
















































Loram delivers comprehensive solutions for ballast optimization and drainage maintenance. Inspection with Loram’s Ground Penetrating Radar and LiDAR technologies ensure targeted ditch and drainage maintenance that will maintain the stability of your ballast and subgrade. Ditch and shoulder ballast cleaning deliver the benefits of increased cycle time between surfacing and lining programs, while preventing premature tie deterioration and loss of stability in track infrastructure.

From inspection and geotechnical services that precisely identify drainage and ballast conditions, to our industry-leading array of maintenance equipment and remediation solutions, Loram is equipped to maximize and protect your infrastructure investment. Learn more at Loram.com



Vol. 119, No. 10
Print ISSN # 0033-9016, Digital ISSN # 2160-2514
EDITORIAL OFFICES
1025 Rose Creek Drive Suite 620-121
Woodstock, GA 30189
Telephone (470) 865-0933
Website www.rtands.com
DAVID C. LESTER
Editor-in-Chief dlester@sbpub.com
JENNIFER M c LAWHORN Managing Editor jmclawhorn@sbpub.com
EDITORIAL BOARD
David Clarke, University of Tennessee

Brad Kerchof, formerly Norfolk Southern William Riehl, Genesee & Wyoming/AREMA
Scott Sandoval, Genesee & Wyoming
Robert Tuzik, Talus Associates

Gary Wolf, Wolf Railway Consulting
CORPORATE OFFICES
1809 Capitol Avenue
Omaha, NE 68102
Telephone (212) 620-7200
Fax (212) 633-1165
ARTHUR J. MCGINNIS, JR.
President and Chairman
JONATHAN CHALON Publisher
MARY CONYERS
Production Director
NICOLE D’ANTONA Art Director
HILLARY COLEMAN
Graphic Designer
JO ANN BINZ
Circulation Director
MICHELLE ZOLKOS Conference Director
CUSTOMER SERVICE: 847-559-7372
Reprints: PARS International Corp.
253 West 35th Street 7th Floor New York, NY 10001
212-221-9595; fax 212-221-9195

curt.ciesinski@parsintl.com
Readers may recall that I announced several months ago that we are expanding the scope of coverage for Railway Track and Structures to include rail passenger station design, build, and maintenance, along with communications and signals. e second half of the title of our publication is Structures, and passenger stations are certainly structures. In addition, one of the most important elements of rail infrastructure is communications and signals. We have not yet published any material on communications and signals but have posted some news stories on passenger stations on our website. is issue includes our rst article about passenger stations.
is article is relatively light and includes some history of passenger stations, along with some material from Amtrak that lays out how that agency classi es stations. We thought this would be a nice way to introduce the subject to the magazine. Passenger stations are complex and subject to many rules and regulations around how they are built and operated. Aside from the building itself, track design in and around the station must account for the mission of the station and how best to get trains in and out, store them if needed, and provision of some degree of maintenance capability
for locomotives and cars depending on the station’s location. Station design must also account for e cient ow of passengers, possibly automobile parking space, and facilities for restocking the train, again depending on its location, if the train o ers any type of food service.
ere are also several requirements stemming from the Americans with Disabilities Act. Electrical and signaling requirements are complex, and the entire station design must be based on ridership projections for a given number of years, and room for expansion may be a consideration if ridership is expected to grow in the relatively near term.
We’ll be looking at these and other topics of interest to engineers involved in station planning, design, build, and operation going forward. We’ll also take a look at stations along Brightline’s new Miami–Orlando route, which inaugurated service just before press time for this issue. e bottom line? A tremendous amount of engineering goes into passenger stations, and we are excited to o er engineering coverage of this critical part of rail infrastructure.
As part of our research for upcoming passenger articles, we recently spoke with consultants from HDR who are involved in passenger station design and build. Roseann Moring at HDR connected us with J.D. Douglas, Suzanne Baumgardt, and Matt Van Hattem, and we interviewed each of them for an hour to get their perspective on rail passenger stations and their speci c areas of responsibility. Although we don’t feature any of that discussion and material in this month’s article, we will certainly do so in 2024. We greatly appreciate Roseann and the consultants’ time and e ort to talk with us and help lay the groundwork for this new part of our coverage.
DAVID C. LESTER Editor-in-Chief
MxV
Rail, Pueblo, COSince 1997, MxV Rail has been investigating new designs and materials that have the potential to improve safety and e ciency and reduce the maintenance required for open deck bridges. Due to the lack of quantitative data on the lateral resistance provided by ties and deck anchorage fasteners on open-deck railroad bridges, the current guidelines or requirements for deck tie fastener spacing are based on limited data and historical experience. At the request of and with guidance from MxV Rail, researchers at Virginia Tech conducted experimental testing on ve tie materials, three hook bolt styles, and multiple vertical loading conditions to quantify the lateral resistance provided by tie friction, hook bolt fasteners, and tie daps for each tie and hook bolt material combination.
MxV Rail investigators then used the lateral resistance values from this experimental testing to evaluate the current American
Railway Engineering and Maintenanceof-Way Association (AREMA) Manual of Railway Engineering (MRE) Chapter 15 recommendations for deck tie fasteners on tangent and curved track. ese recommendations were found to be adequate for most load cases examined. Hook bolt and tie spacing, car weight, and car type e ects all have a signi cant e ect on lateral resistance; however, the degree of curve did not have a signi cant e ect on the lateral resistance.
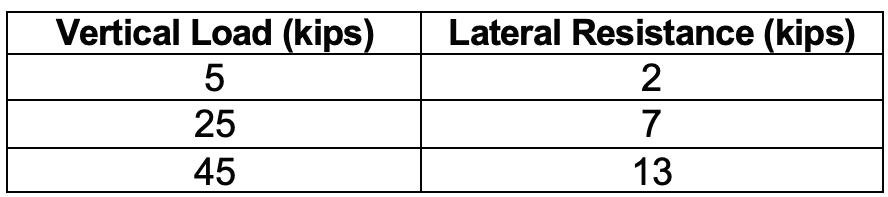
Ties on open deck steel bridges bear directly on the steel superstructure. Ties are typically fastened to the superstructure using hook bolts with a hook, a sprung shoe, or a spring clip at the bottom of the bolt. ese bolts provide movement resistance primarily in the lateral direction and also resist upli . Standards for fastener spacing vary between railroads. Some railroads also used dapped ties, where the bottom of the tie is notched over the top ange. e dap provides a physical restraint to lateral movement, but it can
be costly to fabricate and can initiate horizontal splits in the tie. Many steel spans also have rivet heads or a portion of the girder web protruding. is protrusion provides physical interlocking and increased lateral resistance. Smooth top spans were studied as the worstcase scenario. Figure 1 provides examples of typical hook bolts and dapped ties.

