Scope 1 emission by replacing with natural gas and improving operational efficiency. Moving ahead, our target is more than 50 percent RE power coverage for new onsite plants. Moreover, the company plans to intensity improvement for ASU Energy and Fleet greenhouse gas emissions and also to focus on rainwater harvesting, zero waste for all Linde sites. Plans are on to replace diesel vehicles with CNG in the future.
Challenges faced by industrial gases segment in India.
Some of the major problem that the Indian industrial gas segment faces are - heavy reliance of Air Gas business in the Steel Segment. Further, there is the issue of entry of non-gas players into gases business, which gives rise to complications in the market place.
Added to this we are also seeing aggressive pricing behavior in geographies with surplus capacity. Moreover, adding to the concerns we are also witnessing entry of different players with new investment announcements in overlapping power zones.
Government regulations, quality standards to support industrial gases segment.
There are numerous ways how stricter government regulations and improved quality standards support growth of the industrial gases. Some examples are:
- With stricter norms and regulations related to vehicle emissions, there are requirements of analyzers. These analyzers can be calibrated using calibration gases. Linde manufactures a wide range of such high accuracy calibration gases.
- Govt. regulations related to industrial pollution, if imposed strictly, would mandate industries to treat their effluents and water. Linde has several applications that can help in:
o Water treatments, example - Aerobic treatment, neutralization and remineralization
o Air Emissions, example - VOC emissions control, NOx abatement, Carbon capture, utilization, and storage.
- With improved quality standard expectations, there are several opportunities for the industrial gases segment.
o Traditional methods of stick and Co2 welding needs to change to Argon based Shielding gases and robotic welding that improves the quality and boosts gas demand. Linde has a wide range of welding gas mixes suited for industry specific needs.
o Improved methods of manufacturing, packaging and storage of Food and Beverages requires various gases. Linde has a wide range of capabilities including Food freezing and chilling, Packaging for Food, and Carbonation Blanketing, purging, and sparging for Beverages.
Industrial gases providers to enhance their solutions for chemical industry.
For the industrial gases industry to enhance their solutions for the chemical industry, there is major opportunity in Asia Pacific, South Asia and India markets. The potential lies in collaboration and synergy benefits.
These can be deriving synergy benefits in growing cluster business for building pipeline network and also from the synergies arising from integration and growth forum initiatives. The providers need to actively scout for Decap opportunities with business synergies. Other than this providers can work on the following as well:
• Improve geographic coverage through mergers & acquisitions in Tier-2, Tier-3 cities
• Focus and invest into Resilient market segments
• Revival of investment cycle providing opportunity to PED for 3rd party plant sale
• Distribution: Cost optimization, digitalization
• People excellence through a culture of empowerment, collaboration and accountability
• Do more with flexible work arrangements, efficiency improvements through Digitalization

Phosphoric acid which is the main ingredient in industrial fertilizers is a major environmental threat.
team of BGU environmental scientists has developed a circular process for eliminating the risk posed by phosphoric acid plant wastewater. The process turns the environmentally toxic wastewater into clean water while recovering valuable acids. Phosphoric acid is the main ingredient in industrial fertilizers, a massive industry worldwide.
Their method was published in ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering, a prestigious scientific journal published by the American Chemical Society. Lior Monat, a PhD student in Dr. Oded Nir’s lab led the research under his supervision.

“Phosphoric acid production generates a lot of industrial wastewater that cannot be treated efficiently because of its low pH and high precipitation potential,” explained Nir (in picture), the co-lead researcher, “Today, the wastewater is usually stored in evaporation ponds. However, these are prone to breaches, leakage, and flooding. A few years ago, an ecological disaster in Israel occurred when millions of cubic meters of this acidic wastewater were flushed down a creek. Conventional treatment processes run into difficulties dealing with the acidity, salinity, and hardness of the wastewater. Therefore, we developed an alternative three-step process for the treatment of phosphoric acid wastewater comprised of selective electrodialysis, reverse osmosis, and neutralization.”
The team evaluated the method with synthetic wastewater in the lab, with positive results. The process successfully recovered clean water and phosphate while reducing the volume of wastewater by 90 percent. It also did not generate any appreciable mineral scaling, which could muck up the membranes.
Moreover, the power requirement for the process was also low enough it would seem that the method would be sustainable and techno-economically viable.
“This process is very promising, and we encourage industry players to examine its potential and applicability at their factories,” said Bernstein, co-lead researcher.
Nir, Bernstein, Monat, Wei Zhang, Alice Jarosíkova and Hao Haung are all members of the Zuckerberg Institute for Water Research, part of the Jacob Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research on the Sde Boker campus of Ben-Gurion University. Nir is also a member of the Goldman Sonnenfeldt School of Sustainability and Climate Change.
The research was supported by Israel Ministry of Science and Technology grant.
The authors, from academic institutions including the University of Exeter Business School, have published key knowledge gaps for researchers to help cities and businesses to operate within Earth system limits in the journal Nature.
It comes ahead of an Earth Commission report due out next year that will outline a range of ‘Earth system boundaries’ (ESBs) based on the latest science, modelling and literature assessments.
A decade ago, scientists defined a set of planetary boundaries within which humanity can operate ‘safely’ in nine areas – climate change, the biosphere, nutrients, water, land use, ocean acidification, ozone depletion, aerosols and novel entities – and the soon-to-be-defined ESBs will add a social justice dimension, to ensure quantified boundaries are ‘just’ as well as ‘safe’.
The authors argue for ‘science-based targets’ and say objectives must be ‘measurable, actionable and time-bound’, pointing out that few cities and companies currently have science-based targets and of the top 200 cities with the highest emissions, only 110 have ‘net zero’ pledges that align with the Paris Agreement.

Lead author Xuemei Bai, Distinguished Professor at the Fenner School of Environment and Society at The Australian National University and a member of the Earth Commission said: “It’s a long haul, but humanity needs to stay within our planet’s finite budgets. Developing scientifically-robust and socially-just methods to allocate natural resources and responsibilities is essential to respect them.
“Cities and companies are main contributors to planetary level changes, but also key actors for solutions. There are knowledge gaps in how to translate such boundaries into concrete allocations for businesses and cities, and our recommendations seek to fill those gaps.”
The authors highlight seven recommendations for researchers aiming to translate ESBs into concrete steps for cities and businesses.
1. Develop common procedures: Principles, protocols, methods, metrics, assumptions and uncertainties must be clear. Without such clarity, cities and companies may seek to minimise their own responsibility and maximise the resources they claim.
2. Focus on interactions: Earth system boundaries are linked, so targets need to be aligned.
3. Acknowledge dynamics: Researchers must develop an agile approach – time-sensitive and dynamic goal setting that allows regular checking, adjustment and updating.
4. Allocate for justice and equity: Targets need to reflect socioeconomic contexts, such as income and consumption levels, environmental impacts or capabilities to act. For example, cities with high consumption levels, historical emissions or high revenues should arguably adopt more stringent targets than others.
5. Support monitoring and accountability: Crossdisciplinary scientists should ensure that their proposed ‘global baseline of sustainability-related disclosure standards’ explicitly link cities and companies with ESBs.
6. Establish governance mechanisms: New policies and regulations will be needed to incentivise or mandate cities and companies to adopt targets.
7. Design incentives: Widespread adoption of science-based target setting by cities and companies is essential, as they can also prompt and incentivise national governments to follow the suit. Co-author Johan Rockström, co-chair of the Earth Commission and director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, said that “Earth system boundaries are linked, so targets need to be aligned. Measures that focus on one domain can be beneficial or detrimental to others.

team from the Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources of the Chinese Academy of Sciences investigated the effect of chloride salt on urea hydrolysis in Microbially-induced carbonate precipitation (MICP) and the effect of MICP on the engineering and mechanical properties of coarse-grained soils containing chloride salts. Related results were published in Journal of Cleaner Production.
MICP is a kind of cost-effective and environmentally friendly technology to improve the saline soil. It aims to use urease generated by bacteria to catalyze urea hydrolysis and produce carbonate, which combines with calcium ion in the cementation solution to form calcium carbonate precipitates and calcite crystal. However, the impact of salt on urea hydrolysis and curing effect needs to be further studied to verify its feasibility for solidifying saline soils.
The researchers also analyzed the deterioration mechanism of chloride salt on reinforcement through micro-mechanical tests.
They found that, though curing effect of MICP is excellent, the negative effect of salt cannot be ignored. The rate of hydrolysis and precipitation efficiency decreased with an increase in salt concentration, which results in the deterioration of the mechanical properties of solidified soil.
In addition, the quantity of calcite was significantly more than vaterite, and the salt content, as a guiding agent, can promote the formation of calcite.
The study proves that it is feasible to applying biochemical process driven by microorganism activity for sustainably improving saline soil.

Researchers at DTU have developed a yoghurt bacterium, which can cleave lactose in a costeffective and sustainable manner making it possible to create natural sweetness in yoghurt with less added sugar.
Yoghurt without added sugar is a relatively sour experience. Often fruit or berries are added to improve taste, and sugar or sweeteners are added to increase sweetness. However, consumers are increasingly demanding natural foods with less added sugar.
To meet this demand researchers from DTU National Food Institute have developed a new and natural way to cleave the milk sugar, which relies on safe lactic acid bacteria. The developed lactic acid bacteria create natural sweetness in the yoghurt, thus reducing the need for added sugar.
Lactic acid bacteria with lactase can break down milk sugar
Yoghurt is fermented milk and milk naturally contains around 50 grams sugar (lactose) per liter. Milk sugar
is characterized by its low sweetness, but by breaking down lactose with enzymes, more sweet sugars (glucose and galactose) are released. By breaking down 70% of the lactose in milk, the sweetness can be increased what corresponds to 20 grams per liter of regular sugar.
Commercially available lactase enzymes currently used for breaking down lactose in milk products, are made using microorganisms, which involves, a tedious and costly purification process. Furthermore, transportation from the manufacturer site to the dairy adds to the costs.
With the solution that the DTU researchers have developed, the lactic acid bacteria-based lactase can be grown and used directly at the dairy, and in the milk that ends up being yogurt. In this way the costs for purchasing the lactase and transportation are reduced,
The solution has been tested by a large Danish dairy.
waste and residue streams, for example from used cooking oil. Reusing waste already in circulation instead of fossil fuel-based feedstocks enhances the sustainability of applications made using the Bornewables grades.
The reusable new bottle developed by Borealis and Trexel retains its value over many life cycles thanks to the use of Trexel’s proprietary technology in tandem with Bornewables grades; as a material solution, the new bottle minimises the use of valuable raw materials. Moreover, converters consume less energy in the production process when using the MuCell® technology. The bottle thus helps close the loop on plastics circularity by way of design for recycling, the use of renewable feedstocks, and excellent material performance across multiple life cycles.
“Reuse and recycling are core components of the integrated circular cascade model aligned with our EverMinds platform, which unites committed players across the entire value chain in accelerating the move to plastics circularity,” said Peter Voortmans, Borealis global commercial director consumer products. “This project is an excellent example of how we are working with industry partners to solve the problem of plastic waste while delivering real value to our customers. Combining our polymers and recycling expertise with Trexel’s material processing know-how enables us to re-invent essentials for sustainable living.”
MICP is a cost-effective and environmentally friendly technology to improve quality of saline soil. (File Photo © Unsplash)
Borealis and Trexel, a leading expert in foaming injection and blow moulded parts, announce that they have co-developed a new plastic bottle based on a grade from the Bornewables™ portfolio of polyolefins made using renewable feedstocks derived 100 percent from waste and residue streams.
The lightweight bottle is reusable and fully recyclable. It boasts a significantly lower overall CO2 footprint because it is composed of renewably-sourced feedstock and produced in the foaming process.

The Bornewables Portfolio of circular polyolefins helps reduce the carbon footprint while offering material performance equal to virgin polymers. Using Bornewables grades allows for design freedom and colour flexibility, and helps retain a premium look and feel.
The grades – which are commercially available in Europe – help conserve natural resources because they are derived solely from
Trexel is a global leader in foaming thanks in part to its proprietary MuCell physical (as opposed to chemical) foaming process, which enables greater density reductions, improved mechanical properties, and attractive surface aesthetics.
The larger processing window facilitates its application to a wider range of products. MuCell foamed parts are recyclable and can thus be reintroduced into the polymer stream. The lightweighting benefits of foaming have become particularly compelling as the industry seeks to use less energy in production, minimise the use of materials, and also fulfil growing market demand for more sustainable packaging solutions.
“Having anticipated market demand for more sustainable plastic packaging, we have focused our development resources over the last several years on the circular sphere,” explained David Bernstein, Trexel chairman of the board and interim CEO. “Our foaming solutions for blow moulding and thin-wall packaging enable brand owners and moulders to realise improved sustainability and enhanced product performance while delivering cost savings.”
LyondellBasell together with Rochling Medical, part of Rochling Group, known for producing secure medication packaging, have announced a step forward towards their ambition to advance the circular economy. The companies created eye drop containers made by Rochling Medical using CirculenRenew polymers.

LyondellBasell CirculenRenew polymers offer a variety of polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (HDPE and LDPE) grades that are equivalent to virgin resin quality. LyondellBasell CirculenRenew grades support the use of renewable feedstocks from bio-based sources that are not in competition with food sources.
“We are very proud to work with Röchling Medical on this project. It’s the first time we are supplying CirculenRenew grades for a primary pharmaceutical packaging application. This is an important milestone for us which also supports our ambitious goal of producing and marketing 2 million metric tons of recycled and renewable-based polymers by 2030,” said Mathieu Lecomte, marketing manager at LyondellBasell.
LyondellBasell and Rochling have collaborated closely to find the right grade for Röchling’s eye drop containers. After several trials, the project team has chosen a Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE) not only because of its high purity, which is necessary for pharmaceutical applications, but also because it was ideal for use in blow molding.
“In such a highly regulated environment as the pharmaceutical industry, driving change towards more sustainable solutions for primary packaging is a challenge,” said Grit Pasche, Rochling Group’s global director quality & regulatory affairs. “Therefore, CirculenRenew was the right choice for us. These renewable-based polymers offer the same properties as fossil-based alternatives in terms of product performance.”
This advancement is possible via the principle of mass balancing. The International Sustainability and Carbon Certification (ISCC) Plus certification provides traceability of the renewable content along the supply chain and verifies that the mass balance accounting follows predefined and transparent rules. Customers can use these certificates to verify compliance with sustainability and traceability requirements. As part of an ISCC Plus certified supply chain, pharma customers are able to actively contribute to promoting sustainability and conserving resources, ultimately reducing the CO2 footprint of their products.
This recent project illustrates how value chain collaboration can lead to innovative solutions with sustainability goals in mind. Together, LyondellBasell and Rochling are helping to unlock the circular potential of plastics.


