
04 UNIC ASSEMBLY - NEW LEATHER CHEMICALS - AICC TECHNICAL CONVENTION ISSN 2531-9620 ARSTANNERY1° SUPPLEMENTO AD ARSUTORIA 481LUGLIO 2023POSTE ITALIANE S.p.A.SPEDIZIONE IN A.P.AUT. MBPA/LO-NO/049/A.P./2017 ART.1 COMMA1LO/MI
ARSTANNERY

ERRETRE_FLLI_CARLESSI

ASSOMAC_SERVIZI


Send an e-mail to: arsutoria@edizioniaf.com

to receive a link and read the next issues of ARS TANNERY online for free
ARSTANNERY
Direttore Responsabile
Matteo Pasca
Editorial
Erika Alberti
Emanuela Cecchetti
Alessandro Dorio
Enrico Martinelli
Sara Meneghetti redazione@edizioniaf.com
Digital
Alessandro Capuzzi
Domiziana Desantis
Davide Tufano digital@edizioniaf.com
Pr & Marketing
Mariella Catalano
Mariel Cuba marketing@edizioniaf.com
Advertising
Filippo Crepaldi
Giorgio Gori
Lucio Luiselli
Stefano Migliavacca adv@edizioniaf.com
Operations
Massimo Ledda
Elisa Trasi
Andrea Zampieri operations@edizioniaf.com
Printing
New Everprint neweverprint.it
ARSTANNERY - 1° SUPPLEMENTO AD ARSUTORIA 481 - JULY 2023
Poste Italiane Spa – Spedizione in abbonamento postale – Autorizzazione MBPA/ LO-NO/049/A.P./2017 ART.1 COMMA1 – LO/MI.
Direttore Responsabile Matteo Pasca © Copyright 1967
Tutti i diritti di proprietà artistica e letteraria sono riservati. È assolutamente vietata la riproduzione totale o parziale di articoli, disegni e fotografie, in qualsiasi forma e modo, sia analogico che digitale, anche citandone la fonte, senza espressa autorizzazione della casa editrice. Ogni abuso sarà perseguito a norma di legge
All artwork and copyrights are reserved. Total or partial reproduction is absolutely forbidden of articles, designs and photographs in any form, either analogical or digital, even if stating the source, without the express permission of the publishing house. Any abuse will be punished by law.
ISSN 2531-9620
Le inserzioni pubblicitarie sono pubblicate sotto la totale responsabilità del committente; la casa editrice non si assume alcuna responsabilità per il loro contenuto. Per ogni contestazione si rimanda all’indirizzo del committente pubblicato sulla sua stessa pagina pubblicitaria o, in mancanza, in fondo alla rivista. Adverts are published at the full responsibility of the client; the publishing house does not accept any responsibility for the contents. All notifications must be referred to the advertiser, whose address can be found either printed on his advertising page or, if this is not the case, in the end of the magazine.
Ai sensi dell’articolo 2 comma 2 del Codice di deontologia relativo al trattamento dei dati personali nell’esercizio dell’attività giornalistica, si rende nota l’esistenza di una banca-dati personali di uso redazionale presso la sede di Milano, via Ippolito Nievo 33. Gli interessati potranno rivolgersi al responsabile del trattamento dei dati Ing. Matteo Pasca presso la sede di Milano, via Ippolito Nievo 33, per esercitare i diritti previsti dal D.L.GS. 30 giugno 2003, n.196
Pg. 06 Fabrizio Nuti: "A year of challenges awaits us"
Pg. 08 Leather chemists ask: “Get in our skin”
Pg. 12 European tanners increasingly concerned about the perception of leather
Pg. 16 Prossimapelle's convivial formula hits the mark
Pg. 20 Timeless men's footwear for summer 2024
Pg. 38 Greening of raw hides
Pg. 40 Leather Naturally launches ‘Get the Facts’-icon
Pg. 42 All in China for ACLE 2023
Pg. 44 Application of zeolite based nanocomposites for wastewater remediation: Evaluating newer and environmentally benign approaches
CONTENTS

FABRIZIO NUTI: "A YEAR OF CHALLENGES AWAITS US"


“There are many challenges ahead of us, from the conditions of the general socio-economic context to technological and regulatory ones, but if we were unable to face them and adapt, we would find ourselves in a condition of competitive disadvantage. This absolutely must not happen and I am sure it will not happen ”. With these words from President Fabrizio Nuti, UNIC – Italian Tanneries opened the works of the annual Assembly, held on 30 June in Pozzuoli, in the premises of the Italian Leather Research Institute (SSIP).
THE CURRENT CHALLENGE
From an economic point of view, the 2022 balance drawn up by UNIC shows that "in the end - says Nuti -, we managed overall, as a sector, to limit the damage, closing the year with substantial stability in production volumes and growth in overall value just under 10%. We have therefore not (yet) managed to return to pre-Covid levels". A comment that does not hide the disappointment of having seen, at the end of 2022, "the positive market dynamics that had characterized the first part of the year come to an abrupt end", also due to the "return of an economic opponent who has not we had to face: inflation – continues the UNIC president -. The production drops recorded by the sec-

tor as a whole in the second half of 2022 are also having repercussions in this first part of 2023, highlighting a slowdown that is more or less widespread in almost all of our product destinations". A "change at the top" in the export ranking is very significant. “After more than 30 years, China, with Hong Kong, is no longer the most important foreign destination for our hides, also in terms of the value of the flows. Now in first place we find France and this suggests how our production, our customers, our markets and the elements required by commercial dynamics are partially changing".
THE POLITICAL-INSTITUTIONAL CHALLENGE
A challenge that coincides with a deep concern is that which, for UNIC, concerns the relationship with the institutions. As Nuti points out, “it would be desirable for the institutions, above all, to line up alongside us, at all levels, to defend a strategic sector of Made in Italy. In particular, in Brussels our requests are mostly ignored. It is a problem experienced by “many other productive sectors. It seems that the current European political-institutional framework is developing an idiosyncrasy towards industrial activities in general, which are considered harmful to the environment regardless and are therefore
The annual meeting of UNIC – Italian Tanneries draws up the balance of a 2022 that started well but ended in slow motion with repercussions also on the activity of 2023
6 ARSTANNERY NEWS
subject to technically impossible limits and restrictions, with consequent desertification of the productive fabric, loss of wealth, shift of production to non-EU areas where environmental protections are not comparable". It is time for this inertia to be broken: "we hope that our MEPs will pay great attention to evaluating the decisions to be taken at a European level".
THE SUSTAINABLE CHALLENGE
It is the essential challenge. What Italian tanneries have been facing since time immemorial with strategic, continuous and planned investments. There is a system that seems to bet everything on "formal sustainability" and there are those, like the Italian tannery, that represent an example of "substantial sustainability". This is demonstrated by the fact that "there are not many industries whose raw material derives from waste from another supply chain. In the world, 8 million tons of hides are produced every year resulting from meat processing which, in the absence of us tanners, would have to be burned or disposed of in landfills. This seems to me to represent a good contribution to environmental protection and should guarantee us, already by itself, the right to the green sticker". The Italian tanners, however, went further: "They have put in place a chain of recycling and reuse of their production waste in tanneries that has no equal, treating and reusing them for the cosmetics industry, for the food industry, in agriculture and in building". The result “is a circularity rate of over 99%. And this virtuous process - concludes Nuti - did not begin in recent years, when the race for sustainability became topical, but decades ago, when nobody spoke or even cared about these problems". Making sure that it is understood and understood that "in terms of true sustainability, we have no rivals and we fear no comparisons all over the world" therefore remains the most current challenge for the Italian tannery: the fundamental challenge. A challenge that UNIC shares with the Experimental Station of Pozzuoli, which hosted its Annual Assembly. “We are happy to host the UNIC assembly – commented the SSIP president Graziano Balducci -. Proud to show our team, skills, our laboratories that are available to the entire sector. It is a recognition of our work: an opportunity to relaunch study, research and innovation activities together".
FABRIZIO NUTI:
L’assemblea annuale di UNIC – Concerie Italiane stila il bilancio di un 2022 iniziato bene ma finito al rallentatore con ripercussioni anche sull’attività del 2023
“Le sfide che ci attendono sono tante, dalle condizioni del contesto socioeconomico generale a quelle tecnologiche e normative, ma se non riuscissimo a fronteggiarle e ad adeguarci, ci troveremmo in una condizione di svantaggio competitivo. Ciò non deve assolutamente accadere e sono sicuro non accadrà”. Con queste parole del presidente Fabrizio Nuti, UNIC – Concerie Italiane ha aperto i lavori dell’Assemblea annuale, svoltasi il 30 giugno scorso a Pozzuoli, nel contesto della Stazione Sperimentale Pelli.
LA SFIDA CONGIUNTURALE
Sul piano economico, il bilancio del 2022 elaborato da UNIC, mostra che “alla fine – dice Nuti -, siamo complessivamente riusciti, come settore, a limitare i danni, chiudendo l’anno con una sostanziale stabilità dei volumi di produzione e una crescita del valore complessivo di poco inferiore al 10%. Non siamo quindi (ancora) riusciti a ritornare
ai livelli pre-Covid”. Un commento che non nasconde la delusione di aver visto, a fine 2022, “interrompersi in maniera brusca la dinamica positiva di mercato che aveva caratterizzato la prima parte dell’anno”, anche per colpa del “ritorno di un avversario economico che da tempo non dovevamo affrontare: l’inflazione – continua il presidente UNIC -. I cali di produzione registrati dal settore nel suo complesso nella seconda parte del 2022 stanno avendo ripercussioni anche in questa prima parte del 2023, evidenziando un rallentamento che risulta più o meno diffuso a quasi tutte le nostre destinazioni merceologiche”. Molto significativo un “cambio al vertice” nella classifica dell’export. “Dopo oltre 30 anni, la Cina, con Hong Kong, non è più la destinazione estera più importante per le nostre pelli, anche in termini di valore dei flussi. Ora al primo posto troviamo la Francia e questo fa pensare a come si stanno parzialmente modificando la nostra produzione, la nostra clientela, i nostri mercati e gli elementi richiesti dalle dinamiche commerciali”.
LA SFIDA POLITICO-ISTITUZIONALE
Una sfida che coincide con una profonda preoccupazione è quella che, per UNIC, riguarda il rapporto con le istituzioni. Come sottolinea Nuti, “sarebbe auspicabile che al nostro fianco si schierassero soprattutto le istituzioni, a tutti i livelli, per difendere un settore strategico del made in Italy. In particolare, a Bruxelles le nostre istanze rimangono il più delle volte disattese. È un problema che vivono “molti altri settori produttivi. Sembra che l’attuale quadro politico-istituzionale europeo stia sviluppando un’idiosincrasia verso le attività industriali in generale, ritenute a prescindere dannose per l’ambiente e per questo soggette a limiti e restrizioni impossibili tecnicamente, con conseguente desertificazione del tessuto produttivo, perdita di ricchezza, spostamento della produzione in zone extra-UE dove le tutele ambientali non sono paragonabili”. È ora che questa inerzia venga spezzata: “auspichiamo grande attenzione nel valutare le decisioni da prendere in ambito europeo, da parte dei nostri eurodeputati”.
LA SFIDA SOSTENIBILE
È la sfida essenziale. Quella che le concerie italiane affrontano da tempo immemore con investimenti strategici, continui e programmati. C’è un sistema che sembra puntare tutto su una “sostenibilità formale” e c’è chi, come la conceria italiana, rappresenta un esempio di “sostenibilità sostanziale”. Lo dimostra il fatto che “non sono molte le industrie la cui materia prima deriva da uno scarto di un’altra filiera. Nel mondo, vengono prodotte ogni anno 8 milioni di tonnellate di pelli derivanti dalla lavorazione della carne che, in mancanza di noi conciatori, dovrebbero essere bruciate o smaltite in discariche. Questo mi sembra rappresenti un bel contributo alla salvaguardia dell’ambiente e dovrebbe garantirci, già da solo, il diritto al bollino verde”. I conciatori italiani, però, sono andati oltre: “Hanno messo in campo una filiera di riciclo e riuso dei propri scarti produttivi nelle concerie che non ha eguali, trattandoli e riutilizzandoli per l’industria della cosmetica, per quella alimentare, in agricoltura e in edilizia”. Il risultato “è un tasso di circolarità superiore al 99%. E questo processo virtuoso – conclude Nuti - non è iniziato negli ultimi anni, quando la corsa alla sostenibilità diventava di attualità, ma decenni or sono, quando nessuno parlava e nemmeno si curava di queste problematiche”. Fare in modo che si comprenda e capisca che “sulla vera sostenibilità non abbiamo rivali e non temiamo confronti in tutto il mondo” per la conceria italiana rimane, quindi, la sfida più attuale: la sfida fondamentale. Una sfida che UNIC condivide con la Stazione Sperimentale di Pozzuoli, che ne ha ospitato l’Assemblea Annuale. “Siamo felici di ospitare l’assemblea UNIC – ha commentato il presidente SSIP Graziano Balducci -. Orgogliosi di mostrare la nostra squadra, le competenze, i nostri laboratori che sono a disposizione dell’intero comparto. È un riconoscimento al nostro lavoro: l’occasione per rilanciare insieme le attività di studio, ricerca e innovazione”.
“CI ATTENDE UN ANNO DI SFIDE”
ARSTANNERY 7 NEWS
LEATHER CHEMISTS ASK: “GET IN OUR SKIN”
AICC Conference: an important moment of confrontation between leather chemicals producers, fashion brands and certification platforms to improve collaboration within the supply chain

"Put yourselves in our skin... Leather supply chain actors confront each other" was the title of the Conference organized by the Italian Leather Chemists (AICC) on June 22 in Castelfranco di Sotto (Pisa) as part of the UNPAC Prossimapelle exhibition event. It was an important moment of confrontation between leather chemists and fashion brands, but also managers of platforms such as ZDHC and supply chain associations such as UNIC and ICEC, on topics of extreme topicality such as the proliferation of certifications on the market, the demands for chemical compliance that clash with the insufficiency of chemical analysis methods, issues related to the traceability of hides and much more.
Doing the honors was AICC President Franca Nuti, who moderated a very interesting discussion with much food for thought particularly regarding the demands for restrictions and limits on chemicals. The point of view of brands was represented by Enrico Fatarella, environmental quality product manager of the luxury group LVMH, who pointed out that the compliance demands brands are making-sometimes with limits that are even stricter than current regulations and seemingly excessive-derive from the fact that their products must meet the demands of markets around the world and that the timing of their release on the market requires them to anticipate certain requirements so as not to have to interrupt supplies in the process.
8 ARSTANNERY NEWS
STANDING FRANCA NUTI. FROM LEFT: ENRICO FATARELLA (LVMH), CHIARA MORELLI (PRADA), ELISA GAVAZZI (ZDHC), ANDREA MEUCCI (UNPAC), ELISABETTA SCAGLIA (UNIC) IN PIEDI FRANCA NUTI. DA SINISTRA: ENRICO FATARELLA (LVMH), CHIARA MORELLI (PRADA), ELISA GAVAZZI (ZDHC), ANDREA MEUCCI (UNPAC), ELISABETTA SCAGLIA (UNIC)
Of the same tenor was the speech by Chiara Morelli, sustainability manager of the Prada Group, who reported how leather is the main material for the brand's accessories and how today the market demands maximum transparency and full traceability of the materials used. Morelli recalled the path taken in recent years by fashion brands together with tanneries under ZDHC by overcoming hurdles that at first seemed insurmountable. "Today the world is asking us for true sustainability, which is why we are looking with interest at leather derived from regenerative agriculture," Morelli said.
Elisa Gavazzi, ZDHC director for Southern Europe, spoke about the new strategy that is defining the steps of the roadmap related to chemical compliance between now and 2030. The mission remains the original one from 2011, she said, which is to reduce the fashion industry's chemical footprint. "Back then ZDHC was a group of only 6 brands, today it is a multistakeholder foundation consisting of 320 signatories among fashion houses, suppliers, representative associations." Underlying ZDHC's new strategic plan - hinged on the goal of achieving 100 percent MRSL-compliant chemical formulations - are two guidelines: promoting product circularity and reducing the use of environmental resources (energy, water, etc.) during production. There was much discussion during the conference about the lack of official methods of chemical analysis, which evidently makes it difficult to comply with limits as well as set them. Very important in this regard is the work of the WG6 "Test methods for tannery chemicals" group established in October 2021 at the European Technical Standards Committee CEN/TC 289 "Leather," whose field of action is the standardization of analytical methods for chemicals.
This new group, born out of the Italian request to preside over this important issue, will have to fill the lack of standardized methods in this area, a need that has become increasingly urgent given both the pressures coming from the regulatory environment. Leading WG6 is Dr. Tiziana Gambicorti (former SSIP) who can also count on the active collaboration of UNPAC and UNIC. A supply chain collaboration that confirms Italy's leadership in the leather-related CEN working groups. The tanners' association UNIC, in fact, manages the secretariat of CEN/TC 289, and coordinates WG4 (Leather-Technical specifications on the use of leather and terminology) in the person of Dr. Elisabetta Scaglia, head of the Sustainability Service. Scaglia herself during the conference reported on the latest developments related to European chemical legislation regarding bisphenols, PFAS, disocyanates and glutaraldehyde. On the subject of bisphenols, Scaglia reported on measurement work on discharges from Arzignano and Santa Croce that showed that the amounts of bisphenols found downstream were significantly lower than expected and that this could lead to avoiding restrictions in the tanning sector.
After recalling the progress made by the chemical sector, UNPAC Technical Commission coordinator Andrea Meucci reiterated the need to share at the supply chain level "the harmonization of standards with limits set at a reasoned and reasonable level, consistently achievable." Also important was the speech by Aldo Cavezzali, who spoke about the work done by ICEC to accommodate the growing demand for certification in the tanning sector, also in collaboration with ZDHC. Today ICEC boasts 230 certified companies, 10 percent of which are foreign. Closing the proceedings after a panel discussion devoted to future prospects, regarding the proliferation of certifications, President Nuti stressed the need to simplify, amalgamate and rationalize applications in order to be truly sustainable. "No certification by itself guarantees sustainability."
This was an invitation reiterated by UNPAC President Marco Frediani, who reiterated the commitment of manufacturers of tanning chemical auxiliaries to reducing their environmental impact, while recalling the need to proceed step by step by paying attention to technical issues and the need for clearer and more transparent communication.
Convegno AICC: un
“Mettetevi nella nostra pelle… Gli attori della filiera pelle si confrontano” è il titolo del Convegno organizzato dai Chimici del cuoio italiani (AICC) il 22 giugno scorso a Castelfranco di sotto (Pisa) nell’ambito dell’evento espositivo Prossimapelle di UNPAC.