MxV Rail worked with Virginia Tech to perform experimental testing that would quantify the lateral resistance of various open-deck bridge ties and fasteners. For this testing, various railroads contributed a combination of new and used bridge deck ties, and a supplier provided components for di erent fastening systems. e test setup simulated the loads and movement of a railroad tie on the surface of a smooth steel beam ange.
e resistance values provided in this article are the average value minus two standard deviations. e lowest values of friction and
hook bolt lateral resistance from the experimental tests were used for further analysis.
Dapped ties were tested to determine the peak contribution of the daps as the edge of the dap was placed in bearing. e tests indicated that they provided more than enough lateral resistance as compared to the design lateral forces.
To establish the relationship between normal force and frictional coe cient, various tie species were tested at ve di erent vertical loads (5, 15, 25, 35, and 45 kips). e various levels of vertical force were then used to calculate coe cients of friction. At 0.195, the friction level for freshly treated ties was the lowest for mean minus two standard deviations.
Other ties had values above 0.3. A value of 0.2 was chosen for fastener spacing analysis.
e lateral resistance provided by hook bolts varied based on the type of hook bolt, the vertical load on the tie, and the lateral displacement. Table 1 shows the lowest values of lateral resistance (hook bolt plus friction) for all hook bolt types for three vertical loads.
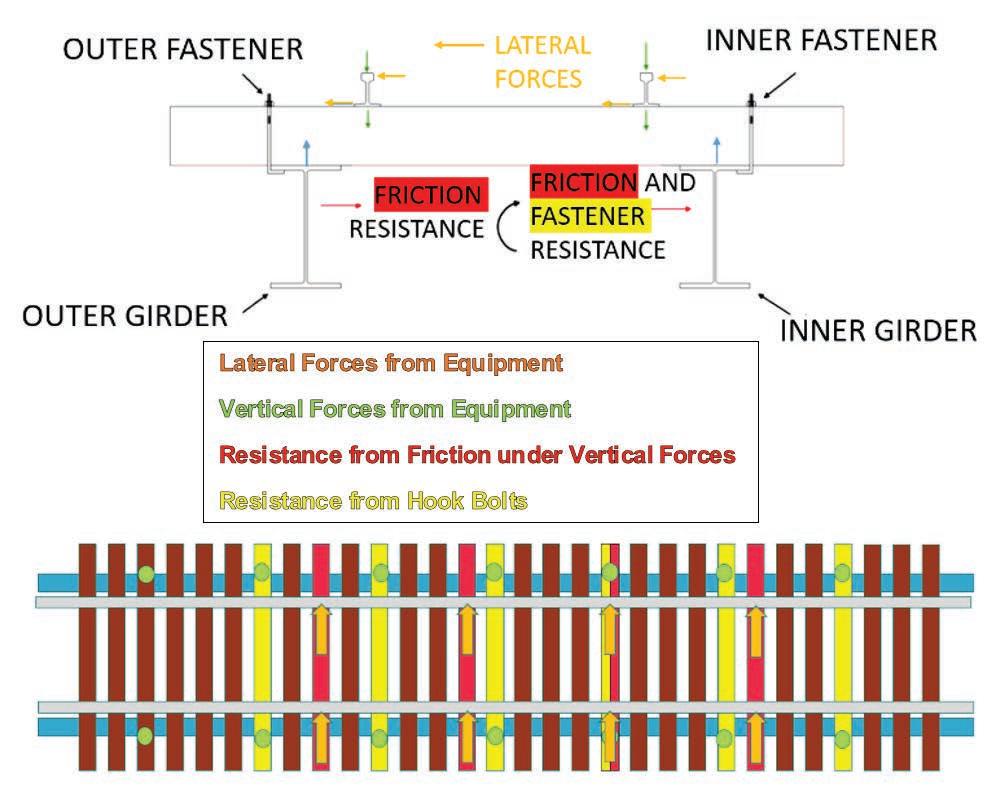
Due to the spacing of ties, anchors, and axles, along with deck construction, the lateral force resulting from a wheel is not resisted by a single tie—the load is carried by multiple anchored ties.
Although hook bolts are typically applied to both sides of the track, only the hook bolts on one side were considered to resist lateral
loads, as illustrated in Figure 2. Friction was assumed to act on both sides under load.
e total lateral loading was assumed to come from three sources de ned by AREMA MRE Chapter 15. First, in Section 15.1.3.9, Lateral Forces From Equipment are de ned as a single load equal to 25 percent of the live load. Second, Centrifugal Force was calculated based on the assumed speed and superelevation. Finally, Wind Force on the train was calculated per Section 15.1.3.7.4. Both the wind force and centrifugal force were limited to a total tip-over force, which is the force required to unload the inner wheel of the rail vehicle.
Figure 3 depicts equipment variables. All vehicle combinations were evaluated with 5-, 25-, and 45-kip wheel loads. Span and
track variables included tie and hook bolt spacing and various amounts of curvature and superelevation. A missing hook bolt case examined the realities of hook bolts breaking, loosening, or dropping.
e MxV Rail team evaluated lateral loads and resistances for all reasonable equipment and speed combinations, as well as ties without daps. e total lateral load was distributed to the deck components (ties and hook bolts) based on the type of car and truck axle spacing. e calculated resistance was compared to the calculated load, and a factor of safety (FOS) was determined for each case. e minimum FOS criteria were de ned as 1.0 in cases with wind and 1.25 in cases without wind. Other designers may choose to use di erent FOS.
e combinations were then compared
against the two hook bolt spacing criteria shown in Table 2. Currently, AREMA recommends hook bolt spacing every four ties on tangent track not to exceed 4 feet 8 inches and having a reduced spacing on curves.

Of the variables considered, wind load and wheel load had larger e ects than other variables. e type of car also had a large e ect with the most signi cant challenges stemming from long lightweight cars, such as autoracks with high wind loads and empty cars where light wheel loads reduce the amount of frictional resistance available. Although lateral loads changed, the degree of curvature did not have a large e ect on hook bolt spacing, thus consistent hook bolt spacing (as with spacing criteria A) may be appropriate for all curves. As expected, tie and hook bolt spacing also