Growing population has definitely led to tremendous growth in the demand for textiles. But today textile is more than just style, colour and design. Amidst changing work environment and demands of modern life, the clothes we wear also needs a transition. Strenuous and long odd-hours of work demand wrinkle-free, odour free fabrics. The adoption of healthy lifestyle calls for sportswear that are sweat-free while being comfortable.
The post COVID era has enforced a new outlook towards hygiene for which clothes need to incorporate anti-bacterial properties to wade off almost every type of infections and viruses. In addition, properties such as water repellent, dust resistance, UV protection etc are also becoming a reality.
Hence, fabrics today need to be multi-functional and serve many purposes. These functional textiles have opened a new vista of applications in diverse field of human life. These wrinkle-free, odour-free, sweat-free properties are not just luxury but has become a necessity.
Many of these applications are highly crucial and these fabrics and materials are going to play an important role in this modern world. This change in attitude towards apparels is also opening up a rejuvenated outlook in textile R&D to see fabrics in a new light.
Textile manufacturing across the globe is moving towards making functional fabrics. Here are some of the ways in which fabrics are becoming more functional in the textile industry:

Odour-resistant: Consumers around the world are paying more attention to health and hygiene. Sweat and odour is a breeding ground for the growth microbes which leads to various skin problems. Many applications like sports-wear, office wear, hospital wear, and professions with heavy duty or long working hours etc, demand for odour and microbe resistant fabrics to keep skin allergy, skin rashes and other dermatological conditions at bay.
Recently, Huntsman Textile Effects and Sciessent entered into a strategic partnership for antimicrobial and odour-control solutions for active wear, outerwear, home textiles and other products with long-lasting protection against microbial growth and odour.
The antimicrobial solution is designed with smart-release technology, that releases active antimicrobial agents when needed. It can be built-in or applied via padding, exhaust or package yarn to any textile. The non-bioactive odour-control solution captures the odour and release them only during laundering making it ideal for sportwear and athleisure wear.
“Huntsman Textile Effects has one of the industry’s most complete end-to-end systems for high-performance protection effects, with a full range of innovative and sustainable protection and comfort technologies from pre-treatment to coloration and finishing,” said Rohit Aggarwal, President of Huntsman Textile Effects.
Anti-Bacterial Textiles: Fabrics have been found to be a vehicle for contamination and transmission of bacteria and viruses. While the pandemic has highlighted the need to wear clean clothes, apparels cannot be kept sterilized at all times especially while on the move.
Taking this into account, Solvay has developed a functional antiviral and antibacterial polyamide textile yarn in its polymeric matrix which eliminates the proliferation of bacteria and inhibits the transmission of viruses on textile items while also giving protection against bacteria and viruses, including influenza, herpesvirus, coronavirus etc. This can be an ideal textile solution not just for daily wear but also for clothes used in hospitals and medical facilities.
Archroma too has several anti-bacterial systems and solutions which are applicable not just in medical textiles but also in segments where the user requires protection from viruses and bacteria in their daily life.
Functional Sportswear and Athleisure: Health and fitness is becoming a part of everyone’s daily life. This has led to the rise in the demand for functional sportswear and athleisure market. Sportswear textile market is under pressure to offer fabrics which are comfortable, functional and sustainable. Many global brands are trying to meet these criteria.
For instance, Solvay’s polyamide 5.6 and 6.6 textile yarns provide intelligent water management and softness that only polyamide microfilaments can provide for sports and leisure wear. Archroma’s Odor Control 2.0 and Hydry 2.0 range too focuses on odour-free sportswear and fashion that is applicable on polyester, cotton and nylon and keep sportswear dry and fresh for longer
Skin Care Textile: A decade earlier, one couldn’t have imagined clothes providing skincare solutions. But this is a reality today. Textile manufacturing is using technology that enables interaction between fabric and skin while using it to give various skin benefits.
For instance, Solvay uses polyamides, polymers and synthetics to impart a variety of critical properties to the textiles. Its polyamide 6.6-based smart yarn, Emana®, creates bioactive apparels for interaction between fabric and skin which improves skin elasticity and reduces the appearance of cellulite. The textile material is also equipped with a far infrared technology that transforms human body heat into skin care benefits due to bioactive minerals embedded in the yarn.
The fabric is used in a range of applications including shapewear, hosiery, socks, sportswear, jeans, etc. Its polyamide 5.6 and 6.6 textile yarns are formulated to give UV protection, antibacterial benefits, biodegradable and bio-based properties and more.
Sustainable Textile: It is not unknown that textile industry is one of the most energy intensive and water intensive industry. Adding to that, textile washing, cleaning and dying process releases a huge amount of pollutants into the environment. The industry is collectively working towards making the manufacturing process more sustainable and environmentally safe. Several companies are working towards this mission.
Solvay has designed its biodegradable polyamide 6.6 yarn in a manner that it quickly decomposes after being disposed and
achieves 96 percent neutralisation of its CO2 emissions with easy recyclability, no harmful decomposition residues and made with safe, raw materials which is free of SVHC substances.
Archroma too has sustainable metal-free* and halogen-free* acid dyes in its Nylosan® S range to dye polyamide and nylon and which usually contain metals. In sportswear manufacturing, creating durable dark colours on nylon is a complex process that uses massive amounts of water and energy. Archroma designed the new system that reduces process time by up to 36 percent, water consumption by up to 64 percent, energy by up to 46 percent, and CO2 emissions by up to 41 percent compared to conventional benchmark process.
“Innovation is a key enabler of the Archroma Way to a sustainable world,” said Mark Dohmen, Head of Competence Center Synthetics. “With the CONSCIOUSLY DEEP system based on the new Nylosan® S navy and black colors we combine all three: safer ingredients free*of metal and halogen, a more efficient process with less water, energy, and greenhouse gas, and enhanced value with a more desirable and durable article.
Irish multinational fashion retailer, Primark, has incorporated Archroma’s EarthColors which uses waste generated by the food and plant industry to create a selection of earthy, neutral and natural fabric dyes. It can be used in menswear, womenswear, kidswear, nightwear and homeware with sustainable cotton or organic cotton.
“We’re really proud of this latest collection, made using organic cotton and cotton from our Primark Sustainable Cotton Programme. It not only looks great but also repurposes something which would have otherwise gone to waste,” said Lynne Walker, Director, Primark Cares.
The role of nano technology in textiles and apparels is gaining importance. Since nano particles have high surface area to volume ratio, it gives increased affinity for fabric giving improved durability, breathability etc.
Nano technology is increasingly being used to bring in many functional elements in textile. For instance, in order to impart wrinkle resistance in fabrics, nano Titanium dioxide and nano silica are used. Nano silver Titanium dioxide and nano Zinc oxide are found to impart sterilizing effect with anti- bacterial property.
Nano size titanium dioxide, zinc oxide, viscous and nano antimony dioxide, tin dioxide have been found to provide anti-static effect, as they are electrically conducting materials causing the effective decay of static charge. Lastly, titanium dioxide, zinc oxide, silicon dioxide and aluminum dioxide are some of the semi-conductors which are used as inorganic UV blockers as these materials in nano size have been found to be highly efficient in absorbing and scattering UV radiation.
Fashion will keep changing, and so will the functionality of clothes. Changes in the environment, workspace, and changes to cope up with the modern world will constantly keep the textile industry on its toes to make better functional fabrics.

Impact of macro-economic changes on the chemical material industry.
Mukund Parthasarathy: The supply chains are globally connected. So, if one part of the world is under threat, the entire value chain gets affected directly or indirectly. Here, we are going through a phase where we are witnessing raw materials cost changes just like everybody else. But, since we work on a global scale, we try to take advantage of that. But there are clear indications on how the macro-economic situations are impacting the chemical industry as well.
Chandrakant Nayak: Uncertain times brings out the best from customer discussions as during these times, customers focus on solutions which will deliver them value, project which are robust enough and can be brought faster to the market. Despite the uncertainty around the global supply chain, cost etc, we see an optimism amongst the customers about India playing a bigger role in these unprecedented times.
If you look globally, India’s GDP growth rate is still looking attractive as compared to many other economies in the world. And that is giving a lot of confidence to customers as they can take advantage of the uncertainty. There is a window of opportunity only if things are innovated and introduced to the market quickly. Few ‘uncertainties’ can be tagged as advantages if used properly.
Advancement in chemical materials, plastic industry in India & Asia Pacific.
Parthasarathy: Most trends are global and are revolving around sustainability and carbon reduction. At Dow, our first goal is ‘Focus on Climate Change’, our second goal is ‘Stop the Waste’ and out third goal is to ‘Close the Loop’. All these goals align with our plastics business.



Our carbon goal is very ambitious. We are taking a 15 percent reduction by 2030 and then targeting for net zero by 2050. We are doing this based on investment in technologies and assets. The best example is our Alberta Asset in Fort Saskatchewan where we intend to create a zero-carbon footprint cracker by capturing the facility’s gases and reutilise them by pumping them into an existing captured carbon pipeline.
We are also looking at the investments in next generation technologies and have also tied up with Shell for e-cracking where we use electricity for cracking instead of fuel. We have also made investments in internal technology development like Fluidized Catalytic Dehydrogenation (FCDh) of propane to propylene. It is a process which scales differently from a capital perspective.
It has 20 percent capital reduction build into it, and is also 20 percent more efficient in terms of carbon reduction. This is a technology that we can look forward to for a huge impact in the commodity chemicals like ammonia, propylene, ethylene etc, which will help scale the impact of the carbon footprint reduction.
Stop the Waste is a value chain goal where we try to understand the entire value chain and create the infrastructure for the waste to be collected. Recently, Dow partnered with Valoregen and Mura technology to help solve the global plastic waste issue with the intention to construct multiple world-scale 120 kilotons (KT) advanced recycling facilities in the U.S. and Europe – collectively adding as much as 600 KT of annual capacity.
The last is the Close the Loop goal, where we ensure that we have circular material throughout the value chain for which we invent upfront in materials development. We believe that the most crucial part of the chain is about creating an article which can be recycled. So, we are looking at design for recyclability and mono-material solutions in our portfolio.
Role of digitalisation in the future development.
Parthasarathy: Digital has many things built into it. One aspect of digital is about automation. However, it does not mean automation for the sake of automation but for the sake of creating an entire R&D loop that allows you to innovate in a much faster and efficient manner. For this, we have invested in high throughput for product development and application development which helps to shorten the innovation cycle which create value for the customers and bring solutions faster to market.
On the other hand, during the COVID pandemic, we have used digital solutions to collaborate with our customers remotely so that we can innovate in collaboration with them while they are distant from us due to pandemic protocols. Today, digital is a way of doing work rather than just a standalone entity. Digital will become a key stake for doing good business.
Nayak: Today, digital is not limited to certain parts of a business. We are talking about manufacturing 4.0 in which digital has become the core of any business. It is a game-changer today. Earlier various processes which was done through human intervention, is now becoming digital making the whole process faster, safer, effective and intelligent. In functionmanufacturing, marketing and product development and innovation, digital has made a wide range of development making the process easy.
During the COVID times, when physical presence was not possible in the lab, AI was relied upon for the formulation development which could predict 90 percent of the performance of the formulation. Earlier, one had to run those experiments manually but now things have changed.
Also, earlier, getting global experts in India to drive certain projects was hard. Now through digital tools, we can do it without them visiting India. The technical expert can be anywhere in the world, but the problems of the customers could be solved quickly in real time. This has brought a lot of agility in our solutions.
Siddhartha Ghosal: During the COVID times, when physical presence was not possible in the lab, artificial intelligence was relied upon for the formulation development which could predict 90 percent of the performance of the formulation. Earlier, one had to run those experiments manually but now they have evolved with advancement of digital technology.
Nayak: DITC is helping us go beyond copy paste. Globally, we have knowledge about many applications, products, and solutions. But those may not be the perfect solution when it comes to customers in India in terms of competitiveness, machine capacity or their ability to use the material to the same level of expertise.
There is a lot of customisation needed to make sure that our customers in India with all the limitations and capability gap can still bring their application and innovation to the customers. So, DITC really works on connecting global knowledge to local customers requirement in India by bridging that gap. That helps us to bring global applications to India in a localised form.
Ghosal: At DITC we work on different application segments. The role of DITC is that when a concept is launched globally, we find ways to see how the concept can be adopted and applied to different applications. For
instance, in textile, we look at ways in which a technology can be applied in segments such as fabrics, fiber processes etc. We are working extensively with big textile brands to see where these innovations can be implemented. Looking at customer preferences, we are also working in other areas wherein we have developed some low viscosity polyethylene glycols. We are also researching on oil soluble polymers which can be turned into lubricants that can give higher friction reduction in automotives and provide reduction in fuel consumption, at the same time giving better milage. These are few of the examples in the areas of sustainability that we are looking into. For our research activities we have filed 20 to 25 plus patents which are on the way towards the approval process.
Sustainability initiatives to be more competitive at a global level.
Nayak: Different industries have different focus areas when we talk about sustainability. It is very important to understand what the industry really means by the word sustainability. Plastic circularity in textile industry will take things in different direction. At Dow we have diverse capability in sustainability solution, and with advanced methods, we can provide the best solutions- be it circularity, water conservation, energy conservation or reduction in the material usage, we need to find ways to deliver the best to our customers.
Parthasarathy: Also, you might have a solution to reduce the carbon footprint. However, are you taking holistic goals to create a solution that meets most of the criteria. If you only look at one portion of the equation, you will probably end up with the wrong answer. At Dow, we try to make holistic sustainable solutions.
Nayak: When we talk about sustainability in the plastic waste space, India has a different problem. We don’t have a very good collection system for the waste. That is an area where a lot of awareness and work is needed which is not required in some other parts of the world. There, they are focusing on developing technologies for up-cycling or advanced re-cycling. It is very important to understand the value chain here and bring the focus on where we can make maximum investment.
Nayak: The Indian market is a bright and innovative market, and this is a globally accepted fact! While the performance expectations from India are very high, so is the expectations on cost innovation. It is a challenge for us to have disruptive innovations and break our own limits. This helps us to think out of the box when we design products, find solutions and formulations.
We innovate without compromising sustainability, safety or the key performance criteria of the product. We aim to deliver solutions that customers can take to the market and become successful. Forcing a product in the market won’t work as the product won’t survive. Hence, customisation is the key.
Nayak: Government plays a key role when we talk about improving the standards and bringing in control over sustainability. There will be learning curves for the government as well as for the industry. The good news is that both the stakeholders want to understand the problems and find the solutions. The government wants to understand the practical challenges of implementing new products and not to rush to conclusion without understanding the finer details.
So, the industry and government collectively need to work together and have a road map on how to reach those goals in a phased manner. We need to upgrade but also need to understand that it should not create any barrier to anyone. One cannot forget that we are still dependent on many imported materials. If we come up with a complex process, it will affect the downstream industry. It is very important to understand the practical challenges and hence a phased approach is always encouraged.