Un importante momento di confronto fra chimici conciari e brand della moda, ma anche responsabili di piattaforme come ZDHC ed associazioni della filiera come UNIC e ICEC, su argomenti di estrema attualità come la proliferazione delle certificazioni sollecitate dal mercato, le richieste di conformità chimica che si scontrano con l’insufficienza dei metodi di analisi dei prodotti chimici, le problematiche legate alla tracciabilità delle pelli e molto altro ancora.
A fare gli onori di casa la presidente AICC Franca Nuti, che ha moderato un interessante dibattito con tanti spunti di riflessione in particolare riguardo alle richieste di restrizione e limiti delle sostanze chimiche. Il punto di vista dei brand è stato rappresentato da Enrico Fatarella, responsabile ambientale del gruppo del lusso LVMH, che ha fatto presente come le richieste di conformità che i brand chiedono –talvolta con limiti anche più stringenti rispetto alle normative in vigore ed apparentemente eccessivi - derivino dal fatto che i loro manufatti devono soddisfare le richieste di tanti Paesi diversi e che i tempi della loro immissione sul mercato esigono di anticipare alcuni requisiti per non dover interrompere le forniture in corso d’opera. Dello stesso tenore l’intervento di Chiara Morelli, responsabile sostenibilità del gruppo Prada, che ha riferito come la pelle sia il materiale principale per gli accessori del brand e come oggi il mercato imponga la massima trasparenza e la piena tracciabilità dei materiali utilizzati. Morelli ha ricordato il percorso fatto negli ultimi anni dai brand della moda insieme alle concerie in ambito ZDHC superando scogli che all’inizio sembravano insormontabili. “Oggi il mondo ci chiede sostenibilità vera, per questo stiamo guardando con interesse alla pelle derivante dall’agricoltura rigenerativa” ha detto Morelli. Elisa Gavazzi, direttore ZDHC per l’Europa meridionale, ha parlato della nuova strategia che sta definendo le tappe della roadmap relativa alla conformità chimica da qui al 2030. La mission resta quella originale del 2011 – ha detto - ovvero ridurre l’impronta chimica del
importante momento di confronto tra produttori chimici, brand moda e piattaforme di certificazione per migliorare la collaborazione all’interno della filiera
“METTETEVI NELLA NOSTRA PELLE”
ARSTANNERY 9 NEWS
settore moda. “Allora ZDHC era un gruppo di soli 6 brand, oggi è una fondazione multistakeholder costituita da 320 signatories fra case di moda, fornitori, associazioni di rappresentanza”. Alla base del nuovo piano strategico di ZDHC - imperniato sull’obiettivo di arrivare a formulazioni chimiche al 100% conformi alla MRSL - due linee guida: promuovere la circolarità dei prodotti e la riduzione dell’impiego di risorse ambientali (energia, acqua, etc.) durante la produzione. Durante il convegno si è molto parlato della mancanza dei metodi ufficiali di analisi dei prodotti chimici, cosa che evidentemente rende difficile rispettare dei limiti oltre che fissarli. Molto importante al riguardo è il lavoro del gruppo WG6 «Test methods for tannery chemicals» istituito ad ottobre 2021 presso la commissione di normazione tecnica europea CEN/TC 289 “Leather”, il cui campo d’azione è la normazione dei metodi analitici per i prodotti chimici. Questo nuovo gruppo, nato dalla richiesta italiana di presidiare questa importante tematica, dovrà colmare la mancanza di metodi standardizzati in questo ambito, necessità divenuta sempre più urgente viste sia le pressioni provenienti dall’ambito regolatorio. Alla guida del WG6 c’è la dottoressa Tiziana Gambicorti (ex SSIP) che può contare anche sulla fattiva collaborazione di UNPAC e UNIC. Una collaborazione di filiera che conferma la leadership italiana in seno ai gruppi di lavoro CEN relativi alla pelle. L’associazione dei conciatori UNIC, infatti, gestisce la segreteria del CEN/TC 289, e coordina il WG4 (Leather-Technical specifications on the use of leather and terminology) nella persona della dottoressa Elisabetta Scaglia, responsabile Servizio Sostenibilità. Proprio Scaglia durante il convegno ha riferito degli ultimi sviluppi legati alla legislazione chimica europea a proposito di bisfenoli, PFAS, disociannati e glutaraldeide. A proposito dei bisfenoli, Scaglia ha riferito di un lavoro di misurazione degli scarichi di Arzignano e Santa Croce che ha dimostrato come i quantitativi di bisfenoli riscontrati a valle siano notevolmente inferiori alle attese e che questo potrebbe portare ad evitare restrizioni nel settore conciario. Dopo aver ricordato

i passi avanti del settore chimico, il coordinatore della Commissione Tecnica UNPAC, Andrea Meucci, ha ribadito la necessità di condividere a livello di filiera “l’armonizzazione degli standard con limiti fissati ad un livello ragionato e ragionevole, coerentemente raggiungibili”. Importante anche l’intervento di Aldo Cavezzali che ha parlato del lavoro svolto da ICEC per assecondare la crescente richiesta di certificazioni del settore conciario anche in collaborazione con ZDHC. Oggi ICEC vanta 230 aziende certificate, di cui il 10% estere.
A chiudere i lavori dopo una tavola rotonda dedicata alle prospettive future, a proposito della proliferazione delle certificazioni la presidente Nuti ha sottolineato la necessità di semplificare, accorpare e razionalizzare le richieste per poter essere veramente sostenibili. “Nessuna certificazione di per sé garantisce la sostenibilità”.
Un invito rilanciato dal presidente UNPAC Marco Frediani che ha ribadito l’impegno dei produttori di ausiliari chimici conciari nella riduzione dell’impatto ambientale, ricordando però la necessità di procedere per gradi facendo attenzione alle problematiche tecniche e alla necessità di una comunicazione più chiara e trasparente.
UNPAC premia i delegati ai tavoli di normazione
Al termine dell’evento tecnico AICC, il segretario UNPAC Maurizio Maggioni ha consegnato targhe di riconoscimento per il lavoro svolto ad alcuni delegati italiani presenti ai tavoli di normazione del settore pelle.
Nello specifico, le motivazioni alla base dei ringraziamenti che UNPAC ha voluto esprimere alle persone hanno riguardato il fattivo impegno professionale dedicato allo sviluppo delle attività in ambito normativo, contribuendo alla creazione in ambito italiano ed europeo, dei Gruppi di Lavoro (WG) per lo sviluppo dei metodi di analisi per gli ausiliari chimico-conciari. Questi i premiati: Tiziana Gambicorti, Franca Nuti, Elisabetta Scaglia, Francesco Troisi, Valerio Talarico, Riccardo Girolami, Massimo De Santis.
10 ARSTANNERY NEWS

EUROPEAN TANNERS INCREASINGLY CONCERNED ABOUT THE PERCEPTION OF LEATHER
was discussed at the COTANCE General Assembly held in Igualada, Spain

outstanding speakers, Gustavo Defeo and Andrea Bertaglio, addressing the image of leather in the public perception and the need to further enhance the communication about its sustainability.
Gustavo Defeo, founder of Ars Tinctoriai, reviewed his research paper, published in the peer-reviewed journal Coatings, “Comparing Materials’ Circularity: A Novel Method for Biobased Carbon Quantification Technique on Leather, Artificial Leather, and Trendy Alternatives”. This paper provides fact-based information about the actual composition of materials marketed to replace leather and will complement the 2021 FILK paper in the sector’s arsenal to fight deceptive or unfair commercial practices related to the abuse of the term “leather” .
Andrea Bertaglio, the Italian Journalist specialized in sustainability, climate change and environmental issues and author of the book “In difesa della carne” is currently Campaign Master in the European Livestock Voice. He spoke about the structuring of communications in the livestock value chain and COTANCE’s cooperation with the meat sector to challenge the myths surrounding the origin of our raw materials.
COTANCE President Manuel Rios invited the European Leather industry to meet in Igualada (Spain) for the mid-year Council and General Assembly meeting. The encounter took place on June 12, 2023 and was hosted by ACEXPIEL. The following visit programme included the Igualada Campus of the University of Lleida, which earlier this year submitted the Erasmus Mundus International Leather Master proposal “LEATECH”, as well as the local Tannery Wastewater Treatment Plant, which has received international recognition of UNEP.
Delegates from Italy, France, Germany, UK and Spain reviewed the activities of COTANCE since the 2022 Assembly General, debating topics including sustainability, advocacy and communication. They addressed the countdown triggered by the publication of the EU Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) in the EU Official Journal. The EU will enforce the Due Diligence requirements in 18-24 months in domestic and extra-EU leather supply chains. COTANCE Members invited the Leather Traceability Cluster (LTC) launched in late 2022, to orchestrate practical solutions to the issue of hide traceability.
COTANCE also reviewed the advocacy actions and alliances in the context of REACH restrictions on chemicals which are key for the competitiveness of European leather and the Global leather trade. European tanners expressed their concern over the outlook for the leather trade & industry and their regret that EU institutions pay little attention to the challenges for the leather value chain in the EU Textiles Strategy. COTANCE adopted a Position Statement addressing the shortcomings of EU measures following the publication of the EP Report on the EU Textiles Strategy.
The Open session of the COTANCE General Assembly hosted two
COTANCE President Rios said: “We wanted to address two important dimensions in relation to the perception of leather: Tanning is a necessary industrial sector and; we, tanners, have to continue to be active with promotional campaigns through new digital media for educating consumers to understand leather and its great environmental and sustainable value for our society.” With regard to the sector’s regulatory challenges, he said: ”… apart from all the constraints that we have to face in our daily lives, European tanners are resilient; small and medium-sized companies with individual strength and creativity, capable of overcoming all these adversities.”
CONCIATORI EUROPEI SEMPRE PIÙ PREOCCUPATI DELL’IMMAGINE DELLA PELLE
Se ne è parlato all’Assemblea generale di COTANCE svoltasi a Igualada, in Spagna, il 12 giugno
Il Presidente di COTANCE Manuel Rios ha invitato l'industria europea della pelle a riunirsi a Igualada (Spagna) per la riunione di metà anno del Consiglio e l'Assemblea Generale. L'incontro ha avuto luogo il 12 giugno scorso ed è stato ospitato da ACEXPIEL, l’associazione dei conciatori spagnoli. Nel programma erano incluse le visite al Campus di Igualada dell'Università di Lleida, che all'inizio di quest'anno ha presentato la proposta di Master internazionale sulla pelle Erasmus
This
12 ARSTANNERY NEWS
COTANCE DELEGATES VISITING IGUALADA TANNING WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANT I DELEGATI COTANCE IN VISITA ALL’IMPIANTO DI TRATTAMENTO DELLE ACQUE REFLUE CONCIARIE DI IGUALADA
Mundus "LEATECH", e all'impianto locale di trattamento delle acque reflue di conceria, che ha ricevuto il riconoscimento internazionale dell'UNEP.
I delegati provenienti da Italia, Francia, Germania, Regno Unito e Spagna hanno passato in rassegna le attività di COTANCE a partire dall'Assemblea generale del 2022, discutendo di temi quali sostenibilità, azioni legali e comunicazione. In particolare, si è molto parlato della pubblicazione del Regolamento UE sulla deforestazione (EUDR) nella Gazzetta Ufficiale dell'UE. L'UE applicherà i requisiti di Due Diligence tra 18-24 mesi nelle catene di approvvigionamento della pelle nazionali ed extra-UE. I membri di COTANCE hanno invitato il Cluster per la tracciabilità della pelle (LTC), lanciato alla fine del 2022, a organizzare soluzioni pratiche per la questione della tracciabilità della pelle. COTANCE ha anche esaminato le azioni di advocacy e le alleanze nel contesto delle restrizioni REACH sulle sostanze chimiche, che sono fondamentali per la competitività della pelle europea e del commercio globale della pelle. I conciatori europei hanno espresso la loro preoccupazione per le prospettive del commercio e dell'industria della pelle e il loro rammarico per il fatto che le istituzioni dell'UE prestino poca attenzione alle sfide della catena del valore della pelle nella strategia tessile dell'UE. COTANCE ha adottato una presa di posizione che affronta le carenze delle misure dell'UE in seguito alla pubblicazione del Report PE sulla strategia tessile dell'UE. Nel corso dell’assemblea generale sono stati ospitati due relatori d'eccezione, Gustavo Defeo e Andrea Bertaglio, che hanno affrontato il tema dell'immagine della pelle nella percezione pubblica e la necessità di migliorare ulteriormente la comunicazione sulla sua sostenibilità. Gustavo Defeo, fondatore di Ars Tinctoria , ha presentato il suo lavoro di ricerca, pubblicato sulla rivista peer-reviewed Coatings, "Comparing Materials' Circularity: A Novel Method for Biobased Carbon Quantification Technique on Leather, Artificial Leather, and Trendy Alternatives". Questo documento fornisce informazioni scientifiche circa l'effettiva composizione dei materiali commercializzati per sostituire la pelle e andrà a integrare il documento FILK del 2021 nell'arsenale del settore per combattere le pratiche commerciali ingannevoli o sleali legate all'abuso del termine "pelle".
Andrea Bertaglio, giornalista italiano specializzato in sostenibilità, cambiamenti climatici e questioni ambientali e autore del libro "In difesa della carne", è attualmente Campaign Master presso la European Livestock Voice. Ha parlato della strutturazione della comunicazione nella catena del valore del bestiame e della collaborazione di COTANCE con il settore della carne per sfidare i miti che circondano l'origine delle nostre materie prime.
Il presidente di COTANCE Rios ha spiegato: "Abbiamo voluto affrontare due dimensioni importanti in relazione alla percezione della pelle: la concia è un settore industriale necessario e noi conciatori dobbiamo continuare a essere attivi con campagne promozionali attraverso i nuovi media digitali per educare i consumatori a comprendere la pelle e il suo grande valore ambientale e sostenibile per la nostra società". A proposito delle sfide normative, ha aggiunto "... al di là di tutti i vincoli che dobbiamo affrontare nella nostra vita quotidiana, i conciatori europei sono resilienti; piccole e medie imprese con forza e creatività individuali, capaci di superare tutte queste avversità".
Cotance Position Statement: The European Parliament fails to acknowledge the challenges of leather
On 1st June 2023, the European Parliament adopted its Report on the EU Strategy for Sustainable and Circular Textiles (EU Textiles Strategy). The ensuing EP Resolution forwarded to the EU Council and the Commission reviews the EU Textiles Strategy and makes specific recommendations to public and private stakeholders for its implementation. Leather appears just one time for indicating that it falls under the scope of the recently adopted EU Deforestation rules. Europe’s leather producers regret that the European Parliament has failed to acknowledge the distinct character of leather within the textile ecosystem and its specific challenges and opportunities in the twin transition towards a green and digital future.
On 12 June 2023, the European Leather Industry, meeting in Igualada (Spain) for the COTANCE General Assembly, expresses its concerns over the poor attention given by EU institutions to its sector and its sustainable development. European tanners wonder whether the EU will roll out any support measure in their transition towards a green and digital future. COTANCE calls on EU institutions to acknowledge and promote the advantages of leather as an intrinsically circular economy material, and to provide the necessary support to Europe’s tanners and dressers for mastering the challenges of the twin transition.
Cotance prende posizione: Il Parlamento europeo sbaglia a non riconoscere la specificità della pelle
Il 1° giugno 2023, il Parlamento europeo ha adottato il Report sulla strategia dell'UE per i tessili sostenibili e circolari (Strategia tessile dell'UE). La successiva risoluzione del Parlamento trasmessa al Consiglio dell'UE e alla Commissione rivede la strategia tessile dell'UE e formula raccomandazioni specifiche alle parti interessate pubbliche e private per la sua attuazione.
La pelle appare solo una volta per indicare che rientra nell'ambito delle norme UE sulla deforestazione recentemente adottate. I produttori europei di pelle si rammaricano che il Parlamento europeo non abbia riconosciuto il carattere distinto della pelle all'interno dell'ecosistema tessile e le sue sfide e opportunità specifiche nella duplice transizione verso un futuro verde e digitale.
Il 12 giugno 2023, l'Industria Europea della Pelle, riunita a Igualada (Spagna) per l'Assemblea Generale di COTANCE, ha espresso la propria preoccupazione per la scarsa attenzione prestata dalle istituzioni dell'UE al proprio settore e al suo sviluppo sostenibile. I conciatori europei si chiedono se l'UE introdurrà misure di sostegno nella loro transizione verso un futuro verde e digitale. COTANCE invita le istituzioni dell'UE a riconoscere e promuovere i vantaggi della pelle come materiale intrinsecamente circolare dell'economia e a fornire il supporto necessario ai conciatori e ai disegnatori europei per affrontare le sfide della doppia transizione.
ARSTANNERY 13 NEWS
MEASURING THE SUSTAINABILITY OF LEATHER? HERE COMES THE LCA SIMULATOR FOR TANNERIES

An LCA simulator for the tanning industry. Basically, software that enables science-based process improvements along the leather manufacturing process. This is a hot topic given the fashion industry's growing demand for reliable and shared environmental footprint measurement tools.
The simulator was developed by SPIN360, a consulting firm specializing in the sustainability of luxury supply chains, and is in the process of being certified by ICEC, the leading Certification Institute for the leather area. "We developed this project in response to the need to provide our clients with 100 percent reliable numbers and data to help them follow their roadmap toward reducing their environmental footprint," explains Federico Brugnoli, CEO of SPIN360.
"The effectiveness of the simulator content," explains a note, "will be evaluated by ICEC with reference to the main requirements included in ISO 14040, ISO 14044 and the European PEFCR for leather. What's more, this system "allows tannery technicians to work on gradual process efficiency improvement for reducing the environmental impact of leather processing." This results in "resulting immediate cost savings in drum processes. Engineers are able to scientifically analyze process performance, formulate hypotheses for improvement, test their ideas and validate the results."
"As a reference institute for more than 25 years in the leather industry," comments Sabrina Frontini, ICEC director, "we have a responsibility to ensure that our partners provide their customers with reliable and verifiable data. This is why we are excited to join forces in this
agreement that will be of great support to the supply chain." The simulator will soon be available on the market as a stand-alone version under a SaaS (Software as a Service) contract, but it can also be integrated into processing machines.
MISURARE LA SOSTENIBILITÀ DELLE PELLI?
Sviluppato da Spin360, il software è in fase di certificazione da parte di ICEC. Fornisce dati affidabili e verificabili, utili a ridurre l’impronta ambientale delle concerie
Un simulatore LCA per l’industria conciaria. In pratica un software che consente miglioramenti di processo su base scientifica lungo il processo di lavorazione delle pelli. Un argomento di grande attualità vista la crescente richiesta del mondo della moda di poter disporre di strumenti di misurazione dell’impronta ambientale che siano affidabili e condivisi.
Il simulatore è stato sviluppato da SPIN360, società di consulenza specializzata nella sostenibilità delle filiere del lusso, ed è in fase di certificazione da parte di ICEC, l’Istituto di Certificazione di riferimento per l’area pelle. “Abbiamo sviluppato questo progetto per rispondere alla necessità di fornire ai nostri clienti numeri e dati affidabili al 100% che li aiutino a seguire la loro roadmap verso la riduzione dell’impronta ambientale” spiega Federico Brugnoli, CEO di SPIN360.
“L’efficacia dei contenuti del simulatore – si legge in una nota – sarà valutata da ICEC con riferimento ai principali requisiti inclusi nelle norme ISO 14040, ISO 14044 e nella PEFCR europea per la pelle”. E ancora, questo sistema “consente ai tecnici delle concerie di lavorare su un miglioramento graduale dell’efficienza del processo per la riduzione dell’impatto ambientale della lavorazione della pelle”. Ne deriva un “conseguente risparmio immediato dei costi dei processi in bottale. I tecnici sono in grado di analizzare scientificamente le prestazioni dei processi, formulare ipotesi di miglioramento, testare le loro idee e convalidare i risultati”.
“Come Istituto di riferimento da oltre 25 anni nel settore della pelle – commenta Sabrina Frontini, direttore ICEC – abbiamo la responsabilità di garantire che i nostri partner forniscano ai loro clienti dati affidabili e verificabili. Per questo siamo entusiasti di unire le forze in questo accordo che sarà di grande supporto per la filiera”.
Il simulatore sarà presto disponibile sul mercato in versione stand-alone con contratto SaaS (Software as a Service) ma può essere anche integrato nelle macchine di lavorazione.
ARRIVA IL SIMULATORE LCA PER LA CONCIA
Developed by Spin360, the software is being certified by ICEC. It provides reliable and verifiable data useful in reducing the environmental footprint of leather processing
14 ARSTANNERY NEWS