had a large e ect, and therefore, a missing hook bolt also had a large e ect. Maintenance and inspection practices should be considered when using undapped ties with wider tie and hook bolt spacings on smooth-top steel spans.
e lateral resistance design of opendeck bridge tie fastenings is now possible with quanti ed data. Additional research into the following would also be recommended: 1) other tie materials, treatment types, riveted-top girders, and changes in friction over time; 2) acceptable safety factors weighed against risk; and 3) a better understanding of lateral load distribution.
Test data for dapped ties indicate that these ties provide a signi cant amount of lateral resistance in excess of what is required. Based on the analysis presented, the current AREMA guidelines accommodate most load cases without the use of dapped ties, even on smooth-top steel spans.
e authors acknowledge the support and guidance provided by the Association of American Railroads (AAR) Bridge Technical Advisory Group; CSX Transportation, Norfolk Southern Railway, and Union Paci c Railroad for tie donations; Lewis Bolt & Nut for hook bolt donations; and Dr. Matt Hebdon and his students at Virginia Tech for their work on the experimental study.
1. Gergel, J., Vasudevan, V., and Hebdon, M. “Railroad Tie Lateral Resistance on OpenDeck Plate Girder Bridges,” Railway Technologies Laboratory, 2019.
2. Gergel, J., “Railroad Tie Lateral Resistance on Open-Deck Plate Girder Bridges,” Master’s esis, Virginia Polytechnic Institute, Blacksburg, Virginia, 2019.
3. Igwemezie, J., “Understanding Stresses in Rails,” Interface J., 2007.
4. AREMA, “Steel Structures,” in AREMA Manual for Railway Engineering, Lanham, Maryland: American Railway Engineering and Maintenance-of-Way Association, 2021
5. Johnson, C., Hebdon, M., and Otter, D., “Lateral Resistance of Timber Bridge Ties and Fasteners on Open Deck Steel Bridges,” Proceedings, AREMA Annual Conference, Denver, Colorado, August 2022.
6. Johnson, C., Otter, D., and DeVencenty, D., “Fastener Spacing for Timber Ties on Open Deck Steel Bridge,” Technology Digest TD22-028, MxV Rail/AAR, Pueblo, Colorado, 2022.





















The establishment of rail passenger service in North America sparked a boom of passenger station construction. While the early depots were little more than four walls and a roof, as passenger tra c grew, stations became centers of communities, particularly in small rural towns. Stations began handling passengers, freight, and express packages and became popular gathering places to purchase the latest newspapers, catch up on gossip, pick up a package, or watch the trains roll by. e ultimate experience was to travel by train from the depot to a large, exciting city with a palatial station that
boggled the mind.

Although the number of passenger stations has diminished since Amtrak took over most privately operated service in 1971, many remain standing, refurbished for continued use as stations, multi-modal terminals, science museums, or other community facilities. Moreover, Amtrak has constructed several stations around the country to provide service in areas without previous service or to build something more suitable for modern passengers.

While passenger stations built in recent years are functional, ones built in the late 19th and early 20th centuries served not only as


functional stations but as grand, welcoming edi ces to showcase the beauty and strength of the railroad and the city served by the station. Two of the most marvelous examples are, not surprisingly, Pennsylvania Station and Grand Central Station in New York City. Penn Station was demolished in 1963 and relegated to an underground facility below Madison Square Garden. Grand Central Station has been refurbished and stands as a monument to railroad history and serves as a functional railroad passenger station for commuter trains in and out of the city.

treatise, Passenger Terminals and Trains (1916), refers to the passenger station of the early 20th century as the “city gate.” “ e passenger terminal has been aptly described as the city gate and for some of the newer and larger stations it would, indeed, be hard to nd a term more tting.” (1) Quoting early railroad historian and writer Edward Hungerford, Droege adds, “ e railroad terminal is the city gate. Without, it rises in the superior arrogance of white marble from an open square as an architectural something. It has broad portals and through these portals come and go a host of folks in cabs and carriages, in trolley cars and
elevated trains –– folk afoot. Within, this city gate is stupendous apartments and monumental dimensions –– a thing not to be grasped in a moment. In a single great apartment –– a vaulted room so great as to have its dimensions sink into distant vistas –– are the steam caravans that come and go. It is a busy place, a place of in nite variety of businesses . . . .
“Rest? Oh, no. There is no rest at the city gate.” (2)











While writing about passenger stations today would likely not include such owery language and awe-inspiring references, many beautiful stations are still standing. Kansas
 By David C. Lester
By David C. Lester
City Union Station, once the third largest passenger terminal in the United States, only behind New York’s Pennsylvania and Grand Central, has been wonderfully refurbished and serves as a science museum and city gathering place. However, few, if any, can fairly be called the city gate anymore. Today, city gates are usually airports, most with relatively uninspiring architecture and appointments.
Investment in rail passenger stations to serve as rail stations or other uses o ers signi cant bene ts. For example, the website e Great American Stations, an Amtrak site, points out several reasons for investing in refurbishing

From architectural treasures to four walls and a roof, there’s a station for every need
rail passenger stations:
1. Stations are at the heart of America’s communities;
2. Station projects can become economic activity centers;
3. Rail stations are an important part of our heritage;

4. Station revitalization catalyzes community revitalization;


5. Station revitalization engages the community. (3)
Rail station development that occurs on new rail lines, such as Brightline, the higherspeed service recently inaugurated between Miami and Orlando, can be part of the model for success. For example, Brightline president Patrick Goddard told Railway Age last year, “In Miami, we invested about $1 billion in 1.5 million square feet of real estate and essentially created a small city around the station, which is a destination. is area on the western side of downtown was in neglect before we came in. ere was no development within ve blocks of this project. Since our development, there has been an additional $3 billion of real estate investment in the ve-block area around our station.” (4) Goddard added that Brightline stations stimulate interest from local transit agencies around how they can connect to the station. Also, real estate developers take note when a new Brightline station is announced. is additional transit and potential real estate development bene t the entire area.
While Brightline’s story is exciting and looks promising, the development of new passenger stations today is largely guided by Amtrak. According to Amtrak, it o ers
three types of service:
1. Long distance, which are routes greater than 750 miles and generally consist of one train per day in each direction;

2. State Supported Corridor, which is a route less than 750 miles, providing inter-city, short-haul service. e services on these routes are nancially supported by the states in which they operate. Hence, new station projects may also be funded and/or led by the state;
3. Northeast Corridor and HighSpeed Rail, where the NEC and connecting network supports a daily schedule of more than 2,200 trains, including more than 150 Amtrak trains, mostly on Amtrak-owned-andoperated tracks. e Acela makes up Amtrak’s current HSR o erings, with more to come in the near future. (5)
To serve these di erent types of service, Amtrak designates ve categories of stations:
Category 1 – Large Stations, which are located in dense urban downtowns with connecting transit services such as commuter rail, subway/metro, light rail and bus. Most of these stations are very similar in character to major airports, with a high level of passenger amenities, including restaurants and retail.
Category 2 – Medium Stations , which primarily serve State Supported Corridor routes, but also frequently accommodate Long Distance service, and are expected to play a signi cant role in
High-Speed Rail service routes.
Category 3 – Caretaker Stations serve Long Distance routes and State Supported corridors with limited rail service.
Category 4 – Shelter Stations serve less than 20,000 passengers annually and are located in smaller communities along either Long Distance or State Supported Corridor routes.
Category 5 – Thruway Service Connection, which connects many communities without rail service to Amtrak stations for State Supported Corridor and Long Distance services. (6)
Amtrak also categorizes stations in terms of their typologies. “ e station site and its relationship to its context is interdependent with the station’s relationship to the tracks. ree station typologies are found within the Amtrak system: Side, Vertical, and Terminal.” We will discuss the characteristics of these in a later article. (7)
1Droege, John A., Passenger Terminals and Trains, McGraw-Hill, 1916, reprinted by Kalmbach Publishing Company, 1969.
2Edward Hungerford, article in Harper’s Weekly, quoted in Droege, John A., Passenger Terminals and Trains, McGraw-Hill, 1916, reprinted by Kalmbach Publishing Company, 1969.
3Website Amtrak, e Great American Stations (https://www.greatamericanstations.com/why-invest/ bene ts-of-restoration/).
4Lester, David C., “Rolling Into Orlando,” Railway Age, October 2022, pp. 36-37.
5Amtrak, Amtrak Station Planning and Development Guidelines, January 2022, V4, p. 6
6Ibid, pp. 23-32.
7Ibid., p. 33










