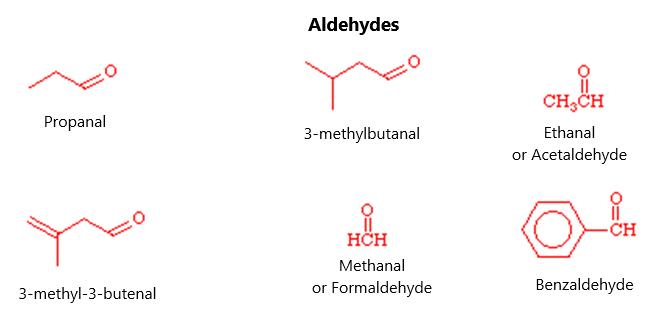
numbered “hydroxy” group in the name of the molecule. This would lead to molecules like 4-hydroxybutanal and 4-hydroxy, 3-methyl-butanal. In the same way, an aldehyde or ketone carbonyl group will take precedence over an alkene functional group. Any carbonyl group will be given the lowest possible number. In order to name the molecule, find the longest chain that contains the alkene and use the “enal” or “enone” ending, depending on whether it is a ketone or an aldehyde. The carbonyl carbon gets the lowest possible number and, because it is an alkene, the designation cis or trans needs to be given. The molecule trans-3-pentenal is an aldehyde with 5 carbon atoms and a double bond between the third or fourth carbon. The CHO fragment is referred to as the formyl fragment, particularly when associated with something that is not an alkane or other carbon group, such as formyl iodide. The acetyl fragment or acety fragment refers to the CH3CO- side chain. This could lead to a molecule called acetyl chloride, which has an acetyl group and a chloride group associated with it.
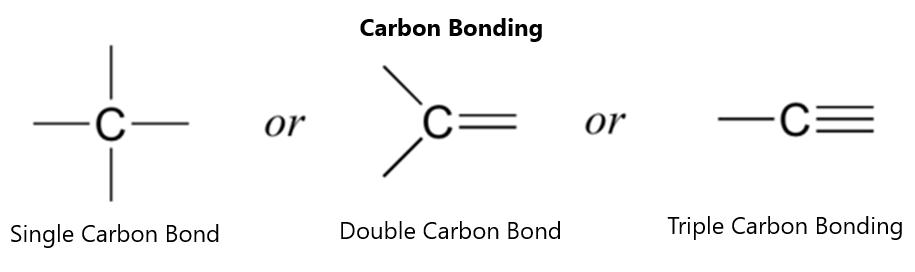
THE CARBONYL GROUP The carbonyl group itself is the CO double-bonded fragment. The carbon and oxygen are bonded with sp2 hybridized bonds. While this is a double bond like the C-C double bond, it is much different in character. The oxygen atom has two lone pairs of electrons associated with it—one in the 2s orbital and the other in the 2p orbital. These lead to electronegativity of the oxygen atom in the carbonyl group, which is very different from the carbon-carbon double bond situation. The double bond is a regular sigma bond and a pi-bond between oxygen and carbon. Figure 42 shows the bonding structure of the carbonyl bond:
80