PROSSIMAPELLE'S CONVIVIAL FORMULA HITS THE MARK
Held at Villa Cerrini di Montefalcone, near Castelfranco di Sotto (Pisa), in the heart of Tuscany's tanning district, was the latest edition of Prossimapelle, the event for tanning chemists that presented the new trends for Fall/Winter 24/25 to the local market on June 22. A new venue that inspired a different format, made up of marquees set up outdoors to convivially welcome visitors, who were able to view fashion and technical items displayed on tables arranged in a serpentine pattern. An innovative concept, designed, as UNPAC explains, "to invite tanners and tannery technicians to live an immersive experience, which combined the commercial part of presenting trends with a moment of technical discussion of the supply chain organized by AICC."
Indeed, the event of tanning chemists appeared on this occasion to be very different from the past when it was held first at the Tanning Museum and then at the Palaparenti in Santa Croce.
The "exhibitors" received visitors in the Villa Cerrini garden by creating a lively and informal event (despite the sultriness of a summer day). Some 15 chemical companies were present, which for the occasion developed a multiplicity of new fashion items, interesting both technically

and aesthetically, which were on display on the exhibition tables divided on the basis of four fashion trends developed by Pier Francesco Pitasi of Trend Lab.
From the point of view of attendance, many tanning technicians from the main Tuscan tanneries attended, who also followed the AICC conference (which we talk about in the following pages) with attention. "Among the visitors we saw many young people, a sign of interest from the new generations that gives us hope," comments Maurizio Maggioni, UNPAC secretary general, who also emphasizes how the new exhibition formula favored dialogue and exchange of opinions among the operators, overcoming the traditional exhibition in the booth in favor of a more convivial moment. Conviviality that culminated in the aperitif and subsequent dinner that further encouraged networking by gathering more than two hundred operators around the tables.
A new formula, that of Prossimapelle, which has also been judged positively by the Tuscan Tanneries Association as a moment of aggregation of the supply chain and which UNPAC is considering replicating with some adjustments also in Arzignano for the similar event in Veneto next fall.
The UNPAC event dedicated to A/W 24/25 trends was held June 22 in Castelfranco di Sotto
16 ARSTANNERY EVENTS
LA FORMULA CONVIVIALE DI PROSSIMAPELLE CENTRA IL BERSAGLIO



L’evento UNPAC dedicato alle tendenze A/I 24/25 si è svolto il 22 giugno a Castelfranco di Sotto

Si è svolta a Villa Cerrini di Montefalcone, a Castelfranco di Sotto (Pisa), nel cuore del distretto conciario toscano, l’ultima edizione di Prossimapelle, la manifestazione dei chimici conciari che il 22 giu-
gno scorso ha presentato al mercato locale le nuove tendenze per l’autunno-inverno 24/25. Una nuova sede che ha ispirato un format diverso, fatto da tendostrutture allestite all’aperto per accogliere in modo conviviale i visitatori, che hanno potuto visionare gli articoli moda e tecnici esposti su tavoli sistemati a serpentina. Un concept innovativo, studiato, come spiega UNPAC, “per invitare conciatori e tecnici di conceria a vivere un’esperienza immersiva, che ha unito la parte commerciale di presentazione delle tendenze con un momento di confronto tecnico della filiera organizzato da AICC”. In effetti la manifestazione dei chimici conciari è apparsa in questa occasione molto diversa rispetto ai precedenti allestimenti visti al Museo della Concia prima, e al Palaparenti di Santa Croce poi. Gli

 ALANCHIM
ALPA
CHIME
ALPA
CHIME
ALANCHIM
ALPA
CHIME
ALPA
CHIME
ARSTANNERY 17 EVENTS
CHIMICA ITALIANA
“espositori” hanno ricevuto i visitatori nel giardino della Villa Cerrini dove si è dato vita ad un evento vivace e informale (nonostante l’afa di una giornata estiva). Una quindicina le aziende chimiche presenti che per l’occasione hanno sviluppato una molteplicità di nuovi articoli moda, interessanti sia sul piano tecnico che estetico, che facevano bella mostra di sé sui tavoli espositivi divisi sulla base di quat-
tro tendenze moda sviluppate da Pier Francesco Pitasi di Trend Lab. L’analisi dei visitatori ha evidenziato la prevalenza di tecnici conciari provenienti dalle principali concerie toscane che hanno seguito con attenzione anche il convegno AICC (di cui parliamo nelle pagine seguenti): “Tra i visitatori abbiamo visto molti giovani, un segnale di interesse da parte delle nuove generazioni che ci fa ben sperare”





 CHIMICA ITALIANA
CODYECO
FGL INTERNATIONAL
CHIMICA VEMAR
FGL INTERNATIONAL
GSC GROUP
CHIMICA ITALIANA
CODYECO
FGL INTERNATIONAL
CHIMICA VEMAR
FGL INTERNATIONAL
GSC GROUP
18 ARSTANNERY EVENTS
commenta Maurizio Maggioni, segretario generale UNPAC che sottolinea anche come la nuova formula espositiva abbia favorito il dialogo e lo scambio di opinioni fra gli operatori, superando la formalità di una tradizionale esposizione negli stand a favore di un momento più aperto e conviviale. Convivialità culminata nell’offerta di aperitivo e cena all’aperto, occasioni che hanno ulteriormente favorito il networ-
king riunendo attorno ai tavoli oltre duecento operatori. Una nuova formula, quella di Prossimapelle, che è stata giudicata positivamente anche dall’Associazione conciatori toscani come momento di aggregazione della filiera e che UNPAC sta valutando di replicare con qualche aggiustamento anche ad Arzignano per l’analogo evento veneto del prossimo autunno.






KLF TECNOKIMICA
REPICO
VITALCHIMICA
REAL COLOR
TECNOCHIMICA
ZAITEX
ARSTANNERY 19 EVENTS
TIMELESS MEN'S FOOTWEAR FOR SUMMER 2024

Creativity, experimentation and cosmopolitan spirit: the evolution of men's fashion continues in a subtle balance between heritage and innovation. Spring summer 2024 presented at the last edition of Pitti Uomo last June in Florence will feature garments that combine different materials and textures, attentive to aesthetics and contemporary design but with a keen eye on sustainability expressed through the increasing use of recycled or recyclable materials. In general, trends propose tailored and versatile garments that are comfortable yet rustproof. Timeless, in spite of ephemeral fashions
and seasonality. Alongside, a repertoire of faithful travel companions that don't lose their polish: bags and accessories for urban adventures, iconic loafers and reissued cult sneakers where leather remains the absolute protagonist. Classic leather formats also for "weekender" duffels that have been embellished over the years, biker backpacks that combine functionality and lightness. Pieces where design dialogues with craftsmanship and fine leather. Color helps to enhance this new harmony of elements. In addition to blue and warm shades such as terracotta, the coming summer
The new trends seen at Pitti Uomo, the Florentine show that was full of energy last June, restoring some confidence to the industry
20 ARSTANNERY FAIRS
will see a prevalence of shades ranging from sand to ivory, from melange grays to pastels such as peach, mint green, pale pink, sky blue, sage and lilac.
In footwear, sneakers still prevail - with ultra-light soles and mostly leather uppers worked with colored inserts - alongside moccasins, multicolor sporty lace-ups but also ankle boots and lightweight beatles offered in vegetable-tanned leather or suede in soft colors. Classic models that are renewed in their lines and color proposals. As for the chronicle of the event dedicated to the 2024 summer


anticipations of men's fashion, 11,900 buyers and more than 17,000 total visitors were registered in Florence from June 13 to 16. Italians exceeded 6,700 attendees (+6%), while foreigners numbered about 5,200 (+24%), accounting for 43% of the total, with Asian buyers returning in force. The main foreign markets were, in order: Germany, Great Britain, Holland, Japan, Spain, Turkey, the U.S., Switzerland, France, China, Belgium and South Korea. A very positive balance that brings back confidence and enthusiasm among the operators. "The final attendance figures, with Italian buyers up 6 percent and

DATE
WUSHU RUYI
ARSTANNERY 21 FAIRS
TESTONI






DOLOMITE W6YZ ELLESSE VOILE BLANCHE FLOWER MOUNTAIN A.S. 98 22 ARSTANNERY FAIRS
foreign buyers up 24 percent compared to June 2022 reward, first and foremost, the commitment and ability to renew shown by the 825 exhibitors at this Pitti Uomo, and confirm a path of recovery for the Salone, which is gradually returning to its pre-crisis dimensions," commented Raffaello Napoleone, CEO of Pitti Immagine.
SENZA TEMPO LA CALZATURA MASCHILE DELL’ESTATE 2024
Le nuove tendenze di Pitti Uomo, il salone fiorentino che a giugno ha fatto il pieno di energia restituendo un po’ di fiducia al settore


Creatività, sperimentazione e spirito cosmopolita: continua l’evoluzione della moda maschile in un equilibrio sottile tra heritage e innovazione. La primavera estate 2024 presentata all’ultima edizione di Pitti Uomo lo scorso giugno a Firenze sarà caratterizzata da capi che combinano materiali e texture diverse, attenti all’estetica e al design contemporaneo ma con un occhio attento alla sostenibilità che si esprime attraverso il crescente utilizzo di materiali riciclati o riciclabili.
In generale le tendenze propongono capi sartoriali e versatili, confortevoli ma inossidabili. Senza tempo, a dispetto di mode effimere e stagionalità. Accanto, un repertorio di fedeli compagni di viaggio che non perdono smalto: borse e accessori per le avventure urbane, mocassini iconici e sneakers di culto rieditate dove la pelle resta assoluta protagonista. Formati classici in pelle anche per borsoni “weekender” che si abbelliscono negli anni, zaini da biker che coniugano funzionalità e leggerezza. Pezzi dove il design dialoga con la fattura artigianale e la pelle di pregio.
Il colore contribuisce a esaltare questa nuova armonia degli elementi. Oltre al blu e alle tonalità calde come il terracotta, l’estate che verrà vedrà un prevalere di nuance che spaziano dal sabbia all’avorio, dai grigi melange ai pastelli come il pesca, il verde menta, il rosa pallido, l’azzurro cielo, il salvia e il lilla.
Nelle calzature prevale ancora l’offerta di sneakers – con suole leggerissime e tomaie perlopiù in pelle lavorate con inserti colorati - affiancate da mocassini, stringate sportive multicolor ma anche stivaletti e beatles leggeri proposti in pelle a concia vegetale o suede dai colori tenui. Modelli classici che si rinnovano nelle linee e nelle proposte cromatiche.
Quanto alla cronaca della manifestazione dedicata alle anticipazioni estive 2024 della moda uomo, a Firenze dal 13 al 16 giugno si è registrata la partecipazione di 11.900 compratori e oltre 17.000 visitatori totali. Gli italiani hanno superato le 6.700 presenze (+6%), mentre gli stranieri sono stati circa 5.200 (+24%), a rappresentare il 43% del totale, con il ritorno in forze dei buyer asiatici. I principali mercati esteri sono stati, nell’ordine: Germania, Gran Bretagna, Olanda, Giappone, Spagna, Turchia, Usa, Svizzera, Francia, Cina, Belgio e Corea del Sud. Un bilancio molto positivo che riporta fiducia ed entusiasmo fra gli operatori. “I dati di affluenza finale, con i compratori italiani in aumento del 6% e quelli esteri del 24% rispetto al giugno 2022, premiano anzitutto l’impegno e la capacità di rinnovarsi mostrata dagli 825 espositori di questo Pitti Uomo e confermano un percorso di ripresa del Salone, che sta gradualmente ritornando alle dimensioni pre-crisi” ha commentato Raffaello Napoleone, amministratore delegato di Pitti Immagine.
ARSTANNERY 23 FAIRS
ANCIENT POMPEII TANNERY OPENED TO THE PUBLIC

Completed the restoration of Pompeii's ancient tannery, the largest artisanal leather processing plant found in the ancient city. The ancient tannery complex has finally been opened to the public, at the end of an extensive restoration operation that was the result of a collaboration between the Pompeii Archaeological Park and the UNIC-Concerie Italiane Lineapelle group, which bore the costs of the intervention. The presentation took place on June 29.
"Another important site of the excavations is returned to fruition, which we are sure will be appreciated by the many visitors who in recent months have chosen Pompeii as their travel destination. - said the Park Director, Gabriel Zuchtriegel - The proposal to include it in an itinerary of artisanal facilities is aimed at telling also the aspects of a productive and commercial city, and not only the Pompeii of the Domus with magnificent frescoes.
The sponsorship of the UNIC-Concerie Italiane Lineapelle group represents a virtuous example of public-private collaboration, it is fully in line with the path taken by the Archaeological Park in this direction - and in a planned manner - through the activity of the Fundraising Office. Thanks to these collaborations, important new synergies are triggered, which are able to give rise to new cultural processes."
"UNIC strongly believes in this restoration operation," explains UNIC Director Fulvia Bacchi, "which has a profound value in many respects and has seen us collaborate with commitment with the Archaeological Park of Pompeii. It is a tribute to history that through the enhancement of the roots of our business allows us to create a bridge between ancient traditions and the future."
"We believe that companies-said Lineapelle President Gianni Russo-can be aggregators of social interests, of stimulus in the territories of reference." "Industry is an expression of a country's cultural background," added UNIC President Fabrizio Nuti, "and the tannery certainly is for Italy, with its internationally recognized leadership role in the relevant sector. The restoration of Pompeii expresses a virtuous synthesis of the dialogue between the world of business and culture with potential beneficial effects on the entire community." The visit to Pompeii's ancient tannery is supported by an exhibition and educational set-up that illustrates how the leather processing process was carried out two thousand years ago. It also displays original tools for tanning, following the model of a widespread museum. A choice already successfully tested in Pompeii, which also includes a 3-D tactile model for the visually impaired with a Braille legend.
APERTA AL PUBBLICO L’ANTICA CONCERIA DI POMPEI
L’associazione italiana dei conciatori ha finanziato l’imponente opera di recupero all’interno del parco archeologico come “omaggio alla storia e valorizzazione delle nostre radici”
Completato il restauro dell'antica conceria di Pompei, il più grande impianto artigianale per la lavorazione delle pelli rinvenuto nella città antica. Il complesso dell'antica conceria è stato finalmente aperto al pubblico, al temine di un'ampia operazione di restauro frutto della collaborazione tra il Parco archeologico di Pompei e il gruppo UNIC-Concerie Italiane Lineapelle, che ha sostenuto le spese dell'intervento. La presentazione è avvenuta il 29 giugno scorso.
“Viene restituito alla fruizione un altro importante luogo degli scavi, che siamo sicuri sarà apprezzato dai tanti visitatori che in questi ultimi mesi hanno scelto Pompei come meta dei loro viaggi. – ha dichiarato il Direttore del Parco, Gabriel Zuchtriegel - La proposta di inserirlo in un itinerario di impianti artigianali è finalizzata a raccontare anche gli aspetti di una città produttiva e commerciale, e non solo la Pompei delle Domus con magnifici affreschi. La sponsorizzazione del gruppo UNIC-Concerie Italiane Lineapelle rappresenta un esempio virtuoso di collaborazione pubblico privato, si inserisce appieno nel percorso intrapreso dal Parco archeologico in tale direzione - e in maniera programmata – attraverso l’attività dell’Ufficio Fundraising. Grazie a queste collaborazioni si innescano nuovi importanti sinergie, che sono in grado di dare vita a nuovi processi culturali.” “UNIC crede fortemente in questa operazione di restauro - spiega il Direttore UNIC, Fulvia Bacchi - che ha un valore profondo sotto molteplici profili e ci ha visto collaborare con impegno con il Parco archeologico di Pompei. È un omaggio alla storia che attraverso la valorizzazione delle radici della nostra attività ci consente di creare un ponte tra antiche tradizioni e futuro”.
“Crediamo che le aziende- ha detto il Presidente Lineapelle, Gianni Russo - possano essere aggregatrici di interessi sociali, di stimolo nei territori di riferimento”. “L’industria è espressione del bagaglio culturale di un Paese – ha aggiunto il Presidente UNIC, Fabrizio Nuti - e la conceria lo è di certo per l’Italia, con il suo ruolo di leadership del relativo comparto riconosciuto a livello internazionale. Il restauro di Pompei esprime una sintesi virtuosa del dialogo tra mondo dell’impresa e della cultura con potenziali ricadute benefiche sull’intera collettività”. La visita all’antica conceria di Pompei è supportata da un allestimento espositivo e didattico che illustra come si svolgeva duemila anni fa il processo di lavorazione delle pelli. Inoltre, espone anche strumenti originali per la concia, secondo il modello del museo diffuso. Una scelta già sperimentata con successo a Pompei, che prevede anche la presenza di un modellino tattile in 3d per ipovedenti con legenda in braille.
The Italian Tanners Association funded the massive restoration work within the archaeological park as a "tribute to history and enhancement of our roots"
24 ARSTANNERY NEWS

LEATHER SUSTAINABILITY, EXPERTS GATHER IN PARIS
Sustainable Leather Forum will discuss the latest developments in CSR and traceability on Sept. 11
-Livestock farming and raw materials: the leather industry is reducing its carbon footprint through best practices and innovative tools -CSR, the DNA of the Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) sector - A key element in the implementation of circular fashion: the care and repair of shoes, gloves, and leather goods. For further info: www.slf-paris.com
SOSTENIBILITÀ DELLA
SE NE A PARLA A PARIGI
L’11 settembre al Sustainable Leather Forum si discuterà degli ultimi sviluppi in tema di responsabilità sociale d’impresa (CSR) e tracciabilità
Torna per la sua quinta edizione il grande evento francese dedicato allo sviluppo sostenibile e alla responsabilità sociale (CSR) dell’industria della pelle che ogni anno riunisce per una giornata di approfondimento circa 400 esperti del settore.
Back for its fifth edition is the major French event dedicated to the sustainable development and social responsibility (CSR) of the leather industry that brings together some 400 industry experts for a day of in-depth discussion each year.
The Sustainable Leather Forum (SLF) is set for Monday, September 11, at Palais Brongniart in Paris. A day packed with lectures and expert discussions - organized by the Conseil National du Cuir under the patronage of the French Ministry of Economy, Finance and Industrial Recovery - to discuss the major challenges facing the leather industry. As many as 18 speakers are scheduled, as well as 4 exclusive keynotes given by Elisabeth Laville (Utopies), Paul Luu (4p1000), Nienke Steen (Cradle to Cradle Certified), Héléne Jessua and Hélène Billard (Zadig & Voltaire).
Also new for this edition is an exhibition area where the latest innovations available on the market in certification, traceability schemes, labeling, training, research and development, and chemical product innovations will be presented. Some 30 companies will attend including ICEC, CTC, Sustainable Leather Foundation, Biokimica, Leather Working Group, Leather Naturally and others. The preliminary program of the Forum includes 4 sessions devoted to as many macro-themes. Here they are:
-How can certification standards contribute to improving traceability and processes in the leather industry?
L’appuntamento con il Sustainable Leather Forum (SLF) è fissato per lunedì 11 settembre al Palais Brongniart di Parigi. Una giornata densa di conferenze e dibattiti fra esperti - organizzata dal Conseil National du Cuir con il patrocinio del Ministero francese dell’Economia, della Finanza e della Ripresa industriale - per discutere delle grandi sfide che l’industria della pelle si trova ad affrontare. Ben 18 i relatori previsti, oltre a 4 conferenze esclusive tenute da Elisabeth Laville (Utopies), Paul Luu (4p1000), Nienke Steen (Cradle to Cradle Certified), Héléne Jessua e Hélène Billard (Zadig & Voltaire).

