KEY TAKEAWAYS •
Enols are basically alkene alcohols that have special reactivity because of their relative instability.
•
Enolates are the conjugate bases of enols and are particularly reactive molecules.
•
Many reactions of aldehydes and ketones involve the relative acidity of the alpha carbon molecule.
•
Acid and base halogenation can occur at the alpha carbon atom.
•
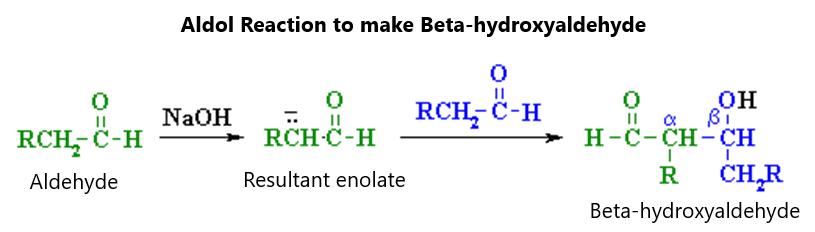
Aldol reactions can occur with ketones and aldehydes, making enals and enones as end products.
•
The various conjugate addition reactions involve the alkyl addition to the beta carbon or conjugate carbon atom of an enone or enal, facilitated by enolate intermediaries.
158