 By Je Tuzik
By Je Tuzik

Preventive rail grinding is a well-established practice for extending rail life. And by optimizing wheel/rail interaction and controlling the development and growth of surface damage like rolling contact fatigue, rail grinding has proven itself to be one of the industry’s best tools for managing one of its most valuable assets. Hardware and software developments have enabled companies like Loram Maintenance of Way, Inc., to yield increasingly more precise rail profiles, less unnecessary metal removal, and a more customized approach to the entire rail grinding process. In recent years, Loram has also undertaken to quantify the effects of these new techniques and technologies on metrics like profiledeviation and rail-life extension.
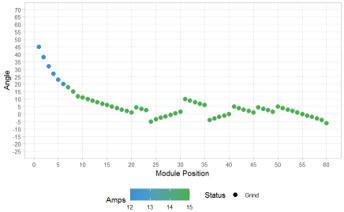
In practice, rail profiles are implemented by grinders running specific grind-patterns to achieve a desired template or rail profile shape. These patterns are essentially lists of angles at which the individual grind modules contact the rail to achieve a specific profile. The amount of power provided to the modules is another variable that can be adjusted based on the desired metalremoval rate. Traditionally, rail grinders had a set number of up to 50 static patterns that were effectively hard-coded into the grinder firmware/software. An operator could then choose the pattern, module amps, and grinder speed at 1 mile-per-hour increments for a given pass. “These static patterns can achieve good results with a skilled operator, but due to the limitations, there is no single ‘perfect’ cut,” Chris Lidberg, a Product Manager at Loram told attendees at the 2023 Wheel/Rail Interaction Conference.
It’s also important to note that a grind pattern will not produce the same result on different rails with different profile shapes. “Static patterns are based on a new-profile shape, but you’re going to encounter a lot of different shapes in the field,” he said.
Figure 2 shows an example grind pattern for a 120-stone rail grinder. On the Y axis, negative angles indicate locations to the field-side of the rail center-line, while positive angles are to the gauge-side. Each dot on the graph represents one module, and the color of the dot represents the power, in amps, supplied to the module.
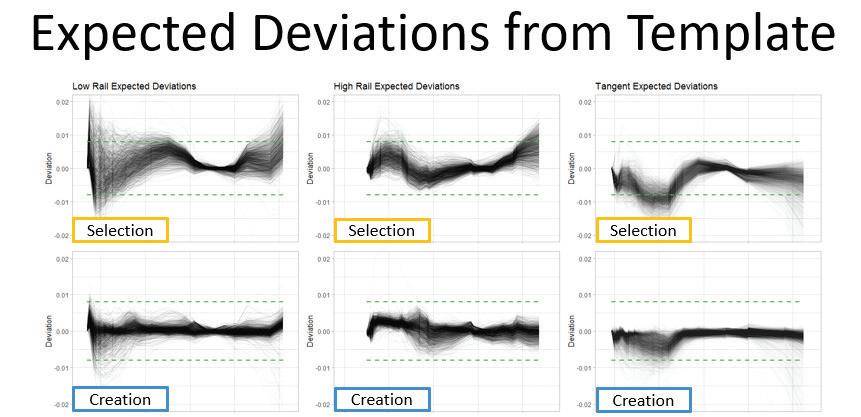
Over the years, a number of techniques
have been developed to ensure that the as-ground rail profile matches the design-profile, and that as little as necessary metal is removed to control the growth of rolling contact fatigue (RCF) and achieve the target profile. One of the ways this is done is by taking rail profile measurements pre- and post-grind (or after a single grind pass) to determine deviation from the target profile, and the amount of metal required to be removed. One of the more recent developments in rail grinding software has been the ability to perform these types of measurements and analyses in realtime, Lidberg said. “Based on [data from] a single pass, we can determine exactly how many more passes it will take to hit the metal-removal target.”
In 2019, Loram began to implement its dynamic pattern creation system. The system compares the target profile to a pre-grind profile measurement and automatically adjusts the modules to grind to the target — hence, the pattern is created rather than selected from a list of static patterns. Instead of 50 static patterns applied at 1-mph increments, the dynamic pattern system can apply a near infinite number of patterns at 0.1-mph increments. “We’re able to achieve a much finer degree of control this way,” Lidberg said. It also makes it easier for the operator to avoid unnecessary metal removal due to a potential mismatch of the rail and grind pattern, he added.
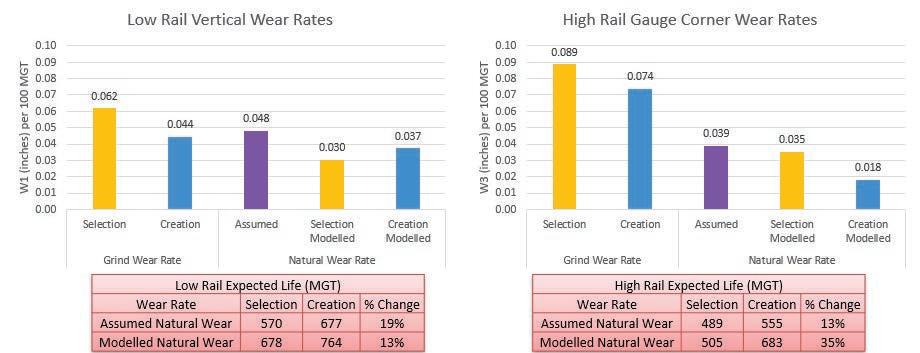
While the value of rail grinding this way is fairly intuitive and easy to demonstrate, it can be difficult to quantify, and thus justify, as a maintenance expenditure. In order to measure and quantify the differences between the standard pattern-selection versus the new patterncreation method, Loram selected a subdivision with a robust history of rail grinding and profile measurement. Beginning in 2019, they began to grind this subdivision under the new patterncreation system and then compared the results. “We could see from the data that we removed less metal, and deviated less from the target profiles when we implemented pattern-creation,” Lidberg said. To quantify the results, Loram looked specifically at low rail vertical and high rail gauge-wear rates.
The findings from this study, which were presented at WRI in 2021, indicate that due to the reduction in vertical wear rates, the low rail is predicted to have a
19% increase in expected rail life, while the high rail showed a 13.5% increase in predicted rail life. Since then, Loram has continued to refine its ability to accurately model natural wear rates and better quantify the effects of patterncreation grinding at a more granular level, Lidberg noted.

Loram’s first step in refining their comparative grinding analyses was to develop a model for each test site based on historical data. The new natural wear rate model considers traffic patterns, wheel and rail profiles, friction conditions, and wheel and rail metallurgy. Using this more robust wear model, rail life can be modeled, out to the point of end-of-life, using data from patternselection and pattern-creation grinding data. “This allowed us to model the evolution of rail wear and damage with a great deal of confidence,” Lidberg said.
Figure
of the evolution of high rail wear over time on a rail ground via patternselection (left) and via patterncreation (right). This Figure is a video illustration included in the IJ article. You won’t have this one.
According to the simulations, sharp curves (sites with a high natural wear rate) saw the greatest bene t under a patterncreation grinding regime. In one such case, the low rail saw a 38.7% reduction in vertical wear over a period of 80 MGT. is was achieved by keeping the contact patch in a more optimal location by better implementing the target pro le, Lidberg said.
e study also found that combined wear rates on the high rail were more predictable and had less variability from site to site under a pattern-creation regime.
Data from these simulations has also enabled Loram to predict natural wear
rates more accurately as a baseline for comparative analyses. While its initial 2021 analysis used an assumed natural wear rate of 0.048 inches vertical wear per 100 MGT for the low rail and 0.039 inches gauge corner wear per 100 MGT for the high rail, the model provided more accurate numbers for both patternselection-ground rail and pattercreation-ground rail. The figures for low rail vertical wear are: 0.030 inches/100 MGT for selection-grinding; 0.037 inches/100 MGT for creation-grinding.
And the figures for high rail gauge corner wear are: 0.035 inches/100 MGT for selection-grinding; 0.018 inches/100 MGT for creation-grinding.
Using these updated gures, Loram predicts an overall life extension of 13% on the low rail life and 35% on the high rail. “ is shows that it’s important to verify your assumed wear rates,” Lidberg said.
Taken altogether, the results of Loram’s simulations and analyses seem to bear out the efficacy of tailoring grind patterns to specific sites, rather than
using pre-set patterns to target a “bestfit” approach. And while skilled operators can, and have, achieved great results via this traditional method of grinding, this new approach of in-situ patterncreation grinding removes a lot of the guesswork and potential for error.
Je Tuzik is Managing Editor of Interface Journal ( www.interfacejournal.com ).This article is based on a presentation made at the WRI 2023 Conference.




Network and collaborate with a diverse group of women and allies who are making a difference in the rail industry. Learn how railroaders can maintain the momentum of inclusion, build strong support networks, and take advantage of ever-broadening career opportunities.
•Discover career advancement and development opportunities









• Learn about the career paths of women leaders and how today’s railways are supporting them

•Explore DEI (Diversity, Equity and Inclusion) initiatives





















• Learn about mentorship best practices—from finding a mentor, to serving as one
•Discover how ERGs (Employee Resource Groups) are established for community building and support
•Connect with your peers—both upcoming talents and accomplished women in rail































































Crossties are the focus of this month’s Vendor Product Spotlight. These crosswise members of track infrastructure hold and support the rails as well as support wheel loads and distribute said loads to the ballast. Crossties, or simply ties, are placed perpendicular to the rails to hold track gauge, and can be made from concrete, wood, steel, or composite material. However, timber ties are an industry standard and account for more than 95% of ties on U.S. railroads, according to the Encyclopedia of North American Railroads . Whatever the material used, these ties need to be
manufactured and maintained properly to ensure a well laid-out track that is capable of handling heavy freight and passenger trains.
Stella-Jones supports the development, upgrade, and maintenance of North America’s railroad infrastructure with over 10 million pressure-treated wooden crossties per year.


Its extensive supplier network of hardwood sawmills allows it to offer crossties, switch ties, and timbers in a variety of sizes and species of wood.
From a network of 12 industrial treating plant locations, Stella-Jones offers a complete line of pressure-treated



wooden railway products with crossties, switch ties, bridge timbers, fabricated bridges, and timber highway crossing panels. These products can be offered in Creosote, Copper Naphthenate and Borate pressure treatments and can be manufactured to meet the specifications of any major railroad in North America. It also offers Pre-Boring and Pre-Plating services at several locations.
A representative of Stella-Jones also told RT&S “In 2024, we will continue to invest in robotics, automation, and special projects like the recent solar panel installation in Clanton, AL. This installation provides approximately 70%


From
of the facility’s electricity requirements, a savings equivalent to 92,000 gallons of diesel fuel annually. This project is an industry first and a meaningful step in our road to decarbonization.”
Encore Rail Systems, Inc responded to RT&S that the “railroad market continues its shift toward advanced technologies that improve uptime, safety, and reliability,” placing a focus on the future of crosstie remediation. While Encore offers crosstie repair equipment, compounds, and epoxies, one of its advancements is a CANbus control
system with on-board diagnostics capabilities that will be integrated into all of its RTP Ride on Tie Pluggers. The new enhancements and upgrades will assist in troubleshooting and provide real-time alerts before problems arise in the field. In addition, the RTP, already setting the standard for safety, will also have cab upgrades in the coming year.
Encore offers leasing for tie plugging and concrete rail seat repair equipment as well as Ride-On, Walk-Behind and Skid-Mounted equipment. Encore also offers the compounds and epoxies and


the service that ensures its customers are getting the most from the equipment to achieve maximum productivity and uptime. Encore told RT&S that equipment is also available for the repair of wood, composite, and concrete ties.

For treatment of wood ties, Nisus Corporation offers a general use preservative in the form of its copper naphthenate oil-born preservative. QNAP® copper naphthenate is a general use preservative and is the fastest growing wood preservative in the U.S. for pressure treating crossties and bridge ties, and Nisus has treatment plants across the country ramping up their production to handle the increased demand for QNAP treated ties.
Testing conducted by the USDA Forest Product Laboratory on ties treated with copper naphthenate demonstrated an estimated service life of over 65 years. Not only do QNAP-treated ties have an extended service life, but they have multiple options for their further use at the end of life, from fencing and residential landscaping to serving as fuel for permitted boilers. QNAP is not a skin sensitizer, and its cleaner handling characteristics mean that crews face less risk of skin irritation when handling treated ties.
Nisus told RT&S that “Bridge crews tell us that QNAP-treated ties aren’t as slippery when wet.” A non-conductive and non-corrosive formula, QNAP has a superior environmental profile compared to other oil-borne preservatives, while also resulting in less drippage in use, a particularly important aspect for environmentally sensitive bridges over pedestrian walkways, roads, and waterways. QNAP2 brings the advantages of copper-based, oil-borne preservatives to the field.
QNAP2 is ready to use and can be applied with a brush on end-cuts, dap cuts, and drill holes, as well as above and below grade. When ties do eventually reach the end of their service life, QNAP-treated ties can continue to be of use, including as valuable boiler fuel. Under the EPA’s Nonhazardous Secondary Material rule, only QNAPtreated ties can be used in any boiler covered by the rule, and only QNAPtreated ties are allowed as boiler fuel with creosote-treated ties. These wood preservatives allow for a longer lifespan, cleaner handling characteristics, lower environmental impact, and
increased cost efficiency.









Omaha Track has been processing railroad ties for forty years across North America. It handles and processes over 3 million ties annually, and its business continues to grow as it expands operations throughout the United States. The journey begins by acquiring secondhand ties from a variety of locations. Omaha Track has a high standard sorting process to ensure the highest-quality ties are resold for landscaping products. Ties of lower quality are reduced in size for reuse as a fuel source for power plants and other industries.




Omaha Track says it is committed to sustainable solutions for crosstie disposal. Currently, it is actively working on making its operations more energyefficient and eco-friendly, with a focus on reducing its carbon footprint. Omaha Track collaborates closely with Class I railroads to safely repurpose crossties, including those treated with creosote. With operational facilities located in LaCrosse and Superior, Wisconsin;

Pueblo, Colorado; Hazen, Nevada; and Chicago Heights, Illinois, these facilities specialize in processing scrap railroad ties and other wooden railroad materials into biomass suitable for co-generation


fuel. Omaha Track offers the flexibility to recover ties during track work, within the right-of-way or from stockpiles nationwide.
Looking toward the future, Omaha
Track told RT&S that the company is “facing several challenges.” It must navigate evolving landscapes in both the fuel and landscaping markets. A spokesperson went on to say that one “significant challenge is the closure of numerous biomass facilities, creating a shifting dynamic in the market. There is a surplus of legacy ties that require proper disposal.”
Omaha Track mentioned that it acknowledges these challenges, and it is approaching 2024 with a sense of caution and dedication to its core mission. “We are determined to repurpose railway ties, reduce waste, and contribute to a greener, more sustainable future despite these hurdles,” said the company.
Well-maintained crossties can last a couple decades, depending on traffic volume, weather, and other related factors. As railroads approach constructing and maintaining track infrastructure, crosstie offerings such as those listed here may help improve longevity.




•Engineering for Operations
•Light Rail Engineering Standards
•Safety Certification
•Operations Planning and Modeling
•Battery and Hydrogen Fuel Cell Propulsion
•Signaling, Train Control and Street-Running Interfaces
•Leveraging Federal Funding
•PLUS Tour NJ Transit’s Hudson Bergen System

Speakers Include SUPPORTING ORGANIZATIONS











 Keynote Speaker Kevin S. Corbett President & CEO NJ Transit
Anna Hooven, P.E. Program Mgr. –Bridges & Buildings SEPTA
Je rey A. Warsh Partner & VP MBI Former Exec. Dir., NJ Transit
Joe Costigan, Jr. Rapid Transit Program Sponsor (Dir.) Metrolinx
Giuseppe Mattoscio, P.E. Chief Safety Engineer Houston METRO
Fred Mills, P.E. Chief Signal Engineer Houston METRO
Rachel J. Burckardt, P.E. VP / Sr. Project Manager WSP USA Inc.
Ken Luebeck, P.E. Public Project Mgr. Benesch
John Mardente Civil Engineer – Passenger Rail Div. FRA
Keynote Speaker Kevin S. Corbett President & CEO NJ Transit
Anna Hooven, P.E. Program Mgr. –Bridges & Buildings SEPTA
Je rey A. Warsh Partner & VP MBI Former Exec. Dir., NJ Transit
Joe Costigan, Jr. Rapid Transit Program Sponsor (Dir.) Metrolinx
Giuseppe Mattoscio, P.E. Chief Safety Engineer Houston METRO
Fred Mills, P.E. Chief Signal Engineer Houston METRO
Rachel J. Burckardt, P.E. VP / Sr. Project Manager WSP USA Inc.
Ken Luebeck, P.E. Public Project Mgr. Benesch
John Mardente Civil Engineer – Passenger Rail Div. FRA
Get PDHS At Your Own Pace With Arema’s On Demand Education
Access to important professional development content is just a few clicks away with AREMA Education. Our On Demand content spans many disciplines of PDH accredited courses that allow you to get your PDHs by learning from experts online without leaving your office.
1. LEARN MORE
Studies show that participants learn more while taking On Demand courses as you can skim through the material you understand and take more time in the more challenging areas.
2. GET INSTANT ACCESS
With AREMA On Demand courses, you don’t have to wait to learn and get your PDH’s as they’re available instantly after purchase.
3. CONVENIENT AND FLEXIBLE
Above all things, On Demand education is meant to take at your own pace and on your time. Study from anywhere in the world, whether from your office or the convenience of your sofa.
4. COURSE VARIETY AREMA On Demand education offers a wide variety of topics for all studies of the railway engineering community.
Register and Start Learning today at www.arema.org.
BECOME A MEMBER AND SAVE
Not an AREMA member? Join today at www.arema.org and get discounts on all AREMA Educational Offerings, from Virtual Conferences to our Webinars.
This month’s message from the AREMA President is being turned over to AREMA Board of Governor, Gery Williams, Executive Vice President Service Delivery & Operations, Amtrak, who has a very special announcement in memory of a close colleague. The column is being dedicated to a former Amtrak employee: Ildefonso Burgos, or “Ilde,” as many folks knew him.
Gery shares, “Ilde was a friend and colleague who passed away suddenly in June 2022. Many of you worked with or knew him. For those who did not, I’ll share a little background:
Ilde came to Amtrak in 2016 as Deputy Chief Engineer, Major Capital Projects, responsible for a portfolio of Major Capital Projects. He was promoted to Assistant Vice President, Project Delivery, and then to Vice President, Infrastructure Maintenance & Construction Services in my group. Idle was detail-oriented, making sure everything got done on time and within budget. He was a
great mentor, co-worker, and friend to us all.
Before joining Amtrak, Ilde worked with WMATA’s Capital Delivery group and DDOT’s Streetcar Program in DC, as well as the San Mateo County Transit District and Puerto Rican Highway and Transportation Authority. He graduated from the University of Puerto Rico-Mayaguez with both a BS and MS in Civil Engineering and was a registered Professional Engineer.