Tra le novità di questa edizione anche un’area espositiva dove saranno presentate le ultime novità disponibili sul mercato in tema di certificazioni, schemi di tracciabilità, etichettatura, formazione, ricerca e sviluppo, innovazioni di prodotti chimici. Una trentina le aziende presenti tra cui ICEC, CTC, Sustainable Leather Foundation, Biokimica, Leather Working Group, Leather Naturally e altri. Il programma preliminare del Forum prevede 4 sessioni dedicate ad altrettanti macro-temi. Eccoli:
- Standard di certificazione: come contribuiscono a migliorare i processi e la tracciabilità dell’industria della pelle?
- Allevamento e pelli grezze: l’industria della pelle riduce la sua carbon footprint attraverso best practices e strumenti innovativi
- CSR, il DNA del settore dei dispositivi di protezione individuali (DPI)
- Un elemento chiave nell’implementazione della moda circolare: la cura e la riparazione di scarpe, guanti e articoli di pelletteria. Per ulteriori info: www.slf-paris.com
PELLE,
26 ARSTANNERY NEWS
BIOKIMICA'S NEW SCIENCE LAB UNVEILED

Biokimica Group of Santa Croce sull'Arno recently unveiled its new in-house scientific laboratory: the "BKLab Innovation Hub." A space equipped with first-class instrumentation and dedicated to the development of products and formulations from the perspective of "green chemistry" as well as the training of new tanning technicians. Hub because, in the idea of Biokimica Group president Massimo Baldini and laboratory director Tiziana Gambicorti, this is also to be a place where ideas can be exchanged between the chemical business world and the university, since the new facility will also be made available to students for the development of theses and research. A laboratory equipped with advanced technologies, the construction of which cost about 500,000 euros and which also fits into a protocol signed about a year ago with the Tuscany Region for the sustainability of the chemical industry and the production of new jobs. Through the BK Lab Innovation Hub's new instrumentation, it will be possible to go and investigate, both in the Biokimica group's products and in the processed leather, the possible presence of elements and compounds considered harmful or banned by the ZDHC protocol or brand specifications, certifying their chemical conformity. Recently bisphenols have come under investigation in addition to the others already "under attention": hexavalent chromium, glutaraldehyde, formaldehyde, Pfas and a number of other compounds. Overall, therefore, the laboratory will contribute to the development of leathers whose processing has minimal or even zero environmental impact, as requested by fashion houses from tanners. In particular, in recent times the Biokimica Group has been very involved in the development of products for leather finishing through the use of substances derived from renewable sources of plant origin in a fully green logic. The new instrumental equipment will make it possible to follow analytically the research and development projects of the group and its clients, autonomously and continuously, supporting the activities of researchers in the identification and development of new products and formulations based on "green chemistry". The laboratory presentation was also an opportunity to take stock of environmental issues
related to the manufacturing world. Speakers at the conference included regional councillor for labor and training Alessandra Nardini and ZDHC South Europe manager Elisa Gavazza, among others.
PRESENTATO IL NUOVO LABORATORIO SCIENTIFICO DI BIOKIMICA
Dotato di strumentazioni all’avanguardia, il BK Lab Innovation Hub punta a diventare un luogo di scambio tra industria chimica e università
Recentemente il Gruppo Biokimica di Santa Croce sull’Arno ha presentato il suo nuovo laboratorio scientifico interno: il “BKLab Innovation Hub”. Uno spazio attrezzato con strumentazioni di prim’ordine dedicato allo sviluppo di prodotti e formulazioni in ottica di “green chemistry” oltre che alla formazione di nuovi tecnici conciari. Hub perché, nell’idea del presidente del Gruppo Biokimica, Massimo Baldini, e della direttrice del laboratorio Tiziana Gambicorti, questo dovrà essere anche un luogo dove scambiarsi le idee tra mondo dell’impresa chimica e università, visto che la nuova struttura sarà messa a disposizione anche di studenti per l’elaborazione di tesi e ricerca. Un laboratorio dotato di tecnologie avanzate, la cui realizzazione è costata circa 500mila euro e che va ad inserirsi anche in un protocollo siglato circa un anno fa con la Regione Toscana per la sostenibilità dell’indotto chimico e la produzione di nuovi posti di lavoro. Attraverso la nuova strumentazione del BK Lab Innovation Hub sarà possibile andare a indagare, tanto nei prodotti del gruppo Biokimica quanto nel pellame lavorato, l’eventuale presenza di elementi e composti ritenuti nocivi o messi al bando dal protocollo ZDHC o dai capitolati dei brand certificandone la conformità chimica. Recentemente sono finiti sotto indagine i bisfenoli oltre agli altri già “attenzionati”: il cromo esavalente, la glutaraldeide, la formaldeide, i Pfas e una serie di altri composti. Nel complesso, quindi, il laboratorio contribuirà alla messa a punto di pelli la cui lavorazione abbia un impatto ambientale minimo o addirittura ridotto a zero, come richiesto dalle case di moda ai conciatori. In particolare, negli ultimi tempi il Gruppo Biokimica si è molto impegnato nello sviluppo di prodotti per la rifinizione delle pelli attraverso l’utilizzo di sostanze che derivano da fonti rinnovabili di origine vegetale in una logica pienamente green. La nuova dotazione strumentale permetterà di seguire analiticamente i progetti di ricerca e sviluppo del gruppo e dei propri clienti, in modo autonomo e continuativo, sostenendo le attività dei ricercatori nella identificazione e messa a punto di nuovi prodotti e formulazioni basate sulla “green chemistry”. La presentazione del laboratorio è stata l’occasione per fare il punto anche sui temi ambientali legati al mondo produttivo. Al convegno sono intervenuti, tra gli altri, l’assessore regionale al lavoro e formazione Alessandra Nardini e la responsabile ZDHC Sud Europa Elisa Gavazza.
Equipped with state-of-the-art instrumentation, the BK Lab Innovation Hub aims to become a place of exchange between the chemical industry and universities
ARSTANNERY 27 NEWS
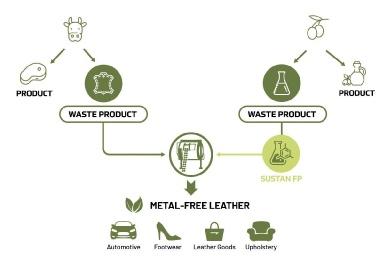
FROM WASTEWATER TO RESOURCE, GSC GROUP'S OMW TECHNOLOGY
A metal-free alternative tanning system obtained from oil milling wastewater, which has many advantages, besides being a perfect model of circular economy
Italy is one of the world's most important producers of leather goods and the second largest producer of olive oil in the world. This has led to the development of a cutting-edge technology that combines two Italian excellences from a circular economy perspective. We are talking about an innovative leather tanning system based on olive oil milling wastewater, of which GSC Group is the exclusivist. This project relies on the valorization of a potentially polluting waste such as olive mill waste-water (OMW), the wastewater resulting from the pressing of olives and the subsequent centrifugation of the aqueous emulsion of pressing. OMWs are free of pathogens, heavy metals and viruses, but contrary to popular belief, they are among the most polluting agro-industrial wastewaters, harmful to the environment because of their high acidity and anti-microbial and phytotoxic power. And it is precisely the high content of phenolic compounds in OMW that represents a great opportunity for the tanning industry.


The main phenolic compounds present in OMWs – such as hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, catechol, methylcatechol, oleuropein caffeic, gallic, vanillic, and coumaric acids – in fact, have extraordinary antioxidant properties. Before being used, this wastewater is properly treated in an ad hoc plant and enhanced with other additives in a complex production process from which the tanning agent Sustan FP is derived.
"After extensive research work, we have developed a revolution-
ary product line by harnessing the tanning power of OMWs in a circular economy perspective," explains GSC Group. "OMW tanning agents are obtained from a food industry waste and applied to a meat production waste (hides and skins). This also has the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions (calculated with the Carbon Footprint) and thus the overall environmental impact of leather processing."
Finished leathers obtained with OMW technology are metal-free and absolutely safe for human use, as they are free from the risk of hexavalent chromium formation and free from the toxicity of glutaraldehyde. The tanning agents are produced in Italy through an exclusive process using OMW from Italian oil companies (mainly from Tuscany and Puglia).
In addition to the safety and sustainability aspects, GSC Group also points out the technical performance of the leathers obtained from OMW. "This type of tanning is extremely versatile, suitable for applications for all leather destination segments, from footwear to leather goods, from automotive to furniture. In fact, it leads to high performance leathers with respect to traditional tans and is therefore a perfect alternative without compromising on quality, performance or appearance," they conclude from GSC Group.
At the upcoming Tanning Tech in September, the Veneto-based company will present a full range of leather items made with OMW technology.
A PLANTATION OF OLIVE TREES UN TERRENO PIANTATO AD ULIVI 28 ARSTANNERY GREEN CHEMICALS
DA ACQUE DI SCARTO A RISORSA, LA TECNOLOGIA OMW DI GSC GROUP
Dalle acque di vegetazione olearie si è ottenuto un sistema di concia metal-free alternativo a quelli esistenti che presenta molti vantaggi, oltre ad essere un perfetto modello di economia circolare

L’Italia è uno dei più importanti produttori mondiali di articoli in pelle ed il secondo maggior produttore di olio d’oliva nel mondo. Da queste premesse si è arrivati allo sviluppo di una tecnologia all’avanguardia che unisce due eccellenze italiane in un’ottica di economia circolare. Parliamo di un innovativo sistema di concia delle pelli a base di acque di vegetazione olearie di cui GSC Group è esclusivista. Un progetto di sostenibilità che prende le mosse dalla valorizzazione di uno scarto potenzialmente inquinante come appunto le acque di vegetazione olearie ((Olive Mill Wastewater = OMW), ovvero i reflui derivanti dalla spremitura delle olive e dalla successiva centrifugazione dell’emulsione acquosa di spremitura. Le OMW sono esenti da agenti patogeni, metalli pesanti e virus, ma, contrariamente a quanto si può pensare, sono tra le acque reflue agroindustriali più inquinanti, dannose per l’ambiente a causa della loro elevata acidità e del
loro potere anti-microbico e fitotossico. Ed è proprio l’elevato tenore di composti fenolici delle OMW a rappresentare una grande opportunità per il settore conciario. I principali composti fenolici presenti nelle OMW - come l’idrossitirosolo, il tirosolo, il catecolo, il metilcatecolo, l’oleuropeina l’acido caffeico, gallico, vanillico e cumarico – hanno infatti straordinarie proprietà antiossidanti. Prima di essere utilizzate, queste acque reflue vengono opportunamente trattate in un impianto ad hoc e valorizzate con altri additivi in un processo di produzione complesso da cui si ricava l’agente conciante Sustan FP.
“Dopo un lungo lavoro di ricerca abbiamo messo a punto una linea di prodotti rivoluzionari sfruttando il potere conciante delle OMW in un’ottica di economia circolare - spiegano da GSC Group -. I concianti OMW vengono ottenuti da uno scarto dell’industria alimentare ed applicati ad uno scarto della produzione della carne (il pellame). In questo modo si possono anche potenzialmente ridurre le emissioni dei gas serra (calcolate con la Carbon Footprint) e quindi l’impatto ambientale dei processi di lavorazione”.
Le pelli ottenute con la tecnologia OMW sono metal-free e assolutamente sicure per l’utilizzo umano, in quanto esenti dal rischio di formazione di cromo esavalente e prive della tossicità della glutaraldeide. I concianti vengono prodotti in Italia attraverso un processo esclusivo che usa OMW di aziende olearie italiane (principalmente da Toscana e Puglia).
Oltre all’aspetto della sicurezza e della sostenibilità, da GSC Group fanno notare anche le performance tecniche delle pelli ottenute da OMW. “Questo tipo di concia è estremamente versatile, adatta ad applicazioni per tutti i segmenti di destinazione delle pelli, dalla calzatura alla pelletteria, dall’automotive all’arredamento. Consente infatti di ottenere pelli con caratteristiche di alto livello e prestazioni paragonabili alle conce tradizionali ed è quindi una perfetta alternativa senza compromessi in termini di qualità, prestazioni o aspetto” concludono da GSC Group. Al prossimo Tanning Tech, a settembre, l’azienda veneta presenterà una gamma completa di articoli realizzati con tecnologia OMW.
THE GRAPHIC OF OMW TECHNOLOGY HIGHLIGHTS HOW IMPORTANT END PRODUCTS ARE OBTAINED FROM TWO WASTE PRODUCTS, SUCH AS HIDE AND OLIVE MILL WASTEWATER LO SCHEMA DELLA TECNOLOGIA OMW EVIDENZIA COME DA DUE PRODOTTI DI SCARTO, OVVERO LA PELLE E LE ACQUE DI VEGETAZIONE OLEARIE, SI OTTENGANO IMPORTANTI PRODOTTI FINITI
A DECANTER USED FOR THE PRODUCTION OF OLIVE OIL UN DECANTER UTILIZZATO PER LA PRODUZIONE DELL’OLIO DI OLIVA
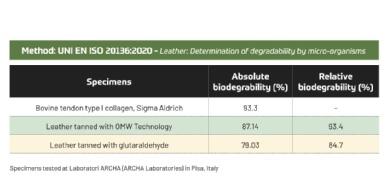
LA TABELLA MOSTRA LA BIODEGRADABILITÀ DELLA PELLE CONCIATA CON OMW TECHNOLOGY
ARSTANNERY 29 GREEN CHEMICALS
THE TABLE ABOVE SHOWS THE BIODEGRADABILITY OF LEATHER TANNED WITH OMW TECHNOLOGY
ROYAL SMIT & ZOON: THE FUTURE OF RETANNING IS NOW
Imagine retanning of the future. Low emissions, bio-based ingredients, no bisphenol and formaldehyde. With the power of a traditional phenolic retanning agent and no compromise on the performance, fullness and softness of the leather. Dear tanner, that future is now with BioTan XP 01L.
Bio-based solution with no detectable bisphenol
BioTan XP 01L is the latest innovation of Smit and part of their recently launched Renewability range. An innovative bio-based retanning agent that is produced by patented technology. It’s not a blend and not a filler. It is your next step in meeting the demand for low emissions and to build further towards a sustainable way of leather making.
The main benefits of BioTan XP 01L
* No detectable bisphenol
* Free of formaldehyde
* Tanning power, no filler
* Very low emission values
BioTan XP 01L gives you sustainable future-proof retanning without compromises on leather perfomance. Like no other retanning agent does.
No detectable bisphenol values

Multiple independent test results confirm this: bisphenol-F and bisphenol-S values are always below detection limit in BioTan XP 01L. On leather, so on Zeo White or wet blue retanned with BioTan XP 01L, analyses also show bisphenol values below detection limits on BPS, BPF, BPA, BPB.
For the sustainable and futureproof tanner
As a tannery your goal is to deliver high-quality leather to meet your customer’s demand. At the same time, you are challenged to continuously improve the sustainability in your processes and in your materials. Sustainable leather production is not an option, but a necessity. For your business and for our planet. Royal Smit & Zoon is your partner in differentiating you as a sustainable and futureproof tanner. With innovative solutions such as BioTan XP 01L, and more. We help you create real impact and maximize environmental benefits by optimizing your entire leather recipe.
Here to help you
With in-depth knowledge on renewability and emission values of our products, we can provide excellent support when developing leather articles with high bio-based content. We can assist from process to products and optimize your leather recipes, together with you.

BioTan XP 01L, an innovative bio-based retanning agent that paves the way towards a sustainable way of leather making
30 ARSTANNERY ADVERTORIAL
Is your company concerned about boosting the sustainability of the leather processing industry and are you ready to play a pioneering role? Contact us and find out how your company and Royal Smit & Zoon can together work towards a sustainable future. Do you want to receive more information about BioTan XP 01L? Go to smitwet-end.com/biotanxp or contact Laurence Irwin, Global Product Manager, laurence.irwin@smitzoon.com.
ROYAL SMIT & ZOON:
BioTan XP 01L, l’agente riconciante a base bio che porta verso la piena sostenibilità della produzione di pelle
Immaginate la riconcia del futuro. Ingredienti a base biologica e a basse emissioni, senza bisfenoli né formaldeide. La potenza di un tradizionale agente riconciante fenolico e nessun compromesso riguardo a prestazioni, pienezza e morbidezza della pelle. Caro conciatore, il futuro è adesso con BioTan XP 01L. Soluzione a base biologica senza bisfenolo rilevabile
BioTan XP 01L è l'ultima innovazione di Smit e fa parte della gamma Renewability lanciata di recente. Un innovativo agente riconciante a base biologica prodotto con una tecnologia brevettata. Non è una miscela e non è un riempitivo. È il prossimo passo per soddisfare la domanda di basse emissioni e per progredire verso un modo sostenibile di produrre la pelle.
I principali vantaggi di BioTan XP 01L
- Nessun bisfenolo rilevabile
- Senza formaldeide
- Potere conciante, nessun riempitivo
- Valori di emissione molto bassi
BioTan XP 01L offre una riconcia sostenibile e a prova di futuro, senza compromettere le prestazioni della pelle. Come nessun altro agente riconciante fa.
Nessun valore di bisfenolo rilevabile
Molteplici risultati di test indipendenti lo confermano: i valori di bisfenolo-F e bisfenolo-S sono sempre inferiori al limite di rilevamento in BioTan XP 01L. Sulla pelle, o su Zeo White o wet blue
riconciati con BioTan XP 01L, le analisi mostrano anche valori di bisfenolo al di sotto dei limiti di rilevamento di BPS, BPF, BPA, BPB. Per un conciatore sostenibile e orientato al futuro In qualità di conceria, il vostro obiettivo è quello di fornire pelle di alta qualità per soddisfare la domanda dei vostri clienti. Allo stesso tempo, siete chiamati a migliorare continuamente la sostenibilità dei vostri processi e dei vostri materiali. La produzione di pelle sostenibile non è un'opzione, ma una necessità. Per la vostra attività e per il nostro pianeta. Royal Smit & Zoon è il vostro partner per differenziarvi come conciatori sostenibili e all'avanguardia. Con soluzioni innovative come BioTan XP 01L e altre ancora. Vi aiutiamo a creare un impatto reale e a massimizzare i benefici ambientali ottimizzando l'intera ricetta della pelle.
Contate sulla nostra assistenza Grazie alla conoscenza approfondita dei valori di rinnovabilità e di emissione dei nostri prodotti, siamo in grado di fornire un eccellente supporto nello sviluppo di articoli in pelle ad alto contenuto di sostanze bio-based. Possiamo assistervi dal processo ai prodotti e ottimizzare le vostre ricette di pelle, insieme a voi. La vostra azienda è interessata a promuovere la sostenibilità dell'industria della lavorazione della pelle e siete pronti a svolgere un ruolo pionieristico? Contattateci e scoprite come la vostra azienda e Royal Smit & Zoon possono lavorare insieme per un futuro sostenibile.