DowIndia held the third edition of its flagship event, Innovation Day 2022, in Navi, Mumbai. Global and local leaders convened to ‘imagine, innovate, and sustain’ the development of meaningful products and solutions for their businesses which ultimately serve the consumer markets.
As the world pivots in the post-pandemic era, from recovery to the reopening of economies, most companies have observed a profound impact the lockdown has had on people’s lives and work. Innovation has been the key driving force, helping us choose alternatives and solutions for a more sustainable planet.
Being a materials science company, Dow India is placed at the beginning of several product lifecycle chains and supply chains. Harnessing the innovation capability in collaboration with key customers is crucial for designing the next category of products that are far superior in performance and sustainability.

Dr. A.N. Sreeram, senior vice president, Research & Development, and chief technology officer for Dow, shared the highlights of how the company has spear-headed innovation and digitalization to deliver products to our customers that are simultaneously more sustainable and better performing. Talking about the organization, Sreeram said, “Our goal from a technology and innovation standpoint is to always have a seat at the design table amongst our key customers and value chain leaders. Our world is changing so rapidly, we cannot precisely predict the future. The one constant, however, is that all humans are continually trying to make their lives and the world around us better and want to be able to do it safely and responsibly. What we can focus on is that products and solutions deliver differentiation and value for our customers, while using fewer resources and lowering collective and individual carbon footprint.”
He added, “Events like Innovation Day provide an opportunity for immersive discussions with customers and are imperative for collaboration. It reinforces our commitment to serving them better.”
Furthermore, Chandrakant Nayak, CEO, Dow India shared, “Through our materials science expertise and collaboration with our partners, we are committed to bringing innovation under one platform for developing solutions for a sustainable future. Innovation cuts across the realms of processes, products, business models, and solutions for us at Dow. In India, we are witnessing a convergence of local demands with an enhanced focus on manufacturing, and India plays a key role in the global supply chain. I believe this trend will benefit the chemical industry significantly, and we see merit in coming together to co-create sustainable solutions for India and the subcontinent”.
The industry leaders participated in panel discussions circling focus on Digitalization - driving innovation and Sustainability- Reuse, recycle and recover. Digitalization has undoubtedly transformed the entire value chain, helping companies drive efficiencies and serve customers in real-time. Sustainability is a path achievable by collaborating and leveraging expertise across the industry. This collaboration will fuel the creation of the most value for society and the planet.



The dyes & pigments market was valued at over $29,000 million in 2021 and is projected to register a CAGR of greater than 4.5 percent during the forecast period 2022-2027.
Due to the COVID-19 outbreak, nationwide lockdown around the globe, disruption in manufacturing activities and supply chains, production halts, and labor unavailability have negatively impacted the dyes and pigment market. However, the conditions started recovering in 2021, which will likely restore the market’s growth trajectory during the forecast period.
Over the medium term, growing demand from the paints & coatings industry of Asia-Pacific and increasing demand from the textile industry are expected to boost the market. On the flip side, environmental concerns regarding the use of dyes & pigments are hindering the market growth. Asia-Pacific region is expected to dominate the global market, with the largest consumption from China and India.
Dyes & pigments are substances used to impart color to a material. The term colorant is often used for both dyes (also called dyestuffs) and pigments. The significant difference between dyes & pigments is particle size. Dyes are much finer than pigments.
Pigments & dyes are the key raw materials for various end-user industries, including paints and coatings, textile, and plastic. The dyes & pigments market is segmented by type, end-user industry, and geography. By type, the market is segmented into dye & pigment. By end-user industry, the market is segmented into paints & coatings, textile, printing inks, plastics, and other end-user industries.
Paints & coatings account for the largest share of the market and are estimated to be the largest and fastest-growing end-user industry.
Architectural and decorative coatings account for the largest consumption of pigments in their production. Thus, rising construction and infrastructure activities in Asia-Pacific are the primary driver for the dye & pigment market.
Various expansions in the paints & coatings industry will augment the pigment markets in the coming years. For reference, in November 2021, Asian Paints announced plans to invest $127 million in the Gujarat plant, India, in the expansion of paints manufacturing capacity from 130,000 kilo liters to 250,000 kilo tons in the next two to three years.
In May 2021, PPG Industries Inc invested $13 million to expand its paints & coatings unit in China, including eight new powder coating production lines and an expanded powder coatings technology center. This expansion will increase the capacity by more than 8,000 metric tons annually.
Furthermore, in the automotive sector, paints & coatings are used in the interior and exterior parts of the vehicle, as they impart protection and appeal to vehicles. They are used in metallic parts and plastic vehicle components of automobiles.
According to the OICA data, global automotive production increased by around 10 percent and reached 57.26 million units in the first nine months of 2021, compared to 52.15 million units in the same period in 2020. The car sales increased by around 29 percent in the first half of 2021 compared to 2020, reaching 44.40 million units, hence driving the market studied in the forecast period.
All the aforementioned factors are expected to drive the global market during the forecast period.
The growth of the textile industry in China and India is rapidly increasing with the availability of a cheap labor force, thus augmenting the dyes & pigments demand. In the global textile market, China holds the largest share of about 40 percent, followed by India with over 5 percent share.
The textile industry of China grew steadily during the first nine months of 2021, with collective profits worth CNY 171.1 billion (approximately $26.80 billion), a 31.7 percent increase year-onyear (YoY), according to the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT).
According to the IBEF, in India, textiles and apparel exports, including handicrafts, totaled $29.8 billion between April and December 2021, up from $21.2 billion during the same period the previous year, thus registering a robust 41 percent increase over the previous year.
In September 2021, Axalta announced that it broke ground for the construction of a state-of-the-art coatings facility in Jilin City, Jilin Province, North China. The 46,000-square-meter new plant will produce mobility coatings to support growing customer demand in China for light vehicles, commercial vehicles, and automotive plastic components.
Furthermore, according to the National Bureau of Statistics of China, about 7.95 million metric tons of plastic products were produced in December 2021, compared with 7.32 million metric tons in November 2021.
According to the Plastics Export Promotion Council (PLEXCONCIL), India’s plastics export increased by 55 percent to $3,417 million (cumulative value) in April to June 2021 as compared to $2,211 million in April-June 2020, thus augmenting the market.
Hence, with the increasing demand from the various end-user industries, like the paints and coatings, textiles, and plastics industries, the demand for dyes & pigments is expected to increase over the forecast period rapidly.
The dyes & pigments market is partially consolidated. In terms of market share, few major players currently dominate the market. Key players (not in any particular order) in the dyes & pigments market include Venator Materials Plc, KRONOS Worldwide Inc, The Chemours Company, HeuBach GmBH and DIC Corporation, among others.

The global ethanol market size is predicted to be $109 billion in 2022 and to expand at a CAGR of 4.6 percent from 2022 to 2032 to reach $170 billion. Previously, the ethanol market witnessed a CAGR of 3.9 percent from 2016 to 2021.
In the medical field, ethanol is frequently utilized to create pharmaceuticals and antidotes that lead to unprecedented growth. New competitors are snatching this once-in-a-lifetime opportunity with a calculated approach to maximize profits. Several studies reveal that the demand for ethanol has actually grown significantly despite numerous troubles. The growth chart is remarkable, with rising demand from the automotive and aviation industries.
The growing interest in using the substance as a biofuel is what is driving up demand for it. Another significant driver of industry expansion is the rise in alcohol consumption. Both natural and
petrochemical feedstock can be used to make ethanol. In the natural process, yeast and natural sugars work together to ferment the sugars.
Due to the surge in shale gas output, ethylene production is rising. It is anticipated that the market will become oversupplied with ethylene as oil production declines and new ethylene production facilities come online. This will result in stagnation in ethanol production.
During the forecast period, it is predicted that the growing usage of ethanol as fuel would accelerate the expansion of the ethanol market. Due to development in the design of compact and high-efficiency motors, the automobile industry has experienced substantial growth in recent years.
However, it has had a lot of issues with reducing air pollution. The mixing of ethanol with gasoline and other extravagant fuel additives handles the issue of increasing automotive air pollution. Since it can be manufactured simply, the demand for ethanol is rising as a biofuel. This makes it a more affordable, clean energy source than gasoline and diesel, which are prepared through a byzantine method. Bioethanol is also used in the automobile sector as an octane booster to lower engine knocking.
Additionally, the aviation sector took advantage of the opportunity to experiment with ethanol blending, which resulted in a significant advance in fuel innovation. Ethanol production is a cost-effective procedure as the raw materials are produced in large quantities globally. It is possible to replace a significant amount of crude oil imported from countries like India, where raw ingredients are generated in abundance.

On the other hand, ethyl alcohol-containing beverages, which were formerly measured as luxury items, are now slowly becoming a need in the majority of households all over the world. Last but not least, government initiatives across the world to assist the production of fuel that is self-sufficient and to encourage the establishment of new businesses have boosted the sales of ethanol during the forecast period.
One of the main obstacles to the expansion of the global ethanol market is the increase in raw material prices which would likely have a detrimental effect on the market expansion. Due to the variation in the production of raw materials, the impact of this limitation is predicted to be moderate during the projected period. Moreover, supply-chain limitation with import restriction is disparaging.
Excessive alcohol intake is bad for the body, especially the liver, which cleans the blood of toxins. As a result, chronic liver disease, often known as cirrhosis of the liver, is more likely to occur among long-term alcohol users. Increasing awareness about these adverse side effects may hinder the sales of ethanol, limiting the market growth.
Government authorities all over the world have made reducing fuel emissions a priority. The usage of ethanol fuel is rising in many countries as part of an effort to lower global carbon emissions. As a result of 10 percent renewable ethanol blending with gasoline, less fossil fuel is needed, which reduces carbon dioxide emissions and aids in the fight against climate change.
Fuel ethanol is produced from readily available, low-cost raw materials such as corn, sugarcane, or grain. These elements are likely to accelerate the expansion of the ethanol market during the anticipated term creating lucrative opportunities.
The prevalence of alcohol-based hand sanitizers has grown as a result of the recent COVID-19 pandemic. The Food and Drug Administration permits the use of ethyl alcohol as an active component in hand sanitizers. So, to get a competitive edge on the world market, the major companies are concentrating on hovering the output of ethanol. Additionally, ethanol vapor inhalation can be used to treat COVID-19, according to findings released by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in September 2020.
with the expansion of the European market. As the temperature rises, gasoline costs have also increased in the European region. The growing demand for ethanol for the development of biofuels is a key factor influencing ethanol pricing. The dynamics of the ethanol market have been significantly impacted by ongoing enduser demand.
Rising fuel consumption and higher industrial activity are expected to cause Asia Pacific to experience the quickest CAGR between 2022 and 2032. Market growth is anticipated to be influenced favorably by the existence of various sectors in the region and consistently expanding economies. India and China are significantly employing ethanol in the pharmaceutical ethanol market in the Asia Pacific region. It is a brand-new renewable energy program that is cleaner and better suited to lower high crude oil and petrochemical imports in developing countries.
Emerging trends in the ethanol industry are being driven by the plethora of startups entering the market.
For instance, LanzaJet, a US startup, creates patented technology to turn waste into bioethanol. From a variety of sources, including municipal solid waste (MSW) and agricultural byproducts, LanzaJet generates sustainable ethanol.
Pushing North America to Emerge as an Opportunity
With an ethanol market share of over 18.6 percent worldwide, North America is the largest regional market. Throughout the predicted years, it is expected that the region is likely to hold the top spot. The main factors contributing to the dominance of North America over the market include the supportive government regulations of the countries for the production of ethanol, deployment of ethanol as a biofuel, and increasing awareness of the necessity to reduce environmental pollution brought on by the use of conventional fuels.
The primary contributor to this region is the US. The US shipped close to 850 million gallons of ethanol to more than 50 countries, according to the Renewable Fuels Association (RFA). The US exports ethanol to many countries, including Canada, India, China and South Korea.
Nearly 16.3 percent of the global ethanol market is held by Europe. Ethanol prices increased during the second quarter of 2022 in line
The ethanol industry players are fiercely competitive, with both foreign and domestic companies fighting for a bigger share of the market. As the demand for ethanol is very high, key players are changing their production strategies. Businesses are focusing on ethanol marketing as a critical strategy for attaining a competitive edge.
• For instance, in January 2022, Wolf Carbon Solutions and Archer Daniels Midland Company declared partnership to accelerate decarbonization of ethanol production.
• In February 2019, Albioma announced the commercial commissioning of Saint-Pierre, Reunion Island’s first peak-load combustion turbine (CT), which runs primarily on bioethanol. The CT uses two types of fuel: bioethanol (80 percent), which is made locally at the Riviere du Mat distillery by distilling sugarcane molasses, and diesel fuel (20 percent), which is used to start the turbine. Source:


Traditional chemicals that are derived from petroleum sources are dominant than bio-based chemicals. However, owing to increasing investment by chemical manufacturers in research & development to establish more efficient process to use bio-resources, bio-chemical industry is expected to gain major traction over the forecast period.
Sustainable manufacturers are shifting their preference towards Bio-chemicals and hence demand for Bio-chemicals is increasing. In order to reduce plastic pollution, leading packaging manufacturers are adopting sustainable strategies to offer environment friendly products.
For instance, in June 2019, Berry Global Group Inc. signed the new Plastic Economy Commitment led by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation to eliminate plastic pollution at its source. The company is developing innovative packaging products to enhance recyclability to create more sustainable packaging in the near future.
Moreover, in October 2019, Henkel manufactured chemically recycled plastic bottles in coordination with Alpha Packaging. This product has been designed as an important step towards circular economy for plastic to reduce plastic pollution. Such activities by key manufacturers operating globally and in Middle East are expected to have positive impact on growth of bio-chemicals market throughout the forecast period.
Raw materials used for the production of the bio-chemicals includes corn, sugarcane, sugar beet, wheat, and cassava, among others. Low costs associated with the production of these raw materials, the overall cost for the production of bio-based chemicals is comparatively low as compared to conventional non-renewable chemicals. These raw materials can also be produced on a large scale without any hindrances.
Owing to stringent regulations on volatile organic substances (VOC’s), bio-based chemicals are higher in demand in the paints & coating industry. In addition, properties such as low corrosion, low toxicity, high solvency power, water miscible, and excellent pigment wetting are expected to fuel demand for bio-chemicals in the paint & coating industries.
Rising demand for natural & safe ingredients from the personal care & cosmetics industry is expected to drive demand for bio-based chemicals in Middle East. Polylactic acid and bio emulsifiers are widely used in the personal care industry for their moisturizing, sebum control, pH adjustment, anti-aging, and antimicrobial properties.
The Middle East Bio-chemicals market was pegged at 1,689.9 Kilo
Tons in 2019, and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 5.3 percent in terms of volume over the forecast period (2019-2027) to reach 2,677.9 Kilo Tons by the end of 2027.