He was survived by his wife, Marti, and two beautiful children.
Out of the many projects Ilde was responsible for, one was a new interlocking north of Washington, D.C. As you may know, it’s been standard practice to name interlockings after a nearby street or landmark. This interlocking was named “Hanson Interlocking.”
It was an especially complex and important piece of the Northeast Corridor. When finished, the project would provide additional capacity and higher speeds, alleviating congestion in 3-to-2 track interlocking that also connects into a freight line.
The location and density of rail traffic made track outages challenging. Additionally, there were high voltage utility overbuilds on the catenary structures that needed to be relocated, not to mention the multi-agency coordination and permitting and challenges associated with completing major construction activities during the height of the COVID pandemic. To say the least, it was quite a complex job.
After considerable effort, the project team has completed this important interlocking. We are honored to share with you that “Hanson Interlocking” will be cut over and in service later this fall, and with that, it will go by the new name “Burgos Interlocking,” in memory of Idle.”
““HANSON INTERLOCKING” WILL BE CUT OVER AND IN SERVICE LATER THIS FALL, AND WITH THAT, IT WILL GO BY THE NEW NAME ‘BURGOS INTERLOCKING,’ IN MEMORY OF IDLE.
Thank you for attending the AREMA 2023 Annual Conference in conjunction with Railway Interchange. If you registered as a full Conference AREMA Attendee, you will get access to the On Demand AREMA sessions recorded during the event. Stay tuned for details.
Registration opens in November for the AREMA 2024 Sustainability & Resiliency Symposium, which will be held February 5-7, 2024, in Tampa, Florida. Take part in this event now by sponsoring and showing off why your company supports sustainability practices: https://srs24. arema.org/
Secure your recognition for the AREMA 2024 Annual Conference & Expo with your booth and sponsorship. Sales are open for the event being held in Lousiville, KY, September 15-18.
NOVEMBER 1
Committee 6 - Rail Facilities, Utilities and Buildings Virtual Meeting
DECEMBER 6
Committee 6 - Rail Facilities, Utilities and Buildings Virtual Meeting
JANUARY 3
Committee 6 - Rail Facilities, Utilities and Buildings Virtual Meeting
FEBRUARY 7
Committee 6 - Rail Facilities, Utilities and Buildings Virtual Meeting
Did you know we have a wide variety of On Demand education for learning on your time? Browse our most popular webinars, seminars, and Annual Conferences to earn your PDH credits on the go. Visit www.arema.org to start your On Demand learning today.
Don’t miss out on the conversation happening in AREMA’s Member Forum. The Member Forum connects you with other Members allowing you to send messages, start conversations, and more. See what everyone is talking about today: https://community.arema. org/home.
If you’re looking for a podcast to binge, listen to AREMA’s Platform Chats. They feature guests from every aspect of the railway industry. Available on all of your favorite listening services.
Leverage the power of your trusted association’s Railway Careers Network to tap into a talent pool of job candidates with the training and education needed for long-term success. Visit www.arema.org/careers to post your job today.
FEBRUARY 8-9
Committee 7 - Timber Structures
Committee 8 - Concrete Structures & Foundations
Committee 9 - Seismic Design for Railway Structures
Committee 10 – Structures
Maintenance & Construction
Committee 15 - Steel Structures
Committee 28 - Clearances
MARCH 6
Committee 6 - Rail Facilities, Utilities and Buildings Virtual Meeting
APRIL 3
Committee 6 - Rail Facilities, Utilities and Buildings Virtual Meeting

APRIL 14-16
Committee 17 - High Speed Rail Systems
Orlando/Ft. Lauderdale, FL
MAY 1
Committee 6 - Rail Facilities, Utilities and Buildings
Virtual Meeting
JUNE 5
Committee 6 - Rail Facilities, Utilities and Buildings
Virtual Meeting
JULY 31 - AUGUST 1
Committee 7 - Timber Structures
SEPTEMBER 15
Committee 17 - High Speed Rail Systems
Louisville,KY
*Tampa, FL - Meeting in conjunction with the AREMA 2024 Sustainability & Resiliency Symposium
Join a technical committee
Joining a technical committee is the starting point for involvement in the Association and an opportunity for lifelong growth in the industry. AREMA has 30 technical committees covering a broad spectrum of railway engineering specialties. Build your network of contacts, sharpen your leadership skills, learn from other members and maximize your membership investment. If you’re interested in joining a technical committee or sitting in on a meeting as a guest, please contact Alayne Bell at abell@arema.org.
For a complete list of all committee meetings, visit www.arema.org.
At the 2022 annual AREMA conference in Denver, the advisor for the University of South Carolina’s AREMA chapter, Dr. Dimitris Rizos, never expected to eat lunch with the incumbent AREMA president. But sure enough, Mr. Trent Hudak just happened to be at the very same table. It was at this lunch where the two began a conversation, and Dr. Rizos asked Mr. Hudak if he would be interested in coming to a meeting where he could not only talk about AREMA, but also his role as director of engineering
services at BNSF railway. It was at this point that the seeds were planted for the meeting that would eventually take place on March 22, 2023.
The day started with Mr. Hudak meeting with faculty members within the Civil Engineering department and the students whose research projects were related to the rail industry. After seeing and hearing about nearly 10 different projects, Mr. Hudak was given an overview of the rail program course, its future at the university, and the AREMA chapter’s activities.

After this informative meeting, Mr. Hudak was presented with a tour of the facilities, including the research labs.
During this tour, students were able to speak with BNSF recruiters about potential job opportunities. Many students took time out of their day to come meet with the recruiters, and many who had never been exposed to the railway engineering profession had their eyes opened to an entire industry. Some students said they would like to explore a profession, or at least an internship, with BNSF, other Class
I Railroads, or railway consulting firms. Others expressed an interest in taking a class about the railroad to learn more about the discipline.


Finally, to close out the day, it was time for Mr. Hudak to give a presentation to the students about the BNSF Railroad and the role of an engineer at BNSF. The more than 30 students in attendance learned about what a typical day at the office looks like, what BNSF looks for when hiring, how the company innovates change and stays ahead of competitors, and perks of the job, such
as being able to travel the entire network. After hearing this, students told me they “never knew companies like this were hiring civil engineering students,” and it would be “a company on the top of their list when applying for jobs.” Afterwards, we were treated to a brief overview of the AREMA organization and the benefits that await students when they register.
To conclude the invigorating day, a Q&A session took place where many intriguing questions were asked, answered, and discussed. After a photo with the AREMA
chapter, it was time for Mr. Hudak to return to BNSF. Overall, the students said that this was one of their favorite events of the year, expressing the desire to have more speakers from AREMA come in. If nothing else, this event demonstrated that there is a large interest in the rail industry, and that students only need to be made more aware of the opportunities that await them. It was apparent to all who were there that the rail industry has a large pool of eager and willing applicants looking to work in an environment that makes a difference.







