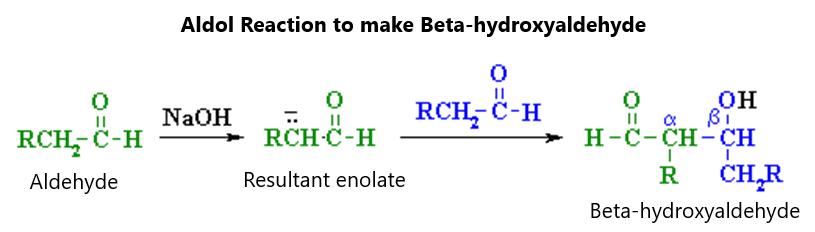
In this excited state (having an unmatched 2s1 and 2p1 orbital), Beryllium could certainly bind with hydrogen in two unmatched orbitals according to this theory. Research, however, has shown that these two bonds are identical. How can this be? Basically, the only way this makes sense is through the process of hybridization. What this involves is combining orbitals that are not equivalent but that are properly oriented to form bonds. These new combinations are called hybrid orbitals because they are made by hybridizing two or more atomic orbitals from the same atom. This leads to a unique hybrid orbital in beryllium that has this energy pattern, as shown in figure 5:
Figure 5.
This obviously leads to the ability of the beryllium to bind with the hydrogen atom in order to make BeH2. This will produce a linear BeH2 molecule. Both promotion and hybridization require an input of energy; however, this is made up for when beryllium bonds with 2 hydrogen atoms. It means that, in situations not associated with beryllium, some compounds are so unstable because they have such a high energy necessary to make the hybrid orbital. This energy is not made up for by the energy recouped in the bonding effort.
CARBON HYBRIDIZATION Carbon has six electrons, with a 2s22p2 configuration. Based on this, one would expect that it would be likely to bond with just two other atoms; we know, on the other hand, that it bonds with four other atoms to make covalent bonds. On the second level, there is one 2s orbital and 3 2p orbitals, which can be hybridized to make four degenerate sp3 10