Among application, the food & beverages segment was pegged at 198.8 Kilo Tons in 2018, and is expected to reach 301.4 Kilo Tons by end of 2027, exhibiting a CAGR of 4.8 percent. Bio-based chemicals are used in the manufacturing of food ingredients, which are used in the food processing industry. Growth of the packaged food industry in the Middle East is expected to drive demand for food ingredients, which is further expected to drive demand for bio-based chemicals.
Saudi Arabia accounted for the largest market share of around 40 percent in 2018. The country is expected to retain its dominance throughout the forecast period. In Saudi Arabia, non-biodegradable plastic packaging products were banned in 2017, and according to the new government regulations, plastics needs to be OXObiodegradable.
According to regulations of the Saudi organizations such as Saudi Standards, and Metrology and Quality Organization (SASO), plastic products must be manufactured from approved OXO-biodegradable material. This regulation is applicable for production and import of plastic packaging in Saudi Arabia. Such government policies and regulations are expected to drive demand for bio-based chemicals and materials in the packaging industry in the region.
Major players operating in the Middle East bio-chemicals market include BASF SE, Clariant AG, Evonik Industries AG, Total SA, Cargill Inc, Biolive, Saudi Biodiesel, Saudi Bio-Acid Company, Sain Bag and Neutral Fuels among others.
Increasing collaborations and partnerships between companies to generate bio-energy from biodiesel is expected to propel the biochemical market growth in Middle East. For instance, in March 2019, Cummins Dubai entered into a partnership with Neutral Fuels to generate power from its diesel generator for RIT Tiger Fest Music and Dance. The power is generated from 100 percent biodiesel (B100). This will help Neutral Fuels to expand its portfolio in the Middle East region.
Source: Coherent Market Insights

Specialty chemicals, also known as performance chemicals, help enhance the manufacturing process. These chemicals have extensive applications across different industrial verticals like mining, water, wastewater treatment plants, construction, pharmaceuticals, food additives, & personal care, among others.
Countries across the Middle East rely heavily on oil & gas, ie, leading to rapidly expanding manufacturing plants, industrial units etc, and playing a crucial role in propelling the demand for Specialty Chemicals in the region. Benefits of specialty chemicals, such as enhanced product performance & improved operational efficiency in industries, shall further stimulate their adoption in the coming years.
The Middle East Specialty Chemicals Market is projected to grow at a CAGR of around 5 percent during the forecast period, ie, 202227. The growth of the market is likely to be driven primarily by the several ongoing & upcoming large-scale construction activities across different countries in the region, in line with their aim to bring economic diversification ie, soaring the demand for specialty chemicals.
In addition, the extensive oil & gas production facilities entwined with the mounting focus on boosting agricultural, construction, pharmaceutical, food processing, coatings & paper trading, & transportation, among others, are also playing a crucial role in stimulating the demand for specialty chemicals and thereby driving the market through 2027.
Moreover, massive investments in infrastructure developments across countries like Saudi Arabia, UAE, & Qatar, among others, are also projecting growth opportunities for the leading players to increase their production, enhance product portfolio, and widen their scalability across the region.
Impact of Covid-19 on the market
The advent of Covid-19 in 2020 had a decelerating impact on the Middle East Specialty Chemicals Market. Hindrance in cross-border trade resulted in the unavailability of raw materials, lack of labor, increased demand & supply gaps, and shutdown of production units, which caused massive financial losses for the leading market players. The severely hampered transportation & logistics led to delays in deliveries of pre-produced chemicals. However, with the gradual improvement in the pandemic situation, governments of different countries in the region uplifted the restrictions. It, in turn, encouraged the leading players to introduce new products and increase their production capacities to meet the burgeoning demand for specialty chemicals, expand the visibility in the region, and offer an extensive range of chemicals for customers
• Pharmaceutical
• Mining
• Water & Waste Water Treatment
• Construction Chemicals
• Oilfield chemicals
• Personal Care
• Food Additives
Here, construction chemicals acquired the largest share in the Middle East Specialty Chemicals Market in recent years, and the same trend is likely during the forecast period. It attributes principally to the increasing need to remove large air inclusions at the concrete’s surface across the building & construction sector.
Besides, the growing number of construction projects, coupled with surging foreign direct investments in the construction sector owing to the mounting establishment of multi-national companies & prominent brands and expanding tourism, are anticipated to positively influence the demand for construction chemicals & drive the market through 2027.
Country Landscape
Geographically, the Middle East Specialty Chemicals Market expand across:
• Saudi Arabia
• UAE
• Qatar
• Kuwait
• Oman
Of them all, the UAE is anticipated to remain a prevalent market for Specialty Chemicals during the forecast period. It attributes primarily to rapidly growing developments across industries like oil & gas, construction, mining, and water & wastewater treatment sectors, among others, ie, propelling the demand for specialty chemicals & boosting the market.
Besides, the rapidly increasing greenfield investments are projecting a mounting number of establishments of new structures. It, in turn, is augmenting the need for construction chemicals like demulsifiers, corrosion inhibitors etc, & positively impacting the market growth. Moreover, the increasing influx of migrants, tourism, and events like World Expo 2021 are other crucial aspects projected to stimulate the market growth across the UAE over the coming years.
Under the plan of economic diversification by several countries in the Middle East, governments of these countries are actively participating in the infrastructural developments & investing substantially in sectors like construction, tourism, pharmaceutical, mining, etc. It, in turn, is displaying a growing demand for specialty chemicals in different applications of end-user industries and would generate growth opportunities for the leading players in the Middle East Specialty Chemicals Market through 2027.

Middle East sulfonic acid market witnessed a slight decline during the period 2018 to 2019 on account of economic downfall due to fall in oil prices. However they recovered in 2021 as a result of several large-scale infrastructure projects in the region.
The upsurge in the construction activities in different horizons of commercial and residential spaces entailing the new projects related to hotels, resorts, entertainment centres, shopping malls and the huge influx of FDI in the retail and construction sectors were the key catalyzers for the overall growth of sulfonic acid across the region.
In year 2020, due to COVID-19 pandemic led measures, lockdowns and restriction on international trade resulted in a slight slowdown in the sulfonic acid market due to supply chain disruption and therefore, refraining the growth of sulfonic acid market during the year 2020.
The government initiatives for broaden your horizons of the oil-based economy led to rapid infrastructural growth including growth of construction sector along with residential sector and commercial sector would act as a critical driving force behind the growth of the market in the country during the forecast period 2022 to 2028.

Moreover, escalating FDI and government spending, and growing tourism are some of the factors leading to the growth of the market. Additionally, the burgeoning surfactants sector is also expected to play a motivating role. The growing need for coating and painting of newly developed infrastructure and government facilities would further augment the demand for sulfonic acid in the forthcoming period.
In terms of Applications, Resins segment accounted for the maximum market revenue share in 2021 owing to government’s focus on the infrastructural projects that boosted the demand for architectural and decorative paints and coatings.
In terms of End Users, Construction segment accounted for the maximum market revenue share in 2021 owing to government aim to diversify the economic due to which large scale investment is provided to ongoing infrastructure development projects in Middle East region.
In terms of Countries, Saudi Arabia acquired highest share in the Middle East sulfonic acid market in 2021 in terms of revenue as the kingdom’s plans to develop sea-ports, railway lines, manufacturing facilities and airports, with an aim to increase investment in non-oil sectors.


The global Sodium Hydroxide market is projected to grow from $49.3 billion in 2022 to $61.1 billion by 2027, at a CAGR of 4.4 percent during the forecast period. The booming construction industry, including both residential and non residential infrastructure across the world, is one of the major factors boosting the demand for paints & coatings. The titanium dioxide market is driven by the paints & coatings application in the construction and automotive industries, which is likely to have a positive impact on the sodium hydroxide market.

of calcium carbonate. Since coral produces food and oxyan to the sea creatures, they are vital is our environment. If you all the coral were to die from lack of survivability, then the fish in our ocean will suffer and most likely die.
Increasing demand from the packaging, building & construction, consumer goods, and automotive industries in these countries increases the need for plastics, aluminum, and others used for various applications in these industries. The emerging economies such as China, India, South Korea, Indonesia, Thailand, Taiwan, Mexico, Brazil, and Argentina with the growth in industrialization are expected to drive the sodium hydroxide market during the next five years.
Caustic soda is used to refine raw bauxite into white power alumina that is then smelted to make aluminum. According to the International Aluminium Institute, the global alumina production in March 2021 stood at 11.832 million tonnes, bringing the total output to 34.199 million tonnes in the first quarter of 2021. The production in March reflected a hike of 11.41 percent month-onmonth from 10.620 million tonnes and 7.50 percent in the year from 11.006 million tonnes.
Aluminum is refined from raw bauxite ore in an energy-intensive process that uses a substantial amount of caustic soda (NaOH) as the dissolving agent. Caustic soda is used because it is readily available and cost-effective.
The major end-use industries of aluminum are building & construction, transportation and containers & packaging. In the building and construction industry, aluminum is used to make frames for doors and windows, staircases, heating systems, roofs, furniture, and others. It is also used in the construction of buildings, bridges, roads, and others.
Sodium hydroxide exposed in the atmosphere could be very dangerous since it readily reacts with other chemicals since it is subject to wet deposition. It can readily react with water vapour in the air and produce aerosol or mist which are very corrosive. Concentrated aerosol compounds (silica, asbestos and etc) may result in a number of diseases such as silicosis and black lung when exposed to it since it can severely irritate upper respiratory tracts.
Sodium hydroxide is a very strong base due to the hydroxide anion in its compound. This is considered to be a contaminant if it were to disposed within water. Sodium hydroxide’s primary effect would cause the water’s pH level to raise. If the ocean became too basic it will produce carbonic acid, which will release even more hydrogen ions and making the ocean even more acidic.
The increase of the acidity level of the ocean will cause marine life (such as clams, mussels and etc) to produce weaker shells and will not survive. Coral will also be affected since their skeletons are made
The global chemicals market has been growing at a fairly strong rate recently. In the forecast period, similarly strong growth is expected. According to a research, the global chemicals market was valued is expected to reach a value of $5,334.5 million in 2022. The Commodity chemicals category accounted for 50.5 percent to the total chemical sales followed by specialty chemicals (19.7 percent), agricultural chemicals (8.4 percent) and other (21.5 percent). As company manufactures and sells various chemicals and has its customers worldwide, favorable trends in the global chemicals market provide it with growth opportunities for sodium hydroxide market
Chemical industries in the US and Europe are mature, and their growth is largely influenced by GDP growth. Rapid industrialization, supported by strong demand due to the improving standards of living, significant population base, and available pools of workforces in the Asia Pacific, the Middle East & Africa, and South America, has led companies to establish their facilities in these regions and cater to the regional demand.
Challenges: Highly corrosive nature of caustic soda and compliance with safety standards
Solid sodium is highly corrosive. It reacts with greases and fats which can lead to irreversible damage to any contact point with the body (for example skin or eyes). Depending on the concentration, solutions of sodium hydroxide in water are corrosive, irritating or non irritating and they cause direct local effects at the contact point with the body. Sodium hydroxide is highly corrosive. NaOH can react with moisture from the air and may generate heat as it dissolves. This heat can be enough to cause a fire if it is near flammable materials.
50 percent W/W Solution is the fastest growing segment by grade in the Sodium Hydroxide market.
Based on grade, 50 percent W/W Solution is estimated to be the largest and fastest growing segment of Sodium Hydroxide. This Sodium hydroxide 50 percent w/w aqueous solution is used as a chemical reactant or neutralization agent in various industries such as chemical, pharmaceutical, textile, pulp & paper, metal, and food industries and in soap & detergent manufacturing. It is also used in the manufacture of synthetic fabrics such as rayon and also for manufacturing food products. It is utilized for pH adjustment and for the formation of in situ sodium methylate in bioethanol and biodiesel processing.
Membrane cell is the fastest growing segment by production process in the Sodium Hydroxide market.
Membrane cell is estimated to be the largest segment in the Sodium Hydroxide market during the forecast period. The sodium hydroxide produced by the membrane cell process is most typically brought up as membrane grade. It conjointly contains a growing acceptance as a rayon grade product in all areas outside of rayon fiber production. The membrane cell process has a relatively lower environmental
impact compared to the diaphragm and mercury cell processes. Companies are shifting toward the use of membrane cell technology due to safe raw materials, low electricity consumption, and the production of high-quality caustic soda.
Asia Pacific is estimated to be the largest market for Sodium Hydroxide
Asia Pacific is the largest and fastest growing market for Sodium Hydroxide, followed by North America and Europe. In Asia Pacific, China, India, and Southeast Asia are expected to witness high growth during the forecast period. The growth of the market in the region is led by rapid industrialization, rising demand from various applications, and increasing government spending. Different companies are focusing on these emerging markets and increasing their footprints by setting up manufacturing facilities, distribution centers, and research & development centers
Global Sodium Hydroxide manufacturers are Tata Chemicals Limited (India), Olin Corporation (US), Westlake Corporation (US), Occidental Petroleum Corporation (US), Dow (US), Solvay S.A (Belgium), BASF SE (Germany), Xinjiang Zhongtai Chemical Co. Ltd (China), Akzo Nobel NV (Netherlands), Brenntag North America, Inc (US) and others.


Aiming to spread awareness, clear the air of misconception and delve into the challenges in drug manufacturing, WorldofChemicals.com and Chemical Today organised a virtual conference Solvents Pharmacopeia: Raising Awareness on Ingredients and Compliance on September 29th, 2022.