IL FUTURE
DELLA CONCIA È ORA
ARSTANNERY 31 ADVERTORIAL
TFL AT THE MICROPHONE FOR SUSTAINABLE LEATHER
TFL was featured at the most recent events dedicated to tanning technology. The first event involved the annual convention of ALCA, the American Leather Chemists Association, held in Wisconsin last June 20-23. There TFL presented a paper entitled, "The way through the legislation maze to renewable leather". At the microphone was Christopher Tysoe, Head of Product Management Wet-end Crusting, who outlined TFL's solutions to help tanners not only comply with legal requirements but also exceed them and go beyond them. "Around the world, tanners are facing very serious challenges, such as new legal restrictions, but also significant new growth opportunities, for example, increased demand for sustainable products," Tysoe said. Against this challenging backdrop, TFL is standing alongside its customers to help them reap the rewards along the path to a new kind of natural and sustainable leather. Topics covered during the conference included a comparison between the status-quo of iconic synthetic tannins and recently launched super tanning products with high performance and low BPS/F technology. A full range of BPS/F-free wet end products was then presented to enable the production of all types of leather goods with the lowest possible BPS/F level.
INNOVATIVE SOLUTIONS
The multinational leather chemical company then participated in the Freiberg Leather Days, the traditional German industry technical event co-organized by VGCT and FILK last June 28-29. In Freiberg, TFL presented a paper specifically dedicated to "Bisphenols in Leather." Dr. Jens Fennen, Global Head of Research & Development, provided an in-depth analysis of the regulatory situation affecting bisphenols, as well as an overview of new technological solutions dedicated to tanneries to comply with future legal requirements. In particular, innovative technical solutions were presented aimed at demonstrating how it is possible to meet the challenges proposed by these regulations thanks to very recently developed products, including synthetic tannins with high tanning power and high fastnesses.
TFL AL MICROFONO PER UNA PELLE SOSTENIBILE
TFL è stata protagonista dei più recenti eventi dedicati alla tecnologia conciaria. Il primo appuntamento ha riguardato la convention annuale di ALCA, l’American Leather Chemists Association, svoltasi in Wisconsin dal 20 al 23 giugno scorso. In questa occasione TFL ha presentato una relazione dal titolo: “La via attraverso il labirinto legislativo per una pelle rinnovabile”. Al microfono Christopher Tysoe, Head of Product Management Wet-end Crusting, che ha illustrato le soluzioni TFL per aiutare i conciatori non solo a rispettare i requisiti di legge, ma anche a superarli e andare oltre. “In tutto

il mondo i conciatori stanno affrontando sfide molto serie, come le nuove restrizioni legali, ma anche nuove importanti opportunità di crescita, per esempio un aumento della domanda di prodotti sostenibili” ha detto Tysoe. In questo contesto sfidante TFL è al fianco dei propri clienti per aiutarli a raccogliere i frutti lungo il percorso verso un nuovo tipo di pelle naturale e sostenibile. Tra gli argomenti trattati durante la conferenza, il confronto tra lo status-quo di tannini sintetici iconici e i prodotti super concianti, con elevate prestazioni e tecnologia a ridotto contenuto di BPS/F lanciati di recente. E’ stata quindi presentata una gamma completa di prodotti wet end esenti da BPS/F, per permettere la produzione di tutti i tipi di articoli in pelle con il più basso livello possibile di BPS/F.
SOLUZIONI INNOVATIVE
La multinazionale chimica conciaria ha poi partecipato ai Freiberg Leather Days, il tradizionale appuntamento tecnico tedesco del settore co-organizzato da VGCT e FILK dal 28 al 29 giugno. A Friburgo, TFL ha presentato una relazione specificamente dedicata a “I bisfenoli nella pelle”. Il Dr. Jens Fennen, Global Head of Research & Development, ha fornito una analisi approfondita della situazione normativa che interessa i bisfenoli, oltre ad una panoramica delle nuove soluzioni tecnologiche a disposizione alle concerie per adeguarsi ai futuri requisiti di legge. In particolare, sono state presentate soluzioni tecniche innovative volte a dimostrare come sia possibile affrontare le sfide proposte da queste regolamentazioni grazie a prodotti di recentissimo sviluppo, inclusi tannini sintetici con elevato potere conciante ed elevate solidità.

La multinazionale chimica conciaria è stata protagonista dei più recenti convegni tecnici internazionali dove ha parlato delle restrizioni ai bisfenoli e di soluzioni tecniche innovative
The multinational leather chemicals company was protagonist at the most recent international technical conferences speaking about bisphenol restrictions and innovative technical solutions
DR. CHRISTOPHER TYSOE AT THE ALCA CONVENTION IN THE U.S. IL DR. CHRISTOPHER TYSOE ALLA CONVENTION ALCA NEGLI USA
DR. JENS FENNEN AT THE FREIBERG LEATHER DAYS IL DR. JENS FENNEN AI FREIBERG LEATHER DAYS
32 ARSTANNERY NEWS

ZSCHIMMER & SCHWARZ ACQUIRES 100% OF SAMIA
The German group expands its range of action to chemicals for leather finishing
how of both companies: "Samia offers outstanding tailor-made products for the leather finishing industry. In combination with Zschimmer & Schwarz’s wet-end product portfolio and our global positioning –with 28 companies in 16 countries on five continents – we can jointly develop new markets. In particular, Samia's expertise in research and development is an important building block here, and we expect great synergy potential in the field of sustainable solutions as well."
ZSCHIMMER & SCHWARZ ACQUISISCE IL 100% DELLE QUOTE SAMIA
Il gruppo tedesco amplia il proprio raggio d’azione ai prodotti per rifinizione
The German group Zschimmer & Schwarz completes the acquisition of the Veneto-based leather chemical company Samia. This is the latest stage in a journey that began in December 2019 when Zschimmer & Schwarz, a global supplier of auxiliaries and specialty chemicals based in Lahnstein, Germany, had acquired a 60% majority stake in Samia Spa, an Italian company based in Arzignano created in 1976 and specialized in the production of chemical products for leather finishing. Samia products are mainly used in the clothing, fashion accessories, automotive and leather furniture sectors. Thanks to the very successful experiences of recent years, the cooperation will be further intensified: On June 27, 2023, the Zschimmer & Schwarz Group acquired the remaining shares of the Italian company. Samia is therefore today a wholly owned subsidiary of the family business based in Lahnstein.
Luigi Ciarlo, Chief Executive Officer of Samia Spa, emphasises the advantages of the takeover: "With Zschimmer & Schwarz, we have a partner at our side that shares our philosophy regarding quality, longterm planning and customer proximity. In an increasingly international and competitive environment, we can benefit from Zschimmer & Schwarz's strong network and offer our products to a wider range of Press release 2/3 customers."
Dr Christoph Riemer, Chief Executive Officer of the Zschimmer & Schwarz Group, also sees great opportunities in the combined know-

Il gruppo tedesco Zschimmer & Schwarz completa l’acquisizione dell’azienda chimico conciaria veneta Samia. Si tratta dell’ultima tappa di un percorso iniziato nel dicembre 2019 quando Zschimmer & Schwarz, fornitore globale di ausiliari e specialità chimiche con sede a Lahnstein, Germania, aveva acquisito una quota di maggioranza del 60% di Samia Spa, azienda italiana con sede ad Arzignano creata nel 1976 e specializzata nella produzione di prodotti chimici per la rifinizione. I prodotti Samia sono utilizzati principalmente nei settori dell'abbigliamento, degli accessori moda, dell'automotive e dei mobili in pelle.
Grazie all’andamento positivo degli ultimi anni, la cooperazione sarà ulteriormente intensificata: il 27 giugno 2023, il Gruppo Zschimmer & Schwarz ha infatti acquisito le restanti azioni della società italiana. Samia è oggi quindi una controllata al 100% dell'impresa familiare con sede a Lahnstein.
Luigi Ciarlo, Amministratore Delegato di Samia Spa, sottolinea i vantaggi dell'acquisizione: "Con Zschimmer & Schwarz abbiamo un partner al nostro fianco che condivide la nostra filosofia in materia di qualità, pianificazione a lungo termine e vicinanza al cliente. In un ambiente sempre più internazionale e competitivo, possiamo beneficiare della forte rete di Zschimmer & Schwarz e offrire i nostri prodotti a una più ampia gamma di clienti."
Anche Christoph Riemer, Amministratore Delegato del Gruppo Zschimmer & Schwarz, vede grandi opportunità dalla sinergia: "Samia offre eccezionali prodotti su misura per il settore della rifinizione della pelle. In combinazione con il portafoglio di prodotti wet-end di Zschimmer & Schwarz e il nostro posizionamento globale - con 28 aziende in 16 paesi in cinque continenti - possiamo sviluppare congiuntamente nuovi mercati. In particolare, l'esperienza di Samia in ricerca e sviluppo è un elemento importante e ci aspettiamo un grande potenziale di sinergia anche nel campo delle soluzioni sostenibili.
DR CHRISTOPH RIEMER, CHIEF EXECUTIVE OFFICER OF THE ZSCHIMMER & SCHWARZ GROUP CHRISTOPH RIEMER, AMMINISTRATORE DELEGATO DEL GRUPPO ZSCHIMMER & SCHWARZ
34 ARSTANNERY NEWS
WORK ON SOLOFRA SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANT READY TO START

Campania region awarded contract to solve odor problem
After years of waiting, something is finally moving. Solofra's tanneries have been waiting for a long time for the purification plant, which requires structural work and upgrades. "Work to contain atmospheric emissions from the Solofra purification plant is starting," reads Il Mattino. The news is that the Campania Region "has summoned the contractor to the site areas to proceed with the formal assignment of the work." Substantial formality, the latter, since it has requested temporary release ("for the time necessary to carry out the work") by the Court of Avellino.
On June 1, 2023, the delivery of works for the "containment of atmospheric emissions" of the Solofrano plant was made by the Campania Region to solve the problem of malodors.
The Solofra tanning district consists of 170 companies, 2,000 employees and an annual turnover of more than 400 million euros. With 1.4 million euros, the Campania Region financed work on the containment of atmospheric emissions from the Solofra purification plant. And with a little more than 1 million the groundwater characterization plan for the area of the same town and the adjoining municipality of Montoro. The most urgent works include covering the tanks, vacuuming, filtering, and odor abatement. The sewage treatment plant, precisely because of the malodor issue, has been under impoundment with authority to use since 2017. The air sucked in from the tanks will be treated with a new scrubbler and an innovative biofiltration system, so that the area will be free of bad smells. Amount of the intervention: 1.4 million euros.
After years of bureaucratic standby, Solofra tanners hope this will be the right time, the first step in a structural work that will allow the local tanning district to finally make a qualitative leap by aligning itself with the rest of the country.
Another important issue is also open on the table in Solofra. It concerns the district's inclusion in SEZs (Special Economic Zones), the approval of which could be forthcoming and which could give a formidable boost to Solofra's tanning industry and its entire supply chain.
PRONTI A PARTIRE I LAVORI DEL DEPURATORE DI SOLOFRA
La Regione Campania ha assegnato l’appalto per risolvere il problema degli odori
Dopo anni di attesa, finalmente qualcosa si muove. Le concerie di Solofra attendono da molto tempo la messa in efficienza dell’impianto di depurazione che richiede interventi strutturali e di adeguamento. “Partono gli interventi di contenimento delle emissioni in atmosfera provenienti dal depuratore di Solofra”, si legge su Il Mattino. La notizia è che la Regione Campania “ha convocato l’impresa appaltatrice presso le aree di cantiere per procedere all’assegnazione formale dei lavori”. Formalità sostanziale, quest’ultima, poiché ha richiesto il dissequestro temporaneo (“per il tempo necessario all’esecuzione dell’intervento”) da parte del Tribunale di Avellino.
Il 1° giugno 2023 è stata effettuata la consegna dei lavori per il “contenimento delle emissioni in atmosfera” dell’impianto solofrano da parte della Regione Campania per risolvere il problema delle maleodoranze.
Il distretto conciario di Solofra è composto da 170 aziende, 2.000 dipendenti e un fatturato annuo di oltre 400 milioni di euro. La Regione Campania ha finanziato con 1,4 milioni di euro i lavori relativi al contenimento delle emissioni in atmosfera del depuratore di Solofra. E con poco più di un milione il piano di caratterizzazione della falda acquifera per l’area della stessa cittadina e del comune contiguo di Montoro.
Tra i lavori più urgenti figurano la copertura delle vasche, l’aspirazione, il filtraggio e l’abbattimento degli odori. Il depuratore, proprio per la problematica delle maleodoranze, è sotto sequestro con facoltà d’uso dal 2017. L’aria aspirata dalle vasche sarà trattata con un nuovo scrubbler e un sistema di biofiltrazione innovativo, così che la zona sarà libera dai cattivi odori. Importo dell’intervento: 1 milione e 400.000 euro.
Dopo anni di standby burocratici, i conciatori solofrani auspicano che si tratti della volta buona, il primo passo di un’opera strutturale che permetta al distretto della concia locale di fare finalmente un salto di qualità allineandosi al resto del Paese.
Sul tavolo di Solofra è aperta anche un’altra importante questione. Riguarda l’inserimento del distretto nelle aree ZES (Zone Economiche Speciali) la cui approvazione potrebbe essere prossima e che potrebbe dare una spinta formidabile alla concia di Solofra e a tutto il suo indotto.
ARSTANNERY 35 NEWS


GREENING OF RAW HIDES
 Edited by Dr. Gianluigi Calvanese SSIP Analysis, Certification and Consulting Area Manager
Edited by Dr. Gianluigi Calvanese SSIP Analysis, Certification and Consulting Area Manager
The purpose of greening is to return the hide to the same condition it was in immediately after separation from the carcass, that is, to restore the moisture content of the hide and fibers to a content similar to that of the live animal (about 65 percent throughout the cross-sectional area of the hides). This operation must also be geared toward achieving an effective separation of fibers and fibrils that will allow the penetration of chemicals that will be used in subsequent operations, primarily hair removal (if any), and eliminate undesirable components such as globular proteins, salt, and dirt. The chemicals that can be used at this stage are the most diverse because of the different effect/interaction they can have on the hide.
For example, the main goal for using acid or alkaline agents is to try to reduce the time required for the operation, due to the fact that collagen in hides has two pH peaks where water absorption is most effective (pH 2.4 and pH 11.6). Acid greening allows the characteristics of the hair to be preserved, so it is mainly used for articles where it is intended to preserve the hair itself until the end of processing. For hides to be depilated, the most common practice is greening in an alkaline environment through usually sodium carbonate, sodium hydroxide, or ammonium hydroxide, which also prepares the leather for the next stage of depilation.
The use of some neutral salts, especially sodium chloride, promotes the absorption of water, but also the solubilization of globular proteins, while preventing bacterial growth. Products that give lyotropic effect, such as cal-
cium chloride, can also be used in the greening of dried leathers, which act by contributing to water absorption by causing hydrogen bonds between fibers to break.
Some products such as calcium chloride are known to have a lyotropic effect on hides and leather structure. This effect is related to the breaking of hydrogen bonds.

Certain products such as calcium chloride are known to have a lyotropic effect on skins and skin structure. This effect is related to the breaking of hydrogen bonds between fibers and may help accelerate water absorption. The use of such products is mainly. These products are not generally used as coarse chemicals, but instead are usually available as commercial compounds and blends produced by companies specializing in leather chemicals.
Given the objectives of greening, substances of a surfactant nature are also usually used, which can be selected, in terms of their predominant action, on the basis of their affinity toward fatty substances. An index of such affinity is given by the HLB (hydrophilic-lipophilic balance), due to which lipophilic surfactants have values below 9, hydrophilic surfactants above 11, and neutral surfactants have intermediate values. In practical application, surfactants with lower HLB are used mainly for their degreasing properties, while those with high HLB are used for their cleansing and moisturizing abilities. In greening, both actions are sought, so the tendency is to use a combination of high and low HLB.
It is also possible to use in greening proteolytic enzyme preparations specifically designed to facilitate the treatment of dried hides, but also to reduce the greening time on hides preserved by other methods. However, as with all enzyme technologies, care must be taken to avoid excessive action that
In the study conducted by the Italian Leather Research Institute, the objectives and technological aspects of a crucial operation in the tanning process are analyzed
38 ARSTANNERY RESEARCH
could lead to irreversible defects on leathers. In any case, favorable conditions for bacterial growth are created during greening, and therefore it is important to implement preventive measures to hinder the resulting degradation processes, i.e., to use appropriate preservatives.
From the technological point of view, the most relevant process parameters are temperature, mechanical action and bath volume.
The choice of process temperature must result from the trade-off between the need to optimize treatment time and the increased risk of bacterial attack. In any case, temperatures must be kept below 40 °C to maintain a certain level of safety against thermal degradation of raw hides since the shrinkage temperature, i.e., the temperature at which hides would begin an irreversible degradation-shrinkage process, is about 60 °C at this stage. For this reason, greening is usually effectively performed at temperatures around 18 °C to 20 °C in order to ensure limited bacterial attack as well. Mechanical action is particularly relevant in the case of greening of dried hides. In this case, the fibers are glued together, the flexibility of the leather is reduced, and mechanical action is likely to break the fibers irreversibly. Therefore, greening normally begins with as little mechanical action as possible, until there is static greening for dried hides. As the hides absorb water, the fibers become more flexible, thus allowing the application of mechanical action to accelerate greening.
Considerations for the choice of bath volume are directly related to mechanical action. Too low a bath volume would significantly increase the mechanical action, so it is never recommended at this stage. Add to this the fact that, during the process, leathers absorb more and more water, with concomitant increase in mechanical action correlated with the reduction in bath volume, which will therefore have to be in an appropriately high ratio to preserve the commodity properties of the leathers.
Source: Newsletter SSIP Leather Update #25/23
RINVERDIMENTO DELLE PELLI GREZZE
Nello studio condotto dalla Stazione Pelli si analizzano obiettivi ed aspetti tecnologici di un’operazione cruciale del processo di lavorazione conciario
A cura di Dott. Gianluigi Calvanese
Responsabile Area Analisi, Certificazione e Consulenza SSIP
Lo scopo del rinverdimento è quello di riportare la pelle nelle stesse condizioni in cui si trovava subito dopo la separazione dalla carcassa, ovvero ripristinare il contenuto di umidità della pelle e delle fibre a un contenuto simile a quello dell’animale vivo (circa il 65% in tutta la sezione trasversale delle pelli). Tale operazione deve essere inoltre orientata ad ottenere un’efficace separazione di fibre e fibrille che consenta la penetrazione di sostanze chimiche che verranno utilizzate nelle operazioni successive, in primis la depilazione (se prevista), ed eliminare i componenti indesiderati come proteine globulari, sale e sporco. I prodotti chimici che possono essere utilizzati in tale fase sono i più disparati in ragione del diverso effetto/interazione che possono avere sulla pelle grezza.
Ad esempio, l’obiettivo principale per l’utilizzo di agenti acidi o alcalini è cercare di ridurre il tempo necessario per l’operazione, in ragione del fatto che il collagene nelle pelli ha due picchi di pH in cui l’assorbimento dell’acqua è più efficace (pH 2,4 e pH 11,6). Il rinverdimento acido consente di preservare le caratteristiche del pelo, per cui è utilizzato principalmente per articoli in cui si intende conservare il pelo stesso fino alla fine delle lavorazioni. Per le pelli da depilare, la pratica più comune è quella di rinverdire in ambiente alcalino tramite solitamente carbonato di sodio, idrossido di sodio o idrossido di ammonio, che prepara la pelle anche alla successiva fase di depilazione.
L’uso di alcuni sali neutri, soprattutto cloruro di sodio, favorisce l’assorbimento dell’acqua, ma anche la solubilizzazione delle proteine globulari, prevenendo nel contempo la crescita batterica. Nel rinverdimento di pelli essiccate possono essere utilizzati anche prodotti che danno effetto liotropico, quali il cloruro di calcio, che agiscono contribuendo all’assorbimento d’acqua causando la rottura dei legami idrogeno tra le fibre.
È risaputo che alcuni prodotti come il cloruro di calcio hanno un effetto liotropico sulle pelli e sulla struttura della pelle. Questo effetto è correlato alla rottura dei legami idrogeno tra le fibre e può contribuire ad accelerare l’assorbimento dell’acqua. L’uso di tali prodotti è principalmente. Questi prodotti non sono generalmente impiegati come prodotti chimici grossolani, ma sono invece solitamente disponibili come composti e miscele commerciali prodotti da aziende specializzate in prodotti chimici per la pelle. Visti gli obiettivi del rinverdimento, sono solitamente utilizzate anche sostanze di natura tensioattiva, che possono essere selezionate, in termini di azione prevalente, sulla base della propria affinità verso le sostanze grasse. Un indice di tale affinità è dato dal HLB (bilancio idrofilo-lipofilo), in ragione del quale i tensioattivi lipofili hanno valori inferiori a 9, quelli idrofili superiori a 11, quelli neutri presentano valori intermedi. Nell’applicazione pratica i tensioattivi a HLB inferiore sono utilizzati principalmente per le loro proprietà sgrassanti, mentre quelli con elevato HLB sono utilizzati per le loro capacità detergenti e idratanti. Nel rinverdimento si ricercano entrambe le azioni, pertanto la tendenza è quella di utilizzare una combinazione di HLB alti e bassi.
E’ possibile utilizzare in rinverdimento anche preparati a base di enzimi proteolitici, studiati appositamente per facilitare il trattamento di pelli essiccate, ma anche per ridurre il tempo di rinverdimento su pelli conservate con altri metodi. Tuttavia, come per tutte le tecnologie enzimatiche, è necessario prestare attenzione per evitare un’azione eccessiva che potrebbe portare a difetti irreversibili sulle pelli. In ogni caso, durante il rinverdimento si creano condizioni favorevoli per la crescita batterica, e pertanto è importante attuare misure preventive per ostacolare i conseguenti processi di degrado, ovvero utilizzare opportuni preservanti.
Dal punto di vista tecnologico i parametri di processo maggiormente rilevanti sono la temperatura, l’azione meccanica e il volume del bagno. La scelta della temperatura di processo deve derivare dal compromesso tra la necessità di ottimizzare i tempi di trattamento e l’aumento del rischio di attacco batterico. In ogni caso le temperature devono essere mantenute al di sotto dei 40 °C per mantenere un certo livello di sicurezza contro il degrado termico delle pelli grezze poiché la temperatura di contrazione, ovvero la temperatura alla quale le pelli inizierebbero un processo irreversibile di degradazione-restringimento, in questa fase è di circa 60 °C. Per questo motivo il rinverdimento viene solitamente efficacemente eseguito a temperature intorno ai 18 °C – 20 °C al fine di garantire anche un attacco batterico limitato.
L’azione meccanica è particolarmente rilevante nel caso del rinverdimento delle pelli essiccate. In questo caso le fibre sono incollate tra loro, la flessibilità delle pelli è ridotta, e l’azione meccanica rischia di rompere irreversibilmente le fibre. Pertanto, il rinverdimento inizia normalmente con la minima azione meccanica possibile, fino ad avere un rinverdimento statico per pelli essiccate. Man mano che le pelli assorbono l’acqua, le fibre diventano più flessibili, consentendo così l’applicazione dell’azione meccanica per accelerare il rinverdimento.
Le considerazioni per la scelta del volume di bagno sono direttamente correlate all’azione meccanica. Un volume di bagno troppo basso aumenterebbe significativamente l’azione meccanica, pertanto, in questa fase, non è mai consigliato. A ciò si aggiunga che, durante il processo, le pelli assorbono sempre di più acqua, con contestuale aumento dell’azione meccanica correlata alla riduzione del volume di bagno, che dovrà essere quindi in rapporto adeguatamente elevato per preservare le proprietà merceologiche delle pelli.
Fonte: Newsletter SSIP Leather Update #25/23
ARSTANNERY 39 RESEARCH
LEATHER NATURALLY LAUNCHES ‘GET THE FACTS’-ICON

