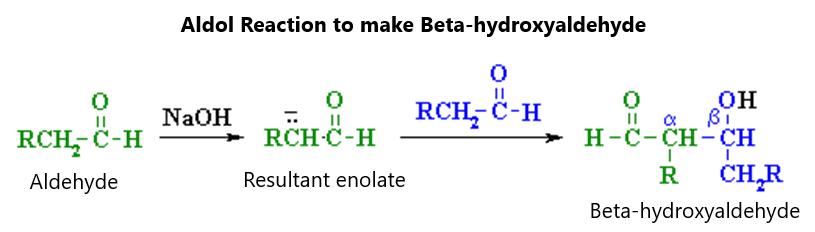
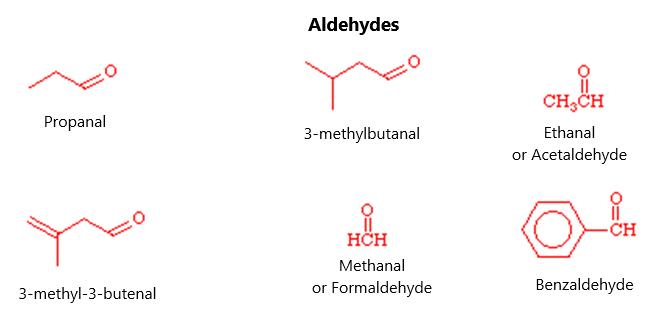
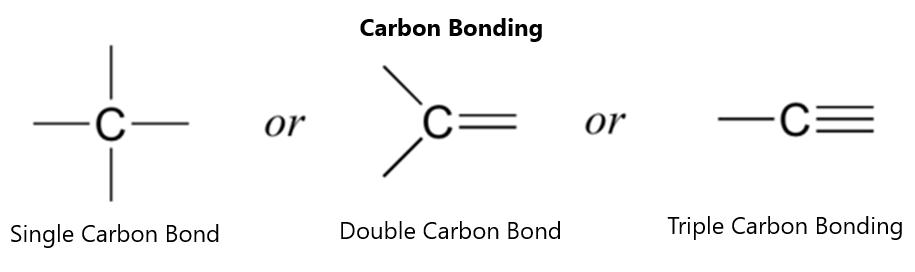
ignitable under 100 degrees Celsius. Other solvents, like methanol, will burn invisibly until they catch other materials on fire. Certain ethers, like tetrahydrofuran and diethyl ether, can form organic peroxides with light and oxygen exposure. These organic peroxides are very explosive. This can happen even with a minimum of light involved. Because they have a high boiling point, they can concentrate during distillation and can form a crystalline substance that will explode if disrupted, such as when turning the jar lid as it precipitates on the lid of a jar. This is a bigger problem in laboratories that do not use up the parent solvent quickly. Ethers need to be stored in an airtight container away from light and air.
SOLVATION This describes the interaction of a solvent with whatever dissolves in it. When the solvent is water, ionized substances interact strongly with the solvent with the characteristics of the solution based on the fact that the solvent and solute are polar. Ions are surrounded with a concentric shell of solvent into “solvation complexes”. There is bond forming (as in ionic bonding), van der Waals forces, and hydrogen bonding that happens in solvation. Solvation in water is known as hydration. Solvation is different from solubility. Solvation is a kinetic process that is quantified by its rate, while solubility helps to quantify the dynamic equilibrium state that is achieved when the rate of precipitation is the same as the rate of dissolution. The dissolution rate is listed in moles per second, while the units for solubility is moles per liter, milligrams per milliliter, etcetera. The different types of bonding that can take place in solvation include hydrogen bonding, ion-dipole connectivity, and the different van der Waals forces, which include dipole-induced dipole interactions, dipole-dipole interactions, and induced dipoleinduced dipole interactions. Exactly which forces take place depend on the nature of the solute and solvent. Less polar solutions of course do not have ion-dipole bonding as a general rule because there are no ions; solvents without dipole moments do not engage much in van der Waals forces.
52