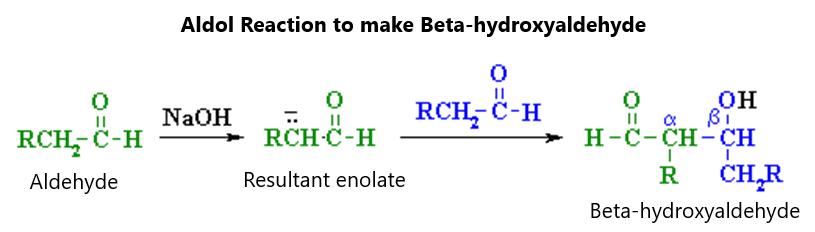
oxygen molecule. There are common names for ethers, with the most obvious being diethyl ether, which is colloquially known as “ether”. Others are named for each side chain plus “ether” at the end of the term (like butyl methyl ether). These involve using the alkanes in alphabetical order. Cyclic ethers or heterocycles have at least one carbon atom replaced by an oxygen atom. In naming these molecules, the prefix “oxa” is used to indicate that oxygen is replacing a carbon atom. They are numbered starting with the oxygen molecule as being “1” and rotating around the ring. An example is 1-oxacyclopentane, which is a 4-carbon, 1oxygen ring. The reference “1” in the name is not truly necessary because the oxygen molecule is automatically going to be number one. When it comes to priority, alcohol has priority over the ether as well as over any halide. The ether also has priority over the halide with the numbering starting with the end that has the side chain at the highest priority. The ring structure with two carbon atoms and an oxygen molecule is called 1-oxirane or oxirane.
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF ETHERS Ethers have oxygen atoms but no hydrogen atom associated with them. This leads to less intermolecular hydrogen bonding between molecules; it means that the boiling points tend to be low—nearly the same as that of alkanes. Boiling point increases with molecular mass but does not increase much because the oxygen alone does not cause an increase in intermolecular bonding. Because ether molecules have an oxygen atom, there will be hydrogen bonding with water molecules. This leads to an ether that has about the same solubility in water as the comparable alcohol. It means that ethanol and dimethyl ether have about the same solubility in water; however, diethyl ether has four carbon atoms associated with it and is nearly insoluble in water.
129