The market demands transparency. Consumers seek clear information about the products and materials they buy. Understanding this, Leather Naturally has developed a ‘Get the Facts’-Icon, which has been created for brands, retailers, makers – indeed anyone that wants to provide access to straightforward, easy to understand information about leather for their audience or customers.
Available as a simple graphic link for online use (by adding the link https:// www.leathernaturally.org/resources/fact-sheets/, or a QR-code enabled icon that can be featured on Point of Sale at retail, in product brochures or magazines, even in training guides. It takes the user direct to the Fact Sheet section of our website, where they will find information they need in English, German, Italian, Dutch, Spanish and Portuguese. Leather Naturally Communications lead, Claudia Spahr commented, “We have seen an increased demand for fast-to-find facts and our new icon provides instant access to what we know is the most frequently searched information, as well the wider content of the Leather Naturally website, including our comprehensive Modern Leather Making Guide, which is also proving an invaluable training resource for brands and retailers.”
The ‘Get the Facts’-Icon is available, free to use for all and interested parties can register for more information about its use at this link https://www.leathernaturally.org/resources/features/get-the-facts-icon/
LEATHER NATURALLY LANCIA L’ICONA 'GET THE FACTS'
pratico per offrire ai consumatori
chiare sui prodotti e sui materiali che acquistano
Il mercato chiede trasparenza. I consumatori cercano informazioni chiare sui prodotti e sui materiali che acquistano. Per rispondere a questo bisogno Leather Naturally ha sviluppato l'icona "Get the Facts", creata per marchi, rivenditori, produttori e tutti coloro che desiderano fornire al proprio pubblico o ai propri clienti informazioni chiare e di facile comprensione sulla pelle.
Disponibile come semplice link grafico per l'uso online (aggiungendo il link: https://www.leathernaturally.org/resources/fact-sheets/), o come icona abilitata al QR-code che può essere inserita nei punti vendita al dettaglio, nelle brochure o cataloghi prodotto, persino nelle guide di formazione. L'icona porta l'utente direttamente alla sezione Fact Sheet del sito web di Leather Naturally, dove troverà le informazioni di cui ha bisogno in inglese, tedesco, italiano, olandese, spagnolo e portoghese.
Claudia Spahr, responsabile della comunicazione di Leather Naturally, spiega: "Abbiamo riscontrato un aumento della domanda di informazioni rapide da reperire e la nostra nuova icona fornisce un accesso immediato a quelle che sappiamo essere le informazioni più ricercate, nonché ai contenuti più ampi del nostro sito web, tra cui la nostra esauriente Guida alla lavorazione moderna della pelle, che si sta rivelando una risorsa informativa preziosa per marchi e rivenditori".
L'icona "Get the Facts" è disponibile gratuitamente per tutti.
Gli interessati possono registrarsi per ricevere maggiori informazioni sul suo utilizzo a questo link: https://www.leathernaturally.org/resources/features/get-the-facts-icon/
Leather Naturally acts as a global voice for the Leather industry to promote the use of certified, responsibly made leather by providing trusted facts and inspiration for consumers, designers and brands.
Un sistema semplice e
informazioni
A simple and effective system to offer consumers clear information on the products and materials they buy
40 ARSTANNERY NEWS
APLF ASEAN RETURNS TO BANGKOK
The second edition of APLF ASEAN will be held Oct. 25-27, 2023 in Halls 1 and 2 of the state-of-the-art Queen Sirikit National Convention Centre (QSNCC) in downtown Bangkok. Launched after APLF Dubai 2022 to offer a dedicated exhibition moment for the Asian market, the first-time Bangkok Leather Fair quickly gained favor with operators and is now being renewed to meet the demand of exhibitors and visitors from the first edition, organizers explain. Requests for participation are on the rise: 250 exhibitors are currently expected (there were 200 last year) including several national groups. Among the largest groups are Thai tanneries and Italian machinery manufacturers, followed by a significant participation of Chinese footwear and leather goods component companies. The Asean area is now a very attractive destination for industry players, just look at the data: this bloc imports $2.5 billion of all types of hides, skins and leathers, not far from the $3.27 billion imported from China. The ten member countries of ASEAN (Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam) have a population of 660 million and generated a total gross domestic product (GDP) of $3.4 trillion in 2021, or 3.5 percent of global GDP. This figure places ASEAN as the third largest economy in Asia after China and Japan and fifth largest globally. The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) that came into effect last year has greatly strengthened trade incentives in the area by reducing tariffs and export costs for the 10 ASEAN countries' trade with Australia, China, Japan, New Zealand and South Korea. With the need to import raw materials, components and chemicals to feed production lines, ASEAN offers multiple export opportunities for Western companies looking to increase their business presence in the region.
APLF ASEAN will include elements of Matching, Education, Experience and Tradeshow. There will be seminars and courses covering the hottest topics in the industry. One of the remarkable events will be the Tanning Master Class, where key leather chemical companies will host trainings for local technicians. The fair also highlights the Designer Showcase and Material Trends area, which offer a wealth of inspiration for designers and manufacturers looking to stay ahead of the curve in the next fashion season.
APLF ASEAN is supported by the Thai Tanning Industry Association (TTIA), the Vietnamese Leather, Footwear and Handbag Association (LEFASO) and the Indonesian Tanners Association (APKI).

For more information about APLF ASEAN: www.aplf.com/asean2023
APLF ASEAN TORNA A BANGKOK
La seconda edizione della manifestazione dedicata all’area ASEAN si terrà dal 25 al 27 ottobre 2023
La seconda edizione di APLF ASEAN è programmata dal 25 al 27 ottobre 2023 nei padiglioni 1 e 2 del modernissimo Queen Sirikit National Convention Centre (QSNCC), nel centro di Bangkok.
Lanciata dopo APLF Dubai 2022 per offrire un momento espositivo dedicato al mercato asiatico, la prima volta della fiera della pelle di Bangkok si è guadagnata subito il favore degli operatori e oggi rinnova il suo appuntamento per rispondere alla richiesta di espositori e visitatori della prima edizione, come spiegano gli organizzatori.
Peraltro sono in aumento le richieste di partecipazione: al momento sono previsti 250 espositori (erano 200 lo scorso anno) tra cui diverse collettive nazionali. Tra i gruppi più numerosi, quello delle concerie thailandesi e dei produttori italiani di macchinari, cui fa seguito una significativa partecipazione di aziende cinesi della componentistica.
L’area Asean è oggi una destinazione molto attraente per gli operatori del settore, basta guardare ai dati: questo blocco importa 2,5 miliardi di dollari di tutti i tipi di pelle, non lontano dai 3,27 miliardi di dollari importati dalla Cina. I dieci Paesi membri dell'ASEAN (Brunei, Cambogia, Indonesia, Laos, Malesia, Myanmar, Filippine, Singapore, Thailandia e Vietnam) hanno una popolazione di 660 milioni di abitanti e hanno generato un prodotto interno lordo (PIL) totale di 3,4 trilioni di dollari nel 2021, pari al 3,5% del PIL globale. Questo dato colloca l'ASEAN come terza economia in Asia dopo Cina e Giappone e quinta a livello globale. Il Partenariato Economico Globale Regionale (RCEP) entrato in vigore lo scorso anno ha notevolmente rafforzato gli incentivi commerciali in quest’area, grazie alla riduzione delle tariffe e dei costi di esportazione per gli scambi dei 10 Paesi ASEAN con Australia, Cina, Giappone, Nuova Zelanda e Corea del Sud. Con la necessità di importare materie prime, componenti e prodotti chimici per alimentare le linee di produzione, l’ASEAN offre molteplici opportunità di esportazione alle aziende occidentali che desiderano aumentare la propria presenza commerciale nella regione.
APLF ASEAN comprenderà elementi di matching, formazione, situazioni esperienziali e fiera. Ci saranno seminari e corsi che copriranno i temi più caldi del settore. Uno degli eventi più importanti sarà il Tanning Master Class, in cui le principali aziende chimiche della pelle terranno corsi di formazione per i tecnici locali. In evidenza anche la Designer Showcase e l’area Material Trends, che offrono una ricchezza di ispirazioni per i designer e i produttori che vogliono essere all’avanguardia per le prossime stagioni.
APLF ASEAN è supportata dalla Thai Tanning Industry Association (TTIA), dalla Vietnamese Leather, Footwear and Handbag Association (LEFASO) e dalla Indonesian Tanners Association (APKI).
Per maggiori informazioni su APLF ASEAN: www.aplf.com/asean2023
The second edition of the event dedicated to the ASEAN region will be held Oct. 25-27, 2023
ARSTANNERY 41 FAIRS
ALL IN CHINA FOR ACLE 2023
The All China Leather Exhibition (ACLE) returns to the spotlight after a fouryear hiatus due to the pandemic and the resulting company closures, travel restrictions and mandatory quarantines that effectively made it impossible to organize China's most important industry event. The return of the Shanghai Leather Fair thus stands as a major event, first and foremost because it will provide an opportunity to test firsthand the changes that have taken place in the Chinese market and reconnect directly with local customers. Now in its 23rd year, ACLE is scheduled for Aug. 29-31 and as always will be hosted at the Shanghai New International Exhibition Centre (SNIEC), located in the Pudong Financial District. On display, over seven pavilions with an exhibition area of 80,500 square meters - of which about 23,000 square meters will be allocated to international exhibitors - will be the entire leather supply chain: from raw hide suppliers to tanners, from chemical auxiliary manufacturers to manufacturers of leather processing machinery and technology.
As always organized by APLF Ltd. and China Leather Industry Association (CLIA), the Shanghai fair this year counts on the participation of more than 950 exhibiting companies and expects the arrival of at least 20,000 buyers, about 80 percent of whom will come from the main manufacturing provinces of mainland China. The organizers are working on an intensive promotional campaign aimed at attracting visitors from all manufacturing regions of China and other countries. In particular, CLIA is organizing buyer groups from 47 Chinese industrial manufacturing areas such as Yinan, Jiangsu, Suzhou, Haining, Jinjiang and Yanshui. The participation of a group of buyers and exhibitors from the leather city of Haining as well as the Xinhaopan Group has also been announced. Among the international exhibitors, national groups from Australia, Brazil, France, Italy, Pakistan, Taiwan the United States interested in re-establishing face-to-face business contacts with their Chinese customers are expected. As always, there will also be numerous side events that will enliven the fair, such as trend presentations and technical seminars. Highlights include a Technological Innovation Conference that will consist of four sessions during the first and second days, each lasting 10 to 15 minutes. Topics include new challenges in leather processing and chemicals. A Tanning Industry Summit will also be held on the first day of the fair, whose topics include the technology roadmap for water conservation and emission reduction for the tanning industry. For more information www.aclechina.com.
TUTTI IN CINA PER ACLE 2023
fine agosto torna l’appuntamento con la fiera di Shanghai, un’occasione imperdibile per scoprire come è cambiato il mercato della pelle cinese
La All China Leather Exhibition (ACLE) torna alla ribalta dopo una pausa di quattro anni dovuta alla pandemia e alle conseguenti chiusure aziendali, restrizioni di viaggio e quarantene obbligatorie che hanno di fatto reso impossibile organizzare la più importante manifestazione cinese del settore. Il ritorno della fiera della pelle di Shanghai si attesta dunque come un evento di primo piano, innanzitutto perché offrirà l’occasione per testare con mano i cambiamenti avvenuti sul mercato cinese e riallacciare relazioni dirette con la clientela locale.
Giunta alla sua 23.a edizione, ACLE è programmata dal 29 al 31 agosto e come sempre sarà ospitata presso lo Shanghai New International Exhibition Centre (SNIEC), situato nel distretto finanziario di Pudong. In mostra, su sette padiglioni per una superficie espositiva di 80.500 metri quadri - di cui circa 23mila destinati agli espositori internazionali – si troverà l'intera filiera della pelle: dai fornitori pelli grezze ai conciatori, dai produttori di ausiliari chimici ai costruttori di macchinari e tecnologie per la lavorazione della pelle.
Come sempre organizzata da APLF Ltd e China Leather Industry Association (CLIA), la fiera di Shanghai quest’anno conta sulla partecipazione di oltre 950 aziende espositrici e aspetta l’arrivo di almeno 20.000 buyers, di cui circa l'80% provenienti dalle principali province manifatturiere della Cina continentale. Gli organizzatori stanno lavorando ad un’intensa campagna promozionale mirata ad attirare visitatori da tutte le regioni produttive della Cina e da altri Paesi. In particolare, CLIA sta organizzando gruppi di buyer provenienti da 47 aree produttive industriali cinesi come Yinan, Jiangsu, Suzhou, Haining, Jinjiang e Yanshui. E’ stata annunciata anche la partecipazione di un gruppo di buyers e di espositori della città della pelle di Haining oltre che del gruppo Xinhaopan. Tra gli espositori internazionali, sono previsti gruppi nazionali provenienti da Australia,Brasile, Francia, Italia, Pakistan, Taiwan e Stati Uniti interessati a ristabilire contatti commerciali faccia a faccia con i propri clienti cinesi. Come sempre saranno numerosi anche gli eventi collaterali che animeranno la fiera, come presentazioni di tendenze e seminari tecnici. Tra gli appuntamenti più importanti, segnaliamo una Conferenza sull'innovazione tecnologica che consisterà in 4 sessioni durante il primo e il secondo giorno, ognuna delle quali durerà dai 10 ai 15 minuti. Tra gli argomenti le nuove sfide della lavorazione della pelle e i prodotti chimici. Il primo giorno di fiera, si terrà anche un Summit dell'Industria Conciaria, i cui temi includono la roadmap tecnologica per il risparmio idrico e la riduzione delle emissioni per l'industria conciaria. Per ulteriori informazioni www.aclechina.com.

