A Guide to Osteoporosis

What is osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a chronic condition that weakens bones over time, making them thinner, more brittle and more likely to break, sometimes from a minor bump or simple fall.
What are the signs of osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a ‘silent’ disease because there are usually no signs and symptoms during the early stages.
However during the later stages, you may experience:
• Back pain
• Loss of height overtime, with a stooped posture usually associated with a rounded hump
• Low trauma fracture of the wrist, spine, hip or other major bones
You are at higher risk of osteoporosis if:
• You have a parent or sibling who has/had osteoporosis/ fractured a hip bone
• You developed early menopause before 45 years old
• You do not take enough calcium and vitamin D
• You are underweight
• You do not exercise regularly or are inactive for long periods
• You smoke or consume alcohol excessively
• You are on prolonged course of steroids (including those found in some traditional medications) or are on certain medications used for treating cancers
How will you know if you have osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is diagnosed either by:
• Presence of a fragility fracture
• Bone Mineral Density (BMD) test. It is painless and non-invasive, and usually takes less than 15 minutes
Osteoporosis Treatment Options
Bisphosphonate
• Alendronate
• Risedronate Works by binding directly to the bone, preventing breakdown of bone material
Bisphosphonate
• Zolendronate
Once a week (Alendronate, Risedronate) Once a month (Risedronate)
Oral
• To take with a full glass of water in the morning on an empty stomach before breakfast.
• Do not lie down after taking the medication for at least half an hour
Once a year
Intravenous
This is injected over 15-30 mins via a cannula through a vein
Denosumab
Teriparatide
Works by reducing bone resorption and increasing bone mass and strength of the bone
Helps to regulate calcium metabolism, promotes the growth of new bone
Once every 6 months
Subcutaneous
This is injected usually into the fatty tissues of the abdomen
Once a day
Subcutaneous
This is injected usually into the fatty tissues of the abdomen
Routine
Name of the medicine What it does
Route
Heartburn, nausea, musculoskeletal aches, diarrhoea, belly ache
Worsening renal function, atypical femoral fracture, osteonecrosis of the jaw
Flu-like symptoms
e.g. fever, malaise, headache, musculoskeletal aches, hypocalcaemia
Musculoskeletal
Side effects Cost (Yearly) Common side effects Less common side effects
$
$$
aches, hypocalcaemia
atypical femoral
osteonecrosis of the jaw $$ Hypercalcemia Osteosacoma $$$$
Cellulitis,
fracture,
Rare but serious complications
Osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) is very rare, affecting between 1 in 10,000 to 1 in 100,000.
To minimise the risk of ONJ:
• Undergo a dental examination before starting drug therapy
• Good oral care and regular dental checkups
• Brush your teeth twice a day
• Use dental floss or interdental brush to clean teeth at least once a day
• Clean the mouth, tongue and teeth after every meal
• Clean the mouth before sleep
• Cut down on sugary food and drinks
Atypical femoral fractures are rare but can happen after long term use of bisphosphonates. Pain in the thigh or groin may be present for several weeks or months before the atypical femoral fracture occurs.
Diet, lifestyle and bone health
Calcium and vitamin D are important for bone, muscle and nerve health.
Tips to increase calcium in your diet:
• Add skimmed milk powder or low-fat milk to soups, smoothies, milkshakes and sauces
• Select breads, cereals and juices that are calcium fortified
• Add cheese to your bread
Tips to get vitamin D:
• Just 15 minutes of daily sunlight exposure is all you need. Sun exposure before 10am and after 3pm is recommended
Add these sources of calcium to your meals
Breakfast Lunch Dinner



Food rich in calcium



2 pieces of canned low-sodium sardines (140g)