The pandemic has set in many new normal to follow within our homes, our way of living and the way we see the world. This has been true of the pharmaceuticals industry as well, which has been advertently or otherwise forced to adopt and adapt to new practices while keeping pace with the fast-growing changes and ensuring continuity with lesser disruptions.
Moving forward we are significantly working towards a ‘contactless world’ which is injected with a lot of digitisation to ensure health and safety. As we return to normalcy eventually, some areas will still need a closer look and attention.
One such area is the pharmaceutical industry where there is a lot of scrutiny on the type of solvents used while making a particular drug, whether guidelines are followed and how aware the governing bodies are.
Health and wellbeing have acquired a center stage after the huge
COVID-19 wave. And hence, safety and hyenine is practiced vehemently in the pharma sector while medications are crafted to perfection!
However, factors such as high cost, absence of proper government regulations and rise in unethical practices have led to the rampant use of low purity solvents in the market which can lead to a dangerous drug manufacturing disaster.
For example, Isoproply Alcohol, commonly called IPA which is a vital raw material used in the pharmaceutical sector, has been increasingly used in the manufacturing of disinfectants and hand sanitizers. The demand of IPA sky-rocketed during the recent years. On the other hand, several hand sanitizer manufacturers have mushroomed all over the world to meet the sudden demand.
The pharmaceutical sector is the primary end-user of IPA in India, consuming around 70-75 percentage of the overall IPA available. Most of the IPA and other active pharmaceutical ingredients are used to make several industrial, household compounds and pharmaceutical industry especially in drug formulations and medicines. But the question remains, how to ensure the purity of the solvents used in pharmaceutical formulations.
According to reports, majority of the IPA consumed are nonpharma grade, which fails to meet the various necessary and critical pharmaceutical parameters across the world. In an attempt to cut down on the cost and to create a middle way between high demand and low supply, many manufacturers are using low purity solvents. This has a direct impact on the quality of the pharmaceutical products manufactured, endangering the lives of millions.
Taking cue from the matter, and with an aim to spread awareness, clear the air of misconception and overcome the challenges in drug manufacturing, WorldofChemicals.com and Chemical Today organised a virtual conference- SOLVENTS PHARMACOPEIA: Raising Awareness on Ingredients and Compliance on September 29th, 2022. The event was organized along with Deepak Fertilizer and Petrochemicals Corporation Ltd as the Presenting Partner.
The event had a panel of eminent speakers including Vikas Biyani, Ex - Incharge Joint Commissioner HQ & Controlling Authority Food & Drug Administration Maharashtra State; Rakesh Dhalbisoi, Associate Vice President - Marketing
(Industrial Chemicals) Deepak Fertilizer and Petrochemicals Corporation Limited; Bangarubabu Rongali, Vice President, New Product Governance of Granules India Limited and Dr. KMV Narayana Rao, Associate Vice President, Head - Analytical Development for Aragen Life Sciences Pvt Limited.
The speakers delved deep into the crucial topic and answered several questions during the virtual conference. These experts touched upon various facets of solvents used in pharma manufacturing such as the opportunity for greener solvents in APIs, use of high purity solvents for bulk drugs, intermediates & formulations and Pharmacopeia solvents usage in the Pharmaceutical Industry.
The transition from overcoming challenges to a bright future will depend on how the Indian pharma industry can tap into the short and long-term opportunities in the solvents business. It is quite clear that the time is right for customers, government and the industry to understand and invest in purity of drug manufacturing.
Risk is inevitable and to dodge that risk, India’s pharma companies should improve their processes, focus on discoveries, and use solvents which fall under the Pharmacopeia standards. Embracing the opportunities and risks will only make the future bright and more professional, eventually enhancing the health of citizens.

use of petrochemicals solvents is the key to most of the chemical process but without severe implications on the environment. The idea of ‘green’ solvent will reduce the environmental impact resulting from its use in processes.
Green solvents are environmentally friendly, bio-based, derived from the processing of agricultural crops, alternates to petrochemicals solvents and least expensive. They are 100 percent biodegradable, easy to recycle, noncorrosive, noncarcinogenic and nonozone-depleting.
Green solvents are of three types:
Supercritical fluids which can either be liquid or gas, used in a state above the critical temperature and critical pressure where gases and liquids can coexist.
Aqueous solvents are water based, mixtures, salt solutions and acid solutions.
Ionic liquids which consist solely of ions and have melting points below temperature. These are greener, as they have low vapor pressures. Imidazolium ionic liquids are often used as solvents in liquids- liquid extraction systems.
Factors to be considered while selecting solvents in API manufacturing process include:
Choose solvents and use them properly without making it complicated.
Introduction of Green solvents for a less hazardous industrial future.
Minimise
The recycling and reuse the solvents. It is necessary to know the method of disposal without destroying the future.
Simple alcohols or alkanes (heptane, hexane) are environmentally preferable solvents in comparison to dioxane, acetonitrile acids, formaldehyde, and tetrahydrofuran. Even the framework of the solvents should have recyclability, life cycle management, less emission.
According to studies, Methanol-water or Ethanol-water mixtures are environmentally favourable compared to pure alcohol or propanol-water mixtures.
The pharma industry needs to understand that the use of greener solvents in API manufacturing process is no more a choice, it is a social and environmental commitment. We need to be more careful what we are using and what can be used for the future products so that customers are safe, and the system works smoothly. Balancing is important in this process.
We must go ‘GREEN’ for a great future.
Note: WorldofChemicals.com and Chemical Today organised a virtual conference Solvents Pharmacopeia: Raising Awareness on Ingredients and Compliance on September 29th, 2022, to spread awareness, clear the air of misconception and overcome the challenges in drug manufacturing.


In Aragen, we believe that in every molecule there is a possibility for better health. Our purpose motivates us to drive the success of your program, so that we can together transform hope into better health, be it humans, animals, or plants.
Role of organic solvents:
Organic solvents in pharmaceutical industry are used as reaction media, purification and cleaning of equipment.
Solvent quality will impact the crystallisation process of the materials
Residual solvents are not desirable substances in a final product due to their toxicity levels, different methods are being used for their removal/ reduce the levels.
After drying of the material, analysis shall be performed to check the residual amount of solvent present in the pharmaceutical compounds to control.
Organic solvents are being used as a mobile phase in HPLC and its quality plays a vital role while performing the analysis as well.
Quality and Purity of solvents
Quality/ purity of the solvents is a prime factor, as very large volume used in the manufacturing process of the pharmaceutical compounds.
It is essential that the impurities of the solvents should be minimised, controlled, and eliminated.
Solvent manufactured on commercial scale must contain the lowest possible impurities below to the specification limits.
This would avoid the corresponding issues during synthetic process of the pharmaceutical compounds and to achieve compliance levels in a regulatory environment.
Pharmaceutical companies require supply-chain partnership who can provide uninterrupted supply but also with consistent and reliable quality.
We have two goals:
Protection of the human health and maintenance of environmental integrity against the possible deleterious effects of chemicals resulting from long-term environmental exposure.
Residual solvents frequently used in the production of pharmaceuticals are listed Environmental Health Criteria (EHC) and integrated Risk information System (IRIS).
Regulatory bodies are working to determine the acceptable expose levels and they are IPCS (International programme on Chemical safety), USEPA (United States Environment protest agency) and USFDA (United States Food and Drug administrations).
Residual solvents should not exceed recommended levels expect in exceptional circumstances.
They are unavoidable components in pharmaceuticals production and will often be a part of drug product.
Classification of Solvents:
Class 1- Solvents to be avoided: Known human carcinogens, strongly suspected human carcinogens and environmental hazards.
Class 2- Solvents to be limited: non-genotoxic animal carcinogens or possible causative agents of other irreversible toxicity such as neurotoxicity or teratogenicity.
Class 3- Solvents with low toxic potential- solvents with low toxic potential to man, no health-based exposure limit is needed.
All in all, there are different grades of solvents e.g commercial, reagent (AR), ACS etc. Not only the purity but also the trace level impurities, pose major challenge in the final quality of the pharmaceutical products. Benzene present in commonly used solvents like Methanol, Toluene must be controlled less than 2ppm due to its toxicity. Some of the reaction by-products due to solvents shall be controlled during the manufacturing process. And, carbon tetrachloride in Dichromethane should be controlled at 4 ppm.
Note: WorldofChemicals.com and Chemical Today organised a virtual conference Solvents Pharmacopeia: Raising Awareness on Ingredients and Compliance on September 29th, 2022, to spread awareness, clear the air of misconception and overcome the challenges in drug manufacturing.
Fertilizers and Petrochemicals (DFPCL) is one of the strongest and renowned company known for their knowledge base and experience in Mining Chemicals, Industrial Chemicals and Crop Nutrients.
With 40-years of industrial experience, they are the suppliers of Isopropyl alcohol, nitric acid, and technical ammonium nitrate in India. To have a pan India outreach, strategic plants have been instilled in western, northern and eastern India and constructed port and gas pipeline infrastructure for raw material import. We are the only producer of technical ammonium nitrate and solid ammonium nitrate covering 42 percent domestic pharmacy and 80 percent market capacity in India for pharmacopeia.
Creating a smart and strategic plan, the company worked on it throughout FY22 on :
Technical Ammonium Nitrate: 487 KTPA
Industrial Chemicals: 1,362 KTPA
Crop Nutrition Business: 1,186 KTPA.
DFPCL is one of the reliable IPA suppliers to Indian Pharma Industry. The company commenced its journey with an aim to serve the Indian Pharma Industry diligently. Out of 220-230 KT of IPA, around 70-75 percent is consumed by pharma Industry. Keeping that information in mind DFPCL works towards the “Atmanirbhar Bharat ’initiative.

DFPCL even obtained Drugs manufacturing licence from FDA, confirmation to IP, BP, EP, USP and CP and secured local GMP and working towards ‘WHO GMP’.
Deepak Fertilizers and Petrochemicals (DFPCL) next strategic theme for the next five years is to shift from commodity section to speciality section. However, in whichever section we go, one thing remains constant for us is our customers. They are the core of our business plan, and we intend to provide the best to them. We introduced some strategies which helped both the parties.
The QR Code
Single digital window to enrich experience Digital CDA: Transition to digitisation Hologram seals
Grade wise packaging
A sperate team to answer quarries about the product Hence, these pointers are safe to call that DFPCL is a “one step” certified solution platform.
Note: WorldofChemicals.com and Chemical Today organised a virtual conference Solvents Pharmacopeia: Raising Awareness on Ingredients and Compliance on September 29th, 2022, to spread awareness, clear the air of misconception and overcome the challenges in drug manufacturing.
pharmaceutical industry is constantly searching for new ways to enhance product safety, quality and efficiency.
Usually, bulk drugs, Pharmaceutical active ingredients (API) and pharmaceutical formulations comply with the monogram given in pharmacopeia. To avoid any kind of bottleneck, solvents used in drugs, transportation of the drugs without getting contaminated, technical upgradation, and other factors, it is mandatory to abide by the rules which are mentioned under the pharmacopeia guidelines.
Pharmacopeial standards are based on: Current scientific knowledge that reflects the quality of pharmaceutical substances and FPPs availability.
Transparency throughout the development and revision of monographs.
Supporting regulatory authorities in controlling the quality of pharmaceutical substances.
Pharmacopeial standards are a vital instrument for marketing authorisations market surveillance and free movement and track of medicines amongst regions and countries. There have been many cases in the history where solvent quality has led to many hazards. For instance, the Elixir Sulfanilamide case in the US is a classic example of use of ‘low purity solvents’ which led to a dangerous drug manufacturing disaster.
In the entire value chain, impurity sources, raw materials, excipients, manufacturing process, methods of manufacturing, chemical process, degradation, heavy metals, etc. need to be checked. However, during purification, ligands, catalysts, other materials like filter aids, charcoal, atmospheric contamination, decarbonisation are impurity sources which needs attention.
Hence few legal provisions and technical aspects are introduced to make the process free flowing.
Section 3(b) of the act ‘drug’ includes- all substances intended for use as components of a drug including empty gelatine capsules. Therefore, all excipient used in medicinal products fall under definition of Drugs.
Section 3 (aa) under the Druga and cosmetic act 1940 includes- any article intended for use as component of cometic fall under this category.
Section 18 ( c ) of the drugs and cosmetics act licensing required for manufacturing, distribution and scale of the drugs (API) and mandatory to manufacture in accordance with the condition of license i.e compliance of GMP, GLP and QMS.
Unknown impurities present in commercial/technical grade excipients may not necessarily be detected in pharmacopeial testing. Quality of those products are beyond the scope of analysis. Therefore, few regulations should be followed:
• API and formulations all are required to be manufactured in GMP, GLP approved facility under statutory license and in accordance with license granted.
• Mandatory use of solvents which are manufactured under license provisions should be used more to create ecosystem for health care.
Note: WorldofChemicals.com and Chemical Today organised a virtual conference Solvents Pharmacopeia: Raising Awareness on Ingredients and Compliance on September 29th, 2022, to spread awareness, clear the air of misconception and overcome the challenges in drug manufacturing.


Anew coupling strategy of photocatalytic water oxidation and catalytic wet peroxide oxidation (PhotoCWPO) for efficient organic wastewater treatment has been developed recently.
The joint research group was led by prof. SUN Chenglin, prof. WEI Huangzhao and prof. LI Rengui from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and the study was published in Applied Catalysis B: Environmental.

