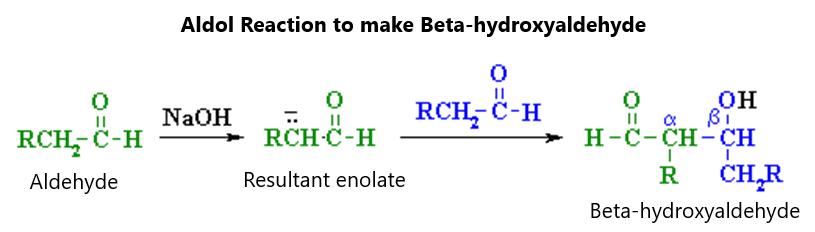
Figure 14.
As you can see, the first CO2 structure is more stable because it has a zero formal charge on all atoms, while the second leaves an unacceptable charge on the two oxygen atoms. In general, the Lewis structure with the set of formal charges closest to zero will be the most stable.
RESONANCE CHEMISTRY A discussion of resonance chemistry can be had by looking at the CO3(2-). This has carbon in the middle, a double bond with one oxygen and a single bond with 2 oxygens and an overall charge of 2-. The big question is this: Which oxygen molecule gets the double bond and which get a single bond? This can be explained in terms of resonance. When more than one Lewis dot structure can be drawn for the same molecule, this is said to have “resonance”. What this means is that, for CO3(2-), the charge is rapidly shifting from one place to another in a sort of blur that gives each CO bond equal stability, so that a third of the time, the double bond will be on one of the three oxygen atoms, so that there is equal sharing of this double bond. Instead of a -1 charge on two of the atoms, there will be a 2/3 charge on each oxygen atom on average. Figure 15 shows the resonance of CO3(2-).
19