A
The Shanghai exhibition returns in late August, an unmissable opportunity to find out how the Chinese leather market has changed
42 ARSTANNERY FAIRS

APPLICATION OF ZEOLITE BASED NANOCOMPOSITES FOR WASTEWATER REMEDIATION: EVALUATING NEWER AND ENVIRONMENTALLY BENIGN APPROACHES
Source: Environmental Research 231 (2023) 116073
Emmanuel Christopher Umejuru a, Tebogo Mashifana a, Vepika Kandjou a,b, Majid Amani-Beni c , Hasan Sadeghifar d, Mahsa Fayazi e, Hassan Karimi-Maleh e,*, Nastassia Thandiwe Sithole a,**
a Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Johannesburg, P.O. Box 17011, Doornfontein, 2088, South Africa
b Department of Chemical Materials and Metallurgical Engineering (CMME), Faculty of Engineering and Technology (FET), Botswana International University of Science and Technology (BIUST), P/Bag 16, Palapye, Botswana
c School of Architecture, Southwest Jiaotong University, 611756, Chengdu, China
d R&D Laboratory, Hollingsworth & Vose (H&V) Company, West Groton, MA, 01452, USA
e School of Resources and Environment, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 611731, Xiyuan Ave, Chengdu, PR China
1. INTRODUCTION
Globalisation and industrialization have culminated into increased discharge of toxic inorganic and organic substances into water bodies (Ameen et al. 2021; Günay et al. 2022). Most of these contaminants are non-biodegradable and are not removed entirely during wastewater treatment (Mohammadnezhad and Behbahan, 2020). These include heavy metals, dyes and pharmaceutical products, which are harmful at minute level and ubiquitous in wastewater (Karaman et al. 2022; Sab- reena et al. 2022). Therefore, devising effective techniques to eliminate toxic substances in wastewater is not only urgent and challenging but highly significant(Marcelo et al. 2021). Different methods such as sedimentation, oxidation, distillation, adsorption, photocatalysis and electrolysis have been used in wastewater treatment (Karimi et al. 2022a; Rahighi et al. 2022). Adsorption is among the outstanding techniques for removal of toxic substance via the use of adsorbents (Alaguprathana et al. 2022). Its advantages include simplicity, cost effectiveness and ease of operation (Hamd et al. 2022). However, the main challenge with adsorption technique is to prepare an adsorbent that is cheap, efficient and reusable(Lin et al. 2020). Typically, for an adsorbent to be effective it must have large surface area, excellent chemical, physical and mechanical stability as well as strong attraction for binding with the contaminant (Huang et al. 2023). Photocatalysis using nanocomposite is another method of wastewater treatment that has gained great attention due to its ability to degrade organic pollutants and achieve complete mineralization in most cases(Gallucci et al. 2022). Several materials are currently being explored as adsorbents, these include the carbon based materials such as carbon nanotubes (CNTs) which offer a significant separation of water molecules from contami- nants as a result of the non-slip phenomenon(Kalra et al. 2003; Holt et al. 2006). Nonetheless, their poor processability, cost ineffectiveness as well as difficulties in preparing CNT matrices for water treatment is a well-documented challenge limiting their use (Kim et al. 2007; Yu et al. 2009). Another carbon based materials that is promising is graphene, this is from its eccentric physico-mechanical characteristics. Its charac- teristics gives the prospect of fabricating mechanically stable and effi- cient membranes in water purification, treatment and desalination. Again, it is increasingly being limited by high costs of production owing to limited large scale production scalability (Kandjou et al. 2019a, 2019b, 2021).
Comparative to the other aforementioned materials, zeolites are cheap crystalline aluminium materials that contain silicate with large surface area and negative charge suitable for adsorption and photocatalysis. Previous research has shown that the large surface area of zeolite in nanocomposite played major role during adsorption (Mirjavadi et al. 2019).
In this survey, the utilization of zeolite based nanocomposites as adsorbents and photocatalysts for extraction of heavy metals, dyes and emerging pollutants is broadly discussed and analysed. Detailed dis- cussion on various fabrication techniques for zeolite based nanocomposites and photodegradation pathways was also reported. In summation, the paper is aimed at shedding light and understanding of the significance and arch advantage of the use of zeolites an ted materials in the purification and treatment of tainted waters.
2. Fabrication and characterization of zeolite based nanocomposite
Thanks to the state-of-developments in science, it is possible to utilize various nanocomposite in different areas such as catalyst (Jafarzadeh et al. 2022; Karimi-Maleh et al. 2022), energy (Karaman, 2021; Karimi et al. 2022b), sensors (Zhang & Karimi-Maleh, 2023a, 2023b; Zoubir et al. 2023), electronics (Zhang et al. 2021; Wang et al. 2022), biotechnology (Ameen et al. 2022; Magne et al. 2022), environment (Lekshmi et al. 2021; Mubarak et al. 2022; Zheng et al. 2022)etc. Amongst the various nanocomposites, the zeolite based nanocomposite adsorbent comprises of multiphase in which different materials such as polymer (Motamedi et al. 2022), carbon (Arabkhani et al. 2021) and metal nanoparticles (Zhang et al. 2020) are incorporated into zeolite material for removal of toxic organic and inorganic substances. Nano- composite combines the benefits of different materials with unique physicochemical features to improve their effectiveness. In various cases, zeolite can be functionalized to enhance its selectivity for removal of organic pollutants and heavy metals (Bien et al. 2021).
Different methods to the fabrication of zeolite based nanocomposite adsorbents are reported in literature. For instance, Shyaa et al., prepared poly- aniline/zeolite nanocomposite through oxidative polymerization of an- iline with zeolite and the cation was exchanged by anilinium ions (Shyaa et al. 2015). In another study, zeolite carbon material was synthesized through hydrothermal technique (Farghali et al. 2021). Zeolite magnetic nanocomposites are prepared by incorporating met-
44 ARSTANNERY RESEARCH
al nanoparticles into zeolite, which can be easily separated after treatment using magnetic field. Evidently, Gaffer et al. prepared magnetic zeolite-chitosan through sol-gel technique for removal of Cr(VI) (Gaffer et al. 2017). The forma- tion of magnetic zeolite is displayed in Fig. 1. The different techniques for fabrication of zeolite based nano- composite adsorbents exists ranging from hydrothermal to oxidative polymerization (Table 1).
The investigation of chemical and physical features of the prepared material is essential for the evaluation of its performance as an adsorbent and photocatalyst. Various analytical techniques help in revealing the coarseness, chemical composition and morphology of the fabricated zeolite based materials. These include transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, Four- ier transform infrared spectroscopy, Brunauer-Emmett-Teller and X-ray diffraction are used to characterize zeolite-based nanocomposite ad- sorbents and photocatalyts. With a target contaminant to be removed, different materials are coupled with zeolite to enhance certain charac- teristics as aforementioned.
A typical example in this realm was demonstrated by Domoroshchina et al. in the fabrication of a nanocomposite of Zeolite Y and Nanosized Titanium Dioxide in situ to improve its photocatalytic performance. A change in several characteristics of the resultant nanocomposite were
observed, for instance, reduction in particle size was demonstrated by means of scanning electron microscopy while XRD characterizations demonstrated pore morphology and the presence of water molecules. X- ray photoelectron spectroscopy on the other hand depicted an increase in the percentage of water content on the surface of zeolite composite relative to the original pristine zeolite Y. Increased specific surface area of the composite was also thereafter demonstrated by the Bru- nauer–Emmet–Teller (BET) method. This increase was advocated to the presence of nanocrystalline NTD on zeolite Y surface as well as the fabrication conditions entailed. In the study, the composite demon- strated higher photocatalytic activity in the decomposition reaction of methyl orange(Domoroshchina et al. 2018).
Fig. 2 shows the different materials used in formation of zeolite-based nanocomposite as well as the adsorbate to be removed.
3. Use of zeolite based nanocomposites as adsorbents
Zeolite based nanocomposite adsorbents have been widely explored for adsorption of various toxic pollutants which include organic dyes, emerging pollutants, heavy metals and metalloids in aqueous media. This section explains the removal of different noxious pollutants by zeolite based nanocomposite adsorbents.
 FIG. 1 SYNTHESIS OF MAGNETIC/ZEOLITE (ANGARU ET AL. 2021).
FIG. 1 SYNTHESIS OF MAGNETIC/ZEOLITE (ANGARU ET AL. 2021).
ARSTANNERY 45 RESEARCH
FIG. 2. DIFFERENT MATERIALS USED IN FORMATION OF ZEOLITE BASED NANOCOMPOSITE.
3.1. Organic dyes
Dye is useful in printing, food and textile industry. However, wastewater containing dye released during the production process is highly toxic, non-biodegradable, complex and persistent thereby mak- ing it difficult to be removed (Xiong et al. 2021). These can cause serious environmental and human health problem. Dyes are mainly grouped into basic, reactive, disperse and acid (Piri et al. 2019). The removal ability of various zeolite based nanocomposite adsorbents for different dyes showed significant difference as displayed in Table 2. This can be attributed to the influence of pH, temperature, nature of nanomaterial, type of dye as well as charges. For example, NaX zeolite/MgO–TiO2 nanocomposite was fabricated and explored for removal of methyl orange (MO) and sorption capacity of 53.76 mg/g was achieved. The study revealed that the process was affected by solution pH (Mirzaei et al. 2020). In another report, polypyrrole/zeolite (PPy/Ze) nanocomposite was used to remove reactive blue and reactive red(Senguttuvan et al. 2022). The removal percentage was 82.6% and 88.3% for reactive blue and reactive red at optimum pH 9. It was observed that pH affected the removal process. The excellent removal percentage was ascribed to the availability of reactive sites in PPy/Ze nanocomposite and its large surface area (Senguttuvan et al. 2022). Furthermore, the adsorption mechanism revealed that functional groups such as amide, hydroxyl and aromatic present in the nanocomposite participated in its interaction with the dyes. Piri et al. (2019) prepared magnetic zeolite/hydrox- yapatite (MZeo-HAP) nanocomposite through microwave-assisted technique and applied it for adsorption of Congo red (CR), Reactive orange 16 (RO), and RO5 in aqueous media. The sorption capacity of 104.05, 88.31 and 92.45 mg/g were obtained for CR, RO16 and RO5 at optimum pH 2. In addition, adsorption mechanism revealed that the interaction between MZeo-HAP and the dyes was electrostatic attraction due to the negatively charged groups of MZeo-HAP and positively charged groups of CR, RO16 and RO5. Increasing the temperature led to an increase in adsorption capacity, according to thermodynamic analysis.
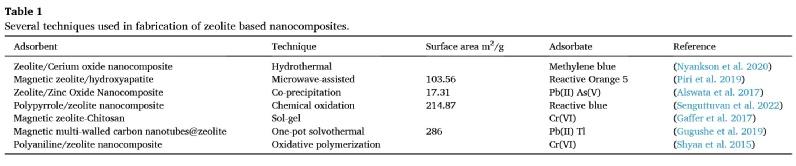
3.2. Heavy metals and metalloids
Industrial activities from batteries, fertilizers, tanneries, mining and metal plating contributes to the increased discharge of heavy metals such as copper(Cu), lead (Pb), zinc(Zn), nickel(Ni), cadmium(Cd), chromium(Cr), as well as metalloids like arsenic(As). Ingestion of these noxious elements causes skin and lungs cancer(Alswata et al. 2017). The removal of these noxious elements from wastewater is necessary to reduce environmental pollution and human exposure to danger. Different zeolite based nanocomposite adsorbents have been utilized for adsorption of these toxic elements in aqueous solution. The modification of zeolite with various materials enhances its adsorption property. For instance in a study by Suazo-Hernandez et al., fabricated a nano- composite of zeolite and nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI) to enhance its performance in the removal of arsenic from water. This was to enhance morphology and physicochemical characteristics (Figs. 3 and 4 for SEM and XRD characterisations respectively)(Suazo-Hernandez et al. 2019). The adsorption of heavy metals using zeolite based nanocomposite adsorbents are influenced by factors such as adsorbent property, pH, temperature, dose and contact time. In a study, Zeolite/Zinc Oxide Nanocomposite (Zeolite/ZnO NCs) was developed by Alswata et al. through co-precipitation technique for removal of Arsenic As (V) and Lead Pb (II) (Alswata et al. 2017). The removal efficiency of 89% and 93% were obtained for As(V) and Pb(II) at pH4. The authors concluded that Zeolite/ZnO NCs can be applied as an effective and inexpensive nanocomposite. Abdelrahman et al. prepared zeolite Y/ faujasite nanocomposite through hydrothermal technique for adsorption of Pb(II) and the surface area was 19.17 m2/g (Abdelrahman et al. 2020). The adsorption capacity of zeolite Y/faujasite nanocomposite toward Pb(II) was 83.26 mg/g at pH 5.5. However, faujasite zeolite was coated with cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for effective removal of Pb(II) (Paris et al. 2020). The nanocomposite demonstrated improved surface area of 434.4 m2/g with magnetization value of 18.93 emu/g which showed magnetic property during the adsorption process. An outstanding adsorption capacity of 602.4 mg/g was recorded for Pb(II)
46 ARSTANNERY RESEARCH
removal. This could be due to the large surface area of the modified adsorbent, fabrication method and the presence of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. In another study, mesoporous zeolite-A/reduced graphene oxide nano- composite was synthesized through hydrothermal technique for removal of Pb(II) (Farghali et al. 2021). The adsorption capacity obtained for Mn(II) and Fe(III) was 94.1 and 150.1 mg/g, respectively. It was observed that the incorporation of TiO2 improved the total efficiency of Zeolites-4A by forming new active functional groups and enhanced its chemical stability. Zeolite/Alginate nanocomposite was prepared through green process for adsorption of nickel Ni(II) (El Hotaby et al. 2021). The result showed that the removal efficiency for Ni(II) was 98% and the isotherm model was best described by Freundlich. It was reported that the chemical and morphological property of Zeolite/Alginate nanocomposite did not change after 5 times reuse. It is interesting to note that zeolite based nanocomposite has been synthesized and applied in removal of multiple heavy metals simultaneously in wastewater. For instance, Zeolite/Polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate nanocomposite was prepared and used for adsorption of Cd, Pb (II), Cu(II), Zn, Mn and Ni(II)(Isawi, 2020). The removal efficiency for Cd, Pb(II), Cu(II), Zn, Mn and Ni(II) was 99.2%, 99.5%, 97.2%, 95.6%, 92.4% and 93.1%, respectively. Although, the various zeolite based nanocomposites have proven to be effective in removal of heavy metals. Nevertheless, most of the studies did not consider the effect of competing ions and use of the adsorbents in actual wastewater sam-
ple. Table 3 shows the various zeolite based nanocomposites used in removal of heavy metal ions in recent studies.
3.3. Emerging pollutants
Emerging pollutants refer to anthropogenic chemicals that are persistent and toxic in the environment with the ability to cause meta- bolic disorder in humans and living organisms. These include agro- chemicals, personal care products, pharmaceuticals, and stimulants that are ubiquitous in drinking water and wastewater (Cukierman et al. 2019). The conventional wastewater treatment has failed to remove emerging pollutants completely from water. They are ineffective to degrade or remove most compounds thereby resulting to their accu- mulation in water bodies (Maharana and Sen, 2021). Recent studies have shown that the use of zeolite based nanocomposite adsorbents with exceptional properties (large surface area, high adsorption capacity, improved chemical and physical properties) for removal of emerging pollutants have been successful. For example, ZSM-5 nanosized zeolite-carbon composite was fabricated and explored for the removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solution(Al-Jubouri et al. 2022). The surface area of the prepared adsorbent was 103.739 m2/g and adsorption ca- pacity of 87.719 mg/g was obtained at wide pH range of 4–6. The thermodynamic result revealed that the adsorption was spontaneous and exothermic. In another study, zeolitic-imidazolate framework (ZIF-
ARSTANNERY 47 RESEARCH
FIG. 3. SEM IMAGES OF (A) NZVI; (B) AS(V)/NZVI; (C) AS(V)–SE(VI)/NZVI; (D) Z-NZVI; (E) AS(V)/Z-NZVI; AND (F) AS(V)–SE(VI)/Z-NZVI.
8) obtained from nitrogen self-doped mesoporous carbons was utilized for adsorption of ciprofloxacin and tetracycline in aqueous media (Dang et al. 2021). Exceptional adsorption capacities of 905.14 mg/g and 772.69 mg/g were recorded for ciprofloxacin and tetracy- cline, respectively. The optimal pH for ciprofloxacin and tetracycline was 8 and 6. Table 4 show the different zeolite based nanocomposite adsorbents used for removal of emerging pollutants (see Table 5).
3.4. Regeneration investigation
The reusability of an adsorbent for long-term is imperative in adsorption technique for economic reason. One of the challenges in wastewater treatment is to find adsorbent with high sorption capacity that can be separated effortlessly from the contaminated media without damaging. Organic solvents, strong acids and bases have mostly been used to investigate the reusability of zeolite based nanocomposite adsorbents. For instance, Alswata et al., explored the regeneration of zeolite/zinc oxide nanocomposite using 0.005 M HNO3 after adsorption of As (V) and Pb (II)(Alswata et al. 2017). The authors concluded that the adsorbent can easily be regenerated and reused after several cycles. In another study, 0.1 M HCl was utilized to desorb multiple ions from zeolite/polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate nanocomposite(Isawi, 2020). The experiment showed that the nanocomposite could be reused for 10 cycles. Abdelrahman et al., used 0.2 M Na4-EDTA to desorb Pb(II) and Cu(II) ions from zeolite Y/faujasite nanocomposite(Abdelrahman et al. 2020). The adsorbent was reported to be stable and without loss of ef- ficiency after 3 cycles.
4. Use of zeolite based nanocomposites as photocatalysts
Zeolite does not only possess important features for adsorption of toxic substances, it also have photocatalytic properties. It has photocatalytic characteristics such as control of electron and charge transfer. The availability of micropores, ion-exchange capacity and surface acidity in zeolite makes it a great support for photochemical reaction (Sun et al. 2014). For example, gold-titania/protonated zeolite composite (Au–TiO2/HZSM-5) was synthesized through impregnation and sol–gel method for photodegradation of methyl orange (MO)(Sun et al. 2014). Control experiment was carried out prior to the photocatalytic investigation of the synthesized catalyst. Firstly, MO was exposed to UV and Visible light without catalyst to study the effect of photolysis on MO. The result showed that the removal was negligible and that photolysis had no effect on the degradation of MO. Also, the experiment was car- ried out in the dark using the catalyst and the result showed that 50% MO was degraded in 30 min. There was no significant degradation thereafter. Fig. 5 shows the experiment in the dark and under UV or Visible light. The catalyst showed good photodegradation ability for the degradation of MO and factors such as pH and calcination temperature affected the catalytic process. The reusability investigation for Au–TiO2/HZSM-5 as a photo-catalyst for degradation of MO, revealed that catalyst was stable within 4 cycles and the degradation efficiency decreased from 96.6% to 86.5% thereafter. This confirmed that Au–TiO2/HZSM-5 showed good photocatalytic reusability. The decrease in percentage degradation after 4 cycles was attributed to the generation of waste materials and their
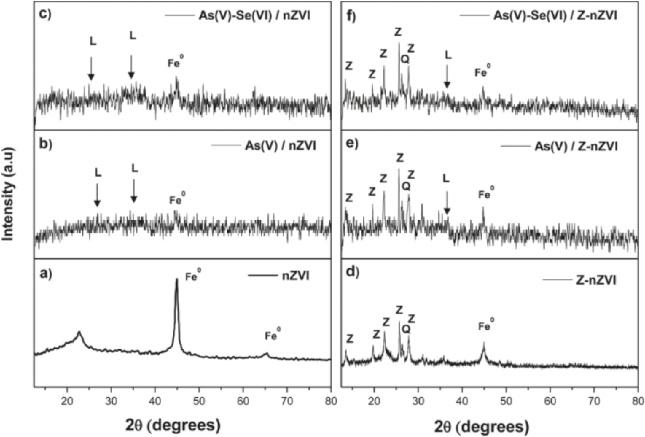
FIG. 4. XRD PATTERNS OF (A) NZVI; (B) AS(V)/NZVI; (C) AS(V)–SE(VI)/NZVI;
Z-NZVI;
48 ARSTANNERY RESEARCH
(D)
(E) AS(V)/Z-NZVI; AND (F) AS(V)–SE(VI)/Z-NZVI (FE° = ZERO-VALENT IRON; Z = ZEOLITE; Q = QUARTZ; L= (FEO(OH)) LEPIDOCROCITE).
buildup on active sites of the catalyst. In another study, zeolite ZSM-5/ ZnO/Ag nanocomposite was prepared for photodegradation of methyl orange(Vaez and Javanbakht, 2020). The degradation efficiency of 90% was obtained at pH 11 and solution concentration of 5 ppm. The regeneration study showed that there was no major variation in the photocatalytic ability of the catalyst after 4 times, which indicates
the high stability of the material under UV light. Agustina et al. synthesized ZnO-natural zeolite nanocomposite via sol-gel technique for degrada- tion of procion red dye (Agustina et al. 2022). Also, the study examined the influence of weight ratio of ZnO and natural zeolite composition as well as pH on the photodegradation of procion red dye. It was revealed that weight ratio influenced the efficiency
ARSTANNERY 49 RESEARCH
of ZnO-natural zeolite nanocomposite during the degradation process. The highest degradation efficiency of 96.3% was obtained using ZnO-natural zeolite ratio 2:1 at pH 5. This shows that the mixing ratio of different materials can affect the effectiveness of nanocomposites in photodegradation. In a similar study, C-dots@zeolite (CDZ) nanocomposite was prepared hydrother- mally at various weight ratios of 1:1, 1:3, 1:5, 5:1, 1:7 for degradation of metronidazole and Rhodamine B (Rathi et al. 2022). The 1:5 C-dots@- zeolite nanocomposite showed the highest photodegradation efficiency of 79% for metronidazole and 90% for Rhodamine B at pH 4 owing to its large surface area, pore-volume, good bandgap energy and low recom- bination rate. The study on real industrial wastewater showed removal of 68% and 62% for chemical oxygen demand and total organic carbon, respectively. In a different study, BiVO4/TiO2/NaY-Zeolite nano- composite was fabricated hydrothermally for degradation of Microcystin-leucine arginine under visible light (Ebrahimi et al. 2021). The degradation ef-
ficiency of 99.88% was obtained at 120 min and pH 5. To understand the photodegradation mechanism Ebrahimi et al. used benzoquinone (BQ, 0.01 mmol/L), isopropyl alcohol (IPA, 0.01 mol/L) and ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA 0.01 mol/L) as scavengers of superoxide anion radicals (•O2- ),hydroxyl radicals (•OH) and electrons holes (h+), respectively. The results showed that the various scavengers affected the degradation process significantly.
A comparative study evaluated the photocatalytic ability of ZnOzeolite nanocomposite and TiO2-zeolite nanocomposite towards the degradation of codeine and acetaminophen (Behravesh et al. 2020). Cutting stone byproduct was used as the precursor for the synthesized zeolite nanocatalyst. The results showed that ZnO-zeolite nano- composite had better removal efficiency of 45.7% and 58.7% for codeine and acetaminophen when compared to TiO2-zeolite nanocomposite with 39.2% and 44.3%. Results from reusability study indicated that the ef- ficiency of the photocatalysts dropped after 4 cycles. The nature
50 ARSTANNERY RESEARCH
FIG. 5. DEGRADATION OF METHYL ORANGE WITHOUT LIGHT AND UNDER UV OR VIS(SUN ET AL. 2014).
of precursor material could have effect on the photocatalytic performance. These zeolite nanocomposites prepared from cutting stone byproduct can be enhanced for better degradation efficiency. Anwar et al. incor- porated TiO2 into natural zeolite to form TiO2-Zeolite composite for photodegradation of procion blue and methylene or-
ange under UV light (Anwar et al. 2020). The photodegradation efficiencies of 54% and 32.2% were obtained for procion blue and methylene orange at pH 4 and initial concentration of 100 ppm, respectively. These results revealed that the photodegradation process is inefficient at higher concentrations.
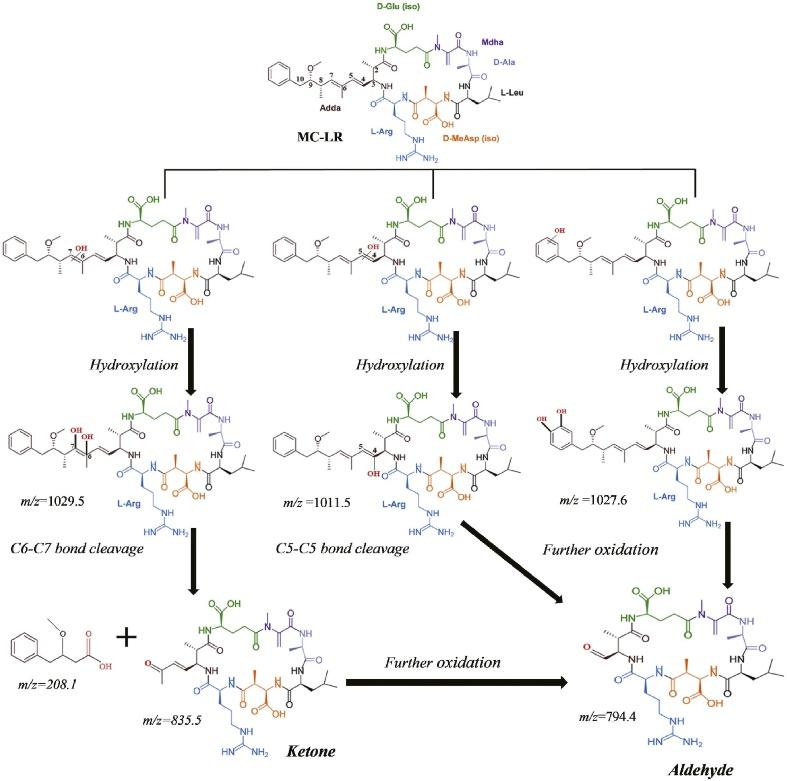
ARSTANNERY 51 RESEARCH
FIG. 6. THE LIKELY PATHWAYS FOR THE PHOTODEGRADATION OF MICROCYSTIN-LEUCINE ARGININE (EBRAHIMI ET AL. 2021).
4.1. Degradation pathways of various organic pollutants
Degradation pathways help in explaining the intermediates and end products. It is necessary to confirm if complete mineralization was achieved during photodegradation. The detailed photodegradation pathways of microcystin-leucine arginine, diclofenac and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) were discussed and there structural byproducts are displayed in Figs. 6–8(Castaneda-Juarez et al. 2019; Samara et al. 2019; Ebrahimi et al. 2021).
The likely pathways for the degradation of microcystin-leucine arginine is shown in Fig. 4 a. The intermediate products from degra- dation of microcystin-leucine arginine by BiVO4/TiO2/NaY-Zeolite nanocomposite were identified using GC-MS(Ebrahimi et al. 2021). Firstly, the unsaturated double bonds (C4–C5 and C6–C7) where attacked by hydroxyl radicals in the Adda side-chain, causing the hydroxylation of Microcystin-LR. Thus, the double bonds cleavage present in C4–C5 lead to the formation of aldehyde derivative and C6–C7 to the formation of ketone derivative. The photodegradation of the Adda chain demonstrated that the toxicity of microcystin-LR was reduced during changes under visible light. Secondly, the hydroxyl radicals cut diene bonds in the aromatic ring or Adda chain, which resulted to intermediate product, m/z 1011.6. This was finally transformed to aldehyde product due to further oxidation (Ebrahimi et al. 2021). The probable pathway for photodegradation of diclofenac using TiO2–Fe/Cu/Zeolite composite is displayed in Fig. 7. Hydroxyl radicals were responsible for the degradation which likely occurred due to the cutting of C–N bond,
whereas the NH2 groups were preserved. Secondly, generation of poly-hydroxylated precursors for ring opening took place with benzoquinone (BQ, 0.01 mmol/L), isopropyl alcohol (IPA, 0.01 mol/L) concomitant release of Clˉ and NH+4 ions. The aromatic rings were broken into carboxylic acids and smaller molecules. The final product resulted to complete mineralization (Castaneda-Juarez et al. 2019). The most dangerous type of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs) known as TCDD was efficiently reduced to less toxic substance using Ag/Zeolite nanocatalyst. The byproducts of the photocatalytic activity were investigated by ELISA method and results showed that there was decline in toxicity after 40 min (Samara et al. 2019). The likely intermediates are structurally displayed in Fig. 8.
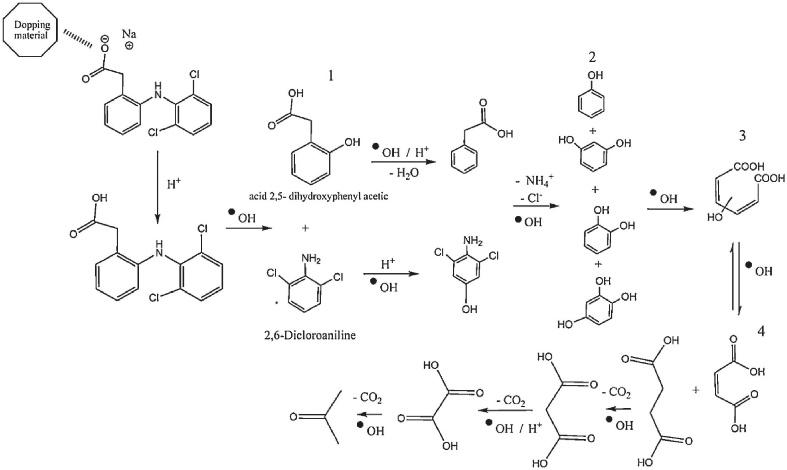
5. Conclusion and future perspectives
This review presents different preparation techniques for zeolitebased nanocomposites and their application as adsorbents and photo- catalysts in water and wastewater remediation within the past ten years. In addition, it revealed that the impregnation of zeolites into carbon, polymers and metal nanoparticles could impart their features and enhance their adsorption and photocatalytic performance. With the advancements made, it is clear that zeolite is a very promising material for synthesizing photocatalysts and immobilized adsorbents for the removal of harmful contaminants from wastewater. The research on zeolite-based nanocomposites is still in its embryonic stage, despite the significant advancements that have been made, its applica-
FIG. 7. PATHWAY FOR PHOTODEGRADATION OF DICLOFENAC BY TIO2–FE/CU/ZEOLITE COMPOSITE (CASTANEDA-JUAREZ ET AL. 2019).
52 ARSTANNERY RESEARCH
tions are yet to reach full potential. Hence, more research work should be investi- gated in the future.
We proposed that it is important to synthesize more efficient zeolitebased photocatalysts with high photocatalytic ability under sunlight irradiation or visible light by using various smart semiconductors. Although, zeolites are not photoactive but when incorporated with photoactive semiconductors they tend to enhance the adsorption ca- pacity of the material. Therefore, effective and practical methods for designing sunlight-driven zeolite-based nanocomposites such as doping with metal or adding additional semiconductors with a narrow band gap should be adopted.
We recommend that researchers must investigate the reaction mechanism involved in the degradation of pollutants using zeolite-based nanocomposites, and the intermediate products must be examined using
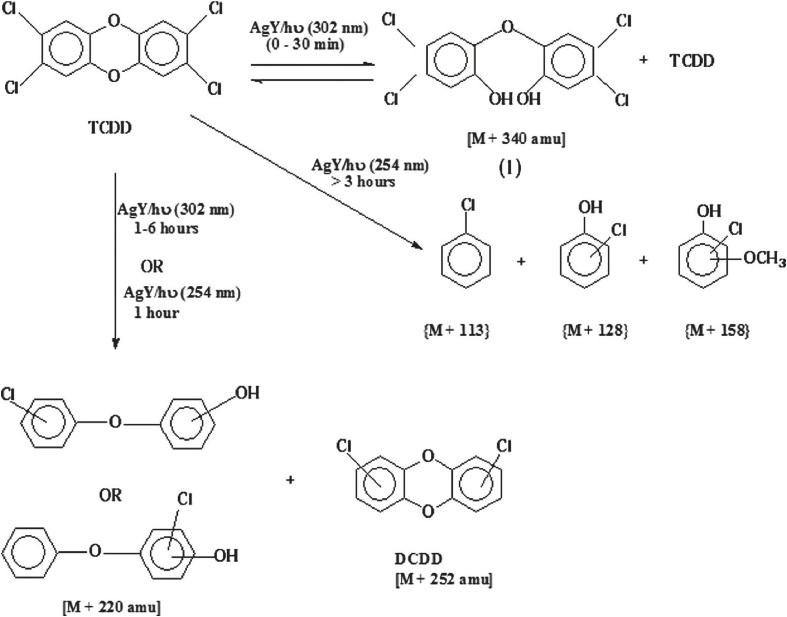
analytical instruments such as Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to name a few. This is to pave a way towards maximised efficiency for zeolitebased nanocomposites.
Finally, we recommend that the application of zeolite-based nano- composite should be carried out on real wastewater sample rather than on single analyte that are mostly reported in the literature, because most wastewater sample contains a conglomeration of various pollutants ranging from dyes, heavy metals and pharmaceuticals. Thus, if this concept is adopted it will be easier for this platform to be used at in- dustrial scale. It is argued that adsorption generates secondary waste due to the release of spent adsorbent. Advanced research on the reus- ability of spent zeolite-based nanocomposite adsorbents should be carried out to reduce the generation of secondary waste.
ARSTANNERY 53 RESEARCH
FIG. 8. POSSIBLE PATHWAY FOR DEGRADATION OF TCDD BY AG/ZEOLITE NANOCATALYST(SAMARA ET AL. 2019).
Design inspirations from the past, present and future
Many of the top shoe and bag designers worldwide use Arsutoria Studio to create their new collections and to find new market opportunities.
We have a simple mission: help you turn your ideas into products
MAGAZINES & BOOKS
ARSUTORIA
10 Issues
Arsutoria offers the most complete information for footwear & leather manufacturers and designers: collections, materials and technology.
FOTO
SHOE 30
6 Issues
An overview on medium-end footwear market: news, articles and pictures. Foto Shoe 30 is a must have for wholesalers and mass retailers..
arsutoriamagazine.com
ARSUTORIA ONLY SHOES / ONLY BAGS

Hard cover book of over 200 pages of shoes and bags presented for each season on fair sand catwalks.



fotoshoemagazine.com

FOOTWEAR DICTIONARY

• 500 illustrated pages
• 1000 terms in five different languages (IT-EN-ES-DE-FR)
• Only Printed edition

subscriptions@edizioniaf.com ph. +39 02 3191 2331 fax +39 02 3361 1619
www.edizioniaf.com
subscriptions@edizioniaf.com
ph. +39 02 3191 2331
fax +39 02 3361 1619
ORDER FORM
Prices include FedEx shipment
CREDIT CARD
EXP. DATE / CVV/CVC
CARDHOLDER NAME
SIGNATURE ____________________________________
BANK TRANSFER
IBAN: IT 49 Z 01030 01604 000002285956
Monte Paschi Siena Swift: PASCITM1MI4
* Prices are subject to VAT: only for Italy and private UE clients
** Available from January 2022
CONTACT EMAIL
VAT NBR COUNTRY +_____/______________________________
COMPANY ADDRESS CITY ZIP
PHONE
_ _ _ __ _ _ __ _ _ __ _ _ _
MAGAZINES & BOOKS ISSUES ITALY EUROPE REST OF THE WORLD ARSUTORIA - magazine 1 YEAR 10 250 € 450 € FOTOSHOE30 - magazine 1 YEAR 6 150 € 250 € FOOTWEAR TECHNICAL DICTIONARY* - book 1 book 1 120 € ARSUTORIA ONLY SHOES - book 1 YEAR 1 2 250 € 450 € ARPEL ONLY BAGS - book 1 YEAR 1 250 € ARSUTORIA STUDIO** USERS DIGITAL ITALY EUROPE REST OF THE WORLD SILVER (1 YEAR) Arsutoria magazine trends webinars 3 200 € 250 € 450 € GOLD (1 YEAR) SILVER +arstrends, photos of collections, catwalks, retail 5 SHOES BAGS FULL 450 € 350 € 500 € 500 € 400 € 550 € 700 € 600 € 750 € PLATINUM (1 YEAR) GOLD +historical archive 10 SHOES BAGS FULL 950 € 750 € 1200 € 1000 € 800 € 1250 € 1200 € 1000 € 1450 € PAPER
ISSN 2531-9620
BIGAGLI
SILVACHIMICA SILVACHIMICA
AICC - ASSOCIAZIONE ITALIANA CHIMICI DEL CUOIO
pag. 8-9-10
APLF LTD.
tel. +852 282.762.11 info@aplf.com www.aplf.com www.aclechina.com www.fashionaccess.aplf.com
www.leatherfair.aplf.com
pag. 41-42-43
ASSOMAC SERVIZI s.r.l. tel. +39 0381.788.83 info@assomac.it www.assomac.it
pag. 3
COMELZ S.p.A. tel. +39 0381.424.01 info@comelz.com www.comelz.com
pag. III cover
COTANCE cotance@euroleather.com

pag. 12-13
DERMACOLOR s.r.l. tel. +39 0571.471.313 info@dermacolor.it www.dermacolor.it
pag. IV cover
DERMAKIM s.r.l. tel. +39 0332.287.623 info@dermakim.it www.dermakim.it
pag. 5
ERRETRE S.p.A. tel. +39 0444.478.312 info@erretre.com www.erretre.com
pag. II cover-15
GSC GROUP S.p.A. tel. +39 0444.670.949 info@gscspa.it www.gscspa.it pag. 28-29
KLF TECNOKIMICA s.r.l. tel. +39 0571.471.090 info@klftecnokimica.it www.klftecnokimica.it pag. 25
PITTI IMMAGINE s.r.l. tel. +39 055.369.31 info@pittimmagine.com www.pittimmagine.com pag. 20-21-22-23
SILVACHIMICA s.r.l. tel. +39 0174.220.254 tan@silvateam.com - www.silvateam.com pag. 57
SMIT & ZOON tel. +31 294.238.800 info@smitzoon.com www.smitzoon.com
pag. Cover - 30-31
SYN-BIOS S.p.A. tel. +39 0444.441.144 synbios@synbios.it www.synbios.it
pag. 36-37
TFL ITALIA S.p.A. tel. +39 0444.644.311 contactitaly@tfl.com - www.tfl.com pag. 32-33
TODESCO s.r.l. tel. +39 0444.340.639 info@todescosrl.com - www.todescosrl.com pag. 11
UNIC - CONCERIE ITALIANE - UNIONE NAZIONALE INDUSTRIA CONCIARIA
tel. +39 02.880.77.11 unic@unic.it - www.unic.it
pag. 6-7-24
UNPAC - Unione Nazionale Produttori Italiani Ausiliari Conciari tel. +39 0331.578.851 segreteria@unpac.it www.unpac.it
pag. 16-17-18-19
58 CONTACTS ARSTANNERY 04 UNIC ASSEMBLY NEW LEATHER CHEMICALS AICC TECHNICAL CONVENTION ARSTANNERY 1° SUPPLEMENTO ARSUTORIA 481 LUGLIO 2023 POSTE ITALIANE S.p.A. SPEDIZIONE A.P. AUT. MBPA/LO-NO/049/A.P./2017 ART.1 COMMA1 LO/MI TAN202304_23P6815_SMIT_ZOON_cover.indd July 2023
























 ALANCHIM
ALPA
CHIME
ALPA
CHIME
ALANCHIM
ALPA
CHIME
ALPA
CHIME





 CHIMICA ITALIANA
CODYECO
FGL INTERNATIONAL
CHIMICA VEMAR
FGL INTERNATIONAL
GSC GROUP
CHIMICA ITALIANA
CODYECO
FGL INTERNATIONAL
CHIMICA VEMAR
FGL INTERNATIONAL
GSC GROUP





































 Edited by Dr. Gianluigi Calvanese SSIP Analysis, Certification and Consulting Area Manager
Edited by Dr. Gianluigi Calvanese SSIP Analysis, Certification and Consulting Area Manager






 FIG. 1 SYNTHESIS OF MAGNETIC/ZEOLITE (ANGARU ET AL. 2021).
FIG. 1 SYNTHESIS OF MAGNETIC/ZEOLITE (ANGARU ET AL. 2021).



