CWPO technology is a kind of advanced oxidation process for advanced treatment of organic wastewater using hydroxyl radical (·OH), which is generated from hydrogen peroxide oxidation catalyzed by Fe2+. Nevertheless, low utilization efficiency of H2O2 and difficulty in iron ions cycling lead to high cost and indirect energy consumption, which limits its further large-scale application.
In the proposed Photo-CWPO strategy, efficient circulating of Fe3+/Fe2+ ions was achieved through Fe3+ ions reduction by photogenerated electrons, and meanwhile, photogenerated holes were used to degrade organic pollutants.
The researchers used decahedron BiVO4 photocatalyst to realize efficient circulating of Fe3+/Fe2+ ions with selectivity of ~100%, owing to the unique spatial photogenerated charge separation between different facets of the BiVO4 crystal, which inhibited the formation of iron sludge in the traditional CWPO process.
H2O2 species could be generated via a two-hole-involved oxidation process of H2O on {110} facets of decahedron BiVO4 crystals during the Fe3+ reduction process on the {010} facets, which could replenish the H2O2 consumption and fully utilize both photogenerated electrons and holes for degradation of pollutions. This strategy achieved a much higher total organic carbon removal rate in the coupling system than CWPO process.
“The Photo-CWPO strategy could be applied to mineralize various organic pollutants and showed great universality and stability,” said SUN.
“We have applied this strategy for the treatment of wastewater from coal chemical industry, methanol to olefin industry and unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine industry, all of which showed good treatment efficiency,” said WEI.
and fired at a target containing plutonium-244, resulting in the formation of a few flerovium atoms per day.
The formed flerovium atoms recoiled from the target into the gas-filled separator TASCA. In its magnetic field, the formed isotopes, flerovium-288 and flerovium-289, which have lifetimes on the order of a second, were separated from the intense calcium ion beam and from byproducts of the nuclear reaction. They penetrated a thin film, thus entering the chemistry apparatus, where they were stopped in a helium/argon gas mixture.
This gas mixture flushed the atoms into the COMPACT gas chromatography apparatus, where they first came into contact with silicon oxide surfaces. If the bond to silicon oxide was too weak, the atoms were transported further, over gold surfaces — first those kept at room temperature, and then over increasingly colder ones, down to about -160 °C.
An international research team has gained new insights into the chemical properties of the superheavy element flerovium, element 114, that it is the most volatile metal in the periodic table. The research was done at the accelerator facilities of the GSI Helmholtzzentrum fur Schwerionenforschung in Darmstadt.
Flerovium is thus the heaviest element in the periodic table that has been chemically studied. With the results, published in the journal “Frontiers in Chemistry”, GSI confirmed its leading position in the study of the chemistry of superheavy elements and opens new perspectives for the international facility FAIR (Facility for Antiproton and Ion Research), which is currently under construction.
“Exploring the boundaries of the periodic table has been a pillar of the research program at GSI since the beginning and will be so at FAIR in the future. The fact that a few atoms can already be used to explore the first fundamental chemical properties, giving an indication of how larger quantities of these substances would behave, is fascinating and possible thanks to the powerful accelerator facility and the expertise of the worldwide collaboration,” elaborated professor Paolo Giubellino, scientific managing director of GSI and FAIR. “With FAIR, we are bringing the universe into the laboratory and explore the limits of matter, also of the chemical elements.”
The experiments conducted at GSI/FAIR to clarify the chemical nature of flerovium lasted a total of six weeks. For this purpose, four trillion calcium-48 ions were accelerated to ten percent of the speed of light every second by the GSI linear accelerator UNILAC

The surfaces were deposited as a thin coating on special nuclear radiation detectors, which registered individual atoms by spatially resolved detection of the radioactive decay. Since the decay products undergo further radioactive decay after a short lifetime, each atom leaves a characteristic signature of several events from which the presence of a flerovium atom can unambiguously be inferred.
International and interdisciplinary collaboration as the key to understanding
“Our accelerator experiment was complemented by a detailed study of the detector surface in collaboration with several GSI departments as well as the Department of Chemistry and the Institute of Physics at JGU. This has proven to be key to understanding the chemical character of flerovium. As a result, the data from the two earlier experiments are now understandable and compatible with our new conclusions,” said Christoph Dullmann, professor of nuclear chemistry at JGU and head of the research groups at GSI and at the Helmholtz Institute Mainz (HIM), a collaboration between GSI and JGU.
In addition to GSI/FAIR and JGU, the HIM, the University of Liverpool (UK), the University of Lund (Sweden), the University of Jyväskyla (Finland), the University of Oslo (Norway), the Institute of Electron Technology (Poland), the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (USA), the Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics and the Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee (India), the Joint Atomic Energy Agency and the RIKEN Research Center (Japan) as well as the Australian National University (Australia) were involved in the experiment (CP).
Engineersat the University of Illinois Chicago have been awarded over $1 million by the US Department of Energy’s National Alliance for Water Innovation to build a system that selectively removes and destroys poly- and perfluorinated substances, commonly called PFAS from industrial and municipal wastewaters. PFAS, also referred to as “forever chemicals,” are man-made chemicals found in many common materials, and the grant will support the team’s work for three years.
Due to widespread use in industrial settings, fertilizers and commercial products that end up in landfills, PFAS seep into groundwater and drinking water supplies. Unfortunately, these ubiquitous “forever chemicals” do not break down in the body and are linked to harmful health effects in humans and animals. Evidence shows that at low levels the compounds can lead to high cholesterol and cancer and have effects on the reproductive and immune system and thyroid.

The UIC team, led by Brian Chaplin, professor of chemical engineering, will develop a prototype of their system and, at the end of the three-year funding, deploy it for scale-up and pilot testing in California’s Orange County Water District. In the county, frequent droughts mean that the utility is investing in new technology to increase the county’s problematic drinking water supply through water recycling and aquifer recharge.
Chaplin’s system works through a treatment process called reactive electrochemical membrane filtration. As the water passes through the REM system, adsorbents and catalysts on the membrane trap and destroy PFAS, respectively.
With the funding, the UIC team will develop, screen, characterize and optimize efficient electrocatalysts so that the system is successful at removing and, notably, destroying PFAS at high levels with low energy consumption. They will also analyze other systems for comparison and best practices in deploying the technology at a large scale in practical, real-world applications.
“While REM filtration is one of the only ways to destroy PFAS, these systems so far work best in a limited number of controlled conditions. Our challenge is to make these systems work in the environment,” Chaplin said. “When we complete this work, this new technology will be ready to be piloted in the industrial and municipal wastewater sectors, which will help us and other practitioners evaluate its impact on facilitating desalination and recycling of nontraditional water streams.”
Chaplin hopes the development of new catalyst materials will operationalize the system for successful destructive removal of PFAS in under two minutes of contact time and with a conversion rate of less than 10 kilowatt-hours per cubic meter, which is an order of magnitude lower than other destructive technologies.
“PFAS contamination is a widespread problem in our industrial society, and unless we can find successful ways to destroy these forever chemicals, the potential adverse health effects will continue to grow as the substances accumulate in the environment,” Chaplin said.
Working with Chaplin on the project are Sangil Kim, associate professor of chemical engineering; Ahmed Abokifa, assistant professor of civil, materials and environmental engineering; and scientists from Argonne National Laboratory, Purdue University, and other industrial collaborators, who also received funding for the project.
PFAS are man-made chemicals found in many common materials, and the grant will support the team’s work for three years.
structure is a double helix that forms when two complementary strands connect. When the sequence of bases (the four building blocks of DNA) in the individual strands match up, hydrogen bonds form between complementary bases, firmly linking the strands together.
Using that behavior for catalyst immobilization involves two steps. First, the researchers attach a single strand of DNA to the electrode. Then they attach a complementary strand to the catalyst that is floating in the aqueous solution. When the latter strand gets near the former, the two strands hybridize; they become linked by multiple hydrogen bonds between properly paired bases. As a result, the catalyst is firmly affixed to the electrode by means of two interlocked, self-assembled DNA strands, one connected to the electrode and the other to the catalyst.
DNA is used to direct the immobilization of catalysts for CO2 conversion via hybridization.
Amajor goal in the energy field has been to chemically convert emitted CO2 into valuable chemicals or fuels. But while CO2 is available in abundance, it has not yet been widely used to generate value-added products.
Two years ago, Ariel Furst, the Raymond (1921) and Helen St. Laurent Career Development Professor of Chemical Engineering at MIT, tried to approach the problem differently.
The challenge begins with the first step in the CO2 conversion process. Before being transformed into a useful product, CO2 must be chemically converted into carbon monoxide (CO). That conversion can be encouraged using electrochemistry, but the conversion requires large energy inputs — and even then, CO makes up only a small fraction of the products that are formed.
To explore opportunities for improving this process, Furst and her research group focused on the electrocatalyst. But there’s one stumbling block: The catalyst and the CO2 must meet on the surface of the electrode for the reaction to occur.
The team needed a way to position the small-molecule catalyst firmly and accurately on the electrode and then release it when it degrades. For that task, Furst turned to “programmable molecular Velcro”: deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA.
“DNA has these really cool physical properties as a biomaterial that people don’t often think about,” she said. “DNA can be used as a molecular Velcro that can stick things together with very high precision.”
DNA was used to direct the immobilization of catalysts for CO2 conversion. Her approach depends on a well-understood behavior of DNA called hybridization. The familiar DNA
In their experiments, the researchers first needed to modify single strands of DNA and deposit them on one of the electrodes submerged in the solution inside their electrochemical cell. For this work, the researchers’ focus was on attaching DNA, but the “tethering” chemistry they developed can also be used to attach enzymes.
The team found that when the DNA-linked catalysts were freely dispersed in the solution, they were highly soluble. The DNAlinked catalysts in solution were also more stable than their unmodified counterparts. They didn’t degrade at voltages that caused the unmodified catalysts to degrade.
Furst and her team have now demonstrated that their DNAbased approach combines the advantages of the traditional solid-state catalysts and the newer small-molecule ones. In their experiments, they achieved the highly efficient chemical conversion of CO2 to CO and also were able to control the mix of products formed.

And they believe that their technique should prove scalable: DNA is inexpensive and widely available, and the amount of catalyst required is several orders of magnitude lower when it’s immobilized using DNA.
Based on her work thus far, Furst hypothesizes that the structure and spacing of the small molecules on the electrode may directly impact both catalytic efficiency and product selectivity.
Using DNA to control the precise positioning of her smallmolecule catalysts, she plans to evaluate those impacts and then extrapolate design parameters that can be applied to other classes of energy-conversion catalysts. Ultimately, she hopes to develop a predictive algorithm that researchers can use as they design electrocatalytic systems for a wide variety of applications.
This research was supported by a grant from the MIT Energy Initiative Seed Fund.
From cloudy glasses to deposits in dishwashers – limescale is a ubiquitous problem. An international research collaboration led by two researchers at FAU has investigated which substances could be added to dishwasher detergent to prevent the build-up of limescale. Knowledge about the mechanisms involved can be used to develop more sustainable ingredients. The results have been published in the journal Angewandte Chemie.

Limescale crystals that occur before limescale, such as the milky film that remains on glasses, form when water dries and leaves a solid residue behind. Phosphates are added to dishwasher powder to tackle this problem and prevent these deposits in dishwashers. However, phosphates are also fertilizers and are transported sooner or later to rivers and oceans via the waste water. There, the phosphates make the water rich in nutrients. This allows certain types of algae to reproduce too quickly, leading to an unwanted algae plague, which can in turn lead to other organisms and plants dying en masse.
In order to abstain from using phosphates in future, the researchers from FAU led by Priv. Doz. Dr. Stephan E. Wolf, Chair of Glass and Ceramics, and Prof. Dr. Dork Zahn, Professorship of Theoretical Chemistry, have investigated how phosphates and other common ingredients prevent residues. They have discovered various mechanisms. They were able to demonstrate how exactly the complex mechanisms work and how they perfectly complement each other.
Their work led to a suggestion for a substance that functions very similarly to phosphate, but which seems to be more environmentally friendly. The substance interferes with the deposits, making them more disorganized and preventing organized crystals forming stable packages with calcium and carbonate ions. This either prevents deposits altogether or makes them easier to dissolve due to their disorganized structure.
The team was not only able to determine which mechanisms prevent limescale deposits, but also gain new insights into how lime is formed. “We discovered that the process behind forming lime is much more complex than we imagined,” explained Prof. Dr. Dirk Zahn. The new insights also help us understand the effect organisms have on lime production in nature. Crustaceans, for example, have to be able to control lime production to form their shells and ensure their survival.
“Especially in view of climate change, we must understand what is particularly detrimental to lime-secreting organisms such as corals, shells and marine gastropods if we are to protect them sufficiently,” said Wolf.
In addition to the teams led by Priv.-Doz. Dr. Stephan E. Wolf and Prof. Dr. Dirk Zahn, researchers from the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, the Julich Center for Neutron Science and the company Procter & Gamble were involved in the project.
Studies have found that a “photogalvanic” spin current can be generated similarly using the magnetic fields in electromagnetic waves. However, we currently lack candidate materials and a general mathematical formulation for exploring this phenomenon.
Now, Associate Professor Hiroaki Ishizuka from Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), along with his colleague, has addressed these issues. In their recent breakthrough published in Physical Review Letters, they presented a general formula that can be used to calculate the photogalvanic spin current induced by transverse oscillating magnetic excitations.
They then used this formula to understand how photogalvanic spin currents arise in bilayer chromium (Cr) trihalide compounds, namely chromium triiodide (CrI3) and chromium tribromide (CrBr3).
“Unlike past studies that considered longitudinal oscillating magnetic fields for generating spin currents, our study focuses on transverse oscillating magnetic fields. Based on this, we found that processes involving one magnon (quantum of spin wave excitations) band as well as two magnon bands contribute to the spin current,” elaborated Dr. Ishizuka, speaking of their findings.
Researchers from Tokyo Tech and Chiba University have developed a general formula that can calculate the spin current induced by oscillating magnetic fields in magnetic materials and aid our understanding of novel spintronics functionality. The formula predicts large spin currents arising from a hitherto unknown contribution in antiferromagnetic chromium trihalides, opening doors to material design for novel spintronics devices.
An ingenious approach toward developing low-power, highspeed, and high-density memory devices is based on spintronics, an emerging frontier in technology that harnesses a degree of freedom of electrons known as “spin.” Put simply, electrons, along with their negative charge, possess a “spin” whose orientation can be controlled using magnetic fields.
This is particularly relevant for magnetic insulators, in which the electrons cannot move around, but the “spin” remains controllable. In these materials, the magnetic excitations can give rise to a “spin current,” which forms the basis of spintronics.
Scientists have been looking for efficient methods to generate the spin current. The “photogalvanic effect,” a phenomenon characterized by the generation of dc current from light illumination, is particularly useful in this regard.
Using their formula, the duo found that both CrI3 and CrBr3 showed a large photogalvanic spin current for magnetic excitations corresponding to electromagnetic waves at gigahertz and terahertz frequencies. However, the current only appeared when the spins showed antiferromagnetic ordering, ie, successive spins were antiparallel, as opposed to ferromagnetic ordering (successive spins were parallel).
Moreover, the spin current direction was governed by the orientation of the antiferromagnetic ordering (whether the spins on the first and second layers were arranged up-down or downup). Additionally, they pointed out that, unlike previous findings that attributed the spin current to only the two-magnon process, their formula showed that a large response was, in general, possible with the single magnon process.
These results suggest that bilayer CrI3 and CrBr3 are strong candidates for investigating the mechanism associated with photogalvanic spin current generation. “Our study not only predicts unforeseen contributions to the spin current but also provides a guideline for the design of novel materials driven by the photogalvanic effect of magnetic excitations,” highlighted Dr. Ishizuka.
The work done, could open up new horizons in spintronics.

