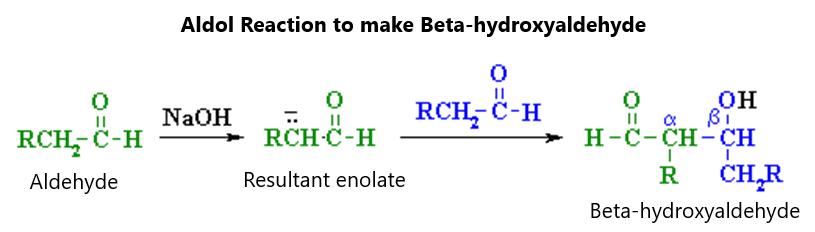
Figure 71.
Figure 71 also shows a cryptand molecule, which is made so that it nearly completely hides the metal ion molecule. Instead of a crown ether, which contains just carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, the cryptand consists of a nitrogen atom as well, which adds to the electronegativity of the center of the molecule along with the oxygen molecule. Both cryptands and crown ethers will help solvate a metal ion because they allow the metal ion to have a place to dissolve.
ESTERS Esters are well-known in nature in that they are responsible for the smells of different organic molecules. The structure of the ester molecule is RCOOR’. These are formed through the mixture of an acid and an alcohol with water as an elimination product. In an earlier chapter, we discussed the oxidation and dehydration of alcohols; this reaction refers to the esterification of alcohols. The naming of esters involves the alkyl chain being the one that contains the carboxylic acid component with the opposite alkane attached as a side chain. The main chain has the “-e” removed and “-oate” added as an ending. Methyl ethanoate is made by the carboxylic acid CH3COOH plus the methyl group attached instead of the hydrogen atom. Instead of ethanoic acid (a carboxylic acid), the methyl group is attached. When an ester group is attached to a ring, the ester is named as a side chain on the ring.
134