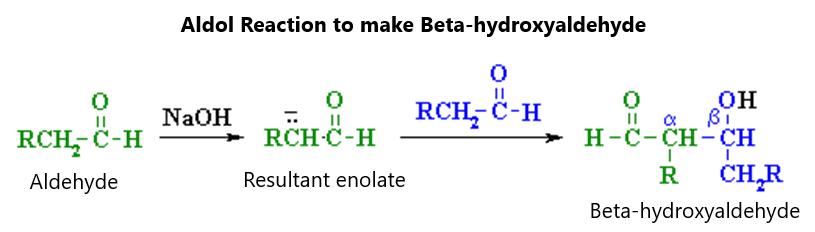
Figure 99.
You do not need to memorize the structures in figure 99 but you do need to have a knowledge of those in figure 98. Many of those seen in aromatic rings will have planar configuration with sp2 hybridization (pi-bonding) or will be in a shallower trigonal pyramidal shape. Those in singular bonded form with three hydrogen atoms or up to three alkyl groups will be in a trigonal pyramidal shape.
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF NITROGENOUS COMPOUNDS The NH bond is polar by nature of the fact that there are electronegative differences between the two atoms. This leads to hydrogen bonding with itself and with other molecules, such as water. What this means is that there will be a higher melting point, high boiling points, and higher water solubility. There will be a higher partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom and a partial negative charge on the nitrogen atom in this bond. The amine bond leads to an amine nitrogen atom that is a Lewis base. The alkyl ammonium has a pKa of about 10, while the aryl ammonium is more acidic, with a pKa of about 5, owing to the delocalization of electrons in the aromatic ring, making the nitrogen atom less likely to donate an electron pair. Because of the electronegativity of the nitrogen atoms in these types of bonds, they can act as bases or nucleophiles at the nitrogen atom. Removal of the proton, leads to the amide bond. The NH group itself is a
178