The chemical industry is under continuous pressure to deliver on tough environmental targets, with businesses looking to improve their sustainability while remaining profitable and competitive.

Plants are becoming larger, more complex and tightly integrated, while engineering departments stretch to bring new products to market quickly and sustainably.
Many chemical businesses have processes that are decades old, and have been optimized over the years to improve reliability and profitability. The challenge now is to develop new processes that are competitive with mature ones, while addressing key sustainability issues such as increasing recyclable content and reducing emissions and waste.
Tools such as data analytics, process simulation and digital twins are helping chemical companies reduce energy and waste, improve circularity and discover more sustainable processes, said Stephen Reynolds, Industry Principal, Chemicals, AVEVA.
A recent AVEVA survey highlighted that sustainability will drive innovation over the next three years, with 85 percent of industry leaders questioned planning to invest in digitalization to work towards meeting their environmental, social and governance (ESG) targets.
Digital transformation can provide a path towards improving sustainability by enabling improved decision-making and realtime performance optimization – leading to reduced energy, waste and emissions. It achieves this through insights derived from the use of technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), process simulation, cloud computing, big data analytics and digital twins which provide information on how systems are running and predict future behavior.
By providing fast and accurate data about what’s happening across the business, and what improvements new processes could offer, it can help reduce operational and maintenance costs by approximately 20 percent and fuel costs by 28 percent, helping organizations take a step closer to reaching their net zero and/or circular economy ESG goals.
Eastman Chemicals, for example, benefited from replacing its legacy documents with a data-centric system that increased collaboration, agility and efficiency. This helped the organization develop new sustainable technologies that enable it to continuously increase the recyclable content in its products.
Process simulation – an important part of your sustainability toolkit
Process simulation is an important part of a chemical company’s digital transformation toolkit, as it enables engineers to quickly analyze complex systems as well as introduce new processes.
The latest simulation technology allows much faster comparison of design scenarios against the desired operating outcomes, from efficiency gains and safety improvements through to carbon impact.
Polymer and plastics producer Covestro has benefited from process simulation in many ways, including improving the energy efficiency of its Germany-based brownfield plants. It used process simulation to directly determine what would be the most energy efficient process and compared this to its current one. This revealed where the inefficiencies lay and opportunities for improvement.
“This was an important tool to improve our energy efficiency and therefore our sustainability, and so we are going to expand this beyond Germany,” said Christian Redepenning, Covestro’s Global Technology Expert, at a recent webinar on process simulation in the chemical industry.
Process simulation can also speed up innovation, enabling organizations to improve the sustainability of their processes and/or products more quickly, Redepenning added.
“Process simulation unlocks the full potential of sustainability and speeds up research through quicker screening…We can screen alternative solvents, operating points – things that without this technology would have taken much longer to develop and use.”
A key feedstock in parts of the chemical industry, current production of hydrogen is carbon intensive. Future demand must be low carbon or no carbon to meet net zero goals, but moving across the carbon spectrum from grey to green is no easy feat.
When you look at how new materials for carbon capture, or new catalysts for hydrogen production are being developed, work begins with companies doing small scale experiments where materials are developed at the microgram or gram level. But when you look at the industrial scale, tons or even megatons are needed, Dawid Hanak, Senior Lecturer at Cranfield University, pointed out.
“Process simulation has a huge impact on this kind of work because when we develop or characterize new materials for carbon capture, for example, we can use process simulation to understand how they will perform at the relevant scale. Once we know whether they have the potential to outperform existing technologies, then we can start testing them at the bench, pilot or demonstration scale.
“Process simulation can help us optimize these technologies and the pilot plants we’re building, but it can also indicate the challenges we’ll face upscaling a technology. Therefore, we can also use it for de-bottlenecking, helping us bring a solution to market faster.”
Take Aker Carbon Capture, for example, its implementation of a single engineering platform helped optimize plant efficiency and sustainability by breaking down data silos and increasing engineering and design efficiency. Using integrated engineering and project execution technologies on the cloud, Aker was able to improve collaboration between teams, resulting in an increase engineering efficiency which allows them to deliver new carbon capture facilities 50 percent faster.
Digitalization drives sustainability Improving circularity and sustainability is a key challenge for the chemical industry, but one it’s embracing with gusto. Whether you’re looking at embracing renewables to power your plants, reducing and recycling waste, or investigating the production of more sustainable raw materials, it’s simple to see that digitalization can help.
The best technology providers can offer guidance and the tools needed to help ensure your company makes the best start on its sustainability journey. From design and planning through to full-scale plant operation, there is a range of solutions that can help enterprises across the chemicals sector reach their sustainability goals.

Quality Control Lab Chemist
Company: LyondellBasell Industries
Date Posted: 18-Oct-2022
Country: Channelview, TX City: UNITED STATES
Chemical Process Engineer Company: PPG Industries, Inc.
Date Posted: 18-Oct-2022 Country: Circleville, OH City: UNITED STATES
Senior Analytical Chemist Company: Pfizer Inc
Date Posted: 18-Oct-2022
Country: Singapore City: SINGAPORE
Project Engineering Manager
Company: Petrofac Limited
Date Posted: 03-Oct-2022 Country: Mumbai City: INDIA
Senior Coating Advisor Company: Hempel A/S
Date Posted: 03-Oct-2022 Country: Sevilla City: SPAIN
Job Description : Assist with recommendations and setting direction for lab HSE, methods, procedures, techniques and technical guidance for Quality Lab through guidance of senior chemist and lab specialist. Work with senior chemists, lab technicians and lab specialists in understanding of laboratory systems, methods, troubleshooting for technical assurance. Develop ability to challenge the status quo in lab practices and methods to provide better response and data to the supporting units and business teams.
Job Description : Monitor the quality of and continuously improves manufacturing methods from raw material receipt to customer delivery to ensure all customer requirements are met. Own the proper operation of reactor systems to ensure compliance with established safety standards, customer requirements and IATF 16949 standards. Lead the scale-up of new products and assures quality systems are in place for process changes to existing products.
Job Description : Perform chemical analysis using analytical instrumentation such as but not limited to UPLC, HPLC, FTIR and GC using existing methods or with modification where required. Set up test methods in the lab as per procedures. Write and maintain accurate, complete and timely data in electronic laboratory notebooks as per good documentation and good laboratory practice. Analyse and interpret test data.
Job Description: Manage and lead a team of Multi-discipline Engineers to coordinate production of engineering deliverables in accordance with the project plan. Manage the interfaces on a project including: multiple disciplines, multiple engineering centers, project controls, procurement, and third party contractors or suppliers. Capable of performing duties with no direct supervision and within agreed schedules and budgets. Support the Project Management Team in planning and identifying technical issues that which could limit progress or impact project budgets.
Job Description : Provide technical advisory and support on all aspects of our technologies, ensuring that our products and systems are used in compliance to our Product Data Sheet, paint specification, relevant technical/industrial standards, working procedures and best painting practice. Provide, lead and identify Service sales opportunities, collaborating with Sales function and Service Sales Partners. Generate accurate company and customer reports and distribute them in a timely manner
Associate QC Chemist Company: Glaxosmithkline Pharmaceuticals Date Posted: 03-Oct-2022
Country: Rockville, MD City: UNITED STATES
Product Development Synthetic Chemist
Company: Momentive Performance Materials Inc
Date Posted: 26-Sep-2022
Country: Tarrytown, NY City: UNITED STATES
Senior Analytical Chemist - HPLC Company: DuluxGroup
Date Posted: 26-Sep-2022
Country: Mount Druitt, NSW City: AUSTRALIA
Senior Research Associate I, Process Development Company: Gilead Sciences, Inc. Date Posted: 26-Sep-2022 Country: Edmonton, AB City: CANADA
Job Description : Conduct and document routine compendial (NF/USP/BP/EP/JP/ACS) and noncompendial raw material testing, in cGMP environment to support manufacturing. Able to seek additional tasks or non-routine functions and accomplish them according to written procedures in compliance with cGMP with general supervision. Overcome minor conflicts with priorities. Consult supervisor with major conflicts of priorities. Work with manager to conduct laboratory investigations related to raw material testing.
Job Description: Independently plan and execute projects with emphasis on synthesis and characterization new materials. Work closely with process team members to assist in scale-up of lab technologies. Prepare invention disclosures and generate IP to keep Momentive at leading edge of innovation. Develop technical expertise to train direct and cross functional team members in the functional area.
Job Description : Maintain and operate HPLC analytical equipment. Ensure testing is conducted in a timely manner and work to enhance analytical testing capability. Investigate customer complaints. Perform instrument qualification (IQ, OQ, PQ) and validation of test methods. Manage deviations or non-conformances, including preparing documentation, conducting product inspection, and performing or supervising rework activities. Support the broader plant to achieve quality targets and continuously improve the quality systems.
Job Description : Plan and safely execute assigned experiments, with increasing independence, to support Process Development activities and project goals. Make key observations during reaction, work-up and isolation. Interpret data effectively, draw conclusions, summarize results and communicate to project and leadership teams. Demonstrate an ability to recognize anomalous or inconsistent results.
Website: http://www.worldofchemicals.com/chemical-jobs.html

Sun Chemical has launched two new bold, chromatic orange effect pigments - Flamenco® Summit Orange and Reflecks™ Dimensions Metallic Orange. The boldest orange on natural mica in the portfolio, Flamenco Summit Orange, is a versatile effect pigment based on patented multilayer technology that provides a rich, clean orange color and bright reflectivity. Flamenco Summit Orange, with its soft shimmering effects, can be used across a variety of cosmetic, skin care and personal care formulations. Reflecks Dimensions Metallic Orange offers eyecatching sparkle and is a borosilicate-based effect pigment with an intense, metallic color. The color can be used globally across all beauty applications.
Contact: Sun Chemical Corporation 35 Waterview Boulevard Parsippany, NJ 07054-1285, USA Tel: +1 708 236 3779 Email: heather.buchholz@sunchemical.com Web: www.sunchemical.com


WithVitralit ® UD 8050 MV F, Panacol has another adhesive system in its range that is certified for use in the medical industry. In addition to its primary curing – UV crosslinking – this adhesive offers secondary moisture postcrosslinking. In this way, components in medical devices can be cured reliably and without thermal influence, even if there are shadow zones in component cavities. Two challenges arise, especially when using plastic bonding or adhesive solutions on PCBs and FPCBs in medical applications: Not every plastic is transparent, which makes it difficult to reliably cure UV adhesives. Thermal post-curing is usually used here. However, that is precisely the second limitation, since electronics and plastic can only be thermally loaded to a limited extent. Heat curing is therefore often not an option.
Contact: Panacol-Elosol GmbH Stierstadter Strasse 4 61449 Steinbach, Taunus, Germany Tel: +49 6171 6202 0 Email: info@panacol.de Web: www.panacol.de

SABIC launched four new LNP™ ELCRES™ FST copolymer resins that comply with the European railway standard EN45545 R6-HL 2 for train seating. Designers can benefit from these new material solutions, which not only meet the new regulatory requirements but also provide expanded opportunities to create sleek seating designs. Compared to thermosets and aluminum, the new ELCRES resins offer lighter weight and efficient processing without requiring secondary operations. To achieve a seamless aesthetic look in an all-in-one seat unit or a design with a separate back shell without painting, SABIC offers precision color matching for its extrusion grade (LNP ELCRES FST2732E resin) and injection molding grade (LNP ELCRES FST2432 resin).
Contact: ESABIC PO Box 5101, Riyadh 11422, Saudi Arabia Tel: +966 (011) 225 8000 Web: www.sabic.com
Master Bond EP4CL-80Med is a one part, optically clear epoxy developed for use in medical device assembly applications. It withstands repeated sterilization cycles and passes ISO 10993-5 testing for non-cytotoxicity. This product cures at moderate temperatures of around 80-85°C within 60 to 90 minutes and faster at slightly higher temperatures. As a one part, non-premixed and frozen system, it contains no solvents, and has an “unlimited” working life at room temperature. Suitable for bonding, sealing, impregnating, and coating, it provides a high glass transition temperature of 155-160°C and has an extremely low viscosity of 50-150 cps at 25°C. EP4CL80Med, and additionally provides notable strength properties.
Contact: Master Bond Inc 154 Hobart Street Hackensack, NJ 07601 USA
Tel: +1-201-614-5859 Web: www.masterbond.com

In pharmaceutical industry, novel drug discovery and development relies on adequate invitro and invivo data. Drug candidates’ bioavailability, bioequivalence, toxicokinetic, and pharmacokinetic characteristics are assessed using bioanalytical techniques. CROs have evolved into strategic partners to ensure high-quality bio-analytical methods for drug discovery, toxicology studies and clinical trials.
LC–MS/MS has played an incredible role in drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics studies. In an analytical lab, processing and setting up samples account for 75–80 percent of job activity and operational costs.

