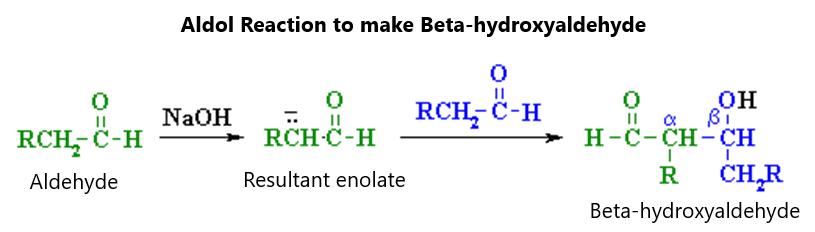
EPOXIDES Epoxides are known as oxiranes, and are three-membered ring structures in which there are two carbon atoms and an oxygen in the middle. There can be side chains on any of the carbon molecules but, of course, there are no side chains on the oxygen molecule. The simplest and most common oxirane is ethylene oxide, which is made by the catalytic oxidation of ethylene with oxygen in air. Further chemical treatment of this molecule will make ethylene glycol, used as antifreeze and used to make polyester and plastic bottles. Figure 68 shows ethylene oxide synthesis:
Figure 68.
More complex epoxides can be made by adding an OH group and a Chlorine atom to an alkene and then adding a strong base. This takes the hydrogen and chloride off of the molecule to create an oxirane. This is shown in figure 69:
Figure 69.
There are other cyclic ethers that have common names that you need to memorize. One of these is furan, which is a five-membered ring that has an oxygen as the fifth member and two double bonds. In common usage, chemicals like 2,5-dimethyltetrahydrofuran, which is made from furan. In determining this molecule, you have to know that this can
132