MAIN OFFICE
JONATHAN CHALON Publisher (212) 620-7224 jchalon@sbpub.com
AL, KY, TN, CHINA
JONATHAN CHALON (212) 620-7224 jchalon@sbpub.com
CT, DE, DC, FL, GA, ME,MD, MA, NH, NJ, NY, NC, OH, PA,RI, SC, VT, VA, WV, CANADA: QUEBEC AND EAST, ONTARIO
JEROME MARULLO
(212) 620-7260
jmarullo@sbpub.com
AR, AK, AZ, CA, CO, IA, ID, IL, IN, KS, LA, MI, MN, MO, MS, MT, NE, NM, ND, NV, OK, OR, SD, TX, UT, WA, WI, WY, CANADA: ALBERTA, BRITISH COLUMBIA, MANITOBA, SASKATCHEWAN HEATHER DISABATO (CHICAGO OFFICE) (312) 683-5026 hdisabato@sbpub.com
AMERICAS, EUROPE, ASIA, AFRICA, AUSTRAL ASIA NORTH AMERICA - CT, DE, DC, FL, GA, ME, MD, MA, NH, NJ, NY, NC, OH, PA, RI, SC, VT, VA, WV, AND EASTERN CANADA. EUROPE EXCEPT GERMANY, AUSTRIA, GERMAN SPEAKING SWITZERLAND, EASTERN EUROPE, ITALY, AND ITALIAN-SPEAKING SWITZERLAND. ASIA EXCEPT JAPAN AND CHINA. JEROME MARULLO (212) 620-7260 jmarullo@sbpub.com
GERMANY, AUSTRIA, GERMAN-SPEAKING SWITZERLAND, LATVIA, LITHUANIA, ESTONIA, POLAND, CZECH REPUBLIC, SLOVAKIA, HUNGARY, SLOVENIA, CROATIA AND SERBIA SIMONE AND SIMON FAHR Breitenbergstr. 17
Füssen 87629
Germany
Tel: +49 8362 5074996 sfahr@railjournal.com
ITALY, ITALIAN-SPEAKING
SWITZERLAND
DR. FABIO POTESTA
Media Point & Communications SRL

Corte Lambruschini
Corso Buenos Aires 8 V Piano, Genoa, Italy 16129 +39-10-570-4948
Fax: +39-10-553-0088 info@mediapointsrl.it
JAPAN
KATSUHIRO ISHII
Ace Media Service, Inc. 12-6 4-Chome, Nishiiko, Adachi-Ku
Tokyo 121-0824
Japan
+81-3-5691-3335
Fax: +81-3-5691-3336 amkatsu@dream.com
IRJ PRO AND CLASSIFIED ADVERTISING SALES

JEROME MARULLO (212) 620-7260 jmarullo@sbpub.com

On Friday, September 15, Brightline inaugurated its Miami to Orlando service. There isn’t a lot that hasn’t been written about what a historic

milestone this is. The first new privately operated passenger service in over 100 years. Wesley Eden’s extension of Henry Flagler’s development of railroads in Florida. A focus on service and quality
not seen very often these days.
Railway Track and Structures will be here to cover the engineering and infrastructure of this truly revolutionary new service. Godspeed, Brightline!


Thisneweditionencompassescurrentdesignmethodsused forsteelrailwaybridgesinbothSIandImperial(US Customary)units.Itdiscussestheplanningofrailwaybridges andtheappropriatetypesofbridgesbasedonplanningconsiderations.
Railroads&EconomicRegulation tracesthedevelopment, failuresandsuccessesofrailroadeconomicregulationby aninsiderwhowasaWhiteHouseappointedchiefofstaff attheSurfaceTransportationBoardandaseniorofficerat theAssociationofAmericanRailroads.
"FrankWilnerhaswrittenanexhaustivehistoryofournation'srailroadsand thecomplicated,intriguingandoftenconfusingfederalregulationand lawmaking."
NickRahall MemberofCongress(WestVirginia,1977-2015)
Themostcomprehensivecollectionofdefinitionsrelatingto track.Over1500termsfromantiquatedforgottenslangto today'sjargon.Clearlyillustratedlineartenhancesthetext.
Railgrindingsavesmillionsofdollarseveryyear!TheArt andScienceofRailGrindingisthefirstbookdedicated exclusivelytothesubject.
"AsanewmemberoftheSurfaceTransportationBoard,thebookwould havebeenindispensabletome.Itplacestoday'sregulatoryissuesinto contextbasedontheirhistoryandpaintsapictureofthecharacterswho havemadetherailroadworldwhatitistoday."
Member,SurfaceTransportationBoard,2014-2018 Hardcover,414pages.
ClassesofTrack1-5;General;Roadbed;TrackGeometry;Track Structure;AppliancesandDevices;TrackInspection;andDefect codes.IncludesGaugerestraintMeasuringSystem(GRMS.).
History does repeatitself.Manyoftheseissuesarebrought tolifebyexploringexampleslearnedfrommitigatingvarious issuesandtacticsusedwhentheNYCTAassumedcontrol oftheBMTandIRTlines.
TheTrackDataHandbook
Reprintedbypopulardemand,thisbookisavaluable referenceforroadmasters,tracksupervisors,trackforeman, surveyorsandothersinvolvedintheplanningandexecution oftrackmaintenanceandconstructionwork. Fold-outdiagrams.Softcover.301pages.
YourGuidetoRailwaySignals isanexcellentguidefor trainingsignalpersonnelespeciallyrailwaycross-function managers,supervisors,andsupportpersonnel.Highqualitygraphicsanddiagramshavebeenusedthroughout. Complieswithallstandardsandcommonlyusedpractices.



Gainadeeperunderstandingoftheevolutionoftrack technology.Thisbookpresentstheknowledgeneededfor rationaldesignandmaintenanceofpassenger,freight,and transittrack. BKFRTE FundamentalsofRailwayTrackEngineering $150.00





TheTrackSafetyStandardsCalculatorisamustfor anyonewhoworksontrack.Thisslideruletype calculatorcontainsmanyofthedetailsforClassesof track1through5.Updatedasof July11,2013.
Only$10.75forordersof50ormore!
Thefiftheditionof TheRailroad:WhatItIs,WhatitDoes is evenmorevaluablethanbefore.Insideyou’llfinda comprehensivelookathowtoday’srailroadsfunction—from equipmenttoproceduresandmarketingtomaintenance. BKRRNN WhatitisWhatitdoes $49.95