The purpose of sample preparation is to selectively isolate analytes of interest from a complex sample matrix in a highly concentrated form prior to identification and quantification. All biological samples are subject to matrix interferences, large biomolecules like proteins, enzymes, peptides, and carbohydrates will compete for ionization during MS analysis.
Without sufficient sample cleanup, this may produce data that is inconsistent. Individual test tubes and vials have traditionally been used as sample containers or collection devices for extraction techniques such as protein precipitation (PPT) and liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) in bioanalysis. solid-phase extraction (SPE) has used individual cartridges.
PPT results in a higher background and increased phospholipid interference, which causes ion-suppression, reduced column lifetime, and instrument downtime. The current trend in sample cleanup is to use the solid-phase extraction (SPE) technique. The SPE method includes the steps of conditioning, equilibration, loading, washing of interferences, eluting analytes of interest, evaporating and reconstituting the eluate before the analysis (eg, LC–MS/MS). The evaporation and reconstitution steps not only take time and effort but can also lead to the loss of valuable samples. Therefore, the ability to elute in very small volumes of solvent is desirable to minimize the amount of time required.
Several advances occurred concurrently at this time, resulting in a shift from tubes to microplates as the preferred sample collection format. Microplates intended for SPE applications contain sorbent media in each well. The sorbents are commonly chemically bonded silica or polymer particles and display chemical affinity for certain analytes. The bed mass will influence the solvent and elution volume requirements, as well as the capacity for analyte and matrix components.
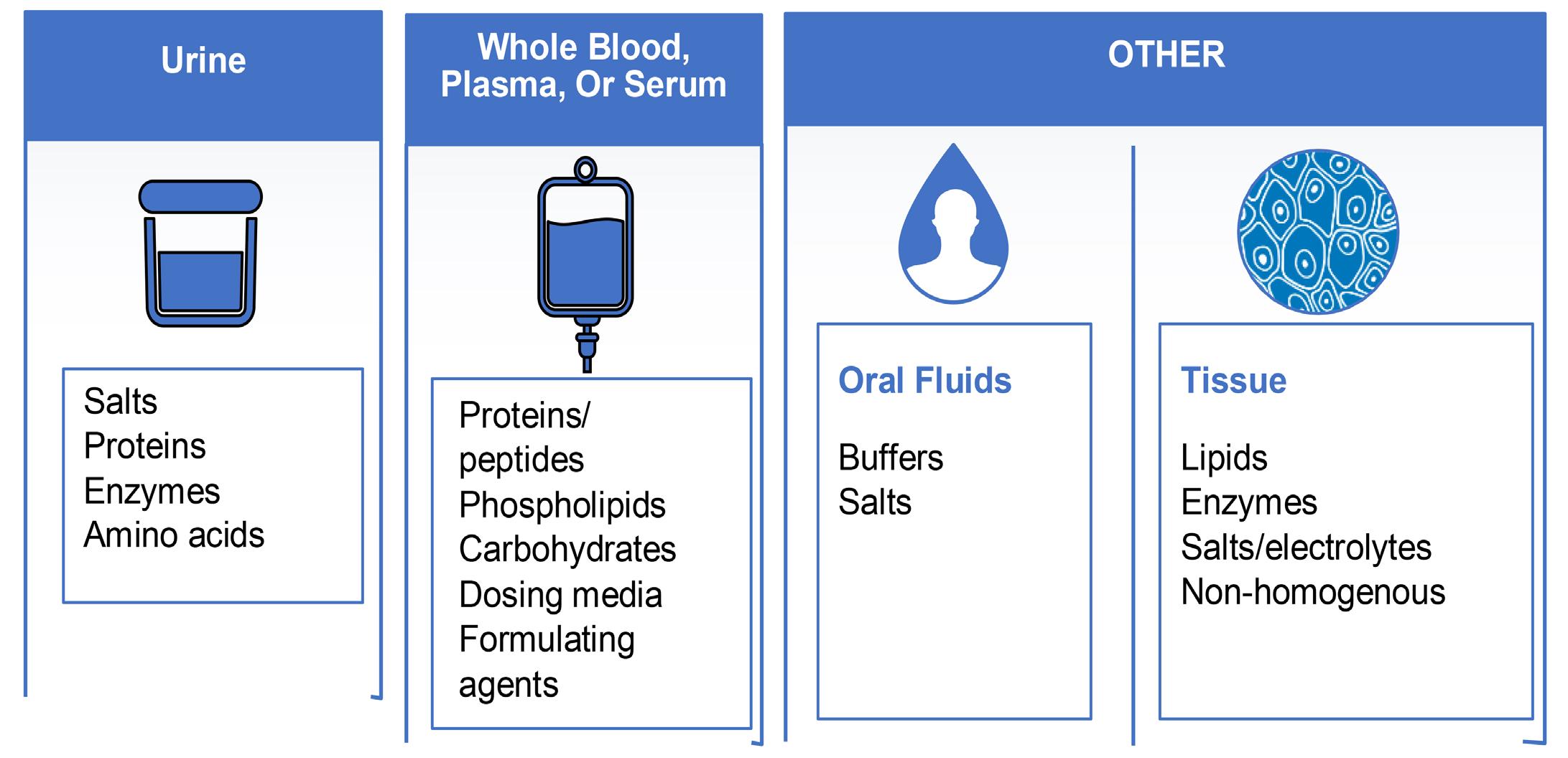
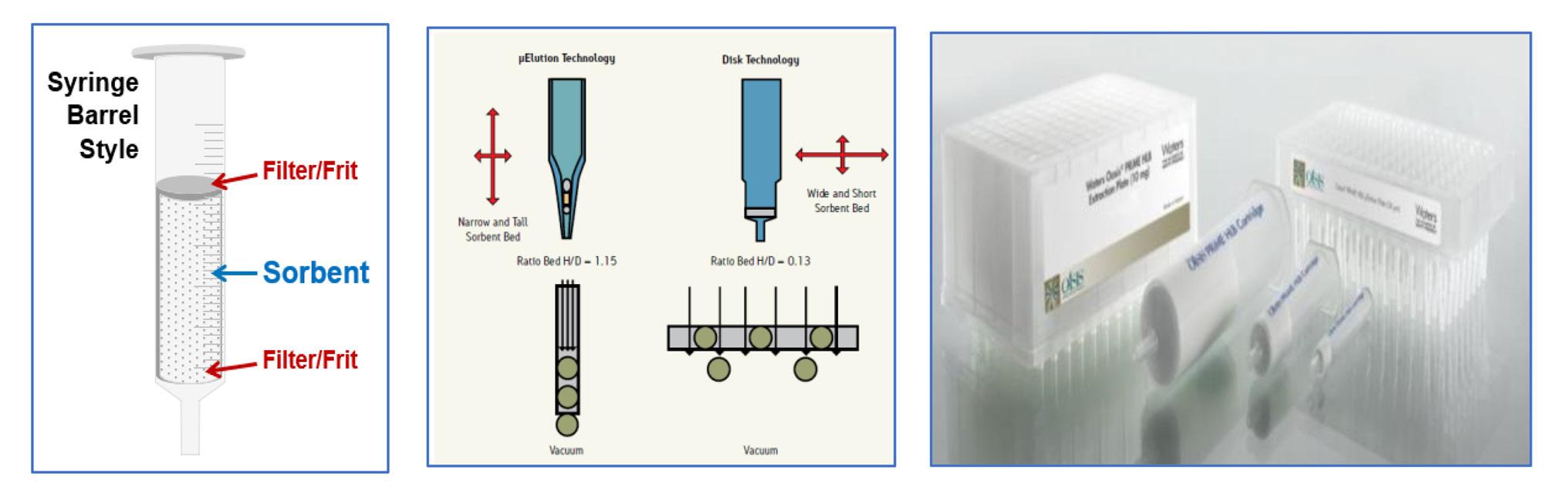
In general, it is suggested to use the smallest bed mass that will provide sufficient capacity for the drug in its sample matrix.
Microplates are 96-well, 8-row by 12-column in a compact format that allows dramatically faster-pipetting throughput. The grid
layout and numbering scheme for each well is uniquely identified by column number and row letter, eg, A1, A2, A3, C5, F8, or H12. The tedious and time-consuming task of individually labeling tubes or vials is now eliminated. The microplate architecture offered the increased proficiency and productivity in sample preparation processes and analyses that were sought.
The time analysts spend in the lab has been greatly reduced by similar sample processing in a 96-well configuration using robotic liquid handling workstations that have been shown to be very reliable and to reduce analyst hands-on time, ensuring their importance in the laboratory for most pipetting tasks.
Using the uElution formation, it is possible to gain as much as a 15X concentration factor over traditional SPE formats which requires larger elution volumes. This reduces the need for drying
down and reconstituting the sample, that will minimizes the adsorption and sample losses. The format also significantly increases throughput and removes a sample handling step, improving reproducibility.

Typical Load: 250-1000 μL of undiluted sample
Minimum elution volume: Typical 200 μL
Larger hold up volume
25-375 μL of undiluted sample (50-700 μL of diluted sample)
Minimum elution volume: 25 μL
Small hold up volume in achieving low elution volumes
Oasis Sorbents are designed to provide exceptionally high loading capacity. Breakthrough will occur when the capacity of the sorbent bed is exceeded. Oasis generic method includes both a centrifugation and evaporation step, which produces the cleanest sample extract possible for protein precipitation.
The Oasis Method enables improved sensitivity by eliminating matrix effect and reducing ion suppression. Oasis µElution Plates achieve superior results compared to protein precipitation in less time.
Applications:
• Ideally suited for small molecules as well as therapeutic peptides and Proteins.
Case study: Sample Enrichment with uElution 96-well plates

Analyte: Risperidone (Conc. 0.5 ng/mL)
Sample prep: 375 µL sample diluted with 375 µL 4% H3PO4 loaded into Oasis® MCX µElution plate
Observations: significant increase in S:N and area counts. This makes the peak easier to identify and provides more robustness in this method b. This could be a great improvement when developing a method to boost confidence.

The new gas analyzer DynamiQ-X NG2210 provides fast and accurate on-line monitoring of natural gas and delivers calorific values for composition control and custody transfer purposes. The DynamiQ-X NG2220 performs the same analysis for natural gas containing hydrogen at concentrations as high as 20 percent using only one carrier gas. The instruments can accommodate two or three gas chromatograph (GC) units working in parallel, each performing a different GC analysis under individually optimized conditions. The GC configuration enables an accurate instrument as well as a very short analysis time of less than a minute.
Contact: Sensirion AG
Laubisruetistrasse 50 8712 Stafa, Switzerland
Tel: +41 44 306 40 00 Email: info@sensirion.com Web: https://sensirion.com
Shimadzu is introducing the LCMS-9050 Q-TOF mass spectrometer. It features one of the fastest and most sensitive quadrupole technologies with TOF architecture to date. Its main characteristics can be summed up in three words: Accuracy, Acceleration and Accommodation of the users’ needs. The LCMS-9050 is a quadrupole Time-of-Flight (Q-TOF) mass spectrometer system that ranks as one of the highest mass accuracy stability levels available. Its proprietary high precision temperature control system inhibits even tiny mass variations caused by external factors so that the system can be used to measure accurate mass values without worrying about mass calibration.

Contact: Shimadzu Europa GmbH
Albert-Hahn-Str. 6-10 D-47269 Duisburg, Germany
Tel: +49 (0)203-7687410 Email: shimadzu@shimadzu.eu Web: www.shimadzu.eu

Worldwide, over 90 million barrels of crude oil, natural gas and refined hydrocarbons are produced, transported, stored, and sold to end customers every day. Any measuring inaccuracy results in enormous shortfalls for suppliers or buyers. This is not the case with Promass Q. With the high-tech Coriolis flowmeter, Promass Q, from Endress+Hauser, is now also available for larger pipe sizes. Furthermore, the implementation of the revolutionary 4-tube technology opens up numerous promising applications in the oil & gas industry – for example, as a highly accurate duty meter for custody transfer and fiscal metering, or as a precision reference device (master meter) for onsite verification measurements.
Contact: Endress+Hauser AG
Kägenstrasse 2 4153 Reinach BL Switzerland Tel: +41 61 715 7700 Email: info@endress.com Web: www.endress.com

AW-Lake offers a new Portable Transit Time Ultrasonic Flow Meter in addition to the full-sized clamp-on version that provides non-contacting flow measurement for the most challenging industrial environments with minimal installation complexity and costs. The hand-held unit is encased in a rugged IP67 housing and works with the same 3 interchangeable transducers as the full-sized meter, which make it suitable for measurements on a wide range of metal and plastic pipe materials. Both Ultrasonic Flow Meters are ideal for measuring the flow rate of clean, non-aerated fluids in full pipes such as water, chemicals, and fuel oils with highly accurate and reliable flow measurement.
Contact: AW-Lake 2440 W. Corporate Preserve Dr. #600 Oak Creek, WI 53154, USA Tel: 414.574.4300 Email: info@aw-lake.com Web: https://aw-lake.com


Asynt introduced the LightSyn Lighthouse – a new photochemical reactor system in their LightSyn range, developed in response to customer demand for higher reaction yields, ease of use, high operational safety, and competitive pricing. Read on to find out more about this breakthrough technology for photochemistry. The LightSyn Lighthouse uses new technology. Using this system, the amount of photons lost over distance is significantly reduced in comparison to that of a more typical photoreactor, therefore maximising the light’s interaction with the sample. The result is faster chemistry and higher
Contact: Asynt
Unit 29 Hall Barn Road Industrial Estate
Isleham, Cambridgeshire, CB7 5RJ, UK Tel: +44 (0)1638 781 709 Email: enquiries@asynt.com Web: www.asynt.com

designed a modular system in the area of dry grinding with the Condux® impact mill series, which can accommodate up to 4 rotor types by means of application-specific housing designs. In addition, the simple housing design makes the mill easier and faster to clean compared to conventional designs. Likewise, a repeatedly expressed customer wish has been met by a narrower gradation of the sizes in the smaller range. Equipped with different grinding tools and stators, a product-optimised mill is now available that can also be used in pressure-shockresistant or inert-gas systems and in cryogenic grinding.
Contact: Erich NETZSCH GmbH & Co. Holding KG
Gebruder-NETZSCH-Straße 19 95100 Selb, Germany Tel: +49 9287 75-0 Email: info@netzsch.com Web: www.netzsch.com
Sierra Instruments announces the release of their new RedyIndustrial® Thermal Mass Flow Meter and Controller for OEMs that features a water resistant housing. Engineers in the biopharmaceutical industry require precise control of the gases used in bioreactors. Sierra’s RedyIndustrial thermal mass flow meter delivers optimized microbial growth that ensures accurate mixing and distribution of the biomass. Food and beverage manufacturers can expect the same precision. The meter also contains no moving parts and is unaffected by upstream temperature and pressure fluctuations. The resulting accuracy and repeatability make them the ultimate mass flow controller for OEM applications.


Contact: Sierra 5 Harris Court Building L Monterey, California 93940 USA Tel: 831-373-0200 Email: sales@sierrainstruments.com Web: www.sierrainstruments.com
BGP series 3-piece high purity ball valves and BRP series hex bar high purity ball valves are designed to meet the requirements of degreasing, low working pressure, high flow rate and bi-directional flow for the clean dry air (CDA) and bulk gas distribution line, which are widely used in specialty gas, semiconductor and chemical industries. The features are it has maximum connection size up to 2” and further various connection types available, including butt weld fittings, tube fittings and face seal fittings. The connection tube in customized length available, the sulfur content of the welded connection material is controlled to 0.003-0.008 percent.
Contact: FITOK GmbH
Sprendlinger Landstr. 115, 63069 Offenbach, Germany Tel: +49 69 8900 4498 Email: info@fitok.com Web: www.fitokgroup.com