1/2 pack of tofu (150g)
1 glass of high calcium low-fat milk (250ml)
1 square piece of taukwa (100ml)
1/4 plate of cooked chye sim
1/4 plate of cooked kai lan
1 glass of high calcium low-fat milk (250ml) / 4 scoops milk powder
1 glass of soybean milk with Healthier Choice Symbol (250ml)
1 slice of low-fat cheese (20g)
1 cup of cooked soy beans (180g)
2 square pieces of taukwa (200g)
1/4 plate of cooked chye sim + 1/4 plate of cooked spinach
1/4 cup of almonds (30g)
Smoking and alcohol are harmful to the bones
The nicotine in cigarettes slows the production of boneforming cells so that they make less bone. Smoking also decreases the absorption of calcium from the diet.
Limit your alcohol consumption to:
• Not more than 3 standard drinks a day (for men)
• Not more than 2 standard drinks a day (for women)
1 standard drink is:

Beer
⅔ small can of beer (220ml)

Stop smoking
or or

Shot
1 nip of spirits (30ml)

Wine
1 glass of wine (100ml)
Physical activity is important
Nutrition alone is not sufficient. Aim for 150 minutes of physical activity weekly for building and maintaining bone mass. Try these 7 easy exercises:
Try these 7 easy exercises
Contact us to find out more about individualised exercise plans by our physiotherapists.
Source: Health Promotion Board
Warm-up Strength Exercises Balance Exercises Flexibility Exercises Cool Down Stationary March with Arm Swing/ Seated March 1 Sit to Stand
Standing Hip Extension 3 Side Leg Raise 4 Single Leg Stand 5 Triceps Stretch 6 Standing Quadriceps Stretch 7
2

Keeping Safe in the Community

Concentrate when walking, avoid multi-tasking such as talking on the mobile phone while walking

Use the lift instead of the escalator if possible
In people with osteoporosis, falls often result in fractures. Thus, reducing the risk of falls is important.

Do not rush. Do not cross the road while the traffic light is blinking

Wait till the bus or train has fully stopped before preparing to stand up to alight
Prevention
Falls = Prevent Fractures
Fall
Prevent
Home Safety Checklist
The home is where you spend most of your time and a few simple steps can make your home safer:



Make sure all rooms are well-lit. Keep a bedside lamp that you can easily switch on at night
Install grab bars for extra support
Bundle up wires and tuck them against the wall



Remove all loose floormats or ensure they are firmly secured with a slip-resistant backing
Keep floor free of clutter and maintain a clear path for walking. Clean all spills and keep your floor dry
Source: Health Promotion Board
Place commonly used items on shelves that can be easily reached. If you need an item from a high cabinet, get someone to help you
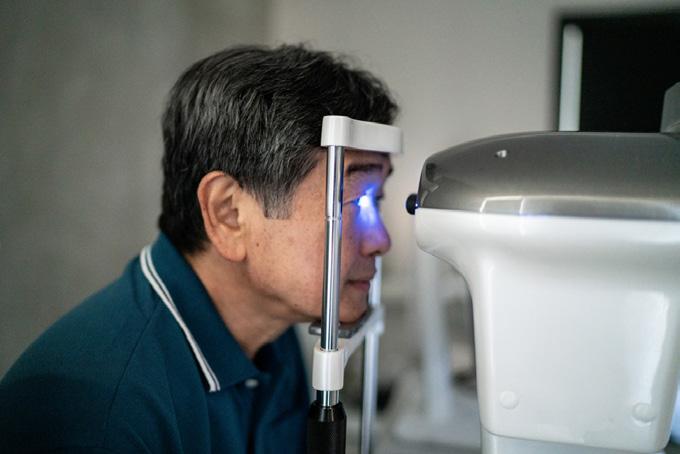
Regular eye vision check
Go for an eye check once a year to check your eyes. This can help ensure you have clear vision, are not wearing glasses with the wrong prescription, or suffering from any eye conditions such as glaucoma or cataracts.
Proper footwear gives sufficient support
• Choose non-slip footwear with buckles, laces or Velcro straps for better grip
• Choose well-fitting shoes
• Avoid heavy shoes
• Remember to replace shoes that are worn out and losing their grip


Regular follow-up


• Regular monitoring of calcium and vitamin D levels in the blood
• Regular monitoring of kidney function
• Repeating bone mineral density scan every 2-3 years to monitor for bone